What is the hepatitis C virus?
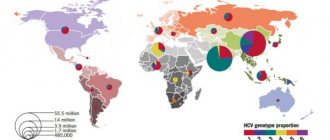
Hepatitis C virus or HCV is a small virus that contains a genetic variant of the material in the form of RNA, coated with an envelope. The disease is very dangerous due to its tendency to constant genetic mutations; the virus is very variable. To date, medical experts have identified six main viral genotypes of this disease. But since the virus is constantly changing and mutating, this number is not final. One genotype can contain more than forty subtypes of HCV, which directly affects the determination of viral persistence and the large-scale development of hepatitis C chronicity.
Due to the peculiarity of the virus being hidden under various ailments, it is not easy to determine its symptoms, especially in women. And as doctors have long confirmed, this type of disease occurs much more often among the fairer sex.
First signs
Clinical symptoms of viral hepatitis C are rarely severe. The first signs of the manifest form of the disease include patient complaints of:
- general weakness;
- decreased performance;
- increased fatigue;
- drowsiness or insomnia;
- loss of appetite;
- weight loss;
- loose stool (diarrhea, constipation);
- feeling of heaviness in the right hypochondrium;
- skin itching.
With significant damage to the liver parenchyma due to a violation of its synthetic function, the concentration of proteins in the blood of patients, including ferritin and proteins of the blood coagulation system, decreases. As a result, women with hepatitis C experience frequent nosebleeds for no apparent reason.
Damage to liver functions leads to hormonal imbalance. In women, this primarily manifests itself in the form of menstrual cycle disorders (extended menstrual bleeding time, increased intensity of bleeding, cycle instability). If a woman has been suffering from chronic hepatitis C for a long time, it can cause her infertility.
During an external examination in women in the initial stages of the disease, the following can be determined:
- yellowness of the skin, mucous membranes, sclera of the eyes;
- hemorrhagic petechial rash on the skin and scratch marks (from itching);
- thickening of the terminal phalanges of the fingers (in the form of “drumsticks”);
- redness of the palmar surface of the hands (palmar erythema);
- low-grade body temperature (up to 38°C).
Palpation and percussion reveal an enlarged liver, painful to the touch, as well as an enlarged spleen. As a result of the fact that the hepatitis C virus is capable of extrahepatic reproduction, when examining women who have been suffering from hepatitis C for a long time, multiple extrahepatic manifestations are detected:
- vasculitis (vascular damage);
- membranous-proliferative glomerulonephritis (damage to the glomeruli of the kidneys);
- cutaneous porphyria;
- uveitis, keratitis;
- cryoglobulinemia (hemoglobin pathology).
How is hepatitis C transmitted?
Hepatitis C is transmitted through blood, sexually, from mother to child at the time of birth in 5% of cases. Hepatitis C is not transmitted through household contact! This means that you cannot become infected through sharing utensils, by hugging or shaking hands, by sneezing, coughing, etc. (by airborne droplets). If infection occurs at home, we are talking about the patient’s blood getting into the blood of the infected person. This is possible with injuries, cuts, abrasions. Patients with hepatitis C do not need special working conditions or restrictions in everyday life.
How to behave when there is a hepatitis C patient in the family?
To prevent transmission of the hepatitis virus within the family, you should always be on alert and take the following precautions:
- Provide the patient with a separate set of hygiene items (towel, toothbrush, floss, shaving and manicure tools) and dishes;
- Store and serve the above items separately from other things of other family members;
- When a sick person cuts himself, immediately treat the wound and cover it with a band-aid so that blood does not come to the surface and infection does not occur;
- Places where drops of the patient’s blood happened to fall should be thoroughly rinsed with Chlorantheine or regular bleach;
- Fabrics must be washed at temperatures above 60°C on a cycle of more than half an hour or boiled for 5 minutes.
Incubation period
Our service will select the best hepatologist for you for free when you call our Unified Appointment Center by phone. We will find an experienced doctor near you, and the price will be lower than if you contact the clinic directly.
The duration of the incubation period of the virus is strictly individual and can reach up to 20-30 weeks. On average, the incubation period is about 2 months. Approximately 45% of patients currently suffer from an acute form of the disease, in which the virus only needs 14-20 days to reproduce. If the patient receives high-quality and effective treatment, in a few months he will forget about this disease forever. In the remaining 55% of cases, the virus immediately becomes chronic and the incubation period is long.
Routes of infection
The main source of the disease remains the virus carrier. In this case, a woman can acquire an infection in two main ways - through unprotected sexual intercourse and parenterally. Thus, the virus enters the bloodstream through the mucous membrane of the female genital organs.
