A diaphragmatic hernia is a fairly common chronic pathology, affecting approximately five percent of the adult population. It is diagnosed most often in women over 60 years of age, as well as in pregnant women. This article will discuss the symptoms and treatment of a hiatal hernia, as well as the causes of its formation.
Causes
Pain in the abdominal region appears when taking a deep breath due to the development of a pathological process occurring near the diaphragm, both above it, that is, in the chest cavity, and below it. The diaphragm separates the thoracic and abdominal cavities. It is involved in the respiratory act, blood circulation and the activity of the digestive tract.
Due to the contraction of the diaphragm, ventilation of the lungs occurs, and food also moves through the esophagus. In addition, the cardiac sac and the lower part of the superior vena cava expand during inhalation, and when exhaling, the pressure in the abdominal cavity increases, which leads to the outflow of blood from the liver into the inferior vena cava. Thus, venous blood flows through the diaphragm into the right atrium.
The static function of the organ is to maintain the abdominal and thoracic organs. If muscle tone is impaired, this leads to the movement of the abdominal organs several centimeters higher into the chest. Any pathological processes in the diaphragm may cause pain when inhaling and discomfort in adjacent organs.
Next to the diaphragm are the lower parts of the lungs and their pleural membrane, the upper part of the esophagus, and part of the mediastinum. Inflammatory processes in these anatomical structures can provoke radiating pain to the epigastric region due to the innervation of the phrenic nerve.
Pain when inhaling is also possible in the absence of pathologies of the respiratory tract or cardiovascular system. Contraction of the diaphragm during active breathing can lead to displacement of the abdominal organs and changes in intra-abdominal pressure, which is why pain appears.
When inhaling deeply, the diaphragm may drop too low and will put pressure on the stomach, which then puts pressure on the intestines and pelvic organs, which will lead to severe pain if there is pathology in the affected organs. Often for this reason, discomfort appears when changing posture or intense exercise.
Pathology occurs in various diseases, especially often it develops with pneumonia. The pain decreases if you lie on the painful side. A pathology of the respiratory system is indicated by a dry cough, weakened breathing, and noise of contact of the pleura. Also, with pneumonia, the temperature rises to 38 ⁰C, chills, weakness, and night sweats may appear.
Discomfort when inhaling can be felt due to changes in the rib frame or vertebrae (for example, due to injury or osteochondrosis), with neoplasms in the pleura, pericarditis, and shortening of the interpleural ligament. If the diaphragm puts pressure on the stomach when taking a deep breath, then you need to pay attention to your posture. Painkillers and a straight back will help ease the pain.
Pain due to gastritis, ulcers
Gastritis can cause pain in the abdominal area.
With gastritis, pain occurs immediately after eating food. The patient regurgitates and the taste in the mouth becomes unpleasant. Heartburn and a burning sensation appear. A person feels tired, tired, weakened.
The functioning of the cardiovascular system is often disrupted. There are pains in the heart. Pressure drops are observed. State of drowsiness, pale skin, sweating, which increases after eating. There is a burning sensation in the mouth.
With a peptic ulcer, the pain syndrome is intense. It appears two hours after eating. Seasonal exacerbations of the disease may occur - in spring and autumn. Sour belching occurs, after eating there is nausea and possibly vomiting.
The patient may lose weight. Acute pain is life-threatening. This indicates that undigested enzymes are thrown from the stomach into the abdominal cavity.
This video will tell you about the causes of pain and rumbling in the stomach:
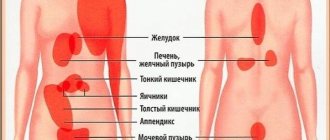
What pathologies cause abdominal pain when inhaling?
If pain when inhaling persists, despite changing body position, then this indicates serious disorders affecting the heart, lungs or abdominal organs. It happens that abdominal pain when inhaling is felt with inflammatory diseases of the gallbladder or cholelithiasis, stomach or duodenal ulcers, as well as with pancreatitis, splenic infarction or viral hepatitis.
Often pain in the right side when breathing occurs due to liver damage, but there may be other reasons, including:
- inflammation of the appendix;
- exacerbation of pancreatitis or cholecystitis;
- disruption of the cardiovascular system, for example, myocardial infarction or angina pectoris;
- renal colic;
- inflammation of the bronchi and lungs;
- kidney diseases, for example, pyelonephritis;
- pinched nerve, osteochondrosis.
Pain in the left side when inhaling can appear with the development of the following pathologies:
- hernia in the diaphragm and its pinching;
- damage to the nerves located between the ribs (intercostal neuralgia);
- appendicitis;
- cardiac ischemia;
- enlarged spleen (splenomegaly);
- exacerbation of pyelonephritis;
- osteochondrosis;
- stomach diseases;
- pancreatic dysfunction.
Pain when inhaling on the right side of the abdomen most often occurs with inflammation of the gallbladder or the formation of stones in it, as well as with progressive liver diseases. In the epigastric region, discomfort when inhaling appears if there are disturbances in the functioning of the stomach or intestines.
Stomach diseases that can cause the syndrome
Since the stomach is located in close proximity to the diaphragm, it can be compressed by it during the respiratory act. And if there is inflammation in the digestive organ, then any impact on the “exposed” nerve endings can result in pain. When you inhale, your stomach sometimes hurts if you have the following disorders:
Gastritis
The pain occurs after eating, because gastric juice begins to be released, which irritates the inflamed gastric mucosa, and also because the tissues are mechanically affected by food. As the food masses move into the intestines, the pain subsides.
In the chronic course of the disease, the pain in the upper abdomen is aching and not very pronounced. Acute gastritis can be recognized by lack of appetite, heaviness in the stomach, taste in the mouth, increased salivation, nausea, and belching. As the symptoms increase, severe pain in the stomach appears when inhaling, flatulence, diarrhea, and fever.
If an ulcer has formed in the stomach, then it makes itself felt with pain “in the pit of the stomach” about an hour after eating or due to hunger. The intensity of the symptom can vary: from mild discomfort to pain that makes it difficult to breathe.
The patient also suffers from heartburn, nausea and vomiting after eating, and sour belching. If a symptom of an “acute abdomen” occurs (severe spasmodic sharp pain, abdominal tension, stool disturbance), this indicates a perforation of the ulcer and urgent surgical intervention is required.
Benign neoplasms
These tumors do not threaten the patient’s life because they are not capable of metastasizing. But they can cause significant inconvenience during meals or when overeating due to the mechanical effect on education. Pain occurs due to the consumption of various foods, as a result of which the patient refuses to eat. Nausea and vomiting, pain on palpation, and bleeding may also occur.
Malignant formations
As cancer grows, the pain is not very pronounced, but it is constant. Symptoms of intoxication also occur: lack of appetite, indigestion, heaviness in the stomach even after eating a small amount, chronic fatigue, anemia. As the tumor grows, the pain also increases, bleeding and vomiting appear.
Poisoning
When poisoned by chemicals, the gastric mucosa becomes inflamed, hence the signs of gastritis (pain, burning in the stomach, nausea and vomiting, lethargy, weakness). In severe cases, loss of consciousness occurs.
In food poisoning, pathological processes are provoked by putrefactive bacteria that entered the digestive tract with low-quality products. The patient feels severe spasmodic pain in the stomach when inhaling, nausea, dizziness, and weakness. As the body tries to remove toxins, vomiting and diarrhea occur.
Infection
Viruses and bacteria that have entered the digestive system can also cause stomach pain when inhaling. The most common infection is gastroenteritis, which is characterized by diarrhea and vomiting.
Diseases of the abdominal organs
Pain when inhaling also occurs with flatulence. The diaphragm lowers, the pressure in the abdominal cavity increases and the intestinal walls, filled with gas, contract. With renal colic, pain when breathing appears in the hypochondrium and “in the pit of the stomach”, then it spreads throughout the abdomen, radiating to the right shoulder blade and shoulder.
