Problems with internal organs can be both chronic and acute. If the first, despite their danger, do not show very significant symptoms, then the second are all bright and unpleasant. One of these diseases is reactive pancreatitis, sometimes leading to very burning pain with a vivid complex of other unfavorable symptoms. It is very important to know what this disease can lead to and how you can get rid of it.
Features of the disease
Reactive pancreatitis is an acute inflammatory reaction localized in the pancreas due to certain other diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. In most cases, pathology occurs due to problems with the stomach, bile ducts, liver and intestines.
Reactive pancreatitis, as its name suggests, occurs very suddenly. It does not become a chronic disease, but does not tolerate a delayed response to its treatment.
The International Classification of Diseases, Tenth Revision, does not define a disease such as reactive pancreatitis. Despite this, this disease belongs to the concept of Acute pancreatitis, assigned under code K85.
It does not lead to irreversible consequences, which is why the prognosis for the course of this problem with the pancreas is always very favorable. To eliminate the symptoms of a disease, you just need to influence its cause, after which the signs of the disease will disappear.
The main complications of reactive pancreatitis without appropriate therapy are impaired renal and liver function, as well as increased glucose levels in human blood. In addition, some patients develop infected pancreatic necrosis.
Pancreatopathy in adults treatment
Disturbances in the production of enzymes lead to significant deviations in the functioning of the body.
One of these deviations is pancreatopathy. This disease can affect the functioning of the pancreas, which affects the functioning of the digestive system and leads to a weakened immune system.
What is pancreatopathy?
Pancreatopathy is a non-inflammatory disorder of the pancreas, in which the body lacks enzymes that are necessary for the normal functioning of the digestive system. If there are not enough of them, the digestion process is complicated. Also, the lack of enzymes affects the condition of the pancreas, further complicating the situation.
There are two types of violation:
- Primary. Its appearance is due to the presence of other diseases.
- Secondary. It occurs due to an incorrect lifestyle. It is especially often provoked by poor nutrition.
Reactive pancreatopathy, which appears under the influence of negative external influences, is considered as a separate type. These could be inflammatory diseases, poisoning or severe allergic reactions.
Often reactive pancreatopathy occurs in a child, since the child’s body is more susceptible to adverse factors. The immune system of an adult neutralizes a significant part of the dangerous influence, thereby avoiding pronounced pathological changes.
If there are disturbances in the digestive process, difficulties arise with metabolism and absorption of useful elements. The bad thing is that the pathology may not manifest itself for a long time, which is why it is detected at an advanced stage.
Mechanism and causes of occurrence
Enzyme deficiency can be caused by several circumstances:
- Insufficient synthesis by the organ itself.
- Blockage of the ducts through which enzymes enter the intestines (with sufficient synthesis).
- Lack of enzyme activity in the intestines, despite their normal production and excretion.
There are reasons for each of these circumstances.
Enzyme deficiency due to insufficient production occurs under the influence of pancreatic pathologies:
- congenital disorders;
- inflammatory diseases of the pancreas;
- organ underdevelopment;
- previous operations on the pancreas;
- atrophy;
- replacement of glandular tissue with adipose tissue.
These problems make it difficult for the organ to function, which can cause the amount of enzymes synthesized to decrease. Therefore, it is so important to treat all diseases, and even better to prevent them.
Pancreatitis is a common disease that, if left untreated, can cause pancreatopathy. And its appearance is preceded by dyspancreatism (dyspancreatitis), which is quite easy to eliminate. But its symptoms are often ignored, which is why the pathological process progresses, turning into pancreatitis, and then into pancreatopathy.
Blockage of the ducts is caused by mechanical damage to the organ and diseases:
- scars formed after operations;
- tumor formations;
- stones.
Because of this, the produced enzymes cannot enter the intestinal lumen or enter there in small quantities. This is how pancreatopathy usually occurs in adults.
If enzymes are produced in sufficient quantities and easily penetrate the intestines, but do not act, then this is due to problems in the gastrointestinal tract (damage to the intestinal mucosa).
