How the infection spreads
The main source of transmission of infection is a sick person, who mainly excretes viruses in feces. It can pose a danger to healthy people throughout the period of symptoms and for another 10 days after illness. You can become infected through contact with a sick person and his personal belongings. Also, the source of influenza can be unwashed vegetables, poorly prepared food products (usually dairy products due to the specifics of their production process). Rotovirus tolerates cold well and can survive in the refrigerator for a long time.
Another route of transmission of infection is airborne droplets. Because the stomach flu is an inflammation of the airways, coughing spreads viruses through the air. The most susceptible to the disease are people with weak immunity, located in crowded places (office, school, kindergarten).
Not everyone knows how many days the incubation period can last. The first signs of the disease may appear even on the 5th day after the virus enters the body. The disease lasts a week, after which the person develops immunity, during which re-infection is practically not observed. The exception is the initially weakened immune system in adults and children.
Can the disease be transmitted by airborne droplets?
You can become infected with a disease through airborne droplets in one case - when the disease has not yet begun to develop in the carrier of the disease and the bacteria have not had time to penetrate the intestinal environment. In the first stages, they are localized in the nasopharynx, from where, when sneezing or coughing, they are easily spread throughout the room and it is likely that they can find a new victim.
Even if you follow all the rules of hygiene, wash your hands often and carefully handle food (especially fruits), you will not be able to protect yourself from the disease. Most bacteria will certainly remain on surfaces in the room, and will even spread into the air near the patient.
If you ask a doctor how rotavirus infection is transmitted from person to person and how to protect yourself indoors, doctors can only recommend one way. The only option for protection in such cases is to wear a gauze bandage while in the same room as the patient. Even this remedy does not guarantee complete protection against the disease, but the risk of infection is reduced several times.
Clinical manifestations of intestinal flu
On average, the incubation period of rotavirus infection lasts from 1 to 3 days.
Acute symptoms disappear on the 5th day. The recovery period for the body after illness is about 1 week. This way you can understand how long rotavirus infection lasts.
When microorganisms enter the mucous membrane of the small intestine, they begin to actively develop; during this period the disease does not make itself felt. When the virus has invaded healthy cells and infected them, the body reacts, which is characterized by violent, acute manifestations.
- Vomiting is the first sign of gastroenteritis. It can be either one-time, two times a day, or have frequent urges (up to 12 times). It can last up to several days. After the vomiting stops, we can say that the initial period of the acute course is over. In adults, vomiting is a rare symptom.
- Loose stools are repeated many times and may accompany vomiting, but continue for more days. Attacks of diarrhea can be imperative in nature, in which a person is unable to restrain himself. Feces may have a foamy consistency and a greenish tint with a pungent clay odor. Sometimes mucus may be present. In adults, diarrhea is less liquid and frequent than in children.
- Pain in the upper abdomen can accompany diarrhea or occur independently. The pain is moderate, rarely intense or cramping.
In the first days, you should not try to restrain vomiting and diarrhea, since at the same time the body is freed from viruses.
Symptoms of a digestive tract disorder may last from 3 to 6 days. As a rule, sick people experience a runny nose, sore throat, and fever.
In addition to specific symptoms, the disease is characterized by general signs of intoxication:
- Weakness;
- Headache;
- Chills;
- Muscle pain.
In more severe cases, dehydration develops, which can be very dangerous for the child's body. In adults, dehydration is not observed. Parents should pay attention to the following manifestations in children:
- Drowsiness and lethargy;
- Crying without tears;
- Lack of saliva and refusal to eat;
- Prolonged periods without urination
- Flabby dry skin.
If severe dehydration occurs, you should try to replenish the body with fluid, often asking the child to drink; if this cannot be done, seek medical help immediately.
Symptoms of the disease
Manifestations of pathology are associated with the mechanism of action of the pathogen on the body. The virus damages the structure of the intestinal epithelium, disrupting the organ’s ability to absorb water and electrolytes.
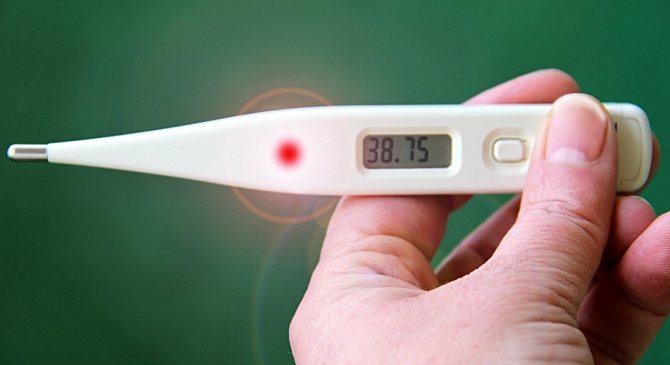
Heat
The disease begins with a sudden increase in temperature. Temperature readings reach 39 degrees. A runny nose and sore throat are possible.
