Main causes of spleen disease
- Congenital defects. In some cases, a person is born without this organ. It happens that its sizes and shapes do not meet the standards. Sometimes two or more of these organs can be observed in the cavity. Problems with weak abdominal muscles can lead to the “wandering spleen” effect, when its location is not clearly defined and is constantly changing;
- Heart attack. This phenomenon occurs quite often. The cause is leukemia and infectious diseases;
- Inversion. The organ is twisted at the base, as a result of which its blood circulation is disrupted;
- Abscesses. The cause of the disease can be a heart attack or typhoid fever. The process is painless and often ends without additional treatment;
- Cysts. Most often, serous cysts are observed, which are the result of injuries and ruptures. Sometimes the organ is affected by parasitic sacs caused by echinococci. They enter the bloodstream and develop over 15 years, causing tissue destruction.
The diseases are asymptomatic. There may be pain on the left under the ribs and a bulge in the same place.
- Degenerative processes. In older people, organ atrophy is common;
- Tumors. More often the organ is affected by lymphosarcoma. Primary malignant tumors almost never occur and there are no metastases;
- Splenomegaly. Enlargement of the organ is associated with the growth of lymph nodes, fever, hepatitis, changes in liver size, anemia, infectious diseases (measles, meningitis, scarlet fever);
- Tuberculosis. The causes of spleen disease are caused by Koch's bacillus.
Causes and symptoms of pathology
Inflammation of the spleen as an independent pathology occurs only when the lining of the organ is damaged by bacteria that cause infection. In other cases, this is a consequence of a malfunction of other organs.
The disease can be caused by:
- Intrauterine developmental defects (as a result of which the shape of the spleen changes) or it is located in the wrong place.
- Past infectious diseases: typhoid, malaria, hepatitis, tuberculosis.
- Pathologies of the circulatory system. By destroying red blood cells, such diseases increase the load on the organ.
- Cysts of various etiologies.
- Infection with echinococcus and roundworms. Worms, penetrating into the spleen, eventually provoke rupture of the organ. The danger is not the parasites themselves, but their larvae.
- Oncological diseases of other organs and benign neoplasms. The spleen is affected by tumor metastases. In the early stages of development, the disease almost does not manifest itself. A comprehensive examination is required.
- Traumatic injuries. These include blows, gunshot wounds and stab wounds. You can damage an organ simply by falling on your stomach unsuccessfully. Inflammation may be a consequence of an accident.
- Surgical operations during which the outer shell of the organ was damaged.
- Abscesses. There can be many of them. But even single suppurations can provoke inflammation and rupture of the spleen.
Regardless of the reasons for the development of the disease, similar symptoms indicate it.
The main sign of inflammation is splenomegaly, or enlargement of the spleen. Pain under the ribs on the left, discomfort in this area can also signal pathology. The intensity of the unpleasant sensations may be weak. Sometimes the pain becomes unbearable. The disease is characterized by tachycardia against a background of low blood pressure, low-grade fever, and a feeling of chills followed by hot flashes. If inflammation occurs against the background of an abscess, the thermometer rapidly creeps up. Its readings exceed 38.5 degrees.
Bruises and hematomas on the body indicate inflammation caused by organ injury.
During laboratory diagnostics, another symptom of pathology may be revealed - a low level of red cells in the blood. The ESR (erythrocyte sedimentation rate) is increased. In addition, blood clotting is significantly higher than normal.
If the disease is not associated with the abdominal organs, it may be asymptomatic.
Symptoms of spleen disease in humans
It is not known for certain, but it is very likely that the spleen is directly involved in filtering the blood and maintaining the balance of metabolic processes in the body. This same organ ensures normal blood clotting.
There are quite a lot of diseases that can affect the spleen. The first signs of spleen disease may differ.
Splenic infarction
Such a disease causes blockage of the blood vessels that supply the organ, causing its functions to be impaired. The patient feels discomfort in the right hypochondrium and abdomen. Very often a heart attack is accompanied by:
- severe nausea;
- vomiting that does not bring the slightest relief;
- fever;
- chills.
Injuries, infectious diseases and inflammations
All these factors can cause the formation of an abscess. The symptoms of this spleen disease are similar to those of a heart attack:
- heat;
- fever;
- chills;
- painful sensations.
The pain is acute, intensifying during movement and changing body position.
Tuberculosis
The spleen is susceptible to infection with Koch's bacillus. It is quite difficult to suspect organ tuberculosis - it does not have pronounced symptoms. One of the most obvious manifestations is a high temperature that does not subside over a long period of time.
