03.04.2017
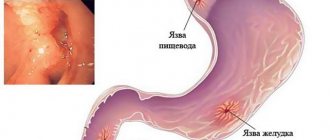
A colon ulcer is not a common, but very dangerous disease that can cause anemia and atrophy of the entire part of the intestine, and at the same time affect the activity of the duodenum and stomach. Another dangerous exacerbation of a colon ulcer can be anal fissures, which ultimately provoke the development of paraproctitis - purulent fistulas around the rectum, which can be eliminated exclusively by a radical method (surgical excision of the fistula canals). And with a colon ulcer, the symptoms do not always indicate the presence of erosions. The reason for this is trivial - neural ligaments do not pass through the intestinal walls themselves, and accordingly, the patient may not feel pain and discomfort for a long time. And they appear only when the lesion affects nearby organs or tissues.
Etiology of colon ulcer
There are a huge number of reasons for the appearance of ulcers in the large intestine. Most often, this is a violation of the digestive diet or dysfunction of the pancreas and liver. As a result, bile in its primary form can enter the intestinal cavity (in a healthy person, it enters the large intestine already decomposed into derivatives), which damages the epithelium. Essentially, a person receives a burn, which after some time transforms into erosion with bleeding or discharge of pus (if an infectious exacerbation has occurred).
The ulcers themselves in the large intestine can be single or multiple, depending on the primary cause of the disease. The latter option most often occurs against the background of Crohn's disease, when the inflammatory process affects the entire intestines or digestive tract (starting from the pharynx). Unfortunately, to this day doctors have not been able to establish the exact causes of Crohn's disease. What is known is that it is indirectly related to the course of autoimmune processes in the patient’s body.
Causes of ulcer formation
The mucous membrane is easily damaged by mechanical damage, infectious diseases and stress. Mechanical ones include: coprolites (stool of a hard consistency), carelessness of doctors during a medical examination, anal sex, insertion of objects into the body through the anus. People with rectal prolapse are at risk. They often have a solitary ulcer.
Infectious diseases accelerate damage to the mucous membrane, provoking the process of ulceration. Stress negatively affects the body and takes away the strength to resist diseases.
Causes of solitary ulcer formation
The exact causes of solitary ulcers in humans have not been identified; research is ongoing. To protect themselves from complications, scientists and doctors were able to prepare a forecast for the risk group. Those with the following diseases are at risk of getting an ulcer:
- Chronic constipation;
- Reduced or low body activity (sedentary work);
- Prolapse of the intestine through the anus at fairly frequent intervals;
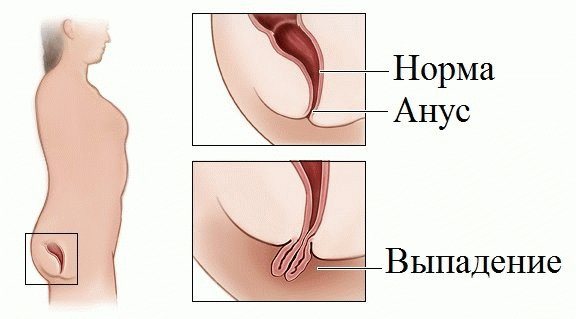
Problems with the rectum in people - Mechanical damage to the intestine due to fractures of the pelvic bones, bone chips, falling on sharp or protruding objects;
- Excess of unhealthy diet over healthy food, constant consumption of unhealthy fatty or fried foods, low fiber content;
- Anal sex.
The first signs of a colon ulcer
Most often, patients seek medical help citing the following symptoms:
- intense pain that worsens with bowel movements;
- massive or minor bleeding (again, worsening with bowel movements);
- the presence of foam, pus or a large amount of mucus in the stool;
- frequent urge to defecate, when the intestines are completely empty;
- chronic constipation;
- itching, pain, painful lumps in the anal area.
The patient may also experience increased pain if hemorrhoids recur. Naturally, not all symptoms will necessarily occur at the same time. They can replace each other, unite, intensify over time and pass without a trace. But intestinal upset doesn't go away.
As for body temperature, in the first stages of the disease it is maintained at a normal level or rises to 37.2–37.5 degrees. And if an infection occurs, the fever can rise up to 40 degrees - it depends directly on the type of infection that has entered the ulcer.
