May 14, 2015
Buy cheap medicines for hepatitis C Hundreds of suppliers bring Sofosbuvir, Daclatasvir and Velpatasvir from India to Russia. But only a few can be trusted. Among them is an online pharmacy with an impeccable reputation, Natco24. Get rid of the hepatitis C virus forever in just 12 weeks. High-quality drugs, fast delivery, the cheapest prices.
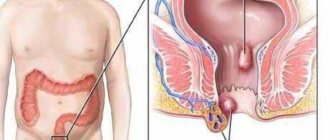
Pneumatosis of the liver is a pathological process of the organ, which results in the formation of air tumors and cysts. That is, this process leads to the formation of hollow spaces (cysts) on the walls of the liver, which are filled with gas. This gas mainly contains nitrogen, hydrogen, oxygen and carbon dioxide, which is no different in composition from air.
This type of disease usually has symptoms:
- stomach ache;
- constipation;
- flatulence;
- vomit.
During palpation of the abdomen, a tumor-like formation or large cysts can be identified, which, when pressed, make the sound of bursting bubbles. During an x-ray, you can see a clearing between the liver and the diaphragm, which disappears when taking a horizontal position.
Intestinal pneumatosis - why is this specific lesion dangerous?
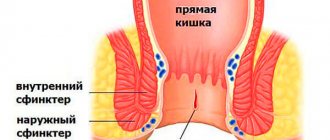
A specific intestinal lesion in which air-filled cysts form in the rectum is called Pneumatosis intestinalis.
Cysts grow, creating discomfort, and if the disease is not treated, air bubbles can spread to the mesentery or lymph nodes. The inflammatory process can be fatal, so pneumatosis should be treated in the early stages.
Severe pneumatosis intestinalis is diagnosed only in conjunction with other concomitant diseases. It is difficult to determine it on your own, since there are no complaints as such.
The most common symptoms include the following:
- Colic in the abdominal cavity due to increased formation of gases. During flatulence, gas formations do not have a natural outlet and stretch the intestinal walls, causing a feeling of bloating and discomfort;
- Pain of varying intensity in the lower abdomen. The nature of the pain is cramping;
- Abnormal stool. There is regular constipation, and in rare cases there is diarrhea. With a large number of air bubbles formed, pressure in the intestines may build up, which in turn can lead to intestinal obstruction or even rupture of the intestine. Death is possible with peritonitis;
- Complete cessation of bowel movements. After a person cannot empty his intestines for several days, and gases are not able to escape naturally, his health sharply worsens, severe pain appears in the lower abdomen, blood pressure decreases, and the patient may die from painful shock;
- In children, symptoms include general malaise, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea and bloating;
- Belching air. At the same time, there is a feeling of fullness and heaviness in the stomach.
Symptoms are irregular. If you experience increased flatulence and complaints of discomfort in the lower abdomen, you should consult a specialist to rule out the possibility of intestinal pneumatosis.
Intestinal pneumatosis most often develops as a separate pathology due to previous diseases of the digestive tract.
The most common causes of the disease are as follows:
- Gases produced in the human body are not absorbed into the circulatory system, but accumulate in the intestines, forming air sacs. As a result, small cysts are formed, visually identified as growths;
- One of the factors for gas retention in the body is also impaired peristalsis or the presence of loops in the rectum, which creates a threat of obstruction of feces through the pipes;
- After suffering infectious diseases, the intestinal microflora is disrupted, and as a result of an increase in the number of pathogenic organisms, gases are formed in excess;
- If there are adhesions in the rectum, the tube is pinched, which increases intra-abdominal pressure. As a result, gas stagnation occurs in the intestinal area;
- In infants, pneumatosis occurs due to lack of physical activity, congenital diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, or the presence of intestinal infections;
- The presence of a tumor process in which gases cannot leave the body naturally. The intestines are subjected to increased stress, as a result of which the risk of cysts increases;
- A sedentary lifestyle in rare cases leads to pneumatosis intestinalis.
In very rare cases, blood flow in the lymphatic capillaries is disrupted, or air from the stomach penetrates the walls of the rectum, which also contributes to the formation of air cavities. Regardless of the reason for the onset of disease development in the intestines, it is easier to prevent it at an early stage than to treat it for a long time.
Only a surgeon can diagnose the disease. Upon palpation, air cysts are detected in the walls of the rectum, but only if they are large. Most often, hollow formations create groups that visually resemble bunches of grapes.
The final diagnosis is made after endoscopy or x-ray of internal organs. Endoscopy examines the general condition of the mucous membrane. If necessary, a rectal biopsy is performed.
Pneumatosis is not a separate disease. It usually develops as a result of other disorders of the gastrointestinal tract. Therefore, therapy is aimed at treating the underlying disease.
In case of a mild form of the disease, the doctor will prescribe antispasmodics to reduce pain (for example, No-shpu or Baralgin), as well as a drug to reduce gas formation (most often recommended is Meteospasmil or Espumisan).
Small infants are prescribed intestinal antiseptics and, if necessary, antibiotics are prescribed.
Depending on the symptoms, antidiarrheal drugs or laxatives (herbs) are prescribed.
If intestinal obstruction or peritonitis develops, surgical intervention is necessary. In rare cases, drainage tubes are inserted into the abdominal cavity during treatment to remove accumulated gases.
Proper nutrition is the key to a healthy gastrointestinal system. Therefore, the diet is aimed at stabilizing the functioning of the digestive organs and treating the underlying disease.
To prevent gases from accumulating, you should follow some rules:
- Fractional meals. It is better to eat five to six times a day in small portions;
- Eliminate from the diet all foods that cause increased gas formation (for example, beans, peas, cabbage, apples, grapes, tomatoes, some baked goods, certain types of cereals, beer, carbonated drinks and canned food);
- Any vegetables should be consumed only after heat treatment. It is better to eat steamed and stewed foods;
- You should absolutely not eat smoked, fried or fatty foods. You should limit your intake of coffee and alcoholic beverages;
- Soups should be cooked either in broth from lean meats, or only from vegetables;
- It is advisable to drink jelly, lactic acid products (kefir, yogurt, fermented baked milk, weak tea and rosehip decoction).
This disease is rare and poorly understood. Therefore, you should be attentive to the problems of gas formation and conduct a timely examination in cases of nonspecific symptoms.
As an aid to combat pneumatosis, you can turn to traditional methods.
