In the modern world, there are a huge number of ailments that, if not treated in time, can lead to negative consequences. Therefore, when the first symptoms appear, immediately seek medical help from professionals. Diseases of the gastrointestinal tract pose a great threat to human health and life. They are much more difficult to treat, especially if the patient has started the pathology and went to the hospital in the later stages of its course.
To avoid many negative consequences and serious complications, it is very important to diagnose the disease in a timely manner. In modern medicine, there are quite a few laboratory research methods that are highly accurate and informative. One of these is intestinal colonoscopy with sedation, reviews of which will be presented below. What is this procedure, what data does it allow doctors to collect and what features does it have? These and many other questions will be answered in detail in this article.
general information
Colonoscopy with sedation is one of the modern research methods aimed at studying the internal state of the intestinal walls using a special device equipped with a camera, which is inserted through the anus. All information is displayed in the form of a detailed picture on the display, thanks to which the doctor can draw up a detailed clinical picture of the patient’s health status and diagnose many gastrointestinal diseases of various origins in the early stages of development.
It is worth noting that this research method is used not only to make an accurate diagnosis, but also to take soft tissue samples for analysis, eliminate internal bleeding, treat intestinal obstruction and perform surgery to remove polyps and tumors. Thus, the scope of application of colonoscopy with sedation (reviews about the procedure are mostly positive) is quite wide. This research method is used everywhere when any gastrointestinal diseases are suspected.
Conducting an examination under anesthesia has many strengths. The person is calm and completely relaxed. And some medications used for anesthesia cause short-term amnesia, so the patient will not remember any unpleasant moments.
Types of procedure
There are several methods for performing a colonoscopy.
- Virtual - information is collected using CT and MRI. Both laboratory research methods are innovative and are highly accurate and informative. This option is the most preferable because it is completely painless and has almost no contraindications or side effects.
- Using an endoscope, a special device is inserted into the intestines through the anus, which is a two-meter long tube, at one end of which there is a video camera that displays the image on the display.
In the latter case, the patient is sedated before the colonoscopy. This is a mandatory condition, since the procedure causes severe discomfort and pain to the person, so it is simply impossible to endure it without anesthesia.
Indications for use
This aspect deserves special attention. For older people who do not have a genetic predisposition to colon cancer, it is recommended to have a colonoscopy with sedation at least once every five years. If a person has had relatives in their family who have had problems with cancer, then it is advisable to undergo examination every 12 months. This is necessary for timely diagnosis of the disease and initiation of treatment. In addition, the following health problems can also be identified among the indications for use:
- suspicion of internal bleeding in the large intestine;
- benign and malignant formations;
- body temperature 37-37.5 degrees, which lasts for a long period of time;
- sudden and unjustified loss of body weight;
- chronic digestive disorder;
- anemia;
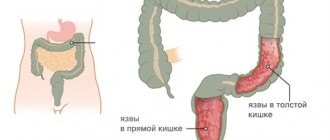
- chronic inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract, occurring in acute form;
- ulcerative colitis.
Preparing for the examination

Colonoscopy under sedation, reviews from patients and doctors fully confirm this, it is highly accurate and informative. However, in order to reduce the likelihood of a false diagnosis, it is necessary to first prepare your body for the procedure. In approximately 3-4 days, you need to eliminate the following foods from your diet:
- cow's milk;
- soda;
- black tea and coffee;
- alcohol;
- pasta;
- any pastries;
- wheat cereal;
- fruits and vegetables;
- legumes;
- nuts;
- fatty foods;
- smoked meats;
- sausages;
- semi-finished products;
- products that contain dyes, preservatives and flavor enhancers.
It is best to stick to proper nutrition. It is recommended to include the following products in the menu:
- natural yoghurts;
- dairy products;
- boiled turkey meat;
- steamed sea fish;
- chicken bouillon.
If you decide to have a colonoscopy with sedation, you need to take it very seriously. Consumption of the products listed above may negatively affect the accuracy of the examination and make it difficult for doctors to make the correct diagnosis. The last meal should be consumed no later than 12 hours before the expected visit to the doctor. During this time, drinking pure water without gas and green tea is allowed. 2 hours before the start of the procedure, it is forbidden to even drink, since the stomach must be empty.
Other preparatory measures are discussed with the doctor individually. In most cases, patients are prescribed bowel cleansing through an enema or taking medications that have a laxative effect, such as Lavacol or Fortrans. The dosage is calculated by the doctor for each patient separately, taking into account body weight and a number of other factors.
How is the procedure performed?
Many people scheduled for a colonoscopy with sedation are afraid to go to the hospital because they have no idea how it works. But there is nothing wrong with this method of laboratory research. Everything happens according to the following scheme:
- The patient takes a lying position on the left side on the couch, pressing his legs with his knees to his stomach.
- The specialist performs complex anesthesia. It may involve general anesthesia, taking sedatives, or lubricating the anus with a special gel containing an anesthetic.
- Once the anesthesia begins to take effect, a probe is inserted into the anus.
- Depending on the specific purpose of the study, the duration of the procedure can range from 15 minutes to the complete completion of all necessary manipulations by the doctor.
- The colonoscope is brought out from the colon.
It is worth noting that during colonoscopy, anesthesia, sedation or other anesthesia methods are performed only in the presence of a qualified specialist. This is necessary not only to calculate the correct dosage, but also to minimize any risks that may pose a threat to the patient's health.
Anesthetic support for gastro- and colonoscopy
The introduction into clinical practice of painful, unpleasant for the patient, invasive diagnostic methods for diseases of the gastrointestinal tract (GIT) requires the development of methods of anesthetic management, allowing, on the one hand, to create maximum surgical comfort, and on the other, taking into account the low invasiveness of these interventions, reasonable minimization of anesthetic management and rapid activation of patients after diagnostic procedures.
However, in the literature we did not find specific works discussing the problem of ensuring the safety of patients undergoing endoscopic examinations.
