Good afternoon, many will be interested in understanding their health and their loved ones, and I will tell you my experience, and we will talk about Biliary pancreatitis - symptoms and treatment. Most likely, some details may differ, as was the case with you. Please note that you should always consult with highly specialized specialists and not self-medicate. Naturally, you can quickly find the answer to the simplest questions and diagnose yourself. Write your questions/suggestions in the comments, and together we will improve and supplement the quality of the material provided.
Prognosis and preventive measures for biliary pancreatitis
Speaking about what the prognosis is for the treatment of biliary pancreatitis, the answer is definitely positive. If the chronic form occurs, surgical intervention will most likely be indicated as a method of treatment. In case of non-compliance with the diet, schedule and diet, menu, alcohol consumption - the prognosis will be definitely unfavorable.
In terms of prevention, it is still the same diet, in the form of dietary dishes and a regimen of eating in small portions. In addition, you should avoid fatty and fried, spicy foods, sweets and baked goods, foods that have a choleretic effect and a large number of medications unless absolutely necessary. Along with this, you should be regularly examined by a gastroenterologist, once every six months.
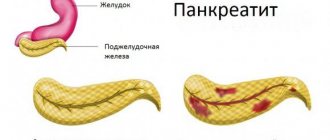
Biliary pancreatitis is a disease associated with inflammatory processes occurring in the pancreas, affecting the entire genitourinary system. If left untreated, it results in a very serious malfunction in the body.
In its course, the disease has two forms - acute pancreatitis and the chronic form of the disease, or as it is also called biliary-dependent pancreatitis.
Possible complications and prevention
Thanks to properly selected therapy by a gastroenterologist, a person can quickly return to a full life, even after removal of the gallbladder. In advanced cases, there is a risk of gallstones moving. In this situation, there will be a need to significantly expand the scope of surgical intervention.
The most dangerous complications can occur with acute biliary pancreatitis.
If you do not immediately pay attention to the signs of this pathology, there is a risk of serious disruption of the functioning of all digestive organs. In such a situation, the pain syndrome will increase after each heavy meal.
Complications of PD:
- Cysts are abnormal formations in the affected organ that contain fluid.
- Abscesses are purulent foci in the tissues of the pancreas.
- Obstructive jaundice - manifests itself in the form of yellowing of the skin as a result of an increase in bilirubin in the blood.
- Diabetes mellitus is considered both a sign and a consequence of the disease.
- Pancreasclerosis is an increase in the volume of connective tissue in the pancreas.
- Pancreatic necrosis is the death of a certain area of the pancreas or the entire organ.
To prevent the development of progressive PD, it is important to adhere to a healthy lifestyle. Doctors advise giving up alcoholic beverages, eating right, and exercising. Timely diagnosis and treatment of diseases of the hepatobiliary system is also of great importance.
In the absence of adequate treatment, biliary pancreatitis can lead to a number of complications:
- shock;
- respiratory failure;
- acute liver failure;
- gastrointestinal bleeding;
- encephalopathy;
- pancreatic necrosis;
- intestinal obstruction.
Later complications include:
- narrowing of the intestines;
- fistulas;
- pseudocysts;
- ascites.
In cases of untimely treatment of the acute form, as well as during the course of a chronic disease, there is a possibility of developing such consequences as:
- disruption of the functioning of nearby organs;
- state of shock;
- acute liver or respiratory failure;
- hemorrhages;
- intestinal obstruction;
- secondary diabetes mellitus;
- diabetic coma;
- jaundice;
- formation of abscesses, pseudocysts and fistulas;
- accumulation of a large amount of fluid in the abdominal cavity;
- intestinal stenosis;
- pancreatic necrosis.
Symptoms of biliary pancreatitis
Speaking about this disease, it is worth noting once again that it can manifest itself in both chronic and acute forms.
Thus, the clinical symptoms inherent in a disease such as biliary pancreatitis in its acute form are similar to other forms of pancreatitis, namely:
If we talk about the chronic form, then during the chronic course of the disease the following reasons can be diagnosed:
- loss of appetite and attacks of nausea.
- gagging and chronic constipation or, on the contrary, diarrhea.