At home, the following medicinal plants will help cope with the problems of excessive flatulence:
- Parsley seeds. A teaspoon of seeds should be poured into one glass of hot water and left to infuse for 12 hours. One teaspoon of the prepared infusion should be consumed hourly;
- Dill water. The healing properties of dill water were noticed many thousands of years ago. The recipe for its preparation has not changed. One teaspoon of seeds is placed in a vessel, after which 300 milligrams of boiling water is poured. After three to four hours, the tincture should be filtered and given to a child a tablespoon, and to an adult a glass half an hour before meals;
- Infusion of medicinal chamomile. A tablespoon of flowers is poured into one glass of boiling water. After three hours, the broth is filtered. You need to take two tablespoons half an hour before meals;
- Infusion of wormwood. A teaspoon of chopped herb needs to be poured with a glass of boiling water. After thirty minutes, the decoction is ready for use. It should be taken one tablespoon fifteen minutes before meals;
- Dandelion root. The roots of the plant must first be crushed and pour one tablespoon of the ground plant into two glasses of warm water. The tincture will be ready in twelve hours. After straining, take 30 grams of the decoction before eating.
Beets promote healing, so it is advisable to include them in the daily diet. Beetroot infusion is prepared very simply: the peeled vegetable is boiled in water for an hour. 200 grams of beets are taken per 200 grams of water. After four hours, the infusion is filtered, 20 grams of sugar and 2 grams of yeast are added to it. After a day, the medicinal kvass is ready for use.
If the symptoms of the disease confirm the diagnosis, you must strictly adhere to the course of treatment prescribed by the doctor.
In order to avoid problems with increased gas formation, you should lead an active lifestyle, avoid excessive physical activity and eat foods that allow you to restore normal bowel function. To avoid constipation, which leads to the formation of hollow cysts, you should eat more nuts, cereals, vegetables and fruits rich in vitamins.
Timely treatment and prevention after it give a clear positive result.
The materials posted on this page are informational in nature and intended for educational purposes. Site visitors should not use them as medical advice. Determining the diagnosis and choosing a treatment method remains the exclusive prerogative of your attending physician.
Source: https://allergology.ru/gastro/pnevmatoz-kishechnika
Causes
Diseases in which pneumatosis of the intestinal wall can develop:
- Intestinal obstruction. Violation of the natural passage of feces leads to the development of stagnation in the gastrointestinal tract, excessive fermentation and rotting. The result of the latter processes is the appearance of an excess amount of gases, which, under the influence of pressure, can penetrate the wall of the organ.
- Intestinal perforation (“rupture” of the wall). This complication can occur with tumors, ulcerative colitis, Crohn's disease, abdominal trauma, or against the background of necrotizing enterocolitis in newborns. In this case, free gas penetrates not only into the abdominal cavity, but also into the submucosal, subserous base of the intestine.
- Enteroinvasive intestinal infections (salmonellosis, dysentery, cholera). In case of infection of the large or small intestine, increased gas formation is also observed. Bacteria and their toxins destroy the intestinal barrier and allow “air” cysts to enter its walls.
- Tumors. Volumetric neoplasms can cause both perforation of the organ wall and intestinal obstruction. In both cases, pneumatosis is a common complication.
Much less often, pneumatosis is a consequence of a sedentary lifestyle, chronic constipation, and irritable bowel syndrome. Sometimes iatrogenic (due to the actions of medical staff) organ injuries occur during colonoscopy or laparoscopy, which also contribute to the appearance of intestinal emphysema.
Pneumatosis intestinalis - what is it and how to treat it
Pneumatosis intestinalis is quite rare in elderly and young children. This pathology is characterized by gas retention within the gastrointestinal tract. For this reason, cysts develop in the gastrointestinal tract, which can reach sizes of more than 5 mm.
Reasons for the development of pathology
Among the causes of the disease, the main one is considered to be obstruction of gases naturally. Their effect on the intestines is that small cavities of air are formed inside the intestines. The cause of the development of the disease may be hidden in the improper development of lymph capillaries. Pathology can occur suddenly, but without the presence of factors this is impossible.
Additional factors influencing the development of the disease:
- Infections transmitted with the participation of pathogenic bacteria;
- Lack of activity in children;
- Spasms inside the intestines;
- Perilstatics is disrupted;
- High pressure inside the abdominal cavity.
Doctors have found out what is the most effective remedy for worms! According to statistics, every 5 Russians have worms. Read on for a recipe that will help cleanse your body of worms in just 7 days...
Read more >>
In young children, this pathological process can develop after surgery. For some pregnant women, this problem can lead to the disease being transmitted to the unborn child.
Symptoms of the disease
The main symptom of the disease is that gas formation in the intestines increases significantly.
Other symptoms that are an indicator of the development of the pathological process:
- Abdominal cramps;
- Attacks of nausea;
- Gagging, vomiting;
- Paleness of the skin;
- The appearance of colitis;
- Change from constipation to diarrhea;
- Painful sensations in the nature of contractions;
- Severe deterioration in general condition;
- Due to the stretching of the intestines, many people experience a feeling of fullness.
Most of the symptoms may resemble in their manifestation other pathological processes of the gastrointestinal tract.
Diagnosis of the disease
The symptoms of the pathological process do not manifest themselves too clearly. Because of this, problems arise with identifying the disease in the early stages of development.
During an examination by a doctor, it is possible to detect by palpation the presence of cysts or air bubbles that will burst.
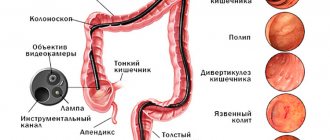
In order to make an accurate diagnosis, a hardware examination using colonoscopy will be required.
If necessary, at the first stage of diagnostic measures, an x-ray examination is performed. Rectoscopy or endoscopy is suitable for diagnosis. During an endoscopy, the doctor performs a biopsy of the intestinal mucous tissue in order to identify the presence of an inflammatory process. The intestinal wall will be shown on the screen, and the presence of cysts will also be visible there.
Therapy of the disease
Most often, pathology develops due to the presence of other pathologies. Therefore, therapeutic measures will be aimed at getting rid of them. In other cases, therapy is carried out in relation to the symptoms. For constipation, you will need to use laxatives; for attacks of diarrhea, it will be necessary to use strengthening drugs, rehydron, to avoid dehydration.
Get rid of increased gas formation, spasms, and vomiting attacks. Therapy should be carried out as a complex in order to quickly achieve positive dynamics in treatment.
Folk remedies
You can speed up the treatment process with the help of folk remedies. Chamomile infusion will help get rid of intestinal pneumatosis, treatment, which can take a long time. For 2 spoons you need a glass of boiling water. Leave until cool and drink before eating.
You can take an infusion of apricots, plums or apples. Such a remedy will not only be tasty, but also reduce the discomfort of pneumatosis.
For half a liter of boiling water you will need a couple of tablespoons of parsley seeds. This product will need to be kept in a water bath for an hour. Then let it brew and take a tablespoon 4-5 times a day.
Add 1 tablespoon of ground dill seeds to a glass of boiling water. Leave for about an hour, take a spoonful of the product every 60 minutes. It is recommended to prepare the infusion in the evening; it is better to take it in the morning after a night of infusion. This infusion reduces the production of gases, while helping the intestines return to normal function.
