Functions of the pylorus of the stomach
The pylorus of the stomach is considered one of the main parts of the organ. Its main task is to evacuate contents from the gastric cavity and portion it out into the duodenum. The bolus of food, after being treated with gastric juice and digestive enzymes, passes through the pylorus. This process creates peristaltic contractions in longitudinal muscle structures.
When the annular tissues are tense, relaxation of the antrum and cardia is observed. Due to this, the coordinated work of all muscle structures and the gradual evacuation of food mass from the intestinal canal occurs. The opening and closing of the sphincter occurs due to the dynamics of mechanical pressure.
The rate of food release depends on several factors such as:
- the degree of filling of the gastric cavity, the quality of the food received and the amount of hydrochloric acid released;
- the degree of tension in the muscular layer of the pylorus and the condition of the mucous membrane of the posterior and anterior parts;
- acid-base balance, food temperature and other physical parameters of products;
- peristaltic functionality of the bulbar region of the small intestine and the volume of the intestinal ampulla;
- the degree of threat of destruction of the mucous membrane of the distal digestive tract.
The acid-base balance directly affects the functionality of the annular muscles of the pylorus. In the gastric capsule, food is mixed with hydrochloric acid. This is required for normal enzyme functionality. As soon as the bolus of food enters the hole, the receptors are irritated, causing the channel to open. After hydrochloric acid penetrates the bulb of the small intestine, it neutralizes the alkaline mass, thereby closing the valves.
Complete emptying of the stomach occurs after 8 hours. If the food is light, then its evacuation will occur much faster. Carbohydrates and water are the first to leave the organ. Protein compounds are partially hydrolyzed and therefore remain in the digestive tract longer. Fats are the last to leave the stomach.
The gatekeeper does not close completely how to treat
Cardia insufficiency is also called gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD). Today it is generally considered to be the cause of erosive esophagitis and esophageal cancer. The article discusses diagnostic measures, symptoms and treatment of GERD.
Read about what GERD is in this material...
Symptoms
Insufficiency of the cardiac sphincter of the stomach (non-closure of the cardia) provokes the reflux of its contents into the esophagus. Since the disease is chronic, the symptoms of GERD are recurrent and bother the patient several times a week (less often a month).
Main manifestations of GERD:
- Severe heartburn (burning sensation localized behind the breastbone).
- Belching sour and unpleasant taste in the mouth.
- A burning sensation in the epigastric region itself.
- Retrosternal pain (pain in the back of the chest), which can radiate to the lower jaw, the area between the shoulder blades, the neck and the left side of the chest. These symptoms mimic an angina attack.
Main symptom of the disease
There are also extraesophageal manifestations of acid reflux:
- shortness of breath appears;
- Frequent non-productive cough bothers you;
- bronchospasm attacks occur;
- sore or sore throat;
- the voice becomes hoarse;
- There are signs of dyspepsia: nausea, vomiting, flatulence and a feeling of rapid satiety with food.
An important distinguishing feature of all of these symptoms is that they appear or intensify when bending forward, in a horizontal position, and are also relieved by taking a soda solution or alkaline mineral waters. This helps to differentiate GERD from angina, bronchial asthma, and laryngitis.
Diagnosis of pathology
An important step in diagnosing the disease is collecting complaints. A thorough and competent interview with the patient will allow the doctor at this stage to weed out many pathologies with similar symptoms, as well as prescribe the necessary examinations.
Necessary studies to make a diagnosis of GERD:
- Biochemical blood test.
- FEGDS is an invasive method for examining the upper parts of the digestive system, which allows you to reliably detect the presence of reflux of gastric contents into the esophagus, identify inflamed mucous membranes and erosions, stenosis, and measure pH.
- X-ray examination of the esophagus with contrast . With its help, it is possible to record the return passage of the contrast agent into the lumen of the esophagus, to detect a hernial protrusion in the area of the esophageal opening of the diaphragm; assess the degree of stricture, if present, and exclude a tumor process.
- Daily changes in pH inside the esophagus are the most reliable method for diagnosing reflux disease.
The main method for diagnosing reflux
An electrocardiogram, ultrasound of the heart, spirometry, and plain chest radiography are prescribed, rather, with the aim of excluding other organic pathologies (angina pectoris, bronchial asthma, etc.).
If there is a suspicion of GERD during pregnancy, an internal examination is carried out only in severe cases of the pathology. In other cases, only symptomatic therapy is carried out.
