General principles
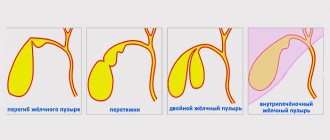
A change in the usual diet will be necessary if the main functions of the organ are suppressed. Basically, the contractile function of the bladder is impaired, and bile stagnation occurs. If motility suffers and bile stagnation forms, the secretion becomes thick, its normal outflow suffers, inflammatory processes develop, and the area of the right hypochondrium continues to hurt. Any pathological changes can be reduced with proper healthy nutrition.
The diet for gallbladder diseases is compiled depending on the stage of the disease, and also depends on the form and its course.
Refusal of harmful foods helps relieve pain and inflammation, and together with drug treatment, this approach will relieve problems with the gastrointestinal tract. A dietary menu must be prepared for people with cholecystitis in the chronic or acute stage, with cholelithiasis, dyskinesia and other problems. People with such pathological changes simply cannot do without adjusting the daily menu.
When changing the diet, each patient adheres to strict rules, including frequent meals in small portions, as well as a diet duration of at least six months. It is not recommended to eat more than 300 grams of food at a time, and the number of meals should be at least 5-6. If the portion is large, it takes longer and is more difficult to digest in the body, so you need to limit the amount of food and switch to fractional meals. It is also important to monitor the temperature of cooked foods and not eat too hot or cold food, which can cause illness.
Gallbladder. Diet: basic approaches, healthy foods
Depending on the severity of the pathological process, the stage of exacerbation, and concomitant diseases, the necessary diet is compiled. The diet involves the following principles:
- Frequent (5-6 times) and fractional (300 ml) meals.
- The duration of the diet should be at least 6 months.
- Adequate intake of proteins and carbohydrates (complex).
- Limit animal fats (lard). It is replaced with vegetable and butter.
- Essential oils and extractives (saturated broths), legumes are contraindicated.
- It is worth giving up drinking coffee, cocoa, and sweet pastries.
- Alcoholic drinks are contraindicated.
- For biliary dyskinesia of the hypotonic type, the use of choleretic products (milk, sour cream, eggs, fresh vegetables, fruits) is indicated.
The Pevzner Diet 5 meets all these criteria. Table 5a provides maximum sparing for functionally impaired liver and gall bladder. For combined pathology of the hepatobiliary system and pancreas, a 5p diet is recommended.
Diet No. 5
Indications for prescribing this diet are diseases of the liver and gallbladder in remission (hepatitis of various etiologies, cirrhosis, cholecystitis, cholelithiasis, bile stagnation).
If there is pathology in the intestines or stomach, tables 2–4 are prescribed.
The diet provides adequate nutrition with a reduction in the functional load on the hepatobiliary system.
Of the main nutrients, only refractory fats are limited, which are replaced with vegetable or butter. Dishes are baked or boiled. The frequency of meals is 5–6 times a day.
Recommended products include:
- Lean poultry, rabbit, veal. Before cooking, remove fascia, tendons, and skin.
- Lenten varieties of fish.
- Wheat, rye or peeled bread from lower grade flour.
- Soups with vegetable broth.
- Fermented dairy products, low-fat cheese.
- Only the white is used in eggs, limiting the consumption of yolks to 1 per day.
- Buckwheat and oats are considered the most healthy cereals. They contain a variety of nutrients, microelements, and vitamins. Oats help remove toxins from the body and support digestive processes. There are many recipes: porridge, jelly, decoction, infusion. It is generally accepted that liquid oat dishes are digested faster. Magnesium, which is included in its composition, has a beneficial effect on the nervous system and helps relax smooth muscles. The oil that is extracted from oats is rich in fat-soluble vitamins, which promotes the healing of ulcerative defects in the stomach and duodenum. Buckwheat is rich in zinc, potassium, phosphorus - microelements necessary for the normal functioning of the gastrointestinal tract.
- Vegetables can be eaten raw, stewed or boiled.
- Limit consumption of chocolate, coffee, cocoa, carbonated drinks, mustard, pepper, horseradish.
Diet 5a
If there is an exacerbation of liver diseases (hepatitis, cirrhosis) or gall bladder (cholecystitis, bile stagnation), then approaches to nutrition and treatment of the patient change.
