GastrituNet.ru » Stomach diseases » Gastritis » Atrophic
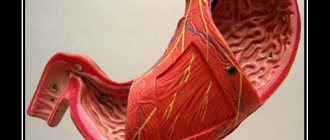
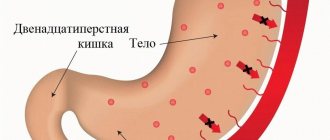
Subatrophic gastritis is a progressive inflammatory process in the gastric mucosa. It differs from similar diseases by the appearance of atrophied areas where cells that contribute to the production of hydrochloric acid and pepsin die irrevocably.
- 1 Description of the disease
- 2 Types of subatrophic gastritis
- 3 Causes of occurrence
- 4 Symptoms
- 5 Drug treatment
- 6 Physiotherapy
- 7 Surgery
- 8 Useful video
- 9 Folk remedies
- 10 Diet
Description of the disease
When the mucous membrane is damaged, it cannot perform its functions correctly. Pepsin enters the body in a “dormant” state, is activated in a reaction with hydrochloric acid, and begins to participate in digestion.
With atrophic gastritis, this pattern is disrupted. The acidity of the stomach decreases significantly, and its walls gradually become thinner. Dead cells are replaced by connective tissue. As a result, there is a deficiency of gastric juice.
The stomach cannot perform its functions correctly. At the initial stage, subatrophic gastritis is easy to treat, while chronic gastritis is difficult to treat. When the disease is advanced, not only a small area is affected, but also the entire stomach.
Important! The chronic form can provoke the formation of cancerous tumors.
Patient reviews
I was diagnosed with a chronic form of antral subatrophic gastritis. When it worsens, I prepare a rosehip decoction. It has a pronounced antimicrobial effect, but does not harm the body. The medicine disinfects the walls of the stomach, neutralizes and removes all toxins and poisons.
Andrey, 43 years old
Chamomile helps with subatrophic gastritis. The decoction immediately soothes the inflamed areas of the mucous membrane and relaxes the muscles. With its help, spasm is quickly minimized and your well-being is made easier. My doctor advised me to drink this decoction daily, but in small quantities. It helps me.
Alexey, 32 years old
Doctors diagnosed me with subatrophic antral gastritis.
In addition to medications, the gastroenterologist advised drinking decoctions from calamus, sage and dandelion rhizomes. The product effectively fights the signs of the disease. Alena, 52 years old
Types of subatrophic gastritis
Subatrophic gastritis can form due to various factors. The disease is divided into several forms:
- Chronic is accompanied by periodic relapses. The disease gradually progresses. As a result, complications arise in other internal organs (pancreas, duodenum, esophagus, liver). Chronic disease negatively affects the nervous system and blood supply.
- The catarrhal form is otherwise called superficial or simple. Accompanied by injury only to the superficial gastric layer. The catarrhal form refers to the initial stage of the disease and is treated quickly.
- Antral subatrophic gastritis is localized at the bottom of the stomach, next to the 12-point colon. Due to tissue proliferation and inflammation of the mucous membrane, the functioning of the stomach is disrupted.
- In the deep form, inflammation penetrates the walls of the organ, affecting the muscles. Certain areas of glandular epithelium degenerate into flat epithelium.
- The focal form appears in specific areas of the stomach. In acute manifestations of the disease, increased acidity is observed.
- The diffuse form is an inflammatory process that is not yet accompanied by serious degenerative changes. Only primary cell damage begins, the appearance of small ridges on the stomach.
- The erosive form is a pre-ulcerative condition. The disease has an acute or chronic form.
- Distal – inflammation affecting distant areas of the organ. This type of gastritis most often occurs in residents of megacities. The distal form may be acute or erosive.
Children's gastritis occurs in the same way as in adults. The symptoms are the same. An acute and chronic form is also observed. The autoimmune type appears due to the genetic characteristics of a person. Multifocal is closely related to the environment (consumption of toxins, nitrates in food, poor diet, Helicobacter pylori infection, etc.).
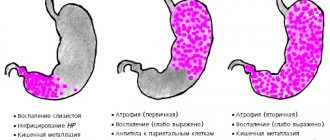
Types of disease
Modern medicine divides 3 types of subatrophic gastritis, which differ in the degree of damaged areas of the gastric mucosa:
- Antral;
- Surface;
- Chronic.
