Can there be a temperature with pancreatitis and why?
When both the pancreas and any other organ become inflamed, toxins are released into the blood , resulting from the death of body cells. The brain perceives these substances as a signal to activate the immune system. Metabolism accelerates, cells become more efficient. Because of this, a large amount of energy is released, which heats the body and increases its temperature.
Considering the mechanism of the disease and the results of examination of patients suffering from pancreatitis, gastroenterologists argue that changes in temperature may accompany inflammation of the pancreas. However, with different forms of the disease, the temperature varies.
In acute
With the development of an acute form of pancreatitis, swelling of the gland and obstruction of the ducts of the organ indicate the disease. The destroyed tissue begins to become inflamed, which is accompanied by a change in body temperature. Temperature allows us to judge the purulent-inflammatory process in the body and its severity:
- Easy. With this degree of disease, the gland suffered minor damage and the inflammation was mild. Therefore, the temperature either does not rise at all or rises slightly. The maximum time the fever lasts is three days.
- Medium-heavy. This degree is characterized by significant damage to pancreatic tissue, widespread inflammation and the onset of the formation of necrotic foci.
- Severe degree and complications. With this variant of the development of the disease, the patient experiences extensive damage to the gland, involving the entire organ or almost the entire organ in the process.
The patient complains of severe pain, vomiting that does not bring relief, and an increase in temperature to 39 degrees. This is due to serious intoxication of the body and activation of the defense system. With moderate pancreatitis, the fever continues for up to ten days, while on the fourteenth day the patient recovers.
In addition, a purulent abscess begins, and inflammation spreads to nearby organs and tissues. In addition, cysts, fistulas and internal bleeding form as complications. The combination of these signs leads to extensive intoxication of the body and the spread of infection. The temperature reaches forty degrees and is difficult to lower.
Separately, cases of decreased temperature during pancreatitis should be considered. Extreme intoxication, profuse internal bleeding and dehydration observed in extremely severe cases of the disease cause vascular collapse. This condition leads to a sharp drop in blood pressure, heart rate and body temperature. The patient loses consciousness.
Without timely assistance from a doctor, the patient dies, therefore, if the temperature drops during an attack of pancreatitis, it is necessary to immediately call an ambulance.
For chronic
In the chronic course of pancreatitis, without exacerbations, the disease is not accompanied by any symptoms . By following a diet and leading a healthy lifestyle, the patient is able to significantly delay or completely avoid the development of an attack.
An indicator such as body temperature in the chronic form of the disease usually remains normal or increases slightly, but not more than 37 degrees.
Patients are advised to measure their temperature regularly and note any changes.
So its sharp increase indicates the following complications:
- tissue necrosis;
- sepsis and abscess;
- paranephritis.
Low-grade fever, which persists for a long period, acts as a signal of possible oncology .
Reasons for temperature changes
The inflammatory process in the pancreas is not always accompanied by changes in temperature. Its fluctuations depend on the form in which pancreatitis occurs - acute or chronic. It may remain within normal limits if the disease manifests itself in a mild form.
The so-called low-grade fever, at which there is a slight increase (up to 37-37.5 degrees), accompanies a pathology of moderate severity.
High values indicate the existence of severe pancreatitis with accompanying purulent inflammation.
An exacerbation that causes acute pancreatitis is accompanied by pain in the upper abdomen. At the same time, vomiting occurs. It usually bothers the patient after eating, 20-30 minutes later.
The abdomen becomes hard and pain occurs in the pancreas area. Pallor of the skin of the face and a bluish tint to the lips appear.
Often the temperature balance is disturbed due to non-compliance with the recommendations prescribed by the doctor and the prescribed diet. Eating fatty, spicy or smoked foods, as well as overeating, can cause temperature disturbances.
As a rule, this occurs in the chronic form of the disease, when the patient complains of a constant feeling of nausea and general weakness of the body. An increase in temperature (no more than 38 degrees) usually occurs in the evening or at night.
For chronic pancreatitis
At this stage of the disease, the temperature is usually normal; with exacerbation and no complications, the temperature does not exceed 37 degrees. Any change in temperature during the chronic stage of the disease indicates the occurrence of complications.
There may be cases when there is a sharp jump in temperature, while the person experiences chills and falls into a feverish state.
Fever is a clear sign that an abscess has begun in the body, that is, pustules have appeared in the damaged tissues of the pancreas . Further progression of the condition in the absence of proper treatment can lead to infection of nearby tissues.
For acute pancreatitis
An increase in temperature is the first sign that an exacerbation of the disease has occurred. Moreover, the temperature balance is disturbed from the first day of illness.
