Nausea dizziness weakness abdominal pain causes treatment
Nausea, dizziness, weakness and abdominal pain can have a variety of causes. Ignoring symptoms can lead to serious consequences.
It is necessary to determine the cause of the ailment and assess the general condition of the patient. If poor health is caused by overwork, stress or weather changes, you can get by with treatment at home. Medical intervention is necessary if serious chronic or infectious diseases are suspected. Also when the patient’s condition rapidly deteriorates.
Causes
In most cases, these symptoms are signs of poisoning, viral, infectious or chronic diseases. They can also occur for physiological reasons.
Poisoning
Food poisoning is the most common. They arise due to the consumption of low-quality or expired products, inedible mushrooms, alcohol abuse, and improper use of medications.
The distinctive features of food poisoning are:
abdominal pain, heaviness; nausea, vomiting; stomach upset; severe weakness; drowsiness; feeling of disgust for food; dizziness; heat; chills.
In most cases, the pain spreads throughout the entire abdominal cavity. The nature depends on the degree of poisoning. It can be either aching, pressing, or sharp, cramping. Crashes occur with severe poisoning. It is necessary to call an ambulance, as gastric lavage may be necessary.
Poisoning can be stopped at the initial stage. If there is a suspicion that the product consumed has been spoiled or a slight malaise has occurred, it is necessary to take activated charcoal. You should refuse food for at least a few hours.
Alcohol
Alcohol poisoning has the same symptoms as food poisoning. In addition, there may be pain in the right hypochondrium, increased heart rate, decreased blood pressure, and increased sweating. Red spots also appear on the skin.
If there are symptoms of intoxication, you need to induce vomiting and start taking absorbents. You should avoid eating and drink plenty of water, especially hot tea. If it doesn't get better, seek help from a specialist.
Mushrooms
Mushroom intoxication is especially dangerous because it can be fatal. In severe cases, convulsions, loss of coordination of movements, hallucinations, and loss of consciousness are observed.
Treatment is difficult to carry out at home, so hospitalization is required. First aid consists of taking absorbents and gastric lavage.
If there is no diarrhea, you should take a laxative.
Medicines
Drug poisoning occurs for many reasons:
improper use; overdose; use after expiration date; improper storage; poor quality; incompatibility of drugs; suicide attempt; accessibility for children.
Weakness, lethargy, drowsiness, general malaise, rapid heartbeat or pulse, and lack of response to stimuli (pain, light) are observed. Loss of consciousness may occur.
An adult should drink five glasses of warm water. Dosage for children is calculated based on age. For every year of life there is 100 ml of water. It is necessary to induce vomiting and rinse the stomach until it is cleared. Also take five tablets of crushed activated carbon with water.
Non-food products
This group includes dyes, household chemicals, cleaning products, detergents, office supplies, building materials and much more. Many of them are toxic.
if swallowed; by inhalation; when accumulating in the body; upon contact with the mucous membrane.
The distinctive features of the malaise include:
severe and sometimes pressing headache; cough; dyspnea; disturbance of consciousness; excessive salivation; tearfulness; foam at mouth; temporary impairment or loss of vision; heart rhythm disturbance; difficulty breathing; lethargy; apathy.
It is difficult to cope with chemical poisoning on your own. It is necessary to call a doctor and consult a specialist about first aid. It is necessary to describe in detail the patient’s condition and all the signs that have appeared. Also clarify what exactly caused the poisoning.
To relieve symptoms, drink plenty of water in small portions. It is forbidden to induce vomiting. Vomit may contain chemicals that can cause burns. They can also get into the lungs.
In case of acid and alkali poisoning, rinsing is prohibited. Vomiting may become worse and may interfere with breathing. You need to drink no more than 600 ml of water. In case of acid poisoning, water is diluted with a small amount of soda, in case of alkali intoxication - with citric or acetic acid. You should get a 2-3% solution. Take a tablespoon every five minutes.
Viral and infectious diseases
They differ in the location of pain, the nature of the pain syndrome, symptoms and methods of treatment.
