- September 26, 2018
- Gastroenterology
- Smirnova Alexandra
Currently, gastrointestinal diseases have a strong upward trend. Most experts believe that the reason lies in constant stress, poor nutrition, and poor environmental conditions.
If you don’t pay attention to your own health and don’t follow the basic rules of a balanced diet, then a problem can develop in your body that you may not be aware of for a long time, and it will only manifest itself during a period of exacerbation. In this article we will try to understand what a disease such as atrophic hyperplastic gastritis is, what are the causes of its occurrence, what symptoms does it manifest, and also consider treatment methods.
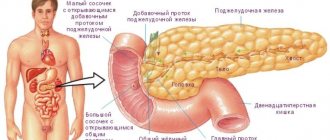
About hyperplastic gastritis
Doctors note a rather rare manifestation of this pathology compared to other gastrointestinal diseases. Hyperplastic gastritis accounts for about 5% of cases of the total number of chronic gastric diseases. A characteristic feature of this disease is excessive and rapid proliferation of epithelial tissues, resulting in the formation of rigid folds and polyps. Hyperplastic gastritis develops as a result of hyperplasia of the gastric epithelium.
Medicine knows that men are susceptible to pathology four times more often than women. When it develops in children, comprehensive and effective treatment allows for complete regression of the disease and restoration of the gastric mucosa. Hyperplastic gastritis in adults most often leads to mucosal atrophy.
Causes
Ordinary gastritis is an inflammation of the mucous membrane lining the stomach from the inside. In the hyperplastic form, a specific lesion of the gastric mucosa develops, in which epithelial cells grow, and the mass and volume of the membrane increases significantly.
In this case, folds, cysts and polyps are formed. These pathological growths can be located on individual parts of the organ or cover the entire internal surface.
The damaged mucous membrane cannot perform its functions normally, so digestion is disrupted. The disease most often develops in middle-aged men; women get sick several times less often.
Main types
Hyperplastic gastritis comes in several types:
- Atrophic hyperplastic gastritis. Characterized by the formation of many polyps on the gastric mucosa.
- Superficial hyperplastic gastritis. It is the mildest form of this disease. Only the upper layers of the gastric mucosa are exposed to pathological processes.
- Diffuse hyperplastic gastritis. Such a diagnosis occurs if multiple changes are present on the gastric mucosa that have different etymologies.
- Focal hyperplastic gastritis. This form of the disease is characterized by the development of a slowly growing benign tumor.
- Granular hyperplastic gastritis. A characteristic feature of this form of pathology is the presence of multiple semicircular growths. As a result of their appearance, the mucous membrane swells and becomes lumpy.
- Erosive-hyperplastic gastritis. It is characterized by the formation of erosive areas and nodular formations on the gastric mucosa. Hypertrophy of the folds cannot be ruled out.
- Chronic active atrophic hyperplastic gastritis. As a result of the chronic course of the pathology, thickening of the walls of the stomach occurs.
- Antral hyperplastic gastritis. This disease is characterized by decreased gastric motility. Changes in the structure of the gastric mucosa are observed.
Etiology and pathogenesis of the disease
The main reasons for the development of the disease are:
- chronic intoxication of the body, which is possible with alcoholism, drug addiction, lead poisoning and other harmful substances;
- eating disorders;
- smoking;
- drug intoxication;
- disruptions in the functioning of the nervous, endocrine and immune systems;
- complications due to viral diseases;
- hypovitaminosis.
The presence of food allergies is of great importance in the pathogenesis, since the influence of allergens on the mucous membrane of the organ increases its permeability, and as a result, epithelial dysplasia develops. This leads to large losses of protein, which is considered a characteristic symptom of almost all forms of hyperplastic gastritis.
Some forms of the disease are characterized by a family predisposition. Another factor that increases the risk of the disease is pathologies in the development of the stomach or the presence of a benign tumor.