The use of traditional recipes is permissible in the absence of complications or allergies to the components. Possible allergies are a disadvantage of this treatment. Among the advantages are high efficiency, low cost, low likelihood of side effects.
Diet food
It is important to remember that dietary nutrition is one of the main points of complex therapeutic measures. Meals should be divided into 6 times per day. All portions should be small. Avoid heavy foods at night.
It is prohibited to consume: carbonated drinks, alcoholic beverages, brown bread, beans, cabbage. Any food that can cause gas should be immediately excluded from your diet. It is forbidden to eat pickled, fried, smoked, sour, salty, sweet foods, as they can provoke unpleasant attacks.
It is recommended to eat: soups, broth prepared with lean meat, milk, cereals, decoction of rose hips. It is better to steam all dishes.
Complications
Complications can arise in the absence of proper therapy.
Most often, patients with pneumatosis develop intestinal obstruction. In this case, mandatory surgical intervention will be required. Invagination, volvulus, more developed adhesions, and necrosis are less common.
There is a possibility of closure of the intestinal lumen, this condition is called hyperpneumatosis. In some cases, the risk that the cyst will develop into cancer increases. Possible perforation in the intestines.
A serious complication in the development of a pathological process, if therapeutic measures are not started, can be fatal.
Prevention
Preventive measures include mandatory detection of pathology at an early stage of its development. To do this, you will need to undergo the necessary studies in a timely manner.
For preventive purposes, you need to be examined every 6 months. If necessary, appropriate preventive measures must be taken using medications.
It is recommended to follow a diet and prefer an active lifestyle.
It is important to remember that severe pneumatosis intestinalis should be treated only with the help of a doctor. Otherwise, serious complications arise that are difficult to get rid of with medication. Prolonged accumulation of gases will have a negative impact on the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract, causing various diseases.
With timely treatment, the patient's prognosis will be favorable. It is not recommended to self-medicate, as this is the first factor that can affect the development of complications. For competent recommendations regarding treatment measures, you should contact a gastroenterologist and proctologist. Basically, the duration of therapy will not exceed the duration of a monthly course.
Source: https://VnutriZhivota.ru/kishechnik/pnevmatoz-kishechnika.html
Candidiasis of the liver
The disease occurs as a result of the penetration of pathogens from the gastrointestinal tract. Very often this problem occurs in patients who have undergone chemotherapy, and at that moment the destruction of neutropenia has occurred. Such patients experience fever, nausea, and abdominal pain.
To confirm this diagnosis, it is necessary to do a liver biopsy, which usually reveals yeast cells and filaments of pseudomycelium. Bleeding may occur, so doctors send patients for radiation therapy as an insurance policy.
The doctor may order an ultrasound examination and refer you to a CT scan, which reveals granulomas. They can also be detected using MRI. During treatment, such patients are prescribed amphotericin. Continue treatment until all symptoms disappear. Patients treated as outpatients are prescribed flucozole.
Pneumatosis intestinalis
Pneumatosis intestinalis
- a pathological process in which air cysts form in the intestinal wall. The disease manifests itself as cramping, diffuse pain and a feeling of fullness in the abdomen. There is upset stool, nausea, belching, vomiting.
Diagnostic measures include examination by a gastroenterologist, radiography of the abdominal cavity, irrigoscopy, and colonoscopy.
Depending on the prevailing symptoms of pneumatosis, carminative, antispasmodic, laxative or antidiarrheal drugs are prescribed, as well as a diet with a reduced intake of gas-forming products.
Pneumatosis intestinalis is a rare gastrointestinal disease in which intestinal gases penetrate the thickness of the organ wall and form air cavities in it. More often, the pathological process is localized in the submucosal or subserous layer of the colon or jejunum.
The disease can affect people of all ages, but mainly occurs in infants and older people due to decreased physical activity and frequent disturbances in the digestive system. The size of air cysts can vary from 0.5 to 5 cm in diameter.
Based on the prevalence of the process, pneumatosis is divided into limited, affecting one area of the intestine, and diffuse. The latter is characterized by a uniform distribution of pathological formations over the entire area of the intestinal tract.
Causes of pneumatosis intestinalis
The disease is rarely an independent pathology, more often it occurs against the background of primary damage to the gastrointestinal tract. The main cause of pneumatosis is the excessive formation and prolonged presence of gases in the intestines, resulting from the following conditions:
- Intestinal infections
. In case of severe infectious diseases of the intestines (dysentery, cholera, salmonellosis, food toxic infections), increased gas formation is a consequence of the fermentation process and the release of gaseous substances by pathogenic microorganisms. - Gastrointestinal tumors
. As a result of malignant and benign neoplasms of the intestine, narrowing or blockage of its lumen occurs, which leads to intestinal obstruction, excessive accumulation of gases and their penetration into the intestinal wall. - Other diseases of the digestive tract
. Atony, inflammatory bowel diseases (colitis, enterocolitis, Crohn's disease), the presence of adhesions between organ loops contribute to impaired utilization of the resulting gas and the formation of pneumatosis. - Unhealthy Lifestyle
. Adynamia, nervous disorders, consumption of excess amounts of foods that cause gas formation (cabbage, bread, etc.) can lead to indigestion, flatulence and the formation of air cavities in the intestinal wall.
Pathogenesis
The mechanism of formation of pathological cysts is not fully understood. Today, there are three theories of the formation of intestinal pneumatosis: pulmonary, infectious and mechanical. According to the pulmonary theory, pneumatosis occurs as a result of chronic lung diseases (bronchial asthma, COPD).
As a result of constant coughing, microtears of the alveoli occur, pneumomediastinum occurs, which leads to the spread of air into the retroperitoneal space. From there, the free gas diffuses into the intestinal wall and accumulates under the serosa.
According to the infectious theory of the origin of the disease, the gases produced by the bacteria penetrate the inflamed intestinal wall and can merge to form large blisters.
In gastroenterology, the mechanical theory of pneumatosis has received the greatest recognition. According to this concept, intestinal air cysts arise from primary pathology of the gastrointestinal tract (tumor, enterocolitis, stenosis) and congenital defects of the blood and lymphatic vessels of the intestine.
Against the background of gastrointestinal diseases, trauma and thinning of the inner lining of the intestine occurs. The gas, under the influence of intraintestinal pressure, passes through microdefects, enters the submucosal lymphatic vessels and spreads through peristalsis in the submucosal layer of the intestine.
Cysts are lined with epithelium from the inside and can contain various gases: nitrogen, oxygen, hydrogen, argon, carbon dioxide, etc.
Symptoms of pneumatosis intestinalis
The clinical picture of the disease depends on the extent of spread and the number of gas cavities. Patients complain of a feeling of discomfort and heaviness in the abdomen, and impaired passage of gases. Periodic cramping abdominal pain without clear localization appears.