- weight loss and increased body temperature.
But still, when diagnosing a disease such as baliar pancreatitis, it is worth remembering that it is also characterized by its own specific features.
So its characteristic symptoms are:
- attacks of pancreatitis pain are distinguished by greater attack intensity and duration.
- in the case of the development of a disease such as baliar pancreatitis, the symptoms are also characterized by prolonged constipation, reaching intestinal failure.
- The pain itself is reminiscent in nature of biliary colic, when the lesion itself is localized in the area of the right hypochondrium or radiates to the lower back, on the right side, arm or under the shoulder blade.
- Baliary pancreatitis and symptoms such as jaundice are inextricably linked.
- many patients report symptoms such as a feeling of bitterness, an unpleasant bitter taste in the mouth and belching.
Causes of biliary pancreatitis
The main reasons leading to the occurrence of this disease are:
- cholelithiasis, which occurs due to stagnation of produced bile in the bile ducts.
- cholecystitis and cholangitis.
- abnormalities in the internal structure of the bile ducts.
- failure in the contractile activity of the gallbladder, leading to the reflux of produced and accumulated bile into the body and, as a consequence, the development of jaundice.
In addition, the acute form of pancreatitis can be caused by eating large portions of fried and fatty foods, sweets and high-calorie foods.
Potato juice
Main reasons
In most cases, the disease develops against the background of gallstone pathology, but there may be other reasons when biliary-dependent pancreatitis appears:
- Malfunctions in the structure of the bile drainage channels.
- Inflammation of the gallbladder.
- Impaired contractility of the gallbladder.
- Cirrhosis.
- Infection with helminths.
- Inflammation or changes in the area of the duodenal papilla.
Biliary pancreatitis refers to a secondary pathology that develops against the background of already developed diseases. This is caused by malfunctions not in the pancreas, but in other organs that are located nearby.
Symptoms
The inflammatory disease can have various clinical manifestations, which makes diagnosis quite difficult. Biliary pancreatitis has characteristic symptoms:
- The occurrence of pain in the abdomen, which radiates to the back and hypochondrium. As a rule, pain occurs after eating “forbidden” foods. It occurs at night or a few hours after eating smoked, fatty or fried foods.
- Severe nausea and sometimes vomiting.
- The pain does not go away for a long time.
- Feeling of bitterness in the mouth.
- Disorders in the functioning of the intestines (diarrhea or constipation), which develops into acute intestinal obstruction.
- Decreased appetite.
- Significant weight loss.
- Temperature rises to 38 °C.
- The appearance of jaundice.
In the case of a chronic form of the pathology, the patient is bothered by painful sensations of an aching nature that do not go away for a long period of time. In this case, painkillers will only give a temporary effect.
The acute form of biliary pancreatitis is characterized by acute pain. When it is possible to eliminate spasms in the smooth muscles, which are a manifestation of strangulation by a stone, the pain goes away. In addition to severe pain, the patient’s body temperature may rise slightly at this time.
Symptoms and treatment will depend on how advanced the biliary pancreatitis is.
Effective diagnostic methods
In order to determine the presence of the disease, as well as establish its cause, it is necessary to conduct a thorough diagnosis.
It consists of actions that we will consider below.
- The acute form of biliary pancreatitis requires diagnosis in a hospital setting. Blood and urine tests are taken, and an ultrasound is performed.
- When a patient is admitted to the hospital, he is prescribed a general blood test. When the results show an increase in the number of white blood cells, it is concluded that the disease is progressing, so immediate treatment must be started.
- Next, a biochemical blood test is performed, which in acute forms of the disease shows a high transaminase level.
- To make a final conclusion, cholangiopancreatography is performed.
Chronic biliary-dependent pancreatitis when taking blood tests shows the following changes:
- increase in bilirubin levels;
- increase in cholesterol;
- increased alkaline phosphatase;
- reduction of proteins.
During diagnosis, an increase in the amount of amylase in the urine is observed. This also suggests that inflammation of the pancreas is present.
After all tests and other diagnostic methods have been carried out, a conclusion is made and treatment is selected.
