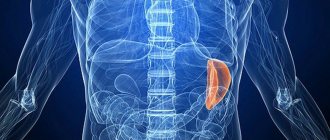
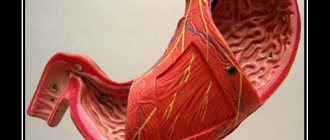
The spleen is a bean-shaped parenchymal organ that lies relative to the 9th and 11th ribs. The spleen is located between the lower part of the stomach and the diaphragm. It is rich in blood vessels and has a reddish-purple color. A healthy spleen is not palpable or felt by the patient. An enlarged or painful spleen may indicate diseases of various etiologies. Treatment for spleen depends on the underlying disease. In the International Classification of Diseases, 10th revision (ICD-10), diseases of the spleen are designated by code D73.
Causes of inflammation of the spleen
Spleen damage can be caused by acute bacterial or viral infections
The spleen destroys old red blood cells and dysfunctional platelets. The organ functions like a sponge through which blood passes: young and flexible blood cells pass through without problems. Old red blood cells - three months old - get stuck in the spleen and are destroyed. Even small blood clots are “caught” from the bloodstream and destroyed. Whatever is destroyed in the spleen will be reused to create new blood cells in the bone marrow
The spleen is about 11 cm long, 7 cm wide and 4 cm thick. The parenchymal organ is located in the left upper abdomen above the left kidney and just below the diaphragm. The spleen is bean-shaped and weighs up to 200 grams. The tight capsule of connective tissue that surrounds the spleen protects it from external injury.
Anatomically and physiologically, the organ is divided into red and white pulp. The red pulp is responsible for the destruction and disposal of old red blood cells; it is a network of connective tissue containing millions of aging red blood cells. The white pulp stores immune cells.
The organ is supplied with blood through the splenic artery. Blood enters the liver through the splenic vein. The spleen is very well supplied with blood; every day all the blood flows through the spleen approximately 500 times.
Pain in the upper abdomen or under the left costal arch may indicate enlargement (splenomegaly) or inflammation of the spleen. Often the inflammatory process is caused by infectious diseases. An enlarged or inflamed spleen is usually not an independent disease, but a symptom of various other diseases - infections or tumors. Inflammation of the spleen in adults is often accompanied by other symptoms: pain in the lower abdomen, bloating, flatulence, nausea, anemia, pallor, fatigue.
An enlarged spleen can be caused by acute bacterial or viral infections. Tuberculosis, malaria and chronic inflammatory diseases such as rheumatism or other autoimmune diseases can cause splenitis. In addition, possible causes may be diseases of the hematopoietic system - blood cancer (leukemia) - and malignant neoplasms of the lymph nodes.
The spleen is also significantly enlarged if the process of hematopoiesis in the bone marrow is disrupted. Then, as in the embryonic period, blood cells begin to form in the spleen again. The spleen can increase to 40 centimeters in length.
Hormones and calcium
In the USSR, it was assumed that the level of hormones affects the mineralization of the blood. Kidney stones were attributed to fluctuations in phosphorus and calcium concentrations. The amplitude was controlled by the brain (pituitary gland). When calcium levels in the blood decrease, parathyroid hormone begins to be produced. Osteocytes actively disintegrate, replenishing the lack of substances in the plasma. The information is useful for people planning to fast: the body begins to feed not only on muscles, but also on the musculoskeletal system. True, part of the calcium is absorbed during the process of urine reabsorption.
The need for calcium increases during intense training; the element actively participates in the contraction of myofibrils and fills the sarcoplasmic reticulum. When the parathyroid gland is removed, experimental animals die in convulsions. Let's return to the thyroid gland.
The hormones thyroxine and triiodothyronine produced are not directly related to the phosphorus-calcium balance. Levels of substances in the blood that are deviated from the norm indicate a disease of the thyroid gland. An easy way to detect pathology is to donate blood. The thyroid gland produces a parathyroid hormone antagonist, medically called calcitonin. The role of formation includes reducing calcium in the blood by issuing a command to bone tissue cells for enhanced construction.
To summarize:
- Parathyroid hormone increases calcium levels in the blood, taking the element away from bone tissue.
- Calcitonin reduces calcium levels by promoting bone hypertrophy.
If the parathyroid gland is not in order, the level of blood mineralization becomes elevated, naturally leading to the deposition of stones along the flow path. The spleen falls into this series. When a suitable nucleus is present, a stone is formed.