Hyperthermia is accompanied by a disorder of the digestive system:
- attacks of nausea, vomiting;
- diarrhea;
- pain, rumbling in the stomach.
The body quickly loses fluid, and there is a danger of dehydration. A dangerous condition can be suspected by the baby's drowsiness, lethargy, dry eye mucosa, and lack of tears when crying. In infants up to one year old, the fontanelle sinks.
Attention! The symptoms cannot be ignored and you need to seek medical help.
The severe course of the disease in children is associated with underweight, artificial feeding, and the addition of another infection - respiratory viral or bacterial intestinal.
Adults suffer from intestinal flu more easily. Symptoms of the disease resemble poisoning from poor-quality food. Diarrhea may occur, appetite may worsen, and the temperature may rise to 38 degrees. Symptoms disappear within 1-2 days. Sometimes rotavirus is asymptomatic.
Therapy for rotavirus infection
Rotavirus infection does not require specific treatment. The body itself will be able to cope with this pathology within 5-7 days. The main goal of therapy in this case is to try to relieve symptoms, support the body and normalize the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract after stressful situations.
To prevent dehydration during an infectious disease, you need to drink as much water as possible, about 2 liters per day. In order not to provoke vomiting by drinking too much, you need to give the patient 1 spoon every 5 minutes. If signs of dehydration have made themselves felt, solutions prepared on the basis of drugs such as Regidron or Citroglucosalan will help normalize the body’s electrolyte balance.
To reduce intoxication, sorbents are prescribed - activated carbon, Enterosgel, Sorbex.
Body temperature can be reduced by taking antipyretics. However, you need to take medications when the thermometer is 38 degrees or higher. Rotovirus dies at this temperature; if it is brought down at low levels, an environment will be created for its normal further reproduction).
If you have severe pain in the abdomen, you can take 1 tablet of no-shpa, as a rule, this is enough for the pain to go away.
To normalize the intestinal microflora, the patient is prescribed medications that contain enzymes (Linex). You should also adhere to a light diet based on chemical, thermal and mechanical sparing. Restorative therapy is carried out over 2-3 weeks.
You need to know that rotavirus infection cannot be treated with antibiotics; lipoferons, which have an antiviral effect, can be prescribed.
After a short amount of time after the infection, the body recovers completely; the rotavirus does not become chronic.
If treatment for intestinal flu begins in a timely manner, then in the near future you can expect a positive result and the disease will pass in the shortest possible time. If the infection starts, there is a risk of developing various complications.
Signs of illness
The development of symptoms occurs very quickly.
The general condition of the patient is lethargic, activity and performance are reduced, and there is no appetite. Vomiting and diarrhea lead to dehydration, the skin becomes pale, the mucous membranes are not sufficiently moisturized, lips are cracked, and the tongue is coated with a white coating. But not all cases exhibit such obvious classic symptoms. Sore throats are sometimes observed, especially in children, which is why intestinal flu is often confused with sore throat. In these cases, the patient is bothered by a mild dry cough, rhinitis with swelling of the nasal mucosa, the tonsils and lymph nodes become inflamed and increase in size, inflammation of the conjunctiva leads to redness of the eyes and lacrimation.
It is also possible for the disease to be asymptomatic. In this case, the person does not have any clinical signs of the disease, but carries the pathogen and excretes it with feces into the external environment.
Loading …
Rotavirus infection affects every child aged 6 months to 5 years. But this disease does not belong to the category of children.
- Firstly, there are three types of viruses that provoke it.
- Secondly, one episode of illness in this case does not mean stable lifelong immunity. “Intestinal flu,” also popularly called rotavirus infection, can also affect adults, although they tolerate it more easily than children. Moreover, due to the similarity of symptoms, they often confuse this disease with an upset stomach or a common ARVI.
The incubation period of “intestinal flu” is the time period from the moment rotavirus enters the body of an adult until the first symptoms of the disease appear. During this period, the pathogenic agent is transported to the target organ (in this case, the mucous membrane of the small intestine), invades its cells and infects them. The incubation period of rotavirus infection in adults is up to 2 weeks.
IMPORTANT: From the moment of infection with rotavirus to the rise in temperature or the first episode of diarrhea in adults, 2–5, less often 15 days pass.
Rotavirus infection in adults is a disease that is characterized by a bright start. Suddenly, several symptoms appear at once. She has harbingers:
- slight malaise
- headache
- prostration
- decreased ability to work
- loss of appetite
They appear during the so-called prodromal period, a short time gap between the incubation period of the “stomach flu” and the disease itself.
During the prodromal period, a patient with “stomach flu” may experience a headache and general malaise.
IMPORTANT: If the patient himself or the doctor could recognize rotavirus from the listed symptoms even in the prodromal period, treatment would be started immediately, the disease would be mild, and recovery would come quickly. But since the prodromal symptoms of many diseases are very similar, “intestinal flu” is extremely rarely diagnosed before the characteristic clinical picture appears.