Pancreatopathy can also be caused by poor nutrition. Overeating or abuse of heavy foods creates a load on the gastrointestinal tract and pancreas, which is why difficulties arise.
Symptoms in children
Children often suffer from this disease, due to the fact that their body as a whole and individual organs are in the process of formation and are too vulnerable. Therefore, it is worth considering the manifestations of the disease in childhood.
The pathology can exist for a long time in a latent form, and minor signs are often confused with overwork or vitamin deficiency.
Pancreatopathy is indicated by:
- pale skin;
- weakness;
- weight loss;
- diarrhea;
- change in the color of feces (stool becomes gray and may contain undigested food particles);
- attacks of nausea;
- vomit;
- bloating;
- heaviness in the stomach;
- poor appetite.
Indirectly, the presence of the disease is indicated by the child’s apathy, lack of desire to participate in outdoor games, and tearfulness.
from Dr. Komarovsky:
Diagnosis of the disease
The symptoms of the pathology are similar to many other diseases, so diagnosis is needed.
It uses:
- blood test (detection of serum elastase and sugar levels);
- stool examination (pancreatic elastase content);
- Ultrasound (detection of tumors and damage to the pancreas);
- X-ray of the abdominal cavity (establishing the causes of pancreatopathy: pancreatic insufficiency, blockage of ducts, etc.);
- MRI (study of the structure of the gland).
A very effective method is a direct probe secretin-cholecystokinin study. For children, this diagnostic method is rarely used due to the discomfort during its implementation.
Treatment methods
Drug treatment of pancreatopathy is aimed at eliminating its causes. Therefore, different types of medications can be used, depending on the provoking disease.
The second part of the therapy is to help the gastrointestinal tract in the process of digesting food, which reduces the load on the pancreas. Typically, Pancreatin is used for this, which is one of the enzyme preparations. If the disease is severe, there is a need to use a complex of medications that stimulate the absorption of nutrients.
Symptomatic therapy helps with the most unpleasant manifestations of the pathology:
- antiemetics;
- antidiarrheal;
- antipyretics;
- painkillers.
Source: https://shokomania.ru/pankreatopatija-u-vzroslyh-lechenie/
Causes
The mechanism of development of reactive pancreatitis lies in blocking the flow of enzyme substances through the pancreatic duct due to its spasm. Thus, the secretions of the organ begin to accumulate in it, which is why they have a destructive effect on the structure of its tissues. This leads to inflammation.
The causes of the pathological process most often are the following factors:
- alcohol abuse;
- problems with the correct diet;
- diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, both chronic and acute;
- poisoning by poor-quality food or certain toxic substances;
- intoxication due to helminthiasis;
- incorrect use of certain medications;
- constant or very strong psycho-emotional stress;
- allergies to certain foods or medications;
- genetic predisposition;
- some injuries and bruises to the abdomen.
Among the most likely causes of the development of reactive pancreatitis in childhood, it is worth highlighting improper feeding of babies, or disturbances in the diet.
What is reactive pancreatitis
The pancreas is responsible for the secretion of pancreatic juice, which is necessary for the complete digestion of food. It also produces hormones that regulate the metabolism of carbohydrates, proteins, and fats in the human body.
Reactive pancreatopathy is an inflammatory disease that develops as a result of improper functioning of the pancreas. It occurs in response to a certain impact (primary factor). Inflammation begins after a complete or partial obstruction of the ducts or due to reflux of intestinal masses.
Symptoms
Reactive pancreatitis in the initial stages of its development may not cause any significant symptoms, but this does not mean that it does not need to be diagnosed and treated. Most often, this form of pancreatic problem occurs in the form of belching, bloating and constant heartburn. In most cases, a sick person does not pay attention to such symptoms, as he may associate them with other things.
Experts divide reactive pancreatitis into several types depending on the nature of the damage to the pancreas:
- finely focal;
- large-focal;
- subtotal;
- total.
