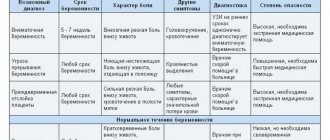
Cause of pain in gastritis
Gastritis pain is spasmodic in nature
The pain that occurs with this disease most often begins due to spasms of the smooth muscles of the stomach walls. Another reason may be excessive stretching of its walls. The mucous membrane of the stomach with gastritis is always inflamed, any mechanical impact on it (when food comes in) causes pain.
With gastritis with high acidity, excess acid irritates the gastric mucosa, a prolonged reflex contraction of the pylorus occurs, this spasm causes pain. The secretion of acid increases when food enters the stomach, and the nerve receptors of the mucous membrane suffer from this effect.
Only a gastroenterologist or therapist can assess the condition of a patient with gastritis and prescribe adequate treatment.
He will conduct a gastroscopy, prescribe laboratory tests, and advise painkillers for gastritis. Self-medicating without knowing the etiology of the disease is very dangerous. Information about medications used to relieve pain symptoms of gastritis is offered for informational purposes only.
Types of painkillers used for gastritis
To relieve pain, medications from different pharmacological groups are used:
- Antispasmodics. They slow down cellular activity that causes muscle contractions and affect the cytoplasm of the cell.
- Anticholinergics. They act on the receptors of nerve endings, effectively neutralizing pain attacks.
- Antacids. They have a therapeutic effect by enveloping the inflamed mucous membrane of the stomach, reducing the destructive effect of hydrochloric acid - the cause of pain.
- Traditional medicine preparations. Gently but effectively, with prolonged use, they help relieve pain in the epigastric area.
When using all medications, you must carefully observe the dosage, duration of use, and take into account contraindications.
Relieving stomach pain with anticholinergics
A gastroenterologist will help you prescribe an effective drug.
This group of drugs acts directly on the receptors of the nervous system, blocking them. An additional consequence of taking such medications is a decrease in mucosal secretion and an antispasmodic effect. This versatility makes anticholinergics indispensable painkillers for gastritis.
- Platifilin (analogue of palyufin). It is used in several dosage forms - tablets (1-3 times a day), drops (10 drops 2 times a day), injections (1-2 ml 2-3 times a day).
- Gangleron. In addition to an excellent analgesic effect, it helps to enhance the motor function of the stomach. You can take it in capsules (0.04 g before meals 3-4 times a day), or do subcutaneous or intravenous injections (2 ml of 1.5% solution 3 times a day).
- Gastrozem. Excellently reduces the excessive activity of the mucosal glands to produce acid, which causes pain. Taken twice a day, 25 mg for 2-3 weeks.
- Histodil. It has a similar effect by blocking cholinergic receptors. It is prescribed 0.2 g three times a day with meals, and a double dose of the drug is taken at night.
- Taking anticholinergics such as Aprofen, Atropine, Buscopan, Ganglefen, Difacil, Gastrocepin will be effective.
Antispasmodics for gastritis
The most famous and frequently used antispasmodic is the drug No-shpa and its cheaper analogue - Drotaverine. Its analgesic effect is carried out due to a component such as Isoquinoline, which acts on the smooth muscle cells of muscle tissue, relaxing them and relieving pain spasms. Drotaverine and Nosh-pu can be taken starting from childhood:
- 3-6 years – 20 mg (half a tablet) 2-3 times a day, no more than 120 mg per day.
- 6-12 years – 40 mg (1 tablet) 2-5 times a day, no more than 200 mg per day.
- 12 years and older – (2 tablets) 3-4 times a day, no more than 400 mg per day.
Contraindications to the use of No-shpa and Drotaverine may be:
- Heart failure
- Severe renal failure
- Liver failure
- Individual intolerance
- Early childhood (up to 1 year)
Antispasmodics are good for pain relief
It is not recommended to take the drug during breastfeeding, during the entire period of pregnancy, with Parkinson's disease, or lactose intolerance. The peculiarity of this drug is that it does not have a negative effect when driving vehicles, machines and mechanisms.
Papaverine has an analgesic effect similar to No-shpe, since it is close to this drug in structure and mechanism of action, but its effectiveness on smooth muscles is several times lower.
Bendazole is a drug used to relieve spasms of the abdominal organs, bronchi, and blood vessels. It is used in the form of intravenous and intramuscular injections (20-30 mg 2-3 times a day), the course of treatment takes 1-2 weeks. Drugs from the group of antispasmodics such as Mebeverine, Halidor, Metacin have a similar effect on the cause of pain.