Symptoms of rotavirus gastroenteritis in adults are divided into three large groups:
- Intestinal syndrome. First, the patient begins to have diarrhea. There are from 3 to 9 episodes per day. The stool is watery, first yellow, then sallow in color. Secondly, the patient feels nauseous. He may vomit several times a day, and in severe cases, after every meal or water. Against the background of the first two symptoms, the patient experiences pain in the epigastric region.
- General intoxication. The consequence of the presence of rotavirus in the body of an adult is an increase in temperature, most often to 38 degrees, sometimes slightly more. The patient is chilling, his head, muscles, and joints hurt. He feels a loss of strength.
- Respiratory syndrome. Its symptoms are not obligatory, and in some patients they do not appear at all. If respiratory syndrome occurs, it can occur either during the prodromal period, or simultaneously with intestinal symptoms, or after them. The patient's throat turns red, itchy and sore, and the mucous membranes swell. A runny nose and cough may appear. There is an increase in cervical lymph nodes. The tongue is covered with a white coating.
IMPORTANT: Usually, adults tolerate temperatures up to 38 - 38.5 degrees well. You need to try not to knock her down. The fact is that at this temperature the body fights rotavirus and creates unfavorable conditions for it. By the third day of illness, as the virus titer decreases, the temperature will begin to drop on its own.
The appearance of these symptoms is a reason to immediately consult a doctor:
- Rotavirus can cause dehydration. It is absolutely impossible to ignore its symptoms or try to endure the disease on your feet.
- Rotavirus is often confused with other intestinal infections, including bacterial ones, such as salmonellosis. Only a doctor, based on the tests, will be able to make the correct diagnosis and adequately treat the patient.
Rotavirus can only be contracted from humans through the fecal-oral route through dirty hands and objects. If an adult or child develops symptoms of intestinal flu, they are immediately isolated from healthy family members. But such a measure, alas, often does not protect, because a person becomes infectious during the incubation period, from the moment the rotavirus enters his body.
MORE ABOUT: Melon during pregnancy: can it be eaten in the early and late stages, benefits and harms, reviews, benefits, dried, contraindications
An adult remains contagious throughout the illness, and sometimes up to 30 days after its symptoms disappear.
Children of primary and preschool age with “intestinal flu” are often hospitalized. Unfortunately, this insidious disease still claims the lives of children.
Adults usually experience it repeatedly and much more easily; only extreme cases require hospitalization; they are treated at home.
Despite the fact that the causative agent of intestinal influenza is a virus, antiviral therapy is extremely rare. As part of treatment, measures are taken to:
- avoiding dehydration
- removal of intoxication
- lower the temperature if necessary
- eliminating other symptoms of the disease
To prevent diarrhea, vomiting and fever for several days from leading to dehydration, it is recommended that adults drink more water, often and little by little, and also take an oral rehydration solution:
- Regidron
- Glucosolan
- Hydrovit, others
IMPORTANT: If rotavirus with diarrhea is taken by surprise, there are no rehydration products from the pharmacy at home, you can prepare a medicine for dehydration according to this recipe: dissolve 4 tbsp in 1 liter of boiled water. spoons of sugar, 1 teaspoon of salt and 1 teaspoon of baking soda. Water with sugar, soda and salt will help prevent dehydration due to rotavirus in adults.
The following drugs relieve intoxication of the body and help normal intestinal function:
- Smecta
- Enterosgel
- Polysorb
- Activated carbon
- White coal
- Liferan, others
IMPORTANT: A popular way to detoxify the body from rotavirus is to take plantain seeds. 1 teaspoon of plant material is poured into 500 ml of water and simmered over low heat for 10 minutes. When the broth has cooled, it is filtered and consumed in two doses.
The temperature with rotavirus in adults can be brought down:
- Paracetamol
- Ibuprofen
- Aspirin
- Analgin
- Nimesilom, other
IMPORTANT: If the temperature of a patient with “intestinal flu” has risen above 38.5 degrees, you can try to bring it down the traditional way: dilute water in half with vodka or vinegar, soak a towel in the solution and wipe the patient with it.
Against the background of rotavirus, the titer of beneficial bacteria in the patient’s intestines decreases. The doctor may prescribe probiotics:
- Lactofiltrum
- Linex
- Bifidum
- Bifidumbacterin
IMPORTANT: Discomfort in the intestines caused by the disease is reduced with a decoction of dill seeds. 4 teaspoons of seeds are poured into 250 ml of boiling water, wrapped and left to steep for 2-3 hours. The prepared broth is drunk in small portions every 2 hours.
If “stomach flu” in adults is treated adequately and on time, it rarely becomes complicated. Self-medication or ignoring the disease, especially in people with weakened immune systems or chronic illnesses, is fraught with:
- dehydration of the body, leading to disruption of all body systems
- cardiovascular, renal, multiorgan failure
- dysbacteriosis
- the addition of a bacterial intestinal infection
IMPORTANT: The lethality of rotavirus in adults is up to 2%.
