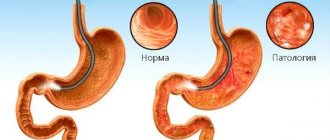
Focal gastritis is an inflammatory disease of the gastric mucosa. A characteristic feature of this type of disease is the presence of hyperplastic lesions of the gastric wall; the most vulnerable place is the antrum of the stomach.
What is this disease, how to treat focal gastritis, what types of disease are there and what measures need to be taken to eliminate the disease - all this is discussed further in the article.
Description and general characteristics of the disease
Let us note right away that such a concept as focal gastritis is not an exact term characterizing the disease. This definition only allows us to characterize the disease from one aspect only—the localization of the inflammatory process. This means that the final diagnosis will differ from the simple name “focal gastritis” - as a rule, the diagnosis will contain a description of the damage to the mucosa, as well as the location of this damage. That is why the focal form of gastritis may be called differently - for example, the superficial antral form of gastritis.
The inflammatory process and the focus of the disease itself can spread both to the entire mucous membrane of the stomach (typical of pangastritis) and to its individual sections. With local lesions, it is appropriate to talk specifically about the focal form of the disease.
The mechanism of development of the disease is no different in nature from other forms of gastritis - the etiology and pathogenesis are in many ways similar to those of other types of gastritis.
Diet
One of the main components of successful treatment of gastritis of any etiology is diet, since food is the main irritating factor for the inflamed gastric mucosa and provokes complications.
It is strictly forbidden to eat:
- Spicy, salted and pickled vegetables;
- Mushrooms in any form;
- Fried meats and stews;
- Pork in any form;
- Fatty fish;
- Fresh bread, pastries and cakes;
- Grapes and drinks made from them;
- Fresh fruits;
- Alcohol, coffee.
Allowed:
- Boiled meat and lean sea fish;
- Dairy and fermented milk products;
- Olive oil and butter;
- Dry white bread and biscuits;
- Porridge, except corn and millet;
- Boiled vegetables;
- Boiled fruits and fresh berries;
- Jam, marshmallow, marshmallow.
Classification and types of focal forms of gastritis
In order to consider in more detail what it is - focal gastritis, we will indicate the types of disease distinguished in medicine:
- When determining the overall picture, superficial, hypertrophic and atrophic forms of focal gastritis are distinguished;
- Depending on the intensity of secretion production (gastric juice), forms with high, low and normal acidity are distinguished;
- According to the form of the disease, a distinction is made between chronic and acute forms;
- Depending on the frequency, the patient may experience the disease in remission or exacerbation.
Let's take a closer look at the most common types of focal gastritis.
Surface form
There is a clear localization of painful sensations. Inflammatory foci form in the area of the surface epithelium in the area connecting the stomach and duodenum. The inflamed focus provokes insufficient production of secretion that protects the walls from the effects of gastric juice, thereby provoking further progress of the disease.
Causes of focal gastritis of the stomach and its treatment regimen
It is difficult to find a person who has never had stomach pain. But if these pains become regular, then you should not take your condition lightly. Perhaps these are signs of inflammation of the mucous membrane of the digestive organ.
One of the varieties of this disease is focal gastritis. The peculiarity of this disease is that the lesion is located in patches and does not cover the entire surface of the mucosa. Thus, the name of the disease characterizes only the location of the foci of inflammation, but not the nature of the lesion.
Causes
Before undertaking treatment, it is necessary to find out the causes of the disease. Gastritis belongs to a group of diseases that can be caused by a number of factors. The most common cause is damage to the mucous membrane by bacteria.
This is a special type of microorganisms that are able to survive in an aggressive, strongly acidic environment. These bacteria are called Helicobacter pylori. Infection does not always lead to the development of inflammation. But under conditions favorable for pathogens, bacteria begin to actively multiply, penetrating into the mucous membrane and causing an inflammatory reaction.
Bacteria can cause gastritis with focal atrophy of the mucosa, which causes a number of digestive dysfunctions and increases the risk of developing malignant tumors. The following factors may play a role in the development of focal gastritis:
- improperly organized nutrition - unbalanced diet, long breaks between meals, fasting or overeating, choice of unhealthy foods - smoked, fatty, fried, etc.;
- drinking large amounts of alcohol, not only strong but also low-alcohol drinks;
- smoking also contributes to the development of inflammation in the digestive organs;
- long-term use of certain groups of medications, in particular anti-inflammatory drugs, antibiotics, hormonal drugs;
- hereditary predisposition, in particular, congenital weakness of the sphincter that separates the lower part of the stomach from the upper part of the intestine.
Advice! Age plays a significant role in the development of the disease. In people over 60-65 years of age, the likelihood of developing focal atrophic gastritis increases.
A common cause of the development of diseases, including stomach diseases, is constant stress. Of course, it is almost impossible to isolate yourself from the world and live in complete peace and harmony with yourself, however, it is not the stress itself that “kills” our stomach, but our attitude towards it.
Namely, the constant “savoring” of one’s grievances destroys the nervous system and our body as a whole.
Atrophic
The most dangerous type is atrophic focal gastritis. A feature of this disease is the formation of atrophied areas of the mucosa and the death of active glands that produce digestive enzymes.
As a result, digestion processes are disrupted, and the mucous layer gradually becomes thinner. In the focal form of the lesion, atrophic processes occur in individual areas, but over time, the affected area expands more and more.
The danger of this disease lies in the formation of tumors; atrophic gastritis can occur with hyperplasia, that is, with tissue proliferation. In this case, polyps or folds are formed. Neoplasms can be either benign or malignant.