Colic appears due to a sudden disturbance in the passage of urine, renal ischemia and an increase in intrapelvic pressure. In addition to pain, there is pain when urinating, nausea and vomiting, flatulence, chills, and hyperthermia.
Splenic rupture is possible after blunt trauma to the abdomen. From the damaged organ, blood flows into the abdominal cavity. Increased innervation of the lymphoid organ causes severe pain, which becomes more intense with movement and even with a full breath.
The pain is characterized as shooting and is felt under the ribs on the left. With pathology, body temperature rises, chills appear, and the skin in the abdominal area becomes blue. A subphrenic abscess causes severe pain during breathing in the sides or under the ribs.
The sensation extends to the shoulder blades and collarbone. Symptoms of intoxication also appear (heat, fever, lethargy, nausea). The patient breathes shallowly, as a deep breath increases the pain. Unpleasant sensations are somewhat reduced if you lie on the sore side or are in a semi-recumbent position.
With a diaphragmatic hernia, the diameter of the esophagus increases, and part of the stomach rises several centimeters. This provokes the appearance of aching pain in the left hypochondrium and difficulty taking a deep breath; the pain intensifies when sneezing or coughing. Frequent regurgitation and heartburn indicate a hernia in the diaphragm.
Acute appendicitis. When the appendix is inflamed, bursting pain can affect the right or left side of the abdomen or the navel area. At the same time, it is difficult for the patient to take a full breath, the pain is more intense when sneezing, coughing, or laughing. As the pathological process develops, pain is concentrated in the right side.
The gallbladder is not in contact with the diaphragm, but it is attached to the liver. When you inhale, both the liver and the gallbladder move, hence the pain in the inflamed organ. Inflammation of the gallbladder can occur in acute or chronic form. Acute cholecystitis is most often caused by the movement of stones blocking the bile ducts.
Pain appears in the right hypochondrium, radiates to the back and is felt in the lower abdomen. They intensify when you inhale. There is also a fever. Lack of therapy can lead to the spread of the inflammatory process to nearby organs.
With chronic cholecystitis, bile stops flowing into the duct, which causes stagnation of the secretion and it begins to damage the bladder tissue. The pathology develops slowly and is provoked by poor nutrition, stress, and infections.
The stomach puts pressure on the lungs, it’s difficult to breathe – Treatment of gastritis
OUR READERS RECOMMEND!
Our readers successfully use Monastic Tea to treat gastritis and ulcers. Seeing how popular this product is, we decided to bring it to your attention. Read more here...
There are many symptoms that indicate a wide range of different diseases. The feeling of a “lump in the throat” is a similar sign. To apply treatment, it is necessary to understand what causes the discomfort.
What is a lump in the throat? Tension, spasm, feeling of a squeezing metal ring, pressing, tickling, making it difficult to swallow. Sometimes a sore throat, pain or choking develops. This is how we can describe the upcoming state. But in parallel, other symptoms indicating the cause of the syndrome are monitored.
Let's look at what diseases a lump in the throat indicates.
- When infectious diseases of the upper respiratory tract (for example, sore throat or pharyngitis) are excluded, the cause may lie in psycho-emotional states. Under the influence of stress, the muscles of the larynx spasm, and a feeling of constriction appears. Soon the disturbance passes, but if the situations are often repeated and the sensations too, neurosis develops and the help of a psychotherapist will be required.
- A lump, sore throat, dryness, discomfort and cough are signs of a serious illness, for example, throat cancer. An additional symptom that distinguishes the pathology from others is hoarseness and loss of voice. It is especially important to monitor symptoms in the early stages, when the tumor has not grown much.
- A sedentary lifestyle leads to degenerative processes in the intervertebral discs and the occurrence of osteochondrosis. When the spine is deformed, the nerve endings are compressed, a spasm of the neck muscles occurs, and a feeling of a lump in the throat is born. Injuries to the neck and back of the head, hernias will also cause the feeling.
- Cardiovascular diseases, heart attack, stroke are characterized by pain in the heart area, manifested by discomfort in the neck, in particular pain and a lump in the throat.
- Thyroid dysfunction is characterized by a sensation of a foreign body in the larynx. Especially if the disease occurs in tandem with disorders in the functioning of other organs and is considered autoimmune.
- Gastritis and other gastrointestinal diseases. The throat is the entrance gate of the digestive tract; any disorders in the digestive system result in unpleasant discomfort - a lump, soreness or burning sensation is felt in the mouth and throat.
Lump in throat with gastritis, its causes
The spread of the disease gastritis, when inflammation of the mucous cells and secretion glands of the stomach occurs, sometimes develops asymptomatically, in most cases it is signaled by a complex of uncomfortable sensations.
Often the feeling of a foreign body in the throat occurs with chronic gastritis, which has not particularly bothered a person for a long time.
Symptoms
Diseases of the gastrointestinal tract show characteristic features. Manifested by local signs:
- heartburn and belching;
- acute or mild abdominal pain, often associated with meals or long periods between meals;
- an unpleasant metallic or sour taste in the mouth and a putrid odor;
- bowel disorders, nausea and vomiting, bloating and a feeling of heaviness in the stomach after eating.
Common symptoms of chronic gastritis are observed:
- weakness, increased fatigue, sweating and irritability;
- shortness of breath, pallor and changes in blood pressure;
- anemia caused by a lack of vitamin B12 is manifested by drowsiness and decreased vitality. There is a burning sensation and pain in the throat, mouth and tongue.
Causes
Depending on the reasons that led to the occurrence of chronic dysfunction, gastritis can be:
- A – Autoimmune. The development of pathology is provoked by malfunctions of the body’s immune system, when lymphocytes attack and damage healthy cells of the internal secretion of the stomach. The process leads to the development of atrophic gastritis.
- B – Bacterial. The most common type of chronic inflammation of the gastric mucosa. Caused by infection with the bacterium Helicobacter pylori, which neutralizes hydrochloric acid and protective mucus, leading to damage to epithelial cells by gastric juice. To neutralize the pathogenic microorganism, the glands increase secretion production. The acidity level of the stomach increases.
- C – Chemical. Occurs with prolonged exposure to various chemicals on the mucous membrane. These are bile acids and pancreatic enzymes (with gastroduodenitis), alcohol, toxic resins and heavy metals from tobacco smoke that enter the stomach with saliva. Selected medications (for example, aspirin), spicy, fried, smoked and spoiled foods, waste products of helminths, etc.
A lump in the throat with gastritis, depending on the form of the disease, is caused by:
- The reflux of gastric juice into the esophagus. Along with the lump, sour belching and heartburn are felt, and the return of food masses into the oral cavity is possible. This happens after eating. Against the background of progressive bacterial gastritis and increased acidity, the cells of the superficial tissues of the muscle ring, which regulates the flow of food from the esophagus to the stomach, are affected. The situation is aggravated when food, moving down, irritates the mucous membrane of the esophagus, creating an unpleasant soreness, burning sensation and spasm of the throat muscles.
- Stomach and duodenal ulcers. If the secretory function of the stomach is increased, chronic inflammatory processes occur, and ulcerations and erosions gradually form. The situation ends with a peptic ulcer, which, if not treated, can spread to the duodenum (through infection with Helicobacter ppylori). Symptoms of a stomach ulcer - in addition to acute abdominal pain, heartburn, cough, belching, nausea, vomiting and a lump in the throat. Occurs due to the reflux of bile acids and pancreatic enzymes from the duodenum into the stomach.
- Atrophic gastritis is characterized mainly by decreased gastric secretion. Under the influence of various unfavorable factors, inflammation leads to the death of a large number of mucosal cells, they cease to perform their role in secreting digestive juice. As a result, pathogenic microorganisms begin to intensively develop in the microflora of the stomach, food is poorly digested and rots. Dysbacteriosis leads to bloating, flatulence and stool disorders, feelings of heaviness after eating, and a bitter taste in the mouth. There is a dry cough, a lump in the throat.