Surgeons, and even anesthesiologists, do not always have an ambiguous idea about the need for anesthesia during gastro- and colonoscopy [1,3,5].
Working for many years with patients during diagnostic and therapeutic procedures of the gastrointestinal tract, we have repeatedly encountered potential risks in this area (unpleasant sensations, severe pain, which is why patients are forced to refuse the procedure, collapse).
Currently, in the foreign literature there are conflicting opinions regarding the use or abstinence from anesthesia during endoscopic procedures.
In North America, Europe and Russia, endoscopic diagnosis is performed under sedation [6].
In Holland, only colonoscopy is performed under sedation.
In Russia, diagnostic invasive procedures are increasingly performed under anesthesia [2,4,5].
At the Institute of Surgery. Over the past 5 years, Mikaelyan has seen an increase in diagnostic and therapeutic invasive procedures, especially colonoscopy and gastroscopy. The number of patients presenting with anxiety is increasing and the procedure cannot be performed without pharmacological support.
The purpose of the study is to develop an optimal method of anesthesiological support for gastro and colonoscopy.
Material and research methods. This study was conducted at the Institute of Surgery named after. Mikaelyan from 2009 to 2011. 1579 gastro- and colonoscopies were performed, of which 520 colonoscopies, 985 gastroscopy, 67 colonoscopies and gastroscopy simultaneously. A total of 131 studies were performed under sedation and anesthesia, of which 55 colonoscopies, 24 gastroscopy, Colonoscopy and gastroscopy simultaneously - 52 patients.
131 patients were examined, of which 85 were men (64.9%), 46 were women (35.1%), who underwent therapeutic diagnostic gastro- and colonoscopy with and without anesthesia.
The age of the patients ranged from 40 to 85 years. According to physical status, patients are distributed as follows: ASA 1-20%, ASA 2-40%, ASA 3-40%.
Depending on the method of protection used, all patients are divided into 4 groups:
- Group 1 (n985) gastroscopy was performed by inhalation of the hypopharynx with a 10% lidocaine solution (3 puffs of 14.4 mg), in the remaining patients (n456) colonoscopy and gastroscopy were performed without anesthesia.
- Group 2 (n80) sedation with propofol (1.23 mg/kg).
- Group 3 (n28) sedation and analgesia was carried out on the basis of propofol (0.76 mg/kg) and ketamine (0.19 mg/kg).
- Group 4 (n5) was a small group of patients who were scheduled for surgery the next day. Spinal anesthesia was performed using bupivacaine (0.5% 2 ml).
Safety monitoring consisted of ECG, heart rate, blood pressure, SpO2.
During the study, an internal audit was conducted to count critical incidents in the study groups.
The time of loss of consciousness and the time after which there was no motor activity in response to manipulation were recorded.
During the period of awakening - the time of restoration of consciousness, incidents of postoperative nausea, vomiting, trembling.
The level of sedation was determined using the Ramsay scale [8].
Table 1.
“RAMSAY” scale
| Points | Definition |
| 0 | Full wakefulness, orientation |
| 1 | Anxiety, worry, fear |
| 2 | The patient is calm and cooperative |
| 3 | The patient is drowsy but communicative |
| 4 | Deep sedation, the patient opens his eyes to a loud shout |
| 5 | Anesthesia, weak reaction to pain |
| 6 | Deep coma |
Recovery of psychomotor functions was determined using tests according to Bidway (1977, disappearance of postoperative drowsiness and restoration of orientation).
Table 2.
“BIDWAY” test.
| Points | Definition |
| 4 | The patient does not respond to painful stimulation and verbal command |
| 3 | The patient responds to painful stimulation, but does not make contact |
| 2 | The patient responds to commands, reacts to painful stimulation, but is not oriented in time and space |
| 1 | The patient responds to all forms of stimulation, is well oriented in time and space, but is drowsy |
| 0 | The patient is well oriented in time and space, there is no drowsiness |
Research results. Almost all 95% of patients who underwent colonoscopy and gastroscopy without sedation reported discomfort and unpleasant sensations during anesthesia. Motor activity was observed in all 100% of patients, which interfered with the work of the endoscopist and lengthened the time of manipulation. Complications included nausea and vomiting in 35 patients (3.55%), desaturation in 11 patients (1.11%), and tremors in 25 patients (2.53%).
In group 2, sedation occurred after 32±2.1 seconds, which was satisfactory for gastroscopy at 15±3.2 minutes. with a medical procedure. During colonoscopy, the dose of propofol was increased in 6 patients (7.5%) to 1.07 mg/kg. Desaturation up to 85% was observed in 2 patients (2.5%).
Motor activity was observed in 4 patients (5%). After the procedure, 5 patients (6.25%) experienced tremors, and 2 patients (2.5%) experienced nausea.
Recovery time of psychomotor functions after 12 minutes. according to the “0” point system.
In group 3, sedation occurred after 28±3.1 seconds. During gastro and colonoscopy, no motor activity was observed. There was a short-term desaturation of up to 80% at the time of insertion of the endoscope in 3 patients (10.7%), which is obviously associated with partial obstruction of the upper respiratory tract.
Awakening after the procedure in this group was somewhat delayed, up to 5-10 minutes, which required constant supervision by an anesthesiologist for 30-40 minutes. The patients did not report any discomfort.
Nausea and vomiting were not observed in this group of patients, which is apparently due to the antiemetic properties of ketamine [9,10,11].
Group 4, the smallest (n5), almost all patients (80%) noted trembling, obviously associated with an emotional background (the presence of the patient during the procedure). Sedation was not performed in this group of patients.
No hemodynamic incidents were observed due to crystalloid infusion therapy (10-15 ml/kg/h).
On average, gastroscopy lasted 10.2±5 minutes, and colonoscopy 30.6±5 minutes.
There are few patients who can safely tolerate endoscopic interventions. 40% of patients refuse anesthesia. Tolerance of upper gastrointestinal endoscopy without anesthesia improves proportionally with age due to decreased oropharyngeal sensitivity [7].
