RECOMMENDED USE SCHEME FOR DISEASES OF THE LIVER AND BILIARY TRACT
| № | Means | Brief description of the product | Daily dosage regimen. Take 20-30 minutes before meals. It is recommended to take thick extracts after dissolving them in 100-150 ml of warm water. | Duration of taking the drug | Number of packages for 1 course |
| HEPATOTRIN Capsules (180 pcs.) or SOLYANKA KHOLMOVAYA Capsules (126 pcs.) Thick extract (95 ml) | HEPATOTRIN 2 capsules 3 times a day. | 1 month | 1 | ||
| Solyanka kholmovaya, capsules. 2 capsules 3 times a day. | 3 weeks | 1 | |||
| Thick extract of Solyanka Kholmovy, 1 scoop (1 ml) 3 times a day. | 1 month | 1 | |||
| 2 | SOLYANKA KHOLMOVA SEEDS Capsules (180 pcs.) | Helps restore the proper structure and functioning of the liver. Reduces cholesterol levels. | 2 capsules 3 times a day. | 1 month | 1 |
| ASPEN Capsules (90 pcs.) Thick extract (95 ml) | 1 capsule 3 times a day. | 1 month | 1 | ||
| 1 scoop of extract (1 ml) 3 times a day | 2 weeks | 2 |
3 courses per year are recommended.
- Limiting fatty, spicy foods, fried and starchy foods, and alcoholic beverages.
- Eat small meals, 5-6 times a day.
DISEASES OF THE LIVER AND BILIARY TRACT
The liver is one of the most important organs, performing many functions, including bile formation and excretion, neutralization of toxins and harmful substances, participation in carbohydrate, protein and lipid metabolism. Liver diseases are among the most common. About 30% of Russians suffer from disorders of the hepatobiliary system, which in addition to the liver includes the gallbladder and bile ducts.
To protect the liver, restore and normalize its functions, hepatoprotective agents are used. Preparations based on Solyanka Kholmovaya extracts have long been used in Tibetan and Chinese medicine. Based on the results of research on Solyanka Kholmova extract at the Siberian State Medical University (Tomsk), 3 doctoral and 19 candidate dissertations were defended, 2 monographs and more than 40 articles were published in peer-reviewed scientific journals, the results of the work were protected by 4 patents. The volume of clinical trials conducted is sufficient for registration of the pharmaceutical product. In HEPATHOTRINA, the effect of Solyanka Kholmovaya extract is complemented by milk thistle seeds.
Indications for the use of drugs in the given scheme:
- for the prevention and enhancement of the effect of drug therapy : acute and chronic hepatitis (mainly medicinal, toxic, alcoholic origin), chronic cholecystitis, cholangitis, the initial stage of liver cirrhosis, to normalize metabolism in the liver during helminthiasis (opisthorchiasis, echinococcosis, ascariasis, giardiasis, etc. );
- to protect the liver during treatment with cytostatics, antituberculosis or other hepatotoxic drugs,
- with severe intoxication of various origins;
- in case of severe food intoxication : poisonous mushrooms, berries, low-quality food products and substitute drinks (especially alcoholic ones);
- for the prevention of disorders and optimization of liver function in practically healthy people when working with factors harmful to the liver or living in environmentally unfavorable regions.
Buy cheap medicines for hepatitis C Hundreds of suppliers bring Sofosbuvir, Daclatasvir and Velpatasvir from India to Russia. But only a few can be trusted. Among them is an online pharmacy with an impeccable reputation, Natco24. Get rid of the hepatitis C virus forever in just 12 weeks. High-quality drugs, fast delivery, the cheapest prices.
Diseases of the liver and biliary tract have characteristic symptoms, which can be used to make a preliminary diagnosis of the patient. Modern medicine identifies several main diseases of these organs.
Biliary tract diseases
The main diseases include: dyskinesia, cholecystitis and cholelithiasis.
Dyskinesia is a disease that is characterized by impaired contractile function of the gallbladder and ducts of the organ, dysfunction of the sphincter of Oddi. As a result, the process of bile excretion is disrupted. There are 2 forms of dyskinesia:
1. Hyperkinetic. characterized by increased tone of the gallbladder, strong and rapid contractions of the organ, and insufficient opening of the sphincters. Young people are more often affected. Symptoms:
- paroxysmal pain that is sharp in nature;
- painful sensations in the hypochondrium on the right.
These signs intensify after emotional experiences, during menstruation.
2. Hypokinetic. This form is characterized by insufficient contraction of the gallbladder. Elderly people are more often affected. Symptoms:
- pain in the right hypochondrium is dull and mildly expressed;
- bursting pain.
