Inflammation of the stomach is one of the most common diseases. It is this pathology that becomes the main cause of the appearance of many other diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. Only a gastroenterologist can confirm the symptoms of gastritis and begin treatment in adults after a full diagnosis.
If pain in the epigastric area and other signs of pathology appear, it is recommended not to delay and consult a doctor. Only early detection of the disease will help stop its further development.
What is gastritis?
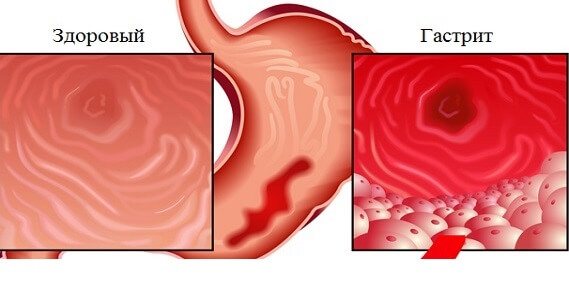
Many people do not fully understand what gastritis is. This disease is an acute or chronic inflammation of the mucous membrane of an organ, which begins to deteriorate over time.
This can happen for various reasons. Most often, it is the low or high acidity of the stomach that affects the destruction of the lining tissue. After each meal, a person is bothered by pain in the epigastric region, which occurs as a result of affecting the nerve endings of the digestive organ.
The pathology is characterized by the ability to progress rapidly without taking medications or following a therapeutic diet.
Types of gastritis
There are basically 2 main types of the disease. First, a person develops an acute form, manifested by sharp pain in the stomach, heaviness after eating, nausea and vomiting, alternating constipation or diarrhea, heartburn, and general weakness.
An attack may first begin after exposure to an irritant: spicy food, coffee, alcohol or long-term drug therapy. If you don’t immediately determine the presence of pathology and start treatment, but let everything go, in 85% of cases it will become chronic.
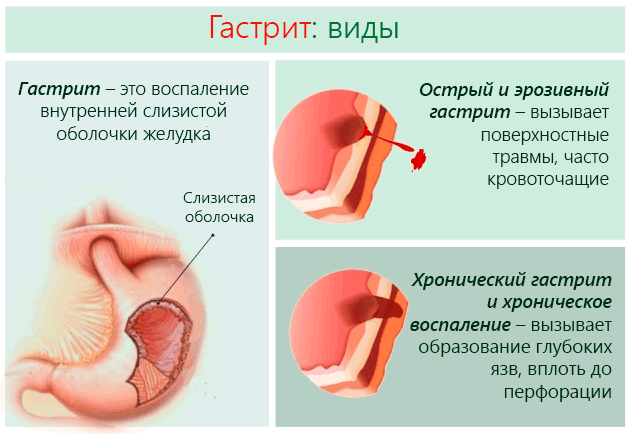
The chronic course of the disease is characterized by alternating periods of exacerbation and remission . As before, a person is bothered by pain in the stomach, nausea after eating, frequent belching, constipation alternating with diarrhea, and flatulence. But all these are only general signs that are characteristic of all forms of the disease.
Gastroenterologists distinguish several types of processes occurring in the stomach, which have individual manifestations, but are united by the name gastritis.
What forms of acute manifestation of the disease can be distinguished:
- simple;
- phlegmonous;
- toxicochemical;
- fibrinous.
Another article on this topic: Where is the duodenum located and how does it hurt?
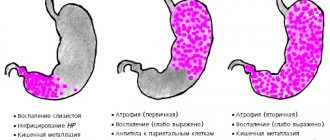
The chronic form is also divided into several types:
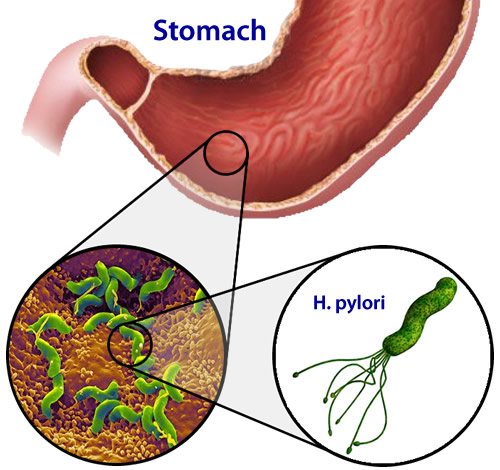
- associated - caused by Helicobacter pylari;
- autoimmune - developing due to the formation of antibodies to gastric cells;
- chemical - caused by long-term use of NSAIDs or developed as a result of constant bile reflux;
- idiopathic - arising due to regular exposure of the stomach to any aggressive factor;
- granulomatous occurring simultaneously with inflammation elsewhere - tuberculosis, sarcoidosis.
