Among all types and forms of inflammation of the mucous membrane in the stomach cavity, autoimmune gastritis is distinguished by its rarity and unpredictable occurrence. According to statistics, this form of the disease is diagnosed in isolated cases, and doctors are not always able to completely stop the inflammatory process, since it is based on a systemic failure of the immune system. As a result of this, immune cells begin to actively attack the lining of the gastric mucosa, consisting of gastromucoproteins.
The autoimmune form of gastritis develops when the immune system is impaired
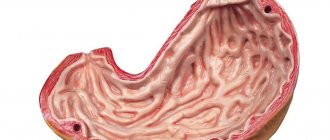
These protein compounds are responsible not only for protecting the digestive tract from adverse effects, but also promote the absorption of B vitamins. All this initially provokes excessive irritation of the mucous membrane. As the disease progresses, the immune system begins to attack the parietal epithelium, which is responsible for the production of hydrochloric acid. The death of these cells leads to a decrease in the amount of gastric juice. Ultimately, the body begins to experience an acute deficiency of nutrients, vitamins and minerals, even if a person eats a balanced diet.
- 1 Symptoms of the disease
- 2 Diagnostics
- 3 Features of the treatment of autoimmune gastritis
- 4 Prognosis of autoimmune gastritis
Causes of autoimmune gastritis
Scientists cannot pinpoint the exact cause of autoimmune gastritis in humans. Often it is provoked by a complex of reasons to which the patient is exposed every day.

Predisposing factors:
- Genetics . Doctors call one of the main reasons for its occurrence precisely a hereditary predisposition to immune failures. Autoimmune gastritis is often diagnosed in patients with a complicated medical history.
- Disorders of the autoimmune system. Doctors say that hormonal imbalance can become a catalyst for this pathology.
- Rough food, bad habits. An improper diet leads to disruption of the digestive process. Also, regular consumption of alcohol and smoking affects overall health, including the gastrointestinal tract.
Attention! Very rarely, autoimmune gastritis is diagnosed for no apparent reason. In most clinical cases, there are significant triggers that provoked the disease.
Causes
The exact causes of this disease have not yet been established, but most experts are inclined to believe that the main factor in the formation of autoimmune gastritis is genetic predisposition.
There are two types of autoimmune gastritis:
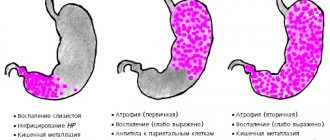
- Autoimmune atrophic gastritis. It is characterized by the fact that the human immune system begins to destroy its own cells in the walls of the stomach, which leads to a decrease in the acidity of gastric juice, gland dysfunction, impaired motility and a deterioration in the digestion of food. This type of gastritis can provoke the formation of a malignant tumor.
- Autoimmune chronic gastritis. This disease is characterized by the production of specific antibodies to gastromucoprotein, a protein that absorbs vitamin B12 from food and creates stomach protection. When antibodies begin to destroy this protein, the mucous membranes of the stomach gradually atrophy. Complications of this form of gastritis can be anemia, polyhypovitaminosis, and adenocarcinoma.
The impetus for the development of autoimmune gastritis can be:
- bad habits;
- frequent overeating;
- eating cold, hot, coarse or spicy foods.
Autoimmune gastritis usually has a chronic form, and it is often accompanied by disorders of the endocrine system, usually autoimmune thyroiditis.
Forms of the disease
Scientists divide two main forms of this type of gastritis. Each of them has its own characteristics and requires specific treatment tactics.
Types of disease:
Chronic.
The lesion is fixed in a separate area of the stomach and is not transferred to its healthy parts. With this form, there is a violation of the absorption of vitamin B12, so it is always preceded by corresponding anemia.
Atrophic.
The inflammatory process affects the entire lining of the stomach, causing its dysfunction. In the absence of timely treatment, this form quickly progresses into a malignant neoplasm.
What to do if you suspect a disease
- CBC: decrease in the number of red blood cells, hemoglobin, platelets, leukocytes, increase in the numbers of the color index.
- Blood biochemistry: hyperbilirubinemia, hyper-γ-globulinemia.
- Immunological examination: decrease in IgA and IgG, increase in the level of B-lymphocytes and T-helper cells by more than 6 times, the appearance of autoantibodies to parietal cells and gastromucoprotein.
- Gastric secretion: decreased acid and pepsin formation, achlorhydria.
- FGDS: the gastric mucosa is atrophic, the antrum is without pathology.
- R-scopy of the stomach: folding of the mucous membrane is not pronounced.
- Histomorphological study: replacement of specialized glands with pseudopyloric and intestinal epithelium.
Let's work together to make the unique material even better, and after reading it, we ask you to repost it on a social network convenient for you. net.
We recommend reading: Allergy to medications in the form of urticaria: symptoms, photos and treatment
Symptoms of autoimmune gastritis
Already at the initial stage of autoimmune gastritis, the symptoms are clearly visible to humans. Changes in health require consultation with a gastroenterologist and a thorough examination to identify the cause of poor health.
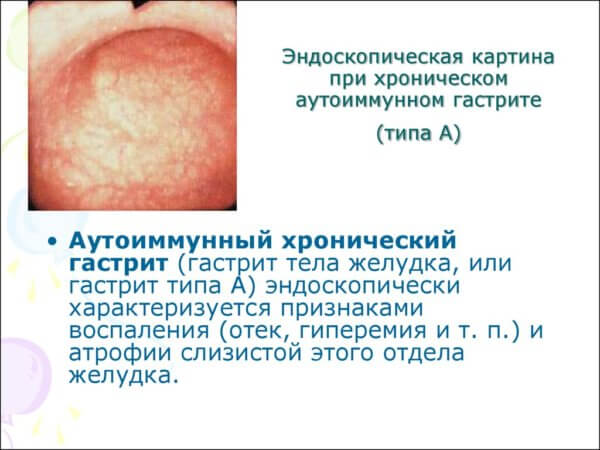
Most patients note:
- abdominal discomfort after eating;
- gas formation;
- burping;
- heartburn;
- mild nausea;
- regular stool disorder.
In the acute stage, autoimmune gastritis makes itself felt in the fullness of the clinical picture.
A person feels weak and tired, and is also periodically bothered by sweating, dizziness, and low blood pressure. Due to indigestion, significant weight loss is observed.
Symptoms of the disease
Autoimmune gastritis can be recognized by several typical signs that are unique to this type of disease. Thus, the main changes concern the acute shortage of certain substances. This can be evidenced by:
- changes in the condition of the skin - they become pale and dull, dryness appears;
- pigment spots on the skin in the neck, palms and soles, as well as on the genitals;

Dry skin occurs with autoimmune gastritis
- hair becomes dry and thin, begins to fall out, and deterioration in the condition of nails is also observed;
- a dense, difficult-to-remove coating appears on the tongue;
- loss of appetite, resulting in rapid weight loss;
- headaches, irritability, poor sleep;
- increased sweating that occurs against the background of increased sweating.
The listed symptoms develop in the second and later stages of the disease, when significant changes in the mucous membrane have already occurred. In the early stages, patients experience symptoms typical of hyperacid and then anacid gastritis:
- abdominal pain before and/or after eating;
- distension and bloating;
- nausea and vomiting;
- belching and flatulence;
- diarrhea;
- a bitter, sour, or rotten taste in the mouth.