Table 5a helps to provide the patient with all the necessary substances and microelements. At the same time, it significantly reduces the functional load on the organs of the gastrointestinal tract (liver, gall bladder, pancreas).
Diet 5a completely excludes foods that cause fermentation and putrefaction in the intestines. Dishes that increase bile secretion, increase the secretion of gastric juice, and irritate the liver are contraindicated.
The products are cooked in a steam or water bath, after which they are pureed until smooth. Cereals (oats, buckwheat) are well boiled and added to soups. It is possible to serve finished products in the form of separate dishes. The diet is 5-6 times a day, in small portions.
Limit fat consumption to 20–30 grams per day (preference to vegetable oil).
The energy value of diet 5a is 2400–2600 kcal, which allows you to cover all physiological needs.
Diet 5p
For combined liver pathology, stagnation of bile in the bladder and diseases of the pancreas, use table 5p. Together with rational treatment, the diet is aimed at normalizing the functional activity of the above organs. The nutritional features are:
- Increased protein content (up to 120 grams per day), vitamins, limitation of carbohydrate and fatty foods.
- Avoid fried, cold and hot foods.
- Food is steamed, boiled, and occasionally baked.
- The diet includes vegetables, fruits, cereals (oats, buckwheat), lean meat and fish, and dairy products.
Authorized Products
Most often, a diet for gallbladder diseases will be needed for cholecystitis, in the acute stage of which only liquid food is allowed. The patient is given tea without sugar, soup from chopped vegetables, and juices diluted with water. You can eat porridge after the attack of acute colic has passed. If the disease is chronic, a different dietary table is selected with a wider list of permitted foods.
The menu should consist of protein foods, significantly reduce the amount of animal fats and leave only vegetable oil, as well as a little butter. Lard and other animal fats remain strictly prohibited. Certain plant and protein foods promote better outflow of bile, and uncontrolled intake of carbohydrates, on the contrary, slows down this process, and the gallbladder begins to hurt again.
The following products have a very beneficial effect on the condition of the biliary tract:
- milk and sour cream;
- boiled eggs;
- certain fruits;
- vegetables (cabbage, carrots, cucumbers, beets);
- among berries, preference is given to strawberries, grapes, and watermelons.

Dietary nutrition for diseases of the bile and liver excretion pathways
Pathologies of the liver and biliary tract are encountered most often in the practice of a gastroenterologist. That is why it is so important to prevent their occurrence and prevent the exacerbation of an existing biliary disease. Complex treatment involves the use of diet therapy as one of the main means of normalizing the patient’s condition and eliminating the manifestations of gallbladder disease. The diet for gallbladder disease and problems in the liver is developed taking into account knowledge about the effect of food on the subtle structures of the hepatobiliary system, the enzymatic action of liver secretions and the characteristics of bile synthesis. The liver is vulnerable to the products consumed, so the slightest disturbance can affect its functionality.
Features of the digestive system
A diet for diseases of the liver and biliary tract involves eating food that restores metabolic processes in the body. Food should create a suitable environment for the liver to function, stimulating the secretion of bile by the gallbladder, neutralizing harmful substances in the functioning of the digestive organs, which are often affected by the same pathology. The main factor is the rhythm of eating.
Bile is secreted by the biliary system only at the time of eating, which is a natural choleretic agent. At night, when the patient does not eat, bile accumulates in the organ, and during daytime nutrition it is evacuated, which prevents stagnation and infectious inflammation. It is forbidden to eat heavily at night, as this significantly disrupts the rhythm of the body.
Features of the chemical composition of the diet
In diseases of the liver and gall bladder, the chemical composition of food is extremely important. The liver is involved in protein metabolism, so the intake of this substance must be carefully regulated by the patient. The diet for gallbladder diseases involves controlling the intake of fats, proteins and carbohydrates.
Protein content
Taking into account gallbladder disease and a diseased liver, you can consume no more than 90 g of protein per day, and animal and plant types should be in equal proportions. It is necessary to add proteins with lipotropic substances, such as cottage cheese, cod, oatmeal or chicken egg whites. It is necessary to limit the intake of these products only in a precomatose state, when there is decompensation in the functioning of the hepatic system. Then the level of protein intake should be reduced to 40g or eliminated altogether in case of hepatic coma.