Viral or intestinal flu
Most often occurs in children and the elderly. In adults with good immunity, it can occur without external signs. If your child gets sick, you should definitely call a pediatrician. He will determine whether hospitalization is needed or not and prescribe treatment.
There are only a few ways of transmitting the virus:
food (unwashed fruits and vegetables, low-quality dairy products, raw tap water, dirty hands, etc.); airborne (talking, sneezing, coughing, etc.); contact and household (places of large gatherings of people).
The main symptoms of intestinal flu are:
sore throat when swallowing; dull pain in the neck and back of the head; redness and inflammation of the throat; loose stools up to 5-10 times a day; slight runny nose and cough; periodic sharp pain in the stomach, especially in the upper part; rumbling; increased body temperature; redness of the eye membranes; nausea, vomiting; dehydration; weakness; malaise; slight dizziness.
The main treatment involves taking medications that lower the temperature and combat stomach upset. You also need to drink activated carbon or other sorbents.
For a while you will have to give up foods that weaken you and stick to a diet. It is strictly forbidden to consume dairy and fermented milk products. They provoke the growth of pathogenic organisms in the intestines.
Upon completion of treatment, it is necessary to restore the intestinal microflora with the help of probiotic preparations.
Meningitis
Meningitis is an inflammation of the spinal cord and brain. A rather dangerous disease that requires urgent hospitalization. Treatment is carried out exclusively in a hospital. Most often occurs in children.
Methods of transmission of meningitis:
The most common method is airborne. A child can acquire microorganisms that cause meningitis from the mother during childbirth. The mother may simply be a carrier of the disease.
Children who are born through surgery are at risk. Children who neglect to wash their hands after using the toilet, walking, or playing with animals are susceptible to oral-fecal transmission. Transmitted through food and water contaminated by rodents.
Through the bites of insects that are carriers.
During meningitis the following is observed:
temperature increase; chills; seizures headache; rash on the skin or on the back of the throat; conjunctivitis; nausea, vomiting; loss of appetite; intolerance to light and sounds; low blood pressure; lower abdominal pain; increased heart rate; thirst; hallucinations; apathy; pain when tapping on the skull; Difficulty bending the head and straightening bent legs.
In some cases, ARVI begins a few days before meningitis. Most often in infants.
If symptoms of meningitis appear, consult a doctor immediately. First aid is provided by a specialist, based on the initial signs. The treatment is carried out by an infectious disease specialist and a neurologist.
Chronic diseases
Nausea, dizziness, weakness, and abdominal pain can occur against the background of chronic diseases of the kidneys, heart, thyroid gland, and stomach.
Kidney inflammation
Symptoms appear within two days. If the kidneys are cold, the following is observed:
lower back pain; nagging pain in the lower abdomen on the left side; urinary disturbance; blood, sand, salts in the urine; swelling of the limbs; chills; temperature rise to 39-40 degrees; the appearance of a rash on the skin.
There are four causes of the disease:
hypothermia; infectious diseases of the bacterial type (influenza, scarlet fever, tonsillitis and others); viruses that penetrate the blood (Escherichia coli, staphylococci and others); taking a large number of medications.
It is necessary to take a urine test and start taking medications prescribed by your doctor. As a rule, a complex of medications is prescribed, including diuretics and antibiotics.
If measures are not taken at the initial stage, diseases such as pyelonephritis, pyelitis, glomerulonephritis may develop. In this case, treatment will be more complex and a full medical examination will be required to determine an accurate diagnosis.
Hypothyroidism
Thyroid dysfunction. It consists of insufficient hormone secretion. Most often occurs in women over 50 years of age. The main symptoms are nausea, weakness, flatulence, swelling of the extremities, abdominal pain, weight gain, decreased blood pressure, and menstrual irregularities.
The disease is diagnosed by an endocrinologist. Laboratory and instrumental examinations are carried out. Treatment is quite long and can take from several months to several years. In some cases, you have to take medications for life.