Symptoms

When the spleen is inflamed, pain appears in the upper or lower abdomen (the symptoms of inflammation resemble appendicitis)
The symptoms that accompany inflammation of the spleen depend on the underlying cause or condition in each individual case. Patients complain of severe pain in the left upper quadrant of the abdomen. In addition to pain, swelling in the spleen sometimes occurs due to an increase in the volume of the organ. In more rare cases, mild fever may occur. Fatigue, pale skin and weakness may occur in patients with a very inflamed spleen. In addition, pain in the spleen can spread in different directions, but in most cases remains in the upper or lower abdomen.
Splenitis mainly occurs with blood diseases - leukemia. With leukemia, the concentration of white blood cells is significantly reduced, making the body more susceptible to infection. Patients lack antibodies produced by plasma cells. The platelet count initially increases, increasing the risk of thrombosis, but after a while the number decreases again.
Even liver diseases - cirrhosis of the liver - cause enlargement and, therefore, inflammation of the spleen.
Causes of the disease
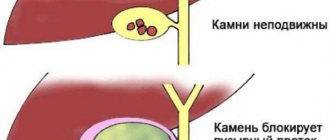
Calcifications in the spleen appear as a consequence of inflammatory processes in the body. That is, this disease is a secondary phenomenon, and in order to prevent it, it is enough to know the basic prerequisites and causes of its occurrence. The disease develops:
- as a consequence of an infectious disease that can affect not only the spleen itself, but also the organs located next to it (most often, experts associate the occurrence of calcifications with pseudotuberculosis, yersiniosis, etc.);
- the second reason is much more difficult to identify - it is expressed in a violation of the metabolism of calcium and phosphate in the body, which is why salt deposits of various sizes may appear.
Regardless of the cause, in most cases this pathology does not require any treatment, but in some situations it is simply necessary, because chronic diseases may begin to worsen and previous ones may return.
- Chicory (20 g) is poured with 200 milliliters of boiling water and left to brew for 40 minutes, after which 2 teaspoons are consumed three times a day, before meals.
- St. John's wort (10 g) is brewed in a glass of boiling water and left for 30 minutes. After cooking, filter the broth and add another 200 ml of water. After the product is ready, drink it 3 times.
- It is also recommended to drink pomegranate or cabbage juice, which is slightly warmed to room temperature beforehand. Use this remedy 3 times a day 30-60 minutes before eating.
Treatment of the spleen with infusions

An infusion of the herb is effective in treating a wide variety of spleen diseases. To prepare it, you need to pour boiling water into a glass and brew ten grams of dried herb, after which it must be infused for 20 minutes. After this, the resulting infusion should be cooled well and then filtered, after which you can drink the medicine 1 tbsp. five times a day.
An infusion of cones is prescribed for inflammatory processes in the spleen. You need to pour one part of hop cones with four parts of 40 percent alcohol, and then infuse this luxurious remedy for 10 days. After the required period, this excellent tincture should be taken three times a day, 40 drops, and so on until such a remedy runs out.
It is necessary to take succession grass, tricolor violet flowers, as well as strawberry leaves and leaves. Plants are taken in equal proportions. Only after this you need to brew 2 tbsp in 500 ml of boiling water. herbal mixture and let it brew well for about one hour. It is recommended to take the resulting product one glass at least three times a day.
In equal proportions you need to take chamomile flowers, grass, St. John's wort, immortelle, fennel, nettle, as well as angelica roots. It is necessary to pour 1 tbsp into a glass of boiling water. collection, and then the resulting mixture needs to brew for about three hours. Take this wonderful decoction half an hour after each meal three times a day, drinking one glass. The duration of this course of treatment is approximately ten days.
Diagnostics and norms
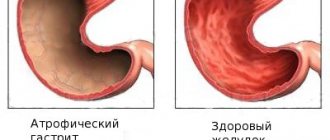
For any signs of inflammation of a parenchymal organ, it is recommended to consult a doctor. First, the doctor will perform a physical examination and take a medical history. The examination begins with palpation of the upper and lower abdomen, which helps determine the strength and nature of the pain. In addition, the doctor may feel the enlarged spleen. When the spleen is enlarged, pressure is felt in the chest. In some cases, breathing also changes.
For accurate diagnosis, imaging methods such as ultrasound or computed tomography are usually used. A general blood test is often prescribed.