Gastritis must be taken very seriously, since the chronic form sooner or later develops into a stomach ulcer, and an ulcer is considered a precancerous disease.
Causes of gastritis
There are many factors that contribute to the occurrence of gastritis in humans. Most often, these are external causes, that is, destruction of the gastric mucosa appears due to the patient’s regular incorrect actions. But sometimes the disease develops due to exposure to internal triggers, which is much more dangerous.
External reasons:
- poor nutrition;
- regular stress;
- parasitic, infectious or bacterial damage to the digestive system;
- burn of the stomach by a chemical substance;
- improper use of medications;
- use of drugs, alcohol and cigarettes;
- dental problems;
- peritoneal injury.
Internal reasons:
- congenital defects of the digestive system;
- hereditary predisposition to the disease;
- autoimmune disorders.
Whatever the cause of gastritis, it must be eliminated first and only then treatment begin. Otherwise, the disease will return again in an even more severe form.
Classification
There are many forms of gastritis. Each of them manifests itself in a special clinic and requires a specific approach to treatment. The disease can provoke the appearance of atrophied areas, giant folds, polyps or erosion on the gastric mucosa. The longer a person delays visiting a doctor, the worse his health becomes.
Depending on the stage, pathology is divided into:
- Acute gastritis.
As a rule, it is diagnosed in a person for the first time. Manifests itself with severe symptoms and severe pain. The patient is taken to the hospital, where a corresponding diagnosis is made based on a number of signs. With proper treatment, long-term remission can be achieved.
- Chronic gastritis.
This form of the disease is characterized by sluggish manifestations. Symptoms of chronic gastritis can increase or decrease depending on the situation, diet and other factors.
Acute form of gastritis
There are many forms of gastritis known in gastroenterology. Each of them is characterized by special signs and symptoms, in addition to the general manifestations of the disease. Although in many cases the disease develops gradually and asymptomatically.
The main signs characteristic of inflammation of the stomach of any form:
- stomach pain, pain on an empty stomach or after eating;
- bowel disorders;
- nausea, vomiting.
The main types of acute gastritis are considered to be:
- Catarrhal (banal).
- Diphtheric (fibrinous).
- Corrosive (toxic-chemical).
- Phlegmonous.
Catarrhal gastritis occurs due to food toxic infections, allergic reactions, rotavirosis, and negative reactions to medications.
With banal gastritis, only the superficial layer of the mucous membrane is affected. Healing begins soon after the irritating element is eliminated.
The main symptoms of this form of gastritis:
- epigastric pain;
- heaviness in the stomach;
- mild hyperthermia (up to 37 - 38);
- bloating;
- general weakness.
Diphtheria gastritis is caused by severe infectious diseases or poisoning with dangerous chemicals.
Corrosive gastritis begins after a burn of the mucous membrane with concentrated chemicals: alkalis or acids. In this case, a deeper deformation of the gastric mucosa is observed. As a result, scar formation or the development of stomach ulcers are often observed.
The main symptoms of this form of stomach inflammation:
- heartburn;
- belching;
- vomiting blood;
- tarry stool.
Phlegmonous gastritis is a consequence of complications of cancer or peptic ulcer, dangerous infectious ailments, injury to the walls of the stomach and its mucous membrane. It is characterized by increased secretion of pus and its spread along the inner surface of the gastric tissues.
The main signs of this form of the disease are fever and intense pain in the epigastric region.
Symptoms of gastritis in adults
The symptoms of gastritis of the stomach in an adult are quite difficult to miss. Especially if the disease has already been diagnosed previously. There are several main signs that you should pay attention to.
Symptoms of gastritis in adults are:
- severe regular pain in the epigastric region, which is most often associated with meals or during fasting;
- belching with an unpleasant odor and sour taste;
- increased gas formation in the intestines;
- diarrhea and constipation most often replace each other;
- sometimes there is nausea, vomiting with or without bile, streaks of blood.
Often, against the background of gastritis, a person is worried about low blood pressure, a general deterioration in health, a change in taste habits, and even weight loss. When the first signs of gastritis appear, you should immediately contact a gastroenterologist.
Signs of illness
Very often, it is possible to determine the form of gastritis by how exactly the stomach hurts and what symptoms most often bother a person.
But we must remember that in the early stages of gastritis, regardless of its type, pain and other symptoms will be minor and short-lived, but it is very important to pay attention to them in time to prevent the development of the disease.
The most common manifestation of gastritis, regardless of type, is pain in the solar plexus. Typically, an attack of pain occurs after eating or after taking junk food, alcohol, or medications.
In some cases, pain appears during hunger, during long periods between meals.