Treatment of pathology
Due to the fact that biliary pancreatitis is a secondary disease, treatment is based on eliminating the root cause, which is why diagnosis is so important. Only based on its results, the gastroenterologist will select treatment for acute biliary pancreatitis and exacerbations of chronic, which includes the following stages:
- pain relief;
- enzyme treatment;
- adjustments to diet and lifestyle;
- elimination of vitamin deficiency.
We recommend reading: Allergic rash on the face: photos, causes and how to remove acne
After the symptoms of acute pancreatitis are relieved, the doctor decides on the need for surgery. If the underlying cause is cholelithiasis, this is an absolute indication for surgery.
In the case of a chronic form of pancreatitis, if the root causes of the disease are cholelithiasis, adenoma of the papilla of Vater, or cicatricial narrowing, surgical intervention is indicated.
Today, low-traumatic surgery is predominantly performed, using micro-instruments and a camera. Operations with this modern method allow the surgeon to carry out all the necessary surgical manipulations through tiny holes that he makes in the abdominal wall, and also make the postoperative recovery period as short as possible.
In some cases, surgical interventions are performed using the laparotomy method, when a large incision is made in the abdominal wall.
When diagnosing small stones in the gallbladder, they can be dissolved. A conservative treatment method is possible here. Therapy is carried out to a sick person exclusively by a doctor and only after receiving diagnostic results, in order to exclude possible contraindications.
Modern medicine today has the ability to treat cholelithiasis by crushing stones with ultrasound (extracorporeal shock wave treatment), after which long-term litholytic treatment is prescribed. This method in most cases makes it possible to avoid abdominal surgery.
Dietary nutrition is an important point in the treatment of chronic biliary pancreatitis. For biliary pancreatitis of this form, the diet should always be followed.
Treatment of chronic biliary pancreatitis also necessarily includes the prescription of the 5P diet, but there is a maximum restriction on everything that has choleretic properties. You should not eat oil (vegetable or butter), caviar, egg yolk, tomatoes, cabbage, strong vegetable broth, or fresh herbs.
No self-medication for such a disease is acceptable; taking medications and procedures only as prescribed by a doctor.
Biliary pancreatitis is a disease of the pancreas that develops when the bile ducts are not functioning properly. As a rule, adults are susceptible to the disease. Symptoms and treatment are similar to other housing and communal services diseases.
Due to the development of the inflammatory process in the pancreas, when it becomes clogged with stones from the choleretic tract and a disease occurs. There are two forms of the disease: acute and chronic.
Biliary pathology has serious complications, including death. It is the result of a complication of inflammation of the biliary tract, when surgical intervention is indicated, and conservative treatment methods are used only as a preventive measure or to correct the course of the disease.
Parenchymal biliary-dependent pancreatitis is chronic and recurrent. If the patient’s diet during the acute stage of chronic biliary pancreatitis is dietary, he does not eat fried, fatty or smoked foods, then recovery is significantly accelerated.
Symptoms of biliary pancreatitis
The clinical manifestations of biliary pancreatitis are similar to other gastrointestinal diseases: antral, viral gastritis, gastric and duodenal ulcers, intestinal tumors, chronic acalculous cholecystitis and others.

In the vast majority of cases, the main symptom of pancreatitis is pain. Pain in the abdominal area can be felt in the epigastrium, radiating to the hypochondrium, back, and right shoulder. Most often, pain appears a few hours after eating food or at night, after drinking drinks with gas that cause spasm of the sphincter of Oddi.
Pain often appears after a diet break. The pain may be accompanied by fever, nausea, and a feeling of bitterness in the mouth. Obstructive jaundice may occur - when the papilla of Vater is completely blocked by a stone - yellowing of the skin and mucous membranes occurs.
During the inflammatory process in the tissues of the pancreas, its endo- and exocrine functions malfunction. Endocrine disorders are characterized by disturbances in carbohydrate metabolism, and exocrine disorders are characterized by pancreatic enzyme deficiency with subsequent disturbances in the digestive process. Such a patient has loose stools several times a day, the stool has a grayish color, a greasy consistency, and a foul odor.
Rumbling in the stomach, flatulence are disturbing; in addition, belching, heartburn, and lack of appetite are observed. Against the background of increased fat loss, diarrhea, and failure of the digestive process, body weight loss occurs.
