Well-being and possible consequences of colonoscopy
Colonoscopy is a method of invasive diagnostic and treatment examination of the lower parts of the digestive system using a colonoscope. Why is an intestinal colonoscopy done, and information about how to prepare for the test and what to take with you to the colonoscopy.
Before the procedure, general anesthesia or sedation is usually used, which suppresses the stress factor and completely eliminates discomfort. We have already written about how a colonoscopy is performed under anesthesia in a separate article.
The examination of the intestinal sections is carried out with a special long probe equipped with optical equipment and illumination.
If necessary, therapeutic procedures can be performed:
Deterioration in health after a diagnostic and treatment procedure is usually considered normal. Discomfort is due to the need to pump up air atmospheres, the invasiveness of the research method and the intended purpose.
Note: discomfort persists after surgical procedures for about 5 days. Complications are indicated when atypical symptoms persist for more than 5 days, as well as when their intensity increases.
Why is sedation used during colonoscopy?
Sedation is a gentle method of pain relief. With the help of special medications, the subject is introduced into a state of superficial anesthesia, or, as it is also called, drug sleep.
Despite the ease of practice of the anesthetic method, sedation is not used unless indicated due to the risks:
- Individual intolerance.
The patient may experience allergic reactions to the medications used to induce medicated sleep. The most harmless manifestation of the body's response is urticaria. There are also more serious risks that may cause doctors to refuse to perform a colonoscopy under anesthesia. For example, the likelihood of anaphylactic shock.
- Side effects.
Each drug has a list of contraindications. There are also side effects associated with the use of anesthesia: dysfunction of the heart muscle, decreased blood pressure, vomiting, nausea, etc.
- Intestinal perforation.
When a colonoscopy is performed under anesthesia, the doctor is not able to focus on the patient’s sensations, and accordingly, on the correct course of the diagnosis. As a consequence, a complication such as perforation may occur, that is, through damage and, in rare cases, rupture.
What to do if your stomach hurts
Pain after colonoscopy does not only indicate the presence of complications. For example, if a patient has a stomach ache after a colonoscopy, the cause of the pain is the presence of gas in the intestines.
It is important to know! During the study, air is supplied to the intestines, through which the intestinal walls are straightened.
Almost every patient complains of stomach pain and discomfort. This is normal and goes away within the first day. To speed up the removal of air from the intestines, you can take sorbents.
The consequences of a colonoscopy, during which the patient feels severe pain, can also be fatal. One of these serious complications is the development of peritonitis. With peritonitis, damage to the intestinal walls occurs, resulting in stool entering the abdominal cavity. If such feces are not removed in a timely manner, this can lead to death. This type of complication is detected mostly immediately, so the doctor has time to eliminate the development of pathology. If a complication is discovered after the procedure, the patient will feel severe pain in the abdominal area after the procedure. To eliminate the complication, extensive surgery or resection of a section of intestine will be required.
What to do if a patient has stomach pain after a colonoscopy? First of all, you need to inform your doctor about this. If the pain is very severe, which should not be the case, then immediate resuscitation of the patient is carried out. If the patient has been discharged and is at home, an ambulance should be called immediately. Any strange sensation after the study must have its own explanation. Stool, diarrhea, blood with diarrhea, as well as fever - all this is the main sign of various complications.
POSTOPERATIVE PERIOD
If a colonoscopy can be called an operation, it is only a minimally invasive one, since it allows surgical manipulations to be performed with restrictions. As soon as the research procedure is completed, the patient is transferred to a ward, where he will need to spend some time under the supervision of medical staff. If the procedure was performed under general anesthesia, the patient is brought to consciousness after being transferred to the ward. If after the examination the patient has no negative symptoms for one hour, then the doctor sends him home, but accompanied by relatives.
To avoid the development of serious pathologies after colonoscopy, the doctor recommends that the patient avoid eating rough foods, which will prevent the development of intestinal constipation. You need to eat easily digestible types of food, for example, broths, cereals, boiled vegetables and fruits. After the endoscopic method, stool appears mainly on days 2-3, but only if the basic condition is met, according to which the patient should eat foods recommended by the doctor. Eating foods with insufficient fiber may result in the patient being unable to go to the toilet.
If the patient is bothered by the symptoms of flatulence, which also causes stomach pain, then it is necessary to take activated carbon tablets. Doing an enema or taking laxatives without a doctor's prescription is strictly prohibited.
Before and after a colonoscopy, the patient is prohibited from taking iron supplements and antiplatelet agents. You should stop taking these medications immediately after your appointment for a bowel test. All types of medications that the patient takes should be reported to the doctor in advance, which will prevent the development of serious complications both during the colonoscopy and after its completion.
Complications of colonoscopy can occur due to the following factors:
- Low level of qualification of the endoscopist who performs the procedure.
- Insufficient preparation of the patient for the procedure. If a patient comes for examination with intestines not completely cleansed, then the doctor has the right to refuse further examination.
- Strong intestinal peristalsis.
- Thinning of the intestinal walls, as well as the development of dystrophic phenomena.
If a patient develops complications, many begin to blame the doctor. When performing a colonoscopy, the qualifications of the specialist who conducts the examination are important. But it should be noted that medical errors occur in rare cases, while patient unpreparedness is much more common.
Pain after colonoscopy
Pain after manipulation can persist for up to 5 days, however, the pain is moderate, similar to a dull pulling sensation in the lower abdomen, radiating to the intestines. The pain may worsen with bowel movements. Painful sensations after a colonoscopy examination usually appear after surgery (removal of polyps, coagulation of blood vessels).
Soreness often causes damage to the intestinal walls by the probe, for example, with pronounced narrowness of the lumen, certain anatomical features of various parts of the intestine.
Pain also occurs with existing intestinal pathologies:
Elimination of pain requires the use of:
- Antispasmodics: No-Shpa, Drotaverine, Papaverine, Spazmalgon;
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs: Ibuprofen, Ketoprofen, Nurofen.
