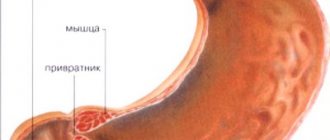
Erosion is a violation of the epithelial integument of the intestinal walls, without affecting the muscle layers. If you pay attention to the main symptoms of the disease in a timely manner and begin treatment, the erosion will heal without leaving any scars or marks. If treatment is not started immediately, then in more advanced stages the disease can pose a serious danger to the body and lead to serious serious consequences. However, the symptoms are often similar to those of other stomach diseases. The disease can affect the mucous membrane of the stomach or intestines anywhere.
Types of erosion
It’s worth noting some clarification right away. Erosion can be of two types: acute and chronic. The acute stage most often has a single localization. While chronic erosion can manifest itself in the form of a whole chain of damage to the intestinal mucosa or even have a chaotic location. Most often you can observe them at the exit from the stomach. If in its acute form the disease requires immediate treatment, then in its chronic form the disease may be present in the patient for 5 years or more.
Folk remedies for erosive duodenitis
For duodenal erosions, treatment with folk remedies can be carried out against the background of drug therapy. If the defect is small, then in some cases you can get rid of erosion without medication.
But the final decision on the method of treatment must be made by the doctor. Typically, infusions and decoctions of medicinal plants, as well as their extracts and oils, are used for this disease.
In the following video you can learn in more detail about herbal medicine for erosive, ulcerative and some other gastrointestinal diseases:
Causes of the disease
The appearance of such a disease can be simultaneously influenced by many provoking factors. Moreover, they can have an effect on the intestinal mucosa, both individually and simultaneously in combination. The main causes of the disease include:
- poor nutrition. Excessive consumption of spicy, bitter, sour, smoked foods. Highly fatty meat and fish also have a negative impact;
- excessive alcohol consumption;
- infectious diseases, frequent poisoning;
- consumption of large amounts of medications. The intestinal walls are especially negatively affected by excessive and frequent consumption of antibiotics;
- eating foods that cause food allergies;
- hereditary predisposition of the body;
- various diseases of the gastrointestinal tract can also provoke the appearance of erosion as a form of complications.
Authorized Products
Diet for erosion of the stomach and duodenum includes:
- Vegetable soups with the addition of oatmeal, buckwheat, rice cereals, which are thoroughly pureed, and when the condition improves - with well-cooked and mashed cereals and finely chopped vegetables. To improve the taste, butter, low-fat cream, egg-milk mixture, meat puree, and non-garden herbs (dill or parsley) are added to first courses.
- Low-fat varieties of red meat and poultry (beef, young lamb, lean pork, turkey, chicken), rabbit in the form of steam cutlets, meatballs, zraz, quenelles, soufflé. When the process subsides, lump meat, boiled/baked in the oven, is introduced into the diet.
- River/sea fish in the form of quenelles, cutlets, meatballs of cod, pollock, pike, hake, ice fish.
- Dried bread made from premium wheat flour, crackers, savory buns.
- Cereals: oatmeal, buckwheat, mashed/well-cooked white rice with milk and butter.
- Mild homemade sauces made with milk/low-fat cream.
- Fresh non-sour cottage cheese, lazy dumplings, cottage cheese soufflé, baked cheesecakes, milk jelly. Cream and sour cream are added to ready-made soups and mashed potatoes. Milk is allowed to be consumed in quantities of no more than 800 ml.
- Soft-boiled eggs/steam omelet (2-3 pieces), added to soups and other dishes. Butter up to 20 g/day and refined vegetable oil as additives to ready-made first and second courses.
- Cooked berries (jelly, jelly, mousse). Apples baked in the oven with honey/sugar. Cannot be consumed fresh. For dessert - honey, caramel, meringues, marshmallows, meringue, jam, marshmallow.
- Free liquid of at least 1.5 l/day in the form of a decoction of wheat bran, freshly prepared diluted juices from berries/fruits, weak tea with milk, rosehip infusion, carrot juice, non-carbonated mineral water.