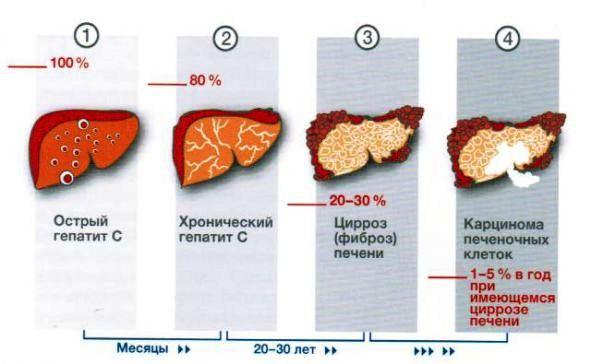
Stages of hepatitis C
These routes of infection are realized in the presence of accompanying conditions:
- If the skin is damaged during service in a beauty salon.
- In case of insufficient sterilization of medical instruments (during surgical intervention).
- When a blood transfusion takes place.
- If the dentist does not follow the rules for disinfecting instruments, the patient can easily become infected with the virus from a previous patient.
- Reusable use of syringes that are intended for single use (this group of people consists of drug addicts who require injection of drugs).
- The procedure for applying tattoos to the body remains dangerous, since damage to the skin occurs, which is accompanied by contact with blood, and, therefore, if the instrument is not properly disinfected, one can easily become infected with hepatitis C.
- Regular sex life, which involves a large number of partners without the use of barrier contraception in the form of condoms.
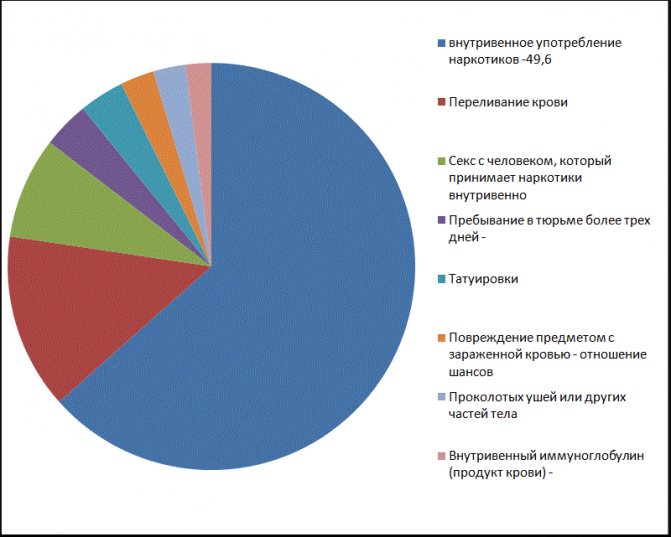
Percentage of hepatitis C infection
Note! One of the main questions is whether it is possible to become infected with hepatitis exclusively through household means. The answer in this case is clear - no. Infection occurs through direct contact with blood.
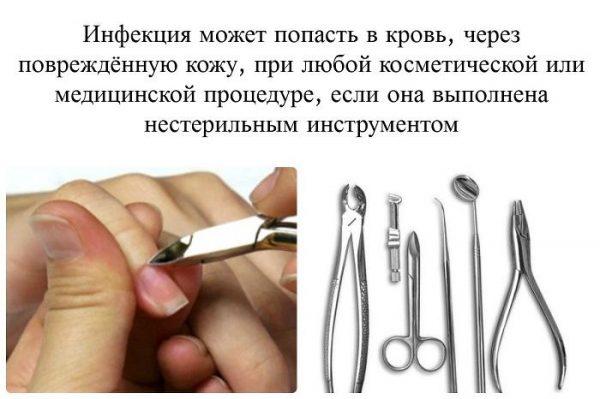
Route of transmission of hepatitis C
Types of viral pathology
The types of virus are determined by the result of the manifestation of primary symptoms:
- acute - the duration of the incubation period is quite short, after which an acute course of the disease occurs with the rapid onset of symptoms;
- chronic is the most common type of pathology among women, as it is observed in almost 90% of all clinical cases. After infection in a latent form, the virus can develop for about twenty years, and no primary symptoms will be observed.
Hepatitis virus
Fact! The fulminant development of the virus, which is characterized by acute liver failure due to massive infectious damage to hepatocytes, cannot be ruled out. However, such clinical pictures in women are extremely rare.