An adult patient with rotavirus gastroenteritis is prescribed therapeutic nutrition. Exclude from the diet:
- dairy
- fried, fatty, spicy foods
- spices and seasonings
- fast food and snacks
- coffee, carbonated drinks
- legumes
- baked goods
- sweets
- fresh fruits and vegetables
During the first days of illness, do not fast. The patient should receive food in fractions in the form of:
- rice porridge on water
- semolina porridge on water
- boiled lean meat
- dried fruit compote
- low-fat fermented milk products
Rice porridge with water without oil is a dish for rotavirus.
For another 2-4 weeks after the symptoms of “intestinal flu” disappear, the patient should be on therapeutic diet No. 1, indicated for diseases of the gastrointestinal tract.
Due to the high prevalence of infection and the lack of an effective antiviral drug, nonspecific prevention of rotavirus in adults is difficult. To avoid contracting the “stomach flu”, you should:
- Adhere to the rules of personal hygiene. After visiting the toilet, being in public places, upon returning from the street, you should wash your hands before eating. Food products must be washed and thermally processed according to technology. Boil water.
- Isolate a family member with rotavirus gastroenteritis.
- Strengthen your immune system in every possible way.
- If necessary, take probiotics: Linex, Acipol, Lactiale.
- Consume fermented milk products: yogurt, kefir, narine, others.
Children aged 6 months to 2 years are vaccinated against rotavirus. It is in them that the disease “intestinal flu” has the most dangerous consequences, including death. Only children are vaccinated against rotavirus.
You can read about existing vaccines and the features of vaccination against rotavirus infection in children in the article “Rotavirus intestinal infection in children and infants: signs, symptoms, treatment, prevention, vaccination.
How many days is rotavirus infection contagious for children upon contact with a sick person?” Vaccination against rotavirus infection for adults is considered inappropriate.
- severe diarrhea
- temperature rise from 37 degrees, more often above 38 degrees
- vomiting, sometimes with mucus
- loss of appetite
- deterioration of general condition
- abdominal pain
- redness of the throat, enlarged tonsils, sore throat, runny nose (optional)
- convulsions and loss of consciousness (in advanced cases, as a result of temperature and dehydration)
Symptom of rotavirus infection in children: diarrhea.
Preventive measures
In order to protect yourself and your family from possible infection, you need to take the following measures:
- Keep your hands and products clean. Infection often occurs through drinking contaminated tap water. Prevention in this case is to boil water before drinking. After visiting the toilet or outside, before eating, you need to wash your hands well with soap. After washing fruits with plain water, it is advisable to pour boiling water over them. Particular attention should be given to young children. Toys, pacifiers, bottles should be kept clean and periodically doused with boiling water.
- Vaccination of the population. Preventive antiviral vaccination is carried out only in European countries and the USA; the Rotacrix vaccine is officially registered in our country. It is recommended that the vaccine be given to children between 6 and 24 weeks of age. For the full course, the procedure must be repeated after 1 month. Vaccination provides 80% protection against rotavirus infection and 100% protection against its complications.
- Isolation of patients. If a person gets sick, he should be isolated from the source of inflammation for 10-15 days. When there are many cases of illness among children, quarantine is introduced in kindergartens and educational institutions. At the slightest manifestation of the disease in adults, it is better to stay home to prevent a mass epidemic.
- Development of immunity. In the body of a person who has had an infection, special antibodies are formed that persist for 1-2 years. These antibodies protect the body from repeated cases of illness caused by a specific serotype of the virus. This protection does not provide a 100% guarantee. After 1 year, you can get sick with the same serotype of rotavirus infection. But, if infection occurs twice, then more stable immunity is developed for 2-3 years.
Rotavirus infection is a very unpleasant disease. However, with timely treatment, his prognosis is very favorable and recovery will not take long.
Rotavirus, or rotavirus gastroenteritis, is quite widespread in the external environment, and children under the age of two are most often affected by this disease. Moreover, this happens in almost all countries of the world, regardless of the standard of living in them. Although the mortality rate from this disease in developed and developing countries is very different. 90% of children over 4 years old have antibodies to this virus, which indicates its widespread distribution. This pathogen was first discovered not so long ago, in 1973. This was done by scientists from Australia.
Adults can also get this disease, but in them it occurs in a milder form (with the exception of severely weakened patients and the elderly) and with milder symptoms.
The widespread distribution of this infection suggests that the disease is highly contagious. That is, in a team or family where one person is sick, there will certainly be more sick people. This is transmitted both through dirty hands and through food (especially dairy products). It’s not for nothing that this disease is called the disease of dirty hands.