Table of permitted products
| Proteins, g | Fats, g | Carbohydrates, g | Calories, kcal | |
Vegetables and greens | ||||
| zucchini | 0,6 | 0,3 | 4,6 | 24 |
| cauliflower | 2,5 | 0,3 | 5,4 | 30 |
| potato | 2,0 | 0,4 | 18,1 | 80 |
| carrot | 1,3 | 0,1 | 6,9 | 32 |
| beet | 1,5 | 0,1 | 8,8 | 40 |
| pumpkin | 1,3 | 0,3 | 7,7 | 28 |
Fruits | ||||
| apricots | 0,9 | 0,1 | 10,8 | 41 |
| watermelon | 0,6 | 0,1 | 5,8 | 25 |
| bananas | 1,5 | 0,2 | 21,8 | 95 |
| melon | 0,6 | 0,3 | 7,4 | 33 |
| nectarine | 0,9 | 0,2 | 11,8 | 48 |
| peaches | 0,9 | 0,1 | 11,3 | 46 |
| apples | 0,4 | 0,4 | 9,8 | 47 |
Berries | ||||
| strawberry | 0,8 | 0,4 | 7,5 | 41 |
| raspberries | 0,8 | 0,5 | 8,3 | 46 |
Cereals and porridges | ||||
| buckwheat (kernel) | 12,6 | 3,3 | 62,1 | 313 |
| semolina | 10,3 | 1,0 | 73,3 | 328 |
| cereals | 11,9 | 7,2 | 69,3 | 366 |
| white rice | 6,7 | 0,7 | 78,9 | 344 |
Bakery products | ||||
| white bread crackers | 11,2 | 1,4 | 72,2 | 331 |
Confectionery | ||||
| jam | 0,3 | 0,2 | 63,0 | 263 |
| jelly | 2,7 | 0,0 | 17,9 | 79 |
| marshmallows | 0,8 | 0,0 | 78,5 | 304 |
| meringues | 2,6 | 20,8 | 60,5 | 440 |
| paste | 0,5 | 0,0 | 80,8 | 310 |
| Maria cookies | 8,7 | 8,8 | 70,9 | 400 |
Raw materials and seasonings | ||||
| honey | 0,8 | 0,0 | 81,5 | 329 |
| sugar | 0,0 | 0,0 | 99,7 | 398 |
| milk sauce | 2,0 | 7,1 | 5,2 | 84 |
Dairy | ||||
| milk | 3,2 | 3,6 | 4,8 | 64 |
| kefir | 3,4 | 2,0 | 4,7 | 51 |
| cream | 2,8 | 20,0 | 3,7 | 205 |
| sour cream | 2,8 | 20,0 | 3,2 | 206 |
| curdled milk | 2,9 | 2,5 | 4,1 | 53 |
Cheeses and cottage cheese | ||||
| cottage cheese | 17,2 | 5,0 | 1,8 | 121 |
Meat products | ||||
| boiled beef | 25,8 | 16,8 | 0,0 | 254 |
| beef liver | 17,4 | 3,1 | 0,0 | 98 |
| boiled beef tongue | 23,9 | 15,0 | 0,0 | 231 |
| boiled veal | 30,7 | 0,9 | 0,0 | 131 |
| rabbit | 21,0 | 8,0 | 0,0 | 156 |
Bird | ||||
| boiled chicken | 25,2 | 7,4 | 0,0 | 170 |
| turkey | 19,2 | 0,7 | 0,0 | 84 |
Eggs | ||||
| chicken eggs | 12,7 | 10,9 | 0,7 | 157 |
Fish and seafood | ||||
| black caviar | 28,0 | 9,7 | 0,0 | 203 |
| salmon caviar granular | 32,0 | 15,0 | 0,0 | 263 |
Oils and fats | ||||
| butter | 0,5 | 82,5 | 0,8 | 748 |
| ghee | 0,2 | 99,0 | 0,0 | 892 |
Non-alcoholic drinks | ||||
| mineral water | 0,0 | 0,0 | 0,0 | — |
| coffee with milk and sugar | 0,7 | 1,0 | 11,2 | 58 |
| black tea with milk and sugar | 0,7 | 0,8 | 8,2 | 43 |
Juices and compotes | ||||
| apricot juice | 0,9 | 0,1 | 9,0 | 38 |
| carrot juice | 1,1 | 0,1 | 6,4 | 28 |
| pumpkin juice | 0,0 | 0,0 | 9,0 | 38 |
| * data is per 100 g of product | ||||
The main symptoms that may indicate the appearance of intestinal erosion
Symptoms, like the underlying causes, can occur individually or together. The main manifestations of the disease include:
- frequent constipation;
- discomfort or pain of varying intensity in the middle and lower abdomen;
- bloating, excessive gas formation, flatulence;
- loss of appetite, sudden weight loss;
- in the later stages of the disease, intestinal bleeding of varying intensity may be observed.