Under the influence of any of these pathogenic conditions, gastric epithelial cells begin to multiply faster, and the mucous membrane thickens greatly.
Causes of pathology
Until now, doctors have not found out the specific reason as a result of which this stomach disease develops. Some experts are of the opinion that the etymology of atrophic hyperplastic gastritis is similar to the etymology of gastrointestinal diseases.
The following factors can provoke the development of hyperplastic gastritis:
- Poisoning with alcohol or chemicals.
- Chemical or thermal burn of the mucous membrane.
- Vitamin deficiency in the body.
- NS diseases.
- Hereditary predisposition.
- Abuse of smoking and alcoholic beverages.
- Metabolic disorders.
- Dysfunction of the endocrine system.
- Diseases of a viral nature, for example, hepatitis, influenza, typhoid.
- Chronic food allergies.
If several of these factors are present at once, the risk of developing atrophic hyperplastic gastritis increases significantly. Symptoms and treatment are often interrelated.
Methods for diagnosing granular gastritis
Granular gastritis is diagnosed using ultrasound, probing and fibrogastroscopy with biopsy. An ineffective diagnostic method is fibrogastroduodenoscopy (FGDS), since with such an examination the gastroenterologist-endoscopist can clearly see neoplasms on the mucous membrane of the stomach wall. FGDS shows the location of the “grains”, their size and quantity. During the procedure, a special tube with a video camera is used that films what is inside the stomach - a fibrogastroscope.
In addition to X-ray examinations and FGDS, diagnostic tests are also used to detect Helicobacter pylori bacteria. Modern research claims that these bacteria do not serve as causative agents of gastritis, but act as a factor predisposing to inflammation of the stomach. Moreover, the bacterium is easy to detect in the stomach secretions of healthy people. To examine the body for the presence of Helicobacter pylori, a stool test is used, which is then examined in the laboratory for antibodies. In addition to stool analysis, doctors use a breath test - a study of exhaled air after the patient has taken a special drug. Thus, these studies can detect the presence of Helicobacter pylori. If the test result is positive, in the treatment of granular gastritis, among other things, antibacterial treatment is used, aimed at creating an unfavorable environment for the life and reproduction of bacteria.
In addition to all of the above, esophagofibrogastroduodenoscopy is used to diagnose granular gastritis; during the study, gastric secretions are collected for bacteriological examination. If necessary, during EGD, the doctor collects tissue material from the growths for subsequent histological examination. If probing is contraindicated for the patient, an acid test is used to determine the acid level. This is a urine test for acidity levels. The patient first takes a specialized drug.
Symptoms
Most often, the initial stage of the disease is asymptomatic. Moreover, any signs may be absent for quite a long time. The development of the pathological process is characterized by the manifestation of the following symptoms:
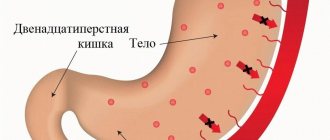
- Pain in the epigastric region.
- Belching and heartburn.
- Bloating. The symptoms of atrophic hyperplastic gastritis are similar to those of other types of disease, but there are still some differences.
- Rapid weight loss despite the fact that the diet remains the same.
- Drowsiness.
- General malaise.
- Digestive disorders.
- Change in stool color.
- Nausea.
- The occurrence of a feeling of overeating with a small amount of food eaten.
If any suspicious signs appear, you should be wary and consult a doctor. This will facilitate timely detection of the disease and, as a result, more productive treatment.
How to identify chronic hyperplastic atrophic gastritis? More on this below.
Symptoms
In the first stages of the development of the disease, hyperplastic atrophic gastritis occurs almost unnoticed by the patient; obvious signs arise when changes in the composition of the epithelium are significant. As the pathological process progresses, the following signs appear:
- feeling of heaviness, fullness after eating even a small portion of food;
- increased gas formation, flatulence;
- belching;
- heartburn;
- aching pain that occurs after the patient eats something.