- Autoimmune gastritis, which is localized mainly in the fundus of the stomach and occurs when there are disturbances in the functioning of the immune system. The victims of the disease are the lining cells of the gastric mucosa, which produce hydrochloric acid and an enzyme that helps absorb vitamin B12. To compensate for the dystrophic changes occurring in the upper part, the antrum of the stomach begins to intensively produce the hormone gastrin (responsible for the production of hydrochloric acid) and the enzyme pepsin (which breaks down proteins). Overproduction of gastrin gradually leads to either the formation of a stomach ulcer or a tumor. More often, autoimmune gastritis in the early stages is asymptomatic. Due to a lack of vitamin B12, anemia develops - weakness, dizziness, pallor, headache, tachycardia, shortness of breath. The peculiarity of autoimmune gastritis is that the disease often occurs in those suffering from other autoimmune diseases. These are disorders of the thyroid gland, adrenal cortex, diabetes mellitus and more. Obvious pathologies of the thyroid gland - thyroiditis and diffuse toxic goiter - are manifested by hoarseness, coughing and a lump in the throat. If you have these symptoms and are diagnosed with an autoimmune endocrine disease, it is important to undergo further testing. Perform an ultrasound, endoscopy and screening for the presence of antibodies to determine fundic gastritis. At an early stage of identifying stomach pathology, it is possible to prevent the development of more serious consequences.
Treatment
Therapeutic measures to eliminate the unpleasant sensation of a lump in the throat are aimed at treating the underlying cause - gastritis. The course and medications are prescribed and selected by the doctor individually.
The following measures will help get rid of throat discomfort and other symptoms of chronic gastritis:
- To eliminate heartburn, belching and a lump in the throat, drugs that reduce stomach acidity - proton pump inhibitors - are used.
- The next step is antibacterial therapy aimed at exterminating Helicobacter, the main causative agent of chronic gastritis. At the same time, medications are taken aimed at restoring the intestinal microflora.
- In the treatment of peptic ulcers, enveloping drugs are used to protect the epithelial cells of the stomach and duodenum from aggressive acids and enzymes.
- To treat autoimmune diseases, replacement therapy is used, which includes injections of vitamin B12, thyroid hormones, gastric juice and enzymes. Corticosteroids are used to eliminate autoimmune inflammation. Sometimes surgery is performed to remove the tumor.
- It is important to adhere to a diet and nutrition regimen when treating chronic gastritis. Eliminating alcohol, smoked, sour, spicy and fried foods that irritate the gastrointestinal tract will help significantly improve your condition and get rid of the sensations of heartburn, coma and sore throat.
Source: https://yazva.bezgastritov.ru/yazva/zheludok-davit-na-legkie-trudno-dyshat/
What to do?
Before being examined by a doctor, it is not recommended to take painkillers, since in some diseases a quick diagnosis will avoid serious complications, such as peritonitis.
Thus, appendicitis does not have specific symptoms; a preliminary diagnosis is made after palpation of the abdominal cavity, that is, it is necessary to palpate the abdomen and determine in which place the pain is stronger or weaker. Taking a painkiller will “blur” the picture and will not allow a quick diagnosis.
Inflammation develops rapidly and can lead to rupture of the organ and penetration of purulent contents into the abdominal cavity. With renal colic, a warm heating pad applied to the sore area can help, but if a purulent process occurs in the abdomen, this will only lead to its rapid development. Therefore, you should not warm the sore spot until the cause of the disease has been determined.
If a symptom appears, you must contact a therapist, who, after taking a history, physical examination (percussion, palpation, auscultation) and general tests, will refer you to a specialist.
The therapist’s task is to understand which system has failed: digestive, cardiovascular or respiratory. If there are diseases of the digestive system, then one or more of the following symptoms appear: abdominal pain, nausea, heartburn, rapid satiety, heaviness in the abdomen, belching, flatulence, bowel dysfunction.
Pathology of the gastrointestinal tract can manifest itself after eating, during stress, and exercise. Diseases of the respiratory system are indicated by the presence of a cough and pathological noises in the lungs. With heart disease, shortness of breath, irregular heartbeat, pain in the heart and behind the sternum, swelling, cough, and headache appear.
Only after a diagnosis is made, therapy is prescribed to eliminate the cause of the disease. Depending on the pathology, treatment can be conservative or surgical. The main recommendation for gastrointestinal diseases is to relieve the load on the diseased organ.
In case of inflammation of the gallbladder or pancreas, it is necessary to fast for several days; in severe cases, nutrition is given intravenously. In the acute stage of gastritis or peptic ulcer disease, you should adhere to a diet so as not to provoke an increase in the production of hydrochloric acid. It is also important to eat small portions, but often.
Treatment of the digestive tract may include taking antibacterial, antiviral, enzyme, antihistamine drugs, as well as antacids, proton pump inhibitors, and H2-histamine receptor blockers.
Abdominal pain when inhaling is a sign of serious illnesses that require urgent treatment. Otherwise, the pathology can become chronic and provoke the development of complications. Therefore, as soon as this symptom occurs, it is necessary to consult a specialist.
source
Recommendations
Following the tips below will help reduce the risk of exacerbations and reduce the severity of hiatal hernia symptoms:

Preventive measures and treatment of symptoms of a hiatal hernia will reduce the risk of serious consequences and the likelihood of future surgery. The operation is indicated for bleeding and in the late stages of axial hernia.
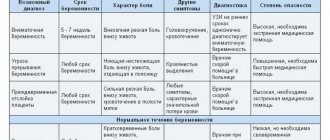
Features of pain in the upper abdomen in the middle
Periodic pain in the upper abdomen cannot be a separate disease. As medical practice shows, this is always a sign of a developing pathology. That is why, at the first manifestations of this symptom, it is recommended to consult a doctor as soon as possible and carry out diagnostic procedures.
Important! Severe pain alone cannot make an accurate diagnosis. In this case, it is necessary to take into account additional symptoms and pain intensity. They will help to more accurately determine the cause of the disease.
In most cases, the cause of pain with this localization is pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract, which are located in this part of the abdominal cavity. At the same time, it is worth noting that sometimes under this sign there may be diseases not related to the gastrointestinal tract, which are accompanied by vague, radiating pain (when it hurts under the ribs, in the chest, radiates to the back, etc.). This, in turn, may indicate neuralgia or a hernia.
In medicine, cramping severe pain has a common name - “acute abdomen”. In this condition, the patient usually requires urgent medical care and hospitalization.
It is especially important not to delay calling a doctor if the patient suffers from severe chronic pathologies or if the patient is a child. Pain in the upper abdomen in the middle part is a sign that can indicate very different diseases. That is why, in addition to him, the doctor needs to pay attention to the patient’s complaints:
- This could be nausea after eating or on an empty stomach, diarrhea and bloating, vomiting, etc.
- How often and with what intensity does pain occur (what provokes it). Thus, pain most often develops when coughing, after drinking alcohol, or after nervous or physical stress.
- The nature of the pain (bursting, dull aching, cutting, etc.).
Only by taking into account all the signs together will the doctor be able to correctly identify the cause of the disease and select the necessary treatment.
Stomach pressure: causes, possible diseases, treatment methods, reviews
Stomach presses. Such complaints arise from every third inhabitant of the planet. This symptom can appear even in a healthy person. Especially often, pressing pain in the stomach occurs after nervous experiences or after eating. What are the causes of this symptom and what to do about it? We'll talk about this in this article.
Pressure in the stomach: reasons
Most often, abdominal pain is associated with improper functioning of the gastrointestinal tract. There are many pathologies that can provoke a condition where the stomach presses.
- Active growth of polyps. It is worth noting that most often this disease does not manifest itself in any way for a long time. If the stomach presses, then the polyps have begun to actively grow, and surgical intervention is necessary.
