It is normal for your abdominal muscles to be moderately sore after strength training. The aching sensation is tolerable and does not cause concern for health. But it also happens that soreness in muscle tissue appears, seemingly for no reason. You should be wary if, in addition to pain, other symptoms occur, for example, weakness, increased body temperature, and abnormal bowel movements.
The abdominal muscles hurt as a result of an inflammatory, degenerative or purulent process. Pain will also be present if the tissues are injured. Abdominal wall tension occurs as a protective reaction of the body during surgical pathologies.
Myalgia
Myalgia (which means pain in muscle tissue) appears when the myocyte is overstrained, which leads to spasm and pain. Tone can be provoked by:
- vascular pathology;
- injury;
- viral infection (eg influenza);
- diseases leading to metabolic disorders (gout, diabetes);
- static loads;
- stress;
- forced uncomfortable positions (usually for this reason it hurts on one side, for example, on the right).
With myalgia, acute pain appears, unrelated to tension in muscle fibers or changes in posture; it does not go away even with complete rest. When blood circulation is impaired, the muscle fibers do not receive enough oxygen, which leads to impaired glucose output and the accumulation of lactic acid.
The acid contains hydrogen and lactate. Hydrogen does not allow the passage of a nerve impulse and affects the speed of contraction of the rectus and oblique muscles, which is why a burning sensation appears. Epidemic myalgia appears when infected with the Coxsackie virus.
The disease causes nausea, chills, and acute muscle pain, including in the abdomen and chest. Those affected experience redness of the throat, enlarged lymph nodes, and skin rashes. The duration of the pathology is up to seven days.
Myositis
One of the forms of myalgia is myositis. Fiber disruption is caused by an inflammatory process occurring in skeletal muscles. It is characterized by increased pain when moving, swelling and, rarely, redness of the skin.
Myositis is often a complication of influenza, acute respiratory viral infection or chronic tonsillitis, but can be caused by excessive physical exertion, mechanical trauma, deterioration of blood supply to tissues, exposure to toxic substances, autoimmune disease, and parasites.
It is assumed that myositis develops due to the action of bacteria on the muscles or due to the action of toxins released by them. Alcohol and cocaine can also provoke inflammation in the fibers; short-term damage can also occur when taking medications (colchicine, alpha-interferon, statins).
A purulent process may begin in the muscle fibers due to infection in an open wound, the presence of a chronic infection in the abdominal cavity, or non-compliance with injection rules.
There are 6 types of myositis:
- infectious non-purulent (develops with viral lesions, syphilis, bruzcellosis, tuberculosis) is characterized by severe pain in the muscle fibers and general weakness;
- acute purulent (diagnosed with purulent as well as necrotic processes) leads to swelling and pain at the site of the lesion;
- parasitic nature (against the background of an allergic reaction, more often develops with toxoplasmosis, echinococciasis, trichinosis, cysticercosis) provokes pain, local swelling, abdominal tension, weakness, low-grade fever;
- ossifying (appears after injury) causes degenerative processes and aching pain;
- polymyositis (formed in autoimmune diseases) provokes pain and growing muscle weakness;
- dermatomyositis. A disease that affects the skin, organs, abdominal muscles, pelvis, neck and shoulder girdle.
As a rule, inflammation affects the muscles of the neck, lower back, lower leg, chest, and much less often other muscle fibers, including the lateral and oblique abdominal muscles. Clinical symptoms include aching pain that increases with movement and touching the abdomen, and muscle weakness also appears.
Hyperemia and swelling in the area of the inflamed tissue, fever or low-grade fever, and headache may occur. The acute form of myositis mainly appears after trauma to the abdomen, excessive stress, or hypothermia.
Chronic forms against the background of infectious and toxic lesions and occurs with less severe symptoms. It reminds you of itself during static loads, overexertion, hypothermia, and weather changes.
If there is a fever, antipyretic drugs are prescribed. Analgesics can reduce pain, and anti-inflammatory drugs (Ibuprofen, Ketoprofen, Diclofenac) fight inflammation. After it has been established why the abdominal muscles hurt so much, antibacterial drugs, anthelmintics or others, that affect the source of infection are prescribed.
For local lesions, warming ointments are effective; due to their irritating effect, they help to relax, which reduces spasm. For purulent myositis, the lesion is opened and antibiotics are prescribed.
Lower abdomen hurts when tense
Hello!
The problem is this. A day ago, in the evening, my stomach became completely swollen (like a board). It became difficult to breathe. I breathe only with my chest. When I took a deep breath 2 days before, I sometimes felt a slight tingling sensation in the lower abdomen (near the inguinal lymph node). Today my stomach is just as bloated. It doesn't hurt itself. No temperature. No vomiting. No nausea. When you take a deep breath, there is no longer a tingling sensation. Gases go away. But I'm constipated all day. I sit on my buttocks and easily feel pain in the lumbar region from the left to the top and a little. Good afternoon. I have this problem, after doing abdominal exercises in the gym, pain appeared in the right side in the lower abdomen, which has not gone away for two weeks. I can't study. What it could be and what needs to be done. Thank you in advance! 18+ Online consultations are for informational purposes only and do not replace an in-person consultation with a doctor. User AgreementYour personal data is securely protected. Payments and site operation are carried out using the secure SSL protocol. Pain in the lower abdomen is a very common symptom, so it occurs in many diseases. It most often occurs in women, but men may experience pain in the lower abdomen. In addition, phantom pain also occurs - this is when the cause has been eliminated, but the woman still has unpleasant sensations. During the examination, the doctor should pay attention not only to general symptoms , but also to individual indicators, to the threshold of pain sensitivity.
