Viral hepatitis A is registered in all age groups. However, the highest incidence is observed among children 3 - 7 years old. Characteristic is autumn-winter seasonality with a rise in September - November. After treatment is completed, the baby develops stable, lifelong immunity. From this article you will learn about how hepatitis A is diagnosed in children.
Course and symptoms
The incubation period is the first of the periods of the disease, which can last from two weeks to 1.5 months. This is the period of time that passes from the moment the body is infected until the first symptoms of the disease appear. It is precisely because of the duration of this period that diseases caused by hepatitis viruses are considered the most dangerous, because they are often asymptomatic.
As a rule, during this stage of the disease a person feels well and does not notice any signs of illness.
After the incubation period, the following phases of hepatitis occur:
- prodromal (icteric, initial) – from several days to a month;
- high phase (icteric) – from a week to 60 days;
- convalescence phase (recovery) – from a month to six months.
The first is where the incubation period begins. – this is the entry of the virus into the blood by any means. Next, the virus enters the liver and begins to gradually destroy it, and hepatocytes - liver cells - cannot protect the organ and die. But their death occurs gradually, as they try to overcome the virus. It is because of this that people who have had hepatitis A develop strong immunity to the virus.
Symptoms
The symptoms of this disease are similar to the development of ARVI, which is why people learn about it already at the progression stage. The main signs of hepatitis A include the following:
- increased body temperature;
- darkening of urine, lightening of stool;
fatigue, lethargy, tiredness;- malaise;
- stomach ache;
- itching;
- increase in liver size;
- diarrhea, vomiting, nausea;
- increased sweating;
- loss of appetite;
- muscle pain.
The first warning sign of the disease is fever, which can last up to ten days. It is worth noting that the virus can be transmitted to another person during the incubation period.
The most dangerous periods of the disease for others are the first and second.
But there are also cases where infection occurred at its peak, but this happened in only five percent of cases.
Forms of the disease
Hepatitis in children occurs as a result of a pathogen entering the body. Inflammation occurs in different forms, depending on the cause that served as the basis for the pathological changes. During the period of an acute condition, the immune system tries to free itself from the action of the virus, and if it succeeds, the child recovers, but if not, the disease develops into a chronic process.
There are several forms of hepatitis in newborns:
- Autoimmune. The reasons for the appearance of a disease of this nature in a child’s body are not fully understood. Theories have been put forward that this is a complication of a herpetic infection. The destruction of liver cells occurs due to the impact of immunity on them.
- Toxic. Such hepatitis is detected in newborns after they are poisoned with heavy chemical compounds contained in drugs, alcohol, mushrooms, and poisonous plants. If you notice the first symptoms of intoxication and start treatment on time, you can reduce the likelihood of complications and increase the chances of a successful recovery.
- Fetal. Infection with hepatitis A or B occurs while the baby is still developing in the womb. Infection in the early stages often leads to fetal death. Even after birth, the probability of such a child surviving to 2 years is 30%.
- Reactive. It manifests itself as serious digestive disorders due to the infectious process. Leads to the development of problems with the lungs and endocrine system. Children with allergic reactions and bronchial asthma are prone to this type of hepatitis.
- Fulminant. One of the most severe forms of the disease, which is characterized by the death of part of the liver. In 95% of cases it ends in death.
The form is determined by a doctor who focuses on the signs of hepatitis in children, the results of tests and studies. This classification allows you to understand risk factors and prescribe the correct treatment regimen. This in turn determines the effectiveness of the tactics and the likelihood of a full recovery.
Disease prevention
As a rule, people find out about a disease such as hepatitis A quite by accident by taking a blood test. But if it is possible to determine the presence of the disease during the incubation period, then the patient’s health can still be protected.
To do this, it is necessary to inject him with immunoglobulin, thanks to which the development of the disease can be prevented. The favorable outcome of the disease depends on the length of the incubation period, the health of the person and the state of his immune system.
But it is worth noting that this preventive measure is considered short-term. And after 4 months the disease can begin to develop again in the human body. But this procedure cannot be carried out too often - at least a year must pass from the previous treatment. Immunoglobulin can be administered no more than 4 times in a person’s entire life.
Therefore, the administration of this drug is most relevant in the following cases:

living of a healthy person in the same area as a sick person;- birth of children from an infected mother;
- sexual contact with an infected person;
- drinking contaminated water.
In addition to this method of prevention, vaccination against hepatitis A is also used. It has many advantages over other preventive measures. They are as follows:
- the vaccine is available to all categories of the population;
- it can protect the human body from the virus for up to ten years.
But it is worth noting that immunity to viruses is developed within two weeks, and if we talk about the administration of immunoglobulin, then immunity is developed already on the second day after the manipulation.
Also, measures to prevent hepatitis A include the following:

Constantly washing your hands before eating and after being in public places;- drinking only purified water;
- vaccination when traveling to areas at high risk of infection;
- washing fruits and vegetables before eating.
In addition, you should try not to swallow water in ponds and rivers while swimming.
Preventive actions
You can protect your child from infection with viral hepatitis by observing the rules of personal hygiene, providing him with high-quality filtered water, and regular antiseptic treatment of space and toys. Measures to prevent infection with virus A will be practically no different from those taken to prevent the entry of E. coli. There are no vaccinations against forms A and C. But universal recommendations for everyone will help protect themselves from infection:
- Do not use syringes more than once.
- Monitor the quality of disinfection of medical instruments used for dental treatment or other manipulations.
- Avoid contact with blood or other biological fluids of an infected person.
Advice! There is the most effective prevention against hepatitis B. Children are vaccinated in the maternity hospital in the first 12 hours after birth. Vaccination is recommended for children in families where one of the parents is a carrier of the virus.
Hepatitis A infection in children
This disease is especially dangerous for children. It should not be confused with jaundice, the symptoms of which are similar. Jaundice, unlike hepatitis, is a harmless disease that does not require treatment and goes away on its own. The disease caused by hepatitis viruses requires long-term and complex treatment.
It is worth noting that hepatitis A is resistant to many environmental conditions; it can survive in both low and high temperatures.
If we talk about this type of virus, it can live in water for up to six months, which is why most often infection occurs this way. The virus can survive during boiling, but in this case its life lasts no more than five minutes.
The main method of infection, including for children, is the fecal-oral route. That is, you can become infected with hepatitis A through contaminated food and water. The risk group includes tap water and products that are allowed to be consumed without heat treatment.
In addition, children can become infected with the virus in the following ways:

in close contact with a sick person;- upon contact with nasopharyngeal secretions or other biological fluid of a sick person;
- at birth, from an infected mother;
- when given an injection or blood transfusion;
- through flies.
Types of viral pathology
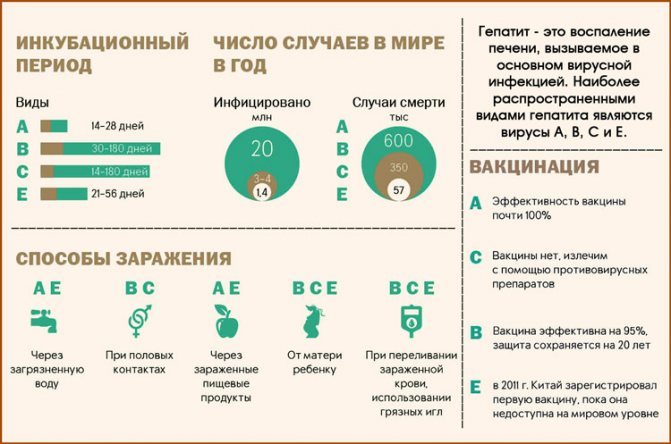
Depending on the pathogen that entered the body, there are several types of hepatitis. To date, 7 forms have been officially registered: A, B, C, D, E, F. Each of them has its own characteristics, routes of infection, symptoms and severity.
| Virus shape | Routes of infection | Incubation period | Features of the course in children |
| "A" | Fecal-oral | 15-30 days | In most cases, complete recovery |
| "IN" | Through blood In utero | 50-80 days | 1/3 of sick children develop cirrhosis |
| "WITH" | Blood contact | 45-60 days | Progresses in a latent form, leading to severe complications |
| "D" | Through the blood | 20-50 days | Only people with hepatitis B can become infected. |
| "E" | Fecal-oral Via blood | 40 days | Leads to liver failure |
| "F" | Fecal-oral Blood-contact | Does not occur independently, accompanies hepatitis A, C | Not fully studied |
Symptoms and treatment of hepatitis in children differ depending on the form, but there are similarities. For example, almost all types of pathology are manifested by yellowing of the skin, and also have a main route of infection through the blood. Viruses type B and C can enter the baby's body while he is still in the womb.
Hepatitis treatment prognosis
Viral hepatitis in children occurs with varying degrees of severity and not all of them result in complete recovery. Most often, the acute period develops into a chronic form. The prognosis of development largely depends on the chosen treatment tactics, timely detection of the disease, severity, stage, age of the child, and type of virus.
- Hepatitis A. Ends with complete recovery, the resulting immunity lasts for life. Cases of complications are rare.
- Hepatitis B. Occurs in severe or moderate form. With the right approach, your health improves within 6 months. In 5% of cases the condition becomes chronic.
- Hepatitis C. In children it is easier than in adults, recovery occurs in 20% of cases. The mortality rate is 1% among infants.
The prognosis in children is largely influenced by the individual characteristics of the body. Full recovery occurs slowly, and more than half of patients subsequently develop residual effects. Usually this is liver failure, cholecystitis, dyskinesia, cirrhosis, damage to the digestive tract. After treatment, children are registered with a hepatologist. They are observed by this specialist for a year. For mild forms, registration is 6 months. For this period, an exemption from sports activities is issued.
Viral hepatitis is a dangerous infectious pathology that often affects children. Simple rules of hygiene, regular examinations by a doctor, and avoiding the use of other people's clothing will help protect them from infection and the development of complications. It depends on the parents how quickly the condition stabilizes and recovery occurs, since they must monitor compliance with all recommendations.