There are also general symptoms of the disease:
- a feeling of bitter taste in the mouth in the morning;
- general weakness;
- decrease in emotional background;
- pain in the right hypochondrium after eating a spicy dish or excitement;
- insomnia;
- decreased libido;
- menstrual irregularities;
- diarrhea or constipation that is regular.
With dyskinesia, the stage of exacerbation is replaced by remission - and so on in a circle.
Cholecystitis is an inflammatory process
With this disease, the wall of the gallbladder becomes inflamed. There are acute and chronic forms. Symptoms of the acute form:
- acute, sharp pain in the abdomen, which is constant;
- feeling of nausea;
- repeated vomiting;
- elevated temperature;
- intense signs of jaundice;
- rapid pulse.
Chronic cholecystitis often occurs without symptoms and manifests itself only during an exacerbation.
Gallstone disease is another pathology. It is characterized by the formation of stones in the bile ducts. In most cases, the disease occurs without symptoms. The most common signs include:
- biliary colic, that is, acute paroxysmal pain;
- painful sensations in the hypochondrium on the right side, which “radiate” to the shoulder;
- vomit.
At the first symptoms, you should consult a doctor.
Causes
Blockage of the gallbladder and ducts can occur for a variety of reasons. In this case, the blockage can occur from the inside or narrow due to external pressure. There are various reasons due to which pathology appears. In particular, a special group of diseases of the gastrointestinal tract leads to the problem - stones, scars and cysts in the ducts, tumors in the pancreas, pancreatitis and hepatitis.
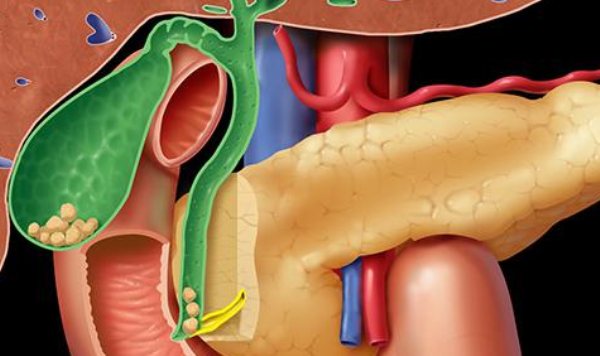
In addition, cirrhosis of the liver may begin, parasitic infection and cholangitis may occur. If the lymph nodes in the hepatic hilum enlarge, then this will also lead to a problem. Even operations and injuries contribute to the occurrence of pathology.
It is worth noting that there are certain risk groups. They are used by people suffering from obesity, infections of the biliary tract, pancreas, and also those with immunity problems.
In any case, when the first symptoms appear, you should consult a medical specialist. Blockage of the bile ducts leads to serious complications, so the problem should not be neglected.
Diseases of the liver and biliary tract: diet
Diet is important for both chronic and acute forms of diseases. The diet promotes long-term remission, and during exacerbation it alleviates the condition. The rules for compiling the diet are as follows:
- Excluded: fatty, spicy foods, alcohol, cold dishes, carbonated drinks.
- Protein. Low-fat meat and fish, milk, cheese, cottage cheese are very healthy. Moderate consumption of raw eggs or omelets is allowed.
- Cereals. Oatmeal and buckwheat are especially valuable.
- Butter and vegetable oil. It is an excellent source of fat. But lard, meat and fatty fish, canned food, margarine, etc. are strictly prohibited.
- Carbohydrates. Fresh vegetables and fruits. But radishes, garlic, onions, radishes, etc. should be discarded. Greens are also useful, especially for stones. It is better not to include sorrel and spinach in the diet.
- Juices. If the patient suffers from diarrhea, it is better to consume vegetables and fruits in the form of juices or pureed. Blueberries, pomegranates, and quince are especially good.
It is very important to follow a diet. You need to eat often and in small portions, especially with cholecystitis.
Common Liver Diseases
The main diseases include: hepatitis, cirrhosis, fatty degeneration and liver cancer.
Hepatitis is damage to the liver by a virus. There are acute and chronic forms of hepatitis. The acute form is characterized by the following symptoms:
- signs of intoxication;
- signs of jaundice: the skin and sclera have a yellow tint;
- the feces acquire a whitish-clayey tint;
- urine darkens to a rich dark color;
- hemorrhagic signs:
- nosebleeds;
- skin itching;
- bradycardia;
- depressed psycho-emotional state;
- irritability;
- damage to the central nervous system;
- enlarged liver and spleen.
In a milder form of exacerbation of hepatitis, symptoms may not be expressed. In severe cases of exacerbation, necrotic changes in the liver and a decrease in its size are observed.
With chronic hepatitis, the following symptoms are observed:
- the liver and spleen increase in size;
- dull pain in the area of the organ;
- skin itching;
- feeling of heaviness;
- loss of appetite;
- belching;
- flatulence;
- hyperhidrosis.
Patients find it difficult to tolerate fatty foods and alcohol.