Why does the lower abdomen hurt in women?
There are many reasons for this pain. They can be both organic and functional. The first often includes inflammation of the female organs . The latter usually include pathologies in the menstrual cycle. It is very important to correctly determine the cause of the pain, as it determines further treatment and its success. Common causes of severe pain in the lower abdomen include:
- The presence of pregnancy and the occurrence of associated complications
When carrying a child, a woman may experience frequent and severe pain in the lower abdomen. This is explained by the fact that the first few months the muscles eat to adapt to changes in the body. However, abdominal pain during pregnancy may also be accompanied by bleeding, placental abruption and indigestion. As for ectopic pregnancy, it is always characterized by severe abdominal pain. But after an abortion, such pain is normal.
- Pathologies of the genital organs
Frequent causes of this phenomenon can be inflammatory processes, infectious diseases that can be transmitted through sexual contact, or the development of uterine fibroids (benign formation). As for gynecological pathologies, their main difference is that pain occurs during menstruation or sexual intercourse .
- Urinary tract diseases
In connection with such pathologies, cystitis and the formation of kidney stones may occur. Accompanying symptoms: high temperature and a feeling of discomfort during urination. Pain in the lower abdomen in women can be caused by abnormal development of the genital organs. Congenital pathologies include: abnormalities in the structure of the genitals, the absence of part or all of an organ.
- Painful menstrual cycle
This is the most common reason and is not a deviation from the norm . Other less common reasons include:
- menopause;
- hypothermia or viral disease;
- climate change;
- oncological problems;
- stress, rape;
- adaptation after surgery.
What tests can be prescribed to diagnose the cause of pain in the lower abdomen?
Firstly, this is a general blood test . Using it, you can determine the presence of an inflammatory process. Secondly, urine analysis using microscopic examination. Such an analysis will indicate the condition of the urinary tract. Thirdly, ultrasound of the pelvic organs. Thus, it is possible to diagnose the presence of space-occupying formations. Fourthly, an x-ray of the abdominal organs. To do this, photographs of the abdominal cavity in different positions. This is necessary in order to determine intestinal obstruction, cyst rupture and the presence of kidney stones. Fifthly, this is laparoscopy. This procedure is carried out for the purpose of a comprehensive examination of the pelvic organs.
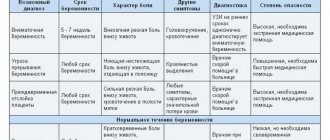
The main types of abdominal pain and their symptoms
Pain in the lower abdomen can be different: localized, paroxysmal, throbbing, constant. It is very important to know the nature of the pain in order to choose the right and effective treatment.
Pulsating type of pain
Pain of this nature can occur due to increased pressure in the genital organs , as well as due to an abscess of the ovaries.
Permanent
If you constantly have pain in your lower abdomen, then one of the reasons may be:
- myoma;
- risk of miscarriage;
- inflammatory processes of the walls of the uterus;
- the occurrence of postpartum pathology;
- disease of the abdominal organs;
- stress.
Paroxysmal
This type of pain requires immediate consultation with a doctor, as the causes may be:
- appendicitis;
- ectopic pregnancy;
- thrush;
- intestinal obstruction;
- placental abruption during pregnancy.
Local
If there is pain in the lower abdomen on the left, then it most likely could be inflammation of the appendage or a benign tumor in the form of a cyst that has grown. If we talk about an oncological tumor, then sharp pain will begin at a very early stage . Pain in the left lower abdomen can also be caused by various diseases of the stomach or the development of a hernia. If there is pain in the lower abdomen on the right and left, then the cause may be twisting of the cyst leg ovaries or inflammation of the appendages. If the pain is in the lower abdomen in the middle, then the cause may be diseases such as endometriosis, problems with the pancreas. In addition, it should be noted that local pain can radiate to the lower back and anus. If the lower abdomen hurts severely and periodically radiates to the lower back, then this may be a symptom of the postpartum period. This pain may indicate that the intervertebral discs are injured or there is a urinary tract disease. But if the pain radiates to the anus, then this is a symptom of an ectopic pregnancy. The list of natural pains includes:
- discomfort during ovulation;
- during menstruation;
- discomfort in the first days after the birth of a child
However, if such natural pain is very intense and lasts for a very long time, you should immediately consult a doctor. It should be noted that pain in the lower abdomen can be combined with many other symptoms. These include: weakness, chills, nausea and vomiting, as well as fever and the possibility of purulent discharge.
Source: https://limto.ru/bolit-niz-zhivota-pri-naprjazhenii/
Muscle pain during pregnancy
Pregnant women often report that the muscles in their lower abdomen hurt. The symptom is caused by natural muscle stretching. More often, such pain occurs after the 26th week of pregnancy, since the stomach is already large and the muscles are not adapted to the load. Pain is felt in the rectus abdominis muscles, running from the ribs to the pubic bone, as they support the uterus and the growing baby.
In order to prevent the occurrence of microtraumas of muscle tissue, with the permission of a doctor, it is necessary to do special gymnastics for pregnant women. If the pain does not go away or is very severe, then you need to tell the doctor monitoring the pregnancy about this.
