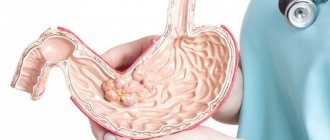
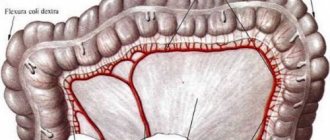
Inoperable cancer is said to be when a malignant tumor cannot be removed using surgical methods. Typically, such situations arise during a common process in the terminal stages. At the same time, the primary focus can be located in almost any organ. In most cases, cancer is inoperable if there are multiple metastases or if the primary tumor is located in those parts of the body where it is impossible to create surgical access.
- Statistics
- How does inoperable cancer manifest?
- Types of inoperable cancer depending on location
- Examples of inoperable cancer
- Treatment of inoperable cancer
What are the types of intestinal obstruction?
There are different classifications of intestinal obstruction:
| Depending on the reason | Mechanical - divided into three types:
Dynamic intestinal obstruction occurs as a result of persistent spasm or paresis (relaxation) of the intestinal wall. |
| Depending on the level |
|
| Depending on the speed of occurrence |
|
| Depending on the degree of intestinal obstruction |
|
According to statistics, if timely medical care is not provided, with acute intestinal obstruction, up to 90% of patients die within 4–6 hours. Therefore, it is important for the patient to know the first symptoms of this condition and, if they occur, to immediately consult a doctor.

Treatment of inoperable cancer
Despite the impossibility of radical treatment, the patient can be helped using conservative methods. Of course, they will not help get rid of the tumor or significantly improve the prognosis, but they can help change the quality of life for the better and increase life expectancy. Among conservative methods of cancer therapy, doctors may offer:
- Chemoembolization. The method involves the introduction of chemotherapy drugs directly into the vessels feeding the tumor. As a result, it is possible to slow down tumor growth by simultaneously blocking blood flow and cell death under the influence of chemotherapy.
- Polychemotherapy. Often used for widespread tumor processes. When prescribing such treatment, it is necessary to take into account the general condition of the patient, because chemotherapy drugs negatively affect not only cancer cells, but also healthy cells of the body. Today, oncologists have a wide variety of chemotherapy drugs in their arsenal, which allows them to be combined in different combinations and achieve the desired therapeutic effect.
- Minimally invasive operations. They are used provided that the patient can tolerate such an intervention. Minimally invasive surgeries can remove a small area of cancer and relieve symptoms. Such methods include cyber-knife, cryodestruction, electrical destruction, radiofrequency ablation, etc.
For inoperable forms of cancer, palliative treatment is also prescribed. It is aimed at eliminating symptoms and improving the psychological and emotional state of patients. In some cases, palliative treatment can be carried out at home, after receiving recommendations from a doctor.
Book a consultation 24 hours a day
+7+7+78
Why does intestinal obstruction occur in cancer?
The causes of intestinal obstruction in malignant tumors are different:
- Blocking of the intestinal lumen by a tumor that grows inside the lumen, narrowing due to inflammation in the intestinal wall.
- Compression of the intestine from the outside by tumors that are located in other organs: liver, kidneys, uterus, ovaries, bladder, prostate gland.
- Adhesions in the abdominal cavity as a result of interaction of the tumor with surrounding tissues after surgery.
- Damage to the intestine due to radiation therapy and chemotherapy.
- Accumulation of dense stool and fecal stones in the intestine as a result of chronic constipation.
- When tumor tissue affects the brain or spinal cord, spastic intestinal obstruction may develop.
- The development of paralytic intestinal obstruction in cancer patients is facilitated by: peritonitis, severe impairment of the liver and kidneys, decreased potassium levels in the blood, impaired carbohydrate metabolism, and diabetes mellitus.
Most often, intestinal obstruction develops in the later stages of cancer; its occurrence is facilitated by previous operations on the abdominal organs and frequent courses of radiation therapy.
How is chemotherapy administered correctly?
Chemotherapy is the treatment of a cancerous tumor by exposing it to powerful chemicals. Malignant intestinal tumors are also stopped and put into remission with the help of cytostatic medications that prevent the proliferation of cancer cells, stop the spread of metastases and promote their destruction.
There are three types of chemotherapy that are given for colorectal carcinoma:
- Neo-adjuvant. This type of therapy is carried out in the period before surgery. The purpose of the procedure: to reduce the number of atypical cancer cells.
- Neo-adjuvant using radio rays. This procedure differs from the previous one only in that it is combined with radiation treatment for greater effectiveness.
- Adjuvant. This type of therapy is used after surgery to reduce the risk of relapses and the spread of metastases. Adjuvant chemotherapy for intestinal carcinoma is carried out only eight weeks after surgery and lasts at least six months.
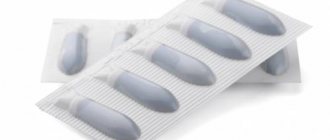
Many patients have a question: how are chemotherapy drugs administered? They can be taken as tablets or administered intravenously through a catheter.
The following are drugs that are used for chemotherapy in patients with bowel cancer:
- Capecitabine (tablets);
- Folfox (solution);
- Fluorouracil (solution);
- Xelox (solution).
