Basic rules of nutrition for gastroduodenitis
The diet requires adherence to certain nutritional principles:
- it is necessary to chew solid food thoroughly - this approach to eating will help the digestive tract digest it quickly;
- you need to eat five to six times a day at regular intervals and the portions should be small;
- food should not be too hot or too cold;
- food should be well boiled or steamed, liquid or mushy consistency.
As the disease worsens, the usual diet becomes stricter, and during remission, some dietary restrictions are lifted.
Also, during an exacerbation, foods that stimulate the secretion of gastric juice are excluded from the diet;
As the pain passes, the gradual introduction of dishes begins, the composition of which is close to the normal physiological needs of the body. For example, meat can be eaten in the form of meatballs. Gradually, a person switches to regular, unprocessed food. You are allowed to eat a small piece of boiled lean meat or a small piece of boiled fish. Limit fresh fruits and vegetables, as they contain a lot of fiber.
Sadly, it is not only older people who suffer from the symptoms that appear with gastroduodenitis; they are also typical for children. And the number of children suffering from this disease is increasing every year.
The main cause of the disease is poor diet. Basically it's eating dry food, overeating, eating hastily. There is a huge temptation to eat all kinds of crackers, chips, and nuts. And when preparing these products, an excessive amount of salt is used, which leads to a deficiency of vitamins and microelements in the body.
Symptoms
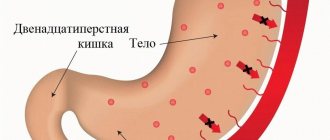
Gastroenterologists distinguish acute and chronic forms. Acute erosive gastroduodenitis in its manifestations is “closer” to simple acute gastritis, chronic - to peptic ulcer. This means that the symptoms resemble those of these two diseases.
Gastrointestinal manifestations
More typical for acute erosive inflammation, the manifestations are:
- pain occurs after eating poor-quality food or getting toxins into the digestive tract;
- pain in the upper half of the stomach and nausea exclusively in the morning and in the first half of the day - gastroduodenitis can be distinguished from an ulcer by the time of pain onset;
- pain occurs immediately after eating or shortly after it;
- heartburn and sour belching after eating;
- periodic bloating;
- vomiting mixed with small blood clots - looks like coffee splashes, since the blood is treated with hydrochloric acid, the blood appears with multiple erosions;
- black feces - an admixture of blood due to numerous erosions;
- decreased appetite is not a necessary sign;
- the addition of cholecystitis and pancreatitis does not happen to everyone.
Acute inflammation occurs suddenly, forming within one or two days. With an exacerbation of the chronic process, the manifestations are less pronounced, but pain, nausea, vomiting and bowel disorders almost always occur.
Extraintestinal manifestations
They are more characteristic of chronic erosive gastroduodenitis. The patient is concerned about unclear symptoms; the person learns about the disease after examination. The following manifestations are of concern:
- weakness, fatigue;
- difficulty falling asleep, decreased sleep duration, tendency to insomnia;
- rapid heartbeat and dizziness due to anemia, which gradually develops from constant mild bleeding;
- astheno-neurotic symptom in the form of headaches, increased irritability, exhaustion, decreased ability to work.
We recommend reading:
H2-histamine blocking drugs and their use in gastroenterology
Quite often, patients begin to suspect a chronic disease of the digestive canal only after black feces appear. The unusual color of excrement and a general deterioration in health prompts a visit to the doctor.
What can you eat if you have gastroduodenitis?
For patients with a diagnosis such as gastroduodenitis, a diet designated as table No. 1 (with high acidity), diet No. 2 (with low acidity) and diet No. 5 is provided.
Table No. 5 normalizes the functioning of the liver and bile ducts, promotes bile secretion. If you have severe pain due to gastroduodenitis in the first week, the doctor will prescribe you a diet with severe restrictions. During this period, baked goods, raw vegetables and fruits are completely excluded. All dishes are only in ground form.
For gastroduodenitis with increased acidity of gastric juice, use table recipe No. 1.