Intestinal or stomach bleeding is the first sign, after which you should immediately consult a doctor. These symptoms are manifestations of quite serious diseases. To avoid more severe consequences, it is necessary to immediately identify the underlying cause and begin treatment.
Types of diagnostics
Even the most qualified doctor will not be able to make such a diagnosis without conducting a series of examinations. In order to choose the right treatment, it is necessary, first of all, to make a correct diagnosis, which may be indicated by characteristic symptoms.
The main diagnostic methods for identifying intestinal erosion:
- stool examination;
- X-ray of the intestines (in which the intestines are filled with some kind of contrast agent);
- fibrogastroduodenoscopy (endoscopic examination, during which it is possible to examine up to 1 meter of the small intestine);
- sigmoidoscopy (a more detailed examination of the intestinal walls up to 30 centimeters long).
Basic methods of treating erosion

Once the diagnosis is confirmed, it is necessary to begin treatment without delay. In this case, therapy should be comprehensive and aimed at:
- elimination of the main symptoms of the disease;
- exclusion of the root cause that could provoke the appearance of intestinal erosion;
- drug therapy, the main task of which is to put the disease into remission and promote the healing of erosion;
- preparing the patient's diet. Nutrition in this case plays an important role, since gastroenterologists identify a number of products that can provoke an exacerbation of the disease. The diet should be selected taking into account the need to introduce into the diet foods that help strengthen the intestinal walls and heal the mucous membrane. It must also be understood that if the patient has a predisposition to erosion, then it will be necessary to limit the consumption of provoking foods not only during the treatment period, but also in the future, since the disease may return again if a provoking factor appears.
Drug treatment should include the following groups of drugs:
- anti-inflammatory;
- antispasmodics (aimed at reducing pain);
- medicines against diarrhea.
In some cases, the gastroenterologist may also prescribe antibiotics. Most often, this measure is used if the disease was provoked by an inflammatory process or frequent intestinal infections.
Treatment most often takes a fairly long period of time. On average, new studies need to be carried out every month to make sure that the treatment was indeed chosen correctly and the erosion healing process is proceeding normally. If therapy does not bring the expected results, then it is necessary to select new treatment methods.
The duration of necessary treatment depends directly on the size of the erosion, its location, as well as the presence of a number of complications. The patient must also understand that the course of treatment will need to be completed. If previously disturbing symptoms are over, this does not mean that the disease has completely receded. If the course is not completed at the first provoking factor, the disease may return with renewed vigor.
If bleeding occurs, it is necessary, first of all, to eliminate this dangerous symptom. Although most often bleeding is not even considered a symptom, but rather a complication of intestinal erosion. Most often, this problem can only be eliminated through surgery.
Description and photo
Wikipedia offers this definition of erosion. This is a defect in the surface layer of the gastric mucosa, which does not reach the muscle plate and does not leave scars when healing.
Very often it forms in the antrum. This place is an important part of the entire peritoneum. At the same time, the quality of the antrum can affect the condition of the entire stomach.
Erosion of the stomach appears only on the surface layer of the mucosa. After treatment, the entire deformity heals and has no scars.
To avoid complications and more serious diseases, you need to identify the problem as early as possible and begin treatment.
There is a high probability that the erosion will transform into a stomach ulcer. This is especially true for multiple erosions.
The ulcer has a low level of healing due to deeper damage to the walls. In addition, after undergoing therapy, there will be scars on the gastric mucosa and markings of the boundaries of the damaged area.
Therapeutic therapy always involves complex treatment. At the same time, the intervention of traditional medicine is not excluded.
Treatment can only be carried out after a complete diagnosis and consultation with a doctor. Only a specialist can determine the type and degree of development of the disease.
At the first examination, the doctor will try to identify the causes preceding the formation of erosion. The most common reasons:
- Poor environment and fast pace of life.
- Poor and unhealthy diet. The quality of the products must be paramount. Various types of preservatives, additives, etc. can cause irritation of the mucous membrane. To avoid stomach problems, experts advise avoiding hot, fatty, and sweet foods. Hot seasonings, sauces and spices are also contraindicated.
- Central nervous system disorder. Recently experienced emotional upheavals and stress contribute to the emergence of serious problems throughout the body and in particular the gastrointestinal tract.
- Drinking alcohol and smoking. It is not so much the products themselves that cause the problem, but their abuse.
- Medicines. Often, gastric erosion can be caused by drugs from the group of non-steroids that were used to treat inflammation in the body.