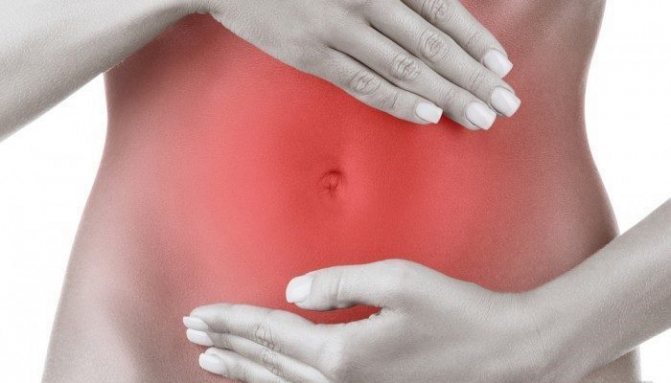
It must be said that the first manifestations of hyperplastic gastritis do not differ from the signs of other stomach diseases. Therefore, it is impossible to make a diagnosis based on an assessment of complaints.
You need to see a gastroenterologist and be sure to undergo a series of examinations. If the disease is not detected in the early stages, the pathology will progress. The following symptoms will gradually begin to appear:
- mild, but almost constant pain that can radiate to the back;
Advice! When the polyp is detached from the mucous membrane, acute cutting pain appears.
- Due to the growth of the mucous membrane, the volume of the stomach decreases, so patients note that a feeling of fullness occurs much faster. Often, after eating even a small amount of food, there is a feeling that there is a “brick in the stomach”;
- there is a decrease in appetite and, accordingly, a decrease in body weight;

- the tongue becomes covered with a white and rather dense coating;
- Nausea often occurs, sometimes vomiting occurs after eating;
- stool upset occurs, diarrhea often occurs, which can alternate with constipation;
- weakness and tachycardia often occur.
Diagnosis of pathology
If problems related to the stomach occur, you should contact a specialist such as a gastroenterologist. In order to establish the reasons that resulted in disruption of the gastrointestinal tract, the following clinical studies are carried out:
- Helicobacter test;
- biochemical examination of stool, blood and urine;
- Ultrasound of the abdominal organs;
- intragastric pH-metry;
- X-ray of the stomach;
- endoscopic biopsy;
- esophagogastroduodenoscopy.
Having the results of these studies, the specialist is able to clarify the diagnosis and prescribe adequate therapy, taking into account all the nuances.
Forecast
The prognosis depends on the form of pathology and the degree of hyperplasia. The chances that pathological changes in the mucous membrane will fully recover are not very high; more often than not, this disease requires lifelong observation and treatment. When polyps form on hypertrophied folds of the gastric mucosa, the prognosis worsens due to the increasing risk of malignancy.
List of references: https://www.obozrevatel.com/health/bolezni/giperplasticheskij-gastrit.htm https://www.krasotaimedicina.ru/diseases/zabolevanija_gastroenterologia/hyperplastic-gastritis https://36on.ru/health/recipes /54402-kak-lechit-giperplasticheskiy-gastrit-narodnymi-sredstvami https://womanadvice.ru/giperplasticheskiy-gastrit https://ilive.com.ua/health/giperplasticheskiy-gastrit-simptomy-lechenie-dieta-prognoz_123875i15938.html Notes from the author of the article, based on personal experience. This material is purely subjective and is not a guide to action. Only a qualified specialist can determine an accurate diagnosis and prescribe treatment.
Last modified: 03/17/2020
Treatment
Due to the fact that the etymology of the disease is not fully understood, with the development of atrophic hyperplastic gastritis, complex therapy should be carried out, which takes into account the manifested symptoms.
Taking into account the form of the disease and its course, the gastroenterologist develops a special drug therapy regimen. Most often, in the treatment of this pathology, drugs belonging to the following pharmacological groups are used:
- Anti-inflammatory drugs, for example, Ranitidine.