In this case, you need to adhere to the following rules:
- Cooking boiled, steamed and pureed dishes. Fried foods and smoked foods are prohibited;
- The white bread you eat should not be fresh. It's better to eat crackers. Buy only biscuits;
- During an exacerbation, soups made from well-cooked, pureed cereals and vegetables are allowed (an exception is made for cabbage). Cereals include rice, buckwheat, oatmeal, and semolina. Vermicelli choose small ones. You can eat baked or boiled potato, pumpkin, beet and carrot dishes. Green peas are subject to restrictions. The food must be pureed;
- You can introduce low-fat fermented milk products and low-fat cottage cheese into your daily diet;
- Lightly brewed tea and cocoa are allowed as drinks;
- Using unsalted butter;
- Meat is selected from low-fat varieties. It can be beef, veal, rabbit, chicken (without skin), turkey. Fish should also be low-fat varieties - pike perch, perch, carp. It is recommended to cook meat and fish by steaming or in the form of a soufflé;
- Fruits and berries cannot be eaten raw. Make compotes, decoctions, jellies, and mousses from them.
Diagnostics
The diagnosis is made after an endoscopic examination - FGDS; the method is the leading one. Visualization of mucosal defects, their location, depth and quantity makes it possible to clearly distinguish between simple catarrhal gastritis, erosive gastroduodenitis and peptic ulcer.
Endoscopic signs:
- redness and swelling of the mucous membrane;
- looseness of the mucous layer;
- bleeding, minor hemorrhages;
- erosions ranging in size from 0.3 to 0.5 mm, covered with a gray film.
For histological examination, material is selected for biopsy in the marginal zone of erosion; the sampling is carried out in the most gentle manner possible. Histological examination is necessary for the morphological study of tissues, as well as the detection of Helicobacter.
Endoscopy followed by histological examination of the biopsy is a reliable diagnostic method that leaves no doubt.
All other examination methods are of auxiliary value in relation to endoscopy.
The following are used:
- general blood test - with long-term existence of erosive gastroduodenitis, there are signs of anemia in the form of a decrease in hemoglobin levels, the number of red blood cells and the color index;
- polymerase chain reaction to detect Helicobacter DNA or breath test;
- Serum ELISA for detection of antibodies to Helicobacter.
We recommend reading:
Duodenal ulcer: how is the pathology manifested and treated?
Diet for gastroduodenitis with low acidity
To treat this disease, diet No. 2 is used. The diet menu includes juice substances, which increase the amount of gastric juice. You can eat boiled, baked, stewed, fried (without forming a rough crust) dishes. You cannot bread it in breadcrumbs and flour. It is advisable to chop the products before use.
Diet No. 2 allows you to consume:
- cocoa, coffee, tea with milk;
- berry and vegetable juices diluted with water, rosehip decoction;
- white and gray day-old bread, bakery products, non-bread cookies, a small piece of dry biscuit;
- mild cheese, milk in drinks, fermented milk products - cheese curds, cottage cheese, kefir, yogurt;
- boiled meat and fish, aspic;
- soaked herring;
- stewed vegetables, vegetable caviar;
- butter, refined vegetable oil, ghee;
- soups with weak fish and meat broths;
- semi-viscous cereal porridges.
Do not eat:
- fried, breaded meat, fish and other products;
- pickles, smoked meats, marinades, various canned foods;
- products made from fresh warm butter dough;
- kvass, cold drinks;
- ice cream, chocolate, pastries with cream;
- cooking oil, lard;
- raspberries, red currants (due to rough grains), gooseberries (due to rough skin);
- onions, garlic, radishes, cucumbers, legumes.
Varieties, differences between acute and chronic forms
Erosive-ulcerative gastroduodenitis does not always occur in the same way. The severity of the symptoms of the disease depends on its type. Experts call 3 forms of pathology.
- Superficial gastroduodenitis. This is the mildest degree of the disease. The mucous membranes of the stomach and duodenum are slightly damaged.
- Diffuse gastroduodenitis. The volume of the lesion increases. The ulcers become deeper. The patient complains of pain.
- Atrophic gastroduodenitis. The most dangerous stage of the disease. There is a high risk of degeneration into a malignant tumor.
The disease can occur in an acute form. All symptoms are quite pronounced. Diagnosis is not difficult. Chronic erosive gastroduodenitis is more difficult to suspect. The pathology may not appear for a long time.
Pain will appear only during an exacerbation. At the same time, internal changes do not stop or slow down. The mucous membranes continue to deteriorate under the influence of negative factors.
Sample menu for one day
For gastroduodenitis with high acidity, the daily menu may be as follows:
- First breakfast: grated oatmeal, tea with milk, a piece of toasted bread with butter;
- Second breakfast: sweet fruit. For example, an apple;
- Lunch: soup cooked in vegetable broth, soft-boiled egg, glass of compote;
- Afternoon snack: several small crackers, a cup of cocoa;
- Dinner: vegetable stew (steamed), steamed chicken cutlet, glass of carrot juice;
- About two hours before bedtime, you can drink a glass of kefir.