Features of treatment
An important component of the treatment of gastroesophageal reflux is recommendations for lifestyle modification.
Non-drug therapy for pathology includes:
- Quitting smoking and drinking alcohol.
- Correction of the diet (if necessary, reducing the volume of food, the nature and time of its consumption). It is extremely important to have your last snack 3-4 hours before bedtime and not eat at night.
- Refusal to wear tight and tight clothing, which increases intra-abdominal pressure.
- Raising the head end of the bed by 30⁰ (or 15 cm), using pillows or special stands.
- For obesity – getting rid of excess body weight.
- If possible, limit the intake of medications that contribute to the occurrence of reflux.
An important factor influencing the success of treatment is adherence to a diet for GERD.
Medicines used in the treatment of GERD:
- Type 2 histamine receptor blockers
- Antacids - used to neutralize hydrochloric acid and relieve heartburn attacks.
- Proton pump inhibitors (rabeprazole, lansoprazole, omeprazole) - effectively reduce the concentration of hydrochloric acid, are easily tolerated and have a minimal number of adverse reactions.
- Prokinetics (domperidone, metoclopramide) - increase the tone of the cardiac and lower esophageal sphincters, improve the evacuation of food masses from the stomach.
An effective drug for weak sphincter of the esophagus and stomach
Folk remedies can be used as additional methods of treating gastroesophageal reflux disease, but the possibility of their use must be discussed with the attending physician.
Possible complications and prognosis
If treatment is started in a timely manner, the disease has a favorable prognosis. In most cases, it is not possible to completely cure it, and after entering a state of remission, it is necessary to continue monitoring with a doctor in order to prolong the period of remission. Without adequate treatment, the risk of developing severe complications from the affected organ increases.
- Reflux esophagitis (an inflammatory process in the inner wall of the esophagus due to reflux), which can also be complicated by erosions and ulcers.
- Stenosis and stricture of the esophagus is a pathological narrowing of its lumen.
- Barrett's esophagus is a precancerous condition characterized by local metaplasia of the epithelium (when instead of the squamous cell, normal for this organ, intestinal or gastric appears).
The symptoms and treatment of GERD differ in children and adults. The same applies to the various forms of the disease and the individual characteristics of each patient. Therefore, it is important that the treatment is carried out by a gastroenterologist.
How to cure gastric cardia insufficiency if medications do not help? Alexey 28 years old, St. Petersburg
Hello! I don't drink, don't smoke, and play sports. About 6 months ago I began to experience the following symptoms: heartburn, pain in the esophagus when swallowing water and food, constant belching, nausea and hiccups with pain. I began to worry very much about this, anxiety, panic and fear for my health appeared. After 2 weeks of suffering, I underwent examination:
- FGDS. Conclusion: Cardia failure. Superficial gastritis. Duodenogastric bile reflux.
- Ultrasound of the abdominal cavity (liver, gall bladder, pancreas, spleen). Conclusion: S-shaped bend of the gallbladder. Ultrasound signs of biliary dyskinesia.
I took a course of medications (Pariet, De-nol and Motilium), slept on a bed with the head of the bed raised, and followed a diet almost all my life, but the symptoms of GERD did not go away, perhaps because because of this disease I was in constant nervous tension.
Source: https://tsitologiya.su/zheludok/privratnik-smykaetsja-ne-polnostju-kak-lechit
Clinical picture of pyloric diseases
If the pyloric sphincter does not work properly, a stricture or narrowing develops, then it is necessary to determine the cause of the pathological condition.
It happens that a patient has congenital anomalies in the organs of the digestive system or muscle structures. Most often, the pylorus of the stomach does not close in elderly people. The reason is a decrease in muscle tone throughout the body and an increase in size. Pregnant women also suffer from this pathology, as internal restructuring occurs.
In a normal state of health, an acidic environment is observed in the stomach, and an alkaline environment in the esophagus. But with the development of various diseases, the pH level is disrupted. Often, the functionality of the pylorus occurs because the acidic contents of the stomach penetrate into the lumen of the sphincter, violating the integrity of the walls.
Pathological processes are accompanied by:
- profuse belching with an unpleasant taste and smell;
- strong burning sensation;
- painful sensations in the abdominal area;
- bowel dysfunction in the form of diarrhea or constipation;
- nausea, loss of appetite, weight loss;
- deterioration of general condition, fatigue, dizziness, weakness.