Medicines – antacids
These drugs are very effective in combating the cause of pain - excessive release of hydrochloric acid. Antacids bind the action of agents that damage the mucosa, and also reduce pain by relieving pyloric spasm.
- Maalox. Precisely balanced mixture of magnesium and aluminum hydroxide. It is used even in infants (4 times a day, 0.2 mg per kg of weight). For children under 12 years of age, the dose is 1 tablet 3-4 times a day, for adults this amount is doubled.
- Almagel. The combination of magnesium and aluminum is supplemented with D-sorbitol. The drug Almagel-A contains Anastezin; it is this modification of the drug that is preferable to use for pain syndrome. For children under 12 years of age, the dosage is 1 scoop, over 12 and for adults – 2 scoops.
- Phosphalugel. Consists of aluminum phosphate, pectin, gel-like algae extract agar-agar. Neutralizes pepsin and hydrochloric acid, has no contraindications even for children under one year old. Used in adults: 2 sachets 3-4 times a day.
Traditional medicine against stomach pain
Traditional medicine methods are also effective
Traditional medicine should never be used as the only method of treating gastritis pain. Despite the environmental friendliness of such drugs, the almost complete absence of side effects, they serve only as an addition to the treatment and diet prescribed by the doctor.
Plantain juice has a very effective effect on the cause of pain. Instead of juice, you can use an infusion of dried leaves of this plant; it also relieves spasms and heals the inflamed mucous membrane. Sea buckthorn juice, drunk an hour before meals, has a similar effect.
For gastritis with low acidity, in order to normalize the condition of the stomach, you can use freshly squeezed aloe juice (a teaspoon) before meals.
Chewing a small piece of propolis (no more than 8 g for the whole day) for a long time will reduce the severity of pain. The use of folk remedies is not recommended in the acute period of the disease.
By selecting medications from various pharmaceutical groups, you can effectively neutralize painful sensations of various etiologies that occur with gastritis.
The following video will introduce you to folk remedies against gastritis:
Noticed a mistake? Select it and press Ctrl+Enter to let us know.
During an attack of gastritis, symptoms may begin in the first 20-30 minutes after eating, associated with the low quality of foods consumed, fatty and difficult-to-digest foods. Sometimes the cause of an attack can be overeating. If left untreated, the disease becomes chronic and bothers the patient with regular attacks of pain.
The main manifestations of an attack are acute and cutting pain that occurs in the epigastric region, that is, in the upper abdomen. Nausea appears, followed by vomiting, belching air with a sour or rotten smell. The patient experiences discomfort in all areas of the abdomen associated with bloating. Symptoms can last from a few minutes to several days.
Where is the mesogastric region located?
Pain in the left side of the abdomen causes a lot of physical suffering to a person. This symptom directly indicates a real problem with those organs that are located in the abdominal cavity on the left.
Any means that a person uses without consulting a doctor and understanding the true reasons for the appearance of a painful symptom can aggravate the dynamics of the disease, and not get rid of the problem.
Nature of pain
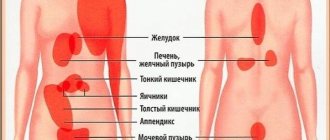
The localization, intensity and nature of painful symptoms in the left lower abdomen may vary. The abdominal cavity contains several organs. Part of the diaphragm, stomach, intestines, pancreas, urinary system, spleen, and internal genital organs are located in the abdomen on the left. Problems that arise in their functioning become causes of discomfort and pain.
Acute, stabbing, weak, nagging pain in the abdominal area can occur with equal frequency in women, men or children. Poor circulation, the presence of an inflammatory process, and irritation of nerve endings cause pain of varying intensity.
Each person perceives this symptom individually. People with a low pain threshold may lose consciousness. On the contrary, those who have a high level of pain perception may not seek help from specialists for a long time due to minor sensations.
Origin of abdominal pain on the left
The localization of abdominal pain on the left depends on the location of the organ inside. Problems with the diaphragm and stomach manifest as unpleasant or painful sensations on the left side of the upper abdomen.
Pathologies of the pancreas or spleen, small intestine are characterized by pain in the left central part of the abdomen.
Malfunctions of the large intestine, urinary system, and internal genital organs in men and women make themselves felt by pain in the lower abdomen on the left.