In addition to the similarity of the clinical picture, there are also features in the symptoms:
- pain in the abdominal area, which is caused by taking medications and foods with a choleretic effect;
- duration of pain attacks. Pain lasts much longer compared to other pathologies;
- the appearance of paresis in the intestinal area. In most cases, this type of pancreatitis occurs with the formation of constipation, other forms of the disease cause diarrhea;
- pain in the right hypochondrium, they resemble biliary colic;
- development of jaundice;
- regular belching with a bitter taste, bitterness in the mouth.
- soups with cereals (during a period of stable remission - with milk), from vegetables;
- boiled beef, poultry, lean fish;
- steamed omelette made from egg whites;
- porridge;
- vegetable oils;
- pasta;
- sweet berries and fruits;
- yesterday's bread;
- low-fat fermented milk products, butter (daily intake no more than 0.25 g);
- honey;
- freshly squeezed sweet fruit juices without sugar, vegetable juices, jelly, compotes.
Surgery for biliary pancreatitis
The need for surgery arises in the following cases:
- In advanced forms of gallstone pathology, when the size of the formed stones cannot be crushed by ESWL, and completely block the bile ducts, preventing bile from moving into the intestinal cavity. A type of operation called cholecystectomy is performed.
- With the development of an adenoma localized in the area of the nipple of Vater.
- Another indication for surgery is scar narrowing, or strictures.
In most cases, surgical specialists perform low-traumatic endoscopic operations using several minimal incisions and micro-instrumentation and a special camera. But, in difficult situations, preference is given to open laparotomy.
Before the surgical intervention, the patient is prescribed a course of treatment consisting of the use of the antibiotic drug Rotacef, which helps prevent infection in the preoperative period.
In the classification of pancreatic diseases, it is biliary pancreatitis that is at the first stage and is the most common form of pathology, affecting more than half of the total number of all patients with pancreatic disease. Biliary pathology can occur at any age, both in a child and an adult, but more often this disease develops in adults. In the materials of the presented review, we will take a closer look at what biliary-dependent pancreatitis is, what provokes its formation, how it manifests itself and possible methods of treatment.
We recommend reading: Immunoglobulin E is elevated: causes, diagnosis and treatment.
Conservative treatment
At the initial stages of pathology development and in the presence of microscopic stones in the gallbladder, treatment of the biliary form of pancreatitis can give positive results using medications. To successfully obtain a favorable prognosis for the medical history, litholytic therapy is prescribed, through the use of Ursosan or Ursofak, which promotes the dissolution of stone-like deposits. This therapy is carried out in the absence of contraindications such as blockage of the biliary tract, the presence of calcium and pigment stones, and also after diagnostic procedures in the form of CT, ultrasound and cholecystography, which provide information about the density and composition of stones. Cholesterol stones are the easiest to dissolve.

One of the most modern methods of conservative treatment of biliary pancreatitis is extracorporeal shock wave therapy, which allows crushing stones using ultrasonic waves.
Symptoms
The symptoms of this type of pancreatitis have very similar signs that occur with disorders of the gastrointestinal tract.
Only a doctor can assess the condition and establish the real causes, after collecting complaints and diagnosing the body.
The patient himself may feel characteristic signs of disorders, which often appear during exacerbation or acute course of the disease.
As a rule, obvious pain begins under the ribs; the pain may be localized in the back. As a rule, the symptom appears at night or in the evening.
Other signs of violations include:
- Temperature rises to 37-37.5 degrees.
- Nausea and vomiting.
- The appearance of bitterness in the mouth.
With the disease, blockage of the ducts and other structural disturbances may occur, in which case the skin becomes yellow, and carbohydrate metabolism malfunctions appear.
After this, the main symptoms change and appear as:
- Frequent diarrhea.
- Burning of the esophagus and belching.
- Decreased appetite.
- Losing body weight.
- Disturbed functioning of the digestive system due to the inability to digest food normally.
- Changes in the color and odor of stool.
As biliary pancreatitis progresses, metabolic processes begin to malfunction and the body loses fats, vitamins and other useful substances.