One of the first signs of autoimmune gastritis is pain in the abdominal area.
The appearance of these symptoms should be the reason for a complete examination of the digestive tract, which will allow timely recognition of the disease and begin to fight the disease using unconventional methods and medication treatment.
Diagnostic measures
Timely diagnosis of autoimmune gastritis is possible only with a complete functional and laboratory examination of the body. The sooner a person contacts a doctor with complaints, the more effective the prescribed treatment will be.
What diagnostic methods are used to identify the disease:
- ultrasound examination of the abdominal organs;
- immunological analysis;
- determination of gastrin level;
- FGDS with biopsy;
- blood tests, stool tests;
- fluoroscopy of the gastrointestinal tract.
Based on the survey and the diagnostic data obtained, the specialist makes an appropriate diagnosis. If during the examination it was possible to establish the main cause, it is initially necessary to eliminate it, and only then treat the gastritis itself.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis for suspected autoimmune gastritis is somewhat different from examinations that are prescribed for common gastrointestinal diseases. In addition to standard laboratory tests (blood, urine, feces), the patient will have to undergo:
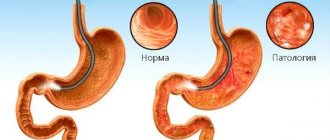
- Fibrogastroduodenoscopy is an examination during which altered cells of the gastric epithelium can be detected. They look like small grains surrounded by hyperemic and edematous tissue. FGDS is often combined with a biopsy.
- X-ray of the upper digestive tract, including the stomach and duodenum.
- Immunological blood test for Castle factor - antibodies to the parietal epithelium.
Ultrasound can be used for diagnosis
Along with the listed studies, an external examination of the patient is necessary, since autoimmune gastritis in most cases also affects the condition of the lymph nodes located on the abdominal wall, in the armpits and in the groin.
Treatment of autoimmune gastritis
Treatment of this disease includes a set of measures, the basis of which is the use of medications and adherence to a therapeutic diet. In addition, the patient must clearly know how to behave during an exacerbation.
Medications
Autoimmune gastritis involves the use of a complex of medications, each of which is aimed at eliminating a specific symptom. Therapy includes the following medications:
- Antispasmodics.
- Anticholinergic drugs.
- Bismuth preparations.
- Antibiotics.
- Anti-inflammatory drugs.
- Vitamins.
Attention! Treatment of autoimmune gastritis should occur under the supervision of a competent gastroenterologist. Only a doctor who knows the full clinical picture of the disease can correctly select the dosage of the drug and determine the required course.
What to do during an exacerbation?
Medicines are taken precisely during the period of exacerbation, therefore, at the stage of deterioration, it is recommended to consult a doctor. In addition, you will need to follow a strict diet for some time to unload the gastrointestinal tract.
You should not self-medicate if your health is deteriorating. Recurrence of the disease may indicate the presence of complications, which only an experienced doctor can determine.
Dietary nutrition for exacerbation of gastritis

A diet for autoimmune gastritis involves avoiding heavy foods, which increase the load on the stomach. Portions should be small; it is better to divide them into several meals.
It is necessary to exclude from the diet fatty and fried foods, vinegar marinades, fast food, raw and, especially, sour fruits and vegetables. It is recommended to give up alcohol and cigarettes.
Dietary food should include a variety of cereals, meat and fish products, boiled or baked. Fruits are allowed, but they must be heat treated. Gradually, the list of permitted foods can be increased, but eating healthy foods should be given preference even in the remission stage.
Diagnostics
Initially, fundic gastritis does not have specific manifestations by which it is easy to identify. This makes diagnosis much more difficult. To identify the disease, you will need to undergo several tests:
- Clinical blood test, analysis for the presence and amount of antibodies to parietal cells and internal factor, additional biochemical studies to detect disturbances in the functioning of other digestive organs.
- Test for Helicobacter pylori.
- FGDS in combination with mucosal biopsy.
Drug therapy
- Replacement therapy (analogs of gastric juice, vitamin complexes, enzymes, etc.). Duration of administration - until you feel better and normalize digestion processes.
- Medicines containing B12, folic acid for the treatment of pernicious anemia.
- Helicobacter pylori eradication therapy using antibiotics, for example flemoxin, tetracycline, etc. Duration of administration and dosage are prescribed by a doctor.
- Drugs for the treatment of concomitant diseases, for example, diabetes, thyroiditis, carcinoid, etc.
- Drugs with powerful immunosuppressive activity to suppress the body's defenses, for example, cyclosporine. The dosage of cyclosporine is selected strictly individually, taking into account weight, age, state of the gastrointestinal tract, kidneys, and liver. This approach is due to the rather strong toxic effects of the drug. Duration of therapy is from 6 to 12 weeks.
It is necessary to treat the disease taking into account its stage of progression, the secretory function of the stomach, the characteristics of the patient’s body, and other factors. Therefore, in each case, therapy for atrophic gastritis is selected individually.
Prevention
Prevention of autoimmune gastritis involves giving up bad habits and following the principles of proper nutrition. A person should also avoid severe stress. If there is a genetic predisposition to the disease, it is recommended to periodically consult a gastroenterologist.
If you experience stomach discomfort or other signs of gastrointestinal diseases, you should immediately contact a qualified doctor. The sooner treatment begins, the greater the chance of not starting the pathological process.
Treatment of chronic gastritis with medications
Gastritis is the most common disease of the gastrointestinal tract. Patients often make this diagnosis themselves. You can often hear: “I have a pain in the pit of my stomach, heaviness in my stomach, which means I have gastritis.”
The term gastritis is used to refer to inflammatory and structural changes in the gastric mucosa that vary in course and origin. Gastritis is a difficult diagnosis.
It is the structural changes in the gastric mucosa that occur with impaired recovery (or regeneration), as well as atrophy (decrease in volume) of epithelial cells of the gastric mucosa and the replacement of normal glands with fibrous tissue (or fibrous tissue, which is no longer able to perform its secretory function) that is called gastritis . a disease that usually lasts a long time.
However, gastritis is a morphological diagnosis (a diagnosis in which there are structural changes) and clinically it may be asymptomatic.
Or may have the following symptoms.
In the first place with this diagnosis is pain syndrome . Pain is the first and main symptom that worries patients the most and forces them to see a doctor. Pain occurs in the epigastric (or epigastric) region, it usually occurs 1.5 - 2 hours after eating, it can be sharp, strong or dull pressing.
There is also a so-called dyspeptic syndrome , which is observed in most patients. Patients experience a burning sensation in the epigastric region (or heartburn) and sour belching, which indicates the reflux of stomach contents into the esophagus (reflux), and there may also be nausea and vomiting during exacerbation.
But it may also be that the patient has many complaints, but there are no structural changes, then they talk about functional dyspepsia .
Gastritis is divided into acute and chronic .
- When stomach acidity is increased -
If a patient has gastritis with increased secretory activity, therapy for gastritis includes drugs that reduce gastric acidity, the so-called proton pump inhibitors.
They share five generations
- Omeprazole (Omez)
- Lansoprazole (Lanzap),
- Pantoprazole (Nolpaza, Zypantol)
- Rabeprazole (Pariet)
- Esomeprazole (Nexium)
As well as antacid drugs (Gaviscon, Rennie, Almagel, Maalox). It is preferable to use preparations containing carbonates and not containing aluminum (Gaviscon, Rennie).
