Adenocarcinoma of the gallbladder is a malignant neoplasm that originates from the cells of the wall of this organ. Neoplasms of this type are quite common and account for about 4% of all malignant neoplasms. 90% of patients with this diagnosis show signs of gallstone disease. Other risk factors for the development of this disease include female gender, surgical interventions on the biliary tract and gallbladder, contact with dangerous substances such as toluene and benzene, parasitic infestations, and ulcerative colitis.
Malignant neoplasms of the gallbladder are quite aggressive and early metastasize to the nearest lymph nodes and liver tissue. Invasive growth of the tumor into the liver tissue is often observed. In the presence of adenocarcinoma of the gallbladder, early seeking qualified medical help is of great importance. The earlier the disease is detected, the more effective the treatment is.
Leading clinics in Israel
Assuta
Israel, Tel Aviv

Ikhilov
Israel, Tel Aviv

Hadassah
Israel, Jerusalem
This abnormal condition is characterized by several features:
- tumors formed in the bile duct or in any of its parts first develop along the walls of the organ. Once the inner epithelium is damaged, the mutated cells grow into the liver parenchyma and beyond;
- inside the resulting cyst there is a lining of the epithelium, which produces mucin (a protein containing polysaccharides);
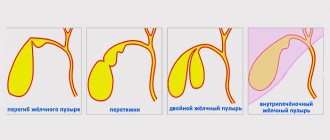
- the disease is also characterized by two types of development - complicated and uncomplicated. With an uncomplicated type of development, the tumor grows slowly without accompanying complications. In the complicated type, foci of suppuration and bleeding areas appear on the tumor capsule.
A tumor is formed from the integumentary and glandular epithelium of the ducts. This type of cancer is characterized by an infiltrative type of growth, develops along the duct, and can invade the pancreas, portal vein, hepatic artery and other organs. Biliary tract cancer metastasizes to the liver and regional lymph nodes.
The main difficulties in diagnosing the disease
The main factors that complicate the detection of cancer can be clearly identified:
- absence of obvious symptoms of this disease;
- similarity of symptomatic manifestations with other diseases of the abdominal organs;
- negative impact of the liver on the process of diagnosing the disease (it covers the gallbladder, significantly complicating the diagnostic process).
Medicine knows of cases of diagnosing gallbladder cancer after the organ was removed, which is a consequence of other diseases. If there are stones, then malignant tumors affect it quite rarely.
To diagnose gallbladder cancer, as well as determine the degree of its growth, not only multiple tests are used, but also many diagnostic procedures of the abdominal organs.
The diagnosis, as well as the extent of its prevalence of the disease (staging), helps to establish visualization of the bladder area and other abdominal organs.
Causes of the disease
There are several risk factors for the formation of extrahepatic bile duct tumors. The leading role in the etiopathogenesis of the disease is assigned to cholelithiasis with the presence of stones in the ducts. This relationship can be explained by mechanical irritation of the duct walls by stones.
Other predisposing factors include:
- pathologies of extrahepatic ducts;
- bacterial or parasitic infections (typhoid fever, opisthorchiasis, clonorchiasis, paratyphoid fever);
- sclerosing cholangitis;
- nonspecific ulcerative colitis and other intestinal pathologies;
- congenital cystic dilatation of bile ducts.
There is a high risk of this type of cancer in patients who have frequent contact with benzidine and beta-naphthylamine.
The occurrence of a cancer process can be facilitated by the use of X-ray diagnostics with a contrast agent - Thorotrast, poor diet, alcoholism, smoking, drug addiction, the presence of the human immunodeficiency virus and viral forms of hepatitis. Predisposing factors also include age over 65 years.