Benign tumor
Cysts often form in the organ. Symptoms of this spleen disease in both women and men do not appear immediately - only when the tumor increases significantly in size. Due to the enlarged cyst, the size of the organ increases.
Parasitic lesion
The spleen also enlarges during leishmaniasis, a parasitic disease that, fortunately, is rare. With leishmaniasis, the patient feels weak and suffers from high fever. During illness, minor bruises and bruises occur on the body. The disease also causes enlargement of the lymph nodes and liver.
Blood pathologies
Blood diseases have a negative effect on the spleen. Werlhoff syndrome is a prime example. The main symptom of spleen disease in women and men in this case is a change in blood composition. Due to the disease, patients feel weak, suffer from dizziness, and bleeding of mucous membranes.
It wouldn’t hurt to get checked by a specialist for those who are constantly affected by infectious diseases. You should suspect a problem and go for an examination if there is a decrease in hemoglobin, bruises appear on the body even with minor injuries, and regular bleeding.
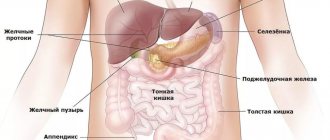
Location and size of the spleen
The spleen is located in the abdominal cavity in the left half of the upper part, near the stomach at the 7-9 ribs. It should be noted that a significant part of the population (about 20%) has additional lobules. The spleen can be vertically, horizontally and obliquely elongated.
Its length is about 150 mm, width 80 mm, weighs about 200 grams.
The sizes may be subject to increase and decrease, depending on the filling with blood. The echostructure of the spleen is homogeneous; normally, the shape should resemble a crescent. Blood supply is carried out through the splenic artery, which has an elastic internal membrane.
Structure of the spleen:
- Serous membrane;
- Fibrous membrane;
- Septa, trabeculae;
- Musculoskeletal apparatus;
- White and red pulp;
- Reticular fibers;
- Vessels and nerves.
The ratio of components changes with age. Thus, the amount of red pulp decreases with age, and the amount of white pulp increases. The white pulp consists of the penumbra arteriosus and the lymph nodes of the follicles. The components of the red pulp are the splenic cords and venous sinuses. Two main features can be distinguished. In the walls of the vessels there are lymphoid sheaths, formed around the pulp arteries, lymphoid nodules around the central arteries, couplings on the walls of the brush arterioles, thus controlling the filling of the spleen with blood. The second feature is the presence of open blood circulation.
Methods for diagnosing spleen diseases
The choice of diagnostic methods depends on how the spleen disease manifests itself and progresses:
- Collection of data from a sick person. When collecting anamnesis, the doctor takes into account past acute and chronic infections that could lead to an enlargement and hardening of the organ, for example, relapsing fever, malaria (acute, chronic), syphilis. Pathologies of the cardiovascular system are taken into account (endocarditis, which provokes repeated infarctions in the spleen, portal vein thrombosis, which causes stagnation). In addition, liver diseases (eg cirrhosis), inflamed gallbladder and disorders of the hematopoietic apparatus (erythremia, leukemia, hemolytic jaundice) play a role;
- Visual inspection. There is a need for this event only with a significant increase in volume, when the left half of the chest and abdominal wall protrudes;
- Palpation. If the edge can be felt, it is considered enlarged. But this is also possible with prolapse of the diaphragm caused by the accumulation of fluid in the pleural cavity, enteroptosis. This can also be observed in women of asthenic physique;
- Radiography. The contours of the organ become clearly visible only when there is a significant accumulation of gases in the large intestine and stomach. So before the procedure, oxygen is injected into the perinephric tissue or abdominal cavity. The procedure allows you to distinguish a tumor of the spleen from a similar phenomenon in the stomach, kidney, adrenal gland;
- Puncture. The study is carried out in case of emergency, as it is associated with a high risk of capsule rupture and bleeding. The obtained material allows us to determine the nature of changes and functions of the organ
- Blood test. In this case, the osmotic resistance of red blood cells is determined. For example, if it is reduced, diseases associated with hemolytic function occur (hemolytic jaundice);
- Functional diagnostic options allow you to assess the contractility of the organ.
What does the spleen look like and where is it located?
Everyone needs to know where the spleen is located in a person in order to pay attention to alarming symptoms and not confuse problems in this organ with the functioning of the digestive system.