Timing of hepatitis C
How long do people with chronic hepatitis C live? The danger of chronic hepatitis C is that it inevitably leads to liver cirrhosis, a pathological condition in which healthy liver tissue is replaced by fibrous tissue. The functioning of the liver is completely impaired, but this is a slow process. If the patient receives high-quality treatment, it may take 25-30 years before the onset of cirrhosis, in some cases up to 45 years. But if the patient does not receive treatment and does not try to lead a healthy lifestyle, this period is reduced to 10-15 years. We should not forget that people live with liver cirrhosis from 1 to 10-12 years, depending on the treatment, age and lifestyle of the patient. The timing of treatment for hepatitis C in the acute form is strictly individual. According to statistics, full recovery may take from 3 to 12 months.
The cost of hepatitis treatment today is high and in various clinics can range from 50 to 700 thousand rubles for the entire period of treatment.
Treatment
Hepatitis C cannot be ignored; the consequences of a progressive pathological process are the most severe:
- steatosis – replacement of liver cells with fat;
- fibrosis – scar formation;
- Cirrhosis is a violation of the architecture and functions of an organ.
Treatment of liver hepatitis in women requires enormous patience and is characterized by duration. If a woman wants to live, she must strictly adhere to all stages of the plan developed by the hepatologist.
The method and duration of the treatment process, the dosage of the drugs used (Interferon and Ribavirin) depend on the genotype of the viral pathology. According to the division into geographical location, specifically for the territory of the Russian Federation, pathologies with genome 1b, 2a, 3 are typical. The peculiarity of viruses is constant mutation, the development of immunity to drugs.
Traditional medicine recipes based on natural ingredients, aimed at increasing a woman’s immune strength and alleviating symptoms, are ineffective in curing pathology.
The prognosis in the case of a correctly selected therapeutic course against hepatitis C is quite favorable. It is difficult to cure the disease completely, but it is possible, because modern drugs are highly effective. In various Internet resources, medical forums, women ask exciting questions about the disease, read reviews of those who have overcome this liver pathology.
The first signs of hepatitis C in women
It is important to clearly understand that the disease does not have clearly defined symptoms and is detected by chance when the patient undergoes a routine medical examination or comes in with complaints of other diseases. And yet there is a small list of signs that may indicate the presence of the hepatitis virus:
- increasing weakness;
- fast fatiguability;
- asthenia (general weakness of all organs and systems of the body).
Such manifestations are typical for any colds, chronic diseases or poisonings (intoxications). Later the following may appear:
- jaundice;
- the abdomen may increase in volume (ascites);
- Spider veins may appear;
- lack of appetite;
- nausea;
- joint pain (a rare symptom);
- possible enlargement of the spleen and liver.
In general, we can say that the first signs are symptoms of intoxication and liver dysfunction. As a rule, patients with weakness and nausea do not rush to see a doctor, take standard medications for poisoning and try to return to everyday activities as soon as possible. This approach leads to complications in the patient’s condition and the development of the virus. The earlier the virus is detected, the higher the patient’s chances of recovery.
It is possible to make an accurate diagnosis and confirm or refute the presence of the virus in the body only after taking tests.
Symptoms in the early stages (acute period)
As already mentioned, viral hepatitis C is practically not registered as an acute infectious disease. Signs of the disease are nonspecific and mild, and therefore are not regarded by the patient as serious disorders and as a reason to see a doctor. Most patients cannot remember the initial episode of the disease.
Among the possible symptoms of the acute stage of the primary process, the most significant are the following:
- constant weakness, decreased performance, prolonged fatigue that is not associated with physical and mental stress, and does not disappear after a long rest;
- loss of appetite, nausea and isolated episodes of vomiting, abdominal pain of moderate intensity and without clear localization;
- darkening of urine and lightening of stool;
- moderate yellowing of the skin combined with itching;
- yellowness of the sclera (see photo).

Symptoms of acute hepatitis C in women do not have age-related characteristics. It is difficult even for a specialist to suspect this infectious disease based on scant clinical symptoms.
Symptoms of hepatitis C in women
As stated above by the author of the article, hepatitis C is an asymptomatic disease and actually does not manifest itself at all. Symptoms do not differ between women and men. However, in most patients with hepatitis, the disease follows a similar scenario. This scenario is considered to be the clinical manifestations of hepatitis C. First, general weakness appears and appetite decreases. Some women report aversion to food or a feeling of heaviness. There is sleep disturbance and performance is noticeably reduced. Joint pain is observed in a small number of patients and mostly in older age, but the appearance of the joints does not change, and no manifestations other than pain are observed. Some patients develop a rash that is very similar to an allergic one, and their body temperature may rise. As a rule, such symptoms are observed for about 7 days. Further changes characteristic of jaundice and liver diseases in general may occur.