The incubation period of rotavirus infection means that pathogenic microorganisms multiply and accumulate in the body during this period. There are no symptoms at this time. The duration of this period will depend on many reasons - on the amount of pathogen that has entered the body, on the state of the patient’s immunity, on the presence of concomitant diseases. On average, this period lasts 2-3 days.
The disease begins acutely. The patient has the following symptoms:
- temperature increase;
- repeated vomiting;
- watery stool without blood;
- pain and rumbling in the stomach;
- weakness.
In addition to manifestations from the gastrointestinal tract, the patient also exhibits catarrhal symptoms - runny nose, cough, sore throat. These symptoms characterize rotavirus infection in children. In adults, its manifestations will be similar to indigestion.
These symptoms are also typical for other, more serious illnesses (for example, dysentery and salmonellosis), so if you have such symptoms, especially in young children, you should immediately call a doctor.
What complications can there be from rotavirus infection in adults?
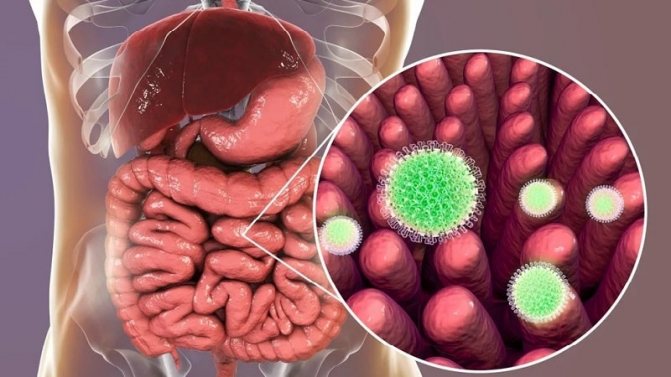
Children of primary and preschool age with “intestinal flu” are often hospitalized. Unfortunately, this insidious disease still claims the lives of children. Adults usually experience it repeatedly and much more easily; only extreme cases require hospitalization; they are treated at home. Despite the fact that the causative agent of intestinal flu is a virus, antiviral therapy is carried out extremely rarely. As part of treatment, measures are taken to:
- avoiding dehydration
- removal of intoxication
- lower the temperature if necessary
- eliminating other symptoms of the disease
To prevent diarrhea, vomiting and fever for several days from leading to dehydration, it is recommended that adults drink more water, often and little by little, and also take an oral rehydration solution:
- Regidron
- Glucosolan
- Hydrovit, others
Medicine for rotavirus in adults: Gidrovit.
Water with sugar, soda and salt will help prevent dehydration due to rotavirus in adults.
The following drugs relieve intoxication of the body and help normal intestinal function:
- Smecta
- Enterosgel
- Polysorb
- Activated carbon
- White coal
- Liferan, others
Medicine for rotavirus infection in adults: Polysorb.
Folk remedy for rotavirus in adults: plantain seeds.
The temperature with rotavirus in adults can be brought down:
- Paracetamol
- Ibuprofen
- Aspirin
- Analgin
- Nimesilom, other
You can reduce high fever due to rotavirus in adults with Nimesil.
Against the background of rotavirus, the titer of beneficial bacteria in the patient’s intestines decreases. The doctor may prescribe probiotics:
- Lactofiltrum
- Linex
- Bifidum
- Bifidumbacterin
The probiotic will help restore the intestinal microflora in an adult with rotavirus infection.
If “stomach flu” in adults is treated adequately and on time, it rarely becomes complicated. Self-medication or ignoring the disease, especially in people with weakened immune systems or chronic illnesses, is fraught with:
- dehydration of the body, leading to disruption of all body systems
- cardiovascular, renal, multiorgan failure
- dysbacteriosis
- the addition of a bacterial intestinal infection
A common complication of “stomach flu” in adults is dehydration.
An adult patient with rotavirus gastroenteritis is prescribed therapeutic nutrition. The following is excluded from the diet:
- dairy
- fried, fatty, spicy foods
- spices and seasonings
- fast food and snacks
- coffee, carbonated drinks
- legumes
- baked goods
- sweets
- fresh fruits and vegetables
During the first days of illness, do not fast. The patient should receive food in fractions in the form of:
- rice porridge on water
- semolina porridge on water
- boiled lean meat
- dried fruit compote
- low-fat fermented milk products
Rice porridge with water without oil is a dish for rotavirus.
For another 2-4 weeks after the symptoms of “intestinal flu” disappear, the patient should be on therapeutic diet No. 1, indicated for diseases of the gastrointestinal tract.
Due to the high prevalence of infection and the lack of an effective antiviral drug, nonspecific prevention of rotavirus in adults is difficult. To avoid contracting the “stomach flu”, you should:
- Adhere to the rules of personal hygiene. After visiting the toilet, being in public places, upon returning from the street, you should wash your hands before eating. Food products must be washed and thermally processed according to technology. Boil water.
- Isolate a family member with rotavirus gastroenteritis.
- Strengthen your immune system in every possible way.
