Can appendicitis hurt for several days and what is the appendix for? Doctors still cannot answer this question for sure: some believe that this is a rudimentary organ that a person absolutely does not need; others - that it, like the tonsils, performs protective and immunomodulatory functions.
There are a number of scientific studies in favor of the second version: American scientists have concluded that intestinal cancer is more common in people whose appendix has been removed. Her observations alone showed that children with an appendix removed in early childhood are inferior in mental development to their peers. That is, if an organ functions normally, then a person needs it.
Classification of appendicitis
Various forms of the disease are distinguished according to several criteria.
- Acute appendicitis is the most common. Clinical manifestations develop quickly and are quite pronounced. Since microflora is always present in the lumen of the appendix, inflammation creates conditions for the development of purulent complications, which do not take long to occur. Therefore, acute appendicitis must be operated on within the first 24 hours.
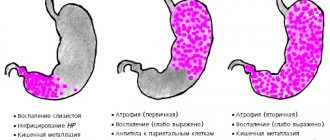
- Chronic appendicitis is a fairly rare form that can develop after acute inflammation. Sometimes it develops primarily. It is characterized by the growth of connective tissue in the wall of the process and atrophy of the mucous membrane. Until now, there is debate among scientists about whether this disease can be isolated into a separate form.
There is also a separate morphological classification based on the nature of the changes occurring in the wall of the process.
- Simple (aka catarrhal) – it accounts for the vast majority of cases of the disease.
- Surface.
- Destructive appendicitis (there are several forms):
- phlegmonous,
- gangrenous,
- apostematous,
- perforated,
- gangrenous-ulcerative.
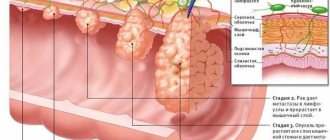
Destructive forms are the most dangerous, as they quickly lead to disruption of the integrity of the wall of the appendix and penetration of its contents into the abdominal cavity. A huge number of bacteria in the lumen of the organ ensures the development of severe peritonitis. In older people, the mortality rate in this case reaches 10-15 percent.
Description of the pathology
Symptoms of suspected appendicitis in adults and children can be very different. Moreover, it is extremely easy to confuse them with other diseases. Appendicitis is one of the most dangerous and fairly common surgical pathologies that develops in the digestive organs.
This disease is developing rapidly. This is where its danger lies. Moreover, life-threatening complications and the most serious manifestations inevitably arise. Almost 5-10% of people are diagnosed with acute appendicitis. Therefore, the likelihood of encountering this disease is quite high.
If you suspect acute appendicitis, you should not hesitate. We need to call an ambulance. The sooner appropriate treatment is carried out, the less adverse consequences of such a condition will be.
Appendicitis occurs in people of any gender and age. Most often it is diagnosed in patients aged 5 to 40 years. Appendicitis is more often suspected in women. Symptoms in this case can be very different. Representatives of the fair sex aged 20-40 years are susceptible to this disease more often than men. These are official medical statistics. But before the age of 20, men are more likely to suffer from appendicitis.
After 40 years, the likelihood of developing this disease decreases significantly, but is not excluded. Appendicitis can occur in rare cases in children under 5 years of age, as well as in older and middle-aged people.
This disease is caused by an inflammatory process that develops in the appendix. It is located in the lower intestine. The functions of this organ are not fully understood to date. Previously it was believed that this was a rudiment. Today, scientists are more inclined to the version that this organ plays an important role in immune and metabolic processes, and also takes part in the formation of intestinal microflora.
It has been proven that people who have had their appendix removed suffer from an insufficient number of beneficial microorganisms in the gastrointestinal tract. However, this organ is not vital. If pathology develops, pus accumulates in this appendage. Due to the narrowness of this organ, it accumulates without any outlet. The appendix increases in size and becomes painful. If no action is taken, it ruptures and pus comes out, causing acute peritonitis. Sepsis and abscesses in the abdominal cavity then develop. This is highly likely to lead to death. With timely treatment, the prognosis is favorable.
Causes of appendicitis in adults
At present, it is not established what exactly triggers the inflammatory process in the appendix. Various authors offer many theories, each of which has a right to exist.
Mechanical theory
According to this theory, appendicitis develops due to the activation of intestinal microflora, which is facilitated by obstruction of the lumen of the appendix. Most often, the organ is clogged with fecal stones, less often there is an enlargement of the lymph nodes (a lot of lymphoid tissue is concentrated in the appendix, for which it is sometimes called the “intestinal tonsil”). Much less often, a parasite (in most cases a helminth) is found in the appendix, which is the cause of the development of the disease.