Symptoms
The main symptom of intestinal obstruction is abdominal pain. They appear suddenly, for no apparent reason, and are cramp-like in nature. Painful sensations periodically subside and appear, intensify again, in accordance with the waves of peristalsis - physiological movements of the intestine. After some time, the pain may become constant.

With strangulation intestinal obstruction, the pain is constant, periodically intensifying during peristaltic waves. If the pain suddenly goes away, this is a bad sign; it indicates that movements in the intestinal wall have stopped and paresis (paralysis) has developed.
With paralytic intestinal obstruction, dull, bursting pain is most often bothered.
Other possible symptoms:
- Constipation: abdominal pain is accompanied by the absence of stool for several hours, and gas does not pass. If the obstruction is severe, the patient may pass stool due to the passage of the contents of a portion of the intestine that is located below the obstruction.
- Nausea and vomiting, which increases over time, can become uncontrollable. Vomiting does not bring relief. At first, it occurs reflexively; the vomit contains stomach contents and bile. Then, with some types of intestinal obstruction, it becomes fecaloid.
- Some patients with partial intestinal obstruction experience diarrhea.
- Loss of appetite.
- Blood in the stool.
- Bloating. It becomes asymmetrical, and intestinal movements—peristalsis—are noticeable. Gradually these movements disappear, which indicates that intestinal paresis has developed.
- Deterioration of the patient's general well-being.
- Dry mouth.
- Apathy, depression of consciousness.
Causes of the disease
The exact causes of the pathology are not clear; more often the disease is diagnosed in patients who have relatives with oncological pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract.
Another risk factor is frequent consumption of foods with high levels of animal fat and fiber. Other factors that can cause the development of pathology in the rectum are:
- hereditary diseases (diffuse polyposis, Turcot and Gardner syndromes);
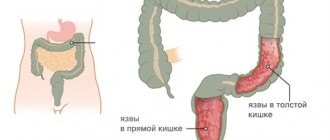
- chronic intestinal diseases (rectal fissures, fistulas, hemorrhoids, polyps, colitis). Precancerous conditions include ulcerative colitis and Crohn's disease;
- anal sex;
- prolonged constipation;
- frequent stress;
- prolonged use of certain types of medications;
- presence of HPV (human papillomavirus);
- long-term contact with harmful substances (amides, asbestos, tyrosine) in production;
- diabetes;
- age after 50 years;
- sedentary lifestyle, obesity;
- drinking alcohol and smoking.
Complications of intestinal obstruction
If the patient is not promptly provided with medical care, intestinal obstruction leads to life-threatening complications. Due to vomiting, fasting, and impaired secretion of digestive juices, the body loses fluid, which is fraught with dehydration, and the water-electrolyte balance is disturbed. Because of this, all organs suffer. Along with the liquid, protein is lost, including albumin, which provides the colloid-osmotic pressure of the blood plasma and is involved in the transfer of certain substances. The situation is aggravated if, as a result of damage by metastases, the function of the liver, the “factory” for the production of albumin, is disrupted. Due to the loss of protein, the oncotic pressure of the blood decreases, fluid from the vessels rushes into the tissues, and edema occurs.
The contents that are in the intestines above the place where the obstruction occurred cannot leave the digestive tract. This leads to rotting and proliferation of pathogenic microorganisms. The barrier function of the intestinal wall is disrupted, and toxic compounds penetrate into the blood.
Due to compression of blood vessels and disruption of blood flow to the intestine, necrosis - part of the intestinal wall dies. A hole is formed in this place, and the contents of the intestine enter the abdominal cavity, where inflammation develops - peritonitis .
All of the above ultimately leads to sepsis, serious disruption of the functioning of all organs ( multiple organ failure ) and death of the patient.
Diagnostic methods
If a cancer patient shows signs of intestinal obstruction, he must be urgently hospitalized in a hospital. The easiest and fastest way to diagnose intestinal obstruction is a plain radiography of the abdominal cavity. In the pictures you can see areas of the intestine swollen with gas and fluid accumulation. One of the characteristic symptoms is the so-called Kloiber cups - accumulations of air and fluid that look like inverted cups or the letter “U”.
The doctor may prescribe other diagnostic methods:
- Ultrasound examination of the abdominal organs.
- Irrigography is an X-ray examination during which a radiopaque substance, a barium suspension, is injected into the intestines using an enema.
- CT scan.
- Colonoscopy.
Prognosis and prevention
The prognosis of rectal adenocarcinoma depends on the stage of the oncological process, the patient’s age, his immunity, the treatment performed and other individual characteristics. If the pathology was identified at the first stage of development, then the five-year survival rate after surgery is about ninety-five percent. Diagnosis of glandular cancer at the second stage reduces this figure to seventy percent. When the pathology spreads to the lymph nodes, that is, in the third stage, only half of the patients survive after treatment. The fourth stage of the disease gives a chance of five-year survival to no more than ten percent of patients.
To prevent cancer, you must follow some recommendations:
- eat right - consume a minimum amount of fatty and meat dishes (with the exception of white meat);
- give up a sedentary lifestyle;
- monitor your weight;
- consult a doctor and undergo timely treatment for gastrointestinal diseases;
- do not abuse alcohol and stop smoking.
After completing therapy, it is necessary to undergo periodic examinations to prevent relapse.