- The inflammatory process in the gastric mucosa also gives this symptom. In this case, discomfort most often occurs after eating, especially if the person has eaten spicy or fried food. And also the inflammatory process on the mucous membrane can be accompanied by frequent belching. Some patients experience an unpleasant taste in the mouth.
- A stomach ulcer is accompanied by distinct pain sensations that begin with pressure on the stomach. These sensations intensify over time, and a person cannot do without painkillers. The pain often appears after eating. The ulcer tends to worsen in the autumn or spring.
- Very sharp pain in the stomach area is considered the most dangerous. Most often, this symptom indicates the penetration of an ulcer. In this case, through the hole that forms in the stomach, juice and digested food are released into the abdominal cavity. Peritonitis begins to develop, which without medical assistance can cause death.
- Often various acute respiratory viral infections and bacterial infections cause complications in the gastrointestinal tract. As a result, the patient begins to feel pain of various types in the stomach area, including pressing pain. Along with this, vomiting and loose stools may occur. This condition is also called intestinal flu.
- Cancers in the gastrointestinal tract may not show themselves for a long time. Over time, the patient begins to feel pressure in the stomach. Moreover, such pain is not associated with eating. Only in the last stages of the disease does a person begin to feel acute pain, vomiting blood appears, and black feces are formed. Stomach cancer is considered one of the most difficult forms to treat.
- Such a symptom may also not be associated with the disease. It can occur after simple overeating. And also the consumption of low-quality products leads to this condition.
Very often, this condition becomes chronic if adequate measures are not taken in time.
Food poisoning
If such a nuisance occurs, then the severity of the pain is directly proportional to the amount eaten and the type of component that caused intoxication of the body. Within a few hours after ingesting a low-quality product, the first symptoms of poisoning appear. Pressing pain in the stomach will only indicate the beginning of the process.
Then other symptoms appear - vomiting, fever, loose stools. In this case, it is necessary to drink plenty of salt liquids and adsorbents. Then you need to stick to a strict diet for some time.
If the condition worsens, you should immediately contact an ambulance so that the hospital can perform gastric lavage and prescribe appropriate treatment.
The reasons are not always in the gastrointestinal tract
People often complain that their stomach hurts and feels tight. Such symptoms do not always indicate pathologies in this organ system.
Many may notice that after suffering from nervous unrest there is pressure in the stomach area. This situation is very common. In this case, you need to drink a sedative and rest.
After some time, the pain will gradually subside. In the future, you need to avoid stress and try as much as possible to relax after a working day. After all, scientists have proven that stomach ulcers in people can occur due to nervousness.
Another cause of such symptoms may be pneumonia or tonsillitis. These bacterial diseases can cause the development of a pathogenic environment on the mucous membranes of the gastrointestinal tract.
In this case, you need to take beneficial bacteria for the intestines during the treatment of underlying diseases. And also while undergoing drug therapy, it is better to stick to a diet so as not to overload the gastrointestinal tract.
People who work in hard physical work may also experience discomfort in the abdominal area. Many people ask the question: “What should I do if my stomach is pressing?”
The answer is quite obvious. Don't overeat before work. And also at this time you should not eat fatty and fried foods. Sometimes it is advisable to abstain from flour.
Discomfort in pregnant women
Pregnant women, especially in the last months, may constantly feel a feeling of heaviness, now in one place or another. This is due to the fact that the fetus is gaining more and more weight and growing. Therefore, it becomes cramped and can squeeze some of the woman’s internal organs.
The gallbladder and stomach are most often affected. Stomach pressure during pregnancy can also be caused by poor nutrition. During this period, the female body is already undergoing great changes, and additional stress is placed on all organs, and overeating only aggravates the situation.
Therefore, during pregnancy, the expectant mother should eat 4-6 times a day, but in small portions. You should also avoid fried and spicy foods.
Often pregnant women really want to eat some interesting combination of foods. But before you fulfill your desire, you need to think about the consequences.
And they will certainly come in the form of stomach pain and other unpleasant symptoms regarding the gastrointestinal tract.
Diagnostics
If a person is sure that the cause of pain is pathology in the gastrointestinal tract, then it is necessary to consult a doctor and undergo a full examination. First of all, you need to visit a therapist. He will write out a referral for a general blood test and biochemical test.
The patient will then have to undergo a series of unpleasant procedures. First of all, this is gastroscopy. Nowadays it is possible to undergo such an examination under anesthesia. In this case, the patient does not feel pain, and the diagnosis is more accurate.
You will also have to do an ultrasound examination. Modern devices are very sensitive, so it will not be difficult for the doctor to identify any pathology. Sometimes another type of diagnosis is required - an x-ray with contrast. In this way, you can determine the general condition of the organ and the presence of foreign objects and various damage in it.
What to do when you can’t see a doctor urgently?
If a person feels unbearable pain and it takes some time to see a doctor, then you can take some measures on your own.
For example, for mild aching pain, you can take “No-shpa”. Before each meal, it is advisable to drink Pancreatin for several days. It will help the pancreas produce the required amount of enzymes, which will reduce the load on the stomach during food digestion.
A prerequisite for stomach diseases is adherence to a diet. Without this point, the use of medications will only bring temporary relief.
Diet
Why does my stomach feel pressure? One of the main reasons may be poor nutrition. To prevent the same problems from recurring after an exacerbation, you need to adhere to a special diet for several months.
In the first days after the onset of pain, it is necessary to simplify the daily menu as much as possible. It will be enough to eat a few spoons of oatmeal cooked in water and a small portion of lean soup. For a snack, you can use small quantities of biscuits or crackers.
In the future, you can slightly expand the diet. For example, boiled poultry or rabbit meat is gradually introduced. As a side dish, mashed potatoes without adding milk or butter are perfect.
On days of exacerbation, it is strictly forbidden to consume sour fruits and fresh vegetables. Only a few days after the condition has eased, you can add a banana to the menu.
After 7-10 days, you can diversify your diet even more. Boiled vegetables, small quantities of baked goods and various cereals are gradually introduced. But it is also advisable to eat lean first courses.
There is a small percentage of the population who are genetically determined to have some peculiarity in the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract. They have weak gastric motility. This condition is not life-threatening, but is manifested periodically by an unpleasant symptom - pressure on the stomach after eating.
In such people, when they overeat, food does not have time to digest in time and stagnates. Then the person begins to feel a feeling of fullness and discomfort in the stomach. In this case, the patient must use special drugs - prokinetics. The most famous of them are “Domperidone” and “Bromopride”.
To prevent this from happening, you need to follow a few simple rules:
- chew food thoroughly;
- have a rich breakfast with viscous porridges;
- do not drink liquid while eating;
- do not have dinner immediately before bedtime;
- Avoid eating hard-to-digest foods.
These points will help you cope with gastric motility problems without the use of medications.
Treatment with traditional methods
Many people frown upon traditional medicine. In this case, you can try several effective folk methods to relieve pressing pain in the stomach.
If such symptoms occur in the summer, you can try eating several large ripe plums. This fruit has antispasmodic properties and helps improve gastric motility.
Another effective way in the summer is rosehip decoction. To prepare it, you need to pour a tablespoon of gooseberries into a glass of water and boil over low heat for 15-20 minutes. This decoction is used in a glass 3 times a day.
The most proven method is to drink warm chamomile tea in small portions throughout the day. This plant has anti-inflammatory properties and also reduces pain in the gastrointestinal tract.
Main causes of pain

Pain in the upper abdomen in the middle can be caused by the following main reasons:
- Systemic overeating.
- Stomach ulcer (can occur in both a child and an adult).
- Acute or chronic cholecystitis.
- Pancreatitis.
- Pathologies of the spleen.
- Improper human nutrition.
- Inflammation of the appendix.