If the drugs are ineffective, other symptomatic treatment is prescribed, aimed at eliminating the cause of pain and the severity of clinical signs.
Constipation after colonoscopy
You can often hear from many patients: “I can’t go to the toilet after a colonoscopy.” Difficulty in defecation after colonoscopy may be long-term. Considering that before the study and several days after a special diet for colonoscopy must be followed, constipation may be the result of a sharp transition from semi-liquid food to the usual diet (flour, meat products, aggressive foods).
This disorder can be easily eliminated by drinking plenty of fluids and including fiber, vegetable oil and fresh vegetables in the diet.
However, constipation can result from other complications.:
- Swelling of the mucous membranes in the area of surgical procedures;
- Incomplete removal of a tumor in the intestine;
- Stagnation of blood in the distal parts of the intestinal tract;
- Decreased intestinal motility (traumatic damage to the walls and smooth muscles).
If constipation persists for more than 5 days and persistent stool disturbances or painful urge to defecate, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Important ! With a general deterioration in condition, fever, severe malaise, an infectious lesion or intestinal obstruction can be suspected.
Diarrhea after colonoscopy
It also happens, on the contrary, that persistent diarrhea develops after a colonoscopy. Liquefied stools often become a long-term consequence of preparation for the procedure.
The main reasons for the development of diarrhea after diagnostic manipulation are:
- Disorders of digestive processes;
- Switching to a different diet (from a slag-free diet to a regular diet);
- Increased intestinal motility;
- Long-term side effects after using laxatives in preparation for the study.
Diarrhea usually goes away 3-4 days after the diagnostic test. You can include rice water, regular boiled rice, and cereals in your diet.
Treatment may require:
- Enterosorbents: Enterosgel, Polysorb, Smecta;
- Preparations for normalizing intestinal microflora: Hilak-Forte, Acipol.
Blood after colonoscopy
Bleeding after the study should be assessed according to the following parameters: color, intensity, nature of appearance.
Bleeding occurs due to a number of factors:
- Insufficient coagulation of blood vessels;
- Incomplete removal of polyps;
- Traumatic damage to the intestinal walls by instruments.
Blood can be released in clots along with feces, released regardless of bowel movements, and remain on paper or linen in the form of bloody discharge.
Attention ! The danger is posed by scarlet blood that is regularly released from the rectal canal, especially associated with a general deterioration in health.
After a colonoscopy, stomach pain
Gurgling in the abdomen is one of the early consequences after a colonoscopy. This is usually caused by residual air after the injection of air atmospheres before the study, as well as sanitization of the intestinal cavity with antiseptic solutions, laxatives and enemas before the test.
Seething is a reaction to a disturbance in the intestinal microflora. The problem can be solved by prescribing probiotic complexes (Linex, Hilak-Forte).
Temperature after colonoscopy
An increase in temperature within the subfebrile range for 2-3 days after the manipulation is the norm and is considered a healthy reaction of the body to stress (sedation or general anesthesia, surgical procedures, exposure to the intestines with a probe and instruments).
If the temperature rises to more than 37.5 3-5 days after the procedure, or a general deterioration in health, a secondary infection may be suspected, caused by insufficient hygiene, or a violation of the surgical technique during colonoscopy.
The infectious process can be caused by a parallel cold, damage to the oropharynx or nasopharynx by a viral, bacterial or fungal infection.
Is irritable bowel syndrome possible after a colonoscopy?
Irritable bowel syndrome is a persistent functional disorder of the intestinal tract for more than 2-3 months without obvious infectious or organic causes.
Pathology is usually a consequence of:
- chronic inflammation,
- intestinal dysbiosis,
- disorders of intestinal smooth muscle motility.
Unfortunately, the true causes of the pathological process have not yet been clarified; rather, it is a combination of several factors at once.
Irritable bowel syndrome can occur with constant aggressive exposure to external or internal factors. Typically, colonoscopy is not the cause of IBS, but if the patient does not respond to various complications after the procedure, the risks of development increase significantly.
The procedure itself is not capable of causing the immediate development of a functional disorder, but it may well become a trigger if the patient does not comply with the doctor’s recommendations or various complications after the study.
Doctor's explanations
First of all, it is necessary to overcome the psychological barrier before a process that is humiliating at first glance, and, in addition, to clear the mind of groundless myths about the possible consequences of anesthesia.
- Firstly, it is worth accepting the fact that the proctologist deliberately chose his specialty, fully aware that he will not often have to talk to people, looking them in the eyes. And your secret place in this sense is unlikely to surprise him;
- Secondly, the prescription of anesthesia for this procedure is, as a rule, quite justified, since unpleasant painful sensations can haunt you in your memories much longer than the colonoscopy itself will last under anesthesia.
Let's differentiate between the concepts of local anesthesia and general anesthesia , which is called anesthesia in our country.
Local (local) anesthesia with xylocaine and similar substances in the case of colonoscopy is very conditional, since the tip of the colonoscope lubricated with an anesthetic is not able to really provide comfort and the absence of unpleasant sensations.
Colonoscopy without anesthesia allows you to ask all questions to the doctor during the examination
It must be sad to admit that government agencies in our country still do not use anesthesia during colonoscopy, except in special cases: the patient’s age is under 12 years, the presence of adhesive and destructive intestinal diseases that can cause severe pain during the procedure, as well as an increased pain threshold and unstable psyche of a person seeking help. You will be very lucky if you get into one of these “special” groups. It is believed that it is even useful to be patient in this situation, since pain at certain points is a diagnostic beacon for a specialist. And if the patient is relaxed, satisfied and, in principle, immersed in a medicated sleep, asking him about his sensations will not work. And in general, black anesthesiological humor says: “a well-fixed (tied to the table) patient does not need anesthesia...”
And those who like “dialogue with a doctor during the procedure” can voluntarily refuse a colonoscopy with anesthesia in order to see with their own eyes on the screen all the findings in their own intestines.
In turn, in the West, doctors are of the opinion that suffering from pain during a diagnostic procedure in the 21st century is unjustified barbarity; every person has the right to count on qualified assistance from an anesthesiologist . If, nevertheless, the procedure is expected without anesthesia, then the antispasmodic Trimedat is recommended for pain relief (official instructions).