Pain in the upper abdomen
Aching pain in the left side, accompanied by belching, periodic heartburn, and a feeling of fullness in the stomach, is characteristic of a diaphragmatic hernia. With this pathology, the upper segment of the stomach partially protrudes into the chest cavity from the abdominal cavity. Often the disease symptomatically resembles pancreatitis.
Diseases of the pancreas provoke pain around the ribs. Intense pain in the left side, as well as in the center of the abdomen, may be a symptom of pancreatitis or pancreatic cancer. If the liver and bile ducts become inflamed, the pain sensations shift to the right. With pancreatitis, the condition is aggravated by poor diet, stress, and physical activity.
Gastritis, erosion and gastric ulcer often cause pain in the upper abdominal segment on the left. Ignoring the symptoms is extremely dangerous.
Stitching pain in the left side may indicate the appearance of a perforated ulcer, the presence of internal bleeding, or penetration of stomach contents into the abdominal cavity. Acute pain prevents a person from moving.
The mortality rate for perforated ulcers is about 10%.
Acute pain in the upper left abdomen is a common symptom of dysfunction of the spleen. Some infectious diseases (mononucleosis) cause an increase in the size of the spleen, which leads to its rupture. In this case, a sharp pain in the left side is accompanied by a change in the color of the skin near the navel. The skin becomes bluish.
Malignant neoplasms and metastases of the stomach and intestines provoke constant pain that periodically intensifies. Typically, a symptom of cancer is not localized in only one part of the abdomen.
Sometimes attacks of angina or myocardial infarction are accompanied by pain in the upper left abdomen. Painkillers do not give the expected effect when relieving pain.
Pain in the mesogastric region
The middle part of the abdominal cavity is otherwise referred to as the mesogastric region. Pain in this part of the abdomen is usually associated with intestinal problems. Inflammatory bowel diseases, obstruction, taking antibiotics, constipation, diarrhea cause bloating (flatulence) and severe pain.
Inflammatory diseases appear in the intestines against the background of enteritis, colitis, enterocolitis, disruption of the normal balance of microflora, and helminthic infestation. Often, in addition to pain in the abdominal cavity, bloating appears. This occurs due to dysfunction of food digestion, the occurrence of fermentation or rotting processes.
Constipation is often associated with impaired intestinal motor function, consumption of certain foods, and certain medications. Fecal retention is characterized by pain in the abdominal area, and bloating creates additional discomfort. The use of some laxatives can cause severe pain, especially in women.
Sometimes foreign formations appear inside the intestine - polyps, tumors, adhesions, diverticula, which create difficulties in the movement of food through it. Bloating, rumbling, severe pain, and intestinal obstruction may occur.
Why does my lower left stomach hurt?
Pain in the lower abdomen on the left side occurs due to diseases of the pelvic organs, urinary system and large intestine. In women, pain is the main symptom of gynecological diseases such as inflammation of the appendages, adnexitis, salpingoophoritis, and benign tumors. Pathologies are often accompanied by general intoxication.
In women, acute pain in the lower abdomen occurs when there is a threat of miscarriage. An ectopic pregnancy is accompanied by increasing throbbing pain. A woman may lose consciousness, and the bleeding that occurs after a rupture of the fallopian tubes provokes peritonitis and can lead to death.
Sometimes during menstruation, women experience tightness in the lower abdomen. Many people perceive this symptom as normal. However, experts associate nagging pain in women with certain gynecological pathologies.
In men, pain and discomfort in the lower abdomen most often appears due to prostate diseases. The pain increases with defecation or urination. In women and men, lower abdominal pain can occur due to pathologies of the urinary system: urethritis, cystitis, pyelonephritis, the presence of kidney stones, as well as diseases localized in the lower intestine.
What to do
To get rid of painful sensations in the abdomen on the left, you should find out the exact reasons for their origin. If such situations arise, you cannot do without the help of a doctor.
And it’s not just about the effectiveness of the therapeutic measures that a specialist can offer to the patient.
A person puts himself in serious danger by ignoring an unpleasant symptom, believing that everything will go away on its own or after using painkillers.
Dangerous indicators when pain occurs are an increase in sensations, the addition of temperature, nausea, vomiting, and deterioration in well-being. Pregnant women should immediately contact their doctor or health care provider if they experience any pain.
Independent use of medications, even the most harmless ones, which previously had a positive effect when such situations arose, is unacceptable.