Diagnosis: liver cirrhosis
With this liver disease, the normal structure of the organ is replaced by scar tissue and takes on a nodular shape. This interferes with the full functioning of the organ. In most cases, the disease occurs without symptoms. The following symptoms are characteristic of cirrhosis:
- general weakness;
- decreased performance;
- painful sensations in the hypochondrium on the right side;
- bloating;
- urine becomes darker;
- weight loss;
- palms turn red.
If the disease is not treated, complications begin:
- accumulation of fluid in the abdomen;
- impaired state of consciousness and memory;
- stomach bleeding;
- jaundice.
Cirrhosis is the cause of liver cancer in most cases. Oncology manifests itself as progressive cirrhosis and is accompanied by pain in the abdominal area.
Another disease is fatty degeneration, or steatosis. In this case, the tissue of the organ is rebuilt, and there is an excessive accumulation of fat in the cells of the organ. The disease may occur without symptoms, or may be accompanied by the following signs:
- increase in liver size;
- pain in the organ area;
- feeling of nausea;
- painful sensations in the hypochondrium on the right side.
Steatosis varies in duration. In this case, phases of exacerbation are replaced by remissions.
Diet for liver diseases
For pathologies of this organ, it is very important to follow a therapeutic diet. It includes the following products:
- Lipotropic products. This is cottage cheese, soy, cod. They are necessary to prevent fatty degeneration of the organ.
- Fats. It is very important to maintain a balance of fats of animal (70%) and vegetable (30%) origin. Ideal sources of fat: fish, meat, cottage cheese.
- Vegetable oils. Olive, sunflower, corn - you can choose any.
- Carbohydrates. The daily norm is 400 - 450 g. However, carbohydrates obtained from honey, sugar and other sweets should not exceed 100 g.
For diseases of the liver and gall bladder, another diet is also indicated.
Nutrition according to diet No. 5
Meals with this diet are frequent (up to 6 times a day) and fractional. Food does not need to be chopped, food processing is important: boiling, steaming, baking are ideal options. Meat and fish are first boiled and then baked. The temperature of the food should be from 45 to 60 °C. Products that are recommended:
- yesterday's bread (rye, wheat), crackers;
- milk soups;
- vegetable soups with added cereals;
- fruit soups;
- lean meat (beef);
- lean poultry (chicken, turkey);
- low-fat fish (bream, pike perch, hake, perch);
- vegetables - raw, boiled, baked;
- vegetable and fruit salads;
- crumbled porridge (cook in water, then add milk);
- egg (no more than 1 piece per day), egg white omelettes;
- fermented milk products (raw and in the form of casseroles, cheesecakes, soufflés, etc.);
- berries and fruits of sweet varieties.
Allowed in moderation:
- spices (cinnamon, vanilla, bay leaf, cloves);
- greens (parsley, dill);
- the tea is not strong;
- coffee with milk or weak.
The following products should be excluded:
- freshly baked bread, muffins, confectionery, etc.;
- fatty meats (pork, lamb, goose);
- fatty fish (chum salmon, stellate sturgeon, beluga, sturgeon) and salted;
- sausages;
- viscera (liver, lungs, brains, kidneys);
- sharp and salty cheeses;
- hard-boiled eggs;
- fat (pork, beef, lamb, margarine, cooking);
- mushrooms;
- legumes (peas, chickpeas, mung beans, beans);
- greens (spinach, sorrel);
- vegetables (radish, turnip, radish, garlic, onion);
- marinades (including vegetable ones);
- broths (meat, mushroom, fish);
- okroshka, cabbage soup;
- seasonings and spices (pepper, mustard, horseradish);
- alcohol;
- sweets (chocolate, ice cream, cocoa).
This diet is indicated for all diseases of the liver and gall bladder. It must be observed especially strictly during periods of exacerbation of the disease.
Biliary dyskinesia
Our readers successfully use Leviron Duo to treat the liver. Seeing how popular this product is, we decided to bring it to your attention. Read more here...
Biliary dyskinesia is a functional disorder of the motor activity of the gallbladder. The coordinated work of the contractile or sphincter mechanism of the biliary system is disrupted due to inconsistency of contractions, too strong or insufficient contraction of the muscles of the bladder itself and the biliary tract. Muscle contraction in the gallbladder is regulated by hormones secreted in the duodenum. Accordingly, any inflammation or irritation of this part of the intestine can provoke disturbances in the processes of bile outflow.
Dyskinesia can be observed with helminthiasis, giardiasis or intestinal infections. Another reason is the constant secretion of bile into the bladder due to abnormal development of the ducts and bladder, the formation of ducts, constrictions or valves. Also, increased or decreased smooth muscle tone in the area of the bladder or ducts may occur.