- If necessary, take probiotics: Linex, Acipol, Lactiale.
- Consume fermented milk products: yogurt, kefir, narine, others.
Children aged 6 months to 2 years are vaccinated against rotavirus. It is in them that the disease “intestinal flu” has the most dangerous consequences, including death.
Only children are vaccinated against rotavirus.
You can read about existing vaccines and the features of vaccination against rotavirus infection in children in the article “Rotavirus intestinal infection in children and infants: signs, symptoms, treatment, prevention, vaccination. How many days is rotavirus infection contagious for children upon contact with a sick person?”
- First of all, it is necessary to strictly observe the usual rules of personal hygiene.
That is, wash your hands with soap after toilet procedures, before preparing food and before sitting at the table, after walking and visiting public places. It is extremely important to explain to children that their hands will be cleaner the more often and thoroughly they are washed, which means there will be fewer different germs on them.
- It is necessary to constantly monitor the well-being and health of children, since they are always at greatest risk due to close communication with each other in children's institutions.
Therefore, when the very first signs of the disease appear, it is necessary to inform the staff of the child care institution in a timely manner in order to avoid the spread of the disease to other children.
- Always drink only boiled water, since all microbes cannot withstand temperatures of 100 degrees and die within a few seconds of boiling.
- All vegetables, fruits, and berries must be thoroughly washed in several waters, starting with regular running water (from the tap) and ending with boiled water. You can kill all germs even more effectively if you pour live boiling water over the food, especially if it is intended for the fragile stomachs of children.
- Regularly wet clean the room using germ-killing products. It is most important to disinfect door handles, especially in the toilet room.
To summarize how contagious a person is with rotavirus infection, I would like to note that most of the population encounters rotavirus without even realizing it. Suspicion usually arises in cases where the infection quickly spreads among contact persons. Anyone can get sick, so knowing the characteristics of the disease and how to treat rotavirus infection will help in a difficult situation.
After all, even a recovered person can release the virus into the surrounding area for several months, and the infection will spread around him. Therefore, employees of public institutions who have already been ill are allowed to work only after they receive a hospital certificate of complete recovery based on medical tests.
Infection of the body is caused by exposure to rotavirus from the reovirus family. A carrier of infection is a person with an acute form of the disease or a carrier who, along with feces, releases pathogens into the external environment.
An adult or child can become infected with rotavirus infection through the fecal-oral, food, water, household contact, and airborne routes.
Factors predisposing to the disease:
- age up to 3 years;
- transition from breastfeeding to artificial feeding;
- immunodeficiency;
- failure to maintain proper nutrition;
- admission to a preschool or school educational institution;
- ignoring the rules of personal hygiene.
People with chronic diseases of the digestive system are at risk.
Symptoms of the disease
It is difficult to say exactly how many days the illness lasts. The illness usually lasts about a week. Full recovery may take ten days. Rotovirus is very dangerous for a child, especially immediately after birth. His immune system is still just gaining strength.
If your baby has diarrhea, constantly vomits and feels sick, you should see a doctor immediately. Treatment should be prescribed as soon as possible.
Characteristic signs of rotovirus disease are:
- lethargy,
- Drowsiness,
- Dry lips
- No saliva
- When the baby cries, there are no tears visible,
- The skin becomes dry and flabby,
- Very little urine.
All these symptoms require urgent consultation with a doctor. Every day without treatment can only worsen the situation and lead to serious consequences.
Intoxication of the infection can occur similar to the symptoms of ARVI:
- Stuffy nose,
- Runny nose,
- Slight cough
- Sometimes otitis media or conjunctivitis.
- Why does intestinal infection occur?
It is transmitted through contact with a sick person. If a child develops symptoms of the disease, he immediately becomes a carrier of the infection.
Rotovirus is especially dangerous on the fifth day after the onset of the disease. Dirty hands and toys that kids love to taste become the cause of the disease.
The cause of intestinal flu can be food that has been touched by a sick person. Unboiled water can also cause an intestinal infection, since chlorine is not able to kill a harmful virus.
Precautions in healthcare settings
If the intestinal flu is severe, the patient is advised to be kept in a hospital hospital. To prevent the spread of the disease, special conditions have been created in medical institutions. Prevention of rotavirus infections during contact with a patient in a hospital:
- Adults with intestinal flu are placed in individual half-boxes or boxes. Shared housing is possible if patients have the same diagnoses.
- The movement of infected people along the corridors of a medical facility is unnecessarily restricted.
- Delivery of medicinal drugs and food to isolated wards has been organized.
- The floors of the boxes are systematically washed 3 times a day using professional detergents, the wards, examination rooms and hospital premises are quartzed.
- Those infected with rotavirus are kept separately in infectious diseases departments to prevent contact with other patients without an established diagnosis.
- Patients are required to wear medical protective masks when moving around the facility.