This distorts the symptomatic picture, complicates the diagnosis, and masks the pain when the disease progresses. You should also not apply cold, a warm heating pad, or take a hot bath to painful areas.
It is important to contact a medical facility as quickly as possible for the necessary help.
Source: https://worldwantedperfume.com/mezogastralnaja-oblast-gde-nahoditsja/
Cause of pain
The cause of the attack of pain is associated with inflammatory processes in the stomach. Inflammation of the walls of an organ occurs in every person, but not everyone reacts to it as a serious disease. Most people ignore heartburn or nausea, which leads to chronic illness over time. There are no pain receptors on the mucous membrane, so the symptom develops when the process affects the muscle layer. The localization of the symptom extends to the left hypochondrium, where most of the organ is located. The intensity of pain directly depends on the course of the attack and cramping movements in the muscle layer of the organ. In some cases, gastritis is also associated with stretching of the esophagus, which causes a feeling of heaviness after eating. And with chronic gastritis, the digestion process is disrupted due to stomach fullness and impaired absorption of food, which causes aching and dull pain.
External factors can provoke an attack, such as diet, poor diet, poor quality foods, and poor chewing of food.
Alcoholic drinks and smoking aggravate the process.
Many drugs irritate the gastrointestinal mucosa: salicylates, anti-tuberculosis drugs and anti-inflammatory drugs. Unfavorable conditions in the workplace associated with chemicals and stress are also provocateurs.
Internal factors accelerate the development of the disease: decreased hemoglobin, the presence of chronic diseases, endocrinological diseases, metabolic disorders, problems with the kidneys and cardiac activity. All these factors combine to weaken the immune system, and the body is easily exposed to bacterial attack. It is the bacterium Helicobacter pylori that most often causes inflammation of the stomach.
Causes of burning sensation in healthy people
The appearance of epigastric heartburn is not always provoked by pathological conditions. Often the symptom appears due to the following external harmful factors:
- abuse of alcohol, smoking, caffeine, seasonings and spices;
- the predominance of fatty, spicy, salty foods, sour vegetables and fruit juices in the menu;
- obesity;
- constant overeating;
- constant stress, depression, panic attacks;
- uncontrolled use of medications, neglect of instructions for use;
- regular intense physical activity;
- tight clothing that tightens the stomach, and with it the internal organs;
- improperly organized sleeping place, for example, a low headboard, which contributes to the spilling of intestinal contents back into the stomach.
First aid for an attack
Most often, pain develops at night and a visit to the doctor is postponed until the morning, so you need to know how to relieve an attack of gastritis at home. To begin with, you should take a horizontal position on your side, pressing your bent knees to your stomach. Immediately drink a glass of warm milk or a decoction of chamomile and mint. The pain goes away quickly with potato juice. If the pain is caused by eating poor quality food, then it is easy to induce vomiting at home. To do this, you need to drink a glass or warmer boiled water and try to induce a gag reflex by pressing two fingers on the root of the tongue. You will vomit food and water and your condition will improve.
Prevention
To prevent heartburn and its unpleasant consequences, you should adhere to certain rules:
- food must be chewed thoroughly;
- do not lie down horizontally after eating, it is better to walk a little or sit in a relaxed position;
- wear loose clothing made from natural fabrics and avoid tight belts;
- do not lift heavy objects;
- quit smoking and alcohol;
- raise the head of the bed by 15 cm;
- drink chamomile or mint tea before bed;
- drink a lot of clean water;
- eat buckwheat on an empty stomach;
- get rid of extra pounds in weight;
- promptly treat all pathologies.
Drug treatment of gastritis attacks
Since it is faster to relieve pain with medications, many people resort to this method. Antacids and antispasmodics are prescribed to relieve pain. Antacids relieve irritation of the mucous membrane, and antispasmodics eliminate the pain symptom. Along with antispasmodics, analgesics and choline receptor blockers are effective. The side effect of these drugs is inhibition of the digestive tract; to avoid this, gastroprotectors (Maalox or Sucralfate) are prescribed.
It is strictly forbidden to inject or take tablets of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.
They will aggravate the process, the pain will intensify, an ulcerative process and other complications of the disease may develop. In any case, you should consult a doctor for treatment recommendations. The doctor will also tell you what to do during an attack of gastritis at home.