- Antibacterial agents, which include Clarithromycin.
- Antispasmodic drugs: Buscopan or No-shpa.
- Enzymatic preparations. Allows you to significantly improve digestion. The most commonly used are Pepsin or Mezim.
- Proton pump inhibitors, for example, Omez.
- Antacids. The most commonly used drug is Gaviscon.
- Medicines that help normalize digestion, for example, Motilium.
- Products that have an enveloping effect, for example, Almagel or Phosphalugel.
- In advanced cases, hormonal drugs can be used to treat atrophic hyperplastic gastritis of the stomach.
The rapidly developing disease provokes the rapid proliferation of cells that transform into polyps. Treatment in this case does not exclude the possibility of surgical intervention.
Chronic inactive gastritis with foveal hyperplasia
In medicine, the term “gastric hyperplasia” refers to a pathological process characterized by an increase in the number of cells of the digestive organ. Its mucous membrane thickens, and over time, polyps form on it. There are several forms of the disease. One of the most common is follicular hyperplasia of the gastric mucosa. The disease is based on cell division, which is normally necessary.
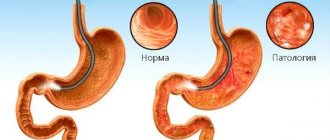
But under the influence of various unfavorable factors, an abnormal process of proliferation of epithelial tissue of the digestive system organ is started. During diagnostic procedures, the doctor has the opportunity to visualize areas of the mucous membrane covered with curvatures. The folds of the organ become deformed and their length increases. In addition, the gastric pits also undergo external changes. As a rule, at the initial stage, deformities and growths are discovered randomly during an endoscopic examination prescribed for another reason.
- In order to destroy pathogens, doctors prescribe the following medications: Antibiotics (for example, Tetracycline, Amoxicillin, Levofloxacin). Drugs that reduce the degree of acid production in the stomach (Omez, Pantoprazole). Products whose active ingredient is bismuth (“De-Nol”, “Ulkavis”)
- The specialist prescribes medications and calculates their dosage individually, based on the results of all studies. In almost all cases, the development of the pathological process is accompanied by the formation of various types of growths. First of all, the doctor must determine whether polyps in the stomach are dangerous. If oncology is excluded and the formations are small, treatment is not required. It is only necessary to periodically undergo FGDS to monitor the course of the disease.
- If the growths increase in size, the doctor decides on the advisability of surgical intervention . If conservative methods of therapy are ineffective, deformed tissues with obvious signs of hyperplasia are removed. It can be carried out in several ways: In the first case, the procedure is minimally invasive.
The doctor, through several incisions in the abdominal cavity, inserts endoscopic instruments into the body and removes pathologically altered tissue. The open method is carried out in the classical way. The doctor uses a scalpel to cut through soft tissue. Having gained access, he removes either the deformed areas or part of the organ, leaving behind a stump of the stomach. After an open operation, the patient needs special care. This is due to the fact that after surgical intervention in this way there is always a risk of developing an inflammatory process in the stomach or suppuration of the sutures.
Nutritional Features
There is no special diet for such a disease, however, taking into account its type and course, the attending physician will be able to advise the appropriate diet. If there is increased gastric secretion, then you should adhere to diet No. 1, if reduced, then No. 2. During periods of exacerbation of the disease, it is recommended to follow diet No. 16.
In addition, there are general recommendations:
- You should eat in small portions.
- Fruits and vegetables must be subject to preliminary heat treatment.
- Dishes should not be too cold or hot.
- When cooking, steaming should be preferred.
- You need to eat slowly, chewing your food thoroughly.
Smoked products, pickles, carbonated drinks, too spicy and fatty foods, all baked goods, as well as food prepared by frying should be completely excluded from the diet. It will not be possible to cope with stomach pathology without following an appropriate diet. What other methods are used to treat atrophic hyperplastic gastritis?