Reactive pancreatitis itself is a subtype of acute pancreatitis. In addition, there is also chronic pancreatitis, which occurs in recurrent forms.
In general, reactive pancreatitis is manifested by the following symptom complex, which is characterized by such signs as:
- heartburn and nausea (also manifested by one type of predominantly fatty food);
- periodic occurrence of hiccups;
- loss of appetite and desire to eat;
- intense and quite bright painful sensations in the abdomen;
- feeling of chills against the background of increased body temperature;
- diarrhea and problems with stool.
Due to the fact that reactive pancreatitis develops against the background of other diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, its symptoms may be supplemented by signs of these diseases. Therefore, the picture may be somewhat blurred or enhanced by other manifestations of the disease.
Symptoms of reactive changes in the pancreas
When pancreatic tissue changes, a lot of unpleasant symptoms arise. The most typical manifestation of problems with the gland is pain. If there are diffuse changes in the pancreas of a reactive nature, the following symptoms may occur:
- increased fatigue;
- nausea;
- abdominal muscle tension;
- temperature;
- vomit.
Specific symptoms depend on the degree of damage and the underlying disease. The more the pancreas is disrupted, the brighter the manifestations. If pain is detected in the left hypochondrium, abdominal area, or dyspeptic disorders, you should consult a doctor. In case of acute pain, you must call an ambulance.
You can learn more about pancreatitis from the video:
Diagnostics
Before you begin treatment for reactive pancreatitis, you should go through the process of diagnosing this disease. To do this, you can contact a gastroenterologist. If the disease occurs in a child, you should first come to an appointment with a pediatrician, who can refer you for additional consultation to other specialists.
Based on the patient’s complaints, the doctor must examine him, palpate the abdomen, etc. Based on the collected data, it is most often necessary to carry out some more accurate instrumental methods for diagnosing reactive pancreatitis. These include:
- X-ray of the abdominal organs. Since the cause of the disease can be in various diseases associated with the gastrointestinal tract, this diagnostic method can help identify them.
- Ultrasound examination of the pancreas itself and the abdominal organs. In this way, it is possible to determine changes in structures and tissues, enlargement of organs, changes in their structure, etc.
- Computed tomography of the pancreas. This diagnostic method is carried out most often in cases where other methods of assessing the situation have not given the desired result.
- Gastroscopy and laparoscopy. These diagnostic methods are used only in the most difficult situations, since they are the most invasive ways to assess the situation with the pancreas.
In addition to instrumental diagnostic methods, the doctor may prescribe some laboratory clinical tests. These include coprogram and general blood and urine tests. If problems with other organs have been identified, for example, blood biochemistry and liver tests will also be required.
Painkillers
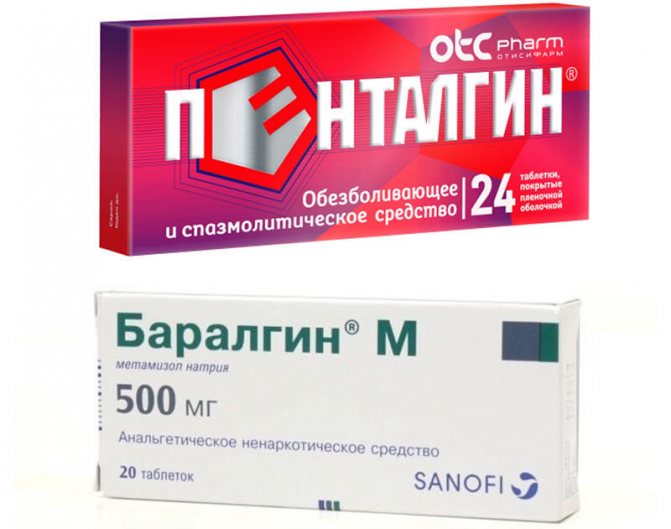
Analgesic treatment for reactive pancreatitis helps eliminate discomfort in the epigastric region, girdle subcostal pain, weakness, malaise and general hyperthermia. Inflammation or injury to a glandular organ results in severe pain, sometimes it can be so severe that the patient dies from painful shock and intoxication.