The formation of air cysts leads to slower peristalsis and constipation. Lack of stool gives way to diarrhea mixed with mucus. Nausea and vomiting, belching with an unpleasant odor occur.
Diffuse spread of pneumatosis leads to a deterioration in the patient’s general condition: pallor of the skin is noted, weakness increases, blood pressure decreases, and heart rate compensatory increases.
Complications
Hemorrhoids kill the patient in 79% of cases
An increase in intraintestinal pressure contributes to a change in the shape of intestinal loops with the formation of volvulus or intussusception. An increase in the number of blisters or an increase in their size leads to complete or partial blockage of the organ lumen with the development of obstructive intestinal obstruction.
Obturation is accompanied by general intoxication of the body, which can lead to infectious-toxic shock and death. The proliferation of cavities contributes to the formation of intestinal adhesions. Pressure on the intestinal wall leads to disruption of its nutrition, development of ischemia and necrosis.
Necrosis of areas of the organ and excess gas pressure can cause ruptures of the intestinal wall and penetration of intestinal contents into the abdominal cavity. In this case, peritonitis occurs, and in the absence of emergency measures, sepsis.
Diagnostics
With limited intestinal pneumatosis, due to the absence of pronounced specific symptoms, diagnosis is difficult. If pain or digestive disturbances occur, patients need to consult a gastroenterologist.
The specialist conducts a comprehensive examination, studies the medical history and concomitant pathology, paying special attention to gastrointestinal diseases.
In some cases, with deep palpation of the abdomen, it is possible to palpate small round formations running in a string along the intestinal tract, resembling a bunch of grapes. To establish a diagnosis, the following studies are carried out:
- Plain radiography of the abdominal cavity
. Allows you to identify gas bubbles of various sizes arranged in a chain. Pneumatosis is characterized by the presence of double ring-shaped shadows in swollen intestinal loops. - Irrigoscopy
. Using this method, excess gas is determined in enlarged loops of the large intestine in the form of several closely spaced round shadows separated by a wall. During the study, areas of narrowing of the lumen, pathological neoplasms, and ulcerations of the intestinal tube can be detected. - Colonoscopy
. Endoscopic examination allows one to visualize gas bubbles, assess the extent of the lesion and the condition of the gastrointestinal mucosa. If necessary, the endoscopist performs a biopsy of a section of the intestine for histological analysis.
Differential diagnosis of pneumatosis is carried out with nonspecific colitis, pneumoperitoneum, diverticula and intestinal duplication. With complete obstruction, intestinal obstruction of another etiology is excluded.
Treatment of pneumatosis intestinalis
Based on the fact that the pathology develops secondary, against the background of other gastrointestinal diseases, it is first necessary to eliminate the root cause of the disease.
Treatment tactics for pneumatosis are aimed at reducing bloating and facilitating the release of gases naturally.
Due to the fact that after resection of the affected area of the intestine, frequent relapses of the disease occur, surgical removal of blisters is used extremely rarely. Treatment of the disease is carried out in the following areas:
- Drug therapy
. Includes the prescription of drugs based on fennel and simethicone, which eliminate the symptoms of flatulence. For pain and cramps in the abdomen, antispasmodics are used, for constipation - laxatives, and for diarrhea - antidiarrheal drugs. When peristalsis slows down, prokinetics are prescribed. The infectious nature of the disease may require the use of antibacterial drugs. - Diet
. A healthy diet for pneumatosis should consist of low-fat, fresh food. It is recommended to eat soups, cereals, lean poultry and fish. Among the drinks, preference should be given to fruit drinks, weak tea, and jelly. Dishes should be consumed in small portions 4-5 times a day, fresh, boiled and stewed. It is necessary to exclude foods that cause increased gas formation: beans, tomatoes, cabbage, apples, fried and smoked foods, canned food, sweet pastries, baked goods, carbonated drinks. You should stop drinking alcohol.
An additional treatment for pneumatosis is hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBO). As a result of active oxygen saturation of the blood, the total pressure of venous blood gases decreases, which can contribute to the resorption of gas bubbles. Surgical treatment methods are used for the development of complications (intestinal obstruction, peritonitis, intussusception, etc.)
Prognosis and prevention
If the primary disease is eliminated, therapeutic measures are carried out and diet is followed, the prognosis is favorable.
The formation of large and/or multiple gas cysts increases the risk of complications (peritonitis, intestinal obstruction) and significantly worsens the prognosis of the disease.
Prevention of intestinal pneumatosis includes timely diagnosis and treatment of gastrointestinal diseases, eating fresh and high-quality food. In the presence of chronic pathologies of the digestive system, it is recommended to undergo a routine ultrasound of the abdominal cavity 1-2 times a year.
Source: https://illnessnews.ru/pnevmatoz-kishechnika/
Pneumatosis of the pancreas: what is it?
Pancreatic pneumatosis is organ dystrophy or, in other words, lipomatosis. This phenomenon can also be referred to as steatosis.
It lies in the fact that damaged gland cells become covered with adipose tissue over time.
Depending on the volume of replacement, the pancreas works as usual or stops functioning due to the fact that fat cells do not produce the required enzymes and hormones.
Causes of pneumatosis
Factors leading to focal proliferation of pancreatic fat cells in the tissues:
- Previous acute pancreatic attack;
- Chronic inflammation of the gland;
- Excessive consumption of alcoholic beverages;
- Hereditary factor;
- Diabetes;
- Chronic form of hepatitis;
- Obesity;
- Low levels of thyroid hormones in the blood serum.
However, doctors say that all of the above factors do not always cause the development of pneumatosis. Even the combination of many diseases is not a guarantee of getting lipomatosis. And sometimes specialists are not at all able to figure out why the replacement began.
The risk group consists of patients diagnosed with hepatitis, cholelithiasis and inflammation of the gallbladder.
Symptoms of pneumatosis
As a rule, patients learn by chance that the parenchyma of the gland is covered with a fatty layer, for example, while undergoing a routine ultrasound examination. If the lesion is less than one third, you will not notice any symptoms. The process is completely neutral. But as the affected area increases, the following signs begin to appear.
Conventionally, they can be divided into two groups.
The first includes symptoms that become noticeable when the function of an organ decreases:
- Heaviness in the stomach area;
- Pain sensations radiating to the stomach;
- Bloating;
- Frequent loose stools with large amounts of fat;
- Nausea and vomiting.
- Increased blood glucose levels;
- Development of diabetes mellitus.
The second group includes symptoms caused by compression of adjacent organs. A benign tumor that does not metastasize.
Its appearance is due to the fact that adipose tissue is concentrated in one place, and does not grow in fragments in islands. If its size is not large, you will not feel any discomfort as such.
But when it increases significantly, the patient’s well-being worsens. Observed:
- Bloating;
- Vomiting after eating food;
- Pain syndrome;
- Increased body temperature, etc.