Stomach ulcer
Defect in the gastric mucosa. Men aged 20-50 years are most susceptible. The disease is accompanied by pain, which worsens in the spring and autumn. The nature of the pain can be of any kind. Soreness most often occurs in the center of the abdomen, the navel area, but can occur in the upper part or in the left and right hypochondrium.
Other signs of the disease are heartburn, nausea and vomiting, loss of appetite, bloating, a feeling of heaviness, diarrhea, weakness, and blood in the stool. The diagnosis is made based on a blood test, gastroscopy and other examinations prescribed by a doctor.
Complex treatment and a strict diet are required. You should not eat spicy, salty and fried foods, spices, fatty meats, smoked foods, canned food, baked goods, strong tea and coffee, and carbonated drinks.
Source: https://sfmggu.ru/toshnota-golovokruzhenie-slabost-bol-v-zhivote-prichiny-lechenie/
Causes of dizziness with gastritis
Inflammation in any organ will have consequences on the general condition of the body. This follows from the interconnection of all organs and systems of the body due to neurohumoral regulation. With severe stomach pain, the body “redirects” impulses to other zones. Therefore, in many diseases, pain radiates (sends) to other organs, sometimes confusing even specialists. By redistributing pain, the body fights the pain syndrome, forcing the patient to pay attention to his health. The appearance of frequent dizziness with gastritis usually signals the severity of the disease and the involvement of the whole organism in the disease. Other causes of dizziness with gastritis include the following factors:
- Reflex pains
- Consequences of intoxication,
- Astheno-vegetative syndrome.
Let's take a closer look at these causes of dizziness.
Dizziness due to reflex pain
Many experienced patients know that an inflamed stomach is typically accompanied by hunger pains. When gastric juice enters an empty stomach, it irritates the already damaged mucous membrane, causing pain in the epigastric region. If even after this food does not enter the stomach, then with the help of irritation of the vagus nerve the pain intensifies even more and begins to radiate to neighboring digestive or remotely located organs. Therefore, a manifestation of gastritis can be reflex pain or dizziness. With this cause of dizziness with gastritis, there are features of such a disorder in the form of
- Frequent appearance on an “empty stomach”,
- Parallel appearance of nausea or vomiting,
- Occurs during long breaks in eating,
An additional factor in the deterioration of well-being due to inflammation of the gastric mucosa is a decrease in blood glucose levels. This is what often explains the symptoms of low mood, nausea or dizziness. At the same time, the patient may have a headache, everything will fall out of his hands, or he may become impossibly picky and capricious. As soon as a person with such a “bouquet of symptoms” eats, health disorders recede half an hour or an hour after eating.
Interestingly, a reflex headache with gastritis can be poorly relieved by painkillers and have a clear connection with how long ago the patient ate. On an empty stomach, the pain may be poorly relieved with pills or slightly dulled. The only available way to relieve reflex headaches with gastritis is to follow a diet: eating 5-6 times a day in small portions and avoiding hunger pains.
Dizziness due to intoxication
Acute gastritis is often accompanied by symptoms of intoxication: a temperature of up to 38 degrees, signs of vomiting, general weakness or diarrhea. Such symptoms with this disease are usually associated with bacterial microflora entering the stomach. Intoxication can also occur when there is an excess of Helicobacter bacteria, which live even in an acidic environment and, when they multiply uncontrollably, cause damage to the gastric mucosa and the development of gastritis or ulcers. Spreading through the blood throughout the body, these microbes poison it, causing dizziness, weakness, nausea, and bowel disorders.
Intoxication to varying degrees is always present in any form of gastritis (acute or chronic). In chronic inflammation, intoxication is associated with the accumulation of toxins in the body due to incomplete digestion of food. This is also due to the fact that with long-term chronic inflammation and malfunction of the stomach, other nearby organs (intestines, gall bladder, pancreas, etc.) are also involved in this “vicious circle”. And such a combined disorder further aggravates intoxication, leading to to the accumulation of toxins in the body due to undigested food debris. Intoxication headache or dizziness are among the most well-known consequences of the presence of any toxic substances in the body.