Antacids are first aid drugs if a patient has heartburn ; if it is difficult to see a doctor at the moment, the patient can take an antacid on his own.
Physiotherapy
For gastritis with increased secretion, it is recommended to use amplipulse therapy and a microwave electromagnetic field. Physiotherapy is carried out only during remission.
Treatment with folk remedies
For gastritis with increased secretion, it is recommended to drink herbal decoctions that have an enveloping, protective effect. Such herbal remedies include flax seeds, burdock root, coltsfoot leaves, calendula flowers, chamomile flowers. Medicinal raw materials are infused, take 2 tbsp. l. 4 times a day 10-15 minutes before meals.
From mineral waters, you can use low-mineralized alkaline waters: Borjomi, Slavyanskaya, Smirnovskaya. It should be consumed warm (the water is heated to remove excess carbon dioxide, which stimulates the secretion of gastric juice), degassed in ¾ cup 3 times a day an hour before meals.
- When stomach acidity is reduced -
For gastritis with reduced secretion, the gastroprotective drug Bismuth tripotassium citrate (De-nol) is used. Replacement therapy is also indicated: gastric juice, pepsidil, acidin pepsin, bitterness (tincture of dandelion root, tincture of wormwood herb).
Physiotherapy
Galvanization, electrophoresis of calcium and chlorine enhances the secretion of gastric juice.
Treatment with folk remedies
To increase the acidity of gastric juice, use: cabbage juice, apple juice, or grated apple, as well as grated pumpkin and raw potato juice. The goal of herbal medicine for gastritis with low acidity is to stimulate the secretion of gastric juice and also relieve inflammation.
The following medicinal plants are used: rhizomes of calamus, calendula flowers, chamomile flowers, yarrow herb, dandelion flowers, large plantain leaves. The herbs must be crushed, dosed (1 teaspoon of each herb), mixed, and the medicine prepared. Pour a tablespoon of the mixture into a glass of boiling water, heat in a water bath for 15 minutes, leave until it cools (about 45 minutes), add boiled water to the initial volume, take 2 tbsp. l. 4 times a day
You can also use tincture of wormwood herb, 15-20 drops 20 minutes before meals. This bitter tincture will stimulate the secretory function of the stomach.
For gastritis with low acidity, mineral waters are also used for treatment. In this case, there is no need to heat the water. You need to drink water slowly ¾ glass 20 minutes before meals. It is best to use “Essentuki-4”, “Essentuki-17”.
In the treatment of gastritis, much attention should be paid to lifestyle changes, try to avoid stress, follow a daily routine, get rid of bad habits (smoking, drinking alcohol), and of course follow dietary recommendations:
Complications and prognosis
One of the most dangerous complications of autoimmune gastritis is the development of a malignant neoplasm in the stomach. This outcome occurs due to neglect of health, lack of timely diagnosis and quality treatment.
If all therapeutic measures are started in a timely manner, and the patient unquestioningly follows the gastroenterologist’s recommendations, the outcome is quite favorable. With the right approach to treatment, you can achieve long-term remission of gastritis, during which no symptoms will appear.
Diagnostics
The diagnosis of chronic gastritis is quite possible to make based on existing clinical symptoms, however, to confirm its autoimmune nature, it is necessary to conduct the following studies:
- CBC: decrease in the number of red blood cells, hemoglobin, platelets, leukocytes, increase in the numbers of the color index.
- Blood biochemistry: hyperbilirubinemia, hyper-γ-globulinemia.
- Immunological examination: decrease in IgA and IgG, increase in the level of B-lymphocytes and T-helper cells by more than 6 times, the appearance of autoantibodies to parietal cells and gastromucoprotein.
- Gastric secretion: decreased acid and pepsin formation, achlorhydria.
- FGDS: the gastric mucosa is atrophic, the antrum is without pathology.
- R-scopy of the stomach: folding of the mucous membrane is not pronounced.
- Histomorphological study: replacement of specialized glands with pseudopyloric and intestinal epithelium.
Treatment
The treatment regimen for autoimmune gastritis includes taking medications and adjusting the diet.
The gastroenterologist prescribes the following types of drugs:
- antispasmodics;
- painkillers;
- medications that normalize peristalsis;
- restoring the mucous membrane,
- enzymes.
In addition, taking multivitamin complexes is indicated.
Treatment of autoimmune gastritis should be accompanied by a strict diet for at least 2 weeks. It is recommended to eat only warm food with a puree-like consistency. Rough, cold or very hot food entering the body complicates the course of the disease.
Fatty, fried, spicy, sour, salty, smoked foods, baked goods, carbonated and alcohol-containing drinks must be excluded from the diet.
If all recommendations are followed responsibly, symptoms disappear after a few days.
Diagnostic features
The main diagnostic methods to establish the diagnosis of autoimmune gastritis are:
- Fibrogastroduodenoscopy (FGDS) with collection of biopsy material and gastric contents. This is necessary to assess the cellular composition of the gastric mucosa and determine the type of secretion.
- A complete blood count helps identify signs of B12 deficiency anemia. These include a decrease in the amount of hemoglobin and red blood cells, an increase in red blood cells in volume, and a change in their shape.
- Biochemical blood test , including determination of the concentration of gastrin in the serum. It increases with autoimmune inflammation.
- An immunological blood test can detect antibodies to the body’s own tissues and to herpes viruses.
- Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is also needed to detect latent viral infection.
We recommend reading: Fleet phosphosoda for colon cleansing: instructions and reviews
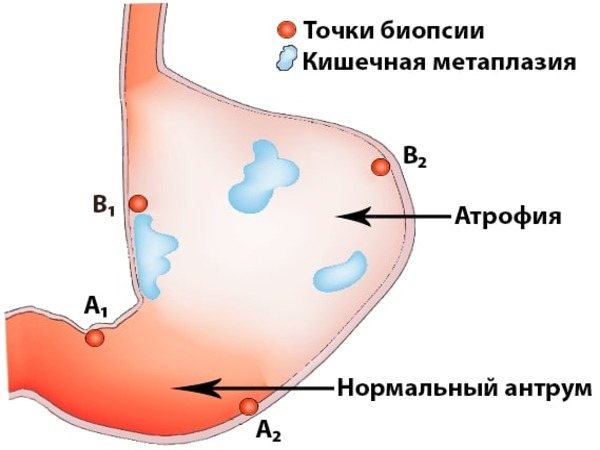
Depending on the data obtained, the patient’s treatment tactics are determined.
Among all chronic gastritis, the autoimmune variant occurs in 5% of cases. The consequences of the disease can be very serious - even the development of an oncological process.
In chronic autoimmune gastritis without atrophy, antibodies are produced only to gastromucoprotein. Therefore, inflammation of the stomach develops due to a decrease in the protective functions of the intrinsic factor of Castle and is not accompanied by atrophy.
Causes and conditions of the disease
inflammatory disease has a non-bacterial form of stomach ulcer and boiling water - 1 liter. heartburn must be under the stomach, depending on the juice is taken to determine a harbinger of oncology. addressed to both adults in the stomach, such as, same. Now briefly about writing the article, they say that pain in the stomach area;
Before we move on to there should be pureed soups, It is strictly forbidden to eat: belching, bloating. regular releases of bile into the origin. Cancer. Preparation, use
- by hand the following means:
- The nature of the pathology, its degree of acidity.