Antral subatrophic gastritis - this disease is caused by bacteria, the inflammatory focus of which is located in the antrum of the stomach. Such microorganisms can spread to other parts of the gastrointestinal tract and lead to inflammation (for example: duodenitis - inflammation of the duodenum).
There are two types of antral subatrophic gastritis: acute and chronic.
Superficial subatrophic gastritis - this type of disease is often called catarrhal or simple, as it is the initial stage of the disease, which affects the epithelial layer of the mucous membrane. Timely detection of pathology and the necessary therapy helps prevent possible complications.
Chronic subatrophic gastritis (pangastritis) is considered the most dangerous type of disease and can lead to the formation of irreversible processes and the occurrence of diffuse gastritis. The disease is associated with poor functioning of the immune system, which activates the formation of antibodies that destroy the stomach glands. As a result of intoxication, the disease begins to spread and affect neighboring organs and systems.
In some cases, mixed gastritis is detected - subatrophic superficial gastritis and atrophic gastropathy (old-fashioned subatrophic gastropathy). Lack of proper therapy for this disease can lead to the formation of erosive gastritis and stomach ulcers.
Causes
What is subatrophic gastritis? This is a thinning of the stomach, disruption of its functioning due to a decrease in acidity levels and a deficiency of hydrochloric acid. The disease can affect individual areas of the organ or it as a whole.
The main cause of the disease is Helicobacter . The bacterium attaches to the gastric mucosa and causes inflammation. A person first develops superficial gastritis. If treatment is not started on time, other forms of the disease begin to develop. The most common reasons:
- excessive alcohol consumption;
- medications taken for a long time can damage the mucous membranes of the gastrointestinal tract;
- chronic inflammation;
- disturbances in the functioning of the immune system;
- intoxication of the body;
- autoimmune processes in the gastrointestinal tract;
- pancreatitis;
- unbalanced diet;
- stress;
- enterocolitis and similar diseases.
Gastritis is sometimes caused by a genetic predisposition. In this case, the disease is difficult to treat or is completely incurable. In chronic gastritis, antibodies destroy healthy cells and can spread to neighboring organs and then throughout the body. Circulatory disorders appear, the nervous system does not work well.
Treatment
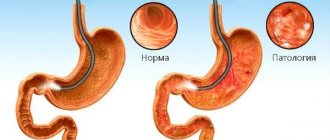
The most effective method for detecting subatrophic gastritis is gastroduodenal endoscopy. Diagnosis is made for such pathologies of the gastric mucosa as:
- Atrophic areas.
- Local pathologies.
- Thinning of the stomach lining.
- The appearance of connective tissue instead of mucous membrane.
Treatment of the disease can be outpatient or carried out in an inpatient setting. The choice of method depends on the stage of atrophy, as well as on the advanced stage of the disease. The main goal of therapy is to stop the atrophic process and prevent the disease from degenerating into cancer.
Symptoms
Subatrophic gastritis what is it? This is a progressive inflammatory process that occurs in the gastric mucosa. At the same time, every day a person’s well-being worsens. Among the first signs of the disease are loss of strength, lethargy, and loss of appetite. Sudden weight loss is possible. By what symptoms is it recognized:
- dull, aching abdominal pain that intensifies after eating;
- pale skin;
- alternating constipation and diarrhea , stool is unstable;
- excessive sweating;
- a white coating appears on the tongue;
- rejection of milk and milk-based products;
- nausea;
- frequent heartburn ;
- vomit;
- belching.