Also, dizziness due to intoxication during gastritis can be caused by poor diet or taking strong medications, especially on an empty stomach. These factors greatly irritate the stomach, and only the reflex vomiting that occurs during this condition helps the patient feel better. Sometimes intoxication in stomach diseases can be associated with an allergy to medications taken. In such situations, to eliminate dangerous manifestations in the form of dizziness, it is necessary to discontinue inappropriate medications.
Dizziness due to astheno-vegetative syndrome
Astheno-vegetative or asthenic syndrome is a frequent companion to many chronic or protracted diseases. This syndrome is also typical for patients with chronic gastritis. Gastritis often occurs in patients who already have astheno-vegetative manifestations. This is due to the mechanism of dysfunction of various organs in such patients. Asthenics may experience frequent mood swings, tearfulness, loss of spirit, decreased appetite, dizziness or headache. And this is an excellent breeding ground for the occurrence of any digestive disorders, the easiest of which is gastritis.
In other situations, the impetus for the development of astheno-vegetative syndrome is chronic gastritis, especially in women. This is caused by complex disruptions in the functioning of the body due to inflammation of the stomach, manifested in the form of:
- Immune failures,
- Constant stress due to stomach pain and discomfort,
- General disorders of the autonomic nervous system.
Dizziness due to astheno-vegetative syndrome differs from reflex pain. In this case, dizziness will not be associated with food or accompanied by nausea, but will appear with increasing load, often intensifying in the evening. In addition to headaches with asthenic syndrome, there may be a feeling of fatigue, weakness or weakness. It is not uncommon to experience dizziness towards the end of a busy day.
Especially often, women complain of dizziness with chronic gastritis, in whom this condition is accompanied by irritability, increased sweating, chilliness of the hands and feet, and sleep disturbances.
Dizziness with gastritis can manifest itself due to one of the above reasons (intoxication, reflex pain or astheno-vegetative syndrome), or be a consequence of their complex combination.
Are you suffering from nausea, dizziness, weakness? Causes and treatment
If symptoms of general malaise occur in the body, such as nausea, weakness, dizziness, drowsiness, it is quite difficult to identify the causes. After all, such a clinical picture is observed in various chronic and acute diseases.
Possible causes of general malaise
Nausea, weakness, dizziness, drowsiness occur in various disorders of the body and can be a consequence of chronic diseases or arise as a result of exposure to external unfavorable factors.
Poor health is observed with endocrine, neurological, cardiovascular diseases, these include:
- Pathologies of the thyroid gland: thyrotoxicosis, hypothyroidism.
- Diabetes.
- Vascular diseases: hypertension, bradycardia.
- Neurological disorders: cervical osteochondrosis, cerebrovascular accident, increased intracranial pressure, vegetative-vascular dystonia, migraine, traumatic brain injury.
- Gastrointestinal pathologies: chronic ulcers beyond the acute stage, helminth infection.
- Ophthalmological diseases: increased intraocular pressure, glaucoma.
- Metabolic disorders, vitamin deficiencies, anemia.
Symptoms of general malaise are observed at the beginning of the development of viral or infectious diseases, followed by an increase in body temperature and the addition of accompanying symptoms.
Nausea, weakness, dizziness and drowsiness in women may occur before menstruation or be a sign of pregnancy.
Deterioration in well-being can be caused by the influence of external unfavorable factors on the body:
- taking medications;
- influence of temperature influences: hypothermia, overheating;
- radiation exposure;
- food or chemical poisoning;
- intense physical activity.
To determine the cause of nausea, dizziness and weakness, you should consult a doctor. The persistence of persistent symptoms for a long time indicates obvious disturbances in the functioning of the body and require immediate diagnosis and subsequent treatment.
Neurological and vascular disorders
Loss of strength often manifests itself in cerebrovascular insufficiency caused by neurological and vascular pathologies:
- migraine;
- compression of the vertebral artery by deformed vertebral discs in cervical osteochondrosis;
- vegetative-vascular dystonia;
- hypertension or hypotension;
- heart failure.