Forms of dyskinesias and treatment
In modern clinical practice, two main forms of dyskinesia of the gallbladder and bile ducts are defined:
- hypertensive – the tone of the gallbladder is increased;
- hypotonic - bladder tone is reduced.
These variants of dyskinesia are sometimes combined with hypotension or hypertension of the sphincter of Oddi or other sphincters of the bile ducts. At the onset of the disease, the hyperkinetic form of dyskinesia often predominates, and with a long course, exhaustion occurs and the hypokinetic form develops.
The diagnosis of dyskinesia of the gallbladder and biliary tract is established by characteristic clinical symptoms and is confirmed by laboratory and instrumental studies. The basis for the treatment of dyskinesia in hyperkinetic and hypokinetic forms is the use of modern drugs - hepatoprotectors, which enhance the secretion of bile and relieve spasm from the biliary tract. Modern hepatoprotectors are prescribed, for example, Ursosan (UDKH).
Possessing persistent polar properties, ursodeoxycholic acid penetrates the membrane of the hepatocyte, cholangiocyte, stabilizes its structure, and protects the cell from the damaging effects of toxic bile acids. Forms non-toxic micelles with apolar (toxic) bile acids, reduces damage to cell membranes in biliary reflux gastritis and reflux esophagitis. Reduces concentration and stimulates choleresis, effectively helps resolve intrahepatic cholestasis. Reduces the absorption of bile acids in the intestine, increases their fractional turnover, stimulates the passage of bile and the excretion of toxic bile acids. Reduces the saturation of bile with cholesterol by inhibiting its absorption, suppressing synthesis in the liver and reducing secretion into bile. Also, it increases the solubility of cholesterol in bile and forms liquid crystals with it; by reducing the lithogenic index of bile, it increases the concentration of bile acids in it. By reducing the saturation of bile with cholesterol, it promotes its mobilization from gallstones, resulting in the dissolution of cholesterol gallstones and the formation of new stones is prevented.
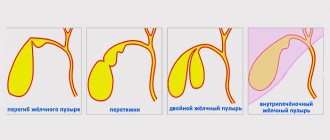
Bend gallbladder symptoms and treatment
Disorders of the gallbladder differ in etiology, causes of occurrence, course, and complications. An imbalance in gallbladder disorders immediately leads to a malfunction of the digestive system and worsens the condition of the entire body. According to medical statistics, gallbladder diseases occur two times less often than liver diseases, and 3 times more often among all gastrointestinal diseases. To a greater extent, people whose age exceeds 50 years are susceptible to the disease. There are many more patients with gallbladder diseases among women than among men. Many patients are reluctant to see a doctor even because they simply do not know which doctor should treat the problem.
The reasons for the bending of the gallbladder, which occurs during embryonic development, are associated with a disruption in the formation of this organ, which occurs in the fifth week of pregnancy (simultaneously with the formation of the liver, bile ducts and duodenum). The future gallbladder is formed by strands of glandular epithelial cells of the abdominal (ventral) part of the embryo - from a diverticulum common to the liver. The fetus is most sensitive to various adverse effects on the formation of the biliary system during this period. And it is at this stage that a congenital inflection of the gallbladder may be “laid”, associated with a violation of the proportions during the growth of the organ.
A disease of this etiology is most often permanent, which doctors define as either persistent or fixed inflection of the gallbladder. But, since the bladder is a hollow organ with a muscular shell (that is, quite mobile), the deformation can change its location and shape. And then the so-called labile inflection of the gallbladder is diagnosed.
Acquired bending of the gallbladder in an adult can be a consequence of such reasons as:
- enlargement of the gallbladder, liver or right kidney;
- increased mobility of the gallbladder (due to its atypical location outside the right longitudinal groove on the lower surface of the liver);
- constant violation of the diet (alternating prolonged fasting and overeating);
- lifting heavy objects, sudden movements, or sitting for long periods of time (functional bending of the gallbladder);
- significant prolapse of internal organs relative to the anatomical norm in old age (physiological inflection of the gallbladder);
- obesity.
In this case, the bend can occur in different parts of the bladder - in the area of its body, bottom or neck. And according to localization, when conducting diagnostics, gastroenterologists distinguish between the inflection of the lower third of the gallbladder, the upper third, the bottom, wall and duct of the gallbladder. More often than other varieties, a bend in the neck of the gallbladder is diagnosed, and the most dangerous consequences are caused by a bend in the gallbladder in the body.
By the way, the forms taken by the gallbladder as a result of deformation are very diverse and depend on the location and degree of pathology. So, it can be a hook-shaped bend, in the shape of an arc or an hourglass. Moreover, there may be a double bend of the gallbladder, which doctors define as S-shaped and consider it the main cause of biliary dyskinesia in young children.