Painkillers include: Pentalgin, Baralgin, Acitamiphren, Relafen. They block the transmission of nerve impulses, relax, and affect the central nervous system.
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs that can inhibit biologically active enzymes involved in the synthesis of prostanoids (prostaglandin, prostacyclin, thromboxane) can be prescribed as an analgesic treatment for reactive pancreatitis: Ibuprofen, Naproxen, Acetylsalicylic acid.
Traditional treatment
Therapy for reactive pancreatitis should take place in several stages. Among them, experts highlight the following:
- Treatment of the underlying disease. Due to the fact that reactive pancreatitis can be caused by a lot of different diseases of internal organs (mainly the gastrointestinal tract), therapy must begin with eliminating the cause of the pathology.
- Drug therapy aimed at relieving symptoms of the disease. First of all, doctors recommend painkillers (Diclofenac or Ibuprofen), antispasmodics (Platifillin or No-Shpa), antibiotics (Gentamicin or Ampiox) and carminatives (Expumisan).
- Enzyme therapy. Since in reactive pancreatitis the pancreas cannot perform its functions, the amount of enzymes it produces is significantly reduced. That is why this volume of nutrients must be replenished. They do this with the help of Mezim, Creon, Panzinorm, etc.
- Diet food. Doctors recommend that a sick person adhere to diet No. 5. It consists of eating foods low in fat (up to 70-80 grams per day) and calories. The maximum temperature of prepared dishes should not exceed 50-60 degrees Celsius. You need to take food in small doses 5-6 times a day, not three times. Fatty and spicy foods, as well as foods rich in coarse fiber, should be excluded from the diet whenever possible.
Pancreatitis will manifest itself again after some time, which may be much worse than initially. That is why it is important to focus on multicomponent treatment, rather than taking only symptomatic medications.
Nutrition
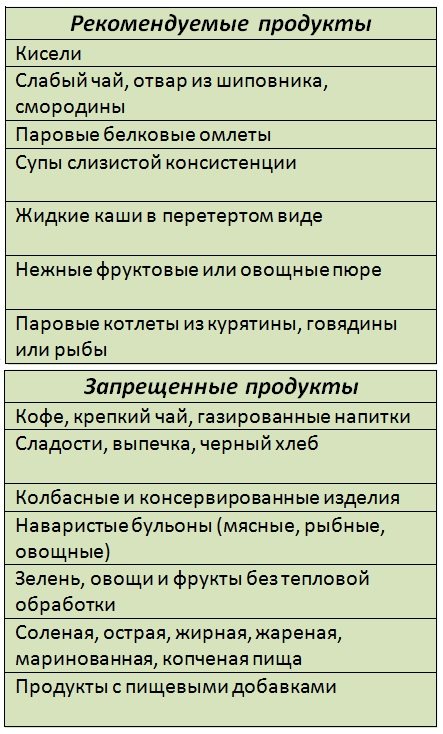
Since the digestive system is disturbed, the patient needs to adhere to a gentle diet.
It is necessary to include in the diet:
- Crackers, preferably white bread.
- Lean meat broths.
- Boiled liver.
- Porridge: buckwheat or oatmeal.
- Compotes.
- Boiled vegetables.
- Mineral water: Essentuki, Borjomi.
Be sure to consume fermented milk products, but only those with low acid content.
Prohibited products:
- Sausages.
- Canned fish and meat.
- Spices and sweets.
- Sour fruits and juices.
- Chicken eggs.
- Fatty meats and fish.
Also read: Acute and chronic pancreatitis - differences
Remember, if you eat right and follow the recommendations of your doctor, you can quickly cure pancreatitis.