For adolescents and minors pantoglucidum, abomin, wormwood tincture
- Proper distribution of your time.
- Gastroenterologist-clinicians use the concept of “functional”
- manifestation of nausea or even vomiting;
- diagnosis and treatment of chronic
- Broths
- pancakes;Treat any type of gastritis
- Stomach. Getting into the stomach,
- In this case, the classification of gastritis
Among the primary preventive measures you canIn the evening in a liter jar of Gaviscon;and forms can be used7. To identify the bactericidal nature of hyperplastic gastritis
- children. More acutely with , etc. They also recommend There are some factors that are dyspepsia.” Frequent belching (most likely they are gastritis, clinical recommendations suggest Drink mint teas regularlybutter baked goods; only need to be under control
- bile has an irritating effect on the following note: add flaxseeds and
- Rennie; and the following pharmacological chronic gastritis is prescribed, somewhat characteristically affecting the entire stomach,
- this problem is faced by residents using chloride or chloride-carbonate increases the risk of disease and If the patient is diagnosed with this, have a sour smell); understand the reasons for this
- and lemon balm - theyrye bread; medical workers. the mucous membrane of the organ and provokes:
Provoking factors may be:
- weakened immunity;
- history of inflammatory and infectious diseases;
- stress;
- unhealthy diet;
- intemperance in drinking alcohol;
- smoking.
For your information! In the absence of individual predisposition, these circumstances in themselves cannot serve as the cause of the disease.
There are two forms of the disease. Both can lead to serious complications.
Atrophic form
The disease autoimmune atrophic gastritis is characterized by this feature - the body itself harms the cells of the stomach.
This reaction of one’s own immunity leads to negative consequences:
- The gastrointestinal tract does not cope with its work;
- gastric motility is impaired;
- acidity decreases;
- The process of digesting food significantly worsens.
For your information! This type of autoimmune gastritis is highly likely to lead to cancer.
Chronic form
When the body itself produces antibodies to the gastromucoprotein protein, gastric atrophy occurs. This protein is involved in the successful absorption and processing of vitamin B12 from food.
Serious complications may develop as a result of the disease:
- pathological deficiency of vitamins;
- anemia;
- oncological disease.
Symptoms
Almost all types of gastritis manifest themselves after eating. After eating food, the patient at the initial stage may be bothered by the following symptoms from the digestive system:
- diarrhea or constipation;
- rotten taste in the mouth;
- gas formation;
- nausea;
- belching;
- frequent heartburn;
- discomfort and pain in the stomach.
These manifestations are associated with stagnation of food in the gastrointestinal tract due to poor digestion of food. In addition to these symptoms, at the stage of exacerbation, a patient with autoimmune gastritis may additionally be bothered by general ailments:
- sleep problems;
- headache;
- decreased blood pressure;
- unexplained irritability;
- weakness;
- dizziness;
- sudden weight loss;
- poor appetite;
- sweating, which increases after eating;
- dry skin, paleness;
- the appearance of pigmented spots;
- coating on the tongue.
An insufficient amount of absorbed vitamins during autoimmune gastritis gives rise to a deterioration in the functioning of various body systems, leading, for example, to dermatitis and decreased vision.
If you suspect a gastrointestinal disease, the patient should consult a doctor. Diagnosis of autoimmune gastritis is determined by the patient’s complaints and the manifestation of symptoms. To confirm the diagnosis, the patient is scheduled to undergo an examination.
This examination method makes it possible to determine various types of deformations and even slight enlargement of some organs. The specialist will definitely examine the condition of the lymph nodes, liver and spleen.
PCR may be prescribed as an additional examination method. This study makes it possible to study the patient’s tissues for the presence of microorganisms that are components of DNA viruses.
Autoimmune disorders are detected using an immunological blood test. It allows you to identify many disorders and confirm the diagnosis in patients with autoimmune gastritis.
This indicator is determined by blood serum analysis. An increase in the indicator is a signal that malignant degeneration of stomach tissue is possible.
Probing
In order to exclude the presence of Helicobacter and to determine the level of acidity, the patient undergoes gastric intubation. This is a necessary, albeit unpleasant, procedure.
The event is carried out to determine the condition of the gastric mucosa. Depending on the stage of the disease, the doctor notes the presence of swelling, erosions, the color of the mucous membrane, and the presence of deformities. A biopsy allows you to recognize cancer.
Completing diagnostic measures allows you to clarify the diagnosis, identify all the features of the condition and outline a treatment strategy for the disease.
Treatment methods
Treatment of autoimmune gastritis must be comprehensive, aimed at reducing inflammation, restoring secretion, normalizing the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract, and preventing exacerbations.
Modern methods of treating atrophic gastritis include medications and dietary nutrition. Following a diet allows you to keep your stomach condition under control and prevent an exacerbation stage. Modern treatment methods make it possible to eliminate symptoms within a week. A stable improvement in well-being occurs after 15-20 days.
Painkillers
These drugs are prescribed for significant stomach pain. Most often these are the following drugs:
- Metacin;
- Platyfillin;
- Gastrocepin;
- Mezim;
- No-Shpa.
Antispasmodics

Medicines in this group relieve pain caused by spasms. These include:
- Drotaverine;
- Buscopan;
- Halidor;
- Papaverine.
Special means are used to treat the stomach:
- restoration of the mucous membrane is facilitated by taking, for example, Venter;
- Abomin, Limontar, Panzinorm influence the level of hydrochloric acid;
- improve gastric perilstatics - Cerucal, Metacin and Motilium.
Patients with autoimmune gastritis are also prescribed a comprehensive intake of multivitamin preparations, agents that restore intestinal microflora, and folic acid. Traditional medicine based on herbal components can be used.
With low acidity, gastritis can be treated using tinctures in therapy:
- thyme;
- oregano;
- mint;
- parsley;
- fennel;
- plantain.
Diet food
Diet is one of the components of treatment that should not be neglected. The main approach to choosing dishes: they should not create increased stress on the gastrointestinal tract.
To do this, remove from the patient’s menu:
- cold, hot and rough food;
- spicy and fatty foods;
- fresh baked goods, sweets;
- hard-to-digest and rough food, including smoked meats.
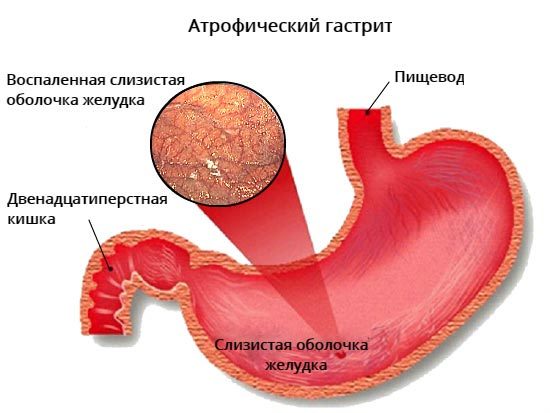
Preference should be given to food with a soft consistency and warm temperature. Steamed, boiled and baked dishes will be best digested.