In rare cases, a woman may develop a bend in her gallbladder during pregnancy - when the uterus enlarges to such a size that it begins to “press” the liver and gall bladder. But more often it is simply a congenital pathology, which did not bother the patient in any way and was discovered only when examining the woman for pregnancy.
Symptoms of a bent gallbladder
- nausea accompanied by vomiting, which can occur with various poisonings, pregnancy and intoxication. In some cases, nausea is constant and becomes a threat to the patient’s life;
- vomiting, which promotes a reflex eruption of food contained in the stomach. Most cases occur through the mouth or nose. As a rule, vomiting occurs after a condition characterized by rapid breathing, nausea, rapid breathing and the release of tears and saliva;
- abdominal pain, usually due to tissue damage and worsened intestinal tract patency. In the case of children, such relapses manifest themselves in the form of intestinal pain. Then the children cry for several hours throughout the week;
- gastric reflux, which can contribute to the mechanisms of erosion, ulcers of the duodenum, stomach, and the subsequent formation of gallstones.
As a rule, by following diets and proper drug treatment, patients feel better, and the need for surgical intervention becomes meaningless.
This gallbladder disease does not always affect the patient’s well-being, but such a disease cannot be left without due attention. When certain internal organs prolapse, this bend can immediately make itself known.
In some cases, sudden movements or heavy lifting can cause incomplete twisting of the gallbladder along the longitudinal axis. This twisting occurs without symptoms. This condition in most cases appears in mature people in the case of significant displacement of internal organs, enlargement of the gallbladder, and the presence of stones in it. In very rare cases, the gallbladder becomes twisted several times. In such cases, circulatory disorders are observed. The consequence of this is the appearance of cracks in the walls, and then the outpouring of bile into the abdominal cavity. In addition, there is the occurrence of sharp pain in the right side of the abdomen, sweating, vomiting, bloating, and weakness. This condition of the patient indicates a violation of blood circulation and the presence of cracks in the gallbladder, through which bile enters the abdominal cavity. In such cases, medical assistance cannot be avoided.
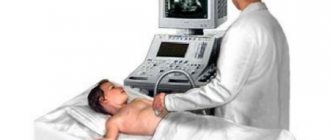
In most cases, symptoms of kinking are detected during an ultrasound examination. If inflammation develops on the outer wall, then adhesions form, deformation of the gallbladder occurs, and as a result, digestive disorders and changes in the composition of bile appear (it becomes thicker and more viscous, prone to the formation of sand).
Diagnosis of gallbladder inflection
The main method for diagnosing gallbladder pathologies is ultrasound. This method has no contraindications or age restrictions, so it is prescribed even to the youngest patients if a bend is suspected.
Using ultrasound, you can accurately determine the functionality of the organ, the presence of a bend, as well as the location of the pathological process.
In order to find out whether the bend is congenital or acquired, adult patients undergo stimulation of the secretory abilities of the organ by taking raw egg yolks or butter.
With congenital bending, the deformation of the bladder after increased bile production remains unchanged. To determine the probable cause of the anomaly, the gastroenterologist collects a thorough history of the patient’s life. Depending on the cause of the gallbladder bend, the doctor will prescribe appropriate treatment.
Treatment of gallbladder inflection
Treatment of a kink in the gallbladder directly depends on the cause of the deformation and the severity of the symptoms. The treatment regimen includes therapy for the underlying disease (cholecystitis, cholelithiasis). However, even after effective treatment, the bend requires additional therapy aimed at improving the outflow of bile and preventing its stagnation.
The treatment course includes:
- Elimination of pain - selective antispasmodics Odeston, Cholestil, Cantabiline simultaneously accelerate the evacuation of accumulated bile;
- Improving biliary excretion - choleretic drugs for inflection of the gallbladder (Flamin - approved for use in children, the herbal remedy Aristochol and the synthetic drug Cyqualon) are taken in courses of 2-4 weeks, after 1 month. after a break, the medication is repeated for 3-4 courses;
- Hepatoprotectors - since stagnation of bile negatively affects the functioning of the liver, it is advisable to take the drug Hofitol, which has choleretic and hepatoprotective properties;
- Herbal infusions and decoctions (chamomile, valerian, mint, yarrow, calendula, corn silk, immortelle) are an excellent addition to drug therapy, but do not replace medications prescribed by a doctor;
- Physiotherapy (ultrasound, medicinal electrophoresis) and therapeutic exercises improve the outflow of bile and help restore the physiological shape of the bladder.
Therapeutic exercises for bending of the gallbladder
With properly selected exercises, gymnastics for the inflection of the gallbladder can become not only a therapeutic measure, but also a preventive measure to prevent deterioration of the condition. Although all gastroenterologists are unanimous that the prevention of gallbladder bending is by definition impossible (of course, if we talk about congenital pathology).