The cause of abdominal tension can be pathological processes that threaten the life and health of the mother and child, for example, rupture of cysts or uterine fibroids, inflammatory processes, placental abruption. Pain in the abdominal muscles during pregnancy will decrease if you wear a bandage. It will reduce the load on the lower abdomen.
What are the consequences of abdominal muscle strain?
An abdominal muscle strain is an injury that affects the internal structure of the abdominal muscles. With this diagnosis, the patient experiences tears or stretching of muscle tissue. In the vast majority of cases, such injuries can cause discomfort.
In such a situation, a stretch of the abdominal muscles is an injury to the muscle fibers of the lateral, anterior or posterior muscles of the peritoneum, which occupy the area between the upper part of the pelvis and the lower contour of the part of the body limited by the ribs.
Degrees of abdominal muscle stretch
Diagram of abdominal muscles
Experts distinguish 3 degrees of abdominal wall muscle strain:
- Moderate, when mild pain subsides within a few days.
- Average degree. Symptoms go away within a couple of weeks. In this case, patients require qualified medical care. Recovery of such patients can be observed after 3-6 weeks.
- Abdominal muscle rupture. In this situation, the patient experiences excessive pain on the left or right side of the abdomen. In this case, the stretched muscle can no longer contract. This type of lesion occurs due to very strong pressure on the rectus abdominal wall muscles. Typically, the rupture occurs in the connecting bridge of the muscles that make up the wall of the abdominal cavity. In some circumstances, when there is a rupture of the abdominal wall with displacement of internal organs, urgent surgical intervention is required. Treatment of such patients can take an average of 3 months.
Abdominal muscle strain: possible causes
Performing physical exercises without previously warming up the muscles
As experts note, there are a number of provoking factors that increase the likelihood of receiving this type of injury (abdominal muscle strain).
These include overstrain or not very good stretching of muscle fibers, weak muscles, fatigue, as well as performing sports exercises in the cold.
If we talk about the main reasons for this problem, they include:
- excessively heavy physical activity;
- strong twisting movements of the body;
- performing physical exercises without prior warming up the muscles;
- lifting excessively heavy things;
- incorrect exercise technique;
- insufficiently well developed muscle corset;
- pregnancy.
Signs of damage
Often, the symptoms that appear with this type of injury may indicate some other health problems. Only the attending physician can make a final diagnosis. The following symptoms of abdominal muscle strain are distinguished:
- pain in the abdominal wall;
- a feeling of discomfort in abdominal tissues that can contract;
- pain when touching muscle tissues, when they are tense or when the body is bent;
- muscle spasms;
- formation of hematomas;
- swelling on the right or left side of the abdominal wall, depending on which abdominal muscles are injured.
Abdominal pain with abdominal muscle strain
Treatment of injury
If one of the peritoneal muscles is stretched, then treatment will directly depend on how pronounced the symptoms of the disease are and the degree of injury suffered. Thus, the degree of stretching of the abdominal wall muscles will determine the duration of therapy.
The key point for such patients is complete rest for the abdominal muscles and the absence of even the slightest stress. At home, the patient should avoid heavy lifting and sudden movements, which increase muscle tone. This is especially important during the first two days after the injury.
If the patient has suffered moderate to severe sprains, then in this case experts recommend applying cold to the injury, which must be done in sessions lasting 15-20 minutes. After they expire, you should take a break.
In order to apply cold to the injury, you can use ice cubes wrapped in cellophane and a towel. It is not recommended to apply them directly to a bare area of the body.
Abdominal muscle strain: tips
In order to relieve unbearable pain, the attending physician may prescribe anti-inflammatory drugs and analgesics in the form of tablets, injections or ointments. This will significantly alleviate the patient’s condition and improve his well-being.
In order to get back into shape after an injury, the patient will have to make some efforts.
Do not forget that if sharp painful sensations occur as a result of lifting heavy objects or performing sports exercises, you must immediately stop the load on the body.
Physical activity should be limited or completely suspended. This will depend on the severity of the injury.
At the same time, during the period of treatment and restoration of health, it is recommended to rest regularly, apply cold compresses for 1-2 days after the injury, do not refuse to take painkillers, and gradually stretch the abdominal muscles when the pain begins to recede.
Prevention of abdominal muscle strain
To avoid such injuries, experts recommend following some rules:
- It is imperative to warm up before starting physical exercise.
- Do not overexert yourself when doing exercises.
- Do not lift heavy objects suddenly.
- You should stop exercising if you feel tired.
- It is necessary to strengthen the abdominal muscles by performing special exercises.
There are also a number of exercises that can strengthen your abdominal muscles, which will help you avoid straining and tearing your abdominal muscles in the future.
A pulled abdominal muscle can be a fairly serious injury. At the same time, if the human body is prepared and physically strong, which regular exercise can achieve, the likelihood of such an injury is practically absent.
Therefore, it is very important to play sports from a young age. And here we are not talking about any serious physical activity. It will be quite enough if you at least do certain exercises at home.
Source: https://nettravm.ru/rastyazhenie-bryushnyh-myshts/
Diastasis
Diastasis occurs when the linea alba (the junction of the broad muscles) separates. The reasons are pregnancy and childbirth, heredity or obesity. Diastasis recti can occur in men and children.
During pregnancy, the connective tissue between the vastus muscles becomes loose so that the belly can expand. After childbirth, the tissue itself strengthens and the shape of the abdomen is restored within a year. But if a woman works hard on her abs or lifts weights, the tissue does not contract.