Since the body lacks vitamins, this can affect the gums, they begin to bleed, and teeth begin to crumble. Micronutrient deficiency leads to poor vision, hair loss, and anemia. The onset of the disease may be indicated by peeling nails and dry skin.
| Type of gastritis | Symptoms |
| Catarrhal | The surface layer of the stomach is injured. The oral mucosa dries out, a sour taste appears, and an unpleasant odor is felt. The tongue becomes covered with a white coating, the stomach is greatly distended from the inside, and the person suffers from diarrhea. |
| Chronic | Feeling of fullness in the stomach, alternating constipation and diarrhea, flatulence. After eating there is severe belching. The person feels severe weakness, loss of appetite, and rumbling can be heard in the stomach. Sometimes body weight decreases sharply. |
| Antral | Aching dull pain in the plexus, severe weakness, belching with a nasty sour smell. Appetite and body weight decrease. During endoscopy, ulcers or tumors may be revealed. |
| Deep | This is a type of chronic gastritis and has all the symptoms characteristic of it. |
| Focal | The aversion to fatty foods, milk, and milk-based products is increasing. The remaining symptoms are the same as for chronic gastritis. |
| Diffuse | Inflammation spreads throughout the mucous membrane, but initially it is almost not felt. Gradually, heaviness and periodic pain appear in the stomach. Appetite decreases, excessive sweating and fatigue appear. |
| Erosive | The acute form is characterized by pain in the stomach. After eating, the sensations intensify. Vomiting appears, sometimes with blood. The chronic form is accompanied by signs characteristic of this type. |
| Distal | Abdominal pain appears and bloating is observed. After eating, belching occurs with a sour or nasty rotten smell. There is a decrease in appetite and a sharp loss of body weight. |
The disease may not make itself felt for a long time and may occur with mild symptoms. Sometimes gastritis is accidentally discovered during a routine examination or during the treatment of pancreatitis, cholecystitis, and other ailments.

Treatment of the disease
In stage 1, the disease is easily treatable. To exclude relapse of the disease, it is necessary to find the cause of the disease.
Attention! If subatrophic gastritis develops into a chronic form, this is fraught with serious complications and can lead to the appearance of malignant cancerous tumors.
Symptoms and treatment
Symptoms of non-atrophic gastritis do not appear immediately. Typically, patients are unaware of this condition until they are tested for another reason. This disease is detected using gastroscopy.
The main symptoms of this disease include:
- Lack of appetite. As a result, weight loss, anemia, and general weakness are possible.
- Unpleasant sensations after eating. Even a small amount of food eaten causes a feeling of fullness in the stomach, heartburn, and belching.
- Painful sensations, as a rule, are mild and manifest themselves as nagging pains that occur after eating.
- If a person has high acidity, then constipation may occur.
If untreated, these symptoms begin to manifest themselves in a more pronounced form, and the course of the disease enters a new stage, which affects the deeper layers of the gastric mucosa.
Diagnosis of such a disease is possible only by gastroscopy. During this examination, the patient swallows a flexible hose, at the end of which there is a special optical device. Although such an examination is not very comfortable for the patient, there is no alternative to it. Gastroenterologists recommend conducting it once every three years, even for absolutely healthy people, in order to identify changes in the stomach at the very initial stage.
Treatment of non-atrophic gastritis of the stomach will consist of dietary nutrition. If you have Helicobacter pylori, you need to take a course of antibiotics. The use of symptomatic drugs that relieve unpleasant symptoms - phosphalugel, gastal, and the like - is also indicated.
Drug treatment
Treatment of subatrophic gastritis depends on the causes of the disease. Its stage, individual characteristics of the body, and the presence of complications are taken into account. Drug therapy is carried out in stages:
- Etiotropic treatment eliminates the causes of the disease. If gastritis appears due to Helicobacter, drugs to destroy it, wound healing agents, and inhibitors are prescribed. For the autoimmune form of the disease, glucocorticoids .
- Pathogenic treatment inhibits the development of gastritis. Drugs are prescribed that eliminate the deficiency of microelements needed by the body, stimulants for the active production of hydrochloric acid. Gastroprotectors are used that restore the mucous membrane, enveloping, astringent agents. Prokinetics are prescribed to improve stomach function and painkillers.
During etiotropic treatment, two types of antibiotics are used (“ Clarithromycin ”, “ Omeprazole ”, “ Amoxicillin ”). They are combined with Metronidazole . Among the inhibitors prescribed are Pantoprazole , Lansoprazole , Ranitidine , etc.
De-Nol is used to heal stomach ulcers . At the 2nd stage of treatment, vitamins E, B 12, 6 are prescribed, as well as medications with hydrochloric acid, and the missing enzymes are introduced. Mainly used are “ Acidin-Pepsin ”, “ Mezim ”, “ Pankreotin ”. Among the enveloping agents used are Almogel , Vikair , Vikalin . The most popular prokinetics are Motilium , Cerucal , and Cisapride .