To improve the functioning of the gallbladder, it is recommended to perform the following exercises when bending the gallbladder:
Starting position: lying on your stomach, arms extended along the body, feet resting your toes on the floor. As you exhale, the head, chest, arms and legs (even at the knees) are simultaneously raised from the plane of the floor. You need to fix the pose for a few seconds, but do not hold your breath. Then slowly, as you exhale, return to the starting position. Perform 5-6 times.
Starting position: lying on your back, straight arms extended behind your head, lower back pressed to the floor. As you exhale, raise your straight legs 20 cm from the floor and hold for 3-5 seconds, then raise your legs higher - 50 cm from the floor and also hold for 5 seconds (do not hold your breath). As you exhale, slowly lower your legs and relax. Repeat 4 times.
Starting position: lying on your back, legs straight, arms extended along the body.
Take as deep a breath as possible, hold your breath for 3 seconds, and then slowly exhale the air, “squeezing” it out, while straining the muscles of the abdominal wall. Repeat 8-10 times.
Diet food
The patient must understand the following: the more carefully he follows the doctor’s recommendations and the stricter he is in taking preventive measures, the faster the disease will be cured. To do this, first of all, it is necessary to establish the norm and composition of nutrition. Diet is the key to successful treatment.
If a person is diagnosed with a bend, then a strict diet is always prescribed, but at the same time it contains all the products necessary to maintain the person’s activity.
You will have to exclude from the diet:
- dishes containing fats, especially of animal origin;
- spicy snacks and condiments;
- sour types of foods (sour berries and fruits);
- legumes;
- sweets;
- carbonated drinks;
- confectionery.
You can eat:
- baked, boiled or steamed vegetables;
- non-acidic fruits and berries;
- various cereal products;
- all types of fermented milk products with a small percentage of fat content;
- lean fish and meat prepared by any method other than frying.
You can eat, or rather, it is healthy to eat pumpkin in boiled and even raw form. You can drink pumpkin juice in the amount of one and a half liters per day. This pumpkin diet allows you to improve the flow of bile and tone the bladder muscles.
A person should know that eating cold food, as well as salty foods, can cause the disease to worsen.
It should also be noted that a salt-free diet has a beneficial effect on the body not only with this disease.
The diet for illness is structured in such a way that a person can get all the nutrients necessary for the body.
It is also important to maintain a water regime, and for this a person needs to drink at least 1.5 liters of water per day every day. An insufficient amount of fluid leads to thickening of the bile, and this is unacceptable if the bladder is bent.
yalechus.ru
Source: www.belinfomed.com
The most interesting:
How to get rid of bile stagnation in the liver
The problem of cholestasis concerns both gastroenterologists and surgeons, depending on the cause of its occurrence and severity. First, let's look at where bile gets from the liver and what leads to its stagnation. After eating, the digestion process begins, which requires enzymes, acids, and other biologically active substances.
To understand how the outflow of bile from the liver occurs, consider the structure of the hepatobiliary system. It includes the bladder, excretory ducts and the liver itself. Thanks to this complex, bile enters the duodenum in parallel with the secretion of the pancreas, which is necessary for the digestion of food. A decrease in the volume of secreted bile or difficulty in its outflow leads to disruption of the breakdown of fats, glycogen synthesis, and an increase in cholesterol levels.
Causes of bile stagnation in the liver
Every day, bile is secreted in the liver in a volume of up to one liter. Considering the complex mechanism of its production and the branched system of ducts, there are many reasons leading to cholestasis. Predisposing factors due to which bile may stagnate and the outflow may be impaired include:
- alcoholism;
- unhealthy diet (abuse of fatty, fried foods, spicy seasonings). This group of reasons also includes long “hungry” periods, due to which temporary cholestasis can occur;
- lack of mobility;
- diseases of the endocrine system;
- pathologies of the digestive organs;
- biliary dyskinesia;
- infectious diseases;
- sclerosing cholangitis;
- frequent stressful situations;
- condition after cholecystectomy (removal of the bladder). Stagnation in this case may occur due to the lack of a “reservoir” for collecting bile. As a result, it can enter the intestine in an unconcentrated form. Its activity is sufficient to digest only a small amount of food, which is why split meals are recommended after surgery. If the principles of the dietary diet are not followed, bile accumulates in the ducts, which is fraught with inflammation and stone formation;
- pregnancy;
- congenital anomalies of the hepatobiliary tract;
- long-term use of certain medications.
Now let's look at the most common causes of cholestasis:
- cholelithiasis;
- inflection of the gallbladder;
- oncopathology;
- parasitic infestations.
Cholelithiasis
The most common cause of stagnation is obstruction (blocking) of the duct with a stone. This complication is observed in cholelithiasis, the development of which is based on the process of stone formation.