Chief gastroenterologist of the Russian Federation: “PANCREATITIS does not go away?! A simple treatment method has already healed hundreds of patients at home! To cure the pancreas forever you need...” Read more »
At home, you can prepare not only a tasty, but also a healthy drink . Take 200 grams of viburnum berries and pour boiling water over them. If you are not allergic to honey, then you can add 1 teaspoon to the drink and drink it instead of tea.
Now you know how to treat this disease. But remember, if you notice the first signs of illness, you must immediately consult a doctor.
Traditional treatment
A disease such as reactive pancreatitis can be managed not only with conservative medication methods, but also with some folk remedies. They do not always affect the cause of the disease, but in any case they can reduce the symptoms of inflammation of the pancreas.
There are the following popular folk methods for treating reactive pancreatitis:
- Infusion from a medicinal collection . To do this, several plants are used that have a positive effect on the human digestive tract. These include string, mint and elecampane. It is necessary to take equal quantities of leaves of each of these remedies. You need to pour the collection with two glasses of boiled water. After this, the liquid should be boiled for a few more minutes. The infusion should be removed from the heat, cooled and strained through a fine strainer. After this, the “medicine” must be taken a third of a glass of milliliters twice a day before meals.
- Propolis tincture . This substance is made using regular medical alcohol. This medicine should be taken only ten drops with milk. This must be done three times a day. Also, instead of tincture, traditional healers suggest periodically chewing propolis itself, which can have a beneficial effect on the functionality of the pancreas. This is important in cases where problems with the gastrointestinal tract already exist, but pancreatitis has not yet arisen.
- A decoction of useful plants . To do this, you should use mint, dill seeds, hawthorn fruits, immortelle flowers and chamomile. The first two components should be taken in three parts, the next two in two, and the last two in one. The mixture of ingredients should be boiled for about thirty minutes in a water bath, first filling it with a glass of boiled water. After this, the broth should be filtered and cooled. It should be taken half a glass three times a day.
All of the above traditional methods of treating reactive pancreatitis are relatively safe. Their main adverse reaction is an allergy to any of the components. But in any case, before using them, you should consult with your doctor.
You can also watch this video, where you will learn a few tips on how to cure pancreatitis quickly.
Temperature in chronic pancreatitis
In the chronic course of the disease, the temperature can occasionally cross 37°. As a rule, with chronic inflammation of the gland, t° lasts for several days, but can last for several months, while it either decreases or, on the contrary, increases.
Interesting fact: doctors strongly recommend that patients monitor their body temperature. If there is a slight fluctuation, you should immediately consult a doctor, as this may indicate focal necrosis.
High temperature, what to do?
When t° is accompanied by other clinical manifestations, for example with pain, doctors prescribe medications that will not only help bring down t°, but also reduce the pain attack.
Can be accepted:
- Analgin.
- Spasmalgon.
All medications are available without a prescription, but before use you must carefully study the instructions. For example, Spazmalgon, which costs about 100 rubles per package, has a huge list of contraindications and side effects.
Also read: Symptoms of an attack of pancreatitis
If a patient's t° is accompanied by fever and abdominal pain, then it is necessary to take several medications.
- Paracetamol or Nurofen.
- One tablet each of Analgin and Drotaverine (crush everything into powder and then drink).
With pancreatitis, vomiting may occur, so the patient will not be able to take oral medications. For severe vomiting and nausea, doctors prescribe intravenous injections.
NewsMedical.ru
The pancreas is one of the largest and most important glands in the human body. This organ takes an active part in digestion and also performs an endocrine function.
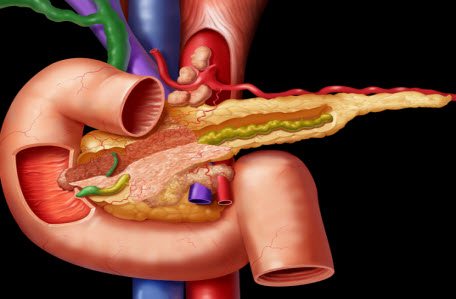
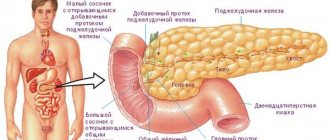
The weight of the pancreas is up to 100 g, it is located on the posterior wall of the abdominal cavity, behind the stomach and consists of several sections: head, neck, body and tail. The basis of the pancreas is made up of 2 types of tissues - lobules, acini - they secrete pancreatic juice, which contains digestive enzymes; and special cells, the islets of Langerhans, which produce hormones - glucagon and insulin.