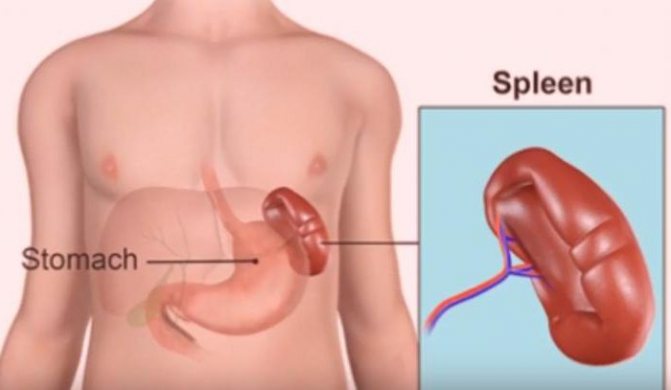
This organ is located on the left side of the abdominal cavity, slightly behind the stomach and just below the diaphragm. The close proximity to the stomach sometimes inhibits the recognition of symptoms of spleen diseases - a person believes that he simply overate or has indigestion.
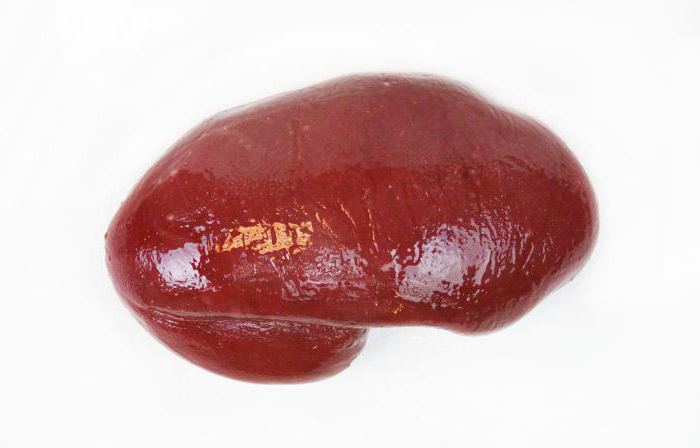
In appearance, it looks like a slightly flattened oval, purple or dark purple in color. A healthy spleen in size does not exceed 12 centimeters and 150 grams in weight: if the mass of this organ is significantly higher and the size is increased, we are talking about pathological processes, as a result of which the spleen is enlarged. The photos located in this section will allow you to see what this organ looks like and where it is located.

Treatment of spleen diseases
Treatment in each case is selected individually, but according to a single principle. First of all, therapy should be aimed at combating the disease that caused signs of problems with the spleen. Usually a course of medication is sufficient. Antibiotics are often used to treat spleen diseases. But do not forget that you can take any medications only as prescribed by a specialist.
Experts try to resort to removing the spleen only in extreme cases, when medications, physiotherapeutic procedures, and alternative treatment methods have proven powerless.
Treatment methods for spleen diseases
Spleen diseases need to be treated comprehensively. Self-medication is prohibited even in the early stages. Only a doctor has the right to prescribe the necessary medications or other methods of therapy. Lack of adequate therapy will lead to dangerous complications. Medicines are selected individually, based on the type of disease and the characteristics of the patient’s body.
Medicines
A heart attack needs to be treated with medications and diet; for severe pain, a strong painkiller is used. Large abscesses cannot be cured with medications and usually require surgery (splenectomy) followed by medication. For small ones, antibiotics are prescribed. For cancer, radiation therapy is prescribed. Radiation treatment is used before and after surgery. In addition to radiation treatment, diet and medications are indicated. Fibrosis is often treated with homeopathy.
When the location of the spleen in a congenital anomaly is a hernia, the hernia is removed along with the organ in infancy, since the spleen is not a vital organ, and the hernia brings a lot of inconvenience. The doctor treats inflammation with antibacterial drugs, which also relieves pain, prescribes allergy medications and B vitamins. Hematological diseases are treated with mandatory splenectomy with further drug therapy. Gas in the splenic flexure of the colon (the bend of the intestine near the organ) causes pain and must be relieved. Gas in the bend is treated depending on the provocateur. In case of dysfunction caused by an impact, surgery is most often indicated.
Folk remedies
Before using folk remedies, you should definitely contact a specialist. If organ function is impaired, healers recommend using the following components:
- honey;
- hop cones;
- sequence;
- violet;
- nettle;
- chamomile;
- St. John's wort;
- celandine, etc.
Traditional medicine recipes for the treatment of spleen diseases
Most often, the spleen is affected by such ailments as neoplasms, inflammation and enlargement of the organ. There are many folk remedies for healing the organ at home. Let's look at the most effective and simplest ingredients and application.