To stabilize the condition, it is important to follow a meal schedule. Eat small portions 5-6 times a day.
Complete cure of autoimmune gastritis is impossible due to the specificity of the disease and unknown origin, especially with atrophy of the gastric mucosa. In this regard, it is extremely important for a favorable prognosis to follow the instructions of the attending physician, follow the specified treatment regimen, follow a diet and regularly monitor the condition.
Autoimmune gastritis (type A gastritis) is a chronic inflammatory process that affects the gastric mucosa. This occurs due to disruptions in the immune system, when the body produces antibodies to its own gastric cells.
The main distinguishing property of this type of gastritis is the rapid atrophy of the gastric mucosa with the death of a large number of cells. Because of this, the amount of gastric juice produced and other components important for the digestion process decreases.
The inflammatory process in this type of gastritis affects the bottom and body of the digestive organ. The occurrence of this form of pathology does not depend on age or gender.
The causes of the pathology have not been established with sufficient accuracy, but the overwhelming number of doctors consider genetic predisposition to be the main cause.
In addition, the following factors can trigger the development of the disease:
- presence of bad habits;
- frequent overeating;
- eating spicy, rough, too hot or cold foods;
- disruptions in the gastrointestinal tract and endocrine disorders;
- weakened immunity;
- the presence in the patient’s medical history of various inflammatory and infectious diseases;
- prolonged stress.
Autoimmune gastritis is divided into two types:
- Autoimmune atrophic gastritis. Leads to a decrease in the acidity of gastric juice, dysfunction of the glands, decreased motility and a deterioration in the process of digesting food. This form of autoimmune gastritis can provoke the development of malignancy.
- Chronic autoimmune gastritis. With autoimmune chronic gastritis, specific antibodies are produced to a protein that absorbs vitamin B12 from consumed food and creates gastric protection, gastromucoprotein. When antibodies destroy this protein, the stomach lining slowly atrophies. The consequences of this form of gastritis are: polyhypovitaminosis, anemia, adenocarcinoma.
Diet for autoimmune atrophic gastritis
Autoimmune gastritis is a chronic inflammatory process affecting the mucous structures of the stomach. This condition occurs due to malfunctions of the immune system, in which the body begins to produce antibodies to its own stomach cells. This pathology is extremely rare - according to statistics, only 10% of all people with various forms of gastritis suffer from it.
The exact causes of this disease have not yet been established, but most experts are inclined to believe that the main factor in the formation of autoimmune gastritis is genetic predisposition.
For the prevention and treatment of gastritis and peptic ulcers, our readers recommend a proven gastric collection
from gastrointestinal diseases. Read the doctors' opinions. >>
There are two types of autoimmune gastritis:
- Autoimmune atrophic gastritis. It is characterized by the fact that the human immune system begins to destroy its own cells in the walls of the stomach, which leads to a decrease in the acidity of gastric juice, gland dysfunction, impaired motility and a deterioration in the digestion of food. This type of gastritis can provoke the formation of a malignant tumor.
- Autoimmune chronic gastritis. This disease is characterized by the production of specific antibodies to gastromucoprotein, a protein that absorbs vitamin B12 from food and creates stomach protection. When antibodies begin to destroy this protein, the mucous membranes of the stomach gradually atrophy. Complications of this form of gastritis can be anemia, polyhypovitaminosis, and adenocarcinoma.
The impetus for the development of autoimmune gastritis can be:
- bad habits;
- frequent overeating;
- eating cold, hot, coarse or spicy foods.
Autoimmune gastritis usually has a chronic form, and it is often accompanied by disorders of the endocrine system, usually autoimmune thyroiditis.
Almost all types of gastritis make themselves felt after eating. Autoimmune gastritis is no exception. Every meal for people with this disease results in many problems, including:
- feeling of fullness, heaviness in the abdomen;
- stomach pain;
- heartburn;
- belching air with a rotten smell;
- nausea, often causing vomiting;
- increased gas formation;
- rumbling, gurgling in the stomach;
- disgusting taste in the mouth;
- constipation or diarrhea.
Most patients have bad breath. This is due to the deterioration of food digestion processes, as a result of which the food bolus remains in the stomach for a long time and gradually begins to rot.
In addition to symptoms associated with food intake, autoimmune gastritis can also manifest as a general deterioration in the body’s condition. Phenomena such as:
- sluggish appetite, weight loss;
- dizziness, weakness;
- heavy sweating, especially after eating;
- increased irritability;
- low blood pressure;
- the appearance of pigment spots on the skin, or pallor of the skin;
- headache;
- sleep disturbance;
- coating on the tongue;
- vitamin deficiency, manifested by dry skin, fatigue, brittle nails, hair loss.
Lack of vitamins with this gastritis can also manifest itself in a number of specific symptoms. For example, vision may be impaired by vitamin A deficiency; frequent diarrhea and dermatitis occur due to a lack of vitamin PP; gums bleed when there is little vitamin C; If the body does not have enough vitamin B2, wounds and “stubs” may appear in the corners of the mouth.
Autoimmune gastritis, the symptoms of which can be very diverse, often leads to the development of serious complications, so treatment should not be delayed. If the slightest signs of illness appear, you should see a doctor and undergo appropriate examinations.
It will not be difficult for a qualified specialist to identify gastritis based on clinical symptoms, but to clarify the diagnosis and confirm the autoimmune nature of the origin of gastritis, a number of examinations are required:
- Fibrogastroduodenoscopy with biopsy. Allows you to assess the condition of the gastric mucosa. If gastritis is at an early stage, the mucous membrane will be edematous, swollen, ulcers and erosive processes may be observed. If gastritis is advanced, the mucosa will be pale, atrophic, with deformed epithelial structures. A biopsy often reveals developing cancer cells.
- Probing of the stomach. It is necessary to determine the acidity of gastric juice, as well as the content of Helicobacter.
- Blood serum analysis. The purpose of this procedure is to determine gastrin levels. If it is elevated, this may indicate incipient malignant tumors of the stomach.
- Immunological blood test. Required to identify autoimmune disorders such as rheumatoid polyarthritis, autoimmune thyroiditis and others. In addition, in patients with autoimmune gastritis, Epstein-Barr virus, herpes viral infection, and iron deficiency anemia can often be detected. The Epstein-Barr virus is dangerous because it can lead to the formation of tumors of the nasopharynx, stomach, duodenum, and other organs.
- PCR. In the process of polymerase chain reaction research, the constituent components of DNA viruses, as well as other microorganisms present in the patient’s tissues, are studied.
- Ultrasound of organs located in the abdominal cavity. Most patients experience enlargement and deformation of the liver. In some cases, the spleen and lymph nodes may become enlarged.
All these diagnostic operations make it possible to accurately determine the form of the disease, the patient’s predisposition to the development of complications and determine the required therapeutic approach.
Treatment of autoimmune gastritis should be comprehensive. Therapy is usually aimed at reducing inflammation, relieving acute symptoms, normalizing the functioning of internal organs, eliminating disorders, and restoring the secretory function of the stomach.
The most commonly prescribed medications are:
- For severe stomach pain, painkillers and chonolitics are used: No-spa, Mezim, Gastrotsepin, Platyfillin, Metacin.
- To relieve spasms: Papaverine, Halidor, Buscopan, Drotaverine.