Diet for pneumatosis
Special nutrition is indicated for those diagnosed with pneumatosis. However, it is not able to stop the spread of substitution. Why then deny yourself some of your favorite dishes, you ask.
The fact is that reducing fat in consumed foods reduces the load on the organ and facilitates the digestion process. Also, the low fat content will help in the fight against excess weight, which, as a rule, haunts people with pneumatosis.
Also, proper nutrition eliminates most of the ailments associated with the replacement of parenchyma with a fatty layer.
Treatment of pneumatosis
Pneumatosis, according to doctors, is a disease that is difficult to recover. Therapy is based on three pillars:
- Lifestyle;
- Medicines;
- Surgical intervention.
It is recommended to increase physical activity and give up bad habits. Alcoholic drinks and smoking are excluded. Doctors advise making efforts to reduce excess weight and adhering to simple nutritional rules: small meals (6 times a day), low calorie content, abstaining from fatty foods.
Drugs themselves cannot have a beneficial effect on the adipose tissue that replaces the parenchyma. It is impossible to reverse the process. However, medications will help get rid of problems with the digestive system, if it is disturbed, and eliminate unpleasant symptoms.
Do not self-medicate. Before taking any medication, consult your doctor for advice. Only a competent specialist will determine whether you really should resort to taking medications.
For example, Ibuprofen has an analgesic effect, Mebeverine relieves spasms, Loperamide is intended for intestinal disorders, Pancreatin is for regulating digestion, Metoclopramide is for dulling attacks of nausea.
The attending physician decides on the advisability of surgical intervention. If this cannot be avoided by other means, the fatty tissue is removed surgically.
Prevention of pneumatosis
Preventive measures can prevent the replacement process.
- Don't abuse alcohol.
- Watch your weight.
- Avoid eating fatty foods.
- Monitor liver function and bile secretion.
A factor such as stress can aggravate the situation, so don’t take everything to heart and rest often.
Source: https://pankreotit-med.com/pnevmatoz-podzheludochnoj-zhelezy-chto-eto-takoe/
Treatment of pneumatosis intestinalis with medications
Intestinal pneumatosis is a complication of infectious and fermentation processes, in which gases do not move naturally, but form multiple blisters or cysts in the wall.
The condition is almost never primary, but develops as a result of other disease processes.
Often occurs in infancy and old age, when intestinal motility is reduced for natural reasons.
According to the prevalence of gas cysts
Depending on the prevalence of gas cysts, two forms are distinguished:
The limited form is more common when the small intestine is involved, namely the ileum and ileocecal angle or the junction of the ileum and the cecum, equipped with a valve (bauginian valve).
The anatomical features of this section - a sharp bend, a valve, different microflora of the small and large intestine - create the preconditions for many disorders. Normally, the contents of the intestine move only in one direction - from the small to the large intestine, and the valve does not allow reverse movement.
Diseases disrupt this balance, and gas cysts develop here easily.
By the number of gas cysts
By quantity, single and multiple gas cysts are distinguished. Multiple are more common; in appearance they resemble a bunch of grapes.
From a practical point of view, it is important how far the gas cyst protrudes into the intestinal lumen. If there is enough space left for food to pass through, then the matter is limited to discomfort and upset stool.
In the case when the cysts completely block the lumen, intestinal obstruction occurs. The swollen loops can be pressed into each other, with one section penetrating into the lumen of the other. This phenomenon is called intussusception. This leads to intestinal volvulus, necrosis of part due to impaired blood flow. Only surgical treatment can help.
Intestinal obstruction due to pneumatosis can lead to peritonitis if, under gas pressure, the intestinal wall bursts and the contents enter the abdominal cavity. Peritonitis begins, an inflammation of the peritoneum that threatens life. Treatment of peritonitis is surgical; the recovery period takes up to six months; the result is adhesive disease.
Local manifestations (at the gastrointestinal tract level)
- Flatulence or excess accumulation of gases.
Normally, the intestines contain about 200 ml of gases, consisting of swallowed air, formed in the lumen of the intestines and coming from the blood. During fermentation processes, lack of enzymes and diseases, more than 2.5 liters of gases can be formed. Intestinal gas is foam covered with viscous mucus. The abundance of this foam disrupts digestion, absorption of nutrients and the concentration of enzymes. Flatulence manifests itself as discomfort, a feeling of fullness and pain in the abdomen, and increased gas production. - Cramping pain occurs during peristaltic waves, when the swollen loops cannot consistently contract.
Intestinal colic is more typical for infants and develops in the late afternoon. The baby is worried, cries hysterically, draws in his legs, and his stomach becomes hard to the touch. This continues until defecation, and after the release of feces it stops. In adults, pain is without clear localization, spreads around the navel, radiates to the epigastric and hypogastric region. - Bowel disorders occur in people of all ages, with constipation alternating with diarrhea. Defecation brings temporary relief, then the symptoms return again.
- Heaviness in the abdomen, airy belching, pain along the intestines, loss of appetite are caused by irritation of the walls.
- Nausea, possible vomiting with severe pain.
Dyspepsia is associated with disruption of the small intestine and stomach due to the formation of cysts.
General manifestations (at the level of the whole organism)
Diffuse spread of pneumatosis leads to the appearance of general symptoms:
- severe weakness;
- pale skin;
- cold sweat;
- increased heart rate;
- decrease in blood pressure.
Such symptoms are observed against the background of abdominal pain and dyspeptic disorders. Urgent consultation with a doctor is required.
If left untreated, the pain will subside after some time, and this is a very bad sign. This means that the nerve endings of the intestinal wall have died. Then peristalsis subsides, and the stage of toxic shock begins. Without surgical treatment, further life is impossible.
Causes
- early childhood, when the innervation of the intestines and the digestive process are imperfect;
- old age, when there is enzymatic deficiency and decreased motor skills;
- intestinal infections - dysentery, salmonellosis, toxic damage when pathogenic bacteria produce a lot of gas;
- benign and malignant tumors, when the neoplasm blocks the lumen and gases penetrate into the intestinal wall;
- impaired motility due to inflammation, congenital defects (Crohn's disease or chronic inflammation of all layers of the intestine), adhesive disease, when the “stagnation” of a food bolus causes local swelling of the wall;
- violation of the natural removal of gases due to diseases of the rectum and anal ring - polyps, tumors;
- repeated stress causing intestinal spasms;
- low physical activity, which impairs motor skills;
- unhealthy diet with consumption of large amounts of foods that cause increased gas formation;
- bronchial asthma and obstructive pulmonary diseases - prolonged persistent cough causes emphysema of the mediastinum, as a result of which air enters the peritoneum, from where it penetrates the intestinal wall.
Treatment
Intestinal pneumatosis is not an independent disease, but develops as a complication of other diseases. Therefore, therapeutic activity is aimed at eliminating the underlying disorder. If it is possible to suppress the infection, remove spasms and restore motility, then the intestinal bloating also stops.