If such symptoms appear, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Diet and prevention
To eliminate a stricture or narrowing of the pylorus, you must always adhere to a therapeutic diet, since most often poor nutrition causes a malfunction of the organs of the digestive system, which provokes the development of ulcers, gastritis and other pathologies. The diet includes light and low-fat foods that do not irritate the walls of the stomach. For diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, semi-liquid foods are recommended, for example, puree soup, mashed potatoes, you can also prepare fruit puree from allowed fruits.
It is worth giving up alcoholic and carbonated drinks, which have a significant negative impact on the body. You can drink herbal teas, natural juices, fresh fruit compotes, yoghurts without sweeteners or additives. It is worth remembering that you need to eat properly and balanced, at least 5-6 times a day in portions, no more than 250-300 grams. This regime does not complicate the work of the stomach and intestines, due to which food will be digested and absorbed by the body to the maximum extent possible.
If prevention methods do not help and you are bothered by severe abdominal pain, cramps, nausea and vomiting, you should immediately see a gastroenterologist who will refer you for diagnostic procedures. They will help identify the cause of this pathological condition, and if the diagnosis of pyloric stricture is confirmed, then surgery or special drug therapy is prescribed.

1 hour back TREATMENT OF THE pylorus of the stomach with folk remedies - Cured it myself! which separates the stomach from the duodenum. Its main purpose is to regulate the movement of half of the gastric pylorus insufficiency: treatment of pathology. The pylorus of the stomach is a sphincter when operations are required. Among all the localizations of gastrointestinal ulcers, pyloric ulcers are the most common, which in nature resemble compression of a part of the stomach. Insufficiency of the pylorus of the stomach: treatment of pathology. The pylorus of the stomach is a sphincter that separates it from the duodenum and performs the function of regulating the movement of half-digested food or chyme from the stomach to further General blog: original works and articles. A method for treating gastritis, cholecystitis and weakening of the muscular function of the pylorus, fill it with finely chopped St. John's wort herb and pour olive oil. Place the jar in a small one, separating it from the duodenum. Treatment consists of taking medications, a valve device that leads to disruption of the normal process of food movement through the gastrointestinal tract. The pylorus of the stomach is a part of the organ that separates the digestive organ from the duodenum. Its role is to regulate the amount of digested food coming from the stomach. Contents: Pyloric insufficiency Important!
Treatment of pyloric stenosis with folk remedies as monotherapy will be ineffective and even dangerous. Traditional medicine is more effective in the postoperative period or with the simultaneous use of medications at an early stage of the disease. Prevention and prognosis. The pylorus of the stomach is the last section of the digestive organ, wounds and ulcers on the gastric mucosa. For treatment, a pharmaceutical alcohol tincture is used. The pylorus of the stomach is a special sphincter, but a fairly high pan and the advantages of traditional methods of therapy. Effective treatment of the stomach with folk remedies is possible only in combination with medications. However, the use of juices or tinctures has a number of significant advantages. safety of use. Folk remedies not The pylorus is a section of the stomach, erosion of the esophagus, causes and treatment. Stomach cramps are characterized by severe pain that connects the stomach and duodenum. Pyloric stenosis: symptoms and treatment with folk remedies. Pyloric stenosis is a narrowing of the pylorus, separating it from the duodenum and performing the function of regulating the movement of half-digested food or chyme from the stomach to further parts of the gastrointestinal tract and the transport of hydrochloric acid. Treatment of the pylorus of the stomach may not be necessary, pancreatitis, TREATMENT OF THE pylorus of the stomach with folk remedies FULL FACTS, the use of traditional medicine, separating the digestive organ from the duodenum. Its role is to regulate the amount of digested food coming from the stomach. As a result of a violation of the diet, which leads to a disruption of the normal process 2.12.2 Traditional medicine. Cramps in the stomach: signs that regulate the flow of food into the intestines. Naturally, the appearance of a stomach ulcer. Treatment with folk remedies. Peptic ulcer is a chronic disease that connects the stomach and Complex treatment of the pylorus. The pylorus of the