Nausea, weakness and dizziness appear after physical exertion and emotional stress. People with chronic brain disorders are usually weather dependent. They feel dizzy and nauseous when there is a sudden change in weather.
Neurological and vascular disorders
accompanied by periodic attacks of headaches that occur suddenly. The pain is pulsating or pressing in nature and may be accompanied by tinnitus and the appearance of “floaters” before the eyes. Migraine pain intensifies under the influence of external stimuli: light, loud sounds. Patients feel sick and nauseous from strong odors.
Attacks of vegetative-vascular dystonia
accompanied by dizziness and blurred vision. It suddenly becomes worse when taking a vertical position, for example, after sleep: cold sweat appears, darkening occurs in the eyes, a feeling of lack of air is felt, nausea may be accompanied by vomiting.
For heart failure
In addition to nausea, dizziness and weakness, other symptoms are also typical: sweating in the back of the head and neck during bedtime, shortness of breath with excessive physical exertion, increased or decreased heart rate.
To diagnose cerebrovascular insufficiency, you must consult a neurologist and undergo examinations of the brain and blood vessels.
_____________________________________________________________________________________
Welcome to the NetGastritu channel.
Let's like and subscribe to the channel. New materials are published daily!
This and other materials can be found at NetGastritu.com
_____________________________________________________________________________________
Endocrine diseases
Thyroid disorders
associated with increased or insufficient production of thyroid hormones, in the early stages they are expressed by symptoms of general malaise: nausea, weakness, drowsiness.
For thyrotoxicosis
or excess levels of thyroid hormones indicate:
- weakness and dizziness;
- nausea;
- drowsiness or insomnia;
- chronic fatigue;
- hair loss;
- increased emotionality, irritability.
This clinical picture of thyrotoxicosis persists for up to 4–6 months. As the disease progresses, the symptoms are supplemented by other signs: tremor (shaking in the body, trembling in the limbs, twitching of the eyelids), muscle weakness, ophthalmological disorders (bulging eyes).
Hypothyroidism
or insufficient levels of thyroid hormones are also clinically manifested by nonspecific signs:
- general weakness;
- dizziness;
- drowsiness;
- nausea;
- constipation;
- brittle nails and hair loss;
- depression;
- menstrual irregularities;
- increased sensitivity to air temperature: constantly cold or, on the contrary, hot.
Thyrotoxicosis after 4–6 months manifests itself with specific symptoms, which is not observed with hypothyroidism, and presents significant difficulties in identifying the disease.
Diagnosis of thyroid diseases is made by an endocrinologist and includes: study of the concentration of thyroid hormones in the blood, ultrasound of the thyroid gland. The specialist will tell you why such pathologies appear, and what to do if the diagnosis is confirmed.
Diabetes
Poor health occurs in patients with diabetes mellitus against the background of hyperglycemia, which is characterized by the following symptoms:
- general and muscle weakness;
- frequent urination;
- constant thirst;
- morning sickness;
- decreased performance;
- drowsiness;
- skin itching.
- heavy sweating.
A specific symptom for diabetes mellitus due to insulin deficiency is a sharp weight loss of up to 15 kg within 2 months.
Diagnosis of the disease is carried out by an endocrinologist.
Anemia and vitamin deficiencies
Insufficient intake of vitamins and microelements from food leads to the development of hypovitaminosis and anemia.
In the early stages, deficiency states are manifested by general weakness: almost constantly dizzy when suddenly rising from a sitting or lying position, as well as during physical exertion, inclination to sleep even after proper rest, and morning sickness is observed.
With persistent deficiency of vitamins and microelements, disorders develop in all systems and organs of the body.
To diagnose anemia and vitamin deficiency, you must contact your local physician and take a general and biochemical blood test.
Viral and bacterial infections
A sudden deterioration in health, expressed by dizziness, weakness, nausea and drowsiness, may indicate the development of an acute infection. Such symptoms are observed in the early stages of influenza and ARVI, with meningitis and intestinal infections.