Treatment consists of diet, medications, hyperbaric oxygen therapy if necessary, and surgery.
Diet
Food should be gentle, warm, boiled and preferably pureed or chopped. Portions are small, no more than a glass at a time. You need to eat often, 4-5 times a day with short breaks. It is required to consume a sufficient amount of liquid, and prepare food from permitted products.
| Recommended Products | Not Recommended Products |
|
|
Source: https://okishechnike.com/info/lechenie-pnevmatoza-kishechnika-lekarstvami/
Hepatic pneumatosis: causes, symptoms, treatment methods
Pneumatosis does not refer to individual pathological processes, but is mentioned in the medical literature as a symptomatic manifestation of a disease.
Pneumatosis is the spontaneous formation of air microcavities in the membranes of internal organs. Hepatic pneumatosis is a controversial diagnosis, the presence of which is denied by many experts. It is believed that the occurrence of the process is associated with the spread of the disease from other organs of the gastrointestinal tract.
Pneumatosis of the liver - what is it?
The pathological process occurs in the digestive organs and is associated with an unusual accumulation of gas and the formation of bubbles on their walls. Gas cysts are not prone to spontaneous resorption and transfer of contents into the systemic circulation.
Hepatic pneumatosis is confirmed when atypical air cavities, reminiscent of tumor-like processes or cysts, are detected during palpation. The gas present in the neoplasms does not contain toxic or poisonous substances and resembles the gas composition of the atmosphere.
The lack of necessary therapy can lead to the spread of the pathological process to the peritoneum, lymph nodes, and intestinal mesentery.
Doctors distinguish several types of pneumatosis - pulmonary, intestinal, gastric, hepatic.
Causes
Experts divide the causes of pneumatosis according to the primary pathological process against which it formed. Normally, gases penetrate through the single-layer epithelium in small blood vessels and pass into the lungs and other internal organs.
Pathology of the gastrointestinal organs occurs against the background of certain factors:
- In childhood, an abnormal deviation occurs against the background of violation of the requirements for the regime and quality of nutrition, and is associated with a variety of food poisoning.
- In diseases of the digestive tract after radical surgical interventions in the abdominal cavity, air accumulates in the cavities or internal organs, especially after suturing.
- The lack of normal peristalsis also contributes to the accumulation of gases.
- The active activity of pathogenic microorganisms in the gastrointestinal tract and digestive organs leads to increased gas formation.
- Hernias, intestinal obstruction, spasms of muscle walls, developing tumors, polyps.
- Pathological accumulation of gases is recorded in the case of colitis, an acute form of appendicitis.
Symptoms
In patients with hepatic pneumatosis, the following clinical signs are recorded:
- Painful sensations in the abdominal area. The organ itself does not have nerve endings and does not provoke the formation of pain.
- Nausea, sudden attacks of vomiting.
- Increased gas formation followed by bloating.
- Constipation.
Diagnostics
When visiting a medical facility, the patient is referred for a consultation with a hepatologist. The specialist collects anamnesis, clarifies the symptoms, and inquires about the peculiarities of life. After the initial diagnosis is made, the patient receives a referral to undergo standard diagnostic techniques:
- X-ray examination allows you to detect the location of the pathological focus and provides information about the condition of the liver.
- Ultrasound is necessary to clarify the information received and determine the severity of the process.
- Clinical and biochemical blood tests reveal hidden inflammatory processes and indicate changes in blood composition.
Based on the data obtained from the examination, the doctor recommends the necessary treatment regimen.
Treatment
Treatment of hepatic pneumatosis includes the main areas:
- changing your usual lifestyle;
- drug therapy;
- surgical intervention.
Leading a healthy lifestyle
Patients need to increase physical and physical activity, get rid of all types of addictions - alcohol, nicotine, drugs. Doctors recommend stabilizing and normalizing body weight through diet and sports training.
A properly selected diet is a prerequisite for the treatment of extensive liver pneumatosis. Patients should switch to fractional meals: meals should be taken at least six times a day with a minimum calorie content of dishes.
All products that lead to high gas formation or cause constipation are excluded. These include:
- all grape varieties;
- all types of cabbage;
- peas, legumes;
- pears;
- green apples.
Useful products for pneumatosis include:
- any variants of porridges;
- fresh fruits, vegetables;
- nuts;
- dairy products;
- fish and meat with a minimum percentage of fat content.
Alcohol, spicy, fried, fatty, smoked, and salty foods are strictly prohibited. Experts recommend avoiding black coffee and strong tea.
As substitutes, it is suggested to use decoctions of peppermint, infusions of anise seeds, flax, parsley leaves, and dill.
Drug therapy
If pathogens of the pathological process are detected, bacteriological culture is performed to determine the type of infectious agent and the level of its resistance to antibacterial drugs.
If intestinal obstruction develops, patients are recommended to undergo urgent surgical intervention. The operation is prescribed for inflammatory processes in the peritoneum, for example, peritonitis.
The most commonly prescribed medications for liver pneumatosis are:
- For severe spasms, patients are recommended to take common antispasmodics - No-shpa, Papaverine, Spasmoneta, Drotaverine.
- Constant constipation serves as the basis for prescribing laxative medications - Forlax, Lavacol, Bisacodyl, Guttalax, Duphalac.
- Antidiarrheal medications - activated carbon, Sorbex, Polyphepan, Enterosgel;
- Carminatives - to reduce gas formation - Espumisan, Meteospasmil, Disflatil, Kuplaton, Pepfiz.
Prevention
To prevent liver pneumatosis, standard recommendations are used to improve its performance and increase its protective functions. Hepatologists advise:
- Eliminate or reduce alcohol consumption.
- Cure existing drug or nicotine addiction: long-term abuse leads to a variety of pathologies, including cirrhosis of the liver;
- Normalize body weight. Extra pounds and various degrees of obesity negatively affect the performance of all internal organs and systems.
- Switch to proper nutrition with a reduction in the amount of fatty, salty, smoked, pickled, sweet, fried foods.
- Visit doctors at least once a year, undergo diagnostics of the liver and ducts, the level of bile secretion and its passage through the biliary tract.
- Avoid stressful situations: a stable psycho-emotional background will not allow the body to lower its protective barriers and allow pathogenic microflora to pass through.
- Normalize your work and rest schedule. It is necessary to go to bed and get up at the same time and get enough sleep.
- Increase rates of motor and physical activity. Together with sports, all metabolic processes in the body are stabilized.
Hepatic pneumatosis requires immediate medical attention when the first symptoms of the pathology appear. Prolonged ignoring of the signs of the disease will provoke a deterioration in the body’s condition and lead to further progression of pathological processes.
© 2020 – 2020, MedPechen.ru. All rights reserved.
Source: https://MedPechen.ru/pnevmatoz-pecheni.html
What is increased pneumatization of intestinal loops?