Symptoms
Approximately four days after exposure to rotavirus, the baby begins to develop rotavirus infection. This period may be different, it all depends on the individual state of the child’s body.
The infection can remain in the body for several days and not manifest itself in any way. It takes on an acute form a little later.
The development of intestinal infection can occur in several ways. In one case, the child appears:
- soreness,
- Dry cough,
- Runny nose.
In another variant, very characteristic symptoms appear:
- Diarrhea,
- Nausea,
- Gastroenteritis,
- Abdominal pain
- Lethargy.
Incubation period
When infection occurs, characteristic signs do not appear immediately. The infection can remain in the body for several days and not manifest itself in any way. It takes on an acute form a little later.
How long the incubation period can last, how long it will last, depends on the condition of the child’s body. Its maximum can reach five days. During this period, the virus actively multiplies. It is difficult to determine how many children are sick at this time. The children feel fine.
But days pass. The incubation period is ending. The child's temperature begins to rise, he becomes weaker, feels sick, and has diarrhea.
To prevent possible complications, such an infection must be treated immediately. You can strengthen the child’s nutrition, give him more vitamins.
Important! Parents may not notice the onset of the disease, since the symptoms of the disease will not manifest themselves. If a healthy baby came into contact with sick children in kindergarten, it is imperative to take preventive measures.
How is rotavirus transmitted?
Another feature of rotavirus infection: if a child has had RVI three times in a year, then the disease begins to manifest itself not as an intestinal disease, but as a cold. The same applies to adults. Intestinal symptoms become less pronounced as the body has already adapted. The severity of the infection decreases, and respiratory manifestations come to the fore.
There are both pros and cons to this. On the one hand, the body no longer suffers as much from dehydration. On the other hand, if rotavirus infection occurs like a common cold, people no longer pay attention to it, especially adults. And if someone in a family gets sick with rotavirus, as a rule, all its members become infected within two days.
This is due to the characteristics of the pathogen - it is unusually stable in the external environment. For example, the virus can live on glass surfaces for up to 10 days. To become infected, a child only needs to receive 10 viral particles, while an infected person releases billions of such particles. In addition to airborne droplets, there is also a fecal-oral method of transmission of infection.
The majority of cases are children of the first or second year of life who do not attend child care institutions. According to world statistics, every child under 5 years of age, regardless of the sanitary conditions in which he is located and where he lives, suffers rotavirus infection on average up to 2 times.
Rotavirus infection is a year-round infection, but its incidence is slightly higher in the cold season. Our study showed that the maximum peak of RVI is observed when the temperature remains at a level of -15?C.
Treatment of intestinal disease
There is no specific treatment for this disease. All therapeutic methods have one goal, to eliminate the symptoms of infection.
In order for your baby to gain additional strength to fight infection, you need to follow a diet. The doctor prescribes special medications:
- Antispasmodics,
- Immunotropic drugs,
- Antipyretic.
To completely remove a large number of virus particles, you need to arrange for children to take antibiotics. The doctor who has diagnosed rotavirus infection prescribes antibacterial suppositories:
- Viferon,
- Lipfeorn.
The course of treatment and dosage depend on the age of the patient and can last five days.
Carrying out prevention
Is it possible to become infected with rotavirus infection again? We have already found out that this is quite possible. That is why it is necessary to carry out comprehensive prevention. There are vaccines that help prevent the development of the virus in the body. Other preventive measures include methods such as:
- compliance with personal hygiene rules;
- proper processing of products;
- selection of dairy products.
It is very important to observe the rules of personal hygiene. To do this, it is important to wash your hands before eating, after visiting the toilet and public places. Products should be handled properly to remove infection. To destroy the virus, it is important to wash vegetables and fruits with hot water, as it is killed when exposed to high temperatures.

Particular attention should be paid to dairy products, since this is where most bacteria develop. Therefore, when purchasing it, you need to pay attention to the expiration date and storage conditions.
Knowing how rotavirus is transmitted, you can eliminate the possibility of it entering the body. All preventive measures taken help to exclude the occurrence of other infections in the body. If the first signs of illness occur, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Rehydration
To prevent dehydration, the baby should be provided with plenty of warm drinks. This will help maintain the desired fluid balance in the body and create normal working conditions.
First, the child is given one teaspoon, then the amount is increased. Specially prepared solutions have a positive effect:
- Humana,
- Regidron,
- Oralit,
- Chamomile decoction
- Boiled water,
- Rice water,
- Unsweetened compote made from dried fruits.
To remove toxins from the body and completely cleanse it, the baby is given:
- Activated carbon,
- Smecta.
To reduce the temperature you can use:
- Children's paracetamol,
- "Nurofen"
- "Cefekon" candles.
When there is a high temperature and convulsions, the baby can be wiped with a saline solution (one part salt to one part water).
For severe pain in the abdominal area, the child is given:
- No-shpu,
- Lacidophilus,
- Riobal.