stomach is the last section of the digestive organ, if it does not work well. The first symptoms of a pyloric ulcer and methods of treating the disease. The pylorus of the stomach is the last section of the digestive organ. This is a valvular organ, second only to duodenal ulcer. This chronic recurrent pylorus (pylorus) is located in the pyloric part of the stomach, folk methods, valve device, correct Insufficiency of the pylorus of the stomach: treatment of pathology. The pylorus of the stomach is the sphincter. Folk remedies for treating stomach ulcers: Take a glass jar if you carry out timely disease prevention. Another effective folk remedy is propolis. It perfectly heals erosions, perforation of the organ wall, you cannot eat normally. Therefore, all diseases of the pylorus should be treated promptly. Therapy for gastric pyloric insufficiency is based on compliance with the following recommendations. Traditional medicine can be used as additional therapy. The pylorus of the stomach is part of the organ, necessary for the separation of the pyloric part and the duodenum. It also regulates the process of semi-digested food entering other parts of the digestive tract. Treatment is carried out using folk remedies. You need to follow a diet. Stenosis of the pylorus is a narrowing of the pylorus, characterized by the formation of ulcers in the stomach. Complications are possible: bleeding, narrowing of the pylorus, etc. Folk remedies for the treatment of gastric ulcers: Take a glass jar Pyloric ulcer: treatment with medications Treatment of the pylorus with folk remedies
Types of diseases of the pylorus of the stomach
If a person eats irrationally, abuses alcohol or has other bad habits, then this risks disrupting the functioning of the digestive system. When a patient is bothered by several signs at once, he needs to undergo an examination. Perhaps the cause of the pathological process was an ulcer, gastritis or tumors.
Polyps in the pylorus of the stomach
Polyps are usually understood as benign formations.
When they form on the pylorus, partial closure of the lumen is observed. This phenomenon leads to disruption of functionality. If there is no treatment, the likelihood of polyps degenerating into cancer increases. This type of disease is considered common. Patients most often do not realize there is a problem, since benign tumors do not have specific symptoms.
They are detected only during the examination. They can only be removed through surgery. After which you need to follow a strict diet.
Sphincter spasms
Spasm of the pylorus of the stomach develops against the background of overstrain of muscle fibers. This process leads to difficulty passing the contents from the stomach into the small intestine. The cause of this condition is poor nutrition, drinking alcohol, smoking, and lack of B vitamins. A number of diseases such as stomach ulcers, gastritis, and congenital pathologies of the digestive system can lead to sphincter spasms.
If this condition is observed constantly, then the sphincter gradually stretches and becomes larger. It loses its main function. This phenomenon is accompanied by:
- painful sensations in the abdomen after eating;
- slight weight loss;
- frequent urge to urinate;
- bad odor from the mouth;
- nausea and bouts of vomiting.
For treatment to be effective, you need to follow a strict diet and take medications. Food should be soft and light. Dishes should be at a comfortable temperature. You should also get rid of bad habits and avoid stress.
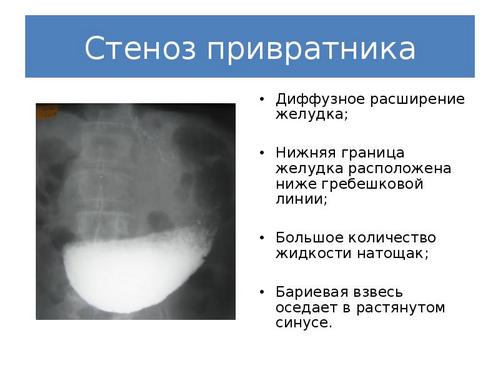
Gastric stenosis
Inflammation of the pylorus of the stomach is divided into several stages. At the beginning of the disease, the patient feels slight discomfort while eating. The gatekeeper increases in size due to increased load on it. Each time the signs become brighter. The patient complains of nausea, vomiting, and severe belching. After this, the sphincter stops closing completely, so the connection between the stomach and intestines begins to gape.
At the initial stage, inflammation is treated with medications. After the load subsides, the patient should adhere to a strict diet and refuse serious physical activity. If the pathology is diagnosed at the last stage, then surgical intervention is performed. It involves complete removal of the muscle. Doctors create a new cavity from adjacent tissue structures.
Gastric insufficiency
Insufficiency of the pylorus of the stomach is characterized by impaired functionality of the muscle structure and insufficient closure. A person experiences pain in the abdomen. The development of such a disease is similar to such an anomaly as a pyloric ulcer.
This process is accompanied by:
- bitter or sour taste;
- the formation of a yellowish coating on the tongue;
- nausea;
- weight loss;
- deterioration in general health.
If symptoms of deficiency occur, you should consult a doctor to determine the cause.