Fat content
For pathologies of the liver system and bile ducts, fats and their composition are no less important. Problems in the functioning of the hepatobiliary system do not require the exclusion of fats, but only their refractory varieties. This is fatty meat from duck, goose or pig. The consumption of 90 g of fat is considered normal, with two-thirds of the total volume being animal, and the rest being vegetable. Unrefined oils contain fatty acids that regulate cholesterol metabolism; regular intake of this product without heat treatment improves the flow of bile. It is used in the treatment of cholestasis, hypomotor dyskinesia in the gallbladder and hypomotility of the intestinal tract. For these diseases, fats are increased to 120g per day.
Patients with calculous cholecystitis and liver disease should be careful when consuming oil. To prevent biliary colic in a sick body, take 30 g of cold-pressed oil per day, distributing this amount over several doses. It is prohibited to consume it on an empty stomach, as well as to subject it to heat treatment. Animal fats can be in the form of butter for dressing porridge or in the form of a breakfast sandwich.
In case of steatorrhea of hepatic etiology, cholelithiasis, cholecystitis, cirrhosis, Botkin's disease and after removal of the gallbladder, it is necessary to strictly limit fat intake to 60g per day.
Carbohydrate content
If there is massive death of liver tissue due to cirrhosis or hepatitis, then the glycogen supply is greatly reduced. Consumption of refined carbohydrates leads to disruption of the production and release of bile, provokes stagnation of bile, increases its concentration and viscosity, as a result of which crystallization of stones in the gall bladder begins. This factor is noted by patients suffering from obesity and problems with cholesterol levels.
The norm for carbohydrates is up to 400g per day; in this amount, simple sugars should not exceed 70g. Carbohydrates enter the body through many foods containing plant fiber. These are baked goods made from wholemeal flour, fruits and vegetables. Coarse fibers interfere with the absorption of cholesterol into the intestinal tract and prevent it from transforming into stone.
What vitamins are needed?
The liver is actively involved in the metabolism of fat-soluble vitamins. For any diseases of the hepatobiliary system, a course of vitamin preparations is administered, and they should also be consumed with food. Rose hips, cabbage, lettuce, currants, tomatoes, strawberries, raspberries, tangerines and parsley contain a sufficient amount of vitamin C. Butter and cream contain a lot of vitamin A, and carotene, provitamin A, is found in green peas and carrots, apricots, lettuce, parsley and cherries.
How much fluid to drink?
The water-salt balance in the body must be maintained at the level specified by the doctor. To do this, it is forbidden to consume less than one and a half liters of clean water, since its deficiency leads to an increase in the concentration of bile, an increase in nitrogenous waste substances, toxic and poisonous products. The amount of water is limited only in the presence of liver cirrhosis.
Salt consumed per day is about 8-10 g, and if swelling is present, then this figure is reduced to 4 g.
The principles of the diet for patients with gallbladder and liver problems are used in clinical practice as treatment table No. 5 and its modifications - diet 5 A, 5 G, 5 P. These tables are prescribed to patients with hepatitis in the chronic stage, cirrhosis (alcoholic and fatty) of the liver and chronic cholecystitis in remission.
What not to include in your diet
The patient’s menu should not include the following:
- radishes and radishes, garlic and onions, since they contain a lot of essential oils;
- any carbonated drinks;
- smoked meats and canned food;
- salt in large quantities;
- legumes and any nuts;
- chocolate, caffeine;
- sorrel.
During treatment, broth made from meat and mushrooms is excluded, since such a concentrate is very harmful to digestion. Reduce consumption of confectionery products, sweet pastries, and fresh bread. A little dried rye bread is allowed. Beer, vodka and other alcohol remain strictly prohibited. The drink should only be natural and healthy, without gas or preservatives.