Pathology appears with obesity or sudden weight loss, when the connective tissue does not have time to contract, which leads to its “excess”. Muscle divergence also causes an increase in intra-abdominal pressure, for example, a hacking cough, heavy lifting, constipation, or playing sports.
With dysplasia, the structure of ligaments and tendons is disrupted, which leads to excessive extensibility of the connective tissue and provokes the occurrence of diastasis or the formation of hernias. Pain in the abdominal muscle fibers when impaired can vary in nature, strength and duration. The pain often intensifies with prolonged walking, physical activity, and heavy lifting.
With diastasis, muscle fibers are weakened and do not perform their function, so pain can appear even with little physical activity. Due to improper distribution of the load, internal organs may become mixed up, an umbilical hernia may form, digestion problems may occur, and pain in the spine may occur.
If your abdominal muscles hurt due to exercise, no special treatment is required, since the symptom will go away on its own in 1-2 days. You can reduce pain by doing a massage or taking a contrast shower. Tension of the abdominal muscles is one of the symptoms of an “acute abdomen”, which requires surgical intervention.
Therefore, if your abdominal muscles hurt severely for no reason (you have not previously engaged in physical labor or exercise), and there are other symptoms, for example, nausea, general weakness, fever, abnormal bowel movements, then you need to seek medical help. Only after finding out the causes of long-term or periodic muscle pain can you understand what needs to be done to eliminate them.
Muscle pain is a normal condition after physical activity. But it happens that the rectus or internal oblique abdominal muscle hurts for no apparent reason. And if you look closely, you can find additional symptoms of an unpleasant condition, indicating the development of certain diseases.
Partial rupture of muscles, ligaments and tendons - symptoms and treatments
Most muscle tears are caused by over-straining the muscles during movement or during repetitive movements.
However, there are risk factors that may predispose to muscle rupture:
- Lack of adequate preparation of muscles for the expected load.
- Excessive fatigue of the muscles, to the point that they are unable to withstand the effort.
- Hard training after a long rest from training.
Another possible cause of muscle tearing is indirect trauma or bruising, that is, when the muscle is hit hard by something. For example, when during football a player receives a strong kick from another partner, which leads to damage to muscle fibers.
The disease is more common in women. The predominant form is diastasis of the rectus abdominis muscles after childbirth.
The most dangerous time for this is the first months. The likelihood of developing pathology increases after a cesarean section, since this disrupts the integrity of the muscle aponeurosis and its ability to contract decreases.
Muscle pain in the abdomen in women and men is also called abdominal pain syndrome. It is also worth noting that gastrointestinal dysfunction is not always the root cause of the formation of abdominal pain, when the abdominal muscles are very sore. In some cases, we can talk about organic, functional, dynamic factors.
The reasons why the muscles in the abdominal area are very sore can be caused by the following problems:
1 Abdominal muscle rupture, ligament rupture. A muscle rupture in the abdomen or ligaments that results in severe muscle pain may be complete or partial.
The main cause of abdominal muscle strain is excessive tension. This can happen due to excessive overvoltage when too much load is applied.
Excessive tension can also be caused by injury or sudden abnormal movement of the body along its axis. This typically occurs due to lifting, pushing, or pulling heavy objects.
Sports activities can cause tension in the abdominal muscles. Peritoneal spasm can occur during breaststroke, ice skating, or playing hockey.
Abdominal spasms can occur when an obese person tries to perform movements that are unusual for him. Even minor deviations from the norm, such as a hacking cough or continuous sneezing, can cause tension and spasm of the abdominal muscles.
Types of Muscle Tears
Depending on the clinical signs, the following degrees of diastasis of the rectus abdominis muscles are fairly conventionally distinguished:
Tension or spasm can be broadly divided into three types of pain. It all depends on the severity of the sprain and muscle damage.
Symptoms of a sprain
A muscle rupture may appear at first even without pain. However, later severe acute pain appears as the main symptom, which may be joined by other symptoms, including:
- Swelling, redness and severe burning of the affected area.
- The presence of edema, that is, accumulation of fluid at the level of the damaged muscle.
- Formation of a hematoma due to rupture of muscle vessels.
- The appearance of failures with a complete rupture of the muscle.
- Sometimes the presence of fever.
MORE ABOUT: How to treat a hand bruise: the limb is swollen - what to do?
According to their course, the symptoms of pain in the abdominal area that appear in the muscles can be of the following types: surgical pain, that is, requiring urgent surgical intervention, the so-called acute pain.
There are also acute non-surgical abdominal pain, chronic functional abdominal pain and organic chronic abdominal pain.
Symptoms of pain in the abdominal muscles:
1 Acute pain - usually appears very quickly, almost spontaneously and continues for a long time
2 Chronic pain in the abdominal muscles - usually develops due to the presence of severe sprains
3 Pain that appears in the abdominal muscles due to disruption of natural blood circulation. Such abdominal pain is usually of a bright, paroxysmal nature.
4 Abdominal cramps and colic, severe pain in the abdominal area. Typically, such pain appears spontaneously, without any previous symptoms. Spasms can radiate to the legs, back, lower back, and are often accompanied by headaches.
As a result of a sprain, a person begins to experience sharp pain in the area where the muscles were damaged. The pain may be so severe that the person cannot contract the abdomen. When you try to do this, the pain intensifies many times over.