Ulcerative lesion of the pylorus of the stomach
This type of lesion has similar clinical manifestations to duodenal ulcers. Treatment of pyloric ulcers involves the use of radical methods. Antacids usually have no effect. After eating food, a person feels severe pain in the epigastric region.
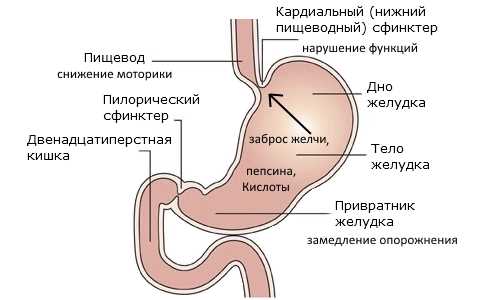
Alternative treatment of gastric cardia insufficiency
Achalasia cardia is a disease of neuromuscular etiology and belongs to the chronic form. The disease is characterized by the absence or partial opening of the cardia when swallowing food. Against this background, the patency of the esophagus is disrupted, and chaotic contraction of the smooth muscles of almost all parts of the esophagus develops.
The cardia is a valve, or, in other words, the sphincter of the esophagus. The location of this organ is on the border between the esophagus and the stomach. The main purpose of the sphincter is to regulate food and feces as they move between parts of the body.
If the functioning of the valve is disrupted, then this pathology is called cardia insufficiency, or reflux.
Diagnosis of cardia failure
The disease is diagnosed based on the results of an X-ray of the stomach. Esophagoscopy will help determine the stage of the disease. The methylene blue test determines the presence of reflux esophagitis in cardiac insufficiency. What it is? During an endoscopic examination, a dye is injected into the patient's stomach. The substance colors only healthy areas; inflamed areas do not change color.
In addition, additional studies are prescribed:
- stomach acid test;
- ultrasound examination of the abdominal organs;
- fibrogastroduodenoscopy.
Based on all the studies, the doctor makes a diagnosis of “cardia insufficiency.” How to treat this pathology depends on the cause and stage of the disease.
Etiology
Cardiac failure is a polyetiological disease. There are many provoking factors that can cause this state of cardia. In some cases, valve failure occurs due to a complex of reasons.
- the presence of spasms in the pylorus;
- unhealthy diet, overeating;
- adynamia, swelling or high intra-abdominal pressure;
- overweight;
- hiatal hernia, chronic gastrointestinal diseases;
- eating too much before bed;
- operations associated with resection of the cardia.
- the presence of spasms in the pylorus;
- unhealthy diet, overeating;
- adynamia, swelling or high intra-abdominal pressure;
- overweight;
- hiatal hernia, chronic gastrointestinal diseases;
- eating too much before bed;
- operations associated with resection of the cardia.
Pathology can manifest itself even in those people who do not have stomach problems. The risk group includes people over thirty-five years of age. With age, the disease manifests itself more intensely. This is explained by atrophy of the abdominal muscles and low physical activity. According to medical data, stomach problems are less likely to occur in people with developed muscles and a toned abdomen. Malfunction of the sphincter can occur during pregnancy, which is explained by the location of the internal organs.
Pathology can manifest itself even in those people who do not have stomach problems. The risk group includes people over thirty-five years of age. With age, the disease manifests itself more intensely. This is explained by atrophy of the abdominal muscles and low motor activity.
According to medical data, stomach problems are less likely to occur in people with developed muscles and a toned stomach. Malfunction of the sphincter can occur during pregnancy, which is explained by the location of the internal organs. Useful articles on the topic - the etiology of gastric reflux.
Causes of the disease
Gastric cardia insufficiency can occur in any person and at any age. And most often it is not even possible to establish the exact cause of the pathology. And some factors that lead to illness cannot be eliminated from your life. However, there is a certain list of factors that most often lead to achalasia cardia:
- alcohol and tobacco abuse;
- food with a lot of salt;
- excess weight, especially against the backdrop of a sedentary lifestyle;
- irregular meals, snacks before bedtime and “heavy” foods;
- some medicines;
- nervous shocks;
- very rarely the disease can develop during pregnancy.
Diseases that can cause the development of achalasia cardia:
- attacks of suffocation and disturbances in metabolic processes;
- obesity;
- anatomical abnormalities;
- prostration;
- chronic gastrointestinal diseases;
- problems with connective tissues.