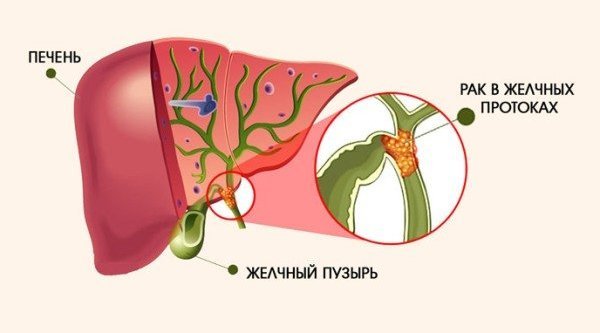
Cancer classification
Malignant neoplasms most often occur at the junction of the bile ducts of the liver and bladder, but can occur anywhere else in the system. This cancer is characterized by slow growth and the ability to metastasize.
The following types of tumors can be distinguished:
- mesenchymal;
- epithelial;
- mixed.
The disease can also be divided into 2 types:
- extrahepatic bile duct cancer;
- carcinoma of the intrahepatic canal.
The bile ducts are partially located outside the liver, where they are more susceptible to infection and most often it is in this place that normal tissues degenerate into malignant ones. Anatomically separate channels are able to come together and grow together, which is considered the beginning of tumor development.
The stage of cancer refers to the size and extent of spread of the tumor beyond the boundaries of the site of formation. According to the TNM classification, the following stages of cancer are determined:
Tis (0) — stage of preinvasive carcinoma;
T1 (IA) - developing tumor is limited to the duct;
T2 (IB) - the tumor penetrates the walls of the duct;
T3 (IIA) - cancer penetrates into the bladder, liver, branches of the hepatic artery or portal vein. Nearby lymph nodes are affected in stage IIB;
T4 (III) - the following structures may be involved in the cancer process: main portal vein, common hepatic artery, other bile ducts, stomach, colon, duodenum, anterior peritoneal wall.
Stage IV corresponds to stages T1-T4, in the absence or presence of secondary tumor foci in regional lymph nodes (N0-N1) and the definition of distant metastases (M1).
According to histology, ductal cancer can be classified as adenocarcinoma of varying degrees of differentiation; undifferentiated and squamous cell forms are less common.
Do you want to know the cost of cancer treatment abroad?
* Having received data about the patient’s disease, the clinic representative will be able to calculate the exact price for treatment.
Based on the type of growth, this type of cancer is divided into:
- diffuse-infiltrative;
- papillary cancer of the extrahepatic bile ducts;
- nodal.
Stages of pathology
Cancer pathology is usually divided into four stages. In this case, you can select one more - zero.
- Zero stage. Cells that have undergone a mutation concentrate on the inner wall of the organ, also affecting healthy tissue.
- First stage. A formation appears that is small in size and oval or slightly elongated and is located on the wall of the gallbladder. It has a small exit into the cavity of the affected organ. In appearance, it can be mistaken for a polyp, but differs from the latter in its rapid growth and development. The first stage is divided into two stages. In the first, the connective and internal tissues of the walls are captured. In the second stage, muscle tissue is also affected, as well as another connective layer.
- Second stage. It is also customary to divide it into two stages. During the first, the visceral part of the peritoneum is damaged. Next, the process moves to the tissues of the liver, pancreas, small and large intestines, and nearby lymph nodes.
- Stage 3. At this stage, the liver vessels are affected, as a result of which metastases spread throughout the body.
- Stage 4. When it occurs, metastatic cells damage distant organs and lymph nodes.
Symptoms of the disease
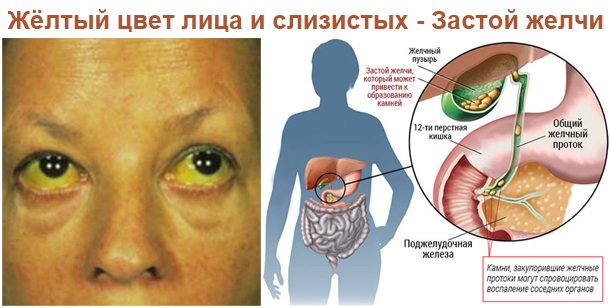
In almost all patients with carcinoma, the process of bile outflow is disrupted, therefore the earliest and main symptom of cancer of the extrahepatic biliary tract is considered obstructive jaundice, which can occur in 97% of cases. In some patients, yellowness of the sclera of the eyes and skin occurs suddenly, in others it occurs gradually over 2-3 months. Jaundice is usually persistent and intense, but can occur in waves or with relapses.