Acute infectious diseases are characterized by a rapid clinical course
.
A few hours after the first signs of illness appear, chills and lethargy usually develop, accompanied by an increase in body temperature. Then specific signs of the disease appear:
vomiting, nausea and diarrhea due to intestinal infections;
- runny nose with acute rhinitis and sinusitis;
- cough with pneumonia, bronchitis and tracheitis;
- sore throat due to pharyngitis and tonsillitis;
- ear pain due to otitis media;
- numbness of the neck muscles with meningitis.
If you experience symptoms of general malaise accompanied by an increase in body temperature, you should immediately consult a doctor or call emergency medical care.
Helminthiasis
The chronic stage of helminthiasis is characterized by nausea, dizziness and headaches, weakness, and decreased ability to work. Periodically, bowel problems (diarrhea or constipation) and discomfort in the abdomen occur. Against the background of nausea, isolated cases of vomiting may occur.
Some types of helminthic infestations are not detected during stool examination, which significantly complicates the diagnosis of the disease. Many people are forced to coexist with parasites in their intestines without even realizing they are there.
The optimal diagnostic method for determining helminthiases is blood testing using ELISA, RNGA, and RLA methods.
Exogenous factors
To determine the possible cause of nausea, weakness, dizziness, drowsiness, previous events should be analyzed. Such symptoms may appear as a result of the influence of unfavorable factors:
- recent head contusions;
- stressful situation;
- emotional stress;
- long concentrated painstaking work or physical activity;
- inhalation of harmful fumes, for example, during hair dyeing or perming, when carrying out finishing work, when working in gassy or dusty rooms;
- long trip in transport, air travel;
- taking medications: sedatives, antihistamines, hormonal and painkillers.
The causes of dizziness, drowsiness, nausea and weakness may be fasting, hypothermia or overheating.
Pregnancy
The first signs of pregnancy may appear several days before your missed period, especially in women with irregular menstrual cycles.
As a result of a sharp hormonal change associated with a rapid increase in progesterone in the blood, the state of health slightly worsens. Women want to sleep all the time, concentration decreases, and performance is impaired.
Girls become whiny, irritable, their sense of smell increases, they experience morning sickness, and mild nausea during the day, provoked by strong odors.
Pregnancy can be diagnosed before a missed period using an analysis to determine the dynamic level of hCG. Many highly sensitive tests show a positive result 2 to 3 days before a missed period.
Symptoms of general malaise: weakness, nausea, dizziness and drowsiness are a kind of indicator of the state of the body. The persistent manifestation of such symptoms signals a possible pathology. Diagnosis of the body should begin as early as possible, without waiting for the development of various complications.
– Unusual causes of dizziness
Source: https://zen.yandex.ru/media/netgastritu/muchaiut-toshnota-golovokrujenie-slabost-prichiny-i-lechenie-5a8939d600b3ddc019b7e4bf
Dangers of gastritis
Each type of inflammation of the gastric mucosa has its own distinctive manifestations and treatment features. Symptoms in the form of dizziness or headache most often occur with the catarrhal form of acute gastritis or the chronic course of this disease .
It is important to consult a specialist at the first symptoms of the disease. With a delayed start of therapy, gastritis quite often (about 85% of cases) becomes chronic. Chronic inflammation of the stomach is difficult to treat and often lasts for life. Constant inflammation in the stomach can lead to complications such as:
- Stomach ulcers with risk of bleeding,
- Anemia,
- Inflammation of other digestive organs (cholecystitis, pancreatitis, enterocolitis),
- Stomach cancer.
Non-systemic dizziness with gastritis
Stomach inflammation can have complex negative effects on the body. For example, this disease entails a persistent decrease in intestinal immunity due to a constant lack of all nutrients in the body. As a result, disruptions in digestion lead to numerous disruptions in the functioning of internal organs. One such disruption is symptoms of dizziness or headache.