Table 3.
Undesirable effects of sedation and analgesia
| Methods of protecting the patient | Motor. motor | Nausea, vomiting | Desaturation | Shiver |
| 1st group (n-985) | 985 | 35 (3.55%) | 11 (1.11%) | 25 (2.53%) |
| 2nd group (n-80) | 4 (5%) | 2 (2.5%) | 2 (2.5%) | 5 (6.25%) |
| 3rd group (n-25) | — | — | 3 (10.7%) | — |
| 4th group (n-5) | — | — | — | 4 (80%) |
60% of patients undergoing endoscopic procedures prefer sedation (anesthesia) and believe that they could go for a repeat examination.
The results of our studies have shown that the optimal option for anesthesia for gastro and colonoscopy is propofol, propofol + ketamine, and in patients going for surgery immediately after the procedure, regional anesthesia.
Literature
- Bolshedvorov R.V. General resuscitation, 2009, 5, 7578
- Gabitov M.V., Grebenshchikov O.A., Mironenko A.V. and other authors, 2011, 5, 2226
- Likhvantsev V.V. “Anesthesia in minimally invasive surgery”, M. Miklos 2005, 130140
- Mustareva M.N., Mshchikov V.M. and other authors, 2009, 4, 2123 and others. Quaid KR, Leine Lgastrointest. Endoc. 2008, vol. 67, N6, P.910923
- Fedorov S.A., Likhvantsev V.V., Kichin V.V. et al. Ar, 2010, 3, 6063
- Cacho G., Dienas C et al. Gastroeterol. Hepatol 2000, vol. 23, N9, P407411
- Knape JTA, Andrialsen H. et al www.critical.onego.ru 2007
- Paspatis FGA, Manolaraki MM et al. Dig. Liver. Dis., 2009, 41(11), 807811
- Ramsay MA, Savage TM et al Brit. Med. J. 1974, vol. 22, P 656
- Sporea F. Popescu A. et al Rom. J. Intern. Med. 2009, 47(1), 1924
- Stella L., Torri G., Gastiglioni C. L. (1979). The relative potencies of tiopentone, ketamine, propanidid, alphaxalone and diazepam. Br.J. Anaesth., 51:119122
- Tverskoy M., Fleyshman G., Bredley EL jr., Kissin I. (1988) Midazolamthiopental, ketamine anesthetic interaction in patients. Anesth. Analg., 67:342345
- Vohra A, et al. Noninvasive measurement of cardiac output during induction of anaesthesia and tracheal intubation: ketamine and propofol compared. Br.J. Anaesth 1991; 67:648
A few words about anesthesia
Colonoscopy is a very unpleasant examination method associated with some discomfort, and in some cases even severe pain. Therefore, it is performed under anesthesia. The following options exist:
- General anesthesia. A person is injected intravenously with a drug that puts him into deep sleep. After the effect of the medication ends, the patient gradually comes to his senses, not remembering anything and without experiencing any discomfort.
- Local anesthesia. The device is lubricated with a special gel before insertion into the intestine. In this case, the pain does not disappear anywhere, but the advancement of the probe becomes almost imperceptible.
- Colonoscopy with sedation. This is the most common pain relief option. It is similar to medicated sleep, but the person is conscious, feeling nothing at all.
The specialist decides which type of anesthesia will be used during the examination based on the patient’s health condition.
Colonoscopy under anesthesia
A sedentary lifestyle and poor nutrition lead to disruption of the gastrointestinal tract (GIT) in both its upper and lower sections.
Modern medicine has gone far in its ability to choose a diagnostic method to establish the most reliable diagnosis.
Now the doctor can not only examine and palpate the patient’s abdomen, but also carefully examine the mucous surface of the organs from the inside.
However, such diagnostic methods can be accompanied by rather unpleasant and even painful sensations, frightening patients and forcing them to postpone procedures, the meaning and importance of which can be decisive. If in most cases it is possible to check the upper parts of the gastrointestinal tract without the presence of unpleasant symptoms, for example, to do a gastroscopy (EGD), then the lower parts are very difficult.
Moreover, it is not easy for both the patient and the diagnostician, who has to constantly be distracted by the patient’s complaints, persuade him to be patient and spend more time on the examination. One of these methods is colonoscopy - a method of examining the intestines from the inside by inserting an endoscope. When this procedure is prescribed, patients panic and try to refuse it.
But since this diagnosis is the most informative method, allowing to detect many pathologies, ranging from polyps to intestinal oncology, colonoscopy is now performed under anesthesia. This makes it possible to painlessly and quickly obtain the necessary information regarding the condition of the intestinal mucosa of patients.
Colonoscopy as an indispensable diagnostic method
Colonoscopy is a progressive examination of the large intestine performed using an endoscope. An endoscope is a long tube with a mini-camera attached to the end, which allows you to examine in detail the entire surface of the mucous membrane and, if necessary, use special forceps to remove polypous growths.
During the study, diagnosticians are able to detect polyposis and ulcerative diseases of the large intestine, inflammatory processes and the presence of neoplasms at different stages of their occurrence.
Removal of a polyp using endoscope forceps - stage of surgical intervention
Timely excised polyps and various benign neoplasms reduce the risk of their degeneration into malignant processes, which saves the lives of many patients.
Of course, the colon can be examined using irrigoscopy (X-ray method) or computed tomography, but both examinations will provide significantly less information, and with the first the patient will have to be exposed to radiation.
Types of pain relief during research
To relieve patients from pain during examination, it is customary to perform a colonoscopy of the intestines under anesthesia. There are several possible options for pain relief during the procedure, and the anesthesiologist selects the method of anesthesia for each patient based on his medical history and health status.
The main and successfully used methods of pain relief include local anesthesia, sedation and general anesthesia during colonoscopy, which reduce sensitivity to what is happening to varying degrees and make the procedure feasible without obstacles and pain. Also, with anesthesia, the risk of complications during the examination is significantly reduced - completely relaxed intestinal walls are less exposed to the risk of perforation and other injuries.