- Surgical interventions in the gastrointestinal tract can also cause disruption of the integrity of the gastric or duodenal mucosa.
- Diabetes.
- Injuries suffered.
- Liver failure.
- Chemical poisoning. You should always be careful when handling all chemical products. When working with such substances, precautions and hygiene must be observed.
- Heart failure.
- Malignant tumors in the intestines or stomach: Crohn's disease, lymphon and other oncological diseases.
- The influence of bacteria - Helicobacter pylori.
- Benign neoplasms.
Proper nutrition for such an illness
When such manifestations of a defect in the walls of the stomach appear, a person may experience long and painful pain immediately after eating. Moreover, if the stomach is empty, then the person may feel the urge to vomit. Vomit may contain a high content of gastric juice.
In this case, it is necessary to completely exclude sour, salty, spicy foods from the diet. You should also not eat fried or smoked foods. You can only eat meat and fish that are not fatty. You should limit your consumption of fermented milk products, sweets, and flour. Alcohol is strictly contraindicated.
At the same time, it is recommended to eat more cereals (necessarily with low-fat butter), chicken broth (preferably boiled, with a low fat content).
Erosion of the duodenum: symptoms, treatment and nutritional correction
Erosion of the duodenum is a pathology that affects its mucosa, but does not affect the muscle layer. The disease can be diagnosed in almost every person. Early treatment guarantees a good result.
Erosion of the duodenal bulb is a relatively little-studied dysfunction of the digestive tract. Accurate diagnosis has become possible due to the widespread introduction of endoscopes into clinical practice.
Erosion is the second most common pathology of the gastrointestinal tract after ulcers. The disease is often detected in patients with severe peptic ulcers, hepatitis, cirrhosis, tumors of the digestive tract, pathologies of the heart, blood vessels and respiratory organs.
Erosion differs from other diseases in etiological factors, severity of the pathological process and healing rate, and general symptoms.
Causes of erosion
The disease can be caused by such reasons.
- Exposure to adverse factors, especially stress. The importance of this circumstance in the formation of erosion allows us to assume that the problem is a psychogenic disease.
- Long-term consumption of indigestible and spicy foods.
- Long-term consumption of alcoholic beverages.
- Uncontrolled use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory tablets, such as Voltaren, Brufen, Indomethacin. Most antibiotics have a similar effect.
- Damage to the nervous system.
- Heart surgeries, organ transplants, severe injuries.
- Erosion often develops in people suffering from acute infectious gastroenteritis. With this disease, symptoms of body poisoning increase.
- Erosion of the duodenum can occur due to disruption of blood flow in the portal vein.
- Hernias in the esophageal opening.
- Inflammation of the vagus nerve.
- Severe kidney dysfunction with the development of kidney failure.
- Contact with hydrochloric acid. The disease may occur due to reduced tolerance of the duodenal mucosa to the high acidity of gastric juice.
In addition, it has been noted that erosions occur much more often in smoking patients.
Classification of erosions
Duodenal erosions can be benign or malignant.
Benign varieties of the disease include:
- acute erosion;
- chronic lesions of the mucous membrane (they can be single or multiple);
- gastritis with the development of erosive lesions;
- erosive-hemorrhagic inflammation of the mucous membranes of the stomach and duodenum.
Erosion is defined as acute if it epithelializes within 2 days to a week. If the area of pathology does not undergo regression within a month, then the disease is chronic.
Symptoms of the disease
The clinical course depends on the severity of the hemorrhagic syndrome, the number and size of defects.
Common symptoms of the pathology include:
- painful discomfort in the area of the duodenum;
- nausea;
- feeling of constant discomfort;
- vomiting, sometimes with a small amount of blood in the vomit;
- general malaise and weakness (appear against the background of hidden and prolonged bleeding);
- decreased number of red blood cells;
- severe pallor;
- drop in blood pressure and fainting (these symptoms appear as a result of massive bleeding or damage to the inner layer of the intestine).
Different types of mucosal lesions can cause heartburn and sour belching in the patient.
Complications
Sometimes this disease is complicated by massive bleeding. In this case, the stool becomes black. At the same time, coffee-colored vomit appears. The release of blood is dangerous due to the development of acute anemia.
Erosion can develop into an ulcer. The progression of the ulcer is fraught with its perforation. Perforation of the ulcer causes inflammation of the peritoneum - peritonitis . This disease can only be treated surgically, and the clock literally counts.
Finally, untreated erosion can develop into cancer.