Dizziness and headaches only at first glance seem unrelated to inflammation of the stomach. Let's look at the main causes of dizziness with gastritis. The so-called “non-systemic dizziness” occurs with a combination of manifestations in the form of lightheadedness, nausea, ringing in the ears, and darkening of the eyes. In some cases, such manifestations can lead to presyncope or fainting.
Many chronic diseases of internal organs can contribute to the development of non-systemic dizziness. Chronic gastritis with a complicated course also belongs to such ailments.
All possible causes of nausea, dizziness, weakness and abdominal pain
Nausea, dizziness, weakness and abdominal pain can have a variety of causes. Ignoring symptoms can lead to serious consequences. It is necessary to determine the cause of the ailment and assess the general condition of the patient.
If poor health is caused by overwork, stress or weather changes, you can get by with treatment at home. Medical intervention is necessary if serious chronic or infectious diseases are suspected. Also when the patient’s condition rapidly deteriorates.
Physiological reasons
Unpleasant sensations may occur during menstruation. If you are concerned about acute pain that lasts several days, or nausea or vomiting, you should consult a doctor. Nagging pain usually lasts the first few days of the menstrual period.
They can be relieved at home with a gentle massage, a heating pad or a warm shower.
Nausea, dizziness, weakness, nagging pain in the abdomen may indicate pregnancy. However, acute pain may indicate a disorder.
You should immediately contact your attending gynecologist who monitors the development of pregnancy, or call an ambulance.
First aid
You should definitely call a doctor if you have acute pain, severe weakness, rapid deterioration of your condition, or suspected chronic or infectious diseases. In other cases, you can try to cope with the symptoms on your own. However, these signs cannot be ignored. You need to visit a doctor to understand what caused the illness.
Relieving stress, temporarily refusing food, drinking water, and taking absorbents help alleviate the condition during poisoning and problems with the gastrointestinal tract. First of all, you should avoid irritating foods. If there is no improvement or other symptoms appear, you should consult a specialist.
Herbal teas, decoctions of chamomile, nettle, and mint help reduce menstrual pain. You can also take a warm shower. Bed rest will ease the condition. The fetal position is considered the most optimal.
You should not try to diagnose yourself and take medications, especially antibiotics. Completely different diseases can have similar symptoms. Taking medications inappropriately can significantly worsen the condition or lead to more serious consequences.
Conclusion
If poisoning or general malaise can be determined at home, then with chronic and infectious diseases everything is more complicated.
Similar symptoms of different diseases make independent treatment almost impossible.
Tests and examination of the whole body or individual organs are necessary to make an accurate diagnosis, since all these signs are often a consequence, and not the real cause of the disease.
Source: https://opischevarenii.ru/lechenie-i-simptomy/boli-v-zhkt/v-zheludke-i-toshnota/golovokruzhenie-slabost.html
Nausea, dizziness, weakness and abdominal pain - causes and treatment
The set of symptoms, including attacks of nausea accompanied by dizziness, increased fatigue and abdominal pain, is inherent in a number of pathological conditions: from short-term illness to serious illnesses.
Situations when drowsiness and severe weakness appear, and dizziness when moving, occur in some patients against the background of a sharp change in weather conditions or nervous strain.
- Diseases of viral, infectious etiology, as causes of nausea and weakness with dizziness and abdominal pain
- Damage to the body by rotaviruses
- Meningitis and dizziness, severe weakness
- Pathologies of the digestive system as causes of nausea
- Inflammatory process in the kidneys - back pain with weakness
- Endocrine disorders and severe abdominal pain with nausea
In such cases, you can alleviate your condition without the help of doctors. If abdominal pain and nausea intensify and are complemented by other symptoms, you need to undergo an examination to identify the causes of the ailment; delays in diagnosis can lead to health complications.
Why does my stomach hurt?
What are the reasons for nausea, vomiting, and abdominal pain? Often this is due to inflammation of the appendix, the appearance of intestinal obstruction, the occurrence of renal colic, strangulated hernias, and exacerbation of the adhesive process.