Local anesthesia
Colonoscopy under local anesthesia involves applying an anesthetic to the tip of the endoscope, which will reduce the sensitivity of the nerve endings of the mucosa as the tube passes through. For this purpose, anesthetics based on lidocaine and novocaine are used.
This will not completely solve the problem of pain, since the main pain does not appear from moving the endoscope, but from forcing air into the intestines.
Air is used to straighten the walls of the colon, making it possible to examine its surface in more detail.
But psychologically it is easier for the patient to undergo the procedure - the very expression “under anesthesia” sets him up that the pain will be less and he will not be so scared before the examination.
Local anesthesia is performed for patients who have reasonable indications for refusing colonoscopy under general anesthesia or sedation: this is the safest method, but ineffective
Sedation
Colonoscopy in sleep is one of the names of the procedure using sedatives that provide superficial medicated sleep. As a result of the administration of the medicine, the patient’s sensations during the examination are dulled, and the examination is painless.
If we take a closer look at what sedation is, it is immediately worth noting the patient’s borderline state. He seems to be immersed in sleep, but at the same time he has slight sensitivity during examination and after waking up, certain memories are retained, most often not giving a negative connotation to the procedure.
For the examination, Midazolam or Propofol are most often used, which have both advantages and certain disadvantages.
The good thing about using Midazolam is that it almost completely eliminates memories of the study, but the patient takes much longer to recover from the sleep state.
Propofol is characterized by rapid awakening, but the price for this is clearer memories of the procedure. The doctor recommends this or that drug based on the wishes of the patient and his state of health.
Sedation during colonoscopy allows the patient to respond to complications that sometimes occur during diagnosis, and to communicate this to the doctor with his reaction. Due to the presence of mild sensitivity, colonoscopy with sedation allows the diagnostician to understand in time that the intestine has been injured by the endoscope and to take appropriate measures.
General anesthesia
An examination of the intestines under general anesthesia is performed in an operating room, fully equipped with all types of equipment to eliminate possible complications: devices for artificial ventilation of the lungs, stimulation of cardiac activity and other devices necessary for first aid.
The patient is given an intravenous drug that puts him into deep sleep, and the intestines are examined under the constant supervision of an anesthesiologist. The patient falls asleep, all his muscles completely relax, he undergoes the procedure, and after waking up, his condition is under the control of doctors for another 15–45 minutes.
For general anesthesia, the following drugs can be used at the discretion of the anesthesiologist: narcotic analgesics - Fentanyl, Promedol, Sufentanil, Alfentanil, or muscle relaxants - Ditilin, Arduan, Tracrium. In special cases, inhalation anesthesia is used.
In some cases, children are prescribed mask anesthesia for colonoscopy.
Due to the potent properties of any drug for general anesthesia, the dose for each patient is calculated individually.
The patient does not feel anything during the examination and there are no memories of the procedure. This significantly reduces the reluctance to undergo research next time.
Colonoscopy with anesthesia provides 100% loss of sensitivity, while under sedation it can be reduced to 95-99%.
Because of this, with general anesthesia, the risk of injury to the colon during the examination increases, but the duration of the examination is significantly reduced, since the diagnostician does not need to be distracted by the patient’s complaints and interrupt the procedure.
Indications for colonoscopy under anesthesia
Of course, the procedure can be carried out without resorting to the help of various analgesics; details about undergoing a colonoscopy without anesthesia can be found in this article, but there are patients with certain pathologies or characteristics that do not provide this opportunity.
These include:
- children under 12 years of age - it is better to save them from fear and pain during the examination process, since perhaps this is not the only procedure in their lives, and it is better to protect children from the fear of “white coats”;
- patients with adhesive intestinal disease - since adhesions interfere with the passage of the colonoscope, and under anesthesia the tone of the abdominal cavity decreases, which contributes to better advancement of the endoscope;
- the presence of strictures (narrowing) of the rectum or anus;
- mental disorders in which the patient may behave inappropriately and get injured during the procedure;
- the presence of a destructive, ulcerative, inflammatory process in the intestines, which will provoke acute pain during examination.
Stenosis (narrowing) of the intestine - contraindications to the procedure
For people with a low sensitivity threshold, it is also worth using anesthesia. Such patients do not tolerate even minor impacts well, and perceive them much more acutely than others exposed to the same.
Manipulations that are quite tolerable for ordinary people can even cause a painful shock in susceptible people, accompanied by loss of consciousness or disruption of organ function. It is better not to subject such patients to experiments and immediately prescribe painkillers.
Knowing that there will be no pain during the procedure will calm them down mentally and set them up for a favorable examination.
Preparing for an examination using anesthesia
In any case, it is necessary to prepare for a colonoscopy, even without anesthesia, using a certain diet recommended by the doctor and drugs that cleanse the intestines. Of course, you can cleanse yourself with an enema, but there will not be such a cleansing effect as with the use of Fortrans, Lavacol or FLIT PHOSPHONE-SODA.
Nutrition after colonoscopy
Special preparation for future anesthesia is not required, but you should definitely consult with an anesthesiologist, who should find out all the important points for the use of anesthesia drugs. To do this, he learns:
- weight and height of the subject;
- the presence of concomitant diagnoses in order to decide which drug and dose to prescribe;
- is there a tendency to allergic manifestations;
- number of early anesthesia.
The day before and before the examination, the patient's pulse, blood pressure and respiratory rate are measured. You cannot eat food 6 hours before the procedure; you can drink still water no later than 2 hours before the procedure. Preparation includes premedication - the subject is administered sedatives within 30-40 minutes (children can be given orally) Relanium, Midazolam, Seduxen.
This will put the patient in a state of peace, reduce anxiety, which will reduce the likelihood of complications during the procedure, and the amount of drugs required for anesthesia depends on the emotional state of the patient.
