What's happened
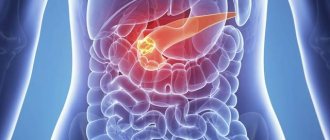
A benign pancreatic tumor is a rare disease that affects approximately 1-3 people per million of the population. In most cases, tumors of the neuroendocrine type are diagnosed, including gastrinoma, insulinoma and glucagonoma.
These pathological processes have specific symptoms, despite the fact that such tumors grow slowly and are small in size. This phenomenon is caused by the production of hormones by these cells, which enter through the systemic bloodstream.
The peculiarity of such tumors is that they may not manifest themselves for a long time; symptoms begin to appear as the tumor increases in size.
Varieties
There are several types of pancreatic adenoma. The following classification is distinguished:
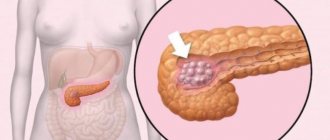
- Serous. Formed from epithelial cells. The main difference between education is that it has many partitions within itself. Such a tumor almost never degenerates into cancer, so it is removed only when it reaches a large size.
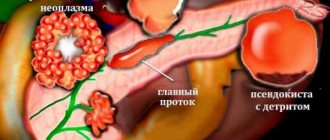
- Mucinous. It has a cystic structure, can reach large parameters, and contains blood or mucus inside. Penetrates into the gland during intrauterine development. Capable of transforming into a malignant form.
- Borderline. This is a transitional form between a benign and a malignant tumor. Therefore, its immediate removal is required.
- Intraductal papillary mucinous. It is very rare and is formed from epithelial cells of the pancreatic ducts. Has the ability to produce thick mucus.
The symptoms and treatment of the pancreas will depend on how the type of pathology develops. All of them are removed surgically, but in different ways.
Classification
Depending on the histological structure and origin, neoplasms are divided into several types:
- fibroma – the basis of the structure is fibrous tissue;
- neuroma - consists of nerve tissues and nodes;
- leiomyoma - smooth muscle tissue takes part in the formation;
- hemangioma - develops from vascular cells;
- lipoma – formed from adipose tissue;
- adenoma - the main component of the structure - glandular tissue.
On this topic
- Endocrine system
How are the lymph nodes connected to the thyroid gland?
- Olga Vladimirovna Khazova
- May 27, 2020
There may also be a type of tumor called neuroendocrine. Its peculiarity lies in the fact that it participates in the process of hormone production.
Such neoplasms include gastromas, insulinomas and VIPomas. They develop for a long time without the manifestation of characteristic symptoms, and also have a predisposition to degeneration into a cancerous tumor.
Causes
To date, the exact provoking factors contributing to the development of pancreatic tumors have not been established, despite the widespread pathological process.
According to most experts, the disease can be triggered by an unfavorable environmental situation or frequent contact with chemotherapy drugs. But more often than not, it is not always possible to establish a direct connection between the development of the disease and the cause of its development.
However, there are a number of factors that can cause a benign pancreatic tumor to develop.
Among them are the following:
- the presence of chronic pancreatitis
- cirrhosis of the liver;
- alcohol abuse and smoking;
- taking narcotic substances;
- cystic lesion.
One of the most common and equally important reasons is poor nutrition. When a large amount of junk food is present in the diet, this can provoke a disruption in the functioning of the organ, which leads to the formation of a tumor.
Another source of pathology development is excess body weight.
When a disease localized in the tail of the body appears, hereditary predisposition is often given first place as a provoking factor.
In cases where close relatives have a history of this disease, the risk of its occurrence increases several times. People who have been diagnosed with diabetes are also at risk.
Symptoms
The early stages of the disease may remain asymptomatic, which makes diagnosing the pathology much more difficult, and it can only be detected by chance during an ultrasound examination to determine another disease.
On this topic
- Endocrine system
How to avoid calcifications in the thyroid gland
- Olga Vladimirovna Khazova
- February 28, 2020
As the disease progresses, it begins to manifest itself:
- decreased appetite;
- general weakness;
- nausea;
- excessive fatigue.
First of all, the presence of a tumor will be indicated by pain in the area of the affected organ where the urinary process is located. Pain syndrome, as a rule, occurs for no reason, and its severity intensifies even during a period of calm.
At an early stage, with a benign tumor formation, the symptoms are mild. As the tumor begins to grow, the following characteristic signs occur:
- rapid loss weight ;
- development of jaundice;
- frequent abdominal pain
- the appearance of a pathological process affecting the head of the pancreas.
The appearance of painful sensations is possible against the background of an increase in benign formation. This is explained by the fact that the growth of the tumor begins to compress nearby organs.
On this topic
- Endocrine system
Normal thyroglobulin levels
- Olga Vladimirovna Khazova
- February 28, 2020
In addition, pressure may be exerted on the bile duct, which will be accompanied by a characteristic clinical picture:
- darkening of urine;
- discoloration of stool;
- excessive sweating;
- pale skin;
- itching;
- chills;
- pain in the area of the liver.