By the way, if you are offered a colonoscopy with anesthesia without an anesthesiologist , I strongly recommend leaving this medical institution at that very moment and forgetting its name, as an indecent word. Sometimes the patient is told: the procedure will be without anesthesia, there is no need to panic - perhaps you are prescribed a “virtual colonoscopy”, this is a different procedure and it is painless.
No matter what they tell you, anesthesia is an unnatural procedure that has its own contraindications and risks, so it can only be performed by a qualified anesthesiologist-resuscitator with a valid certificate, and moreover, in a room adapted for providing emergency care. Not a single self-respecting clinic will violate the legislation presented, among other things, in the Orders of the Ministry of Health and Social Development of Russia “On approval of the procedure for providing anesthesiological and resuscitation care to the population.”
Spend half an hour of your time talking with your anesthesiologist and be sure to tell him about all your past and present ailments, any allergic reactions you know and the medications you are taking. Don't be afraid to seem too meticulous when asking your doctor about the progress of a colonoscopy under anesthesia. The more you learn about the upcoming procedure, the less panic fears and rosy illusions you will have.
One way or another, you will be offered one of two options for general anesthesia.
- The first is intravenous anesthesia using sedatives such as profopol or ketamine. This option for pain relief is, as a rule, preferable, although it has quite a few contraindications. In particular, profopol is prescribed with caution to persons suffering from epilepsy, asthma, coronary heart disease, and impaired liver and kidney function. And ketamine is not used in the presence of cerebrovascular accidents, arterial hypertension and eclampsia. It is also contraindicated for those suffering from alcoholism. It is worth noting that nowadays a combination of several short-term drugs, which contains both a sedative and an anesthetic, is more often used. The doctor selects the ingredients of such a cocktail strictly individually, and you have no choice but to completely trust the specialist.
- The second option is inhalational anesthesia using appropriate anesthetics, such as fluorothane, nitrous oxide or sevoflurane. As a rule, such anesthesia is resorted to in cases where the pain syndrome can be very pronounced, or it can cause serious complications in a person with certain concomitant pathologies. All of these drugs have enough contraindications. Sevoflurane is not prescribed to persons with high intracranial pressure; fluorotane is contraindicated in those with arrhythmia or liver failure. And nitrous oxide is certainly not suitable for a person suffering from a disease of the central nervous system or chronic alcoholism.
In this case, focusing on the fact that during intravenous anesthesia you will experience difficult dreams, which can be avoided by inhalation of the drug, is completely inappropriate. One of the main rules of an anesthesiologist prescribes to correlate the degree of risk from the anesthesia used with the objective need for it. Simply put, you should not have your belly button pierced under general anesthesia.
So, having discussed in detail the progress of colonoscopy under anesthesia with specialists, you should immediately discard all negative thoughts, tune in to a wave of joy and love of life and firmly believe in the successful outcome of this procedure, which is minimal in duration, but not in significance. May you be warmed by the thought of your own consciousness and responsibility, which does not allow you to brush off the problem because of a superstitious fear of going to the clinic. Accurate diagnosis and timely treatment are the key to a full life for many years.
What to do after an intestinal colonoscopy?
After the manipulation, you should follow a therapeutic diet for some time to reduce the load on the digestive system. During surgical procedures, it is necessary to exclude physical activity, control the regularity of bowel movements and immediately respond to signs of constipation.
Intestinal restoration after colonoscopy is aimed at:
- Normalization of internal microflora;
- Elimination of unpleasant sensations;
- Prevention of long-term post-manipulative complications.
source
Why does your stomach hurt after a colonoscopy and what can you do?
Intervention in the human body never goes away without leaving a trace. Therefore, even after invasive diagnostics or micro-surgeries, symptoms arise that are associated with normal recovery processes or are signs of serious complications. We will tell you why your stomach may hurt after a colonoscopy. Which manifestations are dangerous and which are normal.
It is very difficult to examine such a tortuous and extended organ using standard methods - ultrasound, MRI, CT. Today, the most reliable among studies are endoscopic methods, when a video camera or optical device is inserted into the organ, which allows you to see the mucous membrane under magnification. In addition, with the help of such equipment, the doctor can remove polyps of the rectum and other parts of the large intestine, eliminate bleeding and adhesions.
The procedure is carried out only after preliminary preparation:
- Following a diet 3 days before a colonoscopy, the essence of which is not to create a large amount of feces in the organ and prevent gas formation.
- The day before the procedure, stop eating and begin to cleanse the intestines. Today it is not necessary to do volumetric enemas. The pharmacy has preparations for preparing aqueous solutions that gently and effectively empty the intestines of contents. Dosage is calculated by weight. On average, it takes up to 5-6 hours to clean an organ.
Colonoscopy with or without anesthesia, which is better?
What is safer and more effective: colonoscopy with or without anesthesia? If this is the case, then there are certain advantages to performing the procedure without anesthesia. What is this? And do they outweigh the inconvenience and pain that colonoscopy sometimes causes?
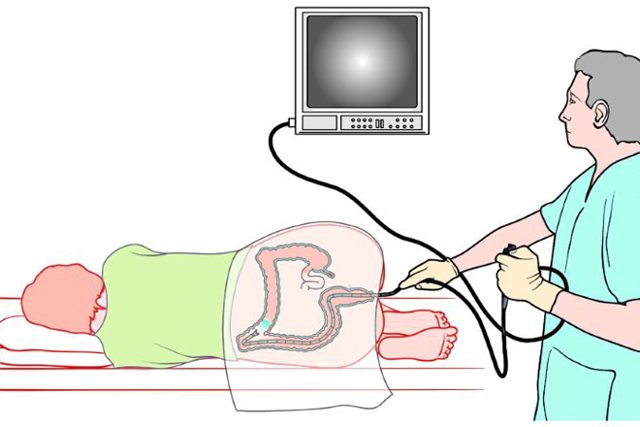
What is a colonoscopy
It is enough to refer to the translation of the term to understand what it means: from Greek colon
- “colon”,
Skopos
- “to consider”.