Pain in the right hypochondrium, in the epigastric region, that occurs with this disease is constant and pronounced. They tend to get worse at night. In addition, patients with bile duct cancer often experience a feeling of nausea, vomiting, noticeable general weakness, sudden weight loss, itching, and fever. There is a change in the color of the stool to a lighter color and darkening of the urine.
When the ducts are blocked, empyema of the gallbladder is formed, dropsy, secondary biliary cirrhosis, and cholangitis develop. In the later stages of the disease, characteristic signs such as hepatomegaly and bladder enlargement occur.
In most cases, there is no increase in temperature. But when bile stagnation or inflammation occurs, hyperthermia may occur. Liver dysfunction occurs and intoxication of the body is observed.
General rules
Diet for gallbladder disease is an essential component of treatment for both acute and chronic forms of cholecystitis , cholangitis (inflammation of the bile ducts), and biliary dyskinesia . The basic diet for these diseases is Table No. 5 and its varieties.
In case of acute cholecystitis, in order to maximize sparing of the gastrointestinal tract in the first days, complete fasting is indicated. Only warm drinks in small portions are allowed: weak sweet tea, berry and fruit juices diluted with water, rosehip infusions. On days 3-4, an anti-inflammatory version of diet No. 5 is prescribed - Diet 5B .
Light food in pureed form without broth and butter is introduced into the diet in limited quantities: slimy soups (oatmeal, rice, semolina), liquid pureed oatmeal and rice porridges with a small addition of low-fat milk, pureed compotes, jellies, vegetable juices. Then include in small quantities well-mashed steamed meat, low-fat cottage cheese, boiled fish, wheat bread or crackers.
Meals are fractional, in small portions (at least 5 times), without sodium chloride , with plenty of liquid (up to 2.5 l/day). The calorie content of the daily diet is 1600 kcal (50-60 g protein, 40-45 g fat, 200-250 g carbohydrates). On days 8-10 the patient is transferred to Diet 5A and then to Diet No. 5 .
In case of chronic cholecystitis (without exacerbation), the main principles of dietary nutrition are maximum sparing of the gallbladder and liver with physiologically adequate nutrition, normalization of bile secretion and cholesterol in the blood, and in the absence of diarrhea , strengthening of intestinal function ( Diet No. 5 ).
Small and frequent meals are provided to promote the outflow of bile. To enhance bile secretion, salads and vinaigrettes seasoned with unrefined vegetable oils are introduced into the diet. The diet includes various vegetables, berries and fruits that stimulate the process of bile secretion, and the high fiber content eliminates constipation .
All easily digestible carbohydrates (jam, sugar, sweets, honey) are excluded or sharply limited from the diet, since their consumption leads to stagnation of bile, as well as vegetables containing oxalic acid (sorrel, spinach) and essential oils in large quantities (citrus fruits). The diet includes chicken eggs (not more than one), but it must be remembered that yolks enhance the motor function of the gallbladder and have a choleretic effect.
For pain or bitterness in the mouth caused by eating eggs, only egg whites are included in the diet. The calorie content of the daily diet is at the level of 2700-2900 kcal (proteins -100 g, including animals - 60%, fats -90 g, including vegetable 30%, carbohydrates -450 g).
Salt consumption is limited (10 g), liquid at the level of 1.5-2 liters. With a sharp exacerbation of chronic cholecystitis, the diet is similar to the diet for acute cholecystitis .
For combined diseases of the pancreas and gall bladder ( pancreatitis + cholecystitis ), Table No. 5P . This table is characterized by an increase in the content of proteins and vitamins and a restriction in the diet of fatty and carbohydrate foods.