If the symptoms described above occur, you should immediately seek help from qualified specialists.
In addition, the symptoms of a benign tumor may depend on the type of tumor.
In the case when the growth of the formation affects the cells that participate in the production of hormones, the patient may be concerned about endocrine system disorders.
Insulinomas are a type of tumor that is involved in the production of additional amounts of insulin, which provokes a decrease in the concentration of glucose in the blood fluid.
On this topic
- Endocrine system
Why do antibodies to thyroglobulin increase?
- Olga Vladimirovna Khazova
- February 28, 2020
Against the background of this condition, symptoms of hypoglycemia may appear, which is characterized by dizziness, rapid heartbeat, and increased irritability. In the absence of appropriate therapeutic measures, a coma begins to develop.
Gastrinoma is another type of pancreatic tumor, consisting of cells involved in the synthesis of the digestive hormone gastrin. In this condition, patients begin to take all possible actions to treat an ulcer of the jejunum, stomach or duodenum. The patient begins to worry about disruptions in the functioning of the intestines, pronounced pain in the epigastrium, heartburn, and vomiting.
Glucagonoma - is involved in the production of glucose in blood fluid and urine. In this case, the patient experiences weight loss, rashes, peeling and dry skin, and inflammation of the gum tissue.
When diagnosing lymphangioma and hemangioma, when they rapidly increase in size, the likelihood of their degeneration into a cystic formation or malignant tumor increases.
Symptoms of tumors on the head of the pancreas
The structure of the tumor is of great importance. Those neoplasms that do not secrete hormones may not manifest themselves in any way until they reach a significant size and begin to impede natural physiological processes. In such cases, if no tumors were noticed during a routine examination, the patient goes to the hospital with acute pain. Pain in the pancreas occurs when the tumor puts pressure on neighboring organs, which disrupts blood circulation and causes intestinal obstruction.
If the neoplasms are hormone-producing, then the patient begins to show changes that an attentive person will always notice:
- increased sweating;
- general weakness in the body;
- fast fatiguability;
- tachycardia;
- hypoglycemic coma is possible;
- deterioration of the digestive process;
- problems with bowel movements (constipation);
- frequent belching.
With cancer of the pancreas, the symptoms are different; the patient first feels pain, but it is mild and can be tolerated. Then the following aspects are added:
- appetite decreases;
- dry mouth;
- constant strong thirst;
- severe stomach pain, most often at night;
- intolerance to fatty foods;
- the body's rejection of coffee and alcohol;
- black stools due to bleeding in the stomach;
- thrombosis in peripheral veins.
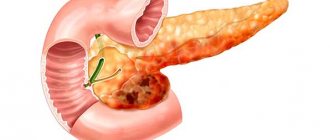
Timely diagnosis is extremely important, which can determine the type of tumor, its size, and the degree of damage to neighboring tissues and organs. Most often, ultrasound clearly visualizes such neoplasms. If an MRI is sought, then the use of contrast is required.
To diagnose a tumor on the pancreas, the patient is prescribed an ultrasound or MRI of the abdominal organs
Diagnosis of organ pathologies
If the presence of tumors in the pancreas is suspected, the doctor will immediately issue a referral for diagnosis. There are several methods, all of them are effective and quite informative:
- An ultrasound examination of the gland will show even small lesions and indicate their properties and quantity. To conduct an ultrasound, the patient needs to prepare, which the doctor will warn him about in advance. The procedure takes little time and does not require hospitalization. Additionally, a colonoscopy may be prescribed.
- CT scan. A highly informative diagnostic option, however, it is unsafe due to radiation exposure and is not recommended for cancer patients. A CT scan takes little time, does not require special preparation, and hospitalization is not required.
- Positron emission tomography or MRI of the pancreas determines the extent of the lesion and finds metastases. Requires about an hour of time spent. It has several stages of preparation, which depend on the patient’s diagnosis.
- X-rays of the intestines and stomach will reveal the extent of the tumor’s impact on neighboring organs and show how affected they are. The procedure determines whether the cancer has grown into neighboring tissues. This is a highly informative method, it requires little time, and does not require a long stay in a medical facility.
- The methods of fibrogastroduodenoscopy and cholangiopancreatography allow not only to determine the nature of the tumor, but also provide the possibility of collecting material for histological examination, that is, performing a biopsy of the pancreas.
Diagnostics
To make an accurate diagnosis, symptoms alone are not enough. It is important to perform routine tests and review your medical history. This will allow us to identify a possible cause that could provoke the development of pathology.
During the initial examination, the specialist must collect information regarding the patient’s medical history and identify existing negative factors. It is also important to find out whether the patient has relatives with a similar disease.
In addition, the doctor interviews the patient and establishes all the symptoms that accompany the health disorder.