Fully or partially limited products
Mushroom, meat and fish broths, green cabbage soup, and okroshka are completely excluded from the menu; solid animal fats (cooking fats, pork, lamb lard), fatty pork, goose meat, duck meat, offal (brains, liver, kidneys), most sausages, smoked meats, canned food, fresh bread, dough (butter, puff pastry), fried pies, fried and hard-boiled chicken eggs, smoked, salted and fatty fish, canned fish, full-fat cottage cheese, cream, whole milk 6% fat, sour cream, salted cheese, seasonings (pepper, mustard, horseradish) and sauces.
Irritating gastrointestinal tract and difficult-to-digest products of plant origin are limited: all types of legumes (peas, beans, chickpeas, soybeans), mushrooms, sorrel, radishes, spinach, radishes, green onions, garlic, pickled and canned vegetables. You cannot include spicy and fatty snacks, various caviar, as well as ice cream, chocolate, confectionery, cocoa, carbonated and alcohol-containing drinks, black coffee, sour berries, fruits, and juices from these products in your diet.
Table of prohibited products
| Proteins, g | Fats, g | Carbohydrates, g | Calories, kcal | |
Vegetables and greens | ||||
| canned vegetables | 1,5 | 0,2 | 5,5 | 30 |
| peas | 6,0 | 0,0 | 9,0 | 60 |
| chickpeas | 19,0 | 6,0 | 61,0 | 364 |
| beans | 7,8 | 0,5 | 21,5 | 123 |
| spinach | 2,9 | 0,3 | 2,0 | 22 |
| sorrel | 1,5 | 0,3 | 2,9 | 19 |
Berries | ||||
| grape | 0,6 | 0,2 | 16,8 | 65 |
Snacks | ||||
| potato chips | 5,5 | 30,0 | 53,0 | 520 |
Flour and pasta | ||||
| vareniki | 7,6 | 2,3 | 18,7 | 155 |
Bakery products | ||||
| sliced loaf | 7,5 | 2,9 | 50,9 | 264 |
| buns | 7,9 | 9,4 | 55,5 | 339 |
Confectionery | ||||
| cookie | 7,5 | 11,8 | 74,9 | 417 |
Ice cream | ||||
| ice cream | 3,7 | 6,9 | 22,1 | 189 |
Chocolate | ||||
| chocolate | 5,4 | 35,3 | 56,5 | 544 |
Raw materials and seasonings | ||||
| mayonnaise | 2,4 | 67,0 | 3,9 | 627 |
Dairy | ||||
| milk 4.5% | 3,1 | 4,5 | 4,7 | 72 |
| cream 35% (fat) | 2,5 | 35,0 | 3,0 | 337 |
Cheeses and cottage cheese | ||||
| gouda cheese | 25,0 | 27,0 | 2,0 | 356 |
| parmesan cheese | 33,0 | 28,0 | 0,0 | 392 |
Meat products | ||||
| fatty pork | 11,4 | 49,3 | 0,0 | 489 |
| salo | 2,4 | 89,0 | 0,0 | 797 |
| bacon | 23,0 | 45,0 | 0,0 | 500 |
Sausages | ||||
| smoked sausage | 9,9 | 63,2 | 0,3 | 608 |
Bird | ||||
| duck | 16,5 | 61,2 | 0,0 | 346 |
| goose | 16,1 | 33,3 | 0,0 | 364 |
Fish and seafood | ||||
| salmon | 19,8 | 6,3 | 0,0 | 142 |
| salmon | 21,6 | 6,0 | — | 140 |
| trout | 19,2 | 2,1 | — | 97 |
Alcoholic drinks | ||||
| white dessert wine 16% | 0,5 | 0,0 | 16,0 | 153 |
| dry red wine | 0,2 | 0,0 | 0,3 | 68 |
| vodka | 0,0 | 0,0 | 0,1 | 235 |
| beer | 0,3 | 0,0 | 4,6 | 42 |
Non-alcoholic drinks | ||||
| soda water | 0,0 | 0,0 | 0,0 | — |
| cola | 0,0 | 0,0 | 10,4 | 42 |
| * data is per 100 g of product | ||||
How to make a menu correctly
To get the maximum benefit from dietary nutrition and cure the disease faster, you must strictly adhere to the restrictions and follow the regime.