Diagnostics
Most often, the patient is prescribed an endoscopic examination of the stomach and duodenum. The procedure is carried out only if there are no contraindications.
X-ray examination is valuable when it is necessary to simultaneously evaluate the presence of infiltrative processes, polypoid formations, fold hypertrophy, and gastric deformation.
Other events are also scheduled:
- tests for the presence of Helicobacter;
- biopsy;
- biochemical blood test.
Treatment
Therapy begins with eliminating the etiological factor. In order to improve the functioning of the digestive tract, patients are prescribed such medications.
- Antibiotics. They are needed to fight Helicobacter bacteria. The most commonly prescribed drugs are penicillin and macrolides.
- The use of proton pump inhibitors is indicated. The most effective of this group is Omez (Omeprazole).
- To reduce the aggressive effect of gastric juice, antacid drugs (Rennie or Almagel) are used.
- To restore normal gastric motility and eliminate nausea, use Cerucal or Domperidone.
- To strengthen the walls of blood vessels and combat anemia, vitamins are used in the form of injections (B6, B9, B12, PP, C).
- Angioprotectors are used to stop internal hemorrhages.
Complicated erosive lesions are treated only in a surgical department. The patient's stomach is washed, hemostatic agents and saline solutions are administered.
How to relieve pain
To relieve pain, the following medications are required:
- bismuth preparations;
- anticholinergic drugs (Platifillin, Gastrocepin);
- ganglion blockers (Quateron).
To prevent an attack of acute pain, it is advisable to drink a little alkaline water such as Borjomi half an hour before its expected appearance. You can take a little milk at night - this is a healthy and effective natural antacid .
Folk remedies
If there are no complications, then it is recommended to take folk remedies:
- sea buckthorn oil (has a pronounced antiseptic and healing effect);
- infusions of chamomile, calamus, celandine, bearberry and gentian (it is best to drink a collection of these plants);
- In the morning before meals, eat 1 banana;
- a mixture of walnut tincture, honey, butter and aloe juice (all these components must be taken in equal parts).
It is not recommended to use alcohol tinctures for erosive diseases of the duodenum.
Recovery criteria
The doctor’s goal is achieved if:
- pain goes away, a person’s well-being significantly improves;
- the activity of the digestive tract is normalized;
- surface erosions begin to heal;
- swelling and redness of the mucous membrane disappears;
- chronic affected areas are covered with healthy epithelial tissue.
Forecast
If you follow a diet and avoid alcoholic beverages, the outcome of the disease is favorable. The acute course usually passes after 14 days.
Chronic pathology can last for many years, but with the help of well-chosen therapy it is possible to achieve stable remission. If you ignore treatment and do not seek medical help, erosion can develop into a malignant tumor.
Nutrition for erosion
Properly organized nutrition helps to get rid of the disease even without the use of drugs. The main requirement for nutrition is its regularity. Meals should be small and frequent. It is recommended to consume no more than 300 ml of food at a time. Long breaks in eating are prohibited.
In case of a pronounced erosive process, it is recommended to introduce an increased amount of protein into the menu. It is necessary for the complete restoration of the damaged mucosa.
Allowed dishes for erosion:
- porridge (from rice, semolina);
- jelly;
- compotes;
- vegetables (except radish and cabbage);
- boiled lean meat (preferably chicken, veal and beef);
- boiled or steamed fish;
- oils (the most useful are butter and olive);
- fresh juices;
- boiled eggs (no more than 1 per day);
- mashed potatoes;
- puddings;
- cutlets cooked in a steam bath.
It is necessary to exclude from the diet:
- alcohol;
- cabbage;
- coffee;
- chocolate;
- dishes with dyes and flavors, preservatives;
- pickles;
- marinades;
- smoked meats
Prevention
Preventive measures consist of strict adherence to the principles of a healthy lifestyle, doctor’s recommendations regarding treatment and proper nutrition. It is necessary to correctly use non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, which can provoke inflammation.
Patients with a history of inflammatory pathologies of the gastrointestinal mucosa should stop smoking and drinking alcohol. It is recommended to maintain physical activity and avoid physical inactivity.
Erosion of the duodenum can sometimes be cured by correcting the diet and using antacids. Early consultation with a doctor helps to improve the condition and stable remission . In the absence of medical assistance, complications develop, the most dangerous of which is cancer.
Source: https://vseozhivote.ru/kishechnik/eroziya-dvenadtsatiperstnoj-kishki.html