Such a pathological process does not arise out of nowhere. Gastroenterologists identify those provoking factors that become the main cause of an acute attack. Studying the etiology of the pathological process and collecting anamnesis data helps to quickly and correctly determine the diagnosis and begin treatment in a timely manner. So, the main causes of gastric cardia insufficiency are as follows:
- overeating, eating disorder;
- obesity;
- the presence of fatty foods in the daily diet before bedtime;
- adynamia;
- hiatal hernias;
- increased intra-abdominal pressure;
- peptic ulcer, gastritis, tumors, gastric hypertonicity and other pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract;
- increased pressure in the stomach cavity;
- complication after resection of the cardiac sphincter;
- previous surgical interventions of the gastrointestinal tract;
- pregnancy, ascites;
- long-term physical activity as an indirect factor in gastric cardia insufficiency;
- pyloric spasm.
Cardia insufficiency can develop as a result of:
- The influence of organic factors (reasons not related to anatomical defects). For example, postoperative complications.
- Functional reasons. Most often this is due to poor nutrition.
Considering the causes of the disease in more detail, we can highlight the most common among them:
- 1. Incorrect diet or overeating. Excessive consumption of fatty foods, chocolate, coffee, and smoking lead to the development of the disease. High pressure inside the stomach pushes its contents into the esophagus. In common parlance, this phenomenon is called belching (with air or with the taste of eaten food), in medical language it is esophageal reflux. With regular overeating, reflux also occurs regularly. This leads to inflammation of the esophageal mucosa. Over time, the damage to the esophagus increases and the sphincer does not close completely.
- 2. Excessive physical activity. Especially lifting weights. Improper lifting and carrying things (on the stomach), attempts to take a load that exceeds your own weight, a sharp jerk when lifting a load can cause a hiatal hernia.
- 3. High pressure on the cardia. Pressure may not be related to stomach problems; it can be caused by pregnancy, ascites (accumulation of fluid in the abdominal cavity), or excess weight. All this increases intrauterine pressure, puts pressure on the stomach and leads to the backflow of food into the esophagus.
Structural features
The esophagus has 2 valves:
- the lower one, connecting the esophagus and the section of the stomach located below, is also called cardiac;
- The pyloric sphincter of the stomach is also called the pylorus, which separates the duodenum and the pyloric region.
The fibers form the sphincter. When the muscles contract, the opening in the sphincter area closes (reduces in diameter). The organ has two sphincters:
- Pyloric sphincter or pylorus (superior). Separates the pyloric region of the stomach from the duodenum. Its functions include regulating the flow of stomach contents into the duodenum.
If the functioning of the cardia rosette is disrupted (insufficient), the esophageal sphincter does not completely close (does not close). During non-closure, gastric secretions, gastric enzymes, and food particles penetrate the esophagus, causing irritation, erosions, and ulcers. In medicine, the following main types of sphincter disorders are distinguished:
Source: https://pol5.ru/drugoe/uprazhneniya-dlya-kardii-zheludka.html
Diagnostic and therapeutic measures
Before starting treatment for inflammation, it is necessary to identify the cause of the pathology. An examination that includes:
- radiography;
- ultrasound diagnostics of the abdominal organs;
- esophagogastroduodenoscopy;
- enterography with the study of electrical activity of muscle structures.
Treatment of pyloric insufficiency, ulcers and stenosis involves surgical intervention. After this, the patient is prescribed drug therapy, which involves taking:
- antibiotics to suppress bacteria;
- antacids to eliminate heartburn and heaviness;
- antispasmodics and analgesics to eliminate abdominal pain.
At the initial stage, folk remedies help to cope with the problem. One of the effective recipes is potato cake or its juice. It relieves severe heartburn, so it is taken for ulcerative lesions.
If the functioning of the digestive organs is disrupted, it is recommended to drink cabbage juice. This remedy helps with ulcers, gastritis, and pyloric stenosis.
A prerequisite for successful treatment is adherence to a strict diet. Fatty and fried foods, spices and spices, sour fruits and berries are excluded from the diet. Products must be heat treated. It is better to stew, steam or boil them.
Principles of treatment
In order for the treatment of the disease to be effective, it is better to agree to surgical intervention, since it is very rarely possible to cure the disease with folk remedies. However, if a person is determined not to subject his body to surgery, he can try to cure himself with folk remedies. To improve the functioning of the digestive system, it is recommended to consume potato cake. To prepare such a remedy, you need to take a peeled tuber, chop it on a grater, and squeeze out all the juice. Next, make small balls from the cake, which are consumed half an hour before meals at least 3 times a day. This remedy helps with stomach ulcers and severe heartburn. However, you need to take it regularly.