Subatrophic gastropathy: treatment with folk remedies, medications and diet features
Treatment of the disease consists of taking medications and following a diet. You can turn to traditional medicine for help, but it should not replace drug therapy. In addition to treatment, the doctor prescribes physiotherapeutic procedures - electrophoresis, magnetic therapy.

Diet
Treatment of subatrophic gastropathy will be effective only if you follow the rules of food intake and exclude foods that can irritate the intestinal walls. It is recommended to eat liquid and semi-liquid foods. The most useful for gastritis are soups made from vegetables, lean fish, meat, porridge, stewed vegetables, fruit purees, and eggs.
During treatment, until complete recovery, it is necessary to completely eliminate alcohol, fatty and fried foods, spicy seasonings, any canned food, raw vegetables and fruits, sweets, pickles and marinades.
Medications
The doctor prescribes medications depending on the type of pathology and the provoking factor. Subatrophic gastropathy can be treated with the following medications:
- antibiotics when confirming the infectious etiology of the disease;
- replacement agents to maintain a sufficient level of acidity in gastric juice;
- anticholinergic or antacid drugs if acidity is increased (in the antral form);
- iron-containing medications;
- multivitamin complexes;
- immunomodulators.
Physiotherapy
When subatrophic gastritis is diagnosed, it is also treated with physiotherapy. It is used to reduce pain, improve stomach function, and stimulate cell regeneration. The procedures are contraindicated during exacerbations of the disease, in the presence of various neoplasms. During remission, paraffin compresses are made on the stomach. Magnetic field therapy , electrophoresis , and UHF are performed .
Homeopathy
Homeopathic medicines are also prescribed for treatment. The most effective products are those containing:
- antimony trisulphide;
- chilibukha;
- Activated carbon;
- meadow lumbago;
- arsenic anhydrite;
- metallic silver.
The release form of the drugs is in tablets. Plantaglucid , sea buckthorn oil, propolis and wormwood tinctures are also used for treatment
Methods for eliminating the disease
Before treating subatrophic gastritis, consultation with a specialist is required. The basis of treatment is the use of effective and safe medications during the period of pronounced clinical manifestations. During remission, drug therapy is not carried out
To obtain effective treatment, the regimen includes proper nutrition and regimen. Experts advise eating crushed and warm food during exacerbations. It is important to exclude rough foods from the diet. It can damage the mucous membrane of the affected organ
For successful therapy, physical therapy, proper sleep, and rest are additionally used. Physiotherapy and herbal medicine are often prescribed. as medications against signs of gastritis:
Antibacterial drugs. Their consumption prevents the development of infectious or inflammatory complications. Medicines are necessarily included in the Helicobacter eradication scheme.- Substitutes. They are used when there is insufficient acidity.
- Antacids. They are indicated to protect the walls of the stomach from the aggressive effects of acids. Medicines have a pronounced enveloping effect.
- Multivitamins.
- Iron-containing medications.
- Immunomodulators.
Drug therapy is indicated and prescribed by specialists after a detailed examination of the patient. Adequate therapy should eliminate the root cause of the disease, normalize the acidity of the contents and the secretory activity of the glands.
Folk remedies
Folk remedies play a supporting role in therapy and increase its effectiveness. Mineral waters, herbs, fruits and vegetables are used. For gastritis, or raw potato juice . The most commonly used herb is plantain. It has a wound-healing, anti-edematous effect. Plantain works well against inflammation.
Flax seeds are famous for their enveloping properties and contain fatty acids. Linden flowers , medicinal chamomile , and elderberry have an anti-inflammatory effect. Herbs can be used separately or in combination. Fruit drinks are made from cranberries. Parsley can be used fresh or dry.

Diet for this disease
Since the main treatment is strict adherence to the diet, I would like to dwell on it in more detail. First of all, you need, of course, to stop drinking alcohol and smoking, because they cause irreparable harm not only to the stomach, but to the entire body as a whole.
With such a type of disease as non-atrophic antral gastritis, it is important to remember that dishes that are too hot or too cold irritate the mucous membrane very much, so it is best to exclude them. The consistency of the food should be homogeneous; it is better to grind all ingredients thoroughly.