Products containing a lot of extractives and purine bases (cabbage broth, meat and fish broths), refractory fats of animal origin, and sugar are excluded from the diet. Avoid hot, spicy, sour, sweet and fatty foods that stimulate the function of the pancreas, as well as foods rich in fiber. Food is cooked mainly by steaming, meals are divided into small portions. The total caloric content of the diet is reduced to 2500 Kcal.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of cancer is carried out using laboratory and instrumental studies.
Thanks to ultrasonography of the bile ducts, dilation of the intrahepatic ducts and intraductal hypertension are diagnosed. Using MRI, the level of occlusion of these ducts is determined. Spiral computed tomography is performed.
Ultrasound helps to study the state of the biliary system and find out the location of the tumor.
Also carried out:
- endoscopy;
- cholangioscopy;
- angiography;
- biopsy.
Laboratory tests include: analysis of CEA (oncofetal protein) and AFP (alpha fetoprotein), which help identify the presence of possible malignant neoplasms.
Based on the examination data, the doctor can give the patient an accurate diagnosis and determine the most effective therapy.
How to detect gallbladder cancer?
To diagnose this pathology, both instrumental and laboratory techniques are used.
Laboratory diagnostic methods can detect “disorder” in the hepatobiliary tract system, but are not able to identify its cause.
For example, a blood test for biochemistry in the presence of a tumor shows an increase in the level of bilirubin, liver transaminase and pancreatic amylase (if the pathology occurs against the background of pancreatitis). The thymol test will show an increase in the gamma globulin fraction of proteins and a decrease in the level of total protein. The coprogram will detect the presence of undigested fats and various dietary fibers in the stool. A complete clinical blood test will show anemia and leukocytosis. Cancer antigens (CA 19-9 and carcinoembryonic antigen) will be detected in venous blood.
Read also: Treatment methods for cysts in the gallbladder
Instrumental diagnostic techniques make it possible to identify the structure and location of a specific tumor. These include:
- Ultrasound of the abdominal cavity;
- X-ray of the biliary tract using a contrast agent;
- Magnetic resonance imaging;
- radiological diagnostics (scintigraphy);
- laparoscopic diagnostics with the possibility of taking a biopsy of tumor tissue.
Treatment of the disease
The choice of treatment regimen for this type of cancer is based on the location and stage of the tumor. Since this disease is often diagnosed in the final stages, this prevents radical surgical intervention.
With timely diagnosis of common bile duct cancer, in the absence of adjacent structures joining the cancer process, excision of the common bile duct is likely, followed by suturing of the proximal part of the common bile duct into the wall of the small intestine or duodenum.
If the supraduodenal part of the common bile duct is affected, cholecystectomy and resection of the duct are performed.
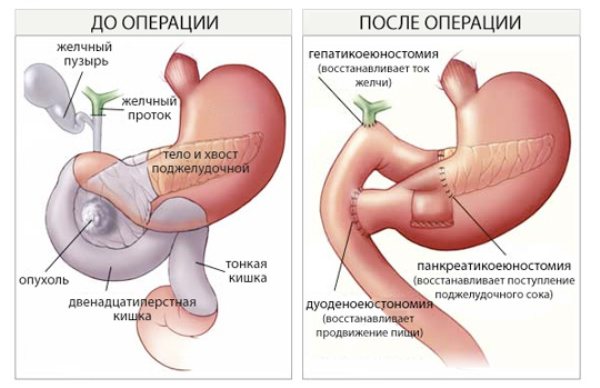
When the tumor is localized in the distal part of the common bile duct, the need for pancreaticoduodenal resection arises.
If metastases spread, partial hepatectomy or Whipple surgery is required.
Palliative surgery in the final stages of cancer serves to relieve symptoms and improve patient well-being. These measures include common bile duct stenting, cholecystogastrostomy, cholecystoduodenostomy, choledochoduodenostomy, etc. After the operation, the patient is prescribed antibacterial therapy.
Surgical treatment of extrahepatic bile duct cancer is supplemented with hyperthermia, chemotherapy and radiation therapy, and others.