Symptomatic manifestations
At first, the disease does not manifest itself in any way, but as it develops, symptoms appear, which largely depend on the level of acidity of the gastric juice:
- Pain in the stomach - it occurs mainly in a state of hunger or 2-3 hours after eating.
- Abnormal bowel movements, diarrhea alternating with constipation.
- Nausea, frequent vomiting, belching, heartburn.
- Bad breath.
- Decrease in body weight, appetite, feeling of rapid satiety.
Hyperplastic gastritis can manifest itself in different ways. Often periods of exacerbation are alternated by a complete lull in symptoms, but this does not mean that recovery has occurred. Chronic hyperplastic gastritis is more often diagnosed. Therefore, if you have at least one suspicious sign, you should seek help from a doctor and identify the disease at an early stage.
Treatment with traditional methods
Traditional medicine also has means to treat the disease. Most often, herbal therapy is assumed. It is recommended to take decoctions of the following plants:
- Blooming Sally.
- Loosestrife.
- Roots of Lyubka bifolia.
- The plantain is big.
- Thyme.
- Calendula officinalis.
- Pharmaceutical camomile.
The roots, flowers or leaves of plants must be brewed as follows: one spoon of the mixture is poured with two hundred milliliters of boiling water and left for 20 minutes. It is better to take infusions before meals, about twenty minutes.
Folk remedies
Traditional medicine in the treatment of hyperplastic gastritis is effective in combination with complex therapy, consisting of taking medications and following a special diet. The most effective means:
- St. John's wort tincture for internal use. Add 2 tbsp per liter of boiling water. Spoons of herbs and incubate for 30–40 minutes. The resulting solution is taken orally in a glass before meals on an empty stomach;
- Preparation of burdock tincture in a ratio of 1 tbsp. Spoon for 500 ml of boiling water. The resulting product is drunk on an empty stomach, 250 ml twice a day;
- Consuming 8 grams of natural propolis daily in the morning on an empty stomach;
- Restoration of the stomach by taking 30 ml of sea buckthorn oil daily on an empty stomach in the morning. Duration of treatment is 25–30 days;

- Drinking a drink made from natural chicory root. This product increases secrecy and reduces acidity. The roasted root is crushed and then brewed in boiling water. The resulting tincture with honey (1 tablespoon) and lemon is taken once a day in the morning on an empty stomach;
- Calendula tincture with honey and lemon. The brewed herb is kept for several hours, and honey and lemon juice are added to the resulting product. Take 120 ml daily on an empty stomach before eating.
Recommendations
Traditional medicine helps restore the mucous membrane, improve appetite, relieve inflammation and normalize the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract. However, it is important to remember that you should not self-medicate, and folk remedies can only be used with the permission of the attending physician and only as part of complex therapy. That is, traditional medicine cannot be used as the only treatment for this pathology. We reviewed the symptoms and treatment of atrophic hyperplastic gastritis.
Characteristic signs
Symptoms of hyperplastic gastritis may vary depending on the type of disease. Nevertheless, for all types of stomach inflammation, the initial manifestations are very similar; patients complain of a feeling of heaviness in the epigastric region. For a long period of time, the pathological process is asymptomatic.
What pain occurs with gastritis of the stomach?
As the disease progresses, the following complaints from patients appear: nausea, heartburn, severe pain in the abdominal area, aching pain can radiate to the area of the shoulder blades, lower back, chest, bloating, heaviness after eating.
There is a feeling of fullness in the stomach, vomiting of food debris, belching with an unpleasant odor, coating on the tongue, general malaise: weakness, increased fatigue, slight increase in temperature. With erosive changes in the mucous membrane, pain may intensify when walking and bending the body. In the autumn and spring, exacerbations occur.
Blood may be present in vomit and feces. Some patients note a decrease in appetite and weight loss.