At the same time, the patient begins to lose weight quite quickly, since the intestines simply do not absorb most of the nutrients, and along with this, intoxication occurs (due to the entry into the gastrointestinal tract of rotting food products and the epithelium itself, an increase in the concentration of pathogenic bacteria). And the pain may intensify during palpation - this is precisely explained by the fact that inflammation begins to penetrate into nearby tissues and muscles.
Diagnosis of colon ulcers
Initially, doctors carry out differential diagnosis. That is, they exclude the possibility of developing gastritis, ulcers, appendicitis and other diseases with similar symptoms. An accurate diagnosis, as well as the stage of the disease, allows us to establish:
- sigmoidoscopy;
- colonoscopy;
- irrigoscopy.
That is, the cavity of the entire intestine is inspected visually. If an erosive process is detected, the patient must be hospitalized. Treatment outside a hospital setting in the acute stage is strictly prohibited.
Diagnostic features
Diagnosis of rectal ulcer is based on laboratory and instrumental research methods . First, blood, feces and urine tests are prescribed as a differential diagnosis, and then the patient is sent for instrumental studies.
The gold standard for studying the walls of the rectum is colonoscopy or sigmoidoscopy . These are endoscopic manipulations that make it possible to accurately determine the location, nature and cause of ulceration. Endoscopy allows you to take a biopsy sample for histological examination.
Important! Additionally, ultrasound of the peritoneal and pelvic organs, X-ray contrast examination (irrigoscopy), and esophagogastroduodenoscopy if a gastric ulcer is suspected may be prescribed. A rectal ulcer is differentiated from tumors, cystic cavities, polyps, anal fissures, hemorrhoids and other pathologies of this localization.
Possible complications

Tumor growth in the colon
A sign of exacerbation of a colon ulcer may be an increase in painful symptoms or peritonitis (inflammation of the peritoneum). The latter directly indicates a perforation of the intestinal wall. That is, the appearance of a through hole through which the contents enter the abdominal cavity, which provokes radical inflammation.
There is also a high probability of internal bleeding, in which the patient may exhibit signs of excessive blood loss (blue lips, a sharp drop in blood pressure, slow pulse, and so on).
Stenosis may also develop, when the intestinal lumen narrows to the point that feces can no longer move through it normally. A dense fecal impaction occurs and this is accompanied by profuse vomiting. The patient cannot eat food at all - the body immediately rejects it due to the overcrowding of the digestive tract.
In all of the above cases of exacerbation of a colon ulcer, the patient is sent for surgery. This is the only possible treatment option. Failure to do so will most likely result in death.
Symptoms of colon ulcers in the early stages of the disease
Symptoms of a colon ulcer at an early stage are less pronounced and in many cases can be completely ignored by the patient. You should pay attention to the following signs:
- attacks of diarrhea for no apparent reason;
- the appearance of anal fissures, acute paraproctitis (if they did not exist previously);
- frequent intestinal disorders;
- periodic pain that occurs 40-90 minutes after eating;
- relapses of constipation;
- weight loss for no apparent reason;
- bad breath (in the absence of diseases associated with dentistry);
- change in the shade of stool to a lighter color (due to bile entering the cavity of the large intestine);
- the appearance of lumps near the anus (paraproctitis) for no apparent reason (previous infectious diseases).
If a patient experiences at least a few symptoms, he should immediately seek help from a gastroenterologist and undergo a comprehensive examination of the gastrointestinal tract.
As for the prognosis of treatment, with timely detection of an ulcer and the use of drug therapy in combination with a gentle diet, it is possible to completely get rid of the signs of the disease in just a few months. If there is at least partial atrophy, it is impossible to do without radical treatment (meaning surgery). You should not refuse the prescribed therapy, since over time, a colon ulcer provokes the appearance of a malignant tumor, which is already colon cancer.
Treatment of chronic obstruction
Treatment of diseases of the small intestine with folk remedies helps to get rid of dangerous pathologies and disorders. Dried fruits help well with chronic obstruction. They help stimulate intestinal motility. They also retain most of the vitamins and are just as healthy as fresh fruits. Doctors recommend adding dried fruits to your usual diet. Raisin decoction is often used in the treatment of many intestinal diseases.