A diet prescribed for gastritis, or simply excluding harmful foods from the diet, usually makes the pain less intense, or it goes away altogether - this is also a characteristic sign of the disease.
In addition to stomach pain, from time to time a person will be bothered by other unpleasant signs of gastritis and stomach ulcers, such as heartburn, belching, and vomiting is possible in later stages.
Bloating and frequent passing of gas are also common manifestations of the disease. The attack may occur or worsen after eating junk food or alcohol.
As a rule, even one of them is enough to suspect a person has gastritis, if at the same time he also systematically has a stomach ache.
Such manifestations most often bother a person at the onset of the disease, but chronic gastritis can be much more difficult to determine.
The chronic form of gastritis often occurs unnoticed and is practically painless for the person himself, especially if it is mild.
For a mild form, an attack of stomach pain is not a characteristic symptom; much more often the disease manifests itself as periodic constipation and diarrhea.
READ How does diffuse gastritis occur and be treated?
Severe forms of the disease are more unpleasant - from time to time a person may experience flatulence, anemia, loss of strength, and sometimes bad breath occurs.
The chronic form of gastritis, regardless of its severity, is also characterized by symptoms such as plaque on the tongue, stool disturbances, and rumbling in the abdomen that is not caused by hunger.
Video:
An attack of gastritis will differ depending on whether the disease is caused by high or low acidity.
High acidity is characterized by pain in the sternum, diarrhea, heartburn after eating, belching and flatulence.
If the acidity is low, a person may experience a feeling of heaviness after eating that is not caused by overeating, an unpleasant taste in the mouth, rumbling in the stomach, nausea, especially in the morning, irregular bowel movements and bad breath.
With prolonged chronic gastritis, exacerbations are inevitable.
An attack of chronic gastritis may look like this: a person experiences severe periodic or constant pain and burning in the solar plexus, nausea, vomiting of undigested food or bile (usually in the morning), diarrhea and constipation, dizziness, increased salivation, unquenchable thirst during the day, metallic taste.
If the disease is in severe form, then the symptoms of gastritis and ulcers may indicate a dangerous condition.
With an exacerbation of the disease in this case, vomiting may be mixed with blood, the feces become black, which means internal bleeding, tinnitus and dizziness appear.
Such an attack can be dangerous for a person if treated independently - the patient requires urgent medical attention.
Diagnostics
To diagnose pathology, a set of measures is used. Initially, the doctor interviews the patient, collects an anamnesis of his life and a specific disease. Next, he performs palpation, which can be painful for a person with gastritis. If inflammation of the stomach is suspected, a number of diagnostic procedures are prescribed.
Functional studies.
The main technique that helps identify all diseases of the gastrointestinal tract is the use of an FGDS apparatus. The fibrogastroduodenoscopy procedure is not very pleasant for a person, but it is the most informative. During the session, the specialist inserts a tube into the digestive tract through the oral cavity and, using a special microcamera, examines all the digestive organs up to the upper intestine. During FGDS, you can also take a tissue biopsy, which will help exclude the presence of malignant cells.
Laboratory research.
The patient must provide biological fluids to assess the condition of the body. Most often, feces are taken for occult blood, a general blood test and urine test.
The totality of all data obtained during the examination gives the specialist the right to diagnose the person. As a rule, a professional can identify acute gastritis without much difficulty.
Treatment of gastritis
Treatment of stomach inflammation is impossible without taking specially selected medications. The course is selected using the same methodology, but may have some differences due to the characteristics of the person’s medical history. That is, the specialist selects medications based on the stage of gastritis and the presence of concomitant diseases in the person.
Drug therapy for gastritis
It must be remembered that medications can only be used after consultation with a doctor. It is not recommended to prescribe medications on your own without prior diagnosis.
What combination of medications is used for therapy:
- antibiotics - if a bacterial infection is detected;
- enveloping drugs - protect the gastric mucosa from the aggressive effects of acid by forming a film;
- antisecretory drugs - reduce acid production;
- antispasmodics - help relieve pain;
- cytoprotectors - also protect the organ from destruction by its own gastric juice;
- medicines for the production of enzymes - help improve digestion;
- antiemetic, antidiarrheal drugs - eliminate symptoms.
Treatment with drugs lasts at least 2 weeks, but no more than a month. In the future, it will be necessary to carry out maintenance therapy, which includes diet and sometimes folk remedies.
Treatment of gastritis with traditional methods
Symptoms of gastritis in adults can be eliminated using traditional methods of treatment. It is first recommended to consult with a gastroenterologist who is monitoring the patient and knows the current state of the stomach.