January 5, 2020
Share: | | OK | TW
Most often, patients come to the doctor with complaints of ailments and problems with the gastrointestinal tract. And only after diagnostic measures, intestinal pneumatosis is detected in a person. The doctor can already determine the accumulation of gases by palpation if the patient has hyperpneumatosis. When pressing on the abdominal cavity, you can hear gas bubbles begin to burst in the abdomen.
Recently, this diagnosis has been made more and more often. It is quite natural that ordinary people want to know the answer to the question: intestinal pneumatization - what is it? After all, the ability to identify pathology in a timely manner and seek help affects the duration and effectiveness of treatment.
Untimely diagnosis and treatment of intestinal pneumatization can lead to serious complications. Therefore, only a doctor decides how to treat pneumatosis and what methods need to be used for the disease.
Pneumatosis intestinalis (intestinal emphysema) is a symptom that can occur with many gastrointestinal diseases. This pathology consists of the formation of cyst-like cavities filled with air in the intestinal wall (under the serous membrane). Most often, lesions are observed in the jejunum and colon, less often in the wall of the stomach. The size of the cysts varies from the size of a pea to a hazelnut.
Causes, symptoms and treatment of pneumatosis intestinalis
The main reason for the development of pneumatosis is disturbances in the digestive system, resulting in increased accumulation of gases.
Pneumatosis is provoked by improper functioning of the gastrointestinal tract. Therefore, treatment is aimed at combating the causes of the disease. Only in advanced stages, when the patient has severe pneumatosis and intestinal obstruction, is surgical intervention resorted to.
As for the appearance of the disease in children, the disease may be associated with a sedentary lifestyle. Immobility and passive time spent (for example, at the computer) often become the cause of pneumatization.
This disease is quite rare and patient reviews are very rare. This diagnosis is most often made during an abdominal ultrasound in children under one year of age, which makes parents worry.
In fact, they have ordinary flatulence (increased accumulation of gas in the intestinal lumen), which should be designated by the term hyperpneumatization of intestinal loops or echo signs of intestinal flatulence.
Read more about pneumatosis intestinalis
The pathology can only be cured surgically; medications are used to relieve discomfort and prepare for surgery.
Pneumothorax of the lung is a dangerous pathology in which air penetrates where physiologically it should not be - into the pleural cavity. This condition is becoming more common these days. The injured person needs to begin providing emergency care as soon as possible, since pneumothorax can be fatal.
Another characteristic symptom is the occurrence of pain. They are not characterized by a clear localization; the discomfort is of a cramping type.
Severe pneumatosis of the intestines, stomach and pancreas begins with the accumulation of gases in large quantities. The patient may feel heaviness in the affected area. The degree of severity depends on the size and number of cyst formations.
What is pneumatosis intestinalis?
Is intestinal pneumatization dangerous? What does this name hide behind it? The diagnosis usually does not involve serious risks. Nevertheless, the present disorders significantly worsen the patient’s quality of life.
The most unpleasant symptoms are diarrhea, gas, bloating. With this disease, changes are observed in the structure of the intestinal walls. Often, the affected areas become the site of the formation of cavities in which air accumulates.
In addition, there is a risk of developing a cyst.
It is necessary to organize 5-6 meals a day. You need to observe moderation in food and try to eat mono food at one time and not combine protein and carbohydrate foods (meat, fish and porridge and pasta).
It has been noticed that when consumed in this way, food takes a long time and is difficult to digest, and conditions are created for fermentation and gas formation. An ideal side dish for meat or fish dishes would be vegetables (boiled or raw).
Fruits should not be consumed immediately after breakfast or lunch, as this may increase bloating.
Pathology is detected in children with intestinal obstruction after surgery. Severe pneumatosis intestinalis in a child affects the tone and reduces intestinal motility.
In infants, this disease can occur due to low mobility or pathology of the gastrointestinal tract.
If a large accumulation of gases is detected in the abdominal cavity during an ultrasound, the pediatrician or gastroenterologist prescribes the child medications that reduce gas accumulation in order to avoid serious complications, and massage.
Red spots on the face and intestines
With the progression of the pathology and the absence of correct treatment, over time the disease spreads to the lymph nodes. The mesentery suffers, and the lesions penetrate into the abdominal cavity.
Acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Pneumatosis intestinalis in AIDS mainly affects the cecum and colon. It is assumed that immunodeficiency causes depletion of lymphoid tissue and, as a result, damage to the intestinal walls.
Intestinal pneumatization - what is it? All adults should know the answer to the question, because this phenomenon is quite widespread. It is often observed in children, so parents should be especially attentive.
Pneumatization of other bones?
There is often confusion in terminology. The meanings of the words pneumatosis and pneumatization in ultrasound examination are different.
The entry in the ultrasound diagnostic protocol – high pneumatization of the intestine – should be understood as excessive accumulation of gases in the lumen of the organ, that is, flatulence.
This is observed in some diseases, as well as in excess consumption of foods rich in plant fiber (legumes, cabbage, pearl barley).
Breakfast can consist of any porridge with butter, dry cookies with a small amount of jam and unsweetened tea. For lunch - vegetable soup, boiled chicken with a vegetable side dish and a decoction of herbs. For dinner - baked fish and vegetables. All snacks should be light and taken 2 hours after the main meal (baked apple, a glass of kefir, a portion of cottage cheese, eggs or just fresh fruit).
ReplyAlexander Zhirnov2 years ago
In some cases, it is impossible to find the right word, especially slang. Personally, “pneumatic” seems to me to be a fairly successful and understandable word.
When performing chest x-rays in patients with a history of mastectomy (on one side), a similar picture can be found - one lung field is darker than the other.
In this case, the situation is associated with an uneven decrease in the volume of tissue through which X-ray radiation passes.
If the patient is positioned incorrectly (during rotation) or with scoliosis, an asymmetry in the transparency of the pulmonary fields can also be detected, which is again associated with different volumes of tissue on the right and left sides.
Adhesive disease. The swollen loops are in very close contact with each other. As a result, local inflammatory processes develop, leading to the formation of adhesions. Adhesive disease leads to the development of chronic pain in the abdominal cavity and intestinal obstruction.
If constipation predominates, but without pronounced signs of irritation, Table No. 3 is indicated. The diet is aimed at enhancing peristalsis. It is recommended to have 4-5 meals a day at the same hours. The entry of products into the upper gastrointestinal tract reflexively enhances contractions of the lower intestines and this speeds up emptying. Long breaks between meals are unacceptable.
Pneumofibrosis of the lungs: what is it, what is dangerous and consequences, treatment with folk remedies
Pneumofibrosis (pneumosclerosis) is a disease characterized by the proliferation of connective tissue in the lungs. The reason for this is inflammatory and dystrophic processes. The function of gas exchange in the affected lung is impaired.