Against this background, patients will experience brittle hair and nails, and the condition of the organs of vision and skin will deteriorate.
Treatment of pathology
The manifesting symptoms and treatment of the biliary form of pancreatitis should primarily consist of eliminating the primary pathology and normalizing the functionality of the affected liver, gallbladder or bile ducts.
To relieve pain, it is necessary to take into account the form of intestinal dysfunction: when spasm of the gallbladder and bile ducts develops, it is necessary to take antispasmodic drugs, in the form of Duspatalin, or Debridat; when atonic processes develop, prokinetic drugs are prescribed, such as Domperidone, Eglonil, Metoclopromide.
To restore the composition and properties of bile, combination drugs with a hepostabilizing effect complemented by an antispasmodic effect, such as Hepatofalk or Odeston, are prescribed.
Treatment of chronic biliary pancreatitis can be carried out through conservative therapy and direct surgical intervention. The most important role in the treatment of the disease is given to a special dietary diet.
The need for surgery arises in the following cases:
Characteristics of pain syndrome
Pain occurs in 90% of patients; only in rare cases is a painless course possible. Localized in the epigastric region, radiating in both directions, to the right shoulder, lower back.
Pain occurs 2.5–3 hours after eating, at night. Acute pain may occur immediately after drinking carbonated water. It causes spasm of the sphincter of Oddi and provokes pain. The most common cause is a violation of the diet: consumption of fatty and fried foods, alcohol, hot sauces and seasonings, marinades and pickles, smoked meats.
Patients describe the pain as “girdling”
Medications
Antispasmodics (Atropine, Platyphylline) are used to relieve pain. To ensure temporary “rest” of the pancreas, drugs that block H2-histamine receptors (Ranitidine, Kvamatel), and a secretion blocker Octreotide are needed.
Taking enzyme preparations containing lipase and proteases (Pancreatin, Panzinorm, Creon) has an inhibitory effect on excess enzymes. The body, without experiencing a lack of these substances, blocks its own production in the pancreas. Depending on the severity of intoxication, Hemodez and Poliglyukin are administered intravenously.
Antibiotics are used to eliminate inflammation; aminopenicillins, cephalosporins, Metronidazole, macrolides, and aminoglycosides are usually used. Patients with a chronic course of the disease and during the recovery period need symptomatic therapy. A complex of vitamins and a supporting dosage of enzymatic agents are prescribed.
M-anticholinergic drugs (Gastrocepin) help eliminate spasm of the sphincter of Oddi
You should be careful when taking choleretic drugs. If there is a tendency to form stones, one must take into account their multidirectional action. Increased motility of the bile ducts and stimulation of bile production can provoke an exacerbation. Perhaps only products that normalize the chemical composition and prevent the loss of mineral sediment will be suitable.
Diagnosis of biliary pancreatitis
Diagnosis of pancreatitis of biliary origin does not differ from standard tests for pancreatic disease. The following must be carried out:
Diagnosis of pancreatic diseases
Shadows of stones on a plain radiograph of the abdominal cavity are rarely detected; contrast cholecystography is more informative
Diet
For the first three days of an exacerbation, the doctor prescribes fasting. Only drinking alkaline mineral water without gas is allowed. Then, basic food products are gradually introduced into the menu. The number of feedings increases to 6 times a day, the portions are small, all dishes must be mechanically processed and boiled.
The preparation of fried and smoked products is strictly prohibited. The patient is limited in fats in his diet, and carbohydrates are monitored. The daily diet should contain no more than 80 g of fat, 350 g of carbohydrates, and the amount of protein increases to 120 g.
Sweets, culinary products, fatty meats are prohibited; butter is placed on the plate in limited quantities. The intake of proteins is compensated by cereals (buckwheat, rice, oatmeal), dairy products (cottage cheese, casseroles), meat and fish meatballs, meatballs, and steamed cutlets. Juices are recommended only fresh, diluted with water. Stewed fruits and vegetables.
The most typical manifestations of biliary pancreatitis are pain and intestinal dyspepsia caused by exocrine insufficiency.
Let's work together to make the unique material even better, and after reading it, we ask you to repost it on a social network convenient for you. net.