For gastroduodenitis with low acidity, the daily menu may be as follows:
- First breakfast: whipped cottage cheese with sugar, cream, a glass of tea, several small crackers;
- Second breakfast: a cup of rosehip infusion and one or two toasts from wheat bread;
- Lunch: soup based on chicken broth with wheat cereal, one piece of slightly dried bread, a glass of berry juice;
- Afternoon snack: a cup of carrot juice;
- Dinner: sweet fruit salad, tea (weak brew);
- Two hours before bedtime, you can drink a glass of yogurt.
The diet menu for gastroduodenitis should be tasty and varied. At the same time, it is difficult to adhere to certain food restrictions. A monotonous diet can lead to breakdowns and the desire to eat something forbidden. Try to dilute the boring menu with new permitted recipes. Try not to overeat.
Diet menu
Option #1
- Breakfast: salad of boiled vegetables with butter, boiled fish, mashed potatoes, tea, butter;
- Second breakfast: cottage cheese pudding with apples, carrot juice;
- Lunch: pureed vegetable soup, meat soufflé with pasta, compote;
- Afternoon snack: milk, biscuits;
- Dinner: lazy dumplings, tea;
- At night: milk (all days).
Option No. 2
- Breakfast: boiled carrots, mashed through a sieve with the addition of vegetable oil, sausages in a natural casing, tea, butter;
- Second breakfast: homemade cottage cheese, rosehip decoction;
- Lunch: oatmeal soup, boiled chicken fillet, buckwheat porridge, pear compote;
- Afternoon snack: plum jelly;
- Dinner: protein omelet, milk rice porridge, tea.
Option No. 3
- Breakfast: boiled beets seasoned with vegetable oil, steamed meatballs with rice, butter, tea;
- Second breakfast: baked apple with raisins and cottage cheese;
- Lunch: cabbage soup, boiled meat, ground through a sieve, oatmeal, compote;
- Afternoon snack: milk, crackers;
- Dinner: semolina porridge, tea.
These diet menu options for gastritis are prescribed during the period of clinical remission. The diet for exacerbation of gastritis with high acidity differs in that all dishes are consumed pureed. Only small pieces of boiled meat or fish are allowed twice a week.
In case of chronic gastritis with reduced secretion during the period of acute exacerbation, food should be taken in the form of purees, in small portions. The diet for atrophic gastritis includes mucous soups from cereals, butter, grated cottage cheese, boiled meat, low-fat fish, pureed vegetables and fruits, viscous porridge from cereals with milk, soft-boiled eggs, white stale bread, crackers, rosehip infusion.
A diet for acute gastritis with reduced secretion is used for 3-4 weeks, and then replaced with a diet that is broader in composition. The diet for gastritis in remission consists of various porridges, steamed meat and fish dishes, and cereal soups with meat broth. Pieces of fish, meat balls, and cutlets fried without breading are allowed.
When following a diet for atrophic gastritis, you should consume fermented milk products (especially kefir), cheeses, various cottage cheese dishes (puddings, soufflés, casseroles), jelly from berries and fruits, and mousses.
- Breakfast: steamed beef patties, tea;
- Lunch: pearl barley soup with meat broth, fried cutlets without breading, mashed potatoes, apple jelly;
- Afternoon snack: tea, crackers;
- Dinner: cottage cheese casserole, pureed oatmeal porridge, tea;
- At night: kefir or fruit and berry jelly.
During exacerbation of gastritis, the diet is supplemented with the prescription of fruit and vegetable juices and vitamin complexes.
Page 1 of 1
Tracked Topics
The main goal of a diet for gastritis is to adhere to a diet that ensures normal digestion.
The treatment table for gastritis (per day) should contain
- 90-100 gr. proteins (60% animal),
- 90-100 gr. fat (75% animal)
- 400-420 gr. carbohydrates.
The total energy value should be 2800-3000 kcal.
No medicine can completely cure acute gastritis or lead to stable remission in the presence of chronic gastritis.
All advertised drugs, available to everyone, are sold without prescriptions in pharmacies. But they only eliminate (temporarily) unpleasant symptoms (heartburn, pain, belching).
Following a diet for gastritis not only makes life easier for the patient, but also disciplines the person.