Having received an appointment from their attending physician, patients have to decide where to have a colonoscopy? They begin to look through clinics, compare prices in private institutions and the quality of service in public hospitals, go online and read reviews from those who have undergone the procedure.
The most popular diagnostic centers, judging by the stories of patients, are MEDSI and INVITRO, whose branches are located almost throughout the entire territory of the Russian Federation. They can undergo both gastro and colonoscopy with or without anesthesia.
In any case, gastroscopy and examination of the intestines is as comfortable as possible for the patient due to the high professionalism of the diagnosticians, as well as the latest specialized equipment of the clinics. You can watch the procedure in detail on the video, and also read reviews from grateful patients.
Reviews
Marina, 46 years old: I had a colonoscopy 1 year ago. Before the procedure, analgin or baralgin was administered intramuscularly 20 minutes before the procedure. The procedure took about 15 minutes, was painless, the only sensation was colic in the intestines due to the pumping of gas, but it was relatively tolerable.
It was somewhat reminiscent of contractions - it hurts, goes away after a short time, then again. I was advised not to tense up and try to relax completely, so that it would be easier for the doctor and then there would be less pain. I believe that there is no need for general anesthesia if there have been no operations in the abdominal cavity and there are no adhesions.
I think that the procedure is absolutely not terrible.
Eleanor, 53 years old: My husband has been working as an anesthesiologist for 26 years, he often told me that internal organs must be checked regularly and it is better to do this with the help of anesthesia, then it is easier for the doctor to check everything and make the correct diagnosis.
And when the patient “twitches,” tenses up, or complains all the time, then more time is wasted and, most likely, the procedure will have to be repeated. Why do you need this? Therefore, it is better to do it immediately with anesthesia. I recently did 2 examinations myself - a colonoscopy with anesthesia and an FGDS.
I didn’t feel anything bad, just dry mouth, which quickly went away after drinking water and eating. But no pain, no fear!
Stanislav, 48 years old: Today I had a colonoscopy with anesthesia. I prepared for two days - I gave up solid food and drank mostly liquids - tea, juices, coffee, broth. Then I cleaned it with Fortrans - a powerful product that cleans perfectly.
I came for the procedure, the anesthesiologist gave me anesthesia. When I woke up, there were no sensations, and after 15 minutes I safely left the clinic. I recommend that everyone undergo a colonoscopy with anesthesia - do not spoil your nervous system with pain and fear.
I hope my information is useful.
Source: https://apkhleb.ru/endoskopiya/kolonoskopiya-pod-narkozom
Advantages and disadvantages of sedation
General anesthesia is used very rarely, since complete immersion of the patient in a state of sleep requires a long recovery of the body. As practice shows, in the vast majority of cases, sedation is prescribed during colonoscopy. This option is considered one of the most optimal. Among its main advantages are the following:
- absence of discomfort, pain, as well as feelings of anxiety and fear;
- the possibility of non-surgical removal of tumors;
- elimination of bleeding in the colon;
- the possibility of performing the procedure on patients of any age category;
- completely relaxes the patient and reduces the risk of damage to the intestinal mucosa;
- helps a person cope with fear of the procedure and stress.
Despite many advantages, colonoscopy with sedation during sleep also has a number of disadvantages. These include:
- the likelihood of developing side effects from administered medications;
- intoxication of the liver and kidneys;
- memory problems.
Modern medications used for anesthesia during gastrointestinal examinations have a unique chemical composition and are safe for the body. They cause almost no side effects or serious consequences for the patient's health. Intravenous sedation during colonoscopy is considered one of the safest. This anesthesia begins to act quickly, and recovery from it does not take much time.
What is sedation?
Sedation is a technique of putting a patient into a state of superficial sleep , in which he does not feel pain, but, if necessary, can respond to the doctor’s instructions. After administering the anesthetic (mostly midazolam or propofol), the patient’s feelings of restlessness and anxiety disappear, he feels relaxed and peaceful, without pain or discomfort.
There are categories of people for whom the use of anesthesia is mandatory:
- Patients with a destructive process in the colon.
- Children under twelve years of age. Even minor pain can negatively affect a child’s psyche.
- Patients with intestinal adhesions. Adhesions will interfere with the passage of the fibrocolonoscope, which will cause pain.
- Patients with a low pain sensitivity threshold.
In other cases, the use of sedation and general anesthesia is carried out at the request of the patient (if there are no contraindications from the anesthesiologist).
Restrictions
Colonoscopy under sedation (reviews of this procedure are more positive than negative) is one of the most gentle and harmless methods for studying the state of the gastrointestinal tract. However, this type of anesthesia cannot be used in all cases. The main contraindications include:
- children under 12 years of age;
- the presence of adhesions in the intestines;
- nasal congestion;
- epilepsy;
- peritonitis;
- sensitivity;
- low pain threshold;
- individual intolerance to the drug;
- the presence of allergic reactions;
- stenosis of the intestine or anus;
- non-compliance with the prescribed diet;
- mental disorders;
- any diseases of the heart, kidneys, respiratory organs and gastrointestinal tract, occurring in a severe form;
- disruption of the functioning of hemostasis mechanisms;
- acute infectious diseases;
- heart and kidney failure;
- pregnancy.
Possible complications

As mentioned earlier, colonoscopy is not the most pleasant examination method. In addition to discomfort and pain, there is a risk of developing various complications. During diagnosis, there is a high probability of mechanical injury to the walls and mucous membrane of the intestine, rupture of the spleen, and even respiratory arrest. But, as medical practice shows, this occurs only in isolated cases. There is also a possibility that after completion of the diagnosis the person will have:
- flatulence;
- increased body temperature;
- weakness throughout the body;
- pain syndrome;
- difficult defecation.
As for the negative impact of anesthesia on the human psyche and the functioning of the central nervous system, there is none. New generation medications are safe and do not harm the body. Therefore, you don’t have to fear anything, but feel free to agree to any type of anesthesia.