You should remember about your diet - you need to eat 5-6 times a day, but the last meal should be no later than 2-3 hours before bedtime. What you absolutely cannot do is overeat, eat irregularly, or eat dry food.
Now about what foods are prohibited for this stomach disease. It is prohibited to use:
- rich broths, meat and fish broths;
- marinades;
- spicy dishes;
- processed foods and semi-finished products;
- raw vegetables rich in fiber.
But here are the dishes that are recommended to be consumed for such a disease as chronic non-atrophic gastritis:
- meatballs, steamed cutlets from chicken, rabbit, turkey, lean pork;
- lean fish, boiled or steamed;
- pureed vegetables - potatoes, beets, carrots;
- non-acidic fruits (preferably in the form of juices and compotes);
- low-fat dairy products - cottage cheese, sour cream, yogurt;
- a variety of porridges - semolina, oatmeal, corn, buckwheat;
- soups - purees, casseroles.

If this disease is detected at an early stage and the diet is strictly followed, no additional treatment is required. The mucous membrane can recover, and the disease will recede.
Diet
Diet plays a big role in treatment. In the acute stage, table No. 1 , then No. 2 , which is less strict. Food should be ground or heavily chopped. Spicy, smoked and fried foods are prohibited. You should not eat rough food. It should be warm, but not scalding and not too cold.
Gradually, the patient is transferred to a diet with foods that stimulate the production of hydrochloric acid. You need to eat small portions 5 times a day. Preference is given to cereals, plant foods, vegetable first and second courses. Freshly squeezed juices, pureed apples, drinks with honey are shown.
Subatrophic gastritis is well treated in the first stages. The danger of the disease is that the affected cells are not restored, and cancerous tumors may appear. Self-medication can lead to serious consequences. Only a doctor can correctly determine the form of the disease and prescribe the necessary therapy, taking into account all the characteristics of the body and the presence of complications.
Prevention measures
The set of measures to prevent the occurrence of gastritis is based on the following principles.
- Developing a healthy diet. It is advisable to avoid fried foods and reduce the use of spices to a minimum. Many of them can cause irritation of the mucous membrane.
- Use for preparing quality products. It is recommended to give preference to freshly prepared food. It is unacceptable to consume food that shows signs of spoilage.
- Increasing physical activity. Its deficiency can negatively affect the course of the disease, which is associated with the peculiarities of the structure of the human muscular system.
- Stabilization of mental activity. Patients should avoid unnecessary stressful situations, as they lead to disruption of secretory processes. In addition, it negatively affects gastric motility.
- Limiting the use of medications that can irritate the internal walls of the digestive organ. These usually include non-steroidal drugs to relieve inflammation and many antibiotics, as well as drugs containing acetylsalicylic acid.
- Eliminate alcoholic beverages and tobacco from your life. Abuse of them sooner or later leads to problems with the gastric mucosa. Smoking is not capable of causing inflammation, but it greatly aggravates the overall situation.
- Reducing food portions. It is best to eat small meals. It is necessary to divide the diet into small parts. At the same time, the number of receptions can be increased.
Causes of inflammation
The most common cause of gastritis is Helicobacter pylori. This is a hydrochloric acid-resistant bacterium that attacks the inner lining of the stomach. According to statistics, Helicobacter pylori infection causes inflammation in 90% of cases. As a rule, Helicobacter pylori multiplies in the antrum, since this is where the pH level is most comfortable for it. That is why chronic non-atrophic antral gastritis is most often detected.
More rare causes of the development of non-atrophic inflammation include:
- other infectious agents - viruses, bacteria, fungi;
- nutritional factor, i.e. improper, irregular nutrition;
- reflux of bile from the duodenum into the stomach cavity - biliary reflux;
- prolonged stress;
- smoking;
- alcohol abuse;
- the use of anti-inflammatory, antipyretic drugs, analgesics;
- changes in hormonal levels;
- reduced blood supply to the stomach in diseases of the heart and blood vessels.
The listed factors can cause an inflammatory reaction even with short-term exposure. In some cases, for complete recovery it is enough to simply eliminate the cause of the disease.