Surface
With focal superficial gastritis, only the upper part of the mucous layer is affected. With this disease, the glands that produce gastric juice are not affected, so the digestive processes are practically not disrupted.
Thus, manifestations of superficial focal gastritis are the initial stage of the disease. At this stage, foci of superficial inflammation are formed. But if treatment is not carried out, the lesions tend to grow.
Inflammation can occur against the background of mucosal atrophy or be primary. The lesions can be localized in one part of the stomach or be randomly located. In this case, the inflamed surface may undergo atrophic processes over time.
With primary superficial gastritis of focal form, coping with the disease is not difficult. In some cases, it is enough to switch to a diet for the mucous membrane to recover. But if the disease is advanced, then long-term and necessarily complex treatment is required.
Antral
Depending on the location of the foci of inflammation, several forms of the disease are distinguished. Most often, cases of focal antral gastritis are diagnosed. In this case, the foci of inflammation are located in the lower section (antrum). This section is connected to the upper intestine and performs very important functions.
With an infectious lesion, secretory function is disrupted, which leads to an increase in the acidity of digestive juices. Therefore, food enters the intestines overacidified, although normally most of the acid should be neutralized.
Signs of focal antral gastritis of the stomach are difficult to miss; the disease manifests itself with pain and frequent heartburn. With timely treatment, you can successfully cope with this disease.
Chronic
If acute focal gastritis is not treated in a timely manner, it will become chronic. Often, chronic focal gastritis develops gradually, since a person in the initial stages simply does not pay attention to the signs.
A characteristic feature of this form of the disease is that the disease occurs in waves. Relatively calm periods alternate with exacerbations. A relapse can be triggered by a diet disorder, any illness, stress, overwork and other negative factors.
Medicines
A number of drugs are used for the medical treatment of focal atrophic gastritis. Focal atrophic gastritis should be treated taking into account the level of acidity. Thus, in the atrophic form, secretory function is reduced, so it is necessary to use replacement therapy.
Enzyme preparations and gastric juice substitutes are prescribed. If the level of acidity is elevated, drug treatment is prescribed aimed at normalizing secretory function. Are used:
- proton pump inhibitors – Omeprazole and analogues;
- antacids - substances that neutralize excess acid, for example, Maalox.
To get rid of nausea, medications are prescribed that normalize the motor functions of the gastrointestinal tract, eliminating the stagnation of food in the stomach. To eliminate pain, antispasmodics or analgesics are used. To exclude dysbiosis during antibiotic treatment, drugs containing beneficial microflora are prescribed.
Folk remedies
Treatment with folk remedies is used as an auxiliary treatment. A course of taking herbs or special preparations that have the following therapeutic effect is prescribed:
- anti-inflammatory;
- regenerating;
- enveloping.
Most often, the following means are used:
Advice! It is convenient to use ready-made gastric preparations, which are sold in pharmacies. The choice of collection option should be discussed with a gastroenterologist.
Diet
Following a diet for focal atrophic gastritis is a prerequisite for recovery. With focal gastritis of the stomach, avoid foods that are difficult to digest and irritate the mucous membranes of the gastrointestinal tract.
The menu for focal atrophic gastritis includes porridges, soups cooked in water or low-fat broth, steamed meat or fish dishes. You need to be careful when preparing your diet; it must be complete, fully providing the body with nutrients.
You need to eat regularly and be sure to eat small meals. Dishes should be served at a temperature of 37-38 degrees. Foods and drinks that are too hot or too cold are excluded. The volume of food that the patient eats at one time should not exceed 250 ml, but the number of meals can be increased to 6-8 times a day.
Prevention
Prevention of the development of focal gastritis involves maintaining a healthy lifestyle. It is difficult to prevent Helicobacter pylori infection, but with a normally functioning immune system, these pathogenic microorganisms cause virtually no harm.
Patients need to follow a diet for a long time. This is not as difficult as it might seem, because the diet during the remission period is quite wide. However, patients need to avoid foods that irritate the mucous membranes.
These are smoked meats, marinades, fatty foods, fried dishes with an appetizing golden brown crust. In addition, you need to avoid stress, try to follow a routine, get proper rest, and be physically active.
So, focal gastritis is a form of the disease in which the affected area is limited. However, over time, foci of inflammation can expand, spreading over increasingly larger areas. The easiest way to cure the superficial form of focal gastritis. More serious lesions require serious treatment and long-term diet.
Source: https://vnorg.ru/zheludok/gastrit/183-ochagovyj-gastrit.html
Causes of the disease
In the case of the development of a focal form of gastritis, the etiological factors for the development of the disease are considered to be the same factors that provoke the development of other types of gastritis. That is why endogenous and exogenous factors include the following:
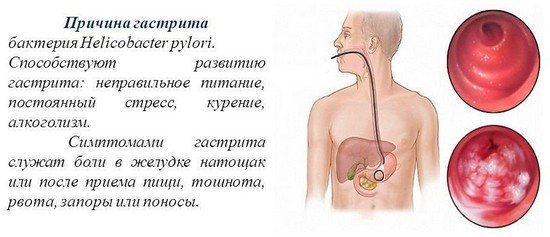
- Poor nutrition with excess spicy and sour foods, bad habits;
- Infection of the stomach by Helicobacter pyloris - bacteria that in 90% of cases cause the development of antral and atrophic forms of gastritis;
- Long-term or uncontrolled use of glucocorticosteroid drugs, as well as non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs;
- Chronic stress and overwork.