- Oncological pathologies.
Let's look at each cause of this symptom in more detail.
Binge eating
With frequent overeating, a person may develop inflammation of internal organs due to disruption of their functions. This will lead to constant pressing pain and discomfort in the upper abdomen.
Typically, these pains go away on their own, even without taking additional analgesics. They are especially pronounced when a person overeats in the evening, since at night it is more difficult for the stomach to digest food. In addition, digestion can be helped by taking medications that improve this process.
Pain of this origin can be eliminated very simply - you just need to normalize your diet and eat small portions.
Stomach ulcer
Stomach ulcers are among those diseases that most often provoke pain in the upper abdomen. An ulcer develops when the acidity of the stomach is high, due to which its walls are not protected by a mucous layer.
As a separate pathology, a stomach ulcer has several stages, each of which is also considered a separate disease.
Gastritis is considered the initial stage of an ulcer. The following factors can contribute to its appearance:
- Damage to the stomach by the Helicobacter bacteria is the most common cause of gastritis. In this condition, a person develops stomach damage, which, if left untreated, leads to a full-blown ulcer.
- Poor nutrition, especially eating foods with high acidity, as well as fasting.
- A sharp decrease in immunity, which makes the stomach more susceptible to various pathologies, including gastritis. In this state, its cells cannot resist pathogenic bacteria.
- Smoking and drinking alcohol greatly irritate the walls of the stomach and provoke chronic inflammation in it. This greatly increases the likelihood of developing gastritis, and then ulcers.
- Stress, according to research, can cause stomach ulcers. This is justified by the fact that in this state a person produces special hormones that lead to metabolic disorders in the gastric mucosa.
- The influence of concomitant gastrointestinal pathologies. For example, liver and intestinal diseases, which are accompanied by a strong inflammatory process, can contribute to the occurrence of ulcers.
It should be noted that a stomach ulcer requires immediate treatment, otherwise the patient’s condition will only worsen, which can ultimately lead to gastric bleeding and extremely sad consequences.
Cholecystitis
Cholecystitis is a disease in which inflammation of the gallbladder occurs. In this state, a person will experience attacks of colic and pain, nausea and vomiting.
Cholecystitis can be treated with diet and taking a number of medications and folk remedies. As a rule, therapy is long and requires maximum patience from a person.
Pancreatitis

Pancreatitis is inflammation of the pancreas. It can be acute or chronic, and cause pain in the upper abdomen that occurs with movement or physical activity.
In acute pancreatitis, the pain will be very intense. At the same time, it can radiate under the ribs and into the back; such pain is called girdling pain. With chronic inflammation of the pancreas, a person will suffer from periodic aching pain in the upper abdomen.
Pathologies of the spleen
The following diseases of the spleen are distinguished, which can cause pain in the upper abdomen:
- A ruptured spleen usually occurs from a direct blow to the abdomen. This condition is very dangerous due to internal bleeding.
- A splenic infarction occurs due to the formation of a blood clot in its artery. The pathology is treated surgically.
- A splenic abscess is a condition in which pus accumulates in the organ. This disease is accompanied by severe intoxication of the body and requires long-term treatment.
Appendicitis
Even though the appendix is located in the lower abdomen, when it is inflamed, a person may feel pain in the upper abdomen. Additional signs of this disease include diarrhea, nausea and vomiting, fever and pallor.
Inflammation of appendicitis requires immediate surgical intervention. Otherwise, it will rupture and all its purulent contents will enter the abdominal cavity, thereby causing terrible peritonitis.
Oncological pathologies
Oncological pathologies can also cause pain in the upper abdomen. At the same time, the tumor itself can be localized in almost any part of the digestive tract.
As a rule, the pain will be very pronounced, aching and pressing.
In such a condition, it is very important for a person to see a doctor as quickly as possible, because timely treatment started significantly increases the success of the entire therapy.
Additional causes of pain
Additional causes of such pain may be:
- Hernia.
- Abdominal injuries.
- Spinal diseases (osteochondrosis).
- Poor nutrition.
- Heart attack.
- Hepatitis.
- Peritonitis.
- Poisoning.
Important! If you have such abdominal pain, it is strictly forbidden to apply warm compresses to it. You should also not take analgesics, as they will only mask the symptoms, which will complicate the diagnosis. The best solution would be to call a doctor and go to the hospital.
Diet food
To obtain good results, it is important to combine the treatment of symptoms of a diaphragmatic hernia and a diet, adherence to which has a positive effect on the patient’s well-being. The diet should include:

Food is steamed, stewed, or baked. Salted, smoked, fatty, fried and rough foods with the addition of various sauces, pepper, onions, garlic and seasonings are prohibited. You need to eat small portions at least six times a day. The fruits are peeled and ground on a fine grater. One teaspoon of honey a day will help relieve heartburn. Drinking a large amount of liquid per day (two to three liters), including compotes, will help protect against constipation.
The following products should be avoided:
Eating solid foods is not recommended. It is advisable to limit the consumption of cabbage, legumes and fresh baked goods. The herb lemon balm and mint can cause an exacerbation of a hernia, as it helps to weaken the sphincter. Therefore, they should be rejected.
Diagnostics

If a person detects pain in this localization, it is recommended that a person contact several specialists at once - a surgeon, a therapist, a gastroenterologist and a neurologist. If necessary and if other pathologies are suspected, the doctor may refer the patient to specialists in a different medical field.
After the initial examination, history taking and palpation of the abdomen, the doctor will prescribe the following mandatory diagnostic measures:
- General clinical blood and urine tests. These studies will show the general picture of the patient’s health condition and identify the inflammatory process, if any, in the body.
- Advanced biochemical blood test.
- An abdominal ultrasound will immediately determine whether there is fluid in the abdominal cavity, inflammation of internal organs or other pathologies.
- Endoscopic examination (EGD), which will help to see erosions, ulcers or bleeding in the stomach and intestines.
- MRI and CT are prescribed if cancer is suspected.
These are classical methods of diagnostic procedures that are mandatory when identifying an “acute abdomen” with pain in its upper part. If more advanced diagnostics are needed, the doctor may prescribe additional procedures.
What to do and how to treat?
Diet correction is the main therapeutic measure

When a patient is bothered by pressing pain in the stomach after eating, it is not always necessary to take a pill. It is enough to adjust your daily diet and the pathological symptom will disappear. The gastrointestinal tract is often compressed after eating spicy, fatty or other unhealthy foods. Such food has a negative effect on the stomach, so you should avoid it or limit your intake for a while. Pressure on the stomach can also occur due to excessive formation of hydrochloric acid and bile. In this case, refuse the following dishes:
- baked goods and desserts;
- smoked products;
- very fatty and heavy broths;
- drinks containing alcohol;
- soda;
- legumes
When there is pressure in the stomach area, you need to take food in small portions, maintaining a time interval of no more than 4 hours. It is possible to reduce pressure on the internal organ by consuming foods containing fiber. You should not eat in front of the computer, while watching TV or reading a book. After eating, the stomach will feel less pressure if a person takes a walk in the fresh air rather than lying or sitting.
Drug therapy
Self-medication can cause irritation of the mucous membrane.
If, after normalizing the diet, the patient still has pain in the stomach area, then you can take a medication. But it is important to consider that taking any drug without first consulting a doctor can aggravate the problem, causing the organ to begin to put even more pressure. Drug therapy has a complex effect, eliminating not only pressing pain, but also other unpleasant symptoms. When the stomach is compressed, you can use the drugs presented in the table:
| Group of medicines | Name |
| Medicines that relieve spasms | "No-shpa" |
| "Almagel" | |
| "Vikalin" | |
| "Buskopan" | |
| "Besalol" | |
| Enzyme preparations | "Festal" |
| "Gastromax" | |
| "Mezim" | |
| "Pancreatin" | |
| Enveloping drugs that reduce the inflammatory response | "Epicurus" |
| "Control" | |
| "Omez" |
Unconventional methods

When there is pressure in the abdominal area, it is possible to use folk remedies. Cucumber juice helps with pressing pain. It is taken several times a day. You can apply hot compresses, but it is important to know for sure that the disorder is not associated with appendicitis. The following recipes help to cope with the disease:
- St. John's wort. Prepare a tincture based on medical alcohol, adding 4 tbsp. l. herbs. Insist for 3 days, after which it is taken orally.