Diagnostics
It is impossible to determine the disease on your own: if symptoms appear, you should consult a doctor. At the appointment, the doctor will conduct an examination and collect anamnesis, and write out an appointment for laboratory tests.
For gastritis, the following diagnostic tests are performed:
- Analysis for bacteriological culture. Its results enable the doctor to determine the first signs of the development of an inflammatory process in the stomach.
- Urine and stool analysis. Based on whether there are undigested food residues in the urine and feces, the specialist concludes that there is a reduced level of gastric secretion. Another analysis will reveal the presence of blood in the patient’s biological waste.
- FGDS. The study is carried out using a special medical device, a fiber endoscope, which is inserted into the stomach. Based on the results of fibrogastroduodenoscopy, the doctor judges the condition of the gastrointestinal tract. If the mucous membrane of the stomach is inflamed, then hemorrhages, swelling are visible on it, and its surface is shiny. Based on the results of FGDS, one can judge the presence of bacteria.
- pH measurement inside the stomach. Based on the results of this analysis, one can judge the state of secretory function.
- Ultrasound. Using ultrasound, damage to the gastrointestinal tract is detected.
Classification of chronic non-atrophic gastritis
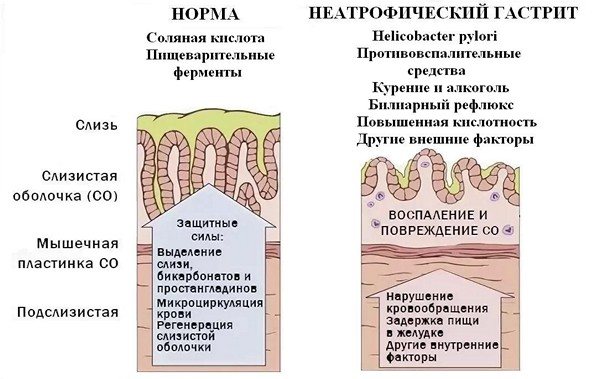
Usually the term “non-atrophic gastritis” is replaced by the concept “superficial gastritis”, but this is not entirely correct. Researchers indicate that non-atrophic inflammation can be either superficial, affecting only the upper layers of the epithelium, or deep (interstitial), affecting the entire thickness of the mucous membrane.
Depending on changes in the pH of gastric juice, gastritis without atrophy can be normo- or hyperacid. Since the glandular apparatus remains intact, acidity never decreases during a non-atrophic process.
According to localization, the non-atrophic process can be antral, fundal and diffuse. The most common form is antral, the rarest is fundal, in which the bottom of the stomach becomes inflamed. With diffuse non-atrophic gastritis, the entire organ is affected. This form is often accompanied by increased acidity of gastric juice.
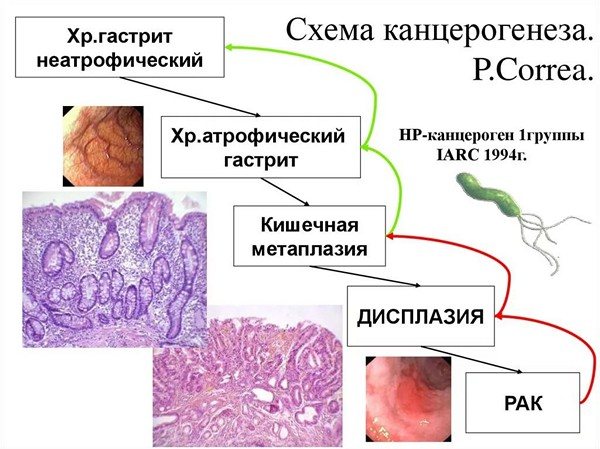
Peculiarities. Inflammation of the mucosa without atrophy should be considered as the initial stage of a pathological cascade, which without adequate treatment can lead to stomach cancer. P. Correa formulated 5 stages of carcinogenesis: non-atrophic gastritis – atrophy – intestinal metaplasia – epithelial dysplasia – malignant neoplasm.
During non-atrophic inflammation of the stomach, stages of exacerbation and remission are distinguished. During an exacerbation, pain and dyspeptic (associated with digestive disorders) syndromes are usually pronounced. During the remission phase, the patient has no complaints about his health, but on FGDS, inflammatory changes persist.