The disease can develop for a number of other reasons - hormonal imbalances, duodenal reflux, poisoning, the presence of other diseases of the digestive system, decreased immunity or age-related changes, however, according to statistics, they cause the development of the disease in no more than 10% of all cases of clinical practice.
Nutrition
During the acute period of the disease, split meals of boiled or steamed foods with a minimum salt content are recommended.
- Portions should be the size of an adult’s fist, according to scientists - this volume is most optimal for the successful functioning of the stomach.
- It is advisable that all food be pureed.
- Only freshly prepared food should be consumed.
Liquid dishes, including tea or compote, should be eaten and drunk first, or an hour after eating.
This is due to the fact that during meals the intensity of gastric juice production is maximum, and food is well digested. Liquid drunk after a meal mechanically washes away most of the digestive enzymes.
It is important to remember that without strict adherence to a diet, gastritis cannot be cured, so you should adhere to the recommended dietary rules for at least a month.
Menu for the day
Breakfast: Soft-boiled egg, a piece of dry white bread, sweet tea. 2nd breakfast: oatmeal on water with a piece of butter without salt and sugar, milk jelly. Lunch: Rice soup with vegetable broth, veal dumplings with a side dish of boiled carrots, dried fruit compote. Afternoon snack: baked apple puree with cottage cheese. Dinner: baked potatoes and boiled chicken breast and sour cream sauce, sweet tea, a piece of marshmallow. 2nd dinner: A glass of fermented baked milk with a piece of dry biscuits.
Symptoms of focal gastritis
Focal gastritis is characterized by the following symptoms:
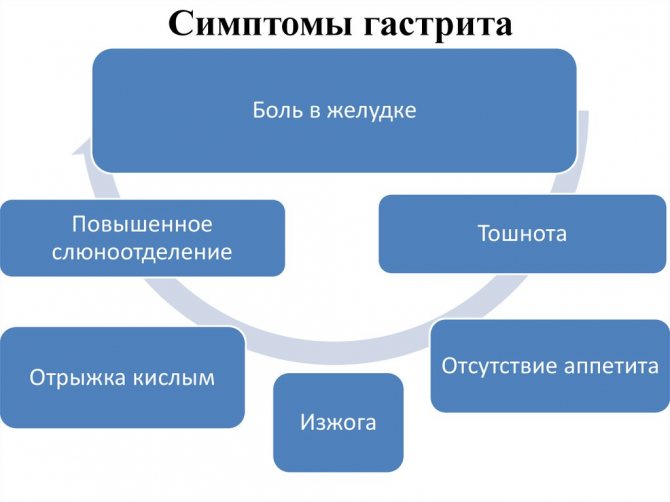
- Painful sensations occurring in the ribs on the lower left side;
- Feeling of fullness and heaviness in the stomach even with a small meal;
- Various dyspeptic disorders, in particular - stool disorders, nausea, bloating;
- Decreased appetite, in some cases - a change in taste preferences;
- In the morning and as the feeling of hunger increases, painful sensations also intensify, which can be relieved with a small amount of food;
- Loss of body weight;
- Heartburn, increased secretion of saliva.
Doctors
A person who periodically experiences pain in the stomach should consult a gastroenterologist to clarify the diagnosis. After the examination, the doctor will prescribe treatment.
In addition to a gastroenterologist, you should definitely try to get an appointment with a nutritionist, since healing depends on a properly formulated diet. Only by following a diet can you permanently get rid of focal gastritis using conservative methods, without resorting to surgery.
Focal gastritis is an inflammation of the inner surface of the stomach, localized in a specific area. The term indicates only the external manifestation of the disease and is usually supplemented during diagnosis with the name of the specific form of the disease. Without treatment, the disease can lead to the development of erosion, ulcers and even oncology, so it is important to consult a doctor in a timely manner.
Diagnosis of focal gastritis
In order to diagnose focal gastritis, special studies are carried out, such as:
- A general blood test, through which you can detect the level of hemoglobin (a low, falling level of hemoglobin is quite often a sign of organ damage and the development of autoimmune cell damage);
- Stool coprogram - analysis of the coprogram helps to identify diseases and exclude the occurrence of damage to the pancreas;
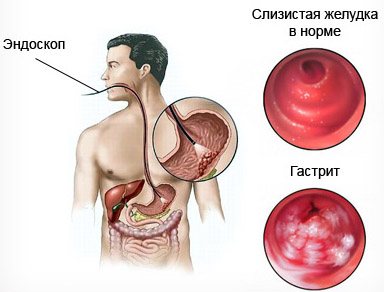
- Fibrogastroduodenoscopy is the best way to determine the reliability of the diagnosis, thanks to visualization of the gastric mucosa, it allows you to accurately diagnose gastritis;
- The breath test determines the level of ammonia, as well as the presence of the bacterium Helicobacter pylori in the body;
- ELISA analysis - a blood test helps to reliably determine the presence of Helicobacter pylori in the body.
Gastroscopy is also an instrumental way to determine focal gastritis. It is carried out thanks to a special probe that is inserted into the stomach. Thanks to the presence of lighting and optics at the end of the probe, you can view the stomach from the inside and assess its condition. During this procedure, a biopsy sample is taken, which is sent for histological analysis to identify cancer cells.
How to treat gastritis of the stomach stump

There are many reasons for it. Almost every person acquires the disease through his own systematic actions, and, sometimes, consciously. In the future, it is quite difficult to overcome yourself and recover by changing your lifestyle. There are cases when the gastric mucosa becomes inflamed and not through the fault of the person himself, but due to surgical intervention. Gastritis of the gastric stump is a chronic inflammatory process in this organ, most often resulting from surgical operations. Usually, they are resorted to in the following cases: progression of oncological tumors, ulcers, hypertrophic gastropathy, Zollinger-Ellison syndrome.