A colonoscopy is an examination of a person's large intestine performed by inserting an endoscope (a device with a camera on the end) into the rectum.
And for most people, one definition is enough to cause anxiety and stop a sometimes life-saving operation.
colonoscopy indications:
- frequent constipation;
- suspicion of inflammatory bowel disease (Crohn's disease, ulcerative colitis);
- hereditary predisposition to colon cancer;
- suspicious symptoms: Blood and mucus in the stool, unnatural color of the stool, pain when moving the bowel;
- irregular bowel movements;
- frequent bloating.
Unlike rectal manoscopy, which can only evaluate the rectum and sigmoid colon (at a maximum depth of 30 cm), colonoscopy can examine the entire colon (at a depth of about 150 cm).
How is it carried out?
To perform a colonoscopy, the patient must lie on his left side and bend his knees. The doctor treats the anus with an antiseptic and carefully inserts an endoscope equipped with a camera and a light source. An enlarged image of the rectum immediately appears on the monitor.
By pushing the flexible tube deeper, the doctor gradually evaluates all areas of the colon. The tube is hollow inside so that the doctor can use it to deliver necessary instruments to problem areas. This may be an irrigation tube (if the mucosa is contaminated with feces) or a polyp removal loop.
In addition to the endoscope that conducts the examination, there is always a nurse nearby who periodically gently presses on the patient’s stomach to continue examining the tube.
Important! The patient must only strictly follow the doctor's recommendations and instructions. He must lie still so as not to harm himself.
The duration of a colonoscopy is from 5 to 30 minutes. The minimum time is sufficient for preventive diagnostics. If there are polyps in the path that need to be removed, or suspicious areas that need to be biopsied, the time increases to half an hour.
What are patients afraid of?
Colonoscopy has a bad reputation due to many negative reviews. And for some reason, patients who want to undergo this procedure pay more attention to negative opinions. Hence there are two main fears.
Pain
Especially if a person suffers from constipation and pain during bowel movements. In this case, he may have pain in the rectum, and even the slightest touch of the anus is painful. Therefore, such a person will never dare to have a colonoscopy.

But even patients who do not have pain are afraid that it will appear during the study. The same negative reviews that can so often be found on the Internet are to blame for this. Some people write that they even screamed during the entire colonoscopy, and that they will never do it again. But it all depends on the pain threshold and the presence of colon disease.
Shame
Patients are also afraid of unpleasant moments that occur when the intestines are inflated or washed out with air (when there is fecal residue and the endoscope cannot move further). This causes discomfort, which is an unbearable desire to deflate. But these are just false incentives associated with air injection. And if you relax, the colonoscopy will be comfortable.
Anesthesia
18 During a colonoscopy, your doctor may use numbing gels or sprays (such as lidocaine) under local anesthesia. This is especially important for people suffering from hemorrhoids. In the case of hemorrhoids, a person simply cannot survive the procedure without anesthesia, so local anesthesia is used.
But nowadays, most people tend to have a colonoscopy under sedation.
This is a type of general anesthesia, but with immersion in superficial sleep and preservation of all reflexes and functions (the patient breathes on his own).
Sedation is achieved by intravenous administration of Propofol, a short-acting hypnotic. It is safe because there is always an anesthesiologist nearby who checks vital parameters: breathing, blood pressure, pulse.
By the way! Anesthesia is a strong name for sedation, but patients prefer to use this term because it means unconsciousness and pain during the procedure.
pros
The advantages of colonoscopy with anesthesia are obvious. Before the procedure, you can sleep peacefully, and then wake up and get the results. No nerves, no shame, no pain. Minor intestinal discomfort will subside within a few hours, and the rest of the anesthesia will wear off within 15-30 minutes. Anesthesia has certain disadvantages that doctors usually talk about, since patients are usually sedated. However, because the patient cannot respond to manipulation of the endoscope, some diseases may be ignored. Because very severe pain may indicate serious problems and the need for more thorough examination.
Another drawback, but it is already expensive for the patient. Sedation can only be performed for a fee, and it costs from 2 to 5 thousand rubles, depending on the severity of the clinic and the anesthetic used.
Stomach hurts after colonoscopy: why does it happen and what to do
Endoscopic examination of the colon is a highly informative and important diagnostic examination procedure with an optical instrument, allowing an accurate diagnosis to be made. Quite often there is a situation when patients have a stomach ache after a colonoscopy. In most cases, this is a short-term, transient phenomenon, but sometimes complications can be the cause of the pain.
Colonoscopy is, in principle, well tolerated by patients and is not considered traumatic, but in some cases the examination cannot be done. It is necessary to know about this, and after the procedure it is necessary to take restorative measures. It is important to be able to distinguish residual pain from dangerous clinical manifestations in order to consult a doctor in time.
When doctors don't do a colonoscopy without anesthesia
Colonoscopy under anesthesia in the hospital is indicated for children under 18 years of age. Here it is worth understanding that when a child finds himself in a medical institution, he is already experiencing stress due to the unknown situation and the fear that he will have to undergo unpleasant procedures. Even minor pain can traumatize a child’s psyche that is not yet fully formed.
Another direct indication is adhesive disease. This condition is quite often diagnosed in people who have undergone surgery on the pelvic or abdominal organs.
People with a low sensitivity threshold also require medication assistance to comfortably undergo a bowel examination. Moreover, it is psychologically easier for such patients to prepare for the upcoming monitoring if they are confident in absolute painlessness.
In the absence of obvious contraindications, a colonoscopy can be done under anesthesia at the request of the patient. To do this, you need to discuss the topic with your doctor and anesthesiologist, who will help you weigh the pros and cons and give an opinion and valuable recommendations.
Description of the procedure and features of preparation for colonoscopy
Colonoscopy is an examination of the inside of the entire colon, which includes the rectum, sigmoid, colon (ascending, transverse and descending) and cecum. The examination is carried out using a flexible fiber-optic colonoscope device, which is equipped with a video camera, a magnification and lighting system.