- Traditional methods
- Breathing exercises in the fight against pulmonary fibrosis
Classification of the disease, its symptoms
In medical practice, local and diffuse types of pneumofibrosis are encountered. A local type of disease is characterized by compaction of a separate fragment of the lung. There are no obvious disturbances in gas exchange processes. Diffuse pulmonary fibrosis leads to the fact that they lose their original structure and shape, their density increases, and ventilation is impaired.
According to medical sources, pneumofibrosis is divided into hilar and linear. The linear form of the disease is a consequence of previous tuberculosis or infections.
Science does not know where hilar pneumofibrosis comes from. It makes itself felt after the patient has had bronchitis or pneumonia. Pneumofibrosis rarely occurs as an independent disease. Its appearance is preceded by a number of provoking factors, which include:
- infections,
- obstructive diseases,
- systematic inhalation of toxic vapors,
- hereditary factor
- sarcoidosis,
- smoking addiction,
- mycoses,
- beryllium disease,
- interstitial pulmonary edema,
- gastrointestinal reflux,
- taking antitumor drugs.
Depending on the period of time after which the patient consults a doctor, he is diagnosed with a progressive or non-progressive stage of pulmonary fibrosis. The non-progressive form of the disease is characterized by the absence of pronounced symptoms.
In this case, treatment of pneumofibrosis with folk remedies is allowed. The progressive form is dangerous due to complications. Relapses of the disease can bother a person throughout his life. It should be remembered that a disease such as pulmonary fibrosis is more typical for men.
Why is pulmonary fibrosis dangerous? Pneumofibrosis is an insidious disease. Tissue proliferation leads to shrinkage of the lungs and respiratory failure. Pulmonary artery pressure increases. This process cannot be stopped or corrected. Death occurs as a result of complications.
Signs of pulmonary fibrosis appear if the connective tissue has grown in both lungs. The first and main symptom of the disease is shortness of breath. At the first stage, it bothers a person after physical activity, later when he is at rest.
Other symptoms of pulmonary fibrosis include:
- cough accompanied by sputum and pus,
- the skin takes on a bluish tint,
- chest pain, worse when coughing,
- prostration,
- body temperature is unstable,
- sudden weight loss,
- swelling of the neck veins,
- wheezing and squeaking in the lungs, especially when exhaling.
At the same time, concomitant signs of the disease that provoked pulmonary fibrosis appear in the picture of the disease.
Many patients diagnosed with pulmonary fibrosis fear that it is cancer. Despite the similarity of the clinical picture, pulmonary fibrosis is not an oncological disease.
Treatment methods for pneumofibrosis
Pneumofibrosis requires timely comprehensive treatment. It is impossible to get rid of it completely, but the likelihood of relapses can be reduced with adequate and timely treatment.
A specialist is able to determine how to treat pulmonary fibrosis by determining the causes of its occurrence. If focal pulmonary fibrosis appears due to inflammation, the patient is prescribed antibiotics and anti-inflammatory drugs. An additional method is procedures aimed at better discharge of sputum.
The operation is indicated when there are aggressive external causes of pulmonary fibrosis. An additional measure is therapy for respiratory failure.
Preventive measures are aimed at eliminating and reducing provoking factors. If a person's profession involves toxic fumes, it is necessary to use respiratory protection. In addition, the work area must have ventilation.
As additional methods of prevention, doctors recommend hardening, increasing physical activity, doing therapeutic breathing exercises, and giving up smoking.
As pneumofibrosis progresses, lung volume decreases and respiratory failure appears. The lungs shrink, and along with it the structure of the bronchi is disrupted. The prognosis is determined by the severity of the disease. If pulmonary fibrosis is diagnosed at a late stage, the prognosis is poor.
Traditional methods
Treatment with folk remedies involves the use of decoctions of medicinal herbs, infusions and compresses.
- Recipe for a decoction based on hawthorn and elecampane. To prepare, you will need the following ingredients: white mistletoe (200 g), elecampane herb (200 g), hawthorn, rose hips, blue cyanosis roots (all 100 g), ephedra two-spikelet (50 g). The crushed vegetable mixture is poured with a glass of water and left to simmer over low heat for 5 minutes. Then the broth is infused for about an hour. The prepared infusion is drunk 100 g during the day.
- Infusion of birch leaves. To prepare the infusion, you need to take crushed birch leaves and thyme in equal proportions (50 g each). Dry herbs are poured with water, boiled for 7-10 minutes, then infused. You should drink one quarter during the day.
- The effectiveness of thyme treatment has been proven by many years of research. Add 1 tbsp to 500g of boiling water. spoon of creeping thyme. The composition should be infused in a warm place overnight. It is recommended to pour the mixture into a thermos. The course of treatment should not exceed 4 weeks.
- A recipe to help clear your airways. Chopped rose hips and elecampane roots, 1 tbsp. each is placed in a saucepan, filled with water in a ratio of 1:3. The composition should be boiled for 15 minutes, then it should be left for 3 hours to infuse. The course of treatment lasts 2 months. You need to take the infusion daily. In case of high acidity, the decoction should be drunk half an hour after the meal. If low - 10-15 minutes before meals.
- Recipe based on rosemary. Cut the plant branches, add a little water and put them in the oven for 2 hours. Then add honey to the plant. When the composition hardens, put it in the refrigerator. It is recommended to use the drug twice a day.
- Recipe for flax seed decoction. Add 1 tbsp to a glass of boiling water. l. flax seed, leave the resulting composition for 20-30 minutes to infuse. You should drink the infusion once a day before bedtime.
- Plant compress. You should take a head of fresh cabbage, tear off the leaves, beat them so that the juice comes out, and apply to the sore spot. Cellophane is placed on the sheet and left overnight. Burdock leaves are used in the same way.
It is not rational to treat pneumofibrosis exclusively with folk remedies. First of all, you should use the methods of official medicine.
Many medicinal plants can cause allergies. Before starting therapy, you need to familiarize yourself with possible contraindications. Treatment of pulmonary fibrosis and smoking are incompatible.
Breathing exercises in the fight against pulmonary fibrosis
Breathing exercises are the most accessible means of treating lungs. Therapeutic exercises help improve gas exchange, easing the patient's condition. Dynamic exercises and diaphragmatic breathing help improve the mechanical properties of the lungs.
A classic example of an exercise is exhalation with resistance. To perform this you need a glass and a straw. Having filled your lungs with air, you need to slowly exhale air through the straw. The duration of the exercise is 10-15 minutes, the number of repetitions is 4-5. It can be repeated several times a day.
With adequate treatment, it is possible to stop the pathological process. Over time, breathing will return to normal, characteristic signs will disappear, and the risk of other diseases will decrease. A person must maintain a healthy lifestyle, eat a balanced diet and systematically monitor the process of growth of lung tissue.
Loading…
Source: https://prof-medstail.ru/bolezni-legkih/pnevmofibroz-legkih-simptomatika-prichiny-lechenie