Most often, the factors contributing to the occurrence of gastritis of the gastric stump are:
- non-compliance with the rules and regulations of the operation;
- incorrectly drawn up rehabilitation scheme;
- a frivolous approach to treating the patient himself.

Often the manifestations of the disease are superimposed on the symptoms accompanying the result of resection. This can be confusing when making a diagnosis. After excision of the damaged lobe of this organ, patients feel: fullness, compression, turning into distension in the pit of the stomach. They have a hard time after eating even a small portion of food. As a rule, any consumption of food is accompanied by belching and a feeling of nausea. This is called stump syndrome. Such manifestations become regular due to changes occurring in the gastric mucosa. It gradually atrophies, and in some places its cells degenerate into similar ones that line the intestines. Naturally, the acidity in the digestive organ also changes. This is expressed in a gradual decrease in the production of hydrochloric acid and pepsin. The release of food into the intestines is noticeably accelerated, which affects the quality of its processing and the absorption of nutrients. Therefore, patients who have undergone resection often suffer from asthenia and anemia. In addition, changes in the mucosa can even spread to the small intestine (more precisely, its upper section). It is often accompanied by the formation of erosions. Since digestion is disrupted already at the initial stages, dysfunction of other organs is added to the processes described above. As a result, the liver, pancreas, and bile ducts also work incorrectly.

Treatment of gastritis of the gastric stump involves the use of a conservative method, expressed in such measures as:
- Taking vitamin complexes containing a set of them: C, B1, B2.
- Consumption of deficient enzymes, hydrochloric acid.
- Gastric lavage procedure using saline solution.
- Drinking mineral waters in a sanatorium.
- Nutrition according to diet No. 1, moving into scheme No. 2 as the patient’s general condition improves.
The patient should treat the last component of the treatment of gastritis of the gastric stump very carefully. What he eats and how it is prepared determines how quickly the unpleasant symptoms disappear and digestion improves. Within the first two weeks a person will feel much better. To do this, you need to organize 4-6 meals a day in small portions. Ready-to-eat food should be no warmer than body temperature. As for food restrictions, during the diet everything unhealthy is excluded: spicy, salty, smoked, fried. You cannot eat strong tea, coffee, fresh juices or fruits without heat treatment. Do not eat cereals that are difficult to digest, fresh bread, sweets, fatty meats and fish. Broths from the latter are also not cooked. The basis of soups should be vegetable broth, and the dressing should be butter or vegetable oil. All dishes must be well boiled or steamed and pureed until pureed. The consumption of milk and non-acidic products made from it is encouraged.
Gastritis of the gastric stump can be treated with fairly simple methods, but they require patience from the patient. Without it, efficiency, if not absent, is noticeably lower than it should be.
source
Inflammatory changes in the gastric mucosa in the patients we examined were found after gastric resection according to Billroth-1 in 27.3% of cases, after resection according to B-2 in 32.7%.
Pathogenesis. Concomitant changes in the mucous membrane that occurred even before surgery contribute to the development of gastritis.
In addition, the throwing of duodenal and intestinal contents into the stomach, both during anastomosis along B-1 and B-2, is important in the origin of inflammatory complications. Often, simultaneous inflammatory phenomena are observed in the area of the anastomosis. The frequency of gastritis depends on the period that has passed since the operation.
When the mucous membrane becomes inflamed, the motor and evacuation functions of the stomach are disrupted. Subsequently, they contribute to the development of such severe complications as dumping syndrome and afferent loop syndrome.
Clinical picture. Patients note pain and a feeling of heaviness in the epigastric region, nausea, heartburn, and belching. At times there is diarrhea. Characterized by decreased or lack of appetite and weight loss. Patients' ability to work decreases.
When palpating the abdomen in the phase of exacerbation of the disease, a mild diffuse pain in the epigastric region is determined.
Diagnostics. The diagnosis takes into account anamnestic data and symptoms of physical examination. According to our studies, the acid-forming function of the stomach was increased in 34.4% of cases, decreased in 56.25%, and normal in only 9.35%.
An X-ray examination reveals symptoms of changes in the relief of the mucous membrane: the folds of the mucous membrane are rough, tortuous, and swollen. Inflammatory changes are most pronounced in the area of the anastomosis. The contrast agent is quickly evacuated into the outflow loop of the anastomosis.
During endoscopy of the mucous membrane of the gastric stump, swelling, hypertrophy, and mucus are often found. In 3.8% of cases, erosions are detected. A morphological study of gastrobiopsy specimens is being carried out. In this case, the following histological changes occur: superficial gastritis in 21.7% of cases, gastritis with damage to the glands without atrophy in 14.5% of cases, atrophic in 47.8% of cases, with pyloric type restructuring of the glands in 24.6% of cases, of the intestinal type in 11.6% of cases and the predominance of inflammatory changes in 60% of cases.
Treatment. Our long-term observations of post-gastroresection disorders have shown that pathogenetic therapy should be structured differentially, taking into account secretory disorders of the operated stomach. Against the background of an appropriate diet, a synthetic analogue of the gastrointestinal hormone, pentagastrin, in combination with the anabolic drug Nerobolil, has a positive therapeutic effect in case of reduced secretory function of the stomach, and in case of increased secretory function of the stomach, the histamine H2 receptor blocker famotidine in combination with Nerobolil.