The severity of clinical signs depends on the location of the stones, their shape and size. Symptoms of stagnation of bile in the liver in this case are manifested by colic, namely sharp pain in the area of the right hypochondrium. It is usually observed after physical activity and diet violations.
Cholestasis is accompanied by pain. Its appearance is due to the blocking of the lumen of the duct, as a result of which the bile ducts expand and the liver increases in size. Stretching of its capsule leads to pain in the right hypochondrium.
The person is worried about nausea, vomiting and fever. Among the complications of the disease, in addition to duct obstruction, it is worth highlighting its inflammation and pancreatitis.
Bend of the gallbladder
The pathological form of the bladder is often congenital, but sometimes appears during life. An inflection can form in the area of its body, neck, bottom, or even be located in the duct. A deformed gallbladder is unable to perform physiological functions and interferes with the excretion of bile.
Often the pathology does not manifest clinical signs. Only sometimes discomfort in the area of the right hypochondrium, flatulence, nausea or poor appetite may bother you. Severe pain is observed when the duct or neck of the bladder is bent.
Deformed organs cannot remove the entire secreted volume of bile, as a result of which cholestasis develops.
The inflection of the bladder is often discovered by chance during a preventive ultrasound.
Oncological diseases
To make a correct diagnosis, it is necessary to analyze each symptom of the disease and take into account the results of additional examination. Quite often, cancer is detected at a late stage, when metastasis occurs and the patient’s quality of life worsens.
Signs of obstructive jaundice appear against the background of blocking the paths of bile movement. A malignant neoplasm, growing into a duct or gallbladder, causes cholestasis. The tumor can be primary or be a metastasis of distant cancer sites (stomach, lungs). In addition, disruption of bile outflow is observed with the growth of pancreatic cancer.
Parasitic lesion
In most cases, the liver is affected by ascariasis and echinococcosis. The first type of helminthic infestation is characterized by damage to the digestive organs, the development of an allergic reaction and severe complications. Roundworms can enter the biliary tract, thereby disrupting bile flow and causing obstructive jaundice. Symptomatically, the pathology is manifested by bursting pain in the liver area, dyspeptic disorders (nausea, vomiting), yellowness of the skin, mucous membranes, itching, discoloration of feces and darkening of urine. When a bacterial infection is attached, purulent inflammation of the ducts develops, and the risk of abscess formation in the gland increases.
As for echinococcosis, the occurrence of cholestasis is caused by compression of the biliary tract by a parasitic cyst. Clinically, the pathology is manifested by nausea, poor appetite, heaviness in the right hypochondrium and intestinal dysfunction in the form of diarrhea. Palpation (palpation) of the abdomen reveals hepatomegaly (increased liver volume) and a round additional formation (cyst).
Types of bile stagnation
The form of cholestasis depends on its cause and the location of the block in the hepatobiliary system. Usually there are two types: intra- and extrahepatic stagnation. It can occur acutely or have a chronic course. Also distinguished:
- partial type when bile production decreases;
- dissociated, in which the delay concerns only individual bile components;
- total is observed in the complete absence of bile flow into the intestines.
Kink in the body of the gallbladder, deformation: symptoms and consequences
A kinked gallbladder is quite common. The shape of the gallbladder, when it is not deformed, is very similar to a pear. But often constrictions can form in the area of the organ, which lead to changes in shape.
Most often, a bend occurs where the cervical canal connects to the body of the organ.
True, it happens that the bends are localized in the bottom area. The disease may not manifest itself in any way for a long time, but over time, when the outflow of bile becomes impaired (the motility of the bile ducts decreases), stagnation may occur. This inevitably leads to disturbances in the gastrointestinal tract. Digestion will suffer, first of all, because the process of breaking down complex fats will be significantly reduced.
Pathology can be of different origins. It all depends on which parts of the organ are deformed.
Causes of inflection
There are two main reasons for the bending of the organ body:
- congenital form;
- acquired disease.
Congenital pathology
It happens that at the very beginning of embryo development (this happens in the first trimester of pregnancy at 5 weeks of fetal formation), a disturbance occurs during the formation of internal organs, in particular the gall bladder.
The organ is formed incorrectly with multiple or single constrictions. Thus, underdevelopment and deformation of the organ occurs - a congenital bend of the gallbladder, which leads to changes in its shape, proportions and prevents proper growth.
The newborn feels normal, the deviation does not manifest itself in any way. But at the time when the child is switched to adult food, the bubble begins to form incorrectly. It stretches out, and sometimes the kinks affect several areas of the organ at once, and then the gall bladder takes on a bizarre shape (hourglass shape, hook-shaped, etc.).
The body of the bubble is a hollow area, quite mobile, so it can periodically change as a result of various deformations. Then the doctor makes a diagnosis called labile inflection of the gallbladder. If the deformation of the organ does not cause significant illness, then medical care is usually not required.