After pain relief, treatment of the underlying disease begins. The first step is to prescribe a course of antibiotics to eliminate the cause of the disease - bacteria. At the same time, enveloping and astringent drugs are prescribed to protect the walls of the stomach from the negative effects of the irritant; bismuth preparations are used. To improve digestion and eliminate symptoms such as a feeling of heaviness in the epigastrium, enzyme agents are used. Enzyme preparations contain pancreatin, the main enzyme of the pancreas, which not only improves digestion, but also helps the gland with insufficient enzyme production. Antacids delay the production of hydrochloric acid, which leads to heartburn and sour belching. If you vomit profusely, you should give an injection of an antiemetic, but do not repeat it regularly.
A special element in treatment is adherence to a strict diet and daily routine. Depending on the type of gastritis, a specific diet is prescribed. To prevent attacks of the disease, give up bad habits and watch your diet. Regular visits to the doctor will help prevent the development of gastritis in the initial stages or reduce the number of exacerbations.
Gastritis pain is a symptom known to many firsthand. To relieve pain from gastritis, more and more new painkillers are being released. Home medicine offers a lot of its own, time-tested recipes. Today, inflammatory damage to the gastric mucosa is widespread.
The cause of pain in the stomach during gastritis is irritation of the internal receptors innervating the wall of the stomach. Irritation is caused by the effect of hydrochloric acid on the receptors, excess food mass in the stomach cavity and a number of other factors. How to relieve pain with gastritis depends on the above circumstances.
Gastritis pain comes in a variety of forms. The stomach hurts either in the epigastric region, or the pain radiates to the right or left hypochondrium, under the shoulder blade, or to the lumbar region. The patient is not always able to recognize the nature of the pain, associate it with gastritis and take pills for stomach pain. The nature of the pain is varied - it can be pulling and dull, sharp, cutting or spastic.
To eliminate pain from gastritis, you need to see a doctor and undergo a thorough examination. Based on the results, the doctor will prescribe adequate treatment and appropriate pain medications for the case.
Therapeutic tactics and the answer to the question of how to relieve stomach pain with gastritis directly depend on the type of gastritis of the patient. To reduce pain during hyperacid conditions, the doctor prescribes drugs that help reduce the production of hydrochloric acid in the stomach cavity. If the body does not produce enough hydrochloric acid, replacement therapy is practiced to enhance its production, which will make the patient feel relief.
Why does it hurt in the epigastric region?
The epigastrium is a triangular region that includes the upper abdomen, liver, stomach, and lungs. Pain in the epigastric region bothers many people, so let's figure out what can cause such discomfort. In medicine, there are many diseases that cause epigastric pain, all of which require timely and appropriate treatment.
Gastritis
Pain in the epigastric region is often provoked by gastritis - inflammation of the gastric mucosa. According to statistics, more than half of people from all over the world suffer from various forms of gastritis.
© shutterstock
Gastritis is caused in most cases by the bacterium Helicobacter pylori. Less commonly, gastritis can occur due to frequent use of painkillers, excessive alcohol consumption, stress, and other diseases and conditions.
Signs of illness
Many people with gastritis have no symptoms. If symptoms are present, they may include:
- discomfort or pain in the epigastric region;
- nausea;
- vomiting;
- loss of appetite.
If gastritis causes bleeding from the stomach lining, symptoms may include:
- shortness of breath;
- dizziness and weakness;
- red blood in vomit;
- black chair;
- pallor.
A person with any signs or symptoms of bleeding in the stomach should see a doctor immediately.
Methods for treating gastritis
Treatment of epigastric pain with gastritis depends on the specific cause that caused this condition.
Sometimes it is enough to stop drinking alcohol or stop taking painkillers. In other cases, antibiotics may be needed to kill the H. pylori bacteria or other medications may be needed to reduce stomach acid production.
Pancreatitis
The pancreas produces insulin and digestive enzymes that help digest food. Pancreatitis occurs when enzymes damage the pancreas and cause inflammation.
Pancreas © shutterstock
The most common causes of pancreatitis are gallstones, alcohol consumption, genetic disorders of the pancreas, and certain medications.
Signs of the disease
Pancreatitis can be acute or chronic.
Acute pancreatitis manifests itself:
- pain in the epigastric region that radiates to the back;
- fever;
- nausea and vomiting;
- rapid heartbeat;
- abdominal sensitivity.
Symptoms of chronic pancreatitis include nausea, vomiting, weight loss, and changes in bowel movements. Epigastric pain may become constant, although some people have no pain at all.