- Pour a tablespoon of St. John's wort into a glass of boiling water and leave, covered, for 30 minutes. Next, strain the broth and dilute with another glass of boiled water at room temperature. We take the decoction 2 – 3 times a day. It is not recommended to store such a decoction for more than two days;
- The spleen, which has undergone any infection, can be easily cured with the help of propolis. It is necessary to dissolve 30 - 40 drops of propolis in a quarter glass of cool water. Take the medicine one teaspoon 4 times a day half an hour before meals. Treatment is carried out within a month. If the spleen is severely infected, then the infusion should be taken every three hours for 10 days;
- Wormwood perfectly relieves inflammation. A bunch of wormwood is soaked in water for a day. Then the infusion is simmered over low heat for about 30 minutes. Add 400 g of honey to the strained broth. After the broth thickens, it can be used 4 times a day, 2 tablespoons before meals;
- Tea with chicory. Brew a spoonful of chicory like ordinary tea. After the drink has infused, you can drink it twice a day, half a glass before meals;
- Chaga is a tree fungus that usually grows on birch trees. It is poured with water at room temperature at a ratio of 1:5 and infused in a cool, dark place for two days. The infusion is taken one tablespoon before meals;
- For spleen tumors, you can take powder from crushed herbs: nettle and sage. The powder is consumed after meals;
- Hop cones are infused with vodka at a ratio of 4:1. It is recommended to use the infusion 30 drops before meals. The infusion helps if you feel pain or inflammation in the spleen area. You can make a decoction of the cones and consume 2 tablespoons before meals;
- Calendula and yarrow. Herbal flowers are mixed in equal proportions and brewed with boiling water. You need to drink 100 g of the decoction after meals. This remedy helps with an inflamed or enlarged spleen;
- Oak bark and soapwort grass. Pour 20 g of one and the other ingredient with water in an amount of 1 liter and boil for 20 minutes. Then leave for 1 - 1.5 hours. The decoction should be consumed 200 g 3 times a day;
- White cabbage juice. The juice is slightly warmed before use. Cabbage juice should be taken before meals, half a glass 3 times a day;
- You can use motherwort. The infusion is prepared from 1 tablespoon of herb and a glass of boiling water. The herb is infused for 1 - 1.5 hours and consumed a tablespoon before meals;
- Radish, beets, carrots. Vegetables are grated and the juice is squeezed out. Next, the juice is poured into a dark container and in the oven at low temperature, infused for 3 hours. Drink 3 glasses of juice per day. This recipe is good for improving blood processing by the spleen;
- Pomegranate juice should be drunk for a long time twice a day;
- Pea porridge helps. Soak the washed peas overnight. Then pour it 3 cm above the level of the peas and boil without adding salt. Eat porridge in the morning and evening, 3 hours before bedtime. Pea porridge will help with the formation of benign tumors on the spleen;
- Grind the leaves of strawberry, violet, jasmine, string and nettle and pour boiling water over it. Leave for an hour. Drink at least 3 glasses a day. This collection also helps well with neoplasms;
- The crushed shepherd's purse herb is poured with boiling water and left for 30 minutes. The strained mixture is consumed in a spoonful at least five times a day;
- A handful of raisins are steeped in grape vinegar for about 8-9 hours. For 50 g of raisins, 200 g of vinegar is enough. In the morning you need to eat 20 g of raisins and a spoonful of vinegar from the infusion. The tincture helps with an enlarged spleen;
- Dried rose hips are poured with boiling water, infused like tea, and taken instead of tea after meals;
- Yellow cucumber. Remove the seeds from an overripe cucumber, dry them and grind them into powder. It is useful for treatment to take 15 g of powder three times a day. Treatment must be carried out within 2 weeks;
- An ointment can be prepared from crushed ginger, honey and ghee to help with enlarged organs. The ointment is applied to the skin at the location of the organ. The spleen should be treated for 50 days, and the ointment should be stored at normal temperature.
Pathologies of the spleen
Under normal conditions, the weight of the spleen is 150–200 grams, size – 4x7x11 cm. The organ is located parallel to the 10th rib, in the upper abdomen, on the left. When breathing, the spleen does not extend beyond the costal arches, so the patient does not feel it. If it is felt, then this indicates the presence of splenomegaly. This pathology can be caused by tumors, metabolic disorders, and infections.
The most important function of the spleen is phagocytosis. Phagocytes neutralize old red blood cells, microorganisms, and other cells. That is, they filter the blood.