In medical practice, such changes in the formation of an organ are often detected purely by chance during a routine ultrasound examination.
In principle, congenital pathology in a child, as in an adult, only leads to digestive disorders.
If a double bend occurs, this often becomes the cause of bile duct dyskinesia, especially in children at an early age. As the child grows up (school age), deviations in the function of bile secretion may appear.
Acquired form of the disease
Causes:
- Increased mobility of the bladder (occurs due to improper location of the organ). The organ is not attached to the right groove, which is located in the lower part of the liver.
- Significant enlargement of internal organs (liver, gall, kidneys on the right).
- Violation of diet (hunger strikes are replaced by excessive food consumption).
- Sedentary work, sudden changes in body position, lifting heavy objects. This is called functional inflection.
- The internal organs are largely retracted. Occurs in old age when organs change their typical position or with sudden weight loss.
- Mechanical injuries.
- During pregnancy. The reason is that the growing uterus begins to put pressure on the internal organs and as a result, their deformation occurs.
- Sudden weight gain (obesity).
A bend can form anywhere in the organ. Usually there is a bend in the cervical part of the gallbladder, but the most dangerous thing is the bend of the body of the organ.
The acquired form of the disease is associated with inflammation of the organ (cholecystitis). It can be acute or chronic. Often accompanied by the formation of stones (cholelithiasis).
With double bends, blood vessels are pinched and blood circulation is disrupted. Some organ cells die, tissue necrosis occurs. Numerous cracks appear in the walls, over time they increase, bile begins to leak out and enters the peritoneum. Then inflammation (peritonitis) occurs and this is an indication for immediate emergency medical care.
Symptoms of bending
There are usually no characteristic symptoms for congenital pathology. Of course, it all depends on the stage of the disease and the area where the death occurred. When there are multiple kinks, a person may feel some discomfort under the costal arch on the right, and the stomach may also hurt. After eating food, especially fatty food, people with this pathology often experience nausea and periodically vomit. From the gastrointestinal tract - diarrhea. At the same time, the bile increases.
The pathology of the acquired inflection can also pass without visible symptoms until a certain time, but over time the patient may develop dyskinesia of the bile ducts and then the disease will make itself felt.
As the disease progresses, the patient complains of general weakness in the body, lethargy, apathy, and loss of appetite. The abdomen is swollen, the patient suffers from heartburn, and air burps often occur.
The pain on the right under the rib, scapula, and in the area of the spine becomes more and more noticeable. At the same time, their character may change. The pain can be dull, sharp, or bursting.
The color of the skin changes, the skin acquires a yellowish (lemon) tint. There is a sudden weight loss for no apparent reason, and profuse sweating occurs.
Common signs of different forms of the disease are as follows:
- frequent attacks of nausea, which are often accompanied by vomiting with and without the release of bile;
- due to the fact that bile is thrown into the esophagus, bitterness occurs in the mouth and heartburn occurs periodically;
- unstable stool (constipation is replaced by loose stool);
- interest in food disappears;
- the stomach swells, a feeling of heaviness appears;
- vegetative syndrome - rapid heartbeat;
- pale skin;
- an attack of pain can last a long time (several days) or occur suddenly and pass quickly (increased pain occurs after eating).
True, according to therapists, the excess is to a small extent and may not manifest itself at all either in childhood or in adulthood.
Consequences of the disease
Failures in the biliary system negatively affect human health, well-being and metabolic processes in the body.
The consequences of the disease usually appear only after some time. Moreover, this period is different for different people. The disease itself, and its consequences, do not fall into the category of terrible diagnoses. You just need to always consult a doctor on time and follow all prescribed recommendations. It is especially important to pay attention to the quality and manner of nutrition.
In the advanced stage of the disease, when the bladder is severely deformed, the most dangerous consequence of the disease may occur - necrosis of organ tissue (this was mentioned earlier).
If the bile outflow channel is completely blocked, a rupture may occur - perforation of the organ, and bile will enter the peritoneum. This causes peritonitis and, without immediate attention from a surgeon, can cause the death of the patient.
Important! If an acute attack of abdominal pain occurs, you should immediately consult a doctor.
The most common complications that can be caused by bending include diseases such as:
- biliary dyskinesia;
- cholelithiasis;
- chronic form of cholecystitis;
- calculous cholecystitis;
- reactive pancreatitis;
- gastritis;
- there is a high probability of developing diabetes;
- Vision may sharply deteriorate, the elasticity of blood vessels will decrease significantly, the ability of muscles to contract will weaken (such consequences occur in the body when the content of fat-soluble vitamins noticeably decreases).
In case of double or multiple kinks with pronounced symptoms that generally do not respond to conservative treatment, the gallbladder must be removed.
We recommend reading:
No comments yet
pechen1.ru