People with chronic pancreatitis may have no symptoms until they develop complications.
Treatment options
Treatment for acute or chronic pancreatitis may include:
- a hospital stay to treat dehydration with intravenous fluids;
- medications to relieve epigastric pain;
- antibiotics by mouth or through an IV if you have a pancreas infection;
- feeding by tube or IV if you cannot eat.
Mild acute pancreatitis usually resolves within a few days with rest and treatment.
Treatment of chronic pancreatitis will help relieve pain, improve pancreatic function, and cope with complications.
Stomach ulcer
The occurrence of epigastric pain often indicates the presence of a gastric ulcer - this is a wound on the gastric mucosa.
© shutterstock
The two most common causes of ulcers are Helicobacter pylori infection and frequent use of medications known as NSAIDs (pain relievers).
There are many myths about peptic ulcers. Ulcers are not caused by emotional stress or spicy foods. Certain foods may irritate an ulcer that is already there, but the food is not the cause of the ulcer. – American College of Gastroenterology
Signs of an ulcer
Dull or burning pain in the abdomen is the most common symptom of peptic ulcer disease. The pain most often occurs when the stomach is empty, between meals or at night. The pain may come and go for days, weeks, or months.
Less common symptoms may include:
- swelling;
- burping;
- nausea;
- poor appetite;
- vomiting;
- weight loss.
The most important symptoms that cause ulcers are related to bleeding. Bleeding from an ulcer may be slow and go unnoticed or may cause a life-threatening condition.
A person requires immediate medical attention if they have:
- acute abdominal pain that does not go away;
- blood in the stool or black stool;
- vomit that contains red blood or looks like coffee grounds;
- fainting or weakness.
These symptoms may be signs that a peptic ulcer is causing a life-threatening condition.
Methods for treating stomach ulcers
An important part of treating ulcers is identifying what causes them. Patients with ulcers caused by NSAIDs should talk to their doctor about other medications that can be used to treat pain.
If a person is infected with H. pylori, the infection should be treated. It is very important to complete the full course of antibiotic treatment. It is equally important to make sure that the infection is destroyed.
Cholelithiasis
The gallbladder is a small, pear-shaped organ that stores bile and is located in the upper right side of the abdomen, under the liver. Epigastric pain can be caused by cholelithiasis - blockage of the gallbladder by gallstones.
Gallstones © shutterstock
Currently, researchers cannot say for sure what causes the formation of gallstones. Doctors believe that gallstones can form when bile contains too much cholesterol or bilirubin, or the gallbladder does not empty completely.
Stomach upset
Often, there is pain in the epigastric region due to dyspepsia - indigestion. This is not a disease. However, an upset stomach can be a sign of certain diseases or conditions of the digestive tract.
More than 25% of people experience dyspepsia every year. Photo © shutterstock
Dyspepsia can be occasional, chronic or functional. Stomach upset without an obvious cause is known as functional dyspepsia.
Among the causes of dyspepsia are:
- difficult to digest food;
- overeating or eating very quickly;
- abuse of caffeine, alcohol or carbonated drinks;
- stress;
- smoking.
Stomach upset is not always related to food. Diseases that can cause discomfort in the epigastric region:
- acid reflux;
- gastritis;
- inflammation of the gallbladder;
- lactose intolerance;
- peptic ulcer;
- stomach cancer.
Signs of dyspepsia
Sometimes people with indigestion experience heartburn, but heartburn and indigestion are two separate conditions.
Dyspepsia manifests itself:
- discomfort and pain in the epigastric region;
- quick satiation during meals;
- heaviness in the stomach after eating;
- nausea;
- bloating.
Stomach cancer
Pain in the epigastric region may indicate the presence of a malignant neoplasm - cancer. The disease is a common oncological disease, which most often affects the male gender.
© shutterstock
Doctors treating epigastric pain
Only an experienced specialist can determine what caused the discomfort in the epigastric region:
- Gastroenterologist;
- Oncologist;
- Traumatologist;
- Surgeon.
© shutterstock
Less popular causes of epigastric pain
Acute epigastric pain may indicate such factors and ailments:
- Various injuries;
- Binge eating;
- Excessive physical activity;
- Infectious lesions;
- Insufficient amount of food;
- Unsuitable climate zone;
- Allergy;
- Stress.
Antispasmodics
Gastritis pain is caused by spasm of the smooth muscles of the stomach. You can relieve an attack of pain with the help of a group of myotropic antispasmodics. This group of medications is in demand today and is widely used to eliminate pain.