A study of Helicobacter pylori in patients with peptic ulcer after gastric resection showed that in most patients Helicobacter pylori (HP) persists even after surgery. A definite relationship has been noted between HP infection and inflammation of the mucous stump of the stomach during gastritis, anastomositis, erosions and peptic ulcer of the gastroenteroanastomosis. This must be kept in mind when prescribing antibacterial drugs as part of complex therapy.
When carrying out anti-Helicobacter therapy, the most popular now is the so-called double regimen (omeprozole 20 mg 2 times a day and amoxicillin 1 g 2 times a day or clarithromycin 500 mg 3 times a day for 2 weeks). At the same time, the so-called “classical” triple schemes prescribed within 1 week have not lost their significance:
a) colloidal bismuth subcitrate 120 mg 4 times a day in combination with metronidazole 400 mg 3 times a day and tetracycline or amoxicillin 500 mg 4 times a day for 2 weeks;
b) omeprozole 20 mg per day in combination with clarithromycin 250 mg 2 times a day or metronidazole 400 mg 2 times a day. In the treatment of HP, combinations of 4 drugs are also used: omeprozole 20 mg per day, colloidal bismuth subcitrate 120 mg 4 times a day, tetracycline 500 mg 4 times a day and metronidazole 400 mg 3 times a day. The effectiveness of these anti-Helicobacter therapy regimens reaches 90% or higher. The effectiveness of antimicrobial therapy is monitored 4-6 weeks after its completion. If HP is preserved in the gastric mucosa, a repeat course of anti-Helicobacter therapy is indicated, that is, the use of a different regimen, in particular a combination of 4 drugs, with subsequent monitoring of its effectiveness also after 4-6 weeks.
Date added: 2014-12-12 | Views: 1855 | Copyright infringement
source
Have you been struggling with GASTRITIS and ULCERS for many years without success?
Head of the Institute: “You will be amazed at how easy it is to cure gastritis and ulcers simply by taking it every day.
Inflammation may appear suddenly (acute gastritis) or develop slowly (chronic gastritis). In some cases, this process can lead to ulcers and increase the risk of stomach cancer. The gastric mucosa contains special cells that produce acid and enzymes that begin to digest food. This acid can potentially break down the lining itself, so other cells produce mucus that protects the stomach wall.
Our readers successfully use Monastic Tea to treat gastritis and ulcers. Seeing how popular this product is, we decided to bring it to your attention. Read more here...
Inflammation and irritation of the mucous membrane develops when this protective barrier of mucus is disrupted - with increased acidity, due to the action of the bacterium H. pylori, after excessive alcohol consumption. For most people, this inflammation is not severe and goes away quickly without treatment. But sometimes it can last for years.
Inflammatory diseases of the mucous membrane can cause:
If the mucous membrane is damaged, this is considered erosive gastritis. Areas of damaged gastric mucosa that are not protected by mucus are exposed to acid. This can cause pain, lead to ulcers and increase the risk of bleeding.
If symptoms appear suddenly and are severe, these are considered signs of acute gastritis. If they last a long time, this is chronic gastritis, which is most often caused by a bacterial infection.
The causes of the inflammatory process in the mucous membrane can be:
- The infectious process is almost always a Helicobacter pylori infection.
- Using cocaine or alcohol.
- Constant use of painkillers from the group of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs).
- Stress for the body is injury, illness or surgery. The exact mechanism of how stress and severe illness can lead to inflammation of the mucosa is unknown, but it may be due to decreased blood circulation in the stomach.
- Autoimmune process. This type of inflammation occurs when the body attacks its own cells in the stomach lining. This autoimmune reaction can lead to a breakdown of the mucosal barrier and is more common in people with other autoimmune diseases, including Hashimoto's disease and type 1 diabetes.
- Antacids – These medications neutralize acid in the stomach, providing quick pain relief.
- H2-histamine receptor blockers (Famotidine, Ranitidine) - these drugs reduce acid production.
- Proton pump inhibitors (Omeprazole, Pantoprazole) – these drugs reduce acid production more effectively than histamine H2 receptor blockers.
If left untreated, the inflammatory process can lead to the formation of ulcers and bleeding. In rare cases, certain forms of chronic gastritis can increase the risk of stomach cancer, especially if inflammation causes the lining to thicken and change its cells.
To detect inflammation of the gastric mucosa, it is necessary to perform an endoscopy. A thin and flexible endoscope is inserted down the throat into the esophagus and stomach. With its help, you can detect the presence of inflammation and take small particles of tissue from the mucous membrane for examination in the laboratory (biopsy). Carrying out a histological examination of tissue under a microscope in the laboratory is the main method of confirming the presence of an inflammatory process in the gastric mucosa.
An alternative to endoscopy is a barium X-ray examination of the stomach, which can detect gastritis or stomach ulcers. However, this method is much less accurate than endoscopy. Tests to detect H. pylori infection can be done to determine the cause of the inflammation.
Treatment of gastritis depends on the specific cause of inflammation of the mucous membrane. Acute inflammation caused by NSAIDs or alcohol can be relieved by stopping the use of these substances. Chronic inflammation caused by H. pylori is treated with antibiotics.
In most cases, the patient's treatment also aims to reduce the amount of acid in the stomach, which relieves symptoms and allows the stomach lining to heal. Depending on the cause and severity of gastritis, the patient may be able to treat it at home.
If a patient with gastritis is found to have this microorganism, he needs eradication (elimination) of H. pylori. There are several schemes for such treatment. The basic regimen consists of a proton pump inhibitor and two antibiotics.
The patient can relieve symptoms and promote mucosal recovery by following these tips:
- You need to eat in smaller portions, but more often.
- Irritating foods (spicy, fried, fatty and sour foods) and alcoholic beverages should be avoided.