Sea buckthorn has a pronounced anti-inflammatory quality. Take 1 kg of fruit, crush it in a bowl, and then squeeze the juice from the berries. Drink 1 tsp daily strictly on an empty stomach. natural freshly squeezed juice.
Ulcerative colitis
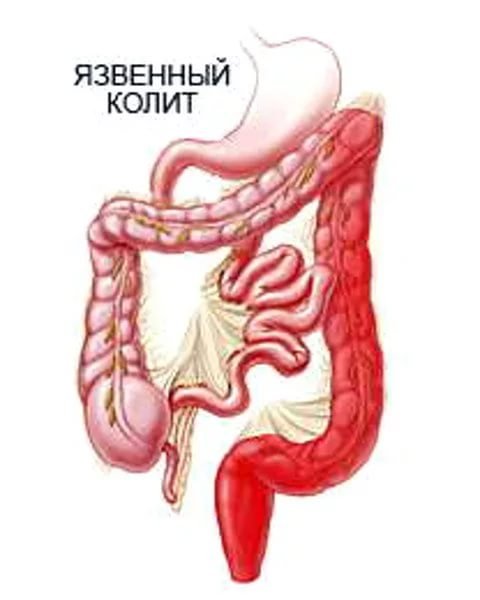
Ulcerative colitis is very similar in etiology to peptic ulcer disease, but most often it is impossible to establish the primary cause of erosions in the large intestine. Most doctors are inclined to think that this disease is entirely associated with hereditary predisposition. The symptoms of ulcerative colitis are similar to peptic ulcers. The only exception is that colitis develops over a long period, without a sharp exacerbation. In this case, not only the colon, but also other parts of the digestive tract can be affected. Treatment is predominantly symptomatic combined with diet. In critical cases, surgery is performed.
In summary, a colon ulcer is a dangerous disease that occurs at an initial stage without noticeable symptoms. The patient complains only of gastrointestinal upset and infrequent constipation, exacerbation of hemorrhoids (if there is a tendency to it). The symptoms of the ulcer are similar to colitis. When these diseases are identified, drug therapy and strict adherence to a strict diet are prescribed. If an aggravation is allowed, then surgery will definitely be required. The worst scenario is the transformation of an ulcerative lesion into a malignant tumor (and it develops very quickly, since atrophy of part of the intestine will occur).
Treatment of the small intestine
In young children, the pathological process occurs simultaneously in the large and small intestines, this is due to their anatomical and physiological characteristics of the digestive system. School-age children are characterized by more isolated damage to the intestinal sections. In any situation, treatment of the small intestine should first begin with the organization of individual therapeutic nutrition, which should take into account the period of illness, general condition, and age.
During the period of exacerbation of enterocolitis in any of its forms, it is necessary to exclude the following products:
- black bread;
- raw fruits and vegetables;
- fresh herbs and berries;
- nuts.
It is also necessary to take into account and exclude those foods that cause an allergic reaction in a person.
If you have ulcerative colitis, the patient should exclude all dairy products from their diet. The only exceptions are butter and cheese. The protein that the body previously received from dairy products must be replaced with foods such as eggs, fish, and meat.
If a child has congenital enzymopathy, then the diet depends on the enzyme deficiency in the body:
- for celiac disease, it is necessary to exclude barley, rye, oatmeal, and wheat;
- if a child has intolerance to cow's milk protein, then it must be replaced with soy milk, or breast milk, or with a mixture prepared from powdered milk;
- disaccharide deficiency excludes the consumption of starch, sugar, and in case of lactose intolerance, fresh milk.
If the condition improves, then you need to gradually expand the diet.
If malabsorption syndrome is severe and occurs with dehydration, forming cachexia, then parenteral nutrition and fluid administration are indications for treatment. It is necessary to administer intravenously drugs that contain fats, vitamins, amino acids, carbohydrates, as well as sodium and potassium salts. Only with secondary infection are children in serious condition indicated for treatment of the small intestine using antibacterial therapy. Biological preparations for restoring intestinal microflora are: bifidum-bacterin, colibacterin.
If there is an increase in intestinal motor function, then antispasmodics are prescribed. Treatment of the small intestine in the complex therapy of enterocolitis involves the use of sedatives. In case of complications of Crohn's disease and nonspecific ulcerative colitis, emergency surgical treatment may be prescribed.