Patient reviews of colonoscopy under sedation
The opinion of the subjects about the diagnosis of the intestines under anesthesia is only good. Getting rid of unpleasant and painful sensations makes everyone happy. There is no evidence of severe consequences due to drug-induced sleep; 9 out of 10 patients felt well after waking up. The only complaints are discomfort and pain in the abdomen, which is natural as a result of the doctor’s manipulations and is eliminated by an injection of an antispasmodic right there in the clinic. Only 1 in 10 experienced mild effects of sedation:
- Nausea;
- Confusion;
- Headache;
- Low pressure.
Attention! Reviews about colonoscopy without anesthesia are not so rosy; in some cases it was even necessary to interrupt the procedure due to the patient’s behavior.
What drugs are used for anesthesia?
Sedation during colonoscopy (you can read patient reviews at the end of the article) involves the patient taking special medications that have a sedative effect. As a rule, doctors prescribe the following drugs:
- "Propofol." It begins to act a short period of time after entering the stomach, but the duration of the effect does not last long. Thanks to this, the patient quickly recovers from anesthesia, retaining memories of all the doctor’s manipulations. Among the main advantages are high tolerance. The disadvantage is the high cost.
- "Midazolam." Causes short-term memory loss. After the procedure is completed, the patient will remember absolutely nothing about it. Many doctors most often prescribe this drug because it has an anticonvulsant effect. The main disadvantage is that the medication has a specific composition, due to which recovery from anesthesia takes longer.
If colonoscopy and gastroscopy are required, sedation is selected by the anesthesiologist individually for each patient. This takes into account his condition, clinical picture and personal experience of the doctor.
Pros of colonoscopy in a dream
- Colonoscopy in a dream allows you to examine the entire large intestine, and the patient will not experience discomfort or pain . Moreover, during the diagnostic procedure, it is possible to remove polyps, stop bleeding in the intestines and other manipulations, saving the patient from additional intervention and surgery.
- The procedure time is reduced - according to studies, intestinal colonoscopy during sleep, on average, takes 15-25 percent less time . Thus, the diagnostician has more time at his disposal for the procedure itself, and not for talking with the patient.
- Many children have a fear of doctors and various procedures; the use of anesthesia will help the child avoid pain. This will reduce anxiety when it is necessary to repeat the bowel examination.
- The likelihood of complications during the colonoscopy itself is reduced. When the patient's bowel is relaxed, the possibility of perforation and other bowel injuries can be almost completely eliminated.
Price
Many people wonder where to get a colonoscopy with sedation. This type of examination is available both in public hospitals and in private clinics. In the latter, everything is done at a higher level, but the cost of services will be noticeably higher. It is quite difficult to give specific figures, since prices vary over a very wide range depending on the region. For example, in Moscow you will have to pay from 4,500 to 20,000 rubles for a colonoscopy. The price includes not only the examination itself, but also all medications.
The patient chooses the method of pain relief independently, based on his financial capabilities. At the same time, doctors always help you decide on the most optimal option, and also talk about all the pros and cons of each method of anesthesia. It would be a good idea to read reviews from patients who already have experience with this type of anesthesia. To avoid many negative consequences, it is recommended to consult a doctor first.
Medication sleep, what is it during colonoscopy?
To diagnose colon diseases, you need a colonoscopy under anesthesia (with sedation) - this is a type of procedure that is done using a colonoscope. This is a thin device that has a light source and a video camera. The device is needed to display images on the screen.
Types of colonoscopy
In medicine, there are two types of colonoscopy:
- virtual;
- using an endoscope.
A virtual colonoscopy is a test based on data that the doctor receives from a computed tomogram or nuclear magnetic resonance imaging. Read more in this article.
With this method, images of the intestine are projected in 2D or 3D form.
Experts say that colonoscopy cannot provide as much information as a full endoscopic examination. But the positive side of virtual colonoscopy is that it is painless.
The duration of the procedure is 10 – 15 minutes.
Colonoscopy using an endoscope performs a couple of functions. At the tip of the device there is a miniature camera, with the help of which the image is projected onto the monitor. This gives the doctor the opportunity to understand the condition of the internal surfaces of the intestines.
One of the main causes of constipation and diarrhea is the use of various medications.
.
To improve bowel function after taking medications, you need to drink a simple remedy
.
Types of anesthesia
General anesthesia (narcosis) - the patient is unconscious during the procedure, sensitivity and memory of the procedure disappear.
Medication-induced sleep (this is sedation) - a patient undergoing a colonoscopy is required to take sedatives and painkillers. The patient is semi-conscious and can remember some aspects of the procedure.
Is a colonoscopy done under general anesthesia?
Colonoscopy is usually performed without anesthesia. In patients who have severe pain, local anesthesia is administered (xylocaine gel, dicaine ointment). Many patients are afraid to have a colonoscopy. They are interested in whether it is possible to do a colonoscopy under anesthesia.
Doctors say that for most people this procedure does not cause pain. Due to a number of reasons, anesthesia is prohibited during intestinal colonoscopy, also in case of heart failure, severe stenosis of the aortic or mitral valves.
But there are cases when anesthesia is necessary for colonoscopy, and there are indications.
The choice is given to sedation - a method of pain relief with special medications, with the help of which the patient is put into a state of sleep.
One of the main causes of constipation or diarrhea is poor diet.
.
Therefore, to improve bowel function, you need to drink a simple drink
.
Preparing for the procedure with sedation
The effectiveness of the study depends on proper preparation. Preparation for the procedure should begin a couple of days before the appointment.
We also wrote about what preparation for intestinal colonoscopy includes.
Diet
The essence of the diet is to prepare the colon for the procedure. The patient needs to eat light, refined foods. Before the procedure you need to drink water.
Colon lavage
To reduce discomfort during colonoscopy, doctors prescribe an intestinal antispasmodic. In private clinics in Moscow, St. Petersburg, Yekaterinburg, Novosibirsk, Yaroslavl, they offer computed tomography of the intestine for colonoscopy.