Breathing exercises for diseases of the spleen
For almost all diseases of the spleen, patients are recommended to rest, therefore, unfortunately, a treatment method such as exercise therapy is not used. But there are several breathing exercises that alleviate the condition and promote faster recovery.
Exercise 1. Starting position - lying on your back, legs bent at the knees, hands under your head. Breathe so that the abdominal wall moves (this breathing is called diaphragmatic breathing), gradually accelerating the rhythm of inhalation and exhalation. Make 10–20 breathing movements until you feel dizzy.
Exercise 2. Starting position – the same. Inhale deeply, and then exhale the air in small portions, pronouncing the syllable “cha” and trying to make the abdominal wall move sharply with each exhalation. For each inhalation there should be 3-4 exhalations. Repeat the exercise 3–8 times.
Exercise 3. Starting position – the same. Inhale, drawing in your stomach, exhale freely. Then inhale, sticking out your stomach, exhale freely. Take 6-12 breaths, alternately drawing in and protruding your stomach.
Exercise 4. The starting position is the same, but the exercise can also be performed standing, placing your hands with your palms on your stomach. Inhale quickly through your nose and mouth at the same time, protruding your stomach. Take a few breaths and then one calm exhale. Start the exercise with 6-10 breaths, gradually increasing their number to 40.
Exercise 5. Starting position – the same. Inhale while making a yawning movement without opening your mouth. After inhaling, hold your breath for 3 seconds, then exhale freely. Repeat the exercise 10–15 times.
Exercise 6. The starting position is the same, only the hands rest on the hips. Take a deep breath, sticking out your stomach, then bring your hand to your mouth and slowly exhale into your palm, pursing your lips into a tube. Take the next breath, drawing in your stomach, and exhale in the same way, changing your hand. Repeat the exercise 6-10 times.
Splenic infarction
Palpation of the spleen
Splenic infarction is a very dangerous disease that can occur without any obvious symptoms. Splenic infarction can occur suddenly, but in most cases it is preceded by severe illnesses that impair the functioning of many organs. That is why a large load falls on the spleen, and sometimes the organ simply cannot cope with it. The main symptoms of splenic infarction include:
- Pain in the upper left abdomen. Usually it appears suddenly, and the person cannot even move. But since each person has a different pain threshold, some patients simply report severe pain
- Fever
- Chills
- Nausea and sometimes vomiting, which appear due to severe pain
- Painful sensations in the chest that can radiate to the left shoulder
- Breathing problems. When inhaling, a person feels severe pain, and because of this he cannot breathe normally.
- Abdominal muscles are very tense
Read: What does impedance testing have to do with digestion?
Sometimes a splenic infarction can be completely asymptomatic. This suggests that the damage is not significant and surgery is not required.
Diet for diseases of the spleen
- Walnuts and other nuts. They contain essential minerals and trace elements;
- Cabbage. The presence of vitamin B9 promotes the creation of new blood cells, vitamin P gives elasticity to blood vessels, vitamin K improves blood clotting;
- Beef liver. It contains little cholesterol and is considered a source of easily digestible iron. It is necessary for the synthesis of hemoglobin in red blood cells. Heparin will prevent thrombosis and myocardial infarction;
- Sea and river fish. Fatty acids and taurine in the composition normalize blood pressure;
- Oranges and lemons. All sources of vitamin C help transport iron and calcium. Vitamin A and natural acids reduce sugar levels and prevent the formation of cholesterol plaques;
- Apples. It is better to consume it baked, since in this form pectin more effectively removes toxins and regulates blood sugar;
- Beet. Natural remedy for treating anemia. The active effect appears with the consumption of carrots, tomatoes or cabbage;
- Avocado. Binds and removes excess cholesterol;
- Honey. Normalizes the functioning of the organ, stimulating the production of blood cells;
- Pomegranate. Improves the hematopoietic capacity of the organ.
During the treatment period, it is better to avoid the following foods:
- Fatty foods. Excess lipids neutralize the calcium needed to create new red blood cells.
- Fried food. The carcinogens contained in it change the blood composition. This causes additional stress on the spleen, which tries to get rid of foreign cells.
- Alcoholic drinks. Their consumption leads to dehydration and inhibition of organ function.
- Preservatives. They form insoluble compounds that block the spleen channels.
To restore the original functions of organs, it is better to try to avoid nervous overload and calmly react to stressful situations. You need to eat regularly in small portions. The diet should be varied, nutritious and include foods high in iron. Divide meals into 4-5 times a day.