- Plantain. The leaves of the plant are simply chewed several times a day.
- Tomato and honey. Juice is prepared from the vegetable by adding a little bee product. The folk medicine copes well with pressing pain in the stomach.
- Flax seeds. They help if there is pressure on an internal organ due to a peptic ulcer or an inflammatory process.
Therapeutic measures

Treatment of pain in the upper abdomen in the middle largely depends on the specific pathology identified, its neglect and the general symptoms of the patient. Also, when selecting therapy, the attending physician must take into account the person’s age, the presence of additional diseases, a tendency to allergies and the form of the underlying pathology (acute, chronic).
Traditional therapy can be medication and surgery. Typically surgery is required in the following cases:
- With peritonitis.
- When cancer pathology is detected.
- When detecting an acute form of cholecystitis and ulcers, which is accompanied by internal gastric bleeding.
- Diagnosis of acute pancreatitis.
If other pathologies are detected, a person requires long-term drug therapy. It is advisable to carry it out in a hospital setting under close medical supervision.
Typically, the following groups of drugs are used for acute pain:
- Analgesics are prescribed for pain. They can be in the form of injections, tablets or syrups.
- Antipyretic drugs are needed when observing high body temperature (Paracetamol).
- Enzyme medications and bifid drugs are prescribed to normalize digestion (Linex, Hilak Forte, Mezim, Pancreatin).
- Antiemetic drugs.
- Anti-inflammatory drugs (excluding peptic ulcers)
- Medicines to normalize stool.
The duration of treatment depends on the specific disease identified. Thus, it can last from 1-2 weeks to several months. It all depends on the complexity and neglect of the pathology.
In order for the therapy to be successful, during its implementation the patient is strongly recommended to completely stop smoking and drinking alcohol. It is also important to avoid physical activity and stress.
In addition, nutrition plays a very important role. The diet includes the following:
- The patient needs to adhere to a fractional diet plan. Thus, you need to eat at least five times a day, but at the same time, portions should be no more than a handful. This way you can avoid starvation, but at the same time, do not overload your stomach with food.
- Complete refusal of seasonings, hot sauces and spices. It is also important to minimize the consumption of salt and foods with added salt.
- Refusal to eat solid, hard-to-digest foods (white cabbage, fatty meat, salted fish, etc.). Instead, the basis of the diet should be liquid dishes and pureed food.
- The menu should regularly include vegetable soups, cereals and boiled meat. Low-fat fermented milk products are also allowed.
- It is better to avoid most fruits during the treatment period, as they are sour. Only sweet fruits or those fruits that have undergone heat treatment (baked apples) are allowed.
- The temperature of food for consumption should be optimal - not too hot and not too cold.
- Complete avoidance of coffee, sweets and black tea, as they can increase the production of gastric juice, which in turn can cause a new attack of pain in a person.
Important! To further support the body in this condition, a person can take vitamin complexes. It is advisable that they be prescribed by the attending physician. This will help the body recover faster.
source
Surgical methods for removing diaphragmatic hernia
Surgical treatment of symptoms of hiatal hernia is the most effective method due to the possibility of strangulation. Removal methods:
All surgical interventions include goals such as creating an anti-reflux barrier and removing the hernial orifice. Abdominal and laparoscopic methods are used. The latter method is the safest and has a short hospitalization period. When identifying both indications and contraindications for surgical treatment of a diaphragmatic hernia, symptoms and their severity, as well as the presence of concomitant diseases, are also taken into account. For example, surgery is not performed for liver cirrhosis, severe cancer, heart problems or decompensated diabetes mellitus. After surgery and following the doctor’s recommendations during the rehabilitation period, most individuals note an improvement in their quality of life.
This is primarily due to the disappearance of such regular symptoms of a diaphragmatic hernia as belching and heartburn. In the future, the patient is obliged to follow all the doctor’s recommendations, which include changing lifestyle, proper diet, reducing physical activity and taking certain medications. The prognosis of the disease is favorable provided that it is detected in a timely manner, high-quality therapy and adherence to a certain diet.
Injuries
Like any muscle, the diaphragm can be damaged, for example, by strong blows to the chest area. Abdominal pain when breathing also occurs after a severe, incessant cough or surgery.
Diagnosing damage to the diaphragm is not easy, because it is often associated with other serious diseases of the abdomen and chest. There is always a chance that symptoms will not appear immediately, but only weeks or even months after the injury.
pain in the abdomen or chest;
The diaphragm must move continuously to support the breathing process. Therefore, in case of injury, it is not enough to rest the muscle; the help of a surgeon is often resorted to.
Diseases
Regurgitation and shortness of breath most often occur due to poor nutrition and violation of food consumption culture. However, this disease hides serious diseases that are sometimes difficult to recognize on your own, which sometimes causes serious complications:
- Diseases of the cardiovascular system cause belching and difficulty breathing. When the heart malfunctions, the functioning of nearby organs occurs. Often with such diseases, the patient experiences pain in the stomach area, he is bothered by heartburn, heaviness in the chest. These signs can be confused with indigestion, which is dangerous, since untimely medical care sometimes costs the patient his life.
- Angina pectoris can also be a cause of the disease. Most often, unpleasant sensations in the form of shortness of breath and regurgitation occur with atypical angina. The pain during an attack is non-localized and can be distributed throughout the entire sternum and on its left side. If the cause of angina is excessive physical exertion or hard work, then in this case it is worth limiting the patient from working with heavy objects. Often the cause of angina is nervous tension and anxiety. You need to try to calm the patient down, perhaps offer him a sedative. If such attacks with accompanying symptoms occur frequently, it is worth getting examined and starting timely treatment.
- In heart failure, shortness of breath, regurgitation and heartburn are heartburn and shortness of breath - common phenomena in heart disease,
the very first symptoms of the disease. At the initial stage of the disease, shortness of breath appears after heavy exertion and goes away after the patient has rested. As the disease progresses, a person begins to feel an acute lack of air, dizziness, and attacks of lack of air appear at night. Therefore, it is important not to miss this symptom and consult a doctor in time.
- Myocardial infarction is the death of individual sections of the heart muscle. This disease has become younger in our time, which is a sign that modern man is leading an incorrect lifestyle. During a heart attack, the patient feels severe burning pain in any area of the chest, rapid heartbeat, while experiencing attacks of fear, and sometimes panic. When the disease occurs, belching, difficulty breathing, and severe heartburn occur. With such symptoms, the patient urgently needs to call an ambulance, since with such a disease it is dangerous to transport the victim yourself.
- Extrasystole is a heart rhythm disturbance when a sharp increase in contractions alternates with the feeling that the muscle is about to stop. Both elderly people with various ailments and completely healthy people can suffer from extrasystoles. Extrasystoles cause a feeling of suffocation, which is accompanied by belching and sometimes heartburn. The patient develops a feeling of fear, anxiety, and sometimes panic. Extrasystoles sometimes pose a danger to the patient’s life, since some types of them lead to cardiac arrest. Often the cause of extrasystole can be severe stress or nervous tension. It is important to identify the disease in time by contacting the attending doctor for advice, and if the patient is already suffering from extrasystoles, then he should be constantly monitored by a doctor.