- You can try to switch from taking NSAID painkillers to taking Paracetamoa (but you need to talk to your doctor about this).
- Stress needs to be controlled.
Herbal medicine can reduce inflammation and irritation of the stomach lining. It is believed that four herbs are especially effective in treating inflammatory diseases of the digestive tract and restoring the mucous membranes:
If even a single symptom of superficial gastritis appears, you should consult a doctor. If it is another disease of the digestive system, timely treatment will speed up recovery. Required research methods:
1. Blood test (general and biochemistry). Detection of leukocytosis, an increase in COE, and the appearance of acute phase proteins indicate a period of exacerbation. Bilirubin, protein, transaminases will help determine the condition of the biliary tract and liver.
2. Coprogram. Undigested proteins and fats in the feces indicate the addition of bulbitis, duodenitis, and damage to the pancreas.
3. The main method by which you can see changes in the stomach is FGDS. In the lower section there are foci of hyperemia and edematous mucosa. Areas of inflammation can be single or combined. Since the main cause is Helicobacter pylori, a biopsy needs to be taken for examination. Treatment and dietary features for gastritis will depend on the results. During remission, changes may be minimal.
4. A urease breath test is also used to determine the presence of bacteria.
5. To choose the right method of treatment and diet, it is necessary to measure acidity. In case of superficial gastritis, the level of hydrochloric acid is determined using pH-metry.
6. Ultrasound reveals pathology of the pancreas, bile, and liver; this method is necessary for differential diagnosis in case of similar symptoms.
Only a doctor, taking into account research data, can make an accurate diagnosis. It is also important to consider the phase of exacerbation or remission when choosing treatment tactics.
In addition to medications, diet and folk remedies play an important role, which will help cure the disease. Therefore, the doctor’s prescriptions also concern dietary habits.
1. Medications.
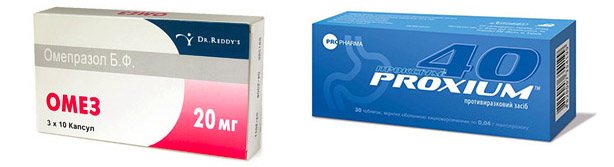
If Helicobacter pylori is detected, the main direction of treatment for superficial gastritis is eradication therapy. For 2 weeks, the patient takes antibiotics (clarithromycin, amoxicillin), bismuth preparations, proton pump inhibitors (Omez, Proxium). No earlier than four weeks later, the effectiveness of treatment for antral gastritis is assessed.
Helicobacter pylori is transmitted by airborne droplets. In order to avoid re-infection, it is necessary to examine relatives for the presence of this bacterium. Sometimes they have gastritis in remission, in which case it is very difficult to cure the disease.
- Medicines that reduce acidity: proton pump inhibitors and histamine blockers, in parallel with diet.
- Antacids: Almagel, Phosphalugel.
- Antispasmodics.
The diet for gastritis is aimed at minimal trauma to the mucous membrane and rapid restoration of damaged areas.
- Eating regularly will help cure the disease much faster. Small portions 5 times a day are recommended.
- The way the food is processed plays an important role. It is allowed to eat boiled and steamed food.
- Avoid fried, fatty, spicy foods.
- The food needs to be slightly warmed. No hot or cold food allowed.
- The basis of the diet is cereals, day-old bread, lean meat, fish.
- Vegetables and fruits during the period of exacerbation of superficial gastritis should be baked. Eat raw as puree. Limit fiber-rich foods.
A good way is to use traditional medicine recipes.
Honey reduces inflammation and relieves pain. You can consume honey itself or its solution one and a half hours before meals. When warm, it reduces acidity and normalizes stomach function. Dissolve two spoons of the product in a glass of water heated to 45-50 °C and drink in small sips. This is a safe way to relieve pain.
Raw potatoes are grated and the juice is squeezed out using gauze. It is recommended to start taking it with 1 tablespoon on an empty stomach, increasing the volume to half a glass. This folk method is used for high acidity, only with the permission of a doctor.
The drink is a good way to relieve spasms, heartburn, and reduce acidity. Pour boiling water over two teaspoons of flowers. Let it brew and consume it in the evening before bed or in the morning.
Our readers successfully use Monastic Tea to treat gastritis and ulcers. Seeing how popular this product is, we decided to bring it to your attention. Read more here...
The symptoms of antral gastritis are mild, but this disease cannot be ignored or self-medicated. This way you risk aggravating the situation, which will lead to complications. Only the doctor will choose an effective treatment method and select a diet. By following a specialist’s prescription, you can forget about digestive problems.
Today, many reasons are already known that lead to the development of superficial gastritis. The signs of superficial gastritis do not look too dangerous at first glance, but this impression is deceptive.
Gastritis, like many other gastrointestinal ailments, has different stages of its development, which can transform into one another if not treated in a timely manner. To better understand the danger of the disease, let's take a closer look at what superficial gastritis is and how many varieties it has.
What is superficial gastritis
And so, the first stage of the disease is superficial. This form of the disease does not cause much harm to human health, because the lesions are superficial. With this disease, the deep tissues of the stomach are not damaged. This ailment is very common, but, nevertheless, it is not mistaken for a dangerous condition. But in order to prevent various complications, treatment of superficial gastritis must be timely.
Unfortunately, many people’s opinion about the importance of the stomach is incorrect, and not everyone realizes its real importance, because human health and condition depend on the normal functionality of this organ. Since initially experts could not give an answer to what superficial gastritis is, this form of the disease was noticed, but no one knew how to treat gastritis of the stomach.
