Poor nutrition and consumption of rough foods that irritate the mucous membranes can lead to inflammation not only in the stomach. The esophageal mucosa is often also affected. If inflammation is accompanied by swelling and hyperemia, catarrhal esophagitis develops. This disease is quite common, but not all patients consult a doctor about this. If the pathology accompanies other gastrointestinal diseases, patients themselves know how to treat it. Moreover, in most cases the disease goes away on its own within a couple of days. But sometimes, without treatment, inflammation can become chronic or lead to the development of complications.
general characteristics
Esophagitis is the general name for all pathologies accompanied by inflammation of the esophageal mucosa. The disease is acute if inflammation occurs due to short-term exposure to aggressive environmental factors. However, it usually lasts from several days to a couple of weeks. If such exposure is constant, chronic esophagitis occurs, in some cases lasting for many years with periodic exacerbations. This occurs when stomach contents constantly enter the esophagus due to pathologies of the esophageal sphincter. In this case, the mucous membrane of the esophagus becomes inflamed, and erosions, hemorrhages, or areas of tissue necrosis may form on it.
The mildest course of the disease is catarrhal superficial esophagitis. It is accompanied only by redness of the mucous membrane due to irritation by aggressive food, as well as slight swelling. The entire surface of the esophagus can become inflamed, but most often the disease affects its distal parts adjacent to the stomach.
This disease is quite common, it is believed that it occurs in every second person. But there are no exact statistical data on this, since patients rarely go to the doctor. After all, it is the catarrhal form of esophagitis that is most often secondary, appearing in other gastrointestinal pathologies. Therefore, doctors can attribute such inflammation to their symptoms, and not to a separate disease.
In this case, terminal esophagitis develops - inflammation of the mucous membrane of the lower esophagus. Most often it is a concomitant pathology with GERD - gastroesophageal reflux disease. The constant entry of stomach contents into the esophagus leads to irritation. At first, the inflammatory process does not develop, but without treatment, inflammation of the mucous membrane occurs over time. As a result of a chronic inflammatory process, the cells of the esophageal mucosa degenerate, which can result in the appearance of a malignant tumor.
Types, degrees
Distal esophagitis can be characterized by morphological damage to the esophageal mucosa of varying severity. According to this criterion, the following types of illness are distinguished:
Rare types of the disease include dysmetabolic and granulomatous esophagitis.
THIS IS REALLY IMPORTANT! Cheap product No. 1 for the stomach and esophagus. FIND OUT >>
More often, distal reflux esophagitis develops with repeated cycles of cardia insufficiency and appears against the background of exposure to acidic contents from the stomach on the esophagus. According to the nature of the lesions, this disease can be:
- superficial, non-erosive;
- ulcerative with foci of necrosis throughout the entire thickness of the mucosa;
- with damage to the submucosal layers to deep defects, causing thinning of tissues and perforation of the esophageal wall with bleeding.
According to the severity of morphological changes, distal reflux esophagitis develops with the following degrees of severity:
- 1st degree - mild focal redness of the mucous membrane. The structure of the mucosa at the junction with the stomach is loose, with smoothed folds.