Important! If you experience abdominal pain that lasts for several days, you should consult a doctor immediately. If the pain extends from the left breast to the shoulder area, a doctor should be consulted as soon as possible. If the patient experiences unusual symptoms on the left side of the body at the level of the stomach or left costal arch, it is recommended to go to the intensive care unit. If the pain continues to spread or becomes more severe, you should call an ambulance.
First, you always need to contact your local physician, who will prescribe a referral to the right specialist. If the cause of inflammation is an infection, the doctor will refer the patient to an infectious disease specialist. For autoimmune diseases, consultation with an immunologist is recommended. In case of cancer, you must contact an oncologist.
Cleaning the spleen - how often, with what means and is it worth it at all?
The spleen is not just an organ of the human body, it is an organ that is entrusted with a lot of vital functions for life. First of all, the spleen is a direct participant in metabolism. It is also responsible for the production of antibodies and the retention of bacteria.
Some believe that a complete cleansing of the spleen should be carried out at the end of the autumn period, or at the beginning of winter. However, the greatest effect can be achieved if you cleanse the body in general and the spleen in particular twice a year. Before cleansing the spleen, the same cleansing process must be carried out with the stomach, intestines, and liver.
Cleansing the spleen, like other organs of the human body, can be done at home, using improvised means and folk recipes proven over centuries. One such recipe is to cleanse the spleen using juice from white cabbage. In order to prepare it, you need to take a small head of cabbage, cut it, grind it using a meat grinder, and then squeeze it through a mesh material. The juice obtained in this way should be drunk in three to four doses throughout the day, only half a glass, a few minutes before eating. The juice is drunk for two weeks, after which there is a break for a week, and then you need to start taking the juice again. A total of three three-week cycles should be carried out.
It has long been established that if you have any diseases of the spleen, you should not eat beef, dairy products and raisins. Both for the treatment of diseases of the spleen and for its cleansing, many recipes have been invented in folk medicine, the use of which or not is up to everyone to decide for themselves. Here are a few of them.
First of all, popular medicine recommends drinking a decoction of a mixture of herbs three times a day. The decoction is prepared from barberry leaves, chicory root, rose hips, strawberry leaves and marigold flowers. Everything is taken in one to one proportions, crushed and mixed. To use, you need to pour one spoon of the mixture into one glass of boiling water and leave for two minutes.
Since traditional medicine is quite “inventive,” it offers another collection, which is now approved by doctors, and which helps in cleansing the spleen. This collection includes ten grams of St. John's wort and madder root, as well as thirty grams of rose hips, marigold flowers and dill stems. Preparing a decoction from this collection is very simple: one spoon of the mixture is poured into a glass of water brought to a boil and infused for several minutes.
To cleanse the spleen, it is useful to constantly eat blueberries, strawberries, grapes, watermelons, garlic, all kinds of greens, and also drink infusions from the leaves of all of these plants.
Some believe that a complete cleansing of the spleen should be carried out at the end of the autumn period, or at the beginning of winter. However, the greatest effect can be achieved if you cleanse the body in general and the spleen in particular twice a year. Before cleansing the spleen, the same cleansing process must be carried out with the stomach, intestines, and liver.
Types of treatment
Conventional therapy includes medications or invasive procedures such as removal of the spleen. Surgery may be considered if the spleen is enlarged or contains a tumor. Although the spleen has important functions in the body, it is not one of the vital parts of the body, so people can live without it. However, after a splenectomy, the risk of developing life-threatening infections increases. For this reason, people whose spleen has been removed should pay attention to a healthy lifestyle. In addition, it is important to regularly get vaccinated against various diseases.
To treat splenitis, it is necessary to make an accurate diagnosis. Therefore, the patient is asked whether the pain is concentrated in the left side of the upper abdomen. It is also necessary to clarify pre-existing conditions - cardiovascular disorders or blood diseases.
Treatment for pain in the spleen depends on the cause:
- Drug treatment: if a certain disease is diagnosed that cannot be treated, symptomatic medications are prescribed. When the causative agent of the disease is identified, etiotropic (causal) therapy is often prescribed. Antibiotics and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are most often prescribed.
- Surgery: tumor as well as vascular diseases, severe injuries and organ enlargement often require surgical intervention. During the operation, severely damaged areas of tissue are removed. If the spleen is close to infarction, splenectomy is recommended.
- Prevention: during treatment, you must adhere to certain doctor's recommendations. Especially in the event of injury, absolute calm must be maintained. After removal of the spleen, severe immune deficiency and an increased risk of infection may occur. Prevention from pathogens through hygiene and proper diet is an important part of life for patients without a spleen.