First example
The menu for patients with disorders of the biliary system takes into account the daily intake of healthy foods and does not contain prohibited ingredients. A dietary table is used, the number of which is determined only by a specialist. The first healthy breakfast is before 9 o’clock and consists of the following products: unsweetened tea, possibly with milk, vinaigrette with sour cream, a little cottage cheese, bread and butter. Lunch no later than 12 o'clock: buckwheat porridge with a piece of boiled or baked lean meat, natural juice diluted with water.

By 16.00 you can cook vegetable soup and add sour cream. For the soup, prepare steamed or boiled fish with potatoes and carrots; make cabbage salad if desired. Fruit compote is prepared from drinks, coffee and strong tea are harmful to the body. For dinner by 7 p.m., the patient can eat cabbage cutlets cooked in the oven, pasta, and compote. Immediately before bedtime, the patient drinks kefir, compote or fresh fruit jelly if he does not like fermented milk products. You should not take a break between each meal for more than 2-3 hours. Large meals before bed are also harmful, as they put a lot of strain on the digestive tract.
Second example
The following breakfast menu includes cottage cheese, oatmeal with vegetable oil, tea or a decoction of medicinal herbs with a choleretic effect. For a second breakfast or snack, choose one apple or carrot. For lunch, prepare soup from permitted vegetables, seasoning it only with vegetable oil. Choose lean meat, for example, beef or chicken; you can prepare a salad of carrots and sour cream. Vegetable salads are combined with vegetable oils, which increase the secretion of bile.
For an afternoon snack, fresh fruit or vegetables and herbal tea are allowed. In addition to vegetables (cabbage, carrots), citrus fruits have a powerful choleretic effect. For dinner, porridge and fish are prepared, steamed or baked in the oven.
Diet recipes
First meal
Zucchini soup
Ingredients: zucchini, potatoes, tomatoes, carrots, onions, parsley (root), butter, vegetable broth, sour cream 10%.
Vegetables: carrots, onions, parsley root, chop and simmer in water with added butter. Place the chopped potatoes into the vegetable broth, and after 15 minutes add the stewed roots, chopped zucchini, tomato, and salt. When serving, sprinkle with chopped herbs. Serve with sour cream if desired.
Vegetarian pearl barley soup
Ingredients: potatoes, cereals, carrots, onions, parsley (root), butter, sour cream 10%.
Boil pearl barley until half cooked. Chop the carrots, parsley root, onion and simmer in water with butter. Combine the cereal with the roots, pour in the vegetable broth, add potatoes, and salt. Serve with parsley and sour cream.
Second courses
Stuffed cabbage rolls with boiled meat and rice
Composition of products. Cabbage, tomatoes, rice, parsley, meat, sour cream, salt.
Disassemble the head of cabbage and cook the leaves until half cooked in salted water. Pass the meat through a meat grinder, combine with cooked rice and herbs. Spread the minced meat on the leaves and wrap. Place the cabbage rolls in a saucepan, add vegetable broth and put on fire. After boiling, add salt. Place chopped tomato and grated carrots on top and cook covered. Serve with sour cream.
Casserole of boiled chicken and vegetables
Ingredients: chicken, flour, butter, milk, carrots, cauliflower, tomato, zucchini, egg white, vegetable oil, salt.
Tips and reviews
Not only a diet, a table, the number of which is determined by the doctor, but also giving up bad habits and a healthy lifestyle will help you recover faster. For people with gallstones and gallstones, this is a healthy carrot salad recipe. Fresh vegetables need to be grated, add a little salt and sour cream, and mix.
Fresh fruits and vegetables contain many useful microelements and vitamins, but not all of them are suitable for the diet menu for pathologies of the gallbladder and its ducts.

Drinking regime
It is important to monitor your daily water intake. The patient should drink at least two liters of liquid, except juices and soups. You can use traditional medicine recipes to prepare a healing decoction.
Latest Nutrition Research
The problem of quality nutrition is very acute, especially for people with gallbladder pathologies. The digestive system will not function correctly if the diet is rich in food with preservatives and flavoring additives, and semi-finished products.