- 2nd - single or multiple erosions of an elongated shape with the possible formation of exudate. Wounds appear predominantly in the folds of the mucosa and affect no more than 10% of the entire distal esophagus.
- 3rd - numerous merged erosions, covered with exudate and necrotic tissue. The affected area is more than 50%.
- 4th - merged erosions are located in a circle, severe exudative-necrotic damage is noted. Severe fibrinous lesion covers the entire area 5 cm above the cardia.
Causes
There are many causes of catarrhal esophagitis. Most often, acute inflammation occurs under the influence of aggressive external factors. This may be accidental or intentional ingestion of acids, alkalis, or iodine. Irritation of the mucous membrane also results from the consumption of alcoholic beverages, very hot or cold foods, spicy foods, marinades or strong coffee. Inflammation can also occur due to mechanical irritation of the esophagus by too hard dry food during diagnostic procedures.
The cause of inflammation can also be infection in the esophagus. This could be stomatitis, scarlet fever, diphtheria, influenza. Catarrhal esophagitis often occurs in patients with immunodeficiency, after radiation exposure, organ transplantation, or treatment with cytostatics.
A separate group includes distal catarrhal esophagitis - inflammation of the esophageal mucosa in the lower part, near the stomach. In this case, the pathology is caused by various gastrointestinal diseases, which lead to the reflux of gastric juice into the esophagus. Since gastric juice has high acidity, and the esophagus is always alkaline, inflammation develops because of this.
The reason for this may be disturbances in the functioning of the cardia - the lower esophageal sphincter. It does not close completely, and the contents of the stomach are thrown into the esophagus. This can happen due to overeating, stomach tumors, gastroduodenitis. The opening of the sphincter can provoke an increase in pressure in the abdominal cavity due to wearing tight clothing, during pregnancy, obesity, and physical activity on a full stomach.
Inflammation of the esophageal mucosa can be caused by eating very hot, fatty and spicy foods.
With the constant reflux of stomach contents into the esophagus, reflux develops - chronic inflammation of its mucosa. This pathology is familiar to many patients suffering from gastritis with high acidity or after gastric surgery. The prolonged presence of acidic gastric juice in the esophagus can lead to the formation of ulcers and erosions on the mucous membrane. In this case, catarrhal-erosive esophagitis develops, which is characterized by a severe course and frequent development of complications.
Diet for catarrhal reflux esophagitis: sample menu
The basis for the treatment of acute and chronic catarrhal reflux esophagitis is diet therapy. The diet for catarrhal esophagitis is based on the following principles and rules:
- The frequency of meals should be 5-6 times a day. You should eat every 3-4 hours.
- You can only eat freshly prepared food.
- It is strictly forbidden to drink food with water or other liquid.
- You should avoid eating foods that stimulate the production of gastric juice - chocolate, coffee, fatty broths, cabbage, fresh fruit and tea.
- It is necessary to stop drinking alcohol and smoking.
- Meals should not be eaten later than two hours before bedtime.
Almost all patients with the development of this disorder of the digestive system are prescribed dietary table No. 1 for the duration of treatment. A diet for catarrhal reflux esophagitis can be based on the following foods and dishes:
- mashed potatoes;
- green soft vegetables;
- bananas, applesauce;
- liquid porridges from white and brown rice, oatmeal, buckwheat, semolina, pearl barley;
- egg whites;
- lean meat, chicken;
- soups, broths;
- water, weak tea.
Approximately the diet menu has the following option:

Breakfast: a glass of green or weak black tea or kefir, porridge with fruit.

Lunch: vegetable broth, fish or chicken breast baked with vegetables, vegetable salad.

Afternoon snack: baked apple, low-fat cottage cheese with sour cream.

Dinner: mashed potatoes or cauliflower, steamed cutlet, baked vegetables.

Second dinner: banana, glass of kefir or warm milk.
Symptoms
In most cases, inflammation is accompanied by slight discomfort, which occurs mainly after eating. The intensity of the symptoms of esophagitis depends on the cause of the mucosal lesion and its severity. In mild cases, a slight burning sensation behind the sternum and heartburn occurs. High intensity of sensations appears when exposed to aggressive factors, for example, a burn of the esophageal mucosa or its mechanical damage.
As the inflammatory process develops, the discomfort becomes more intense. Other signs of esophagitis may also include:
Causes of pain in the esophagus
- difficulty swallowing, scratching sensation in the throat;
- dull or sharp pain while eating;
- severe belching, heartburn;
- increased salivation;
- regurgitation of mucus;
- frequent nausea;
- burning behind the sternum.
In the most severe cases, pain can radiate to the neck, jaw, or under the shoulder blade. In the distal form of the disease associated with reflux esophagitis, heartburn, stomach pain, frequent nausea and vomiting also occur. If the pathology develops in a child, he will experience increased salivation, frequent regurgitation, and vomiting.
Distal catarrhal reflux esophagitis with cardia failure
Insufficiency of the gastric cardia is a disruption of the entrance sphincter. With the development of such a pathological process, reflux occurs, which is considered by gastroenterologists as a complication of cardia failure.
In a healthy stomach, the cardia allows food into the gastric cavity with minimal pressure. In order for food to pass in the right direction, the pressure should not exceed 3.5 mmHg. When reflux esophagitis occurs, the pressure increases 20 times. Such a high level is formed as a result of fermentation and overeating.
Cardia failure in catarrhal esophagitis occurs in the presence of the following factors:
- systematic overeating;
- being overweight;
- chronic form of gastritis;
- sedentary lifestyle;
- eating before bed.
Catarrhal reflux esophagitis with cardia insufficiency has the following manifestations:
- burning pain in the esophagus;
- constant heartburn;
- belching with the smell of stomach contents;
- frequent vomiting.
Catarrhal reflux esophagitis due to cardia insufficiency can be treated with a balanced diet. In this case, it means following a diet and small portions. You should not rush while eating, and after a meal it is not recommended to lie down for an hour; it is better to sit or walk. With this diagnosis, the diet should consist of liquid porridges and low-fat soups.
Therapy for distal catarrhal reflux esophagitis with cardia insufficiency is based on the following principles:
- first of all, measures are taken aimed at curing the underlying disease that caused the development of cardia failure;
- if you are overweight, you should get rid of it;
- with ascites it is important to reduce intra-abdominal pressure;
- strict adherence to the diet prescribed by a specialist.
Diagnostics
If the discomfort does not go away and the intensity of pain increases, you should consult a doctor. Without treatment, catarrhal esophagitis can lead to degeneration of mucosal cells, necrosis and cancer. Therefore, consultation with a gastroenterologist is very important. But it is difficult to diagnose “catarrhal esophagitis” based on symptoms alone. The doctor collects anamnesis, talks with the patient about the causes of discomfort, and finds out what gastrointestinal diseases he has.
After this, he can diagnose esophagitis, but the condition of the esophageal mucosa can only be determined with the help of an instrumental examination. In this case, x-rays are ineffective, since they can only show the presence of edema, erosions or areas of necrosis. But it is definitely prescribed to exclude malignant tumors and stenosis of the esophagus.
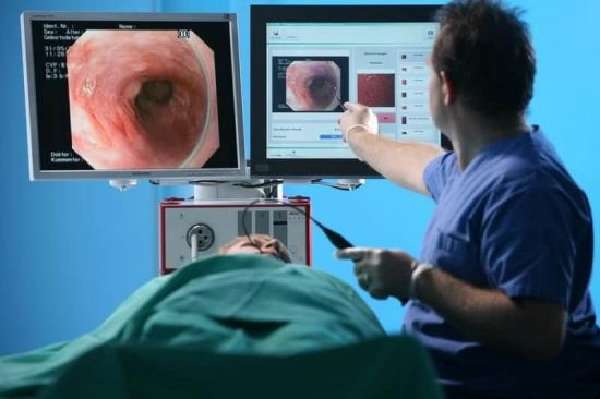
The condition of the esophageal mucosa can be assessed during esophagoscopy.
Basic information about the condition of the esophageal mucosa can be obtained by performing esophagoscopy. Probing reveals hyperemia and swelling. But it is recommended to carry out this examination after the acute stage of catarrhal esophagitis has subsided. After all, the endoscope can additionally injure the mucous membrane, which will aggravate the patient’s condition. Therefore, esophagoscopy is most often performed in the chronic form of the disease. In this case, a section of the mucous membrane is often taken for analysis to exclude malignant neoplasms.
In addition, when diagnosing pathology, intraesophageal pH-metry is performed. It allows you to detect the presence of gastroesophageal reflux. And esophageal manometry determines the insufficiency of the sphincter and motility of the esophagus.
Folk remedies
What is catarrhal duodenitis? Can it be cured using traditional medicine? Many people ask these questions. Non-traditional remedies can indeed speed up recovery, but they can only be used as an auxiliary therapy. Various decoctions that have an anti-inflammatory effect are often prescribed. So, for duodenitis, you can take infusions of chamomile or nettle. Decoctions of mint or centaury have an analgesic and calming effect. You can buy them at the pharmacy. In summer, you can collect and dry the plants yourself.