Inserted through the rectum, the probe is gradually advanced into the overlying parts of the colon, while it is slightly inflated with air to facilitate patency, improve visibility and prevent damage to the wall.
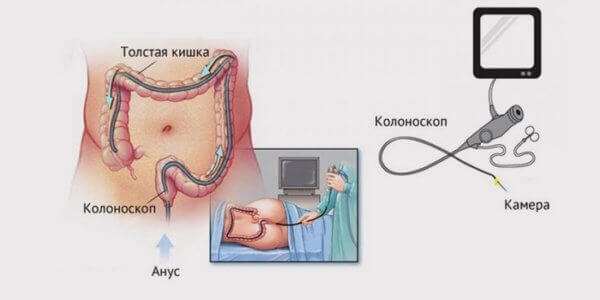
An important condition for obtaining reliable examination data is preliminary preparation of the intestines; it must be absolutely free of feces and liquid. For this purpose, 2 groups of events are carried out:
- diet therapy - 2 days before the study, roughage, fiber, and foods that cause flatulence are excluded;
- cleansing the intestines - using a cleansing enema, microenemas or laxatives.
The method of cleansing the intestines depends on the age and health of the patient; it must be agreed in advance with the doctor.
Preparation
Before the study, perform the following basic steps:
- They follow a diet.
- Consultation about taking medications to thin the blood.
- The optimal means for cleaning the intestines before colonoscopy is selected.
Each of the points is discussed with the doctor individually.
Diet
Meals are changed 5-7 days before the procedure. High fiber foods (cereals, legumes, fresh vegetables, fruits), fatty meats, and dairy products are excluded from the diet. To avoid increased gas formation, you need to give up baked goods, carbonated drinks, semi-finished products, and spices.
The menu includes yesterday's bread, low-fat vegetable broths, rice and potatoes. You can drink black and green tea, jelly, juice.
In cases where endoscopic examination is performed under general anesthesia, you cannot eat on the same day. People arrive at a medical facility strictly on an empty stomach.
Laxatives
The day before the study, adhere to the following plan:
- At 6.00-7.00 a microenema is administered.
- They have breakfast and lunch as usual.
- At 16.00 they begin taking laxatives .
Their dose is calculated depending on body weight.
| Body mass | ˂80 kg | ˃80kg |
| Drug and dose | 3 l Diagnol 3 l Fortrans | 4 l Diagnol 4 l Fortrans |
The drug regimen is different. For example, Diagnol is drunk 100 ml every 10 minutes. The entire dose is taken in one evening. And Fortrans is taken in 2 stages: 2 liters in the evening and 2 liters in the morning. Drink 250 ml every 10 minutes.
Contraindications to colonoscopy
Inserting a probe into the colon may in some cases be unsafe, therefore there are the following contraindications:
- intestinal obstruction;
- presence of hernias;
- inflammation of the peritoneum (peritonitis);
- any acute abdominal pathology;
- infectious diseases;
- heart disease - stable angina, post-infarction condition, heart failure;
- high blood pressure;
- diseases of the bronchi and lungs with respiratory failure;
- decreased blood clotting;
- pregnancy period.
Adverse effects and possible complications
Complications of colonoscopy based on their causes can be divided into 3 groups:
- related to the technique;
- anesthesia-related;
- associated with preparation errors.
Technical complications
If endoscopy is performed too quickly and unprofessionally, there is a possibility of damage to the intestinal mucosa, followed by bleeding and an inflammatory process. In more severe cases, there may be a through perforation with the development of peritonitis. Such complications are extremely rare.
Complications after anesthesia
For children under 12 years of age, as well as persons with increased pain sensitivity, fear of the procedure, with adhesive disease, and at the patient’s own request, the examination is performed under anesthesia. Usually a short-term anesthesia is given with intravenous drugs. After them, there may be such phenomena as headache, nausea, vomiting, and in older people, heart rhythm disturbances. These phenomena are amenable to drug correction.
Preparation errors
If the patient did not adhere to the recommended diet, took food before the study and a large dose of laxatives, loose stools may be observed after the procedure. Against the background of irritable bowel disease, diarrhea may be accompanied by abdominal colic and bloating. If diarrhea persists for more than 2 days, you should consult a doctor.
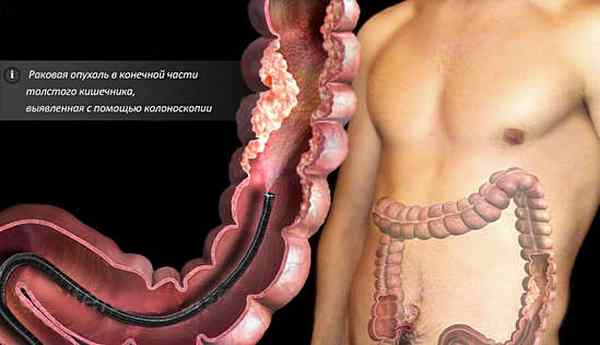
Other consequences of colonoscopy
If a small amount of blood is released in the stool after a colonoscopy, this happens after a biopsy is taken - taking a section of the mucous membrane with forceps for histological examination. This phenomenon can last 2-4 days until the wound heals.
It happens that after a colonoscopy the body temperature rises to low-grade levels. This happens as a result of reactive inflammation of the intestines in response to manipulation. If the temperature is more than 37.4-37.6°, tends to increase, this indicates the development of complications, you need to consult a doctor.
Colonoscopy and its consequences
During an examination of the intestines using a colonoscope, a specialist can not only conduct a visual inspection of the internal walls, but also remove tumors, polyps, and also collect tissue for laboratory analysis. The advantage of this method is the absence of the need to make a surgical incision, as well as the elimination of the development of negative consequences.
If negative consequences occur after colonoscopy, it is only in rare cases. After intestinal colonoscopy, the development of the following possible consequences cannot be excluded:
- Intestinal perforation. This complication occurs most often in 1% of cases, the cause of which is damage to intestinal tissue. If this type of complication develops, emergency care is required.