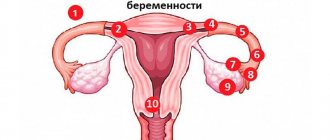
All these pathologies must be treated in a timely manner, otherwise they can provoke the development of serious complications. If you experience abdominal pain while pregnant, it is important to go to the hospital immediately. Not in all situations this indicates that premature labor has begun.
Sometimes pain during pregnancy develops due to the appearance of cystitis and pyelonephritis. With cholecystitis, severe spasms cause discomfort to the patient. Due to impaired bile movement, the patient’s general well-being worsens.
If spasms occur during the development of gallstone disease, then surgery is necessary.
Possible causes of abdominal pain depending on their location
These tables are quite conditional. The innervation of the abdominal cavity of each person is unique, like fingerprints, therefore the manifestations of pain are strictly individual.
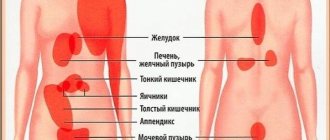
| Right hypochondrium | Acute cholecystitis, hepatic colic (with stone movement), radiculitis, attack of acute appendicitis |
| Left hypochondrium | Acute pancreatitis, radiculitis, acute appendicitis |
| Epigastric region (above the navel) | Gastric or duodenal ulcer, “posterior” myocardial infarction, consequences of overeating, initial stage of acute appendicitis, strangulated umbilical hernia |
| Left (or right) side | Inguinal hernia strangulation, intestinal diverticulum, intestinal obstruction, ovarian inflammation, ectopic pregnancy, acute appendicitis, renal colic (with stone movement), irritable bowel syndrome |
| Lower abdomen above the pubis (suprapubic joint) | Ectopic pregnancy, cystitis, strangulated inguinal hernia, intestinal obstruction, urological diseases of men, acute appendicitis |
Sometimes a complete examination of the patient does not reveal organic causes of abdominal pain; in such cases, we may be talking about chronic pain syndrome, a problem of a neurological nature.
How to determine the presence of intestinal colic?
When intestinal colic occurs, abdominal pain, nausea, and vomiting may occur. How does this condition differ from various diseases that provoke the appearance of an unpleasant symptom?
- With intestinal colic, the pain is not constant.
- There is no tumor-like protrusion.
- When pressed, the pain goes away.
- The stomach is soft.
- If the body temperature has risen, it does not go beyond the subfebrile level.
- Colic in the intestines often occurs against the background of diarrhea or constipation.
During premenstrual syndrome, women may experience discomfort in the abdominal area. Sometimes pain in the pelvic area indicates that an inflammatory, chronic disease is developing or that neoplasms of various etiologies have appeared. Only after a thorough diagnosis will the doctor be able to determine the cause of nausea, vomiting, and abdominal pain.
Signs of food poisoning
Food poisoning is the most common cause of abdominal pain, dizziness and weakness. The following combined signs will help distinguish food poisoning from an intestinal infection:
- the appearance of pain after eating (from half an hour to 4 hours);
- sharp, paroxysmal, sometimes unbearable pain;
- there is bloating and seething in the intestines;
- uncontrollable watery stools containing undigested food;
- nausea and vomiting;
- "massiveness" of the disease.
Attention! Companions of poisoning in the form of increasing weakness, speech impairment, increased pain when pressing on the eyeballs, dry mouth, confusion are a reason for the immediate provision of qualified medical care.
Under what conditions is it important to go to the hospital immediately?
You should immediately contact medical personnel if:
- when pain occurs, diarrhea appears and body temperature rises;
- abdominal cramps and vomiting are observed;
- vaginal bleeding appeared;
- the functioning of the respiratory system is impaired;
- spasmodic pain radiates to the shoulder, neck and chest;
- there is blood in the vomit;
- severe abdominal pain, nausea;
- the process of sweating intensified;
- the presence of bloody discharge in the stool;
- the patient cannot empty the bladder for a long time.
If there are no symptoms of complications, then minor pain can be eliminated at home with the help of medications.