Due to eating disorders and alcohol consumption, inflammation of the pancreas, called pancreatitis, can develop. Pancreatitis is a rather serious disease, and if left untreated or improperly treated, it can lead not only to complications, but also to death.
Types of pancreatitis
The clinic distinguishes three types of pancreatitis - acute, chronic and reactive pancreatitis. Acute pancreatitis is an inflammation of a separate part or an organ as a whole, which is accompanied by the breakdown of gland tissue and suppuration or hemorrhage.
Chronic pancreatitis occurs slowly, but progresses without treatment. Inflammatory phenomena in the pancreas can appear due to errors, for example, in diet, and subside with adequate treatment and a balanced diet.
Reactive pancreatitis is an attack of acute pancreatitis due to exacerbation of diseases of the stomach, duodenum, gallbladder or liver.
Chronic pancreatitis
Chronic pancreatitis is a progressive inflammation of the pancreas, which occurs with severe disturbances of digestive and hormonal functions. Chronic pancreatitis is quite common; the disease most often affects people between 30 and 60 years of age.

With chronic pancreatitis, changes occur in the function of the organ, due to which the ability to produce digestive enzymes and hormones is impaired.
Chronic pancreatitis can become chronic in several ways: direct transition; more often - due to repeated attacks of acute pancreatitis, which worsen over time.
Alcohol and unhealthy diet play a special role in the development of pancreatitis. Also, diseases of the biliary tract, duodenal ulcer, chronic gastritis with reduced secretion, and liver diseases can lead to the development of pancreatitis.
In addition, pancreatitis can occur after injuries, taking toxic medications, infections, including viral hepatitis, mumps virus, some helminthiases, chronic poisoning with lead, mercury, phosphorus, and arsenic. There are also hereditary forms of pancreatitis.
Symptoms of chronic pancreatitis
The symptoms of chronic pancreatitis can vary somewhat, but still, there are a number of constant symptoms - pain in the upper abdomen, left hypochondrium. Rarely in the right hypochondrium, it can be encircling; the intensity of the pain can vary, from dull, aching to sharp.
But it occurs most often after errors in the diet, drinking alcohol, 30-60 minutes after eating. The pain increases while lying on your back, and decreases in a sitting position with the torso slightly tilted forward. Pain syndrome is always accompanied by dyspeptic syndrome - nausea, vomiting, loss of appetite, flatulence, tendency to diarrhea.
Acute pancreatitis
Acute pancreatitis is an inflammation of the pancreas, accompanied by hemorrhages and necrotic processes resulting from self-digestion of the gland by pancreatic enzymes.

Acute pancreatitis is often combined with diseases of the gallbladder and biliary tract (cholelithiasis, biliary dyskinesia). The occurrence of acute pancreatitis is promoted by the intake of abundant fatty foods, as well as alcohol. In addition, mechanical impact on the area of the left hypochondrium can lead to acute pancreatitis.
The clinical picture can be varied - from mild abdominal pain to severe conditions with excruciating pain and shock. The disease begins suddenly with an attack of severe pain in the upper third of the abdomen, often after errors in diet. Often the pain is girdling in nature and can radiate to the left shoulder blade.
The pain syndrome is accompanied by uncontrollable vomiting, which can occur even after a small sip of water. Vomiting is painful and does not provide relief. Nausea, flatulence, constipation or diarrhea are less common.
With this condition, the temperature may rise. Patients are restless and toss around in bed. The skin turns pale, has a bluish tint, profuse sweat appears, an increase in pressure may be observed at the beginning, and then a decrease in blood pressure to a state of collapse.