Homemade recipes for gastritis:
- Warm milk. To treat gastritis at home, you can use low-fat milk, which will be slightly warmed. It helps reduce the acidity of gastric juice and also reduces the symptoms of heartburn.
- Aloe juice. Today, in any health store you can buy ready-made 100% aloe juice. If you have this plant at home, you can prepare the medicine yourself. The only rule is that aloe must grow for at least 3 years. You need to drink 1 tablespoon of juice in the morning on an empty stomach.
- Herbs. Some herbal preparations have anti-inflammatory and wound-healing effects. Medicinal properties are observed in burdock, thyme, chamomile, oak bark, plantain, and mint. A pinch of any dried herb should be poured into a glass of boiling water, let it brew to room temperature and take half a glass twice a day.
If your health condition worsens, you must immediately stop self-medication and urgently seek advice from a specialist.
Diet and prevention
Nutrition plays one of the most important roles when gastritis is detected in an adult. The diet helps improve well-being, eliminate the symptoms of pathology and prevent the development of serious complications.
What to remove from your diet:
- raw fruits, vegetables;
- legumes;
- fat;
- alcohol;
- mushrooms;
- fatty meat and fish products;
- sausages, sausages;
- fresh baked goods;
- high fat dairy products;
- onion garlic;
- sweets;
- coffee, black tea;
- carbonated drinks.
Attention! The longer the composition of the product on the packaging, the more harmful it is for a person with gastritis. Preference should be given to single-component dishes prepared independently from natural ingredients.
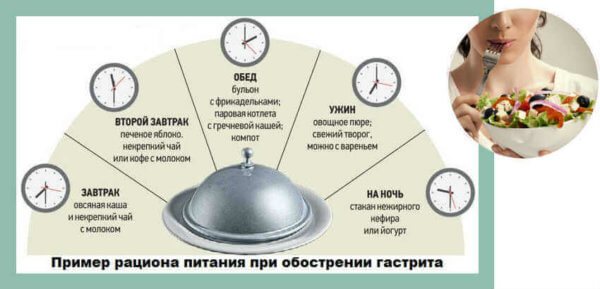
Daily meals should be divided into small portions. In addition to breakfast, lunch and dinner, you should definitely have afternoon snacks between main meals. The choice should be given in favor of steamed, baked or boiled dishes. Food products should not be fatty, salty, fried, or contain large amounts of oil or spices.
Prevention of complications after gastritis:
- Once every six months or as needed, it is recommended to be examined by a gastroenterologist. This will help to promptly detect deterioration of the condition if it happens.
- Eat properly. It is necessary to follow a diet not only during the period of exacerbation, but also during the remission stage. Of course, after treatment you can take some liberties with food, but you will need to give up gastronomic garbage forever.
- Lead a healthy lifestyle. Alcohol, drugs and cigarettes destroy the body and contribute to complications. To stop the progression of gastritis, you need to eliminate all bad habits from your life.
You should also not take non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, hormonal drugs and other medications without a doctor's prescription. In addition, you need to take care of your mental health, since severe stress also triggers the process of stomach inflammation. The disease can only be affected by a set of therapeutic measures.
Diet for gastritis
Treatment of any form of this stomach inflammation requires diet. In particularly severe cases, the patient is instructed to permanently stop eating certain foods.
Patients with gastritis must follow not only a gentle diet, but also a certain diet. You need to take food little by little, distributing the daily portion into 5 - 6 meals.
The acute form of gastritis requires avoiding foods such as:
- fatty broths;
- roast;
- herbs, spices;
- smoked meats and marinades;
- Rye bread;
- canned food and fast food;
- sour fruits;
- carbonated and alcoholic drinks;
- coffee, cocoa, chocolate.
A nutritionist will help you create the right menu. Basically, the menu for gastritis consists of such dishes as:
- pureed semi-liquid porridge;
- soups with low-fat broth;
- vegetable purees;
- jelly.
As the patient's condition improves, the diet gradually expands. However, you need to introduce new dishes into your diet little by little, carefully observing the body’s reaction. All negative consequences must be reported to your doctor.
Complications
Chronic inflammation of the gastric mucosa always contributes to the development of complications in the future. Most of them are difficult to treat and trigger a chain reaction of other pathologies in the gastrointestinal tract.
Patients with gastritis are also diagnosed with:
- malignant neoplasm;
- erosion;
- intracavitary bleeding;
- intestinal inflammation;
- B12 deficiency anemia;
- peptic ulcer.
The appearance of such unpleasant diseases significantly reduces a person’s quality of life. A strict series of dietary restrictions appears, but even with treatment, the patient is often bothered by severe stomach pain. To avoid complications, you need to promptly pay attention to the body’s primary signals and immediately contact a competent gastroenterologist.