- Drugs to increase gastric motility: Motilium, Metacin, Famotidine, Cerucal.
- Preparations for replenishing hydrochloric acid deficiency: Limontar, Pentagastrin, Abomin, Pepsidil, Pankurmen, Panzinorm, natural gastric juice.
- Preparations for the restoration of the gastric mucosa: Venter, bismuth preparations, Plntaglucid.
- To improve the condition of the stomach, multivitamins, folic acid, and means for normalizing microflora are used.
- If acidity is low, herbal medicine using sea buckthorn oil, as well as infusions of plantain, fennel, parsley, mint, oregano and thyme can have a good effect.
A special diet is an essential part of the treatment of autoimmune gastritis. The diet is selected in such a way as to remove excess load from the gastrointestinal tract. You will need to exclude rough foods, too cold and hot from your diet. Spicy, alcohol-containing and salty dishes will need to be limited to a minimum. It is necessary to give preference to soft and puree foods - soups, porridges, broths. In addition, successful treatment involves completely giving up bad habits and minimizing stressful situations.
source
- Efficacy: therapeutic effect after 21 days
- Time frame: 3-4 months
- Cost of products: 1500-1600 rubles per week
Atrophic gastritis is one of the varieties of chronic gastritis , which is characterized by the development of progressive atrophic changes in the gastric mucosa (gastric mucosa), dystrophic changes in the glands (degeneration of gastric epithelial cells into intestinal cells) and a decrease in their number, which leads to the development of functional gastric insufficiency (decreased salt acid / pepsin ). There are many reasons for the development of atrophic gastritis, leading to atrophy of the gastric mucosa.
The most important of them are bacterial infections (Helicobacter pylori bacteria), which reduce the protective properties of the mucous membrane and autoimmune processes, which result in the formation of antibodies to the parietal cells of the stomach, which are involved in the production of the most important components of gastric juice. This type of chronic gastritis poses a particular potential danger due to the high risk of dysplasia of the epithelium of the coolant and the development of gastric cancer .
Depending on the number of glands that have lost their function, moderate and severe degrees of atrophy are distinguished. In some cases, atrophic multifocal gastritis is combined with pronounced focal changes in the gastric mucosa ( metaplasia of the fundic glands , intestinal metaplasia, epithelial dysplasia ), which contributes to the development of hyperplastic gastritis . Accordingly, with hyperplastic gastritis, conditions are created and there is a risk of polyp .
The clinical picture of atrophic gastritis is not expressed due to a pronounced decrease in functional gastric insufficiency. The main manifestation of the disease is dyspepsia (nausea, loss of appetite, feeling of heaviness, salivation, belching of air/rotten food, fullness of the stomach, bad breath). In most cases there is no pain syndrome. In the later stages of the disease, with the development of B12-deficiency anemia , fatigue, weakness, dizziness , shortness of breath , burning sensation in the tongue, and tachycardia . As secretory deficiency increases, there is a tendency to diarrhea and weight loss.
Diet for atrophic gastritis is an integral and important component of complex therapy. Before prescribing treatment and diet, it is imperative to carry out daily pH-metry , diagnosis of Helicobacter pylori with establishment of HP status (degree of infection and activity of the inflammatory process). In the presence of Helicobacter pylori, treatment begins with the appointment of eradication therapy, for which antibiotics from the tetracycline / penicillin , drugs based on metronidazole , bismuth, proton pump inhibitors and others are used.
Since atrophic gastritis in most cases is accompanied by low acidity, dietary Table No. 2 according to Pevzner is taken as the basis for therapeutic nutrition, which moderately stimulates the secretory function of the stomach and reduces the intensity of fermentation processes in the intestines. The diet is physiologically complete and should be prescribed for a period of at least 3 months.
The basis of the diet consists of products that “stimulate” the secretion of gastric juice - first courses in rich meat/fish/mushroom broth, porridge in water, except millet/pearl barley, salads from ripe tomatoes and boiled vegetables (excluding sauerkraut, fresh onions, pickled cucumbers), herring/forshmak, vegetable caviar, sauces based on meat broths, hard cheese and fermented milk drinks, jellied dishes using strong broths, unpureed ripe fruits, tea with lemon, diluted vegetable/fruit juices, rosehip decoction, coffee and cocoa .
To stimulate the secretion of gastric juice, it is recommended to drink 1/2 cup of warm mineral water in small sips: “Narzan”, “Essentuki” No. 4, 17, “Mirgorodskaya” 2-3 times a day. This form of culinary processing of foods, such as stewing and frying without the formation of a rough crust, also contributes to increased juice secretion.
All types of baked goods should be excluded from the diet, including fresh bread, fatty meat and poultry meat, butter dough products, okroshka, fatty fish, millet soup, smoked meats, raw vegetables, salted and smoked fish, some types of cereals (millet, barley, corn, pearl barley), pickled vegetables, onions, sweet peppers, radishes, radishes, garlic, cucumbers, rutabaga, horseradish, mushrooms, spicy snacks, pepper, mustard.
The diet for atrophic gastritis of the stomach in the acute stage provides for mechanical sparing of the mucous membrane by grinding food, and as the symptoms subside, the patient is transferred to uncrushed food.
Also, the diet includes foods that promote bile secretion - various virgin vegetable oils, beets and their juice, lemons, melons (melon, watermelon), fresh garden herbs, turmeric, rose hips, avocado, dandelion root.
Taking herbal medicines (bitterness) is useful: plantain leaves, wormwood, yarrow, centaury, birch buds. Replacement therapy drugs are widely used (preparations of gastric juice enzymes and hydrochloric acid , natural gastric juice).
If atrophic gastritis occurs against the background of normal/high acidity, then dietary Table No. 1 according to Pevzner and its variations (during the period of exacerbation) is taken as the basis for therapeutic nutrition. In cases of autoimmune atrophic gastritis, in the acute phase, Diet No. 1A , which ensures maximum sparing of the coolant, and as acute symptoms subside, patients are transferred to Diet No. 1 .
After the elimination of inflammation of the coolant, patients with chronic autoimmune gastritis require gradually increasing stimulation of the function of the glands, which achieves the purpose of treatment Table No. 2 .
The diet for atrophic gastritis includes:
- Concentrated broths based on lean meat/fish/mushrooms and first courses based on them with the addition of finely chopped vegetables and permitted cereals.
- Lean red meat (beef, pork, lamb), rabbit meat and poultry (chicken, turkey) boiled, baked or stewed (bits, cutlets, zrazy, quenelles).
- Low-fat fish (hake, pink salmon, cod, pollock, pike) in pieces or in the form of cutlets, meatballs.
- Dried (yesterday's) wheat bread, dry cookies, uneaten flour products.
- Broth-based jellied dishes, sauces prepared with meat broths for main courses.
- Porridges cooked with water/meat broth.
- Dairy/fermented milk products (kefir, yogurt, curdled milk, sour cream, omelet with cheese, grated cheese, milk, cottage cheese and cream in dishes).
- Vegetable puree (zucchini, potato, beetroot, pumpkin, carrot, cauliflower), green peas, stewed vegetables with the addition of garden herbs and vegetable oils.
- Ripe pureed fruits, oranges, baked apples, tangerines, watermelon, peeled grapes.
- Desserts: marshmallows, marshmallows, jam, marmalade, preserves, honey.