But, nevertheless, in practice it has become clear that superficial gastritis can be very dangerous and can sharply transform into a chronic form. This is what prompted experienced doctors to develop a system that would help cure superficial gastritis. Further in the article we will tell you what the endoscopic picture looks like, what you can eat and drink, what pills you are allowed to take, and also give recipes from the people, after which many who have experienced it feel much better.
Possible complications of gastritis
Symptoms of superficial gastritis are the first warning signs, upon noticing which a person should immediately go on a visit to the attending physician - a gastroenterologist. It is very important for any person to pay close attention to his stomach in order to notice any, even moderately expressed, sign.
To understand whether and how to get rid of the disease, it is necessary to clearly identify the form of the disease and its type, for example:
- Gastritis with mucosal atrophy.
- Superficial reflux gastritis (as well as DGR).
- Active superficial gastritis.
- Distal superficial gastritis.
- Fundal gastritis is superficial.
- Gastric and many others.
It is worth noting that the appearance of traditional gastritis should not cause excessive concern, but there is no need to let everything take its course. This disease, or rather its advanced form, may be a signal that a malignant process is occurring in the human body, for which it is usually impossible to treat.
Causes of superficial gastritis
I would like to immediately note that the symptoms and signs that exist with superficial gastritis are not always pronounced, and most often with this disease, its presence will become clear to the patient after a certain time, which costs some their lives. Since superficial gastritis does not show symptoms, many patients find out about its presence quite by accident, for example, during a medical examination. The reason lies in the fact that to diagnose this pathology it is necessary to perform gastric bypass surgery or gastroscopy (FGS).
Of course, FGDS, like endoscopy, is not a very pleasant procedure, but only with its help can one conduct a high-quality examination and find out the extent of the disease and other negative consequences. Please note that FGDS allows you not only to obtain photos of damaged cavities, but also to assess the degree of their damage and take a biopsy sample for analysis for subsequent research. Very often, if a patient’s diagnosis of superficial bulbitis is in doubt, doctors prescribe FGDS. The causes of superficial gastritis can be varied:
- Incorrectly composed menu (very often gastritis is diagnosed in children for this reason).
- Bacterium Helicobacter pylori.
- Unreasonable and prolonged use of medications, especially antibiotics.
- Frequent exposure to stress.
- Working with chemicals, etc.
As medical practice shows, if superficial gastritis bulbitis is provoked by a bacterium, the pain is often localized in the right hypochondrium, which is why many patients confuse the disease with pancreatic problems. As a rule, pain occurs after eating food. It happens that with such symptoms it is enough to use drugs that improve the digestive system and bring the patient closer to subremission.
Symptoms of superficial gastritis
In relation to superficial gastritis, it is allowed to use the expression “catarrhal” or “simple”. The younger the patient, the faster the process of restoration of the mucous membranes will be completed, so in a child this process will go much faster than in older people. But please note that the process of restoration of the mucous membrane will be completely completed only if the effect of the provoking factor is completely neutralized. The diagnosis of “superficial gastritis” may differ not only in the stage and form of the disease, but also in the intensity of pain, the nature of which can be:
Also, the symptoms of the disease may depend on the degree of changes, for example, in the chronic course of the disease, atrophy of the glands does not occur. This form can often be found among young representatives of the stronger sex. Sometimes, spasms can be intense (as with a peptic ulcer). At the same time, patient reviews speak of heaviness after eating, heartburn and frequent belching. If the patient has superficial gastritis, duodenitis progresses in an acute form, you may notice:
- Decreased appetite.
- General weakness.
- Dizziness.
- Nausea.
- Belching with a sour taste.
- Diarrhea.
- Dry mouth or, conversely, excessive salivation.
- Pallor of the skin.
- The appearance of a white coating on the tongue.
- Decrease in blood pressure levels.
- Increased heart rate.
Treatment of superficial gastritis
Very often, superficial gastritis and cardia insufficiency lead to increased gas formation. A lot of patients complain that cardia insufficiency makes gastritis unbearably painful, even if its form is not too advanced. This can be explained by the fact that with excessive swelling, weakened mucous membranes become toned and cause additional discomfort.
To minimize the likelihood of such a complication, you need to clearly define the list of foods - what you can eat and what you should not eat. As you should understand, it is absolutely not without reason that an army of negative symptoms accompanies superficial gastritis, and if the cause of the disease is not eliminated, it will not be possible to recover from it.
A disease such as superficial gastritis requires treatment in a complex manner, no matter how much you try, but folk remedies alone cannot do it. Today, you can cure fundic and other types of the disease, as well as superficial bulbitis, with the following pharmacological drugs:
- Enzymes.
- Drugs to improve appetite.
- Substances to stimulate regeneration.
- Glucocorticoids.
- Antibacterial agents.
- Antispasmodics.
- Antacids.
- Anti-inflammatory drugs.
- Acidine-pepsin and natural gastric juice.
The table below shows the most acceptable medications that a doctor can prescribe for gastritis.
Name of the drug:
Amoxicillin No. 2043-49 RUR Clarithromycin No. 1085-90 RUR Omeprazole No. 1420-23 RUR Rabeprazole No. 14159-171 RUR De Nol No. 56 from 520 RURTreatment
For the best result from therapeutic measures, it is necessary to take into account all the characteristics of the body. Treatment is usually prescribed by a gastroenterologist after diagnostic measures have been carried out. Complex treatment is carried out, which includes many different components:
- Following a special diet that excludes the consumption of excessively fatty, sweet, sour and spicy foods. Includes high consumption of vegetables, fruits, grains, dairy and protein products. And also drinking plenty of water every day.