After completing the initial examination, a set of diagnostic measures is prescribed. The following tests are required:
- blood, which allows you to determine the concentration of hemoglobin in the blood (as a rule, with the development of a pathological process, its level noticeably decreases);
- biochemical blood fluid to assess the level of sugar in the composition;
- urine - with the development of jaundice, urobilinogen is determined;
- feces - prescribed without fail if they are discolored;
- for tumor markers - detection of CA 19-9 proteins, CEA indicate tumor formation.
On this topic
- Endocrine system
What consequences can a pancreatic cyst cause?
- Olga Vladimirovna Khazova
- February 28, 2020
After this, instrumental diagnostics are carried out:
- Ultrasound is considered one of the simplest and most accessible methods. Allows you to determine changes in tissues based on morphological characteristics, as well as their echogenicity.
- Computed tomography - determines the size of tumors, location and metastasis to nearby organs.
- MRI is less dangerous than the previous diagnostic method, but is expensive. Allows you to show the direction of tumor growth. Also possible consequences.
- ERCP is a method for assessing the bile ducts.
- MRCP is also used to assess the condition of the pancreatic ducts. Determines their condition and shape.
- Scintigraphy makes it possible to identify the localization of a benign formation and other indicators.
- Angiography is an X-ray examination of vascular structures.
- Biopsy is a method that allows for a full differential examination. In other words, it can be used to determine the level of malignancy of the tumor.
Only on the basis of the diagnostic results obtained, the specialist prescribes a number of appropriate therapeutic measures.
Palliative operations
For inoperable forms of pancreatic cancer, palliative interventions are performed. They are aimed at eliminating severe complications in the body caused by the spread of malignant tumors to neighboring and distant organs. The most famous of them:
- obstructive jaundice due to compression of the common bile duct by the tumor;
- stenosis of the duodenal bulb with impaired passage of food from the stomach into the small intestine or the development of complete obstruction of the duodenum;
- perforation of the stomach wall;
- high pressure of the expanded tumor on the nerve endings and neighboring organs with severe pain.
To alleviate the patient’s condition in the event of the development of obstructive jaundice, the following are carried out:
- cholecystostomy or choledochojejunostomy on the switched-off jejunum (according to Roux);
- external cholangiostomy (performed under ultrasound or CT guidance);
- endoprosthetics of the final part of the common bile duct.
In case of duodenal obstruction, gastroenterostomy is performed. As a result, the evacuation of food from the stomach is restored and digestion improves. Due to the severity of the patient’s condition at such stages of the disease, such operations can reduce suffering, partially restore the functions of the digestive system, and prolong the patient’s life by 7–10 months.
Treatment
Therapy for a benign pancreatic tumor is carried out only through surgery.
Head resection
During the procedure, the tumor is removed along with a fragment of parenchyma. In most cases, it is used when the tumor is localized in the tail of the affected organ.
Carrying out a separate resection in this case is not possible, since the process is hampered by the fact that they have a common blood supply with the duodenum.
Pancreaticoduodenectomy
During the manipulation, the head of the gland is excised along with the gallbladder. The initial gastric section, the part of the stomach itself, which is located in close proximity to the lymph nodes, is also removed.
Enucliation
The isolated tumor is removed. At the same time, it is peeled out of the tissues.
Indications for this type of surgical intervention are clear contours of the formation, its size not exceeding two centimeters, and localization in the caudal region of the gland.
Gastrectomy
This involves removing the entire organ affected by the tumor. At the same time, resection of the initial part of the small intestine is performed.
Types of operations
Radical.
Treatment is possible if the tumor is confined to the pancreas. According to statistics, this is 10% of all cases with a confirmed diagnosis of malignant neoplasm. If pancreatic cancer spreads to neighboring and distant lymph nodes and organs, surgical intervention to remove the tumor itself is possible only in 1–5%.
Palliative.
It is necessary to alleviate the patient’s condition and does not completely solve the problem with the tumor. since it is aimed at reducing pain and other pathological symptoms. Palliative interventions are performed for severe complications of advanced pancreatic cancer.
In addition to the listed types of surgical care for pancreatic cancer, new techniques have been developed and put into practice in recent years:
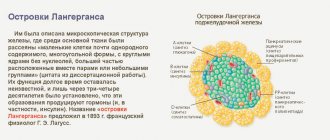
- pancreas transplantation;
- selective transplantation of cells of the islets of Langerhans and acini.
Complications
If the tumor is not removed, this can lead to certain consequences. First of all, with this condition, the risk of malignancy of the pathology increases.
It is also possible to develop jaundice, which is often accompanied by pronounced intoxication of the body. This condition often occurs when there is difficulty in the secretion of bile into the duodenum.
In addition, disturbances of the endocrine system and hormonal levels may occur. Intestinal obstruction and chronic pancreatitis are also possible.