- Osteochondrosis is a dangerous disease that occurs as a result of dyspnea and heartburn, symptoms of osteochondrosis
. With this illness, the back or a certain area of it hurts, the patient suffers from shortness of breath, symptoms of angina pectoris, and heartburn. During sleep, it is difficult for a person to breathe, pain bothers him in any position of the body. If you have such symptoms, you should immediately consult a doctor. - Neuroses cause a feeling of pain in the stomach; with this illness, the gastrointestinal tract suffers first. A person may have loose stools or, conversely, become constipated. People suffering from neuroses experience severe heartburn, feel pain in the throat or esophagus when belching, shortness of breath is accompanied by cold sweat and rapid heart rate. This disease requires an integrated approach to treatment by both a neurologist and a gastroenterologist.
- Vegetovascular dystonia (VSD) is a malfunction of the autonomic system, which entails problems with the cardiovascular system and the general condition of the patient.
With VSD, a general weakness of the body is felt, the patient has chest pain, it is difficult for him to breathe, the heart muscle and blood vessels have reduced tone . Often the patient experiences symptoms such as heaviness in the stomach and chest, heartburn, belching, cold sweat appears with shortness of breath, the heart sometimes beats strongly, and sometimes seems to slow down. With VSD, the patient always has low blood pressure due to decreased vascular tone.
Gastroesophageal reflux disease
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) is a condition in which bile or stomach contents back up into the esophagus.
GERD often causes stomach pain and difficulty breathing. Another common symptom is heartburn, a painful burning sensation that begins in the chest and travels to the throat. However, not all patients with reflux disease suffer from heartburn.
pain in the sternum or upper abdomen;
painful or difficult swallowing;
If the valve located at the bottom of the esophagus becomes weak, GERD occurs. This can be done by:
certain medications (calcium channel blockers, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs);
hiatal hernia.
GERD is treatable. Just a few lifestyle changes will ensure you feel better:
maintain a healthy weight;
do not eat less than 2 hours before bedtime;
eat often and in small portions;
after eating, you should not lie down or bend over; you must keep your body in an upright position;
do not sleep on small pillows; the elevation of your head in relation to the bed should be 15-20 cm.
Some foods also affect the exacerbation of painful symptoms of GERD. Here's what you should exclude from your diet:
Gastroenterologists often prescribe medications to lower the concentration of bile in the stomach. At the same time, choleretic drugs are not always used for GERD; do not take medications without first consulting a doctor.
Stomach pain makes it difficult to breathe
Abdominal pain when breathing is usually associated with the work of the diaphragm. This elastic, thin muscle is located along the lower edge of the ribs under the rib cage.
When a person breathes, it tenses, drawing air into the lungs, and relaxes, releasing it. Sometimes the pain can radiate to the stomach, because it is closest to the diaphragm.
And the reasons for such unpleasant sensations are different: from ordinary bruises or injuries to the development of certain diseases.
Let's consider the possible options.
Injuries
Like any muscle, the diaphragm can be damaged, for example, by strong blows to the chest area. Abdominal pain when breathing also occurs after a severe, incessant cough or surgery.
Diagnosing damage to the diaphragm is not easy, because it is often associated with other serious diseases of the abdomen and chest. There is always a chance that symptoms will not appear immediately, but only weeks or even months after the injury.
Here are some symptoms:
- pain in the abdomen or chest;
- difficulty breathing;
- cough;
- nausea;
- vomit.
The diaphragm must move continuously to support the breathing process. Therefore, in case of injury, it is not enough to rest the muscle; the help of a surgeon is often resorted to.
Gastroesophageal reflux disease
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) is a condition in which bile or stomach contents back up into the esophagus.
GERD often causes stomach pain and difficulty breathing. Another common symptom is heartburn, a painful burning sensation that begins in the chest and travels to the throat. However, not all patients with reflux disease suffer from heartburn.
Other signs of GERD:
- pain in the sternum or upper abdomen;
- labored breathing;
- nausea or vomiting;
- bad breath;
- painful or difficult swallowing;
- caries.
If the valve located at the bottom of the esophagus becomes weak, GERD occurs. This can be done by:
- overweight;
- pregnancy;
- smoking;
- certain medications (calcium channel blockers, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs);
- hiatal hernia.
GERD is treatable. Just a few lifestyle changes will ensure you feel better:
- maintain a healthy weight;
- avoid tight clothing;
- do not eat less than 2 hours before bedtime;
- eat often and in small portions;
- after eating, you should not lie down or bend over; you must keep your body in an upright position;
- stop smoking;
- do not sleep on small pillows; the elevation of your head in relation to the bed should be 15-20 cm.
Some foods also aggravate the painful symptoms of GERD. Here's what you should exclude from your diet:
- chocolate;
- coffee;
- seasonings;
- fatty or spicy foods;
- tomatoes;
- fried, salty foods;
- alcohol.
Gastroenterologists often prescribe medications to lower the concentration of bile in the stomach. However, choleretic drugs are not always used for GERD; do not take medications without first consulting a doctor.
Hiatal hernia
A hiatal hernia occurs when the top of the stomach slips into the chest cavity through a weakened diaphragm. The reasons for this process are still being investigated. Risk factors are considered to be:
- overweight or obesity;
- age exceeding 50 years;
- smoking.
A person can have a hernia from birth and not cause any symptoms. Abdominal pain when breathing occurs if it opens access for bile to the esophagus. All this leads to GERD with all the ensuing consequences. Therefore, the treatment is the same as for reflux disease. In more advanced cases, surgery is performed.
Hiatal hernia
A hiatal hernia occurs when the top of the stomach slips into the chest cavity through a weakened diaphragm. The reasons for this process are still being investigated. Risk factors are considered to be:
overweight or obesity;
age exceeding 50 years;
A person can have a hernia from birth and not cause any symptoms. Abdominal pain when breathing occurs if it opens access for bile to the esophagus. All this leads to GERD with all the ensuing consequences. Therefore, the treatment is the same as for reflux disease. In more advanced cases, surgery is performed.
Symptoms of hiatal hernia
The clinical picture of an esophageal hernia is associated with the entry of acidic contents from the stomach into it and the appearance of a so-called organ in the chest cavity in the form of a section of the cardia. This phenomenon is accompanied by the following symptoms:
Many symptoms of a hiatus hernia are nonspecific, such as cough or chest pain, which makes timely diagnosis difficult and masks the disease. A pressing pain sensation behind the sternum requires the exclusion of such a pathological condition as an attack of angina. Therefore, the patient is always prescribed an ECG. In most cases, hoarseness and cough are present with a hiatal hernia. The reason for this phenomenon lies in the reflux of acid into the laryngopharynx and onto the vocal cords. As a result, symptoms appear in the form of coughing and a dry, obsessive cough, similar to diseases such as laryngitis, pharyngitis or tracheitis. In addition, the symptoms of a hiatal hernia are similar to esophagitis, an ulcerative lesion of the stomach.
Pleurisy
Acute, cutting pain in the abdomen when breathing can be caused by pleurisy. This is an inflammation of the pleura, the thin lining of the lungs. Painful sensations are created by friction between the two layers of the membrane.
Other diseases associated with the pleura occur when gas, liquid or blood accumulates between the layers of the membrane.
If you suspect pleurisy, you should immediately consult a doctor. Treatment options depend on the type of disease, its underlying causes and the severity of symptoms. You may be prescribed anti-inflammatory drugs. In severe cases, a procedure to remove fluids or gas from the pleural space is recommended.
source
What to do for stomach pain
When the stomach hurts, a person experiences internal discomfort. Treatment depends on the disease, which can only be identified after a medical examination and consultation with a specialist. To relieve pain, take medications that reduce spasms: No-shpa, Spazmalgon. If the cause is an incorrect diet, medications that block gastric enzymes and have enveloping properties can help: Omez, Almagel.
During pregnancy, spasmodic pain in the abdomen may indicate that contractions are beginning, in which case you need to call an ambulance. If the severity is accompanied by fever, nausea, and poor health, the woman needs an urgent medical examination and consultation with a doctor.