Separately, scars and adhesions, the formation of which is promoted by a number of diseases of the abdominal organs (colitis, cholecystitis, gastroenteritis, inflammation of the uterine appendages), are considered as the cause of the development of inflammation. Due to the development of sclerosis, bending of the process and obstruction of its lumen may occur.
Casuistically rare causes of the development of the disease include swallowed foreign bodies, tumors of the appendix and cecum.
Pathogenesis of appendicitis development as a result of mechanical obstruction:
- The clogged appendix is filled with mucus, which the mucous membrane of the organ continues to produce. Thick mucous secretion leads to the fact that the diameter of the appendix increases from 4-6 mm to 2 cm or more. It becomes tense due to overflow, which provokes a whole cascade of reactions.
- The pressure inside the lumen of the organ gradually increases, resulting in compression of the veins and lymphatic vessels in the wall of the appendix. This causes an increase in edema and sweating of the contents of the vessels into the appendix, which further aggravates the situation (a “vicious circle” is formed).
- The compressed wall becomes inflamed and gradually dies (especially when it comes to the impact of fecal stone). This is how a zone of necrosis gradually forms.
- The dead wall of the appendix cannot withstand the effects of aggressive microflora, which are present in large quantities in the large intestine. Scientists have counted more than 500 species of bacteria and fungi, the number of which reaches 10 million microbial bodies per gram. That is why the process of seeding the wall and its destruction is rapid (can occur in just 12 hours). If everything develops according to this scenario, and appropriate measures are not applied, then the gradually increasing pressure causes a rupture of the wall of the appendix and its infected contents enter the abdominal cavity, resulting in severe peritonitis.
If you eat an insufficient amount of plant foods, the formation of feces is disrupted, constipation is often a concern, and the likelihood of the formation of fecal stones increases. Therefore, it is necessary to ensure a balanced diet, which will help prevent the development of appendicitis.
Infection theory
Proponents of this theory believe that individual pathogens are capable of independently causing appendicitis (tuberculosis, typhoid fever, amoebiasis and other parasitic diseases). However, no specific microflora has yet been discovered that is likely to cause inflammation.
Vascular theory
Systemic vasculitis is a serious disease that affects blood vessels throughout the body. According to this theory, such diseases can provoke changes in the vessels of the appendix, disrupt the outflow of blood from it and become the cause of inflammation - appendicitis.
Endocrine theory
It has already been proven that the intestinal mucosa contains cells that have endocrine properties and release hormones into the blood (APUD system). In the appendix, these cells are present in large numbers, and one of their hormones is serotonin, a powerful mediator of inflammation, which under certain circumstances can provoke damage to the appendix itself.
Signs of appendicitis in adults
The symptoms of appendicitis are so diverse that they can confuse even the most experienced specialist. It’s not for nothing that this pathology even has a characteristic nickname – “chameleon”. Inflammation of the appendix can resemble almost any disease in its symptoms.
Probably everyone knows that pain with appendicitis is localized in the right iliac region. Indeed, this happens in most cases, but not always. The long process can descend into the small pelvis and manifest itself as a gynecological or urological pathology. Sometimes the appendix is located high under the liver, and the symptoms of its inflammation in such cases resemble cholecystitis. Cases have been described where the inflamed appendage was located in a diaphragmatic hernia located in the chest, but they are extremely rare.
The most typical symptoms that occur with appendicitis
- Pain that occurs in the epigastric region (upper abdomen). Sometimes the patient cannot localize the sensation because the entire abdomen hurts, but not severely. Gradually, the pain sensation shifts downwards to the iliac region on the right. The intensity of pain is moderate and gradually intensifies as the disease progresses. At this stage, an unpleasant phenomenon may occur - as a result of the death of nerve receptors along with the tissue of the appendix, the intensity of pain decreases. The patient notes an improvement in his condition and may refuse to visit a medical facility, which ultimately leads to bad consequences.
- The painful sensation noticeably intensifies when changing body position, walking, coughing, which forces the patient to sit still, sometimes in an unusual position. Irradiation of pain to other areas in the typical form of the disease is extremely rare. This phenomenon is characteristic of inflammation of the appendage located in an atypical location, as mentioned earlier.
- Lack of appetite.
- Dyspeptic symptoms, manifested by nausea and vomiting (1-2 times), which does not bring the expected relief, but is of a reflex nature. If the patient feels nauseous and vomits before pain occurs, one should consider whether it is appendicitis.
- Body temperature rises to low-grade levels (rarely exceeds 38°C).
- An increase in heart rate is triggered by an increase in body temperature.
- Loose stools and frequent urination.
Appendicitis during pregnancy
A pregnant woman is not immune from developing the same diseases that affect other people at different intervals. Acute appendicitis is the most common surgical pathology requiring surgical intervention in pregnant women (1 case in approximately 700-2000 pregnancies). Since the uterus in pregnant women increases significantly, this leads to an inevitable change in the location of the internal organs. Together with the cecum, the vermiform appendix also shifts, which in case of inflammation complicates its timely diagnosis. If severe complications develop, it is possible to terminate the pregnancy.