The treatment table for gastritis is nutritious and healthy food, it is the normalization of lifestyle, the rejection of bad habits and low-quality products. In addition, a diet for gastritis helps to normalize weight (those who have lost weight will gain weight, and people with excess body weight will lose weight), since timely and nutritious nutrition not only normalizes the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract, but also all metabolic processes, and, consequently, strengthens the immune system.
If you refuse to follow a diet for any type of gastritis, the patient may face the following problems:
- vitamin deficiency;
- diseases of the liver, pancreas, duodenum, large and small intestines (as a result of impaired stomach function);
- significant loss of body weight (fear of eating);
- peptic ulcer disease and its consequences: perforation of the ulcer, penetration of the ulcer - germination into the organ, bleeding;
- the formation of atrophic gastritis and its transformation into stomach cancer.
It is advisable to exclude summer preparations: neither jams nor pickles contain useful substances, and there are too many harmful substances - sugar, salt, spices and vinegar. The same applies to home-made canned juices: contrary to popular belief, the vitamins in them are destroyed within a few hours after squeezing.
Delicious fried foods are prohibited, but you can regularly cook them baked in foil or a baking bag, of course, without allowing them to burn. This food is much tastier than stewed food, which is recommended as the main dish. You can cook lean meat or fish in its own juice, vegetables with low-fat sour cream, or a sweet casserole. You just need to monitor the amount of fat: 50 g per day, include both vegetable and butter in your food.
Allowed but unappetizing boiled dishes are often the reason for failure to lose weight. Sometimes, instead of boiled meat, it is better to make steamed cutlets - this food tastes better and will help you stay within your diet.
The main enemy of all those losing weight is sweet food. It would be nice to completely abandon it. Sugar (in the form in which people consume it) is not needed by the body, but sweet foods lift your spirits and are not harmful in small quantities. Its content in all dishes should not exceed 20 g per day.
Often, with problems with the gastrointestinal tract, the consumption of fresh vegetables and fruits is limited. For example, it is recommended to make your own tomato paste and bake apples in the oven.
As a result, the esophageal mucosa is damaged. Gastritis occurs against the background of increased or decreased secretory function of the stomach.
Chronic gastritis is caused by many years of disregard for oneself and the choice of normal food. First, the functional activity of the stomach is disrupted, which can be eaten during an exacerbation of gastritis, then dystrophic changes in the mucous membrane occur, and an exacerbation occurs. When people are not yet treating the disease, the glands of the stomach will also be involved in the destructive process, which gradually weaken. We often, having learned about an exacerbation of gastritis, try to self-medicate.
However, only a gastroenterologist can give treatment recommendations after conducting an examination. We ourselves can help ourselves by choosing the right diet during an exacerbation of gastritis. To do this, it is worth taking into account the acidity of gastric juice.
Doctors say what you can eat during a sudden exacerbation, what you can eat during an exacerbation of gastritis. It has its own rules. A diet for exacerbation of gastritis implies that food should be consumed little by little and. The strict regime is observed for up to two weeks. If the acidity is increased, then you cannot add products to your home diet that can strengthen it; broths: meat, fish, mushrooms, coffee, alcohol, grapes, cabbage, sausages; cause irritation of the mucous membranes; smoked foods; marinades; fried or canned; soda; mushrooms; spices; bread only coarse grind.
What can you eat if you have gastritis? From products for every day: For erosive gastritis, flax seed is used, which creates protection for the mucous membrane, saving it from acid.
As a result, pain decreases and unpleasant symptoms of inflammation go away.
What can you eat during a sudden exacerbation of gastritis?
During an exacerbation, a diet can relieve unpleasant symptoms and reduce inflammation, and proper nutrition for chronic gastroduodenitis prevents the disease from becoming acute and stimulates the stomach to work properly.
The medical table under the first number excludes from the diet foods that increase gastric secretion. Table No. 5 stimulates normal bile secretion and normalizes liver activity. Even a one-time violation of prohibitions in chronic forms of gastritis or gastroduodenitis can lead to digestive problems.
When drawing up the menu, the form and severity of the disease is also taken into account. Thus, a diet with high acidity requires a large amount of liquid to reduce the concentration of hydrochloric acid in gastric juice. The erosive form requires an abundance of porridge and allows the consumption of kefir. Diet for chronic gastroduodenitis excludes any foods that can irritate the gastric mucosa.
- Exclusion from the diet of long-digesting foods;
- Serving food boiled or pureed;
- Serve dishes warm, avoid eating excessively hot and cold foods;
- Six meals a day at strictly defined times;
- Limiting salt intake;
- Refusal of fatty, fried, smoked, pickled foods, spices and herbs, alcohol and canned products.