This procedure shows all pathologies and changes in the intestines.
Compared to colonoscopy, computed tomography differs in that:
- can detect malignant tumors in the early stages of development;
- there are no complications;
- The procedure is painless.
But there are cases when you need to do a colonoscopy, because computed tomography also has disadvantages:
- the color of the mucous membrane cannot be assessed;
- small formations are not visible;
- You can't take a biopsy.
How to do a colonoscopy under general anesthesia
Regardless of whether the doctor said that anesthesia is needed or not, the procedure is the same.
During the procedure, the patient lies on his side, with his legs pulled up to his chin. The colonoscope is inserted into the intestines into the anus. If the procedure is done without anesthesia, the colonoscope must be treated with a special agent, which reduces pain.
Thus, the doctor examines all parts of the intestine.
Before starting a colonoscopy, the intestine needs to be slightly inflated by pumping air inside. This is necessary to straighten the walls of the organ and facilitate the process.
To examine each wall of the intestine, the doctor gradually moves the colonoscope deeper into the intestine. If polyps are found, the doctor can remove them immediately using a snare that is inserted through the colonoscope.
If any neoplasms are fried during the procedure, the doctor performs a biopsy - that is, taking part of the material for analysis to determine how dangerous they are for the patient.
This must also be done using a special instrument that can be seen through a colonoscope.
Polyp removal
Doctors carefully examine the entire intestinal area, then carefully pull the colonoscope out of the anus.
How long a colonoscopy will take depends on how many polyps and other growths are found. On average, the procedure will take no more than 30 minutes.
If the procedure was performed under anesthesia, then at the end the patient will feel a little weakness and possibly a headache.
In some situations, the patient feels a feeling of abdominal distension. This is a situation where the air has not been completely removed from the organ. If polyps were removed, the patient will feel pain in the abdomen, but it can be easily neutralized with the help of analgesics.
In rare cases, gastroscopy can be performed on the same day as colonoscopy. This type of research is carried out very quickly, although there are unpleasant sensations. In total, gastroscopy lasts 5–7 minutes. Read how to prepare for gastroscopy here.
Is it dangerous
Many patients are interested in whether general anesthesia is dangerous and whether anesthesia has consequences. General anesthesia carries certain risks for the patient, but modern medicine and an experienced doctor can significantly reduce them. Especially if the preparation of the procedure is under the guidance of a doctor.
There are no very dangerous consequences of anesthesia. The rumor that “anesthesia affects memory and psyche” is associated with the history of anesthesiology, when a dangerous anesthetic was used. Modern medicine does not have these side effects.
UkrainePrice, UAH.RussiaPrice, RUR.
| Kyiv | 1020 | Moscow | 9843 |
| Kharkiv | 800 | Saint Petersburg | 4294 |
| Odessa | 900 | Kaliningrad | 6547 |
Source: https://tsitologiya.su/zheludok/medicamentoznyj-son-chto-jeto-pri-kolonoskopii
What is a colonoscopy?
Colonoscopy under anesthesia is a painless method of examining the large intestine from the inside. The study is carried out using a flexible, thin and long hose, which is equipped with light and optics. This device is called an endoscope.
Advanced models are equipped with built-in mini-cameras at the end and a device for taking biopsies. With their help, images of the insides of the large intestine are recorded and tissue is taken for analysis. Then the pictures are displayed on the screen, studied in detail and deciphered. Photos can be saved on digital media. Before performing a diagnosis, preparation is required.
Advantages of the method using anesthesia
Previously, the examination took place without anesthesia and was very painful. Now these sensations are warned in advance and the person does not experience negative sensations. After the procedure, he doesn’t even have any unpleasant memories.
This method is especially relevant for children, people with diseases of the large intestine or a low sensitivity threshold. Diagnostics can detect cancer in its early stages. During the study, polyps are removed, eliminating the need for surgery for the patient.
During the procedure, the doctor can stop minor bleeding and take tumor tissue for analysis. The examination also helps prescribe optimal treatment without surgery.
What does a colonoscopy show?
Colonoscopy reveals and allows you to evaluate the inner surface of the intestine, its capillary and vascular pattern, the color of the mucous membrane, as well as:
- muscle condition;
- intestinal motor activity;
- its patency;
- intestinal diameter.
If you have hemorrhoidal disease, it becomes possible to determine the size of the inflamed node. This helps you subsequently choose the optimal removal method.
What types of anesthesia are used?
Colonoscopy can be performed using three methods. First, it is determined whether or not there are allergic reactions to certain drugs, and the type of anesthetic drugs is selected.
Sedation method
General or local anesthesia is not necessary for colonoscopy. A sedation method can be used, which uses the drugs Metazolam or Propofol. They act the same as anesthesia. The person falls into a medicated sleep and feels nothing. However, the sedation method has polar sides. The advantages of the method include:
- The patient does not fall asleep completely, but finds himself in a state of half-asleep. The body is so relaxed that it does not feel pain. However, a person hears everything and can even respond to the doctor’s requests to change position.
- "Metazolam" erases any memories of the procedure from the memory, but the person then wakes up for a very long time.
- After Propofol, the patient, on the contrary, remembers everything. At the same time, he wakes up very quickly.
- The person does not connect to the machines and breathes on his own.
The disadvantages include possible allergic reactions to the drug, and the risk of side effects increases. The doctor has difficulty determining the patient’s sensations, since pain is completely absent.
Indications
Colonoscopy is indicated for people over 45 years of age and in the presence of intestinal cancer. Routine diagnostics are carried out for patients with ulcerative colitis or Crohn's pathology. The examination should be done for people whose relatives were found to have polyps or colon cancer. Diagnostics is also indicated for:
- anemia;
- bloating;
- excessive fatigue and sudden weight loss;
- general weakness and lack of appetite;
- diarrhea;
- pain in the abdomen and intestines;
- mucus discharge from the anus;
- constant constipation;
- bleeding;
- polyps on the intestinal walls;
- genetic predisposition to cancer.