- Complications due to anesthetic drugs. Such complications include allergies, which occur when the body is intolerant to a particular anesthetic drug.
- Development of intestinal bleeding. This consequence is extremely rare, but it cannot be ruled out. This type of after-effects after a colonoscopy can occur within a few days. This type of complication can be eliminated through surgery if the pathology occurs some time after the end of the study. If bleeding develops during the study, it is eliminated by cauterizing the vessels or administering adrenaline.
- Penetration of infection into the body.
- Development of pain after the procedure.
- Splenic ruptures, which occur in isolated cases.
If you have one of the complications or negative symptoms presented above after a colonoscopy, you should immediately consult a doctor or call an ambulance. The main symptoms of the above complications are the following:
- Increase in body temperature to 38 degrees and above.
- The appearance of signs of nausea, as well as vomiting that occurs for no reason.
- Feelings of severe pain in the abdomen.
- Stool is caused by the presence of blood and mucus.
- It is not uncommon for a patient to develop diarrhea, which shows signs of blood.
- The patient becomes weak and exhausted.
Why your stomach may hurt after a colonoscopy - probable causes
In principle, there should be no obvious pain after the study. Basically, patients are concerned about a feeling of discomfort and heaviness in the abdomen, and bloating. Pain is typical if the patient has chronic spastic colitis, nonspecific ulcerative colitis, which may worsen after examination with a probe.
The most common cause of discomfort and pain is the accumulation of gas in the intestines, which was introduced during the procedure for bloating. It is easy to remove using special means.
The cause of the pain may be non-compliance with the diet, eating rough food during the recovery period. Irritation and intestinal spasms occur, accompanied by pain.
Other causes of pain are associated with damage to the intestinal mucosa and the development of inflammation in the intestines, abdomen, and pelvic cavity. Such pain increases in intensity and is accompanied by an increase in body temperature and a deterioration in general condition.
What to do if your stomach hurts?
If your stomach still hurts after a colonoscopy, what should you do in such cases? First, you should understand that the patient cannot independently determine whether this is normal or whether there are some consequences. Therefore, if the pain is intense, if it does not subside in the first 2-3 days and increases, you should not self-medicate, but visit a specialist who did the research.
In common cases, pain and discomfort can be reduced at home with the help of medications and folk remedies.
Providing assistance: medicines, traditional medicine
Among pharmaceutical preparations, sorbents are used - activated carbon , polysorb and analogues. To normalize peristalsis, they give smecta, duphalac , hilak forte , for spastic pain you can take no-shpu , drotaverine , halidor . If the pain is not acute, not severe, or aching in nature, it is allowed to take analgesics.
Among folk remedies, enveloping decoctions - from linden, oats, as well as herbal teas with chamomile, mint, calendula, St. John's wort, and valerian root - will be useful. They should be drunk half an hour before meals, preparing the intestines for food intake.
Prohibited manipulations after the procedure
After a colonoscopy, you should refrain from taking blood thinning medications - anticoagulants, aspirin and its analogues, indomethacin, ibuprofen - for 1-2 weeks. You should also not take strong analgesics in the first days; they can “blur” the clinical picture if a complication develops.
After the study, many patients experience a feeling of fullness in the rectum and abdomen. It is associated with irritation and swelling of the mucous membrane. During this period (up to 2 weeks), it is unacceptable to give enemas or take laxatives that stimulate peristalsis; the condition can only worsen.
When should you urgently consult a doctor?
If you have severe pain in your intestines after a colonoscopy, you should immediately consult a doctor. In addition, the following symptoms are a reason for urgent medical attention:
- severe bloating, no gases;
- lack of stool;
- persistent and severe pain in the abdomen and pelvic area;
- copious amounts of blood in the stool;
- nausea, repeated vomiting, dry mouth;
- abdominal wall muscle tension;
- high body temperature;
- violation of the general condition.
These signs can appear individually or in combination, but they all indicate trouble when urgent treatment is needed.
Some recommendations for intestinal recovery after the procedure
To avoid the development of undesirable consequences of colonoscopy, the intestine needs rehabilitation measures:
- gentle dietary nutrition;
- restoration of normal microflora.
Diet after colonoscopy
In the intestines exposed to enemas and probes, irritation and damage to the cells of the upper layer of the mucous membrane occurs. Their recovery may take 1-1.5 weeks, subject to gentle nutrition.
The menu should only contain products that are easily digestible, do not leave toxins and do not irritate the digestive tract. Avoid raw vegetables and fruits, spicy and sour foods, seasonings, animal fat, legumes, carbonated drinks and alcohol. Food should be well processed, steamed, or oven-baked.
Rice and oatmeal porridge, meat and fish soups, lean boiled meat and fish, fermented milk products, and non-acidic fruit juices without pulp are recommended. The diet is important, it should be fractional - up to 250 ml 6-7 times a day. Half an hour before meals, it is recommended to drink half a glass of still mineral water or herbal tea.
Restoration of microflora
When cleansing the intestines, many beneficial bacteria are lost; their deficiency can lead to stool disorders, inflammation, and hypovitaminosis. Two groups of drugs will help speed up the process of microflora restoration:
- probiotics containing bacterial cultures - Lactobacterin , Bifidobacterin , Bifiform , Linex and other analogues;
- prebiotics, which contain carbohydrates that are a nutrient medium for bacteria “populated” in the intestines - Duphalac, Portalac , Lactusin , Normaze and other representatives of this group; their natural analogues are carrots, pumpkin, asparagus, which can be consumed boiled and stewed.
source
How to prepare for a colonoscopy?