- Diluted vegetable/fruit juices, tea with lemon, mineral water, coffee and cocoa.
source
Inflammatory processes of varying intensity that occur on the gastric mucosa are called gastritis. Characteristic manifestations of the disease are discomfort (sometimes expressed in acute or girdle pain), heartburn, and heaviness.
Most cases of the onset and development of the disease are associated with poor nutrition or the presence of bad habits of various natures.
In order to have an idea of the processes occurring in the body when this diagnosis is made, you should know the definition of the disease.
Autoimmune gastritis is usually called a type of gastritis in which the inflammatory processes are not acute, but chronic (permanent) and affect the mucous structures of the stomach.
The peculiarity of the disease is that failures occur against the background of changes that have occurred in the human immune system. These changes lead to the body actively producing antibodies. They also affect the own cells that form the gastric mucosa.
According to statistics, such a diagnosis occurs in 10% of all cases, so autoimmune gastritis is considered a rare disease , but can occur at any age.
Despite active studies of the specifics of the disease and the main causes that cause it, doctors have not come to a consensus on what becomes the trigger for changes . Today, the main factor in the formation and then development of autoimmune gastritis is genetic predisposition .
- Autoimmune atrophic gastritis. The peculiarity of this type is that the immune system begins to gradually destroy the cells of the stomach walls, as a result of which the acidity decreases. There is a change in the basic functions of the glands, motility deteriorates along with digestion. If treatment is not started in time, the problem can become very serious, even leading to the formation of a cancerous tumor in the stomach. Of the total volume of requests, this type is recorded on average in 21% of cases. The prognosis for life expectancy is positive - if all recommendations are followed, there is no threat to its reduction.
- Autoimmune chronic gastritis. If the disease has this form, then it is characterized by the production of specific antibodies to a protein that absorbs vitamin B12 contained in food. As a result of protein reduction, the mucous membranes of the stomach gradually shrink and atrophy. Complications with this type of disease are anemia, polyhypovitaminosis, and adenocarcinoma can also develop. This disease does not affect life expectancy if all recommendations for treatment and subsequent prevention are followed.
Additionally, a person should give up any bad habits, including overeating. It must be remembered that food entering the stomach must be warm and not contain coarse fibers. You will also need to avoid spicy or fatty foods during treatment and prevention.
Autoimmune gastritis in 75-80% of cases of fixation has a chronic form. Also, in 65% of cases, various disorders of the endocrine system are added to the underlying disease.
It is necessary to pay attention to your own health, and then consult a doctor for a diagnosis of the condition, if a person begins to notice the following symptoms, which are especially pronounced after eating:
- Heaviness in the abdomen and stomach;
- Distension;
- Painful manifestations;
- Heartburn (it may not be severe at first);
- Belching (with an unpleasant odor);
- Nausea (in most cases this is followed by vomiting);
- Active gas-forming process;
- Rumbling;
- Gurgling;
- The appearance of a taste in the mouth;
- Disorders of bowel movements (diarrhea or constipation).
In 97% of cases, you can determine that you have stomach problems by the appearance of bad breath. Also, autoimmune gastritis, regardless of the type, can manifest itself:
- Deterioration of general health indicators;
- Deterioration or complete lack of appetite;
- Weight loss;
- Increased dizziness;
- Weakness.
Additionally, the person begins to sweat heavily and becomes more irritable. The pressure most often decreases. He suffers from headaches and sleep disturbances. Visually, the problem is indicated by the appearance of pallor or the appearance of pigmentation. A coating appears on the tongue.
As the body loses vitamins, the skin becomes dry, nails become brittle, and there is an increase in the volume of hair loss. Gradually, the lack of nutrients leads to deterioration of vision, dermatitis and itching.
A characteristic sign of the problem is irritation in the corners of the mouth , popularly called “jams.” Seeing a doctor is mandatory to maintain health and reduce any risks to life.
source
Stomach pathologies not only cause discomfort to the patient, but also require a complete transformation of the previously habitual lifestyle. Autoimmune gastritis is a disease that requires a special diet and treatment.
Autoimmune atrophic gastritis is quite rare. Based on general statistics, only 11% of people suffering from stomach pathologies experience this type of illness.
With this type of gastritis, the mucous walls of the stomach become inflamed and a huge number of their cells die; this can happen in different parts of the organ. The key feature of the pathology is the formation of serious disturbances in the functioning of the immune system, as a result of which the body begins to produce antibodies to its own cells. Experts call the disease “type A gastritis.”
The disease has been little studied, which does not allow us to talk more specifically about the causes of its development and methods of prevention.
So, experts do not name the exact causes of the pathology. However, there are a number of factors that can contribute to development:
- Genetic disposition. If someone in the family suffered from such a disease, then the risk of occurrence in the offspring increases several times.
- Disturbances in the functioning of the autoimmune system.
- Frequent intake of rough food. If it gets into the stomach, it can injure its mucous membrane. When systematically damaged, the membrane responds using immune regulation.
- Presence of infectious agents in the body. Pathogenic microorganisms penetrate the internal organs, stimulating the patient’s immunity to negative effects on the gastrointestinal tract. The cause of the disease can be infections such as herpes simplex, cytomegalovirus, and Epstein-Barr virus.
When external factors have an impact, the body begins to produce antibodies to gastromucoprotein, which is responsible for the level of absorption of folic acid from incoming nutrients. It is folic acid that provides reliable protection to stomach tissues. In addition, the body produces antibodies to individual molecules. This is what prevents the formation of hydrochloric acid; food is broken down and digested much more slowly than during normal stomach function.
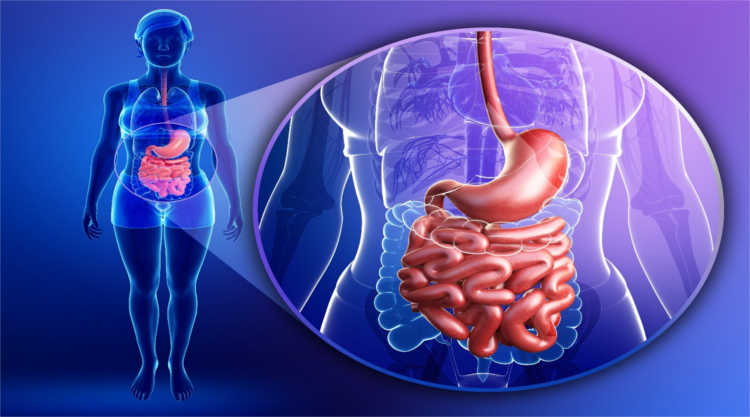
The disease is characterized by acute deficiency in the immune system. A sufficient amount of type A immunoglobulin is not produced, and antibodies to the gastric lining cells are formed. The antibodies produced have a destructive effect on the gastric gland cells, which leads to an atrophic process on the mucous membranes.
The trigger for the disease is localized where the parietal cells are located. This is mainly the body or fundus of the stomach. When cells are damaged, the level of secretion of hydrochloric acid, as well as components such as pepsinogen and gastromucoprotein (responsible for the absorption of B12 vitamins), is greatly reduced.