- For gastritis with high acidity, medications are prescribed that help reduce gastric secretions. Medications that block histamine production may be used.
- Antacids may also be prescribed to reduce acidity.
- The use of prokinetics is prescribed to speed up recovery and improve gastric emptying.
- Enzyme preparations are usually prescribed for insufficient production of enzymes by the pancreas.
- If Helicobacter pylori is found in the body, then antibacterial agents are also prescribed to fight pathogenic microflora.
Various folk remedies can also be used in treatment. However, before using them, it is necessary to consult with a therapist or gastroenterologist, since some drugs can cause more harm than benefit to the patient’s body.
It is recommended to use a mucous decoction, which is prepared from flax seeds and oats. This infusion works great for high acidity of the stomach. You can also take raw quail eggs; they will not harm even if used daily. It is important to remember that treatment with folk remedies is auxiliary and does not replace the use of the remedies prescribed to you by your doctor.
Features of treatment
Let us immediately note that it is possible to carry out treatment using herbal infusions, but only after the doctor’s permission and without a relapse. Therapy begins only after an accurate diagnosis has been made. The choice of drugs depends on the form of the course and the nature of the lesions. At the same time, we can highlight the most commonly used scheme with which inflammation can be treated:
- Treatment begins with suppression of the bacterial flora. In this case, antibiotics are used, for example, Amoxicillin or Clarithromycin. The doctor decides how much to take the drug after assessing the effectiveness of the therapy. Antibacterial agents are necessary in cases where there is a superficial, erosive or even mixed process. But it may also turn out that Helicobacter is absent, which makes it possible to refuse these medications.
- Despite the fact that acidity is often reduced, proton pump inhibitors are prescribed. You can treat gastritis with drugs such as Lansoprazole, Rabeprazole, Ranitidine and so on. This will relieve discomfort and cough.
- Drugs are used to improve motor skills. Treatment can be carried out using gastric juice. Outside of exacerbation, herbal infusions and mineral waters are acceptable. The latter are especially good at relieving coughs due to gastritis.
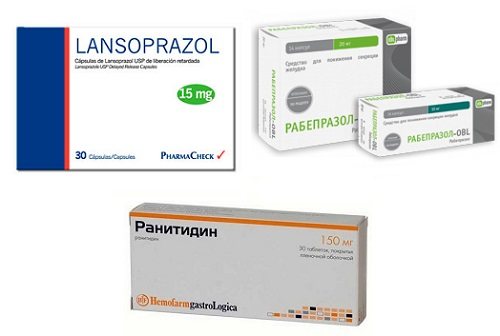
Atrophic gastritis is treated by taking medications to improve gastric motility
- For atrophic phenomena, Riboxin has become increasingly used.
- To protect the mucous membrane, Vikair, Kaolin, Vikalin would be appropriate.
Despite autoimmune processes, the use of hormones and immunocorrectors rarely produces a positive effect. The listed drugs are used in cases where it is necessary to treat an acute process. Chronic, on the other hand, allows you to limit yourself to drugs to improve digestion, herbal infusions and nutritional correction.
At the same time, it is important to carefully monitor the condition and see a doctor regularly. The reason for the consultation may be a growing cough without signs of a cold, deterioration of the condition after errors in the diet using fatty foods, spicy herbs, or carbonated drinks. In such a situation, it is recommended to see a doctor and conduct an endoscopic examination. Only after this the doctor will decide which medications to take and how long to continue treatment.
The video will introduce the symptoms of atrophic gastritis:
Possible complications

Unfortunately, if the problem is not identified and treated, there can be serious complications that will lead to a significant deterioration in health. Inflammatory bowel lesions, ulcers, and chronic gastritis may develop. Bleeding may also occur, which will significantly worsen not only the general condition, but also the treatment of the patient. In addition, inflammatory processes in the stomach and intestines can develop even more and turn into cancer.
Focal gastritis is a fairly common stomach disease.
It is accompanied by unpleasant pain in the abdomen, constipation, heartburn and other aspects of the disease. If treatment for this disease is not started on time, it can bring a lot of negative consequences for the patient’s health. That is why it is necessary to identify it as early as possible and promptly begin competent treatment developed by a doctor.
Symptoms
Mild forms of focal gastritis are accompanied by slight discomfort in the epigastric region, a burning sensation and pain after immediately eating. Nausea and a feeling of heaviness can appear not only after a heavy meal, but even after a light breakfast.
If these symptoms are ignored, the disease progresses:
- the patient loses his appetite,
- heartburn is added to the initial symptoms,
- pain syndrome intensifies
- a person loses weight,
- weakness and low-grade fever appear.
The occurrence of brown vomiting and black diarrhea, which signal the occurrence of gastric bleeding, are considered life-threatening. Sharp, stabbing pain in the stomach is a reason to immediately see a doctor.
Prevention
To prevent inflammation of the gastric mucosa, compliance with the following preventive measures related to nutrition, and not only:
- give up junk food, especially fast food;
- buy only fresh products from trusted places;
- eat little by little at the same time;
- do not overeat, do not eat several hours before bedtime;
- limit the consumption of alcoholic beverages, choose only high-quality alcohol;
- undergo a routine examination with different doctors every year and undergo tests;
- At the first suspicion of gastritis, immediately contact a gastroenterologist.
Focal gastritis occurs for various reasons, most of which are associated with poor diet, bad habits, that is, due to human fault. For treatment, the use of medications and diet are prescribed, and the use of folk remedies is allowed. Compliance with preventive measures will help avoid many problems with the gastrointestinal tract.