Diagnostics - how to determine a muscle tear
A doctor can diagnose a muscle tear by:
First of all, to diagnose pain in the abdominal muscles, it is necessary to completely eliminate all possible physical strain and stress. Any workouts should be cancelled, stop carrying weights.
If such symptoms appear in a woman, the doctor can conduct a pregnancy test.
Next, the doctor usually prescribes a blood test, which measures the level of white blood cells in the blood. A urine test is also prescribed to exclude possible pathologies of the urinary system.
Diagnosis of the cause of abdominal tension can generally only be done through a physical examination. Indirect signs of tenderness, such as swelling, functional loss of muscle strength in a specific area, indicate injury to the abdominal muscles.
A muscle rupture, a hernia and the presence of a gap felt upon touch, upon palpation, clearly indicate the presence of an injury. Hardware diagnostics will help make a more accurate diagnosis. This includes magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), ultrasound or CT.
Exercises
The disease is prone to progression. Often, a late visit to a doctor leads to the need for surgical intervention.
Indications for surgery:
- the duration of diastasis for more than a year and the ineffectiveness of conservative methods;
- Stages 2 and 3 of pathology.
At the medical institution, the attending physician will conduct a thorough diagnosis and examination. Hardware studies such as x-rays, computed tomography of the abdominal cavity and herniography (if a hernia is suspected) may be needed.
If the abdominal muscles are damaged, the patient is provided with emergency care, and further treatment is carried out on an outpatient basis.
If there is an umbilical hernia, then surgical intervention is not excluded. Surgery is performed only after a thorough diagnosis and in the absence of contraindications. Tension hernioplasty and mesh hernia repair can be used to treat hernias.
You can repair the tear yourself if you have the appropriate skills. To do this, place the victim on a flat surface and, through careful palpation, feel the displaced organ.
Then, using pulling movements, carefully move the hernia down from the stomach. The air hernia is removed using spiral movements.
If there is no pain, the entire manipulation is carried out in several steps.
The main treatment is to reduce swelling, pain and bleeding. Treatment of the abdominal muscle is complicated, first of all, by the fact that complete relaxation in this area is impossible.
Therefore, a person should take a lying position in which the abdomen does not stretch. This will relieve the pain to some extent.
The duration of treatment directly depends on the severity of the injury.
In the first two types of tension, applying ice is enough to relieve pain. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs relieve pain within the first two days. MORE ABOUT: How to treat vegetative vascular dystonia
If the pain is significant, the doctor may prescribe pain-relieving injections. Sometimes an elastic bandage is loosely wrapped around the abdomen to limit movement and provide relief.
Muscle rupture is considered a serious injury and cannot be avoided without surgical intervention.
Abdominal muscle strain can be avoided by strengthening your abdominal muscles with proper exercises. It is equally important to perform these exercises correctly. If possible, do this under the guidance of a good trainer. And then tension, spasms, sprains will not be scary for you.
First aid: what to do
If symptoms of abdominal tearing appear, first aid should be provided to the victim:
- Provide the patient with a comfortable position, preferably horizontal. It is advisable to relax the abdominal muscles as much as possible. The surface must be smooth and hard. There is no need to put a pillow;
- It is necessary to fix the affected area. The victim's arms should be placed along the body. Under the lower back you need to place a dense fabric folded several times, and the strip should not be more than 30 cm. Fixation is done by turning the bandage near the groin, along the navel and, if long enough, under the diaphragm. The bandage should be tight, but not tight;
- If the pain is unbearable, the use of a cooling compress and painkillers are allowed.
You should be especially careful when applying a bandage to a woman, as there is damage to the reproductive organs. After carrying out all the necessary actions, the patient should not stand up straight, but carefully from the side.
Of course, you should never engage in self-diagnosis, much less treatment. Therefore, the best help for the victim is to call an ambulance or transport the patient to the nearest medical facility.
Pain in the abdominal muscles during pregnancy - what could be the complications and consequences?
The main threat that appears with symptoms of pain in the abdominal muscles during pregnancy is abortion, the risk of miscarriage. Also, the main possible complications that are accompanied by pain in the abdominal muscles during pregnancy include uterine rupture, placental abruption, pyelonephritis (acute), fibroids , ectopic pregnancy of a woman, rupture of an artery (rupture of an aneurysm), hematoma that forms in the abdominal muscles.
During a tear, the navel is displaced, which leads to various kinds of pathological conditions. Moreover, these consequences may manifest themselves differently in men and women.
Source: https://momentpereloma.ru/rastyazheniya/kak-proyavlyaetsya-i-lechitsya-rastyazhenie-myshc-zhivota/
Common causes of abdominal muscle pain
The most common situation is pain in the abdominal muscles associated with natural physiological causes: overexertion, sports, sudden stretching. However, there are also pathological factors that lead to discomfort:
- Stretching of organ walls. Pain in this area may result from an increase in the size of the stomach, intestines and arteries. These processes occur not due to overeating, but due to dangerous pathological processes, as well as during pregnancy in women. Symptoms of organ stretching affect only smooth muscles, and the pain is called visceral.
- Mechanical damage to muscle tissue. If there is a strong blow to something, or a person is pierced with a sharp object, the muscle tissue tears, swells, and pain appears.
- Psychological disorders. Some people experience muscle pain as a result of stress and overexertion.
- Dysbacteriosis. One of the reasons for the increase in intestinal size. With dysbacteriosis, the organ becomes greatly stretched, symptoms such as constipation or diarrhea appear, the temperature rises, and nausea occurs.