Diet for gallbladder diseases should not contain low-quality products, since the condition of the gastrointestinal tract will worsen sharply, and the pain will intensify despite treatment. It is useful to start monitoring your diet even before the onset of the disease, because the abundance of preservatives in food, smoked foods, spicy marinades and pickles will sooner or later lead to increased cholesterol and gallstones.
What can happen if you don't follow a diet?
Eating during an illness should be correct, because with the help of competent diet correction you can avoid complications, the formation of gallstones and surgical intervention. If you do not follow the doctor’s recommendations or violate your diet, over time the gallbladder will become very painful, and medications will be ineffective, so the organ will have to be removed. The best prevention for such patients is to eat only from the list of permitted foods, eating every 2-3 hours.
The principle of fractional consumption of food promotes the timely outflow of bile and is the best prevention of fluid stagnation in the gallbladder. If you constantly follow a diet, you can not only relieve pain, heaviness and other symptoms, but also prevent further complications of the disease. A diet for gallbladder disease is prescribed only by a specialist in combination with drug treatment, then it gives the best results. The table is selected according to the patient’s condition and the nature of the pathological process.
Diet for cholecystitis
With cholecystitis, inflammation of the gallbladder occurs, so without following a diet, the disease cannot be cured - it will only become chronic. Diet is the main regulator of the functioning of the gallbladder, since when it becomes inflamed, the functioning of the organ is disrupted, after which the outflow of bile is disrupted and stagnation occurs. By the way, stagnation of bile leads to quite serious consequences - calculous cholecystitis.
With calculous cholecystitis, stones form in the gallbladder, and this disease is most often solved in a non-conservative way, that is, by removing the gallbladder.
To avoid such consequences, you just need to strictly follow all the recommendations of your doctor and not deviate from your diet.
List of health products
For cholecystitis, therapeutic diet No. 5 is usually prescribed. The purpose of the diet is to provide functional rest for the bile excretion system. As a rule, when symptoms of cholecystitis occur, patients are advised not to eat at all in the first days, but to drink plenty of fluids. If the patient was hospitalized with an acute attack, then nutrition in the first 5 days is carried out intravenously, as well as the administration of medications.
If the patient is being treated at home, then in the first 2 days the following drinks should be consumed:
- weak tea with sugar;
- berry and fruit juices;
- non-carbonated water;
- rosehip tea
After the symptoms of acute cholecystitis have passed, after another 2 days you are allowed to add some foods to your diet. In the first period, you should (number of days individually) eat only food in the form of purees. It is best to thoroughly rub the cooked food through a fine tea strainer. Among the first foods introduced into the diet may be the following:
- oatmeal, rice and semolina porridge;
- fruit jelly and berry mousses;
- rice and oatmeal soups.
Rice, oatmeal and semolina are not without reason the beginning of a patient’s dietary treatment. It is these foods that, when cooked, have a mucous effect and envelop the walls of the human stomach, after which the digestion process occurs much easier and faster. In this case, as soon as the patient begins to feel relief, the diet can be replenished with meat and fish. Fish and meat should not be fatty, and it is better to steam or boil them. For meat, it is better to give preference to beef, chicken and turkey, and fish should be chosen from sea varieties. In addition, you can eat cottage cheese, but it should also be low-fat.
It should be remembered that in any case, meals should be at least 5-6 times a day, but in fractional portions. This is necessary so that food is quickly and easily digested, without creating additional stress on the biliary system.
If a patient experiences an attack of acute cholecystitis, care should be taken to ensure proper gentle nutrition not only for the biliary system, but also for the entire gastrointestinal tract as a whole.
If we talk about chronic cholecystitis, then the principle of the diet is almost the same as for ordinary cholecystitis. The only difference is that with chronic cholecystitis there are two periods of the disease: exacerbation and remission. During an exacerbation, symptoms of acute cholecystitis occur, in which a full diet of food is provided for relief, and drinking large amounts of drink, and remission is a lull in the disease. During remission, you should adhere to diet No. 5, without deviating from its principles. As a rule, exacerbation of chronic cholecystitis occurs precisely because a person at some point neglected the doctor’s recommendations and allowed himself fatty foods, alcohol, etc. However, exacerbations occur as a consequence of a cold, and, of course, stressful situations .