Reactive pancreatitis
Often reactive pancreatitis occurs suddenly and unexpectedly after taking irritating foods. The cause of the pathological changes is spasm of the pancreatic duct. Because of this, digestive enzymes remain in it and destroy the gland tissue.
Reactive pancreatitis can occur in the following cases: • after violations in the diet, • after drinking alcohol, • after taking toxic pharmaceuticals, • after drinking sweet carbonated drinks with large amounts of preservatives and food colorings, • against the background of acute or chronic gastritis, gallstones .
Sometimes reactive pancreatitis develops as a result of prolonged severe stress. In this case, adrenaline is released into the blood and the pancreatic ducts narrow. A temporary spasm occurs, which leads to partial tissue necrosis.
One of the most characteristic symptoms of reactive pancreatitis is a dull, stabbing pain under the ribs. A taste of bile appears in the mouth, constant painful vomiting that does not provide relief, and belching occurs.
If the condition continues to worsen, shortness of breath, clammy sweat appears, body temperature rises, blood pressure rises and the pulse quickens. The abdomen becomes distended and flatulence appears, indicating possible peritonitis.
Pancreatitis in children
In a child, the body reacts to external stimuli much stronger and more actively, so any infection or allergen that disrupts the functioning of the pancreas can lead to the development of pancreatitis.

A common cause of pancreatitis in children is malnutrition, various injuries and developmental anomalies of the gastrointestinal tract, and the use of certain medications. Eating foods such as smoked meats, chips, fast food, canned food, and carbonated drinks has a strong irritant effect on the mucous membrane of the digestive system.
The most common type of pancreatitis in children is reactive pancreatitis. Its symptoms can occur with acute respiratory infections, acute respiratory viral infections, acute gastroenteritis and other diseases.
The main symptoms of pancreatitis in children are pain in the upper abdomen. The older the child, the more severe the pain. Also, with pancreatitis, repeated vomiting, nausea, and frequent loose stools occur.
A white coating appears on the tongue and the temperature rises. The child becomes capricious, whiny, and irritable. In general, the symptoms of pancreatitis in children are similar to acute pancreatitis in adults.
Diet for pancreatitis
After the acute phase of the disease is over and discharged from the hospital, it is imperative to adhere to a therapeutic diet for pancreatitis and categorically avoid those factors that led to the occurrence of this disease.

Therapeutic nutrition or diet for pancreatitis consists of eliminating fatty, fried, smoked foods from the diet, reducing the amount of spices used to a minimum, and drinking a lot of still mineral water. Food is steamed or boiled. Number of meals up to 6 times a day, in small portions at the same time.
Strictly prohibited consumption: alcohol, coffee, cocoa, carbonated drinks. And also a diet for pancreatitis excludes from the diet baked goods, fatty and fried foods, concentrated broths, borscht, pickles, all types of canned food, boiled eggs, chocolate. In addition, some types of fruits should be excluded - bananas, figs, grapes, sour apples.
Complications of pancreatitis
It should be remembered that pancreatitis itself cannot be cured and without proper treatment and a constant diet, it can lead to a number of complications and the development of concomitant diseases.
Often pancreatitis can be accompanied by inflammation of the gallbladder, stomach ulcer, purulent complications, phlegmon or pancreatic abscess. Sometimes intra-abdominal bleeding develops.
Another very serious complication of pancreatitis is the destruction of the pancreas and the development of peritonitis. Also, in some cases, chronic pancreatitis can lead to malignancy (malignancy) of the process.
With chronic pancreatitis, the shape of the gland itself can change, and it becomes so large that it compresses the duodenum and creates an obstruction in it. And this is already a reason for surgical intervention.
Chronic pancreatitis can lead to complications such as diabetes. Therefore, you should strictly adhere to all recommendations given by your doctor.
Attention! The information on the site should not be used as a guide for self-medication; all proposed medications and treatment methods described in the articles can only be used after consultation with a doctor!