Treatment
In most cases, a mild form of the disease does not require special treatment, because after a few days the discomfort goes away on its own. But it is imperative to eliminate the influence of factors that provoke inflammation. First of all, a special diet is used for this, which consists of consuming foods that have a gentle effect on the mucous membrane. All of them must be pureed, spicy and fatty foods, hot and cold, salt and spices are excluded. You should not drink alcohol, coffee, chocolate, citrus fruits, or tomatoes. In the most severe cases, complete fasting is recommended for 2-3 days, sometimes they also switch to parenteral administration of nutrients.
In most cases, treatment of catarrhal esophagitis is limited to the use of medications to reduce inflammation and pain. They are prescribed taking into account the severity of symptoms and the cause of the pathology. You may have to switch to injecting medications so as not to irritate the mucous membrane. Surgical treatment is used very rarely, only in the presence of complications such as tumors or narrowing of the esophagus.
Treatment of esophagitis should be comprehensive, especially if it accompanies stomach diseases
It is imperative to treat the underlying disease that caused inflammation of the mucous membrane. For example, if an infection is present, antibiotics, antiviral or antifungal agents are prescribed. If the pathology occurs against the background of stomach diseases, it is necessary to adjust their treatment. It is important to reduce the harmful effects of gastric juice on the mucous membrane and prevent the occurrence of reflux. For this, medications alone are not enough. An integrated approach is very important: eliminating bad habits, proper nutrition, adequate physical activity.
Drug therapy
Medicines are not always prescribed. In mild cases, when discomfort occurs only after eating, you can limit yourself to following a special diet. But when the symptoms intensify, the burning sensation continues for a long time, the diet is supplemented with drug therapy.
Medicines are prescribed individually, depending on the cause and severity of the inflammatory process:
- Antacids effectively relieve heartburn. These are Rennie, Phosphalugel, Maalox, Almagel.
- To protect the mucous membrane from the aggressive effects of acids from the stomach, Solcoseryl, Actovegin, as well as magnesium and sodium alginates, for example, Gaviscon or Laminal, are prescribed.
- No-Shpu or Papaverine are used to relieve pain and spasms. They are often administered intramuscularly to protect the mucous membrane from their irritating effects. Sometimes local anesthetics are prescribed, for example, Novocain.
- To normalize esophageal motility, prokinetic drugs are also used: Reglan, Motilium, Cerucal.
- Gastroprotectors are prescribed to protect the mucous membrane and accelerate its recovery processes. These are bismuth-based products: De-Nol, Venter, Novobismol.
- If reflux is present, the stomach must also be treated. Medicines are taken to normalize stomach acidity. These are mainly antisecretory agents: Omeprazole, Lansoprazole, Famotidine.
Folk remedies
Additionally, you can alleviate your condition with folk remedies. There are many medicinal plants that have enveloping properties, protect the mucous membrane and promote its restoration. First of all, this is a decoction of flax seeds; it can be drunk warm, like jelly. Sea buckthorn oil, taken a teaspoon half an hour before meals, is also effective. Drinking carrot juice is also beneficial.
Medicinal herbs used to protect the mucous membranes include sage, plantain, marshmallow root, calendula, chamomile, and oak bark. It is also recommended to brew rowan or dogwood fruits as tea.
Prevention
It is quite possible to prevent the development of catarrhal reflux esophagitis by adhering to the rules of a healthy diet, avoiding harmful foods, eating in moderation, sparing and protecting the mucous membrane of the digestive organs from aggressive influences. Smoking and alcohol have a destructive effect on the entire human body. Therefore, it is better to try to get rid of them. Overeating and excess weight are risk factors for the development of the disease. They will also have to be eliminated.

In children, manifestations of the disease are very rare, but can be caused by an allergic reaction to certain substances or foods. Therefore, you need to carefully monitor and promptly eliminate the impact of allergens on the child’s body in order to avoid the occurrence of problems with the gastrointestinal tract.
It is very important to undergo timely medical examination and medical examination by specialists, including a gastroenterologist. Those working in hazardous working conditions, for example, in chemical production, are required to use personal and collective protective equipment: ventilation, aeration, irrigation, respirators, gas masks, medical nutrition. This will help prevent the impact of an aggressive production environment on the worker’s health and reduce the risk of occupational disease or poisoning.
We recommend: What is a sliding hiatal hernia and how to cure it?