If you have chronic diseases, you can suspect their exacerbation when pain appears in the rectus or oblique abdominal muscles.
Abdominal muscles hurt – oblique abdominal muscle hurts, causes and treatment
Usually, painful sensations in the abdominal cavity are associated with pathology of the internal organs, for which you should urgently consult a doctor. However, everyone knows that discomfort is often caused by pain in the abdominal muscles.
It should be noted that this problem is faced not only by athletes, but also by ordinary people who, due to certain circumstances, have to engage in physical labor.
Muscles can ache in the same way both after abdominal exercises and after long work in the garden, since in both cases the same mechanisms are triggered.
Spread of pain from the rectus abdominis muscle
Myofascial trigger points located in the abdominal muscles may present with referred pain, which can be difficult to diagnose. False visceral pain, manifested from myofascial trigger points embedded in the abdominal muscles, can arise not only in the same segment of the abdominal wall; in addition, it can also radiate to the back.
Painful sensations caused by trigger points are often accompanied by somatovisceral reactions, in the form of violent vomiting, nausea, loss of appetite, intestinal colic, loose stools, spasm of the sphincters and bladder, and menstrual irregularities.
Such symptoms, accompanied by abdominal pain, may resemble acute diseases of the internal organs, for example, cholecystitis or appendicitis.
The rectus abdominis muscle is attached inferiorly along the crest of the pubic bone, with intertwining fibers at the level of the symphysis. At the top, the rectus abdominis muscle is attached to the cartilages of the ribs V, VI and VII.
The fibers of this muscle are interrupted by three or four transverse tendinous septa, one of the three permanent septa located near the apex of the xiphoid process, another at the level of the umbilicus, and the third septum located midway between them.
In some cases, there are also one or two bridges, partially formed, and they are located below the navel.
The fibers of the upper rectus abdominis muscle can sometimes overlap the abdominal portion of the pectoralis major muscle, which can cause pain caused by myofascial trigger points in this area and radiating down the front of the chest.
The functions of the abdominal muscles are aimed mainly at increasing intra-abdominal pressure, flexion and rotation of the spine.
The rectus abdominis muscle is the primary mover, providing flexion of the lower thoracic and lumbar spine.
The rectus abdominis muscle is largely involved in the tension of the anterior abdominal wall, thereby causing an increase in intra-abdominal pressure.
A single group of muscles of the abdominal wall of the abdomen is involved in the implementation of rapid and complete exhalation during rapid breathing, helping to drive blood from the veins of the abdomen to the heart. When the abdominal wall relaxes at the moment of inhalation, blood flow in the abdominal veins increases, which stimulates the outflow of blood from the lower extremities.
When exhaling, in the absence of pathology of the valves of the veins of the lower extremities, the muscles of the abdominal wall contract and the blood tends upward to the heart.
The rectus abdominis muscle responds during walking to each step cycle during walking.
The rectus abdominis muscle is actively involved during a jump at the moment the feet lift off the support, but is not always active when landing.
When walking uphill, the abdominal muscles will be more active than when walking on the plain.
The rectus abdominis muscles, when flexing and extending the spine, are antagonists of the group of paravertebral muscles, especially the latissimus dorsi, and are synergists with the iliopsoas muscle, acting together during flexion of the lumbosacral region.
Due to menstrual cramps
This is one of the most common causes of regular discomfort in the lower abdomen in women. The uterus contracts to expel the unfertilized egg and endometrium, and this sometimes results in pain that resembles mild cramping.
What to do about it
Most often, menstrual pain does not require treatment, you can simply endure it. If you don't feel like it, take an over-the-counter pain reliever like ibuprofen or paracetamol. And consult a gynecologist if ailments during menstruation are poisoning your life. The doctor will prescribe a more effective remedy or suitable hormonal contraceptives.
Due to endometriosis and other diseases of the uterus, ovarian cysts
Also a common purely female problem. With such diseases, nagging discomfort in the pelvic area is not necessarily associated with menstruation: they can appear at any time of the cycle. Menstruation with such disorders lengthens and becomes more painful.
Due to ectopic pregnancy
During an ectopic pregnancy, the fertilized egg implants and begins to grow not in the uterus, as it should normally be, but in the fallopian tube, cervix or ovary. This does not lead to anything good: sooner or later, the growing embryo breaks the walls of the organ to which it is attached. The result is massive and deadly internal bleeding.
Due to increased gas formation
When bacteria in the small intestine break down incoming and partially processed food, they release carbon dioxide and other gases. If there is too much gas, pressure in the intestines increases. Parts of the small intestine dilate, pressing on nerve endings in the abdominal cavity, causing bloating and pain, sometimes severe.
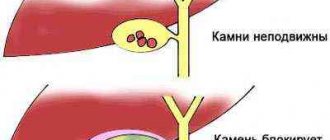
Due to stones or kidney disease
Pyelonephritis, urolithiasis or other kidney disorders cause sudden, excruciating pain in the lower abdomen, closer to the lower back. This pain waxes and wanes.
What to do
If you suspect something wrong with your kidneys, go to a nephrologist as soon as possible. The doctor will make an accurate diagnosis and prescribe the necessary medications. In some cases, you may be hospitalized for surgery.
Due to urinary tract and bladder infections
Most often, such disorders make themselves felt by problems when urinating: burning sensation, cutting pain, frequent urge to go to the toilet.