Considering that during the diagnosis the doctor will examine the colon, it is extremely important to first clean the mucous membrane. The desired effect is difficult to achieve with an enema. That is why patients are advised to prepare in advance using diets and medications sold in any pharmacy. Proper preparation for a diagnostic colonoscopy usually includes the following two steps:
- Three days before the procedure, you must stop eating fatty meats. It is prohibited to consume fish along with dairy products, cereals, cereals, and rye bread. It is also important to avoid fresh vegetables and fruits. Alcoholic drinks, carbonated water, hot spices and canned food are prohibited. It is allowed to eat white bread and broths along with lean meat, eggs, pasta, rice, boiled potatoes, and butter. You can drink juice or jelly. Colon cleansing for colonoscopy is important.
- On the eve of the procedure, the patient must take a laxative. As part of bowel preparation for examination, a solution of polyethylene glycol or drugs such as Duphalac and Fortrans is prescribed. In addition, the person will need to drink two liters of fluid the night before the test. Another two liters are drunk on the day of the procedure if it is scheduled for the afternoon. If less than a day is allotted for preparation, the entire volume of the solution is drunk from four to eight o’clock in the evening.
Preparation for anesthesia during colonoscopy is carried out directly on the day of the procedure itself. In this case, you should refuse food and drink in the morning. It is also important to remove contact lenses with dentures before the corresponding manipulation.
Where to get a colonoscopy? The procedure can be performed at any medical facility or diagnostic center.
A few words about colonoscopy
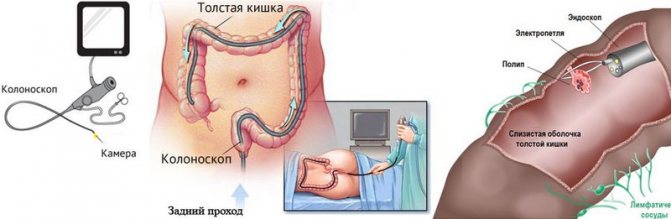
Its essence is to insert a special tube into the patient’s rectum - a probe, which contains a camera, a flashlight and a manipulator for controlling the device. Everything that the camera sees is displayed on the monitor screen, and the doctor can immediately assess the condition of different parts of the intestine, carefully examine polyps, diverticula, neoplasms and other pathologies on the walls of the rectum. In addition, right during a colonoscopy, a specialist can carry out medical manipulations, namely, remove small polyps, cauterize blood vessels that pose a danger to the patient’s life. These advantages of this method have made it the most popular among all types of intestinal diagnostics.
If the actions performed by a doctor for diagnostic purposes bring almost no unpleasant sensations to the patient, then the same cannot be said about therapeutic manipulations. In this case, the integrity of the intestinal mucosa is compromised, and of course this cannot go unnoticed by the patient. If this procedure is performed correctly, all pain after a colonoscopy should go away within a few days.
Possible risks, complications and contraindications
Colonoscopy under anesthesia is not performed if the patient suffers from chronic diseases, such as:
- Psychosomatic disorders;
- Bronchial asthma or bronchitis;
- Heart failure;
- Ulcerative colitis and other IBD in an advanced stage;
- Peritonitis;
- Diseases associated with insufficient blood clotting.
The following are also contraindications:
- Recent stroke;
- Pregnancy and the postpartum period in women;
- Inflammatory processes in the abdominal cavity;
- Mitral valve stenosis.
Different forms of anesthesia help to avoid pain and discomfort during a colonoscopy, but do not guarantee the absence of complications. Therefore, some clinics offer patients to remain under inpatient observation for several days after diagnosis. Elderly people are more susceptible to the risks of complications, since anesthesia cannot but affect vital organs.
Possible consequences include:
- Nausea and vomiting before and after meals;
- Bloody discharge during bowel movements;
- Allergic reactions on the skin;
- Increased temperature and blood pressure;
- Painful sensations in the back and abdomen;
- Exacerbation of chronic cardiac and pulmonary pathologies;
- Attachment of infections (rare);
- Damage to the walls of the intestinal tract and hepatitis B (rare);
- Blood poisoning (virtually excluded);
- Stopping breathing during diagnosis in case of an unexpected reaction to anesthesia.
Within 2-3 days after a colonoscopy, the process of defecation may be disrupted. If there are any disturbing signs, you should consult a doctor.
Follow us on social networks
Consequences of colonoscopy
They appear in extremely rare cases, but the specialist is obliged to warn the patient about them in advance, even before the procedure. The list of such consequences is as follows:
- Intestinal bleeding. It occurs in one patient out of 1000. Blood may appear in the patient’s stool both immediately during the procedure and immediately after it, and even several days after its completion. There may be several reasons for this. Most often this happens due to minor trauma to the intestinal mucosa by the device. This especially often affects patients with an abnormal, complex intestinal structure with an excessively large number of bends.
- Intestinal perforation. We are talking about a severe violation of the integrity of the intestine, namely, a piercing of one of its walls. Such complications after colonoscopy can be fatal, and therefore the patient requires urgent medical attention. Such consequences of colonoscopy can only be eliminated by surgery, when the doctor surgically restores the damaged mucosal tissue.
- Infection with viruses, including the most serious ones - hepatitis C and B, HIV infection, syphilis, salmonellosis. Despite thorough disinfection and the responsible attitude of medical personnel to their work, such cases still occur. Colonoscopy is an invasive procedure, which means there is always a risk of infection. The thin intestinal mucosa has excellent absorption and does not protect against infection.
- At the end of the colonoscopy, the patient may experience respiratory distress after the procedure. Anesthesia often leads to such consequences.
- Increased temperature and pain in the lower abdomen. Most often they occur when inflamed areas of the intestine are affected during the procedure.
Why does my stomach hurt after a colonoscopy?
Almost all patients feel discomfort immediately after surgery, but after a couple of days everything usually returns to normal. But what to do if the stomach hurts after a colonoscopy, and the patient’s sensations are too strong? Why did the pain appear at all?
The most common source of pain is air entering the intestines. The air is not absorbed by the villi and tries to find a way out, migrating between different parts of the intestine. This movement of air causes severe pain to the patient.