Patients complain of heaviness and pain in the epigastrium
Possible complications of the disease
Lack of timely treatment can provoke the development of some complications. These include:
- Stomach carcinoma.
- Cancer tumor.
- Ulcer development.
- Reduced whey protein.
- Decline of digestive functions as a result of damage and a decrease in the number of parietal cells.
- Gastrointestinal motility disorder.
- Fast weight loss.
- Development of anemia.
- Varying degrees of mucosal atrophy.
- Damage to the mucous membrane.
When the first unpleasant symptoms of antral atrophic hyperplastic gastritis with symptoms of exacerbation appear, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Diagnostics
The examination begins with a consultation with a gastroenterologist. The final diagnosis can be made after the conclusion of the endoscopist. Fibrogastroduodenoscopy will help assess the condition of the mucous membrane.
During this study, you can determine the acidity of the stomach, as well as test for the presence of Helicobacter pylori infection. The doctor may also prescribe an ultrasound or x-ray. A clinical and biochemical blood test will also help to comprehensively assess the patient’s condition.
Disease prevention and prognosis
The presence of hyperplastic gastritis requires constant monitoring by a specialist. In addition, the patient must strictly adhere to the diet and prescribed treatment regimen. Especially if there are polyps. Complete restoration of the mucous membrane in adults is a very rare occurrence, but absolute recovery in childhood is possible. The prognosis of the pathology depends entirely on the form of the disease and the degree of hyperplasia.
As such, prevention does not exist due to the unknown reasons influencing the development of the disease. However, following the general rules for preventing stomach diseases will not be superfluous. The following recommendations must be followed:
- Compliance with diet.
- You should eat often, in small portions.
- You need to eat enough vegetables and fruits, drink vitamin complexes.
- Nutrition should be moderate.
- You should not abuse fatty and fried foods, flour products, and carbonated drinks.
- It is necessary to give up bad habits such as alcohol and smoking.
- You should take medications strictly as prescribed by your doctor.
- It is recommended to periodically drink herbal remedies for the stomach.
- Do not neglect protective equipment in hazardous industries.
- Wash fruits and vegetables thoroughly.
- Adhere to a healthy lifestyle.
In the article we looked at atrophic hyperplastic gastritis. What this is is clear from the information above.
Treatment of the disease
Symptomatic treatment depends on the manifestations of gastritis. The main component in the drug treatment of the disease are proton pump inhibitors. Depending on the acidity of the stomach, antacids are prescribed to normalize the acidity of the stomach.
When atrophy develops, replacement therapy with natural gastric juice is carried out. In the presence of multiple erosions or peptic ulcers, therapy will be similar to the treatment of gastric ulcers. The presence of Helicobacter pylori in the body requires treatment with antibiotics. For diarrhea, astringents are prescribed.
Surgery is performed when polyps are present, with frequently recurring bleeding (then a partial or complete resection of the stomach is performed).
Folk remedies
Traditional medicine, in particular herbal medicine, is used as an auxiliary therapy. Decoctions of herbs such as:
- calendula;
- pharmaceutical camomile;
- plantain;
- thyme;
- blooming Sally.
Diet for hyperplastic gastritis
When diagnosing hyperplastic gastritis, following a diet is one of the prerequisites for getting rid of the pathology.
The basic principles of the diet are:
- fractional consumption of food;
- eating small portions;
- chewing foods thoroughly;
- food temperature is room temperature;
- cooking food by boiling, baking or steaming.
For this pathology, during the period of remission, the “Table No. 5” diet is recommended. In case of exacerbation, more stringent restrictions are introduced into the diet. When the disease develops against the background of increased acidity, diet No. 1 is followed, and against the background of reduced acidity, diet No. 2 is followed.
Confectionery products, fresh baked goods, canned, fried foods, and instant dishes are excluded from the menu. It is recommended to minimize the use of salt and spices. Limit consumption of fresh fruits and vegetables.