CT (computed tomography) of the abdominal cavity is a modern diagnostic method that allows you to understand the exact condition of the internal organs, including blood vessels and lymph nodes.
CT image of the abdominal cavity with contrast
As a result of a CT scan of the abdominal cavity, a high-precision three-dimensional image is obtained, which allows one to see changes in internal organs that are invisible with other studies.
When can the procedure be scheduled?
Computed tomography of the abdominal organs (hereinafter referred to as CT) can be performed in the following cases:
- If you suspect the presence of various types of tumors.
- With damage to the lymph nodes.
- For urolithiasis, kidney prolapse, cirrhosis, hepatitis.
- For problems with the gallbladder and pancreas.
- If abscesses, phlegmons, cysts are suspected.
- For injuries to internal organs.
Also, a CT scan of the abdominal cavity and retroperitoneal space is performed if neither radiography nor ultrasound helped to create a clear picture of the disease; these research methods turned out to be ambiguous and dubious.
For accurate diagnosis of the abdominal cavity, computed tomography is the optimal way to scan the body. Thanks to CT scans, specialists have a clear picture of the health of the liver, pancreas, intestines, gallbladder, kidneys, and lymph nodes.
Indications and contraindications
Multislice computed tomography of the abdominal organs is performed after an ultrasound examination (ultrasound) or x-ray. Indications for its use are, as a rule, clarification of the diagnosis or a more thorough study of the identified deviation. This method is excellent for planning surgical treatment and postoperative monitoring of the patient.
Contraindications are mainly due to the presence, albeit relatively small, of x-ray radiation, but in emergency cases they can be neglected. Undesirable signs for MSCT include:
- less than fourteen years of age;
- pregnancy and lactation;
- weight more than 120 kg;
- the presence of an allergic reaction to contrast enhancement;
- kidney diseases;
- the presence of metal objects in the patient’s body.
Preparatory measures
Preparation for a CT scan of the abdominal cavity is carried out in order to achieve truthful, informative results of the study. The doctor must tell you how to prepare for the procedure. In order for the study to be successful, it is necessary to start preparing for a CT scan of the abdominal cavity 2 days in advance. To do this you need to do the following:
- Go on a diet, giving up foods that cause flatulence. Eliminate cabbage, legumes, whole milk, fruits, bread and pastries from your diet. You should also not drink carbonated drinks or alcohol.
- Many people are interested in: “Can I eat before a CT scan? " . Immediately before the procedure, eating any food is prohibited, as this may complicate the procedure. If the study is scheduled for the first half of the day, then you can sit down at the dinner table for the last time the evening before. If the study is carried out in the afternoon, a light breakfast is allowed.
- When preparing for a computed tomography scan of the abdominal cavity, it is imperative to take enterosorbent medications that prevent the occurrence of flatulence. You can drink activated carbon, Smecta tablets.
- Drink a laxative (for example, Fortrans) to cleanse the intestines. The drug should be taken on the eve of a CT scan of the retroperitoneum (in the evening or in the morning, depending on the time of the tomography).
- If the patient complains of pain in the abdomen, then he needs to drink any antispasmodic drug before starting the scan.
- Preparation for a CT scan of the abdominal cavity without contrast is slightly different from the same diagnosis, only with contrast. In the latter case, the patient needs to be injected with an iodine-based radiopaque agent. If intravenous infusion is planned, it is carried out only on an empty stomach.
- If the contrast agent will be administered rectally, then the evening before you need to give an enema.
- Often, patients are prescribed an abdominal CT scan with contrast , where the contrast agent is used orally. That is, a person takes the drug orally. Often doctors prescribe substances such as Urografin or Omnipaque.
You need to prepare for a CT scan of the abdominal cavity with contrast in the same way as without contrast, adhere to a diet, take laxatives, and enterosorbents. If a person has an allergic reaction to iodine, then a medical scan with contrast of the abdomen will be contraindicated for them.
CT using Urografin
Computed tomography of the abdominal cavity is often performed using a contrast agent, namely an iodine-containing composition, which helps to better identify tumors of various origins and vascular pathologies. In this case, the contrast agent can be introduced into the patient’s body orally, intravenously or rectally.
The method of introducing contrast in this case depends on which particular area will be examined. So:
- the upper parts of the gastrointestinal tract are contrasted by taking a special solution orally;
- the large intestine is contrasted by performing an enema with a contrast agent;
- blood vessels, liver, kidneys, pancreas and spleen are contrasted intravenously.
In this case, as a rule, Urografin is used as a contrast agent, which is eliminated from the body naturally after a few days.
Urogrofin is a medication that increases image contrast due to the fact that iodine, which is part of the active substance of the drug, absorbs X-rays.
What is Urogrofin and why should it be used before an abdominal CT scan? Let's try to figure it out.
General recommendations for preparing for a body scan
For the procedure to be successful, you need to take into account every detail, know how to prepare for a CT scan so that the results of the study are complete and reliable:
- Take care of comfort. Wear comfortable clothes without zippers, fasteners, or buttons. Do not wear jewelry.
- Take the necessary documents - passport, results of previous examinations, medical card, etc.
- Breath control. During the procedure, the specialist instructs the patient to hold his breath for a few seconds at a certain time (before each new cut).
- Before CT scanning of the abdominal cavity, it is necessary to remove existing dentures.
- Be sure to inform your doctor about the presence of any diseases or pathologies. And also inform him about the presence of a pacemaker, an allergy to iodine and other factors due to which the diagnostic process may be disrupted.
Proper preparation for computed tomography allows you to obtain the highest quality images, from which the doctor assesses the patient’s condition and makes an accurate diagnosis.
Safety of the procedure
Since diagnosing internal organs using computed tomography involves irradiating the body, it is logical that many people ask the question: “How safe is the procedure and how often can an abdominal CT scan be done?”
The safety of the procedure depends on the equipment used and the area of exposure. In modern installations, the radiation dose is small compared to a conventional X-ray machine, so there is no need to worry about side effects. If the diagnosis is carried out once, it will not be hazardous to health. In cases of repeated or frequent CT scanning, it should be understood that radioactive substances accumulate in the body, so it is advisable to perform tomography once a year. If it is necessary to carry out the procedure more than once, an interval of 1–2 months should be maintained.
Only a doctor can determine how often a CT scan of the abdominal organs should be done.
Preparing for a CT scan of the abdominal cavity: taking Urografin orally, what can you eat and drink?
Computed tomography is a modern, in-demand diagnostic method. It is used to identify various diseases - detecting a tumor in the lungs, tuberculosis, assessing tumors in the brain, etc.
d. Let's figure out in what cases CT is used to study the chest organs, and when - for other purposes. We will also consider how to prepare for the examination and whether it is worth agreeing to a procedure with the introduction of contrast.
What do CT scans show when examining organs?
First, let's figure out what a CT scan shows when examining a patient? Computed tomography is a modern diagnostic method that combines X-ray radiation with simultaneous software processing of the obtained data.
It is prescribed in a number of cases, which are not possible to list. Doctors consider CT to be an informative procedure, but are in no hurry to use it at the first symptoms of any disease - the radiation load on the body is quite high.
What studies are carried out more often?
- Tomography of the pelvic organs shows morphological and functional changes in the rectum, ureters and bladder. The doctor will see the coccyx, sacrum, pelvic bones and muscles in the image. Women may need a pelvic CT scan to check the condition of the ovaries, fallopian tubes, and uterus. For men – to check the prostate gland.
- Most often, a CT scan of the abdominal cavity and retroperitoneal space is prescribed when the doctor wants to see and evaluate the organs located in it. These are the liver, gall bladder, spleen, pancreas, adrenal glands, kidneys. Also, a CT scan of the abdominal organs (abdominal organs) shows the intestines, stomach walls, visible part of the spine, diaphragm, etc.
- Examination of the chest using CT is the most informative method. It allows you to see the general condition of the lungs and bronchi, the pulmonary artery, and the shape of the alveoli. This method of examination also helps to detect lesions in the lungs, pneumonia, tuberculosis or malignant tumors. In addition, this research method makes it possible to see pulmonary vessels, even miniature ones.
Preparing the patient for a CT scan of the pelvis, abdomen and chest
Now let's talk about what preparation should be for a computed tomography scan. It matters which organs are planned to be examined.
For example, when examining the chest organs, no special preparation is required. You just need to make sure that the clothes can be easily removed if necessary.
In addition, CT results can be affected by metal jewelry, dentures, and hairpins in women.
General preparatory activities
If an event is planned with the administration of intravenous contrast, you should first check the level of creatinine in the blood (three days before CT). This substance is secreted by the muscles because it participates in the body’s metabolic processes.
Creatinine is excreted exclusively by the kidneys, and therefore its level in the blood is a key indicator of the functions of the urinary system.
The contrast agent is considered potentially harmful to the kidneys, which is why it is recommended to do a creatinine test before the session.
You should also find out if the patient is allergic to iodine. Sometimes the doctor preventively stops a possible allergic reaction to iodine-containing contrast by administering steroids. Now let's look at what you need to remember before the procedure and how to prepare for it:
- Before a CT scan of the abdominal cavity, pelvis and gastrointestinal tract, it is advisable to abstain from solid food for a couple of hours, or better not eat at all.
- The bladder should not be full, but not completely emptied. To do this, you need to drink about 1 liter of water an hour before the test. It is not recommended to urinate 40 minutes before the procedure.
- It is advisable to have a bowel movement before testing. Sometimes laxatives (Fortrans) are prescribed before a CT scan.
Diet before examination
Preparation measures also include a special diet, which is necessary only before a tomography session of the abdominal organs and lower abdomen. Its task is to reduce gas formation in the intestines, so you should remove the following foods from your diet:
- vegetables - cabbage, zucchini, eggplant, etc.;
- fruits and berries - grapes, peeled apples, pears;
- legumes;
- milk, fermented milk products;
- sausage, sausages;
- carbonated drinks.
It is recommended to use:
- boiled meat;
- cheese;
- broth with white bread croutons;
- tea, coffee, compote, non-carbonated drinks;
- cookie.
It is advisable to finish eating eight hours before the session. If it’s difficult to tolerate, you can eat a little a couple of hours before your visit to the clinic. However, do not overeat, try to keep your stomach only half full.
Taking Urografin
Let's look at how to take or administer a contrast agent before a CT scan. Most often, doctors recommend using Urografin. The active components of this drug act as radiocontrast agents. This phenomenon is achieved due to the absorption of rays by iodine molecules included in the preparation.
However, it is worth remembering that this medication has side effects. The annotation indicates such manifestations as fever, dizziness, nausea, tachycardia, cyanosis and others. However, these phenomena do not happen often.
How can the drug be administered?
The method of administering the medication depends on which area of the body is being examined. There are three ways to use Urografin:
- intravenously - for the study of blood vessels, bronchi, lungs, heart, kidneys, liver, pancreas, spleen;
- using an enema - if you need to examine the large intestine;
- orally (by mouth) – to study the upper gastrointestinal tract.
You need to take the drug like this. You will need 20 ml of medication (20 ml), it must be diluted in 1 liter of water. Then, 10-12 hours before the procedure, drink half the volume, and the second part - two hours before the session.
If intravenous administration is required, the substance is warmed to body temperature, then slowly injected into a vein. Use 20-40 ml of a 60-76% solution immediately before the session.
Why is contrast needed?
Contrast is an additional way to make a photo brighter and more informative. Doctors often determine the presence of foci of inflammation only after contrast is administered.
In this regard, it is recommended, in the absence of contraindications, not to abandon Urografin in order to increase the effectiveness of the procedure. Contrast is an effective CT diagnostic method.
At the same time, preparation for a session with contrast is quite simple and affordable.
When should a CT scan be done without contrast?
Recently, doctors often suggest doing a CT scan with contrast, since then the results of the procedure are most indicative.
Contrast is not recommended:
- people with a history of an atypical reaction to a contrast agent – convulsions, respiratory arrest;
- severe allergies, bronchial asthma;
- disease of the thyroid gland with an increase in its function;
- extreme degree of renal and liver failure;
- pregnancy, breastfeeding.
Advantages of MSCT examination with contrast
Computed tomography is not a completely harmless test. During the procedure, the patient is exposed to x-ray radiation; therefore, it is advisable to do it in such a way that the session does not have to be repeated again. The use of contrast in MSCT (multispiral computed tomography) allows you to obtain the most accurate results and avoid a new study.
Source: https://vedmed-expert.ru/kt/brushina-taz/podgotovka-k-kt-bryushnoj-polosti.html
CT technique
It's time to find out how the tomography procedure works:
- After presenting all the necessary documents, previous test results, consultation, the patient is asked to take a horizontal position, lie down on the tomograph table and lie still.
- If a patient undergoes a CT scan with contrast, then he is first given an injection with a contrast agent (provided that he did not take the contrast agent orally).
- After the patient lies down on the couch of the device, he is automatically moved inside the ring of the device. This is where the CT scan procedure is performed.
- During a CT scan of the retroperitoneal space and abdominal cavity, the specialist can ask questions to the patient via two-way communication, give commands to hold his breath, ask how he feels, etc. When CT scanning the abdominal organs, and indeed any organ in general, it is forbidden to move .
The duration of a medical scan of the abdominal organs depends on the type of study and the quantitative indicators of checking the internal organs. Typically, a CT scan with contrast lasts no longer than 30 minutes, without it – 15 minutes.
Computed tomography does not cause pain or discomfort. All that is required of the patient is to lie still and listen to the doctor.
How is MSCT of the peritoneal organs performed?
The examination does not cause pain or discomfort in the patient. Before lying on the couch of the MSCT machine, you should remove all objects consisting of metal (including metal dentures). During an abdominal multislice computed tomography scan, a scan of the insides is made.
During MSCT of internal organs, the doctor is in the next room, observing the patient through glass, voice communication is maintained through a special speaker located in the device.
After the procedure is completed, the doctor gives the patient pictures of the examined areas: intestines, stomach, liver, kidneys, spleen and other organs and tissues, as well as a written report.
Using Contrast
A contrast agent during MSCT of the abdominal cavity and retroperitoneal space is used for differentiated diagnosis of the detected abnormality. It is completely safe for humans (if there is no allergy), and is eliminated from the body naturally after 24 hours. Contrast enhancement is administered intravenously using an automatic injector immediately before starting the tomograph. Examination of the abdominal cavity with contrast allows a more thorough examination of the disease, namely:
- determine the location of tumors;
- identify the location of metastases;
- differentiate cysts;
- identify abnormalities of the aortic vessels and disorders in the inferior vena cava system.
How long does an MSCT study take?
The procedure does not take much time. MSCT of internal organs lasts approximately fifteen minutes.
Results of the analysis
A CT scan of the abdominal cavity is interpreted immediately after the diagnosis is completed. The specialist receives the finished images and begins to decipher them. This process usually takes 1 hour. After deciphering the results, the patient is given the photographs, as well as a doctor’s report with his signature and seal.
What does an abdominal CT scan show? Based on the results of the procedure, specialists are able to obtain the following data:
- The exact location, size and shape of the organs being examined.
- The presence of benign or malignant tumors, metastases, infections, bleeding, excess fluid.
- Detection of stones in the kidneys and gall bladder.
- Presence of inflammation in internal organs, etc.
Abdominal CT is a modern, accurate method for diagnosing diseases of internal organs. This research method is performed only according to doctor's indications. A CT scan is prescribed if the specialist is unable to obtain accurate information about the condition of the organs during an ultrasound scan.
Preparation for a CT scan is not complicated and is carried out before almost any study. No preparation is required in cases where examination of any area of the body except the abdomen and pelvis is carried out without the use of a contrast agent. However, even in this case, it is advisable to refrain from eating for at least 4 hours before the procedure, since the doctor may see changes in native images that cannot be identified without additional contrast enhancement. This means that contrast may be needed in cases where its use was not originally planned.
Indications
Multislice computed tomography is most often prescribed in the following cases:
- there is severe pain in any part of the body that does not go away after taking painkillers;
- oncopathologies of the hepatobiliary region, pancreas, kidneys or bladder;
- to confirm or detect neoplasms in the peritoneum and retroperitoneal space;
- blockage of the pulmonary artery or its branches by a piece of blood clot;
- after serious injuries;
- identification of tuberculosis foci at various stages;
- spina bifida;
- pathology of the lymph nodes.
MSCT of the brain allows you to confirm or refute oncopathology. In addition, it clearly visualizes the ischemic focus and clarifies where the source of bleeding is located during a hemorrhagic stroke. And in case of acute traumatic brain injuries, it allows one to assess the extent of damage to bone structures and violations of the integrity of soft tissues and blood vessels.
MSCT of the paranasal sinuses is widely used by otolaryngologists to study the smallest structures in this area. It helps identify inflammatory processes, neoplasms, structural bone damage, fluid accumulation and swelling. MSCT of the lungs with contrast perfectly demonstrates the lung tissue, windpipe, tubular branches of the trachea and blood vessels. This helps the pulmonologist at an early stage to diagnose tuberculosis, pneumonia, increased airiness of the lung tissue, narrowing of the lumen of the bronchi, oncopathology and other diseases.
Multislice tomography of the abdominal cavity perfectly visualizes any pathological foci and processes in its organs and tissues. After the procedure, the diagnostician can easily detect metastases and primary tumors that have reached 2 mm in size. This diagnosis is very informative in case of suspected cysts, as well as for confirming cirrhosis of the liver, inflammation of the pancreas or purulent tissue inflammation.
Multislice CT provides clear visualization of many processes that cannot be recognized with standard or spiral computed tomography.
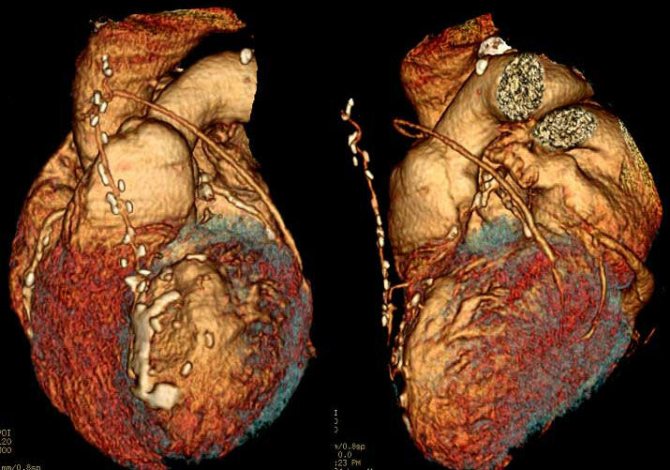
MSCT of the heart allows you to create three-dimensional reconstructions of this organ, identify defects in the valves, cardiac muscle, pericardium and heart chambers
Preparing for an abdominal examination
Typically, this examination involves the most labor-intensive preparation, which takes 2-3 days.
- Diet . It is necessary to exclude from the diet foods that promote fermentation and excessive gas formation in the intestines. These include: carbonated drinks, baked goods, sweets, vegetables, legumes. In the evening before the examination and on the day of the procedure (if the CT scan is performed in the afternoon), it is recommended to limit yourself to light meals, such as mashed potatoes, jelly, soup. The study is carried out on an empty stomach. The last meal before a CT scan should be at least 6 hours before the examination.
- Colon cleansing . To completely cleanse the intestines of contents, the drug Fortrans is used. To prepare, you will need to take Fortrans solution according to a special regimen. The dose of the drug required to cleanse the intestines is calculated as follows: for every 15-20 kg of weight you need to take 1 sachet of the drug. Thus, a patient weighing 60 kg will need 3 sachets. 1 packet of Fortrans is diluted in 1 liter of water. The solution should be taken the evening before the examination. Every 15 minutes you need to drink a glass of solution.
- Oral administration of radiocontrast agents . The drug must be taken long before the examination. A solution of a contrast agent (Urografin, Urofina) is prepared as follows: 1 ampoule of the drug must be dissolved in a liter of water. Ingestion of Urografin before a CT scan of the abdominal cavity will need to be carried out according to a special scheme:
- 250 ml of solution at 18.00 on the evening before the examination;
- 250 ml of solution at 23.00 on the evening before the examination;
- 250 ml of solution 3 hours before the start of the procedure;
- 250 ml of solution before starting the examination.
Your doctor may prescribe a different dosage regimen. For example, in some cases when it is necessary to examine the esophagus or duodenum, a contrast agent will need to be taken only before the procedure begins.
Oral administration of Urografin before CT
As mentioned earlier, one of the ways to use Urografin before an abdominal CT scan is to take it orally. This procedure is performed as follows.
In the evening of the day preceding a CT scan of the abdominal cavity, 2 ampoules of 75% Urografin are dissolved in one and a half liters of boiled water. Immediately after this, half a liter of the product is drunk.

One of the ways to use Urografin before an abdominal CT scan is to take it orally.
The remaining solution is divided in half.
One dose of the drug is drunk in the morning, and the second – half an hour before the start of the procedure. Adverse reactions to taking Urografin orally are usually absent or mild.
For example, after taking the solution, nausea, vomiting, and allergic reactions may occur.
Is a CT scan with Urografin painful?
The CT scan procedure is absolutely painless. And, naturally, taking Urografin orally cannot in any way affect the severity of pain.
Preparing for a pelvic CT scan
In order to obtain informative images of organs located in the pelvis, it is necessary:
- following a diet aimed at reducing gas formation in the intestines;
- cleansing enema or taking the drug "Fortrans";
- oral administration of a contrast agent according to the schedule.
When performing a CT scan of the pelvis, special attention is paid to the degree of bladder filling. To obtain informative images of the organ, it is necessary that the bladder is moderately full. To do this, an hour before the start of the examination, you need to drink 1 liter of clean still water and not urinate.
Preparation
In most cases, special preparation for multislice computed tomography is not required. If the head, neck, chest or spine will be examined, then you can come by appointment on the day of the intended manipulation without changing your usual routine. If the abdominal and pelvic organs will be examined without contrast, then the following simple preparatory steps must be performed: 48 hours before the procedure, you must adhere to a slag-free diet.
The day before the tomography, you should cleanse the intestines (enemas or special medications). The day before the procedure, take medications that reduce gas formation (Espumizan, Activated carbon). The last meal should be no later than 8 hours before the intended procedure.
Before performing MSCT with contrast, more thorough preparation is required:
- 48–72 hours before the procedure it is necessary to determine the creatinine level;
- the day before the tomography, exclude solid foods from the menu, as well as those that increase gas formation;
- on the eve of the scheduled diagnosis, it is necessary to thoroughly cleanse the stomach and intestines;
- You should stop eating no later than 5 hours in advance;
- liquid is not only possible, but also necessary to drink in large quantities before MSCT with contrast;
- 3 hours before the procedure you should drink Urografin 76% (1 ampoule diluted in 2 liters of water).
When going to the diagnostic center, you must take with you a referral for the procedure, an outpatient card, materials from other examinations, as well as extracts after operations. The doctor's referral usually indicates a preliminary diagnosis, diagnostic tasks, and whether there is a need to use contrast.
General recommendations for preparing for a CT scan, regardless of what area will be examined
In some cases, the following conditions will need to be met to safely perform an abdominal CT scan:
- if examinations such as irrigoscopy, passage of barium through the intestines, fluoroscopy of the stomach have previously been carried out, then it will be necessary to wait at least 7 days before performing a contrast-enhanced CT scan of any area of the body;
- often CT is performed only after ultrasound, FGDS, X-ray examination: in the absence of serious clinical indications, computed tomography may be inappropriate;
- If it is planned to use an iodine-containing contrast agent, it is recommended to conduct additional tests to exclude the presence of acute or chronic renal and hepatic failure.
To feel comfortable during the examination, you need to choose comfortable clothing without metal fasteners or trim elements, and leave jewelry at home.
It is recommended to take any medical documentation the patient has with you to the clinic. Previous examinations, diagnoses made and treatment received can help the doctor who is engaged in decoding to make a more complete, detailed and informative conclusion.
Urografin is a radiopaque diagnostic drug intended for intravenous and abdominal administration. The main active ingredient of the product is sodium amidotrizoate.

Preparation for the procedure
MSCT of the abdominal organs does not require special preparation from the patient. Before the procedure, you should follow a diet that prevents gas formation and bloating. Compliance with this rule will prevent obtaining a false, inaccurate image and eliminate the occurrence of artifacts in the images. MSCT of the peritoneal organs is performed on an empty stomach, that is, on the day of the diagnostic procedure, you should stop eating. If the patient has bloating, you need to drink a carminative.
Contraindications
There are complete and conditional bans on the use of Urografin.
Strict restrictions are:
- Heart failure in the stage of decompensation.
- Hyperthyroidism.
- Pancreatitis during an exacerbation - if the patient is indicated for endoscopy of RCP.
- Gestation, inflammation in the pelvic cavity - when prescribing hysterosalpingography.
Possible contraindications for the use of contrast include:
- Decompensated myocardial dysfunction.
- Deviations in the functioning of the kidneys and liver.
- Finding a person in serious condition.
- Emphysema.
- Diabetes in the stage of decompensation.
- Subclinical form of hyperthyroidism.
- Generalized myeloma.
- Individual reaction of the body to iodine.
With these diseases and conditions, the administration of Urografin is carried out under the supervision of physicians.
By-effect
The development of adverse symptoms depends on the method of administration of the substance.
Intravenous
The drug is generally well tolerated. Unpleasant sensations are mild and pass quickly. The most common concerns are nausea, vomiting, hot flashes, and slight pain in the injection area.
Other side effects include:
- Violation of myocardial contractile function and blood pressure indicators.
- Thromboembolic complications.
- Shortness of breath, cough, swelling of the lung tissue.
- Pain in the intestines.
- Deviations in kidney function.
- Tremor of the limbs, photophobia, cephalalgia, dizziness.
- Drowsiness.
- Skin itching, rashes.
- Conjunctivitis, urticaria, runny nose.
Intracavity
Unpleasant reactions do not form immediately, but several hours after receiving the contrast. This is explained by the slow absorption and redistribution of Urografin.
An increase in amylase during ERCP cannot be ruled out. Visualization of acini in rare situations becomes an impetus for the development of pancreatitis.
Systemic allergic reactions are uncommon and are expressed in the form of skin rashes and itching.
Instructions for use
The method of use and dosage depend on the type of procedure.
Intravenous urography
Injections . The composition is administered slowly - 20 ml/min. To obtain a large volume - over 100 ml - the procedure lasts at least half an hour. The dosage is determined by the patient's age group.
The rate of contrast solution for adult patients (in ml): 76% - 20, 60% - 50.
In children, 76% Urografin is used in the following doses:
| Age, months/years | Volume, ml |
| 0–12 | 7,0–10,0 |
| 1–2 | 10,0–12,0 |
| 2–6 | 12,0–15,0 |
| 6–12 | 15,0–20,0 |
| Over 12 | As for adults |
An image of the kidney parenchyma is taken immediately after receiving contrast. To visualize the pelvis, ureter and bladder, the first image is obtained after 3–5 minutes, the second:
In infants and children of primary preschool age, the study is carried out after two minutes. If the picture turns out to be uninformative, then the pictures are taken a little later.
Drip infusion . When using the system, the time for administering 100 ml of a solution of any concentration falls within the range of 5–10 minutes.
If the patient is diagnosed with heart failure, it increases to half an hour. The first image is taken immediately after the infusion is completed. Subsequent ones - after 20 minutes.
Retrograde urography
The procedure is prescribed to visualize the bladder. The drug is injected directly into its cavity using a catheter.
The duration of the procedure is half an hour, since the main reactions occur during this period. A 30% composition is used, obtained by diluting 60% Urografin with cold boiling water in a 1:1 ratio.
The dosage is determined by the following factors:
- Age.
- Weight.
- Myocardial contraction frequency.
- General health.
Angiography of the abdominal cavity
Preparation for the procedure involves complete cleansing of the human intestinal tract. For these purposes, two days before the expected date of the study, foods that increase the formation of gases are excluded from the menu:
Dinner should take place the day before the procedure no later than 18:00. Before going to bed, take a laxative.
To reduce anxiety, you are allowed to drink a sedative. If a person has myeloma, decompensated diabetes, or gout, he can consume any amount of liquid; drinks are unlimited. This also applies to infants and very young children.
For confirmed pheochromocytoma, alpha-adrenergic blockers are recommended. This measure helps prevent the formation of a hypertensive crisis.
Difference from MRI
The choice of diagnostic method differs greatly in each clinical case. The most informative examinations today are MRI and MSCT. Magnetic resonance imaging allows you to obtain high-quality and informative images of organs and systems located within the radius of the magnetic field. It does not expose the body to radiation, so this examination can be performed an unlimited number of times in a short period of time.
During a multislice CT scan, scanning is carried out using x-rays. Penetrating through tissue structures, it is sent to special sensors that convert the data into electrical signals. After processing the information with special programs, the radiologist receives high-quality images of the internal organs.
The difference between MRI and MSCT is that in the first case, objects placed in a magnetic field are subject to imaging, while MSCT provides spiral sections of internal organs. If, unlike conventional CT, MRI better demonstrates hollow organs and soft tissues, then in the case of MSCT they are not inferior to each other in this matter. In order to perform MSCT of the abdominal cavity and retroperitoneal space, it is enough to briefly hold your breath once.
While other diagnostic procedures can cause much more inconvenience to the patient.
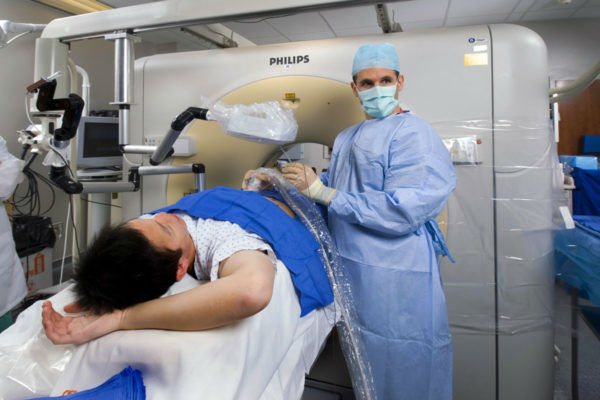
MSCT is indispensable for emergency examination of patients in critical condition
special instructions
Against the background of the administration of Urografin, the development of turnip hypersensitivity is possible. Signs of the condition are:
- The appearance of shortness of breath, a feeling of lack of air in the chest.
- Severe redness of the skin as a result of dilated capillaries.
- Hives.
- Itching.
In exceptional cases, there is a possibility of the formation of angioedema - the vocal apparatus may be affected - anaphylactic shock and bronchospasm.
Reactions to the administration of a contrast agent occur and fully develop no later than 60 minutes after receiving it. Delayed symptoms are also likely: side effects occur after several hours or days.
The possibility of forming a response to iodine-containing drugs is significantly increased if a person has already had similar reactions in the past. In case of predisposition, it is permissible to use antihistamines and glucocorticosteroids for prevention purposes.
With bronchial asthma, there is also a possibility of symptoms of a hypersensitivity reaction or bronchospasm.
When signs of an allergic response of the body develop, the administration of Urografin is stopped immediately. If necessary, symptomatic therapy is performed.
Intravenous administration of Urografin
The drug, ready for intravenous use, is a clear, colorless solution. A pale yellow tint may appear.
The solution cannot be administered if there is a change in color, the appearance of a suspension visible to the naked eye, or if there is a suspicion of a violation of the integrity of the ampoules.
The prepared solution should be drawn into the syringe immediately before the test. Contrast residues unused during the study must be disposed of; they cannot be used for subsequent procedures.
The dose of the administered drug is prescribed by the doctor and depends on how old the patient is, how much he weighs, what his cardiac output is and the state of his overall health.
The prepared Urografin solution should be drawn into a syringe immediately before the study.
Remains of contrast unused during the study must be disposed of - they cannot be used for subsequent procedures. In the presence of heart or kidney failure, the dose of contrast should be as low as possible.
In such patients, it is necessary to monitor renal function for at least three days after the study. Side effects associated with intravenous administration of Urografin are usually mild and quickly transient. However, more severe reactions also occur.
The most common reactions to the administration of the drug are nausea, vomiting, pain and fever. In addition, the following effects occur:
- on the part of the respiratory system - a change in respiratory rate, the appearance of shortness of breath, the development of respiratory failure, cough (rarely - pulmonary edema, complete cessation of breathing);
- skin reactions - facial redness, rash, itching, erythema;
- from the central nervous system - the appearance of headaches, dizziness, confusion, disturbances of visual, auditory and speech functions, the appearance of drowsiness, tremor, convulsions;
- on the part of the heart - changes in heart rate and rhythm, surges in blood pressure (rarely - thromboembolic complications that can lead to more serious complications);
- from the urinary system - impaired renal function;
- allergic reactions.
How to take orally before an abdominal CT scan
In preparation for the study, it is proposed to take Urografin orally. It takes place in two stages:
- In the evening, stir 2 ampoules of 75% composition in cold boiling water (1.5 l), take 500 ml immediately.
- Divide the remainder equally. Drink the first part after waking up. The second – 30 minutes before the CT scan.
The development of side effects is possible:
- Mild nausea.
- Attacks of vomiting.
- Skin itching and rashes.
Pain does not occur while taking Urografin.
Analogs
There are substitutes for radiopaque contrast agents, but with slightly different compositions (contain sodium amidotriosate):
- Angiographin.
- Visitor trust.
- Urovizin.
- Urotrast.
- Verografin.
- Trazograph.
- Triombrine.
Triombrast solution is also used. In addition to sodium amidotrizoate, the drug also contains meglumine.
The cost of the medicine is high, which is explained by the peculiarities of its composition and scope of application. But at the same time, it is fully justified by the effectiveness of Urografin. The price of 1 ampoule largely depends on the region of sales. A dose of the product sells for 200–260 rubles.
Conditions of release and storage
The medicine is a prescription drug. You can buy Urografin in Moscow in large pharmacies.
To prevent the solution from losing its original properties, it is stored at room temperature. Choose a dark place out of direct sunlight.
Urografin belongs to the group of radiopaque iodine-containing drugs and is not a drug in the usual sense of the term. Its independent use is unacceptable. Prescription of the solution is possible only according to indications.
Progress of the procedure
At SM-Clinic, MSCT angiography is performed on an outpatient basis.
Before the procedure begins, the nurse will insert a catheter into the vein, through which contrast will be injected. The volume of the contrast agent and the rate of its administration are selected individually depending on the area being studied, the age and constitutional characteristics of the patient. The patient is placed on a table, which during the study will smoothly move horizontally through the aperture of the device. During the study, the doctor observes the patient and communicates with him through two-way communication. During the scan, the patient may be asked to hold their breath. If you experience any unpleasant sensations, you should immediately inform your doctor.