The type of diet used in the treatment of different types of gastroduodenitis depends on the acidity of gastric juice, on the form and stage of the disease.
The average daily food intake for chronic gastroduodenitis should include:
- 10 g of plant and 60 g of animal proteins;
- 80 g fat;
- 230 g carbohydrates.
Based on the above information, the list of allowed foods for the diet for gastroduodenitis is as follows:
- fruits and fruit juice;
- pasta, cereals;
- dried fruits;
- milk, cream;
- starch;
- sugar;
- chicken meat, fish;
- eggs;
- sour cream;
- tea.
The average daily calorie intake for this diet is 1900 kilocalories.
The basic principles of the diet for gastroduodenitis are the following:
- minimize hard-to-digest foods (mushrooms, bananas, mussels);
- It is strongly recommended not to get carried away with delicacies, but to prefer dishes of national cuisine;
- eat 4 to 6 times a day, in small portions;
- It is desirable that there be equal breaks between each meal;
- food should preferably be at room temperature;
- Consume sweets exclusively in their natural form (honey, jam);
- Mineral and purified water without carbon is recommended for drinks.
When dieting for the treatment of gastroduodenitis, it is recommended to consume dishes in the following form:
- low-fat vegetable, meat and fish broths;
- puree soups;
- steam cutlets and meatballs;
- boiled eggs and in the form of omelettes;
- skim cheese;
- fresh juices;
- herbal decoctions;
- weak tea;
- vegetable and fruit puree;
- honey, jam, marmalade.
- Breakfast: cottage cheese casserole, a glass of warm berry jelly.
- Second breakfast: a mug of warm tea, a couple of pieces of mild, low-fat cheese and a piece of day-old bread.
- Lunch: vinaigrette without cucumbers, cereal soup in secondary meat or fish broth, steamed meat or fish cutlet, a glass of juice at room temperature.
- Afternoon snack: light salad of sweet varieties of fruit, with bio-yogurt dressing, a mug of chicory diluted with milk.
- Dinner: a couple of steamed meatballs, buckwheat porridge, a glass of herbal infusion.
- An hour before bedtime: a mug of yogurt or matsoni.
- Breakfast: a mug of warm, not strong tea or brewed chicory. An omelette made from two chicken eggs, cooked in a double boiler.
- Second breakfast: a mug of warm compote or rosehip decoction with a couple of biscuits.
- Lunch: creamy vegetable soup, thin oatmeal porridge, a glass of warm milk.
- Afternoon snack: a piece of baked pumpkin, freshly squeezed carrot juice.
- Dinner: viscous milk pureed buckwheat porridge, a glass of warm milk.
- An hour before bedtime: a glass of warm yogurt.
- Breakfast: pumpkin porridge with rice with milk, a piece of cottage cheese casserole, a mug of weak sweetened tea.
- Second breakfast: baked pear, warm coffee or chicory with milk.
- Lunch: seafood puree soup, to which you can add vegetables, 100 g of sauerkraut, non-acidic, a couple of sausages, fresh vegetable salad.
- Afternoon snack: mousse or pudding, a glass of juice.
- Dinner: a piece of boiled or steamed fish with vegetables, mashed potatoes or zucchini, fruit jelly, a mug of weak tea or rosehip infusion.
- An hour before bedtime: a mug of kefir or drinking yogurt.
- Table No. 1a is prescribed for patients suffering from peptic ulcers and gastroduodenitis in the acute phase. The diet includes liquid and semi-liquid porridges, mashed soups, and cream soups. Boiled eggs in a “bag”, steam omelet, soufflé, jelly, mousse, jelly.
- Table No. 1b is indicated for patients whose condition has passed a particularly acute phase of the disease. Vegetable purees are introduced into the diet, and white bread crackers are allowed.
- Table No. 1 is prescribed during the period when the exacerbation of gastroduodenitis subsides. It is divided into table No. 1 (mashed dishes) and table No. 1 (non-mashed dishes). The diet is less sparing, more saturated. The following products are included in the diet: pasta, dry biscuit, vegetable and fruit purees, compotes, mild hard cheeses, boiled or steamed fish, meat.
- Breakfast: an egg boiled in a “bag”, pureed oatmeal porridge with water, weak tea diluted with milk.
- Second breakfast: a piece of baked pumpkin sprinkled with sugar, a glass of rosehip infusion or herbal tea.