Due to muscle pain
Perhaps you just tried too hard to pump up your lower abs. Or they overextended their abdominal muscles by singing along to their favorite band at a concert too actively. Myalgia (as muscle pain is called) can also be caused by other reasons that cannot always be determined.
Due to appendicitis
A ruptured appendix begins with a nagging pain in the navel or right lower abdomen, sometimes radiating to the thigh. If, with such symptoms, your temperature rises, your appetite disappears, nausea and bloating appear, the diagnosis of “appendicitis” becomes more and more real.
Due to inflammatory bowel disease
A variety of factors can lead to inflammation of the intestinal mucosa:
- bacterial or viral infections (swallowed lake water or ate an expired product);
- food and alcohol poisoning;
- the influence of parasites - the same helminth worms;
- antibiotic abuse;
- diseases of the gastrointestinal tract - gastritis, pancreatitis, cholecystitis, ulcerative colitis, Crohn's disease, hepatitis.
As a rule, inflammatory bowel lesions are accompanied by diarrhea or constipation, bloating, nausea, and fever.
Due to bowel cancer
This deadly disease hardly makes itself felt in the initial stages. It is manifested only by some discomfort, slight pain in the abdominal area, and symptoms - often not very pronounced - of digestive disorders.
Innervation of the rectus abdominis muscle
The rectus abdominis muscle is innervated by 7-12 intercostal nerves, originating from the corresponding spinal nerves. The muscle fibers between the different tendon bridges are innervated by the nerves of different segments, especially in the upper half of this muscle.
Inside the rectus abdominis muscle or in its transverse sheath, compression of the anterior branch of the spinal nerve can occur, thereby provoking true rectus abdominis syndrome, which is characterized by pain in the lower abdomen or pelvic area, simulating a gynecological disease in women.
Pathologies that provoke myalgia
Myalgia is pain in muscle tissue, which is accompanied by spasms. Among the most common diseases that cause myalgia in the rectus and oblique abdominal muscles are:
- pathologies associated with metabolism - diabetes, gout, metabolic syndrome;
- viral infections – for many people, one of the first symptoms during the flu is muscle pain;
- vascular disorders, including aortic aneurysm.
However, myalgia can also be triggered by such trivial factors as prolonged stay in an uncomfortable position.
Myalgia can be distinguished from simple tension by such a sign as long-term persistence of pain. The symptoms in this case do not go away after rest, as they are associated with more serious processes. With myalgia, a burning sensation, nausea, and chills often occur.
Myositis as a form of myalgia
Myositis is an inflammation that occurs in skeletal muscles. One of the most serious forms of myalgia, which can be associated with serious diseases of the musculoskeletal system. But in some cases, myositis develops as a result of ARVI, tonsillitis, or with excessive physical exertion.
Some forms of myositis are thought to develop due to exposure to bacteria and toxins. This condition can be caused by abuse of alcohol, cocaine, and certain medications (statins, interferons, colchicine).
With myositis, a purulent process begins in the muscles, associated with chronic infections in the abdominal cavity. Symptoms rarely affect only the abdomen: not only the external oblique muscle hurts, but also the fibers of the neck, lower back, lower leg and chest. Myositis is accompanied by swelling, fever, fever and headaches.
Causes of muscle pain not associated with myositis
Acute muscle tension can occur in the following conditions when the abdominal wall becomes hard:
- inflammation of the appendix - pain is usually located on the right in the iliac region;
- intestinal obstruction – combined with symptoms of acute intoxication, accompanied by prolonged constipation and a strong increase in the size of the abdomen;
- perforation of the ulcer - acute dagger pain is associated with gastric bleeding, blood is present in the vomit and stool;
- vascular accidents - infarction of the intestines and other organs, thrombosis;
- acute cholecystitis - pain is located on the right hypochondrium, requires immediate surgical assistance;
- acute pancreatitis - symptoms are similar to cholecystitis, but the pain can be localized on the left;
- rupture of the fallopian tube during an ectopic pregnancy - the woman’s well-being rapidly deteriorates;
- rupture of an abdominal aortic aneurysm - a person feels acute diffuse pain;
- inflammation of the ovaries or uterus - endometritis, adnexitis, as well as hemorrhage in the ovary.
All these pathologies require immediate surgical care - when the first signs appear, you should consult a doctor. These symptoms are usually distinguished by unbearable pain, pallor, vomiting and nausea, fainting and bloody discharge in women.
Other conditions in which pain in the rectus abdominis muscles are severe include: strangulation of an umbilical or inguinal hernia, acute strain of the muscles of the anterior abdominal wall as a result of lifting heavy objects or injuries. Similar symptoms can be observed in people with diseases of the spine: tuberculosis, spondylolisthesis, osteochondrosis, trauma.
Features of pain during pregnancy
In pregnant women, constant pain in the oblique or rectus abdominal muscles may be associated with some serious abnormalities:
- Placental abruption. The pain is severe, localized at the bottom, often combined with bleeding and watery discharge. There is a high risk of fetal death as a result of hypoxia.
- Risk of miscarriage. The pain is combined with small amounts of blood, and a pulling sensation appears in the lower back.
- Ectopic pregnancy. The pain is very strong, radiating to the groin and back, the symptoms are localized on the left or right side - depending on where the egg is implanted.
- Digestive system disorders. Due to compression of the intestines and stomach by the growing fetus, constipation, flatulence, and bloating often occur.