Diagnostics
It is completely impossible to diagnose a viral infection by visual examination or regular questioning due to the presence of symptoms that are also characteristic of other diseases. Laboratory tests make it possible to accurately determine a viral infection and make a diagnosis. First of all, the following studies are carried out:
- blood test for increased ESR (erythrocyte sedimentation rate), increased activity of liver enzymes (transaminases), the presence of antibodies to the virus and HCV;
- stool examination;
- Analysis of urine;
- MRI (magnetic resonance therapy);
- Ultrasound (ultrasound examination);
- ECG (electrocardiogram).
After the infection has been diagnosed, it is necessary to determine the degree of damage to hepatocytes (tissues) and the stage of cirrhosis (replacement of cells with connective tissue). To do this, a biopsy is performed to remove a piece of liver tissue, followed by examination under a microscope.
With cirrhosis, a viral infection in women manifests itself with the following symptoms:
- liver failure with accumulation of fluid in the abdominal cavity;
- bleeding from the veins of the esophagus;
- disruption of the central nervous system (CNS) up to coma.
Pregnant women, as well as blood donors, are tested for markers of a specific virus for early detection of cases of infection.
Urine for hepatitis
Urine is characterized by 4 main criteria - odor, foam, transparency and color. Normally, urine is clear, without impurities. It has no sharp unpleasant odors, a light yellow tint, the foam is light and distributed evenly over the surface of the urine. A person with hepatitis C may have the following abnormal urine:
- flakes may appear in the urine;
- the foam becomes yellowish, small bubbles may form, which quickly disappear;
- a sharp unpleasant odor may appear;
- urine becomes brown (due to excess hemoglobin).
Since urine can be significantly influenced by the patient’s diet and foods eaten the day before, monitoring the state of urine should be carried out several times. At home, you can determine 1 free day, during which the patient monitors the condition of his urine from morning to evening. But it is important to understand that self-diagnosis cannot be objective due to the observer’s lack of knowledge and experience.
How does a woman’s well-being change?
As already mentioned, the general condition of a woman does not change significantly. Few modern people pay attention to weakness, increased fatigue, dizziness and appetite disturbances. Such nonspecific symptoms are associated with an unbalanced diet and a modern, stressful lifestyle - most will say so.
Only symptoms of chronic hepatitis - with severe fibrosis and significant deterioration in liver function tests - will force the patient to contact her doctor and undergo an examination. But a situation often arises when markers of viral hepatitis are detected as an accidental finding during a routine examination or a disease of another etiology.
An important feature of the female body against the background of viral hepatitis C is a variety of menstrual irregularities. The most common among them are:
- an increase in the duration of bleeding and the volume of discharge due to a decrease in the concentration of coagulation factors;
- decreased interval between menstrual bleeding due to hormonal imbalance;
- the appearance of pain syndrome.
In the process of a comprehensive examination to determine the cause of a gynecological disease, it would not be superfluous to analyze markers of viral hepatitis. Perhaps it is hepatitis C that is the cause of dysfunctional uterine bleeding.
What to remember about hepatitis C?
- The disease is asymptomatic and may not manifest itself at all for decades.
- An accurate diagnosis can only be made based on the results of tests and examinations.
- Approximately 70% of people with acute hepatitis develop a chronic form.
- If the virus is detected within the first months after entering the body, the patient will be able to recover completely without specific treatment, but hepatitis is detected very rarely in such an early period. This usually occurs in people who, due to their work or lifestyle, encounter sick people and regularly get tested.
- Some infected people are carriers of the virus (they can infect others), but they themselves do not get sick. They have neither traditional symptoms of hepatitis C nor changes in the results of tests and examinations.
- Since the virus is constantly mutating and there are many types of genomes, even those who have recovered from it, there is always a chance of becoming infected with hepatitis again.
Prognosis for women
The chance of complete recovery is high: according to various sources, from 60 to 80% of those infected recover completely. Hepatitis C type 1 is poorly treated, but hepatitis types 2 and 3 are easier and faster to treat. The effectiveness of treatment is directly affected by:
- body weight (obese or even overweight patients find it more difficult to overcome the virus than people with normal weight);
- age (the younger the person, the easier the treatment is. Although children also have a hard time with the disease);
- the number of viruses in the body (the so-called “viral load”, the lower it is, the easier it is to cure the patient);
- gender (women respond better to treatment compared to men);
- results of histological examination of the liver (it is important to identify the virus at the stage of minimal pathological changes);
- the patient’s lifestyle (people who smoke and frequently drink alcohol get sick more seriously).