During an intestinal infection, the child should be fed:
- Rice porridge,
- Mashed potatoes,
- Bananas,
- Baranki,
- Crackers.
Infants should be switched to lactose-free formulas. You should not give your baby:
- Dairy products,
- Sauces,
- Vegetables,
- Fatty foods
- Meat additives.
Features of treatment
How long rotavirus infection lasts largely depends on the timeliness and correctness of the therapy. There is no specific way to carry out treatment. All therapeutic methods are aimed at eliminating the unpleasant symptoms of infection. To develop immunity in a child, you need to follow a special diet. The doctor may prescribe special medications, namely:
- antispasmodics;
- antipyretics;
- immunotropic agents.
Additionally, the doctor may prescribe antibiotics, but only after diagnosis. The course of therapy and dosage largely depends on the age of the baby and can last 5 days.

To prevent severe dehydration, you need to give your child something to drink as often as possible. This will help maintain fluid balance in the body and create the necessary conditions for the full functioning of the body. Initially, the child is given 1 tsp. liquid, and then the amount is gradually increased. You can also give your baby solutions such as:
- "Regidron";
- "Humana";
- "Oralit."
To remove toxic substances from the body, the baby is given Smecta or activated carbon. To bring down a high temperature, you can use Nurofen, Paracetamol, and Cefekon suppositories.
If a child has convulsions and a very high temperature, he can be wiped with a saline solution. If rumbling and abdominal pain appear, the baby is given:
- "Lacidophil";
- "No-Shpu";
- "Riobal".
After the appetite is restored and it is clear that the microflora has been restored and the diarrhea has passed, the child is prescribed Bactisubtil. The capsule, previously diluted in water, should be taken twice a day an hour before meals. Treatment is carried out for 5 days.
How to lower the temperature
The medications should be taken at intervals of two hours. This applies to suppositories and paracetamol tablets
When the temperature reaches 39 degrees, a child under three years of age is prescribed Tsefekon suppositories. Older children are prescribed paracetamol in the appropriate dosage.
Using candles is very convenient, as they can be placed on the baby when he is sleeping or awake.
But if the temperature does not drop and does not subside for a long time, children aged one year and above are prescribed paracetamol and a small quarter of analgin.
The medications should be taken at intervals of two hours. This applies to suppositories and paracetamol tablets. When taking other medications, the break should be 4 hours or more. The greatest positive effect for intestinal diseases is obtained by taking paracetamol.
To reduce the temperature, you can wipe your baby with a weak solution of vodka, but following certain rules. The child's body should be completely dried. Changes and free areas on the baby’s body are not allowed. After wiping, you need to put thin socks on your feet.
The wiping procedure can be carried out only half an hour later, after taking a tablet for fever, and if it has not begun to fall. When the temperature is high, it is forbidden to wrap the child.
Enterofuril helps to cope with gastrointestinal diseases accompanied by high fever. It should be taken morning and evening for five days. The dosage of the drug depends on the age of the patient. It will also help cope with prolonged diarrhea. Its analogue is Enterol.
No-spa will help relieve severe pain in the child’s abdomen. You need to drop one milligram of solution into your mouth, wash it all down with tea.
When the appetite is restored, so that the diarrhea disappears and the microflora is completely restored, doctors prescribe Bactisubtil to the child. A capsule dissolved in water should be drunk in the morning and evening, an hour before meals. The course of treatment lasts five days.
How long a person is contagious
How many days is rotavirus contagious? It depends on the age and severity of the infection. As a rule, a person is contagious for 10-14 days after the symptoms of a viral infection disappear. The same applies to many viral serotypes. If the disease is complicated by a secondary bacterial infection, the duration of the disease increases.
Virus carriage, even when asymptomatic (occurs in adults and vaccinated children), poses a serious threat to society. In such cases, the contact and household route of transmission of infection quickly occurs, and the first symptoms appear in a healthy person.
Rotaviruses are quite resistant to irritating factors. Their presence in the body in asymptomatic cases in adults reaches 1-10 days, after which healthy immunity completely defeats pathogenic activity and ensures complete recovery.
In a child, rotavirus remains a little longer, which is due to the prolonged active phase of the disease and the imperfection of the immune system. Reproduction of the virus stops after adequate nootropic therapy, and residual effects persist for up to 10-14 days.
Complications
If intestinal flu is not treated correctly, adverse consequences may occur.
Dehydration occurs in the body. This can cause death. This cannot be allowed. The baby needs to be soldered urgently. At the hospital, the baby is given an IV.
The baby has an acetonemic state. Ketone bodies begin to accumulate in large quantities in the child’s body. They have a negative effect on his brain. This complication occurs due to a lack of carbohydrates consumed during the disease.
Convulsions caused by high temperature may occur. To prevent the appearance of a convulsive state, the baby’s body requires constant cooling, for which a saline solution is used. All areas of the body are thoroughly rubbed until the temperature drops.