For the listed indications, diagnosis can be carried out both with and without anesthesia. Anesthesia is necessary if the examination is performed on young children under 12 years of age, as well as for:
- Patients with intestinal adhesions. They appear after surgical operations, during peritonitis, which was caused by gynecological pathologies or as a complication after surgery. Adhesions interfere with the advancement of the probe. As a result, the pain syndrome increases significantly.
- People with destructive intestinal changes.
- Patients who have very low sensitivity. In them, even mild pain can provoke loss of consciousness and disrupt the functioning of the body.
Anesthesia is indicated for a number of diseases or the appearance of neoplasms, the localization of which is near the intestines. In this case, the patient may experience severe pain without anesthesia. Diagnosis is mandatory for people whose tumor has been excised.
The examination is done to prevent relapse. After 50 years, colonoscopy is carried out as planned. At this age, the risk of various diseases increases significantly.
Important!
Diagnosis is carried out for hemorrhoids, anal fissures, and all women who are scheduled for surgery in the pelvic area (in particular on the uterus, ovaries).
Contraindications
Contraindications are divided depending on the diagnostic method. Colonoscopy under general anesthesia cannot be performed on people with obvious heart failure, mental or neurotic diseases (including lungs and bronchi) in an acute stage. For children, the list of contraindications expands:
- high temperature with no known cause;
- pustular skin lesions;
- light weight;
- respiratory tract diseases in the acute stage;
- severe stage of rickets.
Contraindications for any type of colonoscopy under anesthesia include colds or intestinal exacerbations, severe valve stenosis. The procedure is not performed if the patient has any serious conditions that could worsen the situation or contribute to the introduction of infection into the intestines or its spread.
Alternative laboratory methods
Colonoscopy with sedation is not the only way to examine the condition of the inner walls of the intestine. Therefore, if you do not want interference in your body or are afraid to plunge into a state of sleep, then there are alternative options. These are:
- Capsule endoscopy. An innovative method that is highly effective. It is based on the introduction into the colon of a special small device equipped with a camera. Carrying out such a procedure does not cause the patient any discomfort or pain. Also, the likelihood of injury to the mucous membrane is minimized. A few hours after insertion, the probe is removed from the body naturally. After this, the recorded information is removed from the integrated drive and the results are decrypted. However, capsule endoscopy is not available in all medical institutions, and its cost is prohibitive.
- Magnetic resonance imaging. This type of research is considered one of the best. It allows doctors not only to diagnose various diseases at the primary stage of development, but also to determine their etiology, as well as get a complete picture of the patient’s health status. During the examination, a special device is fixed on the body and takes detailed, high-quality images in three projections. Any pathologies are clearly visible in the photographs. In this case, the examination is carried out as comfortably and safely as possible. Therefore, if for some reason a patient cannot be sedated during a colonoscopy, for example due to the presence of certain contraindications, then doctors in the vast majority of cases prescribe an MRI. However, magnetic resonance imaging has one significant drawback. This method cannot detect cancerous tumors smaller than 10 millimeters in size. In addition, the body receives a certain dose of radiation.
According to experts, colonoscopy is still preferable. This is due to the fact that alternative diagnostic methods are only informative. Therapeutic measures cannot be carried out with their help.
Transnasal gastroscopy: pros and cons
— Swallowing an endoscopic probe—some of the patients are unable to do this feat. How successfully does transnasal endoscopy replace an unpleasant procedure?
— The main advantage is that the device has a much smaller diameter, and in most patients it is able to pass freely through the nasal passages, then along the back wall of the pharynx, without touching the root of the tongue. This feature is greatly appreciated by patients who experience gagging during traditional examinations.
But, unfortunately, there are people whose gag reflex is very pronounced, and transnasal endoscopy is not a salvation. In such situations, you must listen to the doctor's instructions. During the endoscopy, he tells you how to behave and how not to concentrate on the problem.
For example, during traditional and transnasal gastroscopy it is best to breathe through the mouth, evenly, deeply, slowly and rhythmically, without thinking about anything else. Such breathing in itself allows you to somewhat neutralize the urge to vomit, and for some, reduce it to almost zero. Anesthesia is performed with a 10% lidocaine solution. Irrigation occurs not only of the mouth and pharynx, but also of the nasal passages in order to minimize discomfort.
This method has another advantage. During the transnasal study, the patient is not given a mouthpiece, which is necessary with the traditional “through the mouth” method (then it is installed so that the person does not bite the device). Therefore, the patient can talk to the endoscopist. And during a regular gastroscopy, you should not even swallow saliva, as this can provoke vomiting.
During a transnasal endoscopy, your doctor may take a biopsy if necessary. But the device is very thin, and its instrumental channel is significantly smaller than that of conventional gastroscopes, so only very small pieces of tissue can be pinched off.
Unfortunately, this method has disadvantages - it is not suitable for those who have a deviated nasal septum. Although there are exceptions. In addition, the picture that the doctor sees during endoscopy “through the nose” is not clear enough. This is due to the size of the device and the optics itself, which is built into the gadget. In traditional devices, the camera and matrix allow you to achieve full HD quality, there are zoom capabilities and dual focus.
But if we talk about screening patients who need to examine the esophagus, stomach, duodenum and at the same time suffer from a pronounced gag reflex, this is a very good method for them. Another plus: both transnasal and traditional gastroscopy are covered by the compulsory medical insurance policy.
What do patients say about the procedure?
Medical statistics show that many people undergo colonoscopy with sedation. Reviews about this research method are quite contradictory. Some claim that the procedure went well and there was no discomfort or pain during it, while others say that they could hardly stand it. But everyone is of the opinion that anesthesia is necessary. In addition, much depends on the level of professionalism of the specialist.
As for pain management methods, sedation is the best option. It is safe for health and does not require long recovery after anesthesia, and modern drugs have relatively few contraindications and cause almost no side effects.