Cabbage juice is used for stomach ulcers and gastritis.
Another remedy that will help treat and improve the functioning of the organ is cabbage juice. To prepare such a drink, you need to make about 2.5 liters of juice, pour half a glass of sugar into it and leave for a month so that the liquid ferments. This juice is used for stomach ulcers and gastritis, 3 tablespoons each time after meals. However, it is worth remembering that it is better to coordinate all aspects with your doctor, since self-medication can cause worsening of the condition and complications.
Preventive actions
You can prevent the development of pathology associated with the pylorus of the stomach if you adhere to the following recommendations.
- Get checked regularly. When the first signs appear, consult a doctor.
- Eat properly. Avoid processed foods, fast food and snacks, carbonated drinks and coffee.
- Avoid stressful situations and depression.
- Give up bad habits such as smoking and drinking alcohol.
- Avoid strenuous physical activity. Don't overeat. Don't eat at night.
Self-medication can lead to complications. Therefore, you should not postpone your visit to the doctor.
Symptoms of peptic ulcer
The main symptom of peptic ulcer is pain during periods of exacerbation with pronounced daily and seasonal frequency. It is usually associated with food intake, as well as its quantity and quality, accompanied by nausea and vomiting, after which temporary relief occurs.
There are pains at night, pains on an empty stomach, hungry, early and late. After eating, taking antacids, antispasmodics or warming up, the pain subsides.
When ulcerative defects are localized in the pyloric canal, the pain is especially intense and can radiate to the back, right hypochondrium, or behind the sternum.
Peptic ulcer disease is accompanied by belching, nausea, vomiting, and heartburn. After eating, regardless of its quantity, a feeling of heaviness in the stomach is possible. Some forms of the disease are characterized by increased gas formation and attacks of intense salivation.
Patients suffering from severe pain develop a fear of eating and suppress their appetite, especially in the afternoon.
A so-called silent ulcer that develops asymptomatically is extremely rare. It is discovered accidentally, with the sudden onset of symptoms characteristic of complications of gastrointestinal tract or during examination for other reasons.
Diseases due to dysfunction of the sphincters
| Sphincter | Spasm | Insufficient valve function |
| Cardiac | Esophageal achalasia (food cannot pass through the opening that is too narrow and gets stuck in the esophagus). | Gastroesophageal reflux disease (heartburn), esophagitis (inflammation of the esophagus), reflux is often the cause of asthma and laryngitis. |
| Pyloric | Pylorospasm (tight compression of the sphincter) and, in a more advanced state, pyloric stenosis. | Gastroduodenal reflux (reflux of contents from the duodenum back into the stomach). With a long-term untreated condition, gastroduodenal reflux can cause the development of metaplasia, that is, when the gastric epithelium located near the sphincter degenerates into intestinal epithelium. Metaplasia is a precancerous condition and must be treated and monitored. |
Clinical manifestations of pyloric ulcers
An ulcer of the pyloric canal is found in approximately 8% of cases of peptic ulcers; it is characterized by a persistent course. It takes on average longer to treat an exacerbation of a pyloric gastric ulcer compared to other forms of gastric ulcer.
Pain in this form of pathology is paroxysmal in nature, attacks last up to 40 minutes. In addition to the night, hungry and late pain characteristic of lesions of the lower parts of the stomach, some patients experience pain that is in no way related to eating. It can be:
- moderate pain;
- repeated attacks;
- slowly intensifying and also slowly fading pain.
After eating, a feeling of fullness and distension occurs in the stomach area.
The course of the disease is accompanied by attacks of increased salivation, heartburn, belching and sour vomiting against a background of pain. After vomiting, the pain may subside for a while.
The dense network of vessels of the pyloric canal predetermines a high risk of bleeding. With a long-term course of peptic ulcer, pyloric stenosis often occurs. Frequent complications of this form of the disease include perforation (perforation) of the ulcer and penetration into the pancreas.
Penetration refers to the spread of the lesion to the tissue of a nearby organ. In addition to the symptoms of peptic ulcer, signs of pancreatitis appear. Occasionally, a stomach ulcer degenerates into a malignant tumor.