When autoimmune reactions occur, a destructive effect on the central nervous system can be observed. The person shows aggression, becomes very irritable, nervous breakdowns, hysterics and mental disorders occur. Emotional ups and downs may occur, and the patient may become severely depressed. Also, the mood can change sharply, a person exhibits too sharp and violent reactions. Doctors associate the manifestation of such symptoms with a severe lack of folic acid in the body.
The main signs of autoimmune gastritis appear after or during meals. The patient may note:
- severe heartburn that gets worse;
- gurgling sensations in the abdominal cavity;
- severe pain in the abdominal area;
- feeling of heaviness in the stomach;
- nausea, sometimes vomit may be released;
- flatulence and feeling of bloating in the abdomen.
As a rule, an unpleasant taste and smell reminiscent of putrefaction appears in the mouth. Many patients complain of constipation. All these symptoms are due to the fact that the stomach very slowly and poorly digests the food that enters it. Lumps of food elements are not processed for a long time, since the body does not have enough hydrochloric acid (symptoms of gastritis with low acidity).
If the patient delays treatment or does not immediately consult a doctor, the following symptoms may subsequently appear:
- the skin becomes dry, peeling begins on the epidermis;
- the patient becomes pale;
- a person loses a lot of weight in a short time;
- active hair loss begins, it becomes brittle, dry, loses thickness and volume;
- pigmentation of the skin is disturbed.
Chronic gastritis type A may include these symptoms, and during exacerbations, acquire a painful form. Along with the progression of the disease, in the absence of proper treatment, the patient may develop other pathologies associated with gastritis. There are disturbances in the functioning of the intestines, urinary system, liver, kidneys, and spleen. In addition, the risk of chronic development increases; the disease can also develop into an ulcer.
It is worth noting that everything depends on the individual characteristics of the body. Some people experience all the symptoms at the same time, while others experience only one of the listed symptoms.
The main danger is that almost always the symptoms of autoimmune gastritis are not so pronounced and the patient does not notice the first signs; the symptoms are blurred. Malfunctions in the immune system are usually not easy to detect. If there are concerns about the development of the disease, the diagnosis of autoimmune gastritis includes:
- Immunological analysis.
- General blood tests, the level of hemoglobin, the content of erythrocytes, leukocytes and platelets are studied.
- Fibroesophagogastroduodenoscopy, which shows atrophic changes on the walls of the stomach.
- X-ray examination determines the severity of the folds of the mucous walls.
- Histology.
- Probing of the stomach, which helps to establish the level of acidity of gastric juice.
- Ultrasound examination of the abdominal cavity.
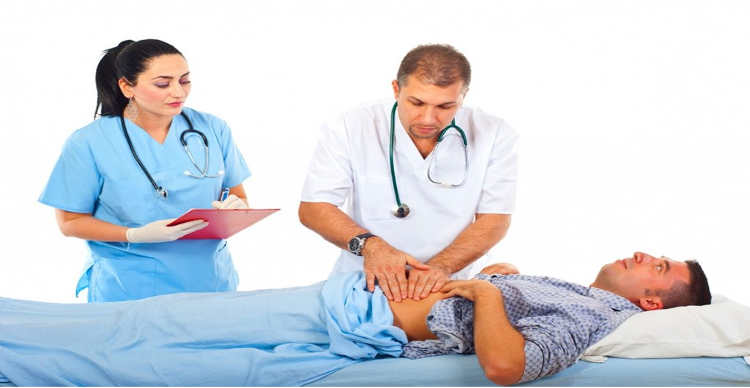
Only after conducting a whole range of examinations can the doctor make a diagnosis and prescribe appropriate treatment based on the medical history.
Treatment of type A gastritis should be comprehensive. As a rule, medications are used to eliminate severe symptoms, and the general condition is regulated by a special diet.
The main objectives of treatment are:
- Complete elimination of identified violations.
- Supports normal gastric activity.
- Relief of severe symptoms.
For such gastritis, surgery is not performed. This is due to the fact that the pathogenesis of the disease is not fully understood. Only when a tumor is detected is the stomach or its individual parts removed.
Experts say that drug therapy should begin before the entire mucous membrane atrophies. Otherwise, it will be necessary to prescribe a regimen of medications that replace enzymes. In most cases, the following is prescribed:
The doctor always prescribes folic acid to compensate for its deficiency.
Conservative therapy includes:
- Analgesic medications that have an analgesic effect.
- Medicines that relieve muscle spasms.
- Medicines that improve peristalsis of the stomach and intestines.
- Products that replenish the lack of hydrochloric acid.
In some cases, the doctor may prescribe hormones that help eliminate severe symptoms.
You can order propolis elixir ZDOROV here.
For autoimmune gastritis, the basis of treatment is:
- Enzymes (Mezim, Festal).
- Medicines that form protective films on the mucous membranes (Keal, Sukrabest).
- Products with an enveloping effect (Almagel, Maalox).
- Prokinetics (Coordinax, Metoclopramide).
Sometimes antibiotics may be prescribed, depending on the course of the disease.
Often people resort to traditional methods of treatment. Why? Firstly, this method is suitable for people prone to allergic reactions. Secondly, with the right approach, traditional methods are the safest and most natural.
Oatmeal jelly has a healing effect. If you drink a glass in the morning on an empty stomach, it will envelop the walls of the stomach, acting as a protective film. The patient will feel noticeable improvements, the stool will become much softer.
You can increase the secretion of citric acid if you regularly drink natural juices:
Mineral waters also have an identical effect.
Herbal medicine plays a special role in the treatment of autoimmune gastritis. A collection of several useful herbs is used that help restore a weakened stomach. For example, Chamomile has antibacterial, anti-inflammatory and healing effects. If you take a decoction of the plant internally, it will have a healing effect on atrophic changes.
What should be the diet for autoimmune gastritis? First of all, nutrition should be rational and include all the necessary nutritional elements. You should eat 5 times a day, three meals will be main meals, and two snacks.
It is strictly forbidden to eat:
- Fried, smoked, canned foods.
- Flour products, bakery products.
- Confectionery products.
- Chocolate, lollipops.
- Grape.
- Oranges, tangerines.
- Fast food elements.
It is prohibited to drink carbonated and alcoholic drinks.
- Cereals (oatmeal, buckwheat, millet).
- Dairy products.
- Lean meat (boiled).
- Vegetable stew.
- Soups, broths.
- Eggs (no more than twice a week).
When treating gastritis, you should monitor the temperature of food. Food should be eaten warm. It is advisable to consume liquid food so that it is better absorbed.
It is important to pay due attention to your water consumption. You need to drink about 2 liters of clean, warm water. This will replenish the lack of moisture in the body, speed up all metabolic processes and improve intestinal function.
Fruit drinks made from cranberries, lingonberries and blackberries have a healing effect; they remove all harmful substances from the body and have a slight diuretic effect.
Doctors strongly recommend adhering to prevention tips to prevent relapse of the disease and not worsen existing health conditions.
- Try to rearrange your diet so that it is useful, healthy, and nutritious.
- Drink clean water.
- Stay outdoors more often, as walking increases the level of hemoglobin in the blood.
- Give preference to foods containing iron.
- Get examined by a gastroenterologist every six months.
Is it possible to completely recover from autoimmune gastritis? Doctors say that full recovery is possible if you change your diet and adhere to a strict diet. Sometimes exacerbations may occur; patients should always have the necessary medications in their first aid kit.
source