In drugs, the antispasmodic mechanism of action is aimed at eliminating spastic contractions of the smooth muscle tissues of the stomach and intestines. By eliminating malfunctions in the sodium and potassium pumps, spastic contractions are eliminated.
Spastic contractions can be relieved with the help of drugs belonging to the antispasmodics group:
- No-shpa or drotaverine.
- Galidor.
- Papaverine.
- Spasmalgon
- Baralgin.
- Metacin.
In case of an overdose of drugs from this group, side effects are observed in the form of neurological and psychotic disorders, seizures and disorders of urination and defecation.
Drotaverine
Drotaverine or no-spa, like any antispasmodics, helps eliminate spastic contractions of smooth muscles and helps soothe irritation of stomach receptors. It is permissible to drink in the form of tablets, take parenterally - intramuscularly or intravenously.
Take the drug with caution during pregnancy and breastfeeding. This pain reliever for gastritis is effective and safe.
When pain relief is contraindicated
Sometimes the patient's medical history reveals a severe concomitant disease that prevents the prescription of analgesics. A list of contraindications to taking this group of medications is described.
- Crohn's disease.
- Megacolon.
- Nonspecific ulcerative colitis.
- Tuberculosis.
- Acute intestinal infections.
Severe pain in the stomach sometimes becomes a signal not only of the presence of gastritis, but also acts as a sign of more serious diseases. In particular, perforation of an ulcer, peritonitis or appendicitis. In this case, it is not necessary to relieve pain until the patient is examined by a surgeon.
Before taking pills, you should consult your doctor. The doctor will prescribe an appropriate examination and decide which medications will be effective. You should not be guided in your decision by the fact that a certain medicine was effective for a neighbor or relative.
Nature of pain and accompanying symptoms
For pain in the stomach, there are several features that distinguish it from damage to other organs. It usually intensifies a few minutes after eating and does not spread to another area. Sharp pain in the stomach rarely occurs in attacks. During physical activity (due to increased pressure in the abdominal cavity), the unpleasant sensation may intensify, but there is no posture that would bring relief to the patient. When pressed in the epigastric region (under the xiphoid process), the aching pain intensifies.
With the development of perforation of the ulcer, the area of pain gradually spreads (as the peritoneum is drawn into the inflammatory process). When pressed in the epigastrium, tension in the muscles of the abdominal wall is felt.
Acute pain may also be accompanied by other symptoms:
- nausea, one-time vomiting;
- feeling of heaviness in the stomach;
- tendency to constipation or diarrhea;
- pronounced decrease in appetite;
- weight loss;
- increased gas formation in the intestines (bloating, flatulence);
- the presence of a white or gray coating on the tongue;
- increased body temperature;
- heartburn or burning sensation in the chest;
- impaired absorption of nutrients (primarily proteins);
- black feces (with the development of bleeding);
- pronounced general weakness.
Pain relief for gastritis with low acidity
With low acidity, you may experience aching pain in the abdomen, nausea and a feeling of fullness. If there is a deficiency of gastric secretory activity, the pain can be easily relieved with the help of replacement therapy. To prescribe the correct treatment, you must consult a doctor.
For pain relief in hypoacid conditions, enzymes are used - mezim, panzinorm, creon. Hydrochloric acid with pepsin is prescribed. It will alleviate the condition and activate digestive processes in the cavity of the stomach and intestines.
Comprehensive diagnostics and treatment
Effective treatment of epigastric heartburn will require careful diagnosis, since symptomatic therapy will only give temporary results. To completely get rid of the unpleasant sensation, the cause must be eliminated. To do this, the patient is referred to a therapist and gastroenterologist, who, after examination and evaluation of complaints, prescribe:
- Ultrasound - to assess the condition and performance of internal organs;
- daily pH-metry of the environment in the stomach and esophagus - to measure the acidity of digestive juice;
- esophageal manometry - to assess the functions of the esophageal sphincter.
Heartburn can only be cured using a comprehensive method, including:
- Treatment with medications: non-absorbable antacids;
- medications to reduce the secretion of hydrochloric acid;
- enzymes and prokinetics to stimulate gastric motility and prevent reflux.
- Diet therapy with avoidance of low-quality food products, improperly prepared dishes, but with increased consumption of alkaline mineral waters and fortified foods.
- Refusal of heavy loads and bad habits.