- Lunch: milk soup with noodles, zucchini puree, meatballs cooked in a steamer, a cup of jelly.
- Afternoon snack: a piece of dry biscuit, a glass of warm milk.
- Dinner: fish aspic, mashed potatoes, weak tea diluted with milk.
- An hour before bed: a mug of drinking yogurt.
- Breakfast: omelet cooked in a double boiler, 100-150 g of cottage cheese, you can season with 1-2 tablespoons of sour cream, not strong coffee, diluted with cream.
- Second breakfast: fruit jellies or mousse, rose hip decoction.
- Lunch: vegetable puree soup with white bread croutons, meat cooked in a steamer with vegetables, a mug of compote.
- Afternoon snack: marshmallows or marshmallows, a glass of warm milk.
- Dinner: meat cutlets cooked in a double boiler, buckwheat porridge, herbal tea.
- An hour before bedtime: a warm mug, maybe with a little sugar or kefir.
Table of permitted products
Below is a list of foods allowed in diet No. 1. For ease of reference, a table has been compiled.
| Fruits | apricot | bananas | apples | nectarines | peaches | melon | |||
| Vegetables | potato | carrot | beet | tomatoes are not sour | cauliflower | ||||
| Berries | strawberry | raspberries | watermelon | ||||||
| Cereals | cereals | semolina | buckwheat core | ||||||
| Meat | beef | veal | rabbit | turkey | |||||
| Bread | dried wheat | ||||||||
| Confectionery | honey | jam | cracker | paste | marshmallows | jelly | |||
| Dairy products | milk | kefir | cream | sour cream | curdled milk | ||||
| Eggs | soft-boiled chicken, no more than 2 pieces per day | ||||||||
| Fish, seafood | pollock | hake | navaga | blue whiting | bream | zander | flounder | cod | pike |
| Fats | butter as a seasoning for soups | ||||||||
| Beverages | mineral water | weak tea with milk | chicory | apricot juice | carrot juice |
Principles of nutrition
Gastroduodenitis, as a chronic disease, requires constant adherence to certain dietary rules and principles. That is, it is important not only what exactly you can and cannot eat, but also how exactly to eat. Here are the basic nutrition rules:
- All dishes and drinks should be slightly above room temperature, permissible temperature limits are from 35 to 45 degrees;
- You need to eat in small portions; you can have up to 6-7 meals a day;
- You must completely avoid fried, spicy and fatty foods, and cook everything exclusively by steaming, stewing or baking, but without forming a crust;
- All dishes should be finely chopped, and during an exacerbation period, pureed to a paste or puree, and what is not ground must be thoroughly chewed;
- Never overeat or eat before bed. At night it is permissible to drink a glass of kefir or milk.
Another important rule applies to everyone with chronic gastrointestinal diseases - alcohol is not recommended at all, in any doses. It is also worth giving up ice cream, cold dishes (aspic, jellied meat) and soda.
Symptoms and diagnosis
The main manifestation of the disease is epigastric pain, acute or aching. Feeling of fullness and heaviness in the stomach, loss of appetite, nausea, heartburn, belching, bad breath in the morning.
Also – stool disorder: constipation alternates with diarrhea. Abdominal bloating may occur. Often – weakness, increased irritability, insomnia.
In the presence of erosions, bleeding is possible: dark blood clots are noted in the vomit, stools are the color of tar.
With prolonged bleeding - signs of anemia: weakness, drowsiness, pallor of the mucous membranes and skin, decreased blood hemoglobin.
We recommend reading: Verbena officinalis: medicinal plant, use, reviews, beneficial properties, contraindications
The diagnosis is made on the basis of endoscopy, ultrasound of the abdominal organs and laboratory research methods: breath test for urease activity, feces for occult blood and antigens to Helicobacter, blood serum for antibodies to bacteria, biopsy examination.
Prohibited Products
There is also a list of prohibited foods that can make the disease even worse. You will have to completely abandon:
- Tough, fibrous vegetables and fruits;
- Fresh baked goods and confectionery;
- Sour fruits and berries, as well as strawberries, grapes (they contain small seeds);
- Sorrel, cabbage (except cauliflower), radish, turnip;
- Nuts and seeds;
- Lard, margarine;
- Vinegar, hot pepper, mayonnaise;
- Strong coffee and tea, alcoholic drinks;
- Smoked meats, canned food;
- fried foods.
Coarse porridges - millet, corn, barley, and all legumes except green peas - are also undesirable.