The clinical picture is somewhat blurred by the fact that a pregnant woman undergoes metabolic, hormonal and physiological changes in her body. The anterior abdominal muscles are relaxed as a result of being stretched by the ever-growing uterus.
Depending on the stage of pregnancy, pain can be located both in the right iliac region (typical of the first trimester) and in the right hypochondrium (late stages). Diagnosis is carried out with special care, and if an inflamed appendix is detected, intervention is performed immediately. Anesthesiologists for pain relief choose those drugs that are safest for the child, and surgeons try not to disturb the enlarged uterus.
Duration and nature of the disease
There are cases when chronic appendicitis can bother a patient for several months, and patients living with this diagnosis can feel constant abdominal pain for a long time. The inflammatory process can manifest itself for several days, and then go away and not bother you for a long time, or constantly create discomfort and remind you of itself.
Sometimes the appendix cannot be surgically removed due to the formation of an appendiceal infiltrate (a case where the density of the lump contains connections with other organs). If a repeated attack of appendicitis occurs under such circumstances, the disease becomes chronic and at this stage can persist for a long time, sometimes for several months. During this period, the patient may experience both constant aching pain and impulsive attacks that bother from time to time.
At the stage of chronic appendicitis, other manifestations of the disease are possible. An attack can pass quickly - literally in one day, and this is explained by the peculiarity of the foci of inflammation. In response to the question whether appendicitis can hurt for a long time, experts say that only at the chronic stage can this disease bother you for a long period.
Diagnosis of appendicitis in adults
All diagnostic measures begin with a general examination, during which an experienced doctor can detect some symptoms characteristic of this disease.
- Pain on palpation in the right iliac region, as well as at characteristic points (on the line connecting the navel and the iliac spine, as well as the line passing through the upper anterior iliac spines).
- More than a hundred symptoms of appendicitis have been described, which have become “family” as a result. Listing them all is pointless, so only the most relevant ones will be listed. Bartholomew-Michelson's symptom is the occurrence of pain on palpation of the cecum with the patient positioned on the left side.
- Voskresensky's symptom - the physician pulls the patient's shirt over his stomach and, during exhalation, makes a rapid sliding movement downward. The patient will experience a sharp increase in pain.
- Kocher's symptom is the occurrence of pain initially in the epigastric region and its gradual (after 1-3 hours) displacement to the right iliac region.
- Obraztsov’s symptom – pain intensifies when applying pressure to the cecum and simultaneous raising of the right leg, straightened at the knee joint.
- Ostrovsky's symptom - the patient raises his right leg up in a straight position and holds it there. The doctor quickly unbends her and puts her in place. In this case, a sharp increase in pain is noted in the right iliac region.
- Razdolsky's symptom - when percussing the anterior wall of the abdominal cavity, pain is detected in the right iliac region.
- Rovsing's symptom is an increase in pain in the right iliac region when applying pressure to the sigmoid colon (it is located in the left iliac region) and jerking effects above the sigmoid colon.
- Sitkovsky's symptom - when the patient is positioned on the left side, there is an increase in pain. This occurs due to the fact that the mesentery of the cecum is stretched and the appendix experiences some tension.
- The Shchetkin-Blumberg symptom is an increase in pain when, after applying pressure to the right iliac region, the physician abruptly removes his hand. This is called inverse sensitivity.
- Laboratory testing can detect an increase in the level of leukocytes in the blood, as well as the erythrocyte sedimentation rate.
- Ultrasound examination - free fluid is determined in the abdominal cavity (either directly near the appendix, or in the pelvis, under the influence of gravity). The process itself can be seen infrequently (only in the case of significant hypertrophy). When the wall of the appendix is perforated, free gas is detected in the abdominal cavity.
- Diagnostic laparoscopy is an invasive method, but at the same time very informative. They resort to it only in the most doubtful cases. Modern instruments have a very small diameter, are inserted near the navel through a small puncture and leave virtually no traces behind. Doctors use a video camera to examine the contents of the abdominal cavity and, if an inflamed appendix is detected, they immediately remove it.
- Computed tomography is an expensive and informative method that is not available to all clinics.
Differential diagnosis
As has already been said many times, appendicitis can disguise itself as a variety of diseases, therefore, its differential diagnosis is carried out with a host of pathologies:
- acute cholecystitis,
- viral mesadenitis,
- pyelonephritis on the right,
- renal colic on the right,
- acute right-sided adnexitis,
- ovarian cyst rupture
- ectopic pregnancy,
- exacerbation of peptic ulcer disease,
- intestinal obstruction, etc.