Radiation therapy is used as an adjuvant treatment to reduce the risk of relapse. A course of radiation is also carried out when the tumor is inoperable or very large. This helps slow the spread of cancer. Chemotherapy drugs help destroy tumor cells, while causing intoxication of the entire body.
One of the effective methods of therapy is photodynamic treatment. Special photosensitizing substances are used for it. The method involves the effect of a light wave on the tumor. As a result of the use of photodynamic equipment, the blood vessels that feed the tumor are destroyed. Left without them, the tumor dies.
Innovative targeted therapy used to treat this type of disease is based on the work of certain bioactive substances that can suppress the development of tumor cells. However, such substances do not affect normal tissues.
Hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemoperfusion. During the operation, cytostatic drugs and the method of exposure to high temperatures are used. This method is effective even for metastases.
Traditional methods of treatment
When treating this type of cancer, it is possible to use folk remedies as an additional treatment:
- radish juice with honey. Mix these two ingredients and drink the mixture twice a day, a quarter glass before meals;
- a decoction of their corn silks. 1 tbsp. pour a spoonful of corn silk into a glass of clean water and cook for half an hour over low heat. Drink 20 ml twice a day. Course – 50 days;
- a mixture of immortelle, St. John's wort and corn silk (1 tablespoon each). The mixture is poured into 0.5 liters of boiling water and infused for at least 3 hours. Take the drug 1 glass per day for a month;
- tincture of black henbane. 2 tbsp. spoons of henbane are poured into 0.5 liters of vodka, left for 2 weeks in a dark place. Take 2 drops of tincture in the morning on an empty stomach;
- An infusion from aconite is prepared in the same way as from henbane, used according to the following scheme: 1 day - 1 drop, increase the dose drop by drop every day until it reaches 25 drops at a time, then begin to reduce to 1 drop. Course – 50 days. The course is repeated after a short break.
Don't waste your time searching for inaccurate cancer treatment prices
*Only upon receipt of information about the patient’s disease, a representative of the clinic will be able to calculate the exact price for treatment.
What are called tumors of the bile ducts in the body, as well as the gallbladder?
Based on statistical data, we can safely say that of the total number of oncological formations, cancerous tumors of the gallbladder ducts account for no more than 5%, namely 4.3%. Only one percent of male patients are diagnosed with oncological tumors, and subsequently undergo surgery on the bile ducts and gallbladder. Women's statistics are less pleasant, because here the rates increase exactly three times, which confirms the fact that women are more susceptible to gallbladder cancer than men. Experts around the world try every year to reduce these numbers to zero. Israeli doctors have achieved particular results in this area. Thanks to the constantly increasing level of qualifications, cutting-edge equipment, the latest diagnostic and treatment methods, as well as an individual approach to each case, Israeli specialists have achieved worldwide respect and authority in the treatment of such diseases. A successful combination of practical and theoretical skills helps thousands of patients forget about their illnesses forever and live a full life.
Today, despite all the modern achievements of technological, scientific, medical and other progress, the etiology of this type of disease is unknown. Gallstone disease is found in almost 90% of all people with cancer. Adenocarcinomas account for almost 82% of all carcinomas present in the gallbladder of the average patient with a similar problem. Local invasiveness of growth into the liver tissue is very typical for this type of tumor. Metastases of these tumors penetrate through the lymphogenous route into the liver, pancreas and duodenal lymph nodes.
Read! What is choledocholithiasis
The clinical picture is as follows: patients complain of pain that is localized in the right upper abdomen, as well as frequent vomiting and nausea. In rare cases, it is possible to establish a diagnosis before surgery.
How long do people live with bile duct cancer?
The prognosis depends on the stage of the disease, the possibility of surgical removal of the tumor without any residue, primary or recurrent lesions, the patient's age and general health. For widespread tumors, the prognosis is unfavorable.
When the pathology is diagnosed at an early stage, the patient’s life expectancy is 3-5 years from the moment of diagnosis. But it is rarely possible to identify a disease at the very beginning of its formation. In patients with this diagnosis, life expectancy after tumor removal is 1-2 years.
Video on the topic: