How does cramping pain in the stomach manifest?
Cramping pain occurs as a result of obstruction of a hollow organ, which is the stomach. This paroxysmal pain is sometimes called colic. Attacks of pain may alternate with painless intervals of varying duration and intensity. The nature of the pain does not depend on the position of the person experiencing it.
Gastritis and ulcers can cause cramping pain.
There are several types of stomach spasms:
- total (general) – accompanies a disease of the nervous system, occurs infrequently;
- regional (partial) – manifests itself in the form of a spasm of a separate area of the gastric muscles, for example, in a bi-cavitated stomach, which occurs after the healing of an ulcer, tuberculosis scar, gumma;
- limited - diagnosed in case of a disorder of higher nervous activity, as well as after the administration of morphine, systematic smoking, violations of the work and rest regime.
Additionally, there is a feeling of heaviness in the stomach, bloating, a feeling of fullness, nausea, and discomfort in the pit of the stomach.
Types of diarrhea
There are acute and chronic diarrhea.
- Acute diarrhea. It occurs suddenly and lasts from 2 to 10-12 days, depending on the cause of its appearance, the method of treatment and the timeliness of assistance provided to the body. Most often, the cause of acute diarrhea is poisoning, various intestinal infections, and allergies to any drugs.

The most common cause of acute diarrhea is poisoning
- Chronic diarrhea. Occurs with a certain frequency. Its causes are chronic diseases: ulcerative colitis, gastritis, hormonal diseases. Chronic diarrhea requires immediate attention to a gastroenterologist, examination and surgical treatment, because it may cause electrolyte imbalance as a result of dehydration over a long period of time.

If diarrhea occurs periodically, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Causes of diarrhea
| eating poor quality, spoiled food | irritable bowel syndrome |
| change of climatic zones | ulcer |
| eating exotic foods that have not been eaten before | gastritis |
| intestinal infections | hormonal disorders |
| allergic reactions | a reaction to long-term use of any drug (usually more than a month) |
| stress (the so-called “bear disease”) | consequences of previous surgical interventions (especially after operations on the gastrointestinal tract) |
Possible reasons
Diseases of the digestive system provoke the appearance of colic in the stomach. There are organic and functional disorders of this organ. Gastrointestinal pathologies causing spasms:
- gastritis;
- ulcerative lesions of the gastric mucosa;
- colitis;
- intestinal obstruction.
Additional functional reasons that provoke cramping pain in the stomach:
- side effects of medications;
- intoxications associated with food toxins or alcohol abuse;
- eating disorders;
- smoking;
- neuroses, stressful situations;
- coffee addiction
- allergic reactions to foods or other provoking factors, injuries to the stomach and intestines.
Diagnosis of intestinal spasm
Most often, when an intestinal spasm occurs, the patient seeks advice from a gastroenterologist or therapist. These specialists carefully study the medical history, accompanying complaints and, if necessary, schedule a consultation with a surgeon.
To identify the underlying disease that could lead to the development of intestinal spasm, a number of laboratory and instrumental studies are carried out. A general blood test can reveal anemia and inflammatory changes in the leukocyte formula. A general urine test will indicate a catastrophe in the pelvis (pelvioperitonitis), disorders of the exchange of bile acids and glucose. A biochemical blood test is an indicator of the condition of the liver, pancreas, and kidneys. To exclude intestinal pathology, a coprogram and stool analysis for occult blood are examined.
To identify organic pathology of internal organs, ultrasound, plain radiography (including contrast), computed tomography or MSCT of the abdominal organs may be required.
Quite often, to establish the exact causes of intestinal spasm, a consultation with an endoscopist is required. Esophagogastroduodenoscopy, colonoscopy and sigmoidoscopy make it possible to visualize changes in the mucous membrane of different parts of the intestine and identify the exact cause of the pathological condition.
What pathologies do stomach cramps indicate?
The nature of spasms differs in each specific case, as it depends on the course of the disease and the individual characteristics of the patient.

When changing positions, the cramping pain does not subside.
- Stomach ulcer - attacks almost never appear on an empty stomach; they occur more often after eating, after half an hour to an hour, and subside with the end of digestion of food.
- Pylorospasm - occurs in patients with a weakened nervous system, is characterized by attacks of vomiting and the appearance of a pain symptom after eating; after emptying the stomach, spasms and pain are not felt;
- Pancreatitis - pain during spasm radiates to the right hypochondrium or lower back;
- Dyskinesia of the gallbladder, cholecystitis - the appearance of painful spasms in the epigastric region after errors in nutrition (smoked, salty, fatty, overly sweet foods);
- Gastritis - severe spasms are accompanied by weight loss, vomiting, and sour belching.
- Acute intestinal obstruction - can be caused by a tumor, helminthic infestation, fecal conglomerate after constipation, accumulation of fiber, volvulus of intestinal loops. It is manifested by the inability to excrete gases and feces, bloating, painful spasms of the stomach and intestines, severe vomiting with bile and intestinal contents that acquire a putrid odor.
- Erosion of the gastric mucosa is characterized by prolonged, regularly occurring powerful spasms. The pain appears at night, and may be accompanied by bleeding, which indicates that the process has worsened and become chronic.
Medicine for intestinal pain
We have already found out that recurring pain in the intestines can be a manifestation of Irritable Bowel Syndrome, a functional disease in which there are no so-called organic (structural) disorders of the organ, but its functions are impaired. Treatment of IBS requires a targeted approach to restoring motor or intestinal motility function.
In addition to adjusting the diet and stabilizing the emotional state, the drug Duspatalin ® 135 mg in tablet form can come to the rescue. It acts focally - exclusively in the intestines. In addition, the drug “smartly” approaches the control of motor activity of the intestinal muscle walls, due to the fact that it does not just relax the spasmodic cell, but regulates its activity.
Duspatalin ® 135 mg coordinates the motor activity of both the transverse and longitudinal muscles of the intestines, ensuring a harmonious rhythm of the intestines. The tablets not only help relieve pain, but with a 14-day course of use they restore the functioning of the “irritable” intestines 2, 4. Thus, Duspatalin ® 135 mg helps eliminate bloating, flatulence, constipation, diarrhea or their alternation 5.
Duspatalin ® 135 mg is recommended to be taken 1 tablet 3 times a day 5.
You can learn more about the drug here.
Duspatalin ® 135 mg was created for a comprehensive solution to the problem of “irritable” intestines: it relieves spasms and pain in the abdomen, and when taken in a course, restores intestinal function 1.
Recommended course of treatment for IBS from 28 days 2.
Surely many are familiar with the situation when, against the background of stress, the stomach suddenly “grabs”: spasm and pain and diarrhea occur. In common parlance, this condition is called “bear disease.”
Surely many of us have at least once in our lives encountered an unpleasant problem when our usual daily routine is disrupted by discomfort and pain in the abdomen. Why does this happen?
1 1. According to the World Organization of Gastroenterology, IBS affects from 9 to 23% of people in the world. Irritable bowel syndrome: a global perspective. World Gastroenterology Organization Global Guideline 2020.
2 2. Minushkin O.N., Elizavetina G.A., Ardatskaya M.D. Drug therapy for functional disorders of the intestines and biliary system, occurring predominantly with abdominal pain and flatulence. Clinical pharmacology and therapy. 2002;1:24-26.
3 3. Spiller R, Aziz Q, Creed F, et al. Guidelines on the irritable bowel syndrome: mechanisms and practical management Gut 2007;56:1770–98.
4 4. Belousova E.A. Antispasmodics in gastroenterology: comparative characteristics and indications for use. Pharmatheca 2002;9:40–46.
5 5. Instructions for medical use of the drug Duspatalin ® (mebeverine) 135 mg film-coated tablets dated May 24, 2017
Intestinal spasm
- a symptom of a huge number of diseases of the digestive tract, characterized by high-intensity visceral pain associated with significant contraction of the intestinal wall. The main symptom of intestinal colic is cramping pain, usually combined with other symptoms of the underlying disease. To determine the cause of this condition, various laboratory, x-ray, ultrasound and instrumental research methods may be required. Treatment of intestinal spasms is conservative: sedatives, antispasmodics, heat on the abdominal area, antidiarrheals and a special diet.
Cramping pain and diarrhea
The addition of diarrhea to stomach colic indicates the penetration of a viral infection into the body, called “intestinal flu” or infectious gastroenteritis. Its causative agents:
- adenovirus;
- rotavirus;
- astrovirus;
- coronavirus;
- calicivirus;
- norovirus.
Additionally, symptoms such as fever above 37.5⁰, nausea and vomiting, and general weakness may appear. Viruses invade the cells of the stomach and intestines, disrupting the processes of transport and absorption of food.

If the pain does not go away within 2-3 days, consult a gastroenterologist.
Viral gastroenteritis is transmitted by the fecal-oral route; most often it affects adults and children, who spend part of their time in large groups. The disease lasts no more than 10 days. Accurate diagnosis is carried out by analyzing the patient's stool and observing the nature of diarrhea.
Another cause of diarrhea along with cramping abdominal pain may be dysentery, an infectious disease caused by Shigella. In this case, the following symptoms will additionally be felt:
- pale skin;
- hyperthermia;
- false urge to defecate;
- the appearance of blood streaks in the stool.
Features of pathogenesis
Considering the specific localization of stomach pain and diarrhea, they are of two types: small intestinal, large intestinal. Painful sensations appear in all cases, only their concentration differs. If the diarrhea is colonic, then pain is observed in the lower abdomen. When diarrhea is small intestinal, the pain manifests itself as severe cutting in the umbilical region, as well as in the epigastric region.
Stomach pain and diarrhea occur against the background of various symptoms - vomiting, fever, headaches. The nature of the clinical picture directly depends on the disease that is the cause of the illness. There are different forms of pain:
Sharp stings
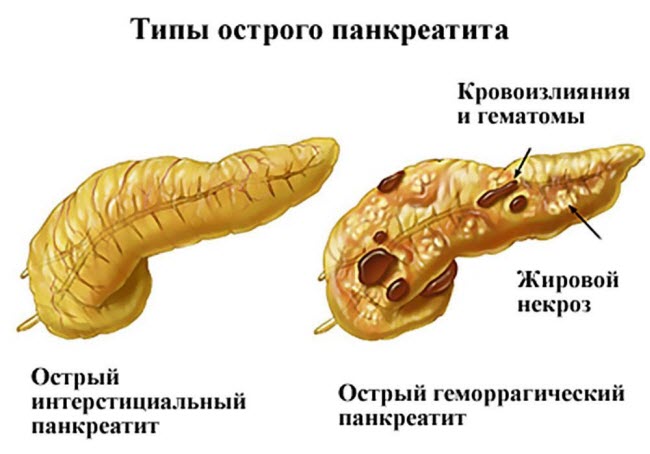
Long-term cramping pain is considered the most unpleasant and painful for a person. They signal the onset of such diseases - appendicitis, acute pancreatitis, peritonitis. The pain syndrome intensifies during probing and palpation. Pain with cutting can occur due to infection of the digestive organs. Diarrhea does not occur in all cases; defecation disturbance may occur.
Pressing pain syndrome
This type of pain indicates the presence of irritation of the esophagus caused by spicy, salty, hot or too cold foods, as well as smoking on an empty stomach. The greatest intensity of pain occurs in the case of an ulcer. Such symptoms can be a consequence of the inflammatory process of the duodenum.
Cramping pain
Convulsive pain syndrome is provoked by pathologies of the gallbladder. If stones form in it, spasms are observed in the right side, which can radiate to the shoulder blade. Fats of animal origin have a detrimental effect on the gallbladder. Spasmodic pain may accompany inflammation of the appendix.
Allergic pain syndrome
This type of pain is familiar to people whose digestive system is not able to tolerate nuts, gluten or lactose. When such products penetrate the gastrointestinal tract, inflammation of the pathways is observed. The phenomenon is accompanied by stomach pain and diarrhea, as well as skin rash.
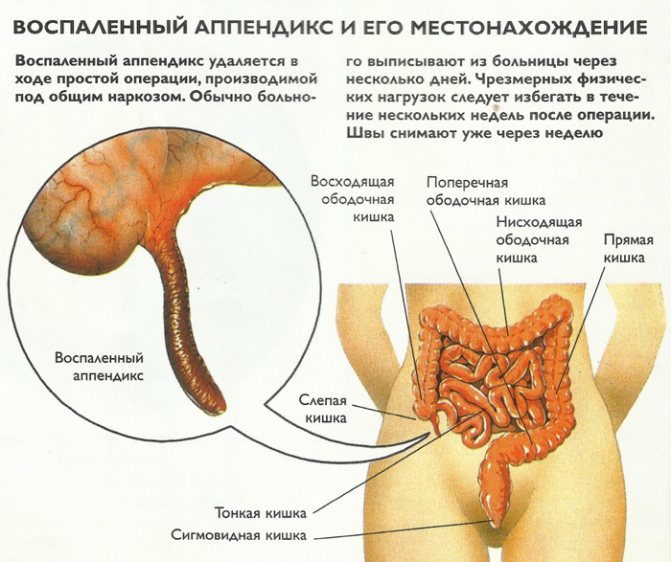
Appendicitis is an inflammation of the cecum. The pains associated with this disease are located in the lower right part of the abdomen or around the navel. Pancreatitis is a serious disorder in the production of digestive enzymes, for which the pancreas is responsible. The pathology provokes a violation of the consistency of stool, as well as destruction of the pancreas, which causes severe pain. Peritonitis is an inflammatory process occurring in the serous layer of the peritoneum, caused by a bacterial infection. The disease is fatal in 40 percent of cases.
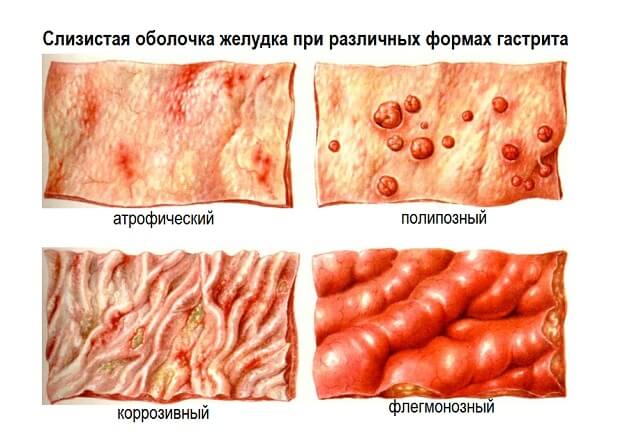
Pain and aching nature are inherent in cholecystitis - inflammation of the gallbladder. The provocateur of this disease is the formation of stones, which disrupts the full outflow of bile. In the case of an acute form of pathology, increased pain is observed. Aching pain localized in the liver indicates hepatitis. If you have diarrhea, then most likely the cause lies in the course of hepatitis A.
Pain on the left side
If pain is observed in the left side of the stomach, this may indicate chronic gastritis. The cause of the pathology is Helicobacter pylori, a pathogenic bacterium that has a detrimental effect on the walls of the stomach. Pain accompanied by dull cuts indicates sigmoiditis (an inflammatory process in the sigmoid colon). There are three main forms of sigmoiditis: ulcerative, erosive and catarrhal. They are characterized by varying depths of damage. The disease may be accompanied by constipation or diarrhea, but diarrhea is more common.
Diarrhea can be a consequence of anxiety or a stressful situation. This is due to the fact that excessive nervous tension provokes a spasm of the muscles of the gastrointestinal tract, as a result of which the immune system noticeably weakens and a malfunction occurs in the digestion process. The seasonal and temporary severity of pain is of particular importance. In the case of gastritis, pain in the stomach bothers you in the spring and autumn.
Crohn's disease
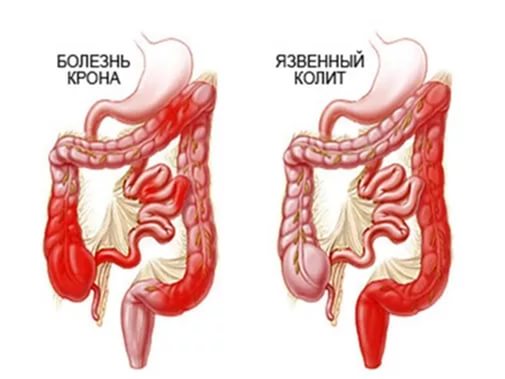
This pathology occurs in the form of inflammation in the small intestine. Moreover, it can affect any part of the gastrointestinal tract. In the initial stage of the disease, abdominal pain, diarrhea, flatulence and colic are observed. An advanced stage of the disease can cause anorexia.
Oncology
A malignant tumor affecting the digestive tract provokes severe pain in this area. Clinical picture: weight loss, weakness, fatigue, nausea, diarrhea, vomiting, abdominal pain.
If abdominal pain and diarrhea are observed in a small child, you should immediately call a doctor and take all relevant tests. Based on the examination and test results, the doctor should prescribe a course of therapy, which should begin immediately. It is not recommended to delay treatment or choose medications on your own to eliminate the child’s symptoms. The protective functions of the child’s body are not always able to fight the disease. For this reason, even banal poisoning can threaten the development of dangerous complications.
Most often, such symptoms in children appear in the following cases:
- appendicitis;
- use of antibiotics;
- poor diet or poisoning;
- allergies, the presence of dysbacteriosis and other gastrointestinal pathologies;
- intestinal infection.
It’s interesting to read: what diseases can cause abdominal pain, fever and diarrhea?
Help with stomach cramps
Any ailment, if it is accompanied by pain and is noted regularly, and not occasionally, requires a thorough examination. In most cases, according to the results of the examination, there is no reason for concern, and a small adjustment of the diet and compliance with the doctor’s recommendations is enough to regain your previous health.
If it is not possible to consult a doctor in the near future, to relieve paroxysmal pain, you need to drink a glass of water at room temperature or another neutral liquid. It is advisable not to eat for 3-4 hours, and if vomiting occurs, abstaining from food lasts up to 6 hours. After the cramping pain stops, it is recommended to limit the following foods in your diet:
- dishes containing coarse fiber;
- freshly baked bread;
- spices, spicy dishes;
- refractory animal fats;
- strong coffee or tea;
- fatty, fried, smoked foods.
It is imperative to follow a diet; you need to eat often, but in small portions, using light, low-fat foods. It is not recommended to eat too cold or too hot food. At night, you can drink a glass of warm low-fat milk.
Antispasmodic drugs will help relieve the intensity of stomach colic: No-Shpa, Drotaverine hydrochloride, Spazmalgon. The drug Iberogast selectively relaxes the muscles of the bottom and body of the stomach and tones the muscles of its bottom, which helps to quickly evacuate the food bolus into the duodenum. It is possible to use traditional methods:
- Mint leaf tea;
- Motherwort juice solution;
- An infusion of a mixture of nettle, St. John's wort, and meadowsweet flowers.
In occasional cases of spasmodic pain in the stomach, massage of the epigastric region helps relieve it.
Treatment of intestinal spasm
Before the ambulance workers arrive, you should not independently relieve intestinal spasms with painkillers and antispasmodics, a warm heating pad, or enemas. Only a doctor will be able to correctly assess the identified symptoms and exclude such serious diseases as acute appendicitis, peritonitis, and intestinal obstruction. Self-treatment of intestinal spasms can lead to blurring of symptoms, diagnostic errors and delay of treatment measures.
After acute surgical pathology has been excluded, pathogenetic treatment is prescribed. If intestinal spasm has developed against the background of emotional stress, or the appearance of this symptom has led to increased nervousness of the patient, sedatives are prescribed. Drotaverine and belladonna preparations relax the smooth muscles of internal organs, eliminating intestinal spasms. A warm heating pad on the abdominal area has a similar effect. In case of increased gas formation, a diet is prescribed (therapeutic fasting for 12 hours, then foods that lead to increased gas formation are excluded), enemas to remove feces and gases. If intestinal spasm occurs due to diarrhea, it is recommended to take smecta and other antidiarrheal drugs.
For periodic intestinal colic that is not associated with other pathology of the internal organs, it is recommended to take long-term sedatives, follow a diet excluding fried, spicy, fatty, pickled and smoked foods, canned food, carbonated drinks, yeast dough and some vegetables (legumes, cabbage, corn, radishes).
Reason for urgent hospitalization and prognosis for the development of the disease
In case of an “acute abdomen” that threatens the patient’s life, the prognosis for the development of the situation depends on how quickly the patient is taken to the hospital. Hospitalization is necessary for the following symptoms:
- Cramping pain changes its character and becomes diffuse and constant - suspicion of intestinal obstruction;
- An admixture of blood appears in the stool - suspicion of dysentery;
- The pain lasts for several days, constantly increasing, and is not relieved by antispasmodics;
- Vomiting appears mixed with blood, similar to coffee grounds;
- The stool turns black (“melena”), which indicates gastric or intestinal bleeding;
- Colic is accompanied by severe night pain, from which the patient wakes up;
- Paroxysmal pain occurs in a child, an elderly person, or a patient with a history of chronic diseases;
- Symptoms of colic in the stomach include dizziness, the appearance of delirium, and rapid pulse;
- After an abdominal injury, attacks of stomach cramps periodically appear;
- The patient shows signs of dehydration: the skin is dry and not elastic, the nose is pointed, the eyes are sunken, the urine is dark and there is little of it.
For most conditions that cause paroxysmal stomach pain, the prognosis is favorable. If the diet and nutrition regimen are followed, the health of such patients quickly returns to normal. Untimely diagnosed and treated diseases of the stomach and intestines can affect the condition of hair, nails, skin and teeth.
The consequences of stomach cramps can be the appearance of stomach erosion, atrophy of the gastric walls, ulcerative and oncological lesions of the stomach and intestines. To eliminate the possibility of developing severe pathologies, they should be examined in a timely manner and treated at an early stage.
RepostTweet
Diet for diarrhea
If you have diarrhea, you should not eat foods that stimulate intestinal motility:
- black bread;
- fresh fruits and vegetables;
- dairy products;
- fatty, fried, salty;
- legumes (lentils, beans, peas);
- mushrooms;
- flour products, especially baked goods;
- sweet carbonated drinks;
- coffee.
Don't drink coffee if you have diarrhea
It is best to eat boiled or steamed food. For example, rice, crackers, soups with cereals, lean meats, boiled eggs.
If you have diarrhea, it is better to eat boiled food
As you feel better and the symptoms of diarrhea reduce, the list of allowed foods is gradually expanded to avoid depletion of the body due to a lack of vitamins and nutrients.
Throughout the treatment, the body must receive a sufficient amount of fluid. These can be herbal teas, dried fruit compotes, still mineral water.
During treatment you need to drink more fluids
Nature of pain
In addition to the location of pain, one can also predict the prerequisites for this by the nature of its manifestation. In general, the manifestation of pain can be sharp, sharp and sudden, constant, aching and pulling. In addition, pain can radiate to other parts of the body, in men it can be the genitals, lower back, anus.
Acute and sharply manifested pain is most likely a consequence of exacerbation of pathology, ranging from diseases of the genitourinary system and gastrointestinal tract, ending with ruptures of tissues and organs. Dull but growing pain is usually a signal of the development of an inflammatory process. The rate of increase in inflammation can be judged by the rate of increase in pain. Throbbing pain is a consequence of increased pressure in the genital area, such as intestinal obstruction, obstruction of the urinary ducts, etc. Paroxysmal pain is most often a signal of pathological processes in the peritoneal organs.
If the pain radiates to other parts of the body when coughing, active movements, sneezing and bending the body, the man should call emergency help, as this may be a hernia or an exacerbation of appendicitis, requiring immediate treatment. You can contact a therapist, who, based on the medical history, can redirect the patient to the right specialist.
Quite well-known symptoms - diarrhea and abdominal cramps - usually signal the presence of an inflammatory process in the body. And this combination can occur in both children and adults as a result of food poisoning, intestinal infection, or the presence of serious gastrointestinal pathologies. We will talk about how to get rid of these symptoms in some diseases later in the article.

Drug treatment for diarrhea
If diarrhea does not go away on the third or fourth day, contact a specialist to find out the cause. After making a diagnosis and clarifying the cause that triggered the onset of diarrhea, the doctor will prescribe appropriate treatment. Usually it consists of taking the following drugs:
- Sorbents (“Smecta”, “Activated carbon”).
- Antidiarrheal drugs (Imodium, Loperamide).
- Drugs aimed at restoring ionic balance (Regidron). They are needed after dehydration of the body.
- Pro/prebiotics (“Linex”, “Bifiform”). They are needed to restore the microflora inside the intestines.
If the diarrhea is of an infectious nature, the specialist prescribes:
- Intestinal antiseptics (“Sulgin”, “Fthalazol”, “Furazolidone”).
- Antibiotics (macrolides, tetracyclines, amoxicillins).
You should not use these medications for self-medication for diarrhea. Each of the drugs should be selected taking into account such features as: the condition of the patient, the cause of diarrhea. Medicines are prescribed in a course that should be completed to the end, and not stopped after the unpleasant symptom (diarrhea) disappears. Also, don't forget about your diet. It is an important aspect in the treatment of disorders of the gastrointestinal tract.
gastrosapiens.ru
Folk remedies for loose stools
Diarrhea that lasts 3 days cannot be ignored. In addition to medications, folk recipes will help normalize intestinal function. It is important to understand that such therapy is not appropriate in all situations. So, in case of infectious diseases you cannot do without pharmaceutical drugs. If diarrhea is caused by poisoning or stress, then supplementing the main treatment with folk remedies is quite possible.
- The use of rice water is popular. To prepare the product, add 2 tablespoons of cereal to two glasses of water. The mixture is heated and then cooled and infused. You need to drink it throughout the day in small sips.
- Another effective remedy for loose stools is rowan juice. You need to drink it twice a day, half a glass. It is advisable to do this before eating on an empty stomach. The drink is useful not only because it helps stop diarrhea. Rowan berries are rich in vitamins, which is extremely necessary for weakness and fatigue that accompany intestinal disorders.
Diarrhea is an unpleasant symptom, which is much easier to get rid of if the exact cause of the condition is known. To determine the pathology, you need to see a doctor, who will not only examine you, but also recommend tests. After examining stool and blood samples, the specialist will draw a conclusion about the factors that provoke the disorder and explain how to restore the normal functioning of the gastrointestinal tract as soon as possible.
1zhkt.ru
Prevention
To prevent diarrhea and abdominal pain, it is recommended to observe good personal hygiene. You should not eat unwashed vegetables and fruits, expired products, or raw water. Nutrition should be balanced and contain all the necessary vitamins. It is recommended to exclude fried, spicy and smoked foods, and fast food from the diet. Hands should be washed before every meal and after going outside. It is recommended to do gymnastics daily, lead an active lifestyle, and give up bad habits.
Often, abdominal pain and diarrhea are short-term phenomena caused by temporary indigestion. These symptoms can be treated on your own. However, if they recur or other negative manifestations occur, it is important to immediately consult a doctor. This will allow you to timely identify the source of the disease and prescribe an effective treatment regimen.