In some cases, the air does escape naturally. This usually occurs after active physical activity. But if the pain does not leave the patient, it cannot be tolerated. It is necessary to contact a proctologist and inform him about the consequences of the diagnostic procedure. The doctor may remove the air using a colonoscope. The patient may also be prescribed to take enterosorbents, for example, activated carbon or microcellulose, which perfectly absorbs not only toxins, but also gases. The patient may also be prescribed laxatives or enemas with medicinal decoctions, but such restoration of the intestines after colonoscopy is allowed only under the supervision of a doctor.
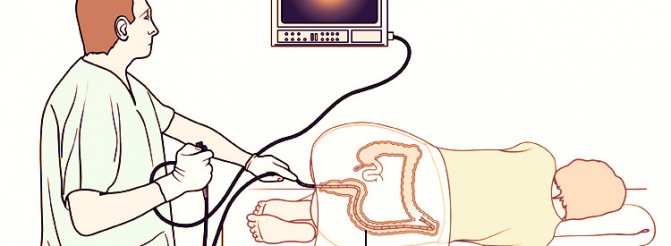
Development of adverse consequences after colonoscopy
During the procedure, the doctor, using a colonoscope, can not only visually examine the intestinal tract, but also remove benign formations, polyps, and also take pieces of tissue for laboratory testing.
The main advantage of this technique is that there is no need for a surgical incision. In addition to all this, colonoscopy is one of the safest methods that rarely leads to adverse consequences.
If complications arise after the procedure, it is only in extreme cases when the doctor’s recommendations are not followed or the specialist is inexperienced.
The main complications include:
- intestinal perforation. This type of complication occurs in only one percent of patients. The main cause of the pathology is considered to be damage to the tissue structures of the intestinal tract during insertion of the endoscope. In this case, urgent surgical intervention is required;
- allergic reaction to painkillers. Occurs when the patient is not aware of how his body reacts to anesthetics;
- intestinal bleeding. This type of complication is as rare as intestinal perforation. Bleeding appears a few days after the procedure. Bleeding can be stopped with surgery. But it also happens when blood flows during the examination. Then the pathology is eliminated on the spot by cauterizing the vessels;
- infection entering the body;
- the appearance of pain syndrome;
- rupture of the spleen.
If a patient experiences pain after an intestinal colonoscopy, it is necessary to urgently visit a doctor. You also need to pay attention to other symptoms such as:
- temperature rise to 38-39 degrees;
- the appearance of nausea and vomiting for no reason;
- detection of mucus or blood in the stool;
- development of diarrhea;
- weakness and exhaustion of the body;
- general malaise.
These signs indicate the occurrence of serious complications that require urgent examination by a specialist and surgical procedures.
Why is the recovery process after colonoscopy so important?
It seems that the diagnostic and treatment procedure itself is important, and everything that happens after it is no longer so important.
A responsible and qualified doctor should explain to the patient that recovery after a colonoscopy is an extremely important stage in completing the procedure, and it does not last a few minutes or hours, but about 20 days!
Why is this so important? It should be remembered that in preparation for the procedure, the patient’s intestines were cleansed with an enema, that is, all flora from this section of the digestive tract was completely removed. Of course, normalizing the bacterial balance simply requires restoration. Otherwise, diarrhea after colonoscopy is highly likely to affect the patient. Frequent bowel movements and diarrhea are dangerous not only due to dehydration, but also due to the activation of pathogens that are somehow present in the large intestine. All this can ultimately result in the appearance of persistent dysbiosis, colitis and even peritonitis.
How to restore the intestines after a colonoscopy according to all the rules? There are rules and recommendations that the patient must follow. They mainly concern temporary changes in the patient’s diet:
- During the first 2-3 days, the patient is allowed to eat only boiled or steamed foods. Such food will not add work to the intestines, and the organ will be able to recover.
- Mandatory inclusion in the diet of such products as low-fat cottage cheese, river fish, natural unflavored yogurt, low-fat kefir. They help restore microflora in the stomach and intestines, which means they help quickly get rid of discomfort in the stomach and intestines.
The amount of fat after intestinal colonoscopy should also be limited. It should be noted here that a complete rejection of fats will also not benefit the patient, otherwise it will be very difficult to go to the toilet to defecate. Constipation after a colonoscopy is especially often complained of by patients who take all the doctor’s recommendations too literally and do not understand that a healthy diet is only a limitation of some foods, but not an absolute exclusion of them from the diet.
- The main food in the first days after the procedure should be light broths. The calorie content of such a diet will be low, but this is exactly how the gradual transition to normal, habitual life occurs.
- For some time, the following products will be prohibited for the patient: whole grain porridge, sausages, sweets, and fresh baked goods.
As an additional measure of assistance, the doctor may prescribe the patient to take probiotics - bacteria that the body needs for normal digestion and well-being. It should be noted that such drugs must be taken in liquid form, since the tableted solid form of drugs can increase discomfort in the abdominal area.
How can you help yourself at home?
If your lower abdomen hurts, you can help yourself with folk remedies. Such means can be used when consultation with a specialist is unavailable for some reason. In other cases, it is better to consult a doctor.

Recipe 1. Decoction of plantain seeds. 1 tbsp. seeds are poured with a glass of boiling water and left for half an hour. Now filter the composition and take 1 tbsp. 30 minutes before meals. This decoction promotes the natural rapid release of gases and thereby relieves discomfort in the lower abdomen.
Recipe2. For severe bloating, it is recommended to take activated charcoal. The amount of the product depends on the patient’s weight. On average, a single dosage is 4-5 tablets, which must be crushed, dissolved in a glass of water and the contents drunk. This product can only be used between meals.
Recipe3. Abdominal massage. Gently massaging the abdomen in a clockwise, downward direction helps combat gases and promotes their rapid passage. Such movements must be done very carefully so as not to increase pain. The patient should be as relaxed as possible. Comfortable air temperature is also important. The feeling of cold interferes with and worsens the flow of all processes in the body, and can also cause spasms in the intestines and stomach.
Recipe4. Suppositories with analgesic effect. These include the simplest remedies, for example, suppositories with papaverine, which gently relieve pain in the anus, intestines and lower abdomen. The effect of such candles lasts about 3 hours.