At home, decoctions of chamomile, yarrow, mint, and flax seeds are used for calming. These substances have a calming effect and help relieve spasms.
Regardless of the cause of the discomfort, it is recommended to follow a diet to relieve symptoms and prevent the condition from getting worse. A proper diet will allow you to more accurately determine the need to see a doctor. In case of exacerbation of pain caused by poor nutrition, it is advisable to refrain from eating for at least one day, the body will “rest”. After a hunger strike, you need to gradually expand your diet, starting with soft foods: cottage cheese, yogurt, low-fat sour cream. It is advisable to exclude fried, spicy, smoked foods. Replace meat with steamed fish. Vegetables should be treated with caution; some aggressive substances contained in citrus fruits and other fruits and vegetables can be dangerous.
Shortness of breath due to stomach
Every person is familiar with the symptoms of shortness of breath; it occurs after heavy physical exertion or after suffering stressful shocks. But another reason for its appearance is gastrointestinal pathologies caused by poor diet. This is due to the fact that proteins and fats are not broken down and do not create the necessary building material for the restoration of the gastric epithelium. Pathological shortness of breath is considered to be in cases when it begins to cause discomfort and significantly impede air intake.

Physical exercise
For the most part, all symptoms of a diaphragm hernia increase due to physical activity, and especially with lifting weights, as a result of which the pressure on the diaphragm from below increases. The most dangerous loads are considered to be after eating food, since during this period the stomach also puts pressure on the diaphragm. You can give an impetus to the appearance of signs of a hernia within thirty minutes after eating by doing the following:
This is due to the fact that the above processes are accompanied by the transition of part of the overfilled stomach into the chest cavity. At the first symptoms of a diaphragmatic hernia, you should consult a doctor for examination and subsequent treatment.
Shortness of breath from the stomach: causes and symptoms
This is a condition in which a person feels a lack of air and oxygen starvation. At such moments, it is difficult for the patient to breathe; he acutely feels the need for constant air intake. Often shortness of breath develops against the background of gastrointestinal pathologies, which result in impaired respiratory function due to spasms of the diaphragm. With poor nutrition, accumulation of gases or damage to the mucous membrane of an internal organ, dysfunction of the digestive process occurs. Air accumulates in the stomach and respiratory tract, the exit of which is difficult due to compression. After physical activity, dyspnea is characterized as a normal condition in which a person reflexively compensates for the lack of air with frequent and systematic breaths. A number of these processes and disruptions in the body cause shortness of breath, characterized by difficulty breathing. There are other causes of the pathological symptom:
- obesity;
- stomach ulcer;
- dysfunction of the digestive organs;
- pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract;
- duodenal diseases;
- gastritis;
- oncology.
Return to contents
Symptoms
Often, if the pathological condition is ignored, belching begins to develop along with shortness of breath, which is accompanied by an unpleasant odor and taste in the oral cavity. Such symptoms indicate disturbances and imbalances in the gastrointestinal tract, especially if the patient has been diagnosed with stomach diseases. The condition occurs both periodically and as a permanent phenomenon. In certain cases, shortness of breath occurs on its own, for no apparent reason. Symptoms include the following:
- it becomes difficult to breathe;
- presses in the stomach area;
- stomach ache;
- rapid breathing;
- need for fresh air;
- inability to produce a full air intake;
- feeling of panic;
- pressure on the diaphragm;
- dry wheezing when inhaling;
- It hurts to swallow and inhale air.
Difficulty in breathing is also observed in older people, as well as overweight patients. The heavy load on the body limits the ability to breathe deeply, since the process is accompanied by cramping pain and pressure on the chest. Shortness of breath from the stomach is a common phenomenon among patients with disorders and pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract, so doctors, when diagnosing, assume the possibility of pathological dysfunction occurring in the future.
The appearance of shortness of breath for no reason is a pathological condition that requires medical intervention. Ignoring the problem can transfer the disease to a chronic stage.
Causes of hernia
There are several known factors contributing to its formation:
- High pressure in the peritoneum. Provocateurs of this condition are cough, excess weight, prolonged flatulence or constipation. In rare cases, the formation of a hernia is associated with obstructive pulmonary disease, which results in expansion of the lung tissue, i.e. emphysema. All of the above phenomena provoke an increase in abdominal pressure.
- Weak ligamentous apparatus that holds the esophagus in the diaphragmatic opening. A change in the elasticity of the ligaments and the inability to perform their functions of holding the stomach and esophagus in the desired position may be due to pathologies associated with connective tissue deficiency. In some cases, such changes occur with age and the individual exhibits symptoms of a hiatal hernia.
- Impaired gastrointestinal motility, which is mainly caused by the following anomalies: gastritis with high acidity, cholelithiasis, gastric ulcer.
Treatment options
It is difficult to get rid of dyspnea right away. To do this, the patient is recommended to eat something sour after eating or take acid-lowering drugs that will help digestion and the process will go smoothly. Typically, patients experience bloating, stomach pain, heaviness and gas formation, which compresses the diaphragm, causing difficulty in heartbeat and breathing. Therefore, many people confuse shortness of breath from the stomach with signs of pathologies of the cardiovascular system. Therapy for the disease is prescribed only after determining the causes of its occurrence. It includes comprehensive treatment:
Medicines will help get rid of the troubling problem.
- medicines;
- acid-lowering agents;
- diet;
- folk remedies;
- prevention procedures (sanatoriums, physiotherapy, proper nutrition).
Return to contents
Drug therapy for hiatal hernia
In this case, doctors recommend medications that restore the motility of the stomach and esophagus, reduce secretory activity, antihistamines, as well as antacids, which also relieve the symptoms of a hiatal hernia. Treatment begins immediately after diagnosis. Commonly Prescribed Medicines:
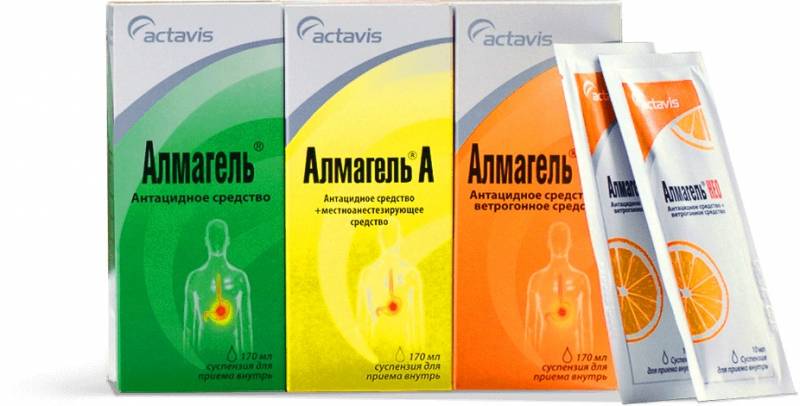
The dosage and frequency of administration are determined by the attending physician.
Prevention
To avoid the appearance of this unpleasant symptom, it is initially necessary to completely cure the underlying disease that caused the dyspnea. Qualified treatment will help prevent this phenomenon and other associated complications. Patients with gastrointestinal diseases are advised not to load the stomach, and eat small portions 5-6 times a day. Avoid foods that increase acidity and stick to a prescribed diet. Periodically undergo diagnostics, which will allow you to determine the prerequisites for pathology in the early stages. It is important to control weight for people with signs of obesity; they are recommended to lose weight. It is useful to take herbal decoctions for daily preventive treatment of the gastrointestinal tract. You should be in the fresh air more often and give up bad habits.
source
Causes of a sliding hiatal hernia
The causes of the disease are congenital (natural) and acquired factors. Of the latter, it is worth highlighting:
Congenital factors include:
In addition, symptoms of a diaphragmatic hernia can be triggered by obesity, pregnancy, and stomach diseases, which increase pressure in the peritoneum.