Medication
A single dose, if necessary, can be taken 3-4 times a day with an interval of 4-8 hours
For bacterial infections, broad-spectrum antibiotics are prescribed. If the antibiotic does not work, bacteriological culture of the microflora is performed. After receiving the results, the doctor will be able to prescribe an effective narrow-spectrum antibiotic.
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are specific inhibitors of the enzyme cyclooxygenase (COX). COX is involved in the conversion of arachidonic acid into inflammatory mediators. Thromboxane and prostaglandins, inflammatory mediators, are involved in the development of pain and inflammatory reactions. NSAIDs are most often prescribed for the symptomatic treatment of various diseases.
Inhibition of these enzymes by NSAIDs has an antipyretic effect. Prostaglandin is an important mediator for the activation of the nerve center for regulating body temperature in the brain - the hypothalamus. High levels of prostaglandin E2 during inflammatory conditions (such as infections) increase fever.
The analgesic effect is associated with a decrease in local prostaglandin synthesis during inflammation. Prostaglandins, if produced, will enhance the response of local pain receptors in response to irritant or tissue damage.
The anti-inflammatory effects are also largely dependent on the inhibition of prostaglandins, as they are important mediators of vasodilation, pain and the recruitment of more leukocytes to the site of infection.
Another drug that is often prescribed for inflammation is acetylsalicylic acid. Aspirin can worsen the rheological properties of blood and the condition of patients with spleen injuries. If a splenic rupture is observed, it is recommended to avoid the use of the drug.
Surgical
Some abdominal surgeries may require removal of the spleen (stomach surgery). Due to the proximity of the spleen to the lower part of the stomach, any manipulation can lead to rupture and subsequent postoperative splenectomy. The spleen may also be removed after trauma that has caused it to rupture and for some malignant lymphomas.
In surgery there are open and laparoscopic surgery. In cases of trauma or large tumors of the spleen, open surgery is performed. The procedure requires general anesthesia.
Typically, patients without a spleen can lead a relatively normal life and perform daily activities without restrictions. To prevent possible infections, regular vaccinations are recommended.
Treatment methods for spleen diseases
Many people ask: how to cure a spleen? First, an attempt is always made to treat the underlying disease that led to splenomegaly. If the underlying disease cannot be treated effectively, surgical removal of the spleen (splenectomy) may be considered. Splenomegaly without hypersplenism does not need to be treated. However, the consequences of uncontrolled hypersplenism - anemia, decreased immunity and increased bleeding - require immediate treatment.
If the spleen is accidentally ruptured, depending on the extent of the damage, an attempt is made to save as much tissue as possible. Once the organ is completely removed, the affected patient is more susceptible to infection, so partial removal of the spleen or tissue-sparing surgery is the goal today.
Chemotherapy and radiotherapy
Radiotherapy and chemotherapy are used to treat cancers in the spleen area. The decision to prescribe chemotherapy is made by the oncologist after confirming the diagnosis. Not all cases require taking cytotoxic drugs; In some situations, expectant therapy is recommended.
Radiation therapy is used in most cases to remove any remaining cancer. Early radiotherapy for some diseases (slow-growing non-Hodgkin's lymphoma) may worsen the patient's condition. Therefore, the decision to undergo the procedure should be made by a strictly qualified medical specialist, taking into account all the risks and benefits. Aggressive malignancies almost always require both chemotherapy and radiotherapy.
Anti-inflammatory drugs, antibiotic therapy
If a quick therapeutic effect is needed, the tablet is taken half an hour before meals, in other cases after or during meals
Anti-inflammatory medications are used to treat inflammatory diseases. In medicine, non-steroidal and steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (capsules and other forms of medication) are distinguished. Nonsteroidal medications are most often prescribed in clinical practice because they are better tolerated and cause fewer side effects. The most common international nonproprietary names of tablets from the NSAID class are ibuprofen and diclofenac.
Antibiotics should only be taken when absolutely necessary. They can only be used for bacterial infections, since they are ineffective for viral ones.
Antibiotics usually kill not only pathogenic bacteria, but also beneficial ones. These include gut bacteria, which are important for digestion, or lactic acid bacteria, which maintain an acidic pH in the vagina.
Main side effects of drugs:
- Gastrointestinal complaints (eg, diarrhea and flatulence);
- Vaginal thrush infections.
In addition, there are a number of other undesirable effects that may occur in the context of antibacterial or anti-inflammatory therapy. Adverse reactions depend on the specific drug.