- Stretching the abdominal muscles. This is a normal process that intensifies in the 3rd trimester.
Pulled stomach what to do: treatment and prevention
The human body consists entirely of muscles, ligaments and tissues, which are subject to various injuries in everyday life.
The abdomen is no exception, a sprain of which is understood as an injury characterized by a tear or rupture of the muscular structures of the abdominal cavity.
Since in the vast majority of cases such injuries are accompanied by unpleasant symptoms that cause discomfort, it is important to begin treatment measures in a timely manner.
Causes
Overstrain of the abdominal muscles, causing sprains, occurs due to the influence of the following factors:
- unusual increased physical loads that have a negative effect on unprepared muscles.
- incorrect execution of exercise techniques during sports activities.
- if you lift too heavy objects for a long time and a lot.
Risk factors
A special category of the population that is more susceptible to abdominal muscle strains are those who have:
- weak muscle extensibility;
- muscle strain;
- weakened back muscles;
- chronic form of fatigue.
Symptoms
If a person has pulled the abdominal muscles, then the general symptomatic signs are as follows:
Click on the picture to enlarge
- Discomfort in the injured area.
- The occurrence of severe pain when trying to bend the torso or strain muscle tissue.
- Increased pain in a sharp direction when touching the affected area.
- Spasmodic phenomena.
- The occurrence of severe swelling and hematoma, which is typical for serious injuries.
If a microtear occurs in the tissues, then all the symptoms described above intensify significantly and begin to be pronounced.
Degrees
Also, the severity of signs of sprain depends on the degree of injury:
Light
Does not require special treatment. All unpleasant sensations and conditions disappear on their own after a week. However, such a favorable outcome is possible if a gentle regimen is strictly observed.
Average
It is characterized by a moderate degree of symptoms that, at best, subside after a couple of weeks. Some patients require specialized treatment.
Interesting Basic actions if a child is choking
Heavy
In this case, the abdominal muscles rupture, which manifests itself in pronounced and intense symptoms. In the vast majority of cases, there is a rupture of the connective tissue, which is deprived of the ability to contract. Treatment measures can be conservative or surgical, but in both options the rehabilitation period lasts several months.
Treatment
Therapeutic measures to restore abdominal muscles should be characterized by an integrated approach:
- Peace. It assumes the absence of even minimal stress on the abdomen in order to provide the muscles with complete rest. In everyday life, you should not lift heavy objects, make sudden movements, or carry out activities that provoke muscular contraction of the peritoneum. This gentle regimen is especially important to follow during the day after injury.
- Cold compresses. Useful for severe or moderate severity. Cold exposure should last at least 20 minutes, after which hour breaks should be taken. As a compress, the ideal option is ice, which must first be wrapped in a towel before applying to the skin. It is not recommended to use ice in its pure form, since then completely different reactions occur that are not aimed at alleviating the condition. If ice is not available, compresses can be made using frozen food bags or cold water.
- Medications. To relieve painful symptoms, anti-inflammatory painkillers are used, which can be used in different forms. Good painkillers are Acetaminophen and Ibuprofen. To reduce external skin damage resulting from stretched abdominal muscles, it is advisable to use special healing creams.
- Exercises. After eliminating painful sensations, it is recommended to carry out stretching procedures aimed at restoring abdominal tissue. For this purpose, it is necessary to do special exercises, the complexity of which should increase over time.
Prevention
To prevent another abdominal muscle strain, you should take note of the following useful tips:
- Before you begin training related to physical activity, you need to thoroughly warm up, thereby warming up all the tissues and ligaments of the body.
- During training sessions, you should not overexert yourself. To do this, it is important to be able to calculate your strengths and capabilities.
- Exercises aimed at strengthening the abdominal muscles will be useful.
- If you want to lift very complex objects, you should first familiarize yourself with this technique, and the first lesson is best done under the supervision of a trainer or a more experienced friend.
- If you feel tired, you must immediately stop the training process.
Source: https://vseopomoschi.ru/prochee/potyanul-zhivot-chto-delat.html
Methods of diagnosis and treatment for muscle pain
Diagnosis of pain in the abdominal muscles occurs in several stages. The first is palpation. The doctor determines the condition of the abdominal wall. Next, they take blood and urine tests, and also do an ultrasound. In some cases, x-rays and an ECG are required.
Treatment methods depend on the type of disease. Gynecological disorders are treated by a gynecologist; for gastrointestinal diseases, therapy is prescribed by a gastroenterologist. In acute conditions, surgical intervention is often required, followed by antibacterial therapy: removal of a ruptured ovary and fallopian tube, elimination of an inflamed appendix.
Symptomatic therapy includes taking antispasmodics, NSAIDs, probiotics, and anti-inflammatory drugs when necessary. Be sure to prescribe a gentle diet to avoid unnecessary stress on the internal organs.
To prevent pain, it is important to monitor your health and treat chronic diseases in a timely manner. You should not overexert yourself when playing sports; you should always warm up before training. To prevent pain from appearing, you need to train different muscle groups on different days.
Why else can your abdominal muscles hurt?
Some people who don't exercise may also suffer from abdominal muscle pain due to a relatively rare condition called myositis. This pathology is characterized by inflammation of muscle fibers due to an infectious, autoimmune or post-traumatic process.
Pregnant women often face this problem: their lower abdomen hurts when they stand up or sit down. As a rule, this occurs in late pregnancy and is associated with pressure from the enlarged uterus on the internal organs.