After doctors are convinced of the correctness of their diagnosis, the patient is immediately treated, which can only be surgical.
How does it manifest in young patients?
If appendicitis is suspected, symptoms in children may be mild. It is especially difficult to identify the disease in children under 5 years of age. Sometimes appendicitis in children has symptoms of stomach upset. Moreover, it is worth noting that diarrhea in adults with the development of this disease occurs much less frequently than in children.

Often the painful sensations are not located in the right iliac region. Small children generally cannot explain where it hurts. Therefore, diagnostic methods in this case are special. In addition to diarrhea, the child may experience anxiety and the tongue may become coated. The temperature rises to 38 ºС. These symptoms are very similar to poisoning. Therefore, self-medication is extremely undesirable.
Only after a full diagnosis can the exact cause of such symptoms be established. The child will definitely need to be seen by a pediatrician.
Treatment of appendicitis in adults
Treatment for patients with appendicitis involves removing the appendix. Currently, experienced surgeons perform this intervention quickly, through a small incision and with high quality. According to unofficial statistics, some professionals manage to complete all manipulations in about 10-15 minutes. Of course, doctors do not strive to do everything as quickly as possible and set a record; the patient’s health is always the main priority.
Technique for removing the appendix by open surgery
- An oblique incision is made in the right iliac region, and all tissues of the anterior abdominal wall are dissected layer by layer. In this case, the muscles are separated in a blunt manner, which ensures less tissue damage.
- The cecum, together with the appendix, is brought out into the wound, clamps are applied to the mesentery of the appendix, and its vessels are ligated (sometimes special clips are applied to them). Thanks to this, it is possible to avoid bleeding when dissecting the mesentery of the process.
- A special purse-string suture is placed on the cecum near the base of the appendix, which will be useful to doctors a little later. A clamp is applied directly to the appendage, it is tied with thread, and then intersected. The stump is treated with an antiseptic to prevent contamination of the peritoneum with bacteria from the intestinal tract.
- The previously applied purse-string suture is tightened, making it possible to immerse the resulting stump into the cecum. Another special seam is placed on top, which provides greater reliability.
- Sutures are placed on all layers of the anterior abdominal wall, and a sterile bandage is placed over the wound.
Sometimes the process grows tightly together with the surrounding tissues, which forces doctors to resort to other techniques.
- First, the cecum with the base of the process is found and it is cut off (the same as in the previous case).
- Gradually, the process is carefully separated from the surrounding tissue until the doctor reaches its tip. At this point, it is important to ensure that everything at the site of its cutting is securely bandaged, since infected contents may enter the abdominal cavity and increase the risk of complications.
Otherwise, this operation does not differ from the standard intervention.
Laparoscopic intervention
Today, technology has come a long way, allowing surgery to be performed with minimal damage to the patient’s body. More and more often, appendicitis is treated using a laparoscope and special manipulators.
- This intervention is performed only under general anesthesia (anesthesia).
- Carbon dioxide is pumped into the abdominal cavity and creates pressure, which “lifts” the overhanging abdominal wall and forms a kind of dome, under which space is created for the surgeon to act.
- A small incision is made near the navel (less than a centimeter), and a video camera is inserted through it, which will ensure that everything that happens “in the stomach” is displayed on the screen.
- Two more incisions are made slightly lower and through them manipulators are inserted, which are controlled by the doctor, and they perform the function of his hands. Everything is done under magnification, due to which it is possible to achieve high accuracy.
- All actions are the same as when performing a traditional operation.
- The manipulators are removed from the abdominal cavity, the gas exits independently through the formed holes. Sutures are placed at the puncture sites (1-2, no more).
Techniques have emerged that make it possible to remove the appendage through the natural openings of the body. Successful operations performed through the mouth have already been described. In this case, the incision is made from inside the stomach, manipulators are inserted into the abdominal cavity and the intervention is carried out in much the same way as with standard laparoscopy. The undeniable advantage of the method is that no traces remain on the patient’s body. There is also evidence that this method of performing the operation ensures a speedy recovery for the patient.
As can be seen from everything said above, appendicitis in adults is a well-studied disease that doctors successfully treat. However, the patient must also provide assistance, which consists of timely contacting specialists and fulfilling all their requirements.
Appendicitis or gynecological disease?
The first signs and symptoms of appendicitis in men are practically no different from the complex of manifestations of this pathology in girls. The only necessity due to the anatomical and physiological differences of the female body is the importance of excluding gynecological disorders.
To differentiate inflammation of the appendix from adnexitis, they resort to vaginal (less often rectal) examination. Promptov's symptom is considered positive if a woman experiences increased pain when the cervix is displaced. The sign indicates the presence of inflammatory changes in the appendages and highly likely excludes appendicitis.