If the thermometer readings reach a critical level of 39 degrees, you should immediately consult a doctor to prescribe an examination of the body and identify existing complications.
In some cases, with an advanced form of the disease and prolonged neglect of the treatment process, surgical intervention may be necessary, otherwise there is a risk of death.
Reasons why temperature deviates from the norm during acute inflammation:
- The course of the inflammatory process is accompanied by the formation of substances that cause an increase in body temperature.
- Decay products poison the body.
- The inflammatory process is accompanied by complications.
In a febrile state, a patient with acute pancreatitis may experience other symptoms:
- Weakness and malaise.
- Dizziness, headache.
- The person feels muscle weakness.
- The pulse quickens, the pressure drops.
- As a result of a sharp decrease in appetite and its absence for a long time, the patient loses a lot of weight.
- Problems with the gastrointestinal tract appear: vomiting, nausea, problems with stool.
Peculiarities
Temperature readings correspond to the degree of damage and type of disease. If this is not the first time a person has encountered pancreatitis, then by the severity of the symptoms he will be able to determine the danger of inflammation.
The sluggish condition does not cause a person virtually any discomfort if you follow the recommendations of a specialist. Exacerbation of chronic pancreatitis can be provoked by: unhealthy diet, alcohol consumption, early cessation of treatment. An exacerbation will make itself felt by an increase in temperature and pain.
With calculous
This type of disease is characterized by the formation of stones in the ducts. Stones interfere with the outflow of pancreatic juice. All this leads to an increase in the inflammatory process. The disease can be acute or chronic. Fever occurs when inflammation increases. The formation of stones occurs due to the influence of other chronic diseases (cholecystitis, hepatitis, ulcers). In this case, low-grade fever may appear long before the first clinical manifestations of calculous pancreatitis.
Exacerbation of the disease
If an exacerbation begins (usually 30-45 minutes after eating), the fever rises rapidly. The values reach 38-39 degrees. Other symptoms of the disease also become brighter. To combat an attack, you will need to temporarily stop consuming food and liquids, as well as provide bed rest.
In acute form
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=r1P-TPolitI
It is difficult to differentiate between exacerbation and transition of the disease into the acute phase. In both cases, the person’s condition worsens significantly, the temperature rises, and pain makes itself felt. Acute inflammation of the gland poses a great threat, so if you suspect the disease has progressed to an acute form, you need to call an ambulance.
In children
The temperature in children rises in the same cases as in adults, but it can be slightly lower even in the acute course of the disease. If a child suffers from chills and pain, you need to call a local doctor or an ambulance. Chronic inflammatory damage to the pancreas in childhood is extremely rare.
Temperature is measured several times a day
Need to know! If a person experiences fever, pain, nausea, or diarrhea, a diagnosis needs to be made. Several diseases can cause such symptoms. To conduct effective therapy, an accurate diagnosis is needed.
Chronic pancreatitis low-grade fever
The largest gland in the human body is the pancreas. It secretes enzymes for processing proteins and fats in the small intestine, insulin and glucogen, which regulate blood sugar levels, and other substances necessary for the normal functioning of organs. A malfunction of the pancreas results in severe pain and pathologies in the tissues, disturbances in the nutrition of blood and cells.
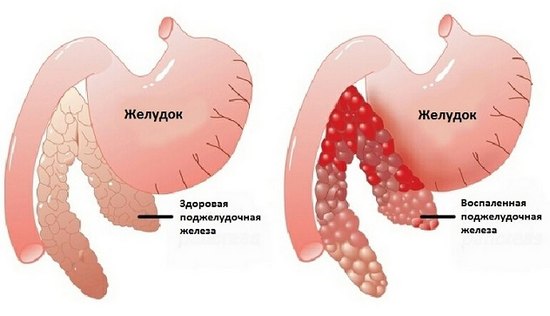
Pancreatitis - inflammation of the pancreas
Can there be a temperature with pancreatitis, and what is the mechanism of its occurrence? In the chronic form of the disease, low-grade fever appears. It is unstable and slightly elevated. Basically it stays within 37 degrees, falling by 0.1 or rising by no more than 0.4, or rather the maximum is 37.4 degrees. With sluggish pancreatitis, low-grade fever can last for several hours or days and appear continuously for years if the pancreas is not treated, but also does not provoke an exacerbation.
Characteristic symptoms for an attack of chronic pancreatitis are:
- epigastric pain;
- low-grade fever;
- chills;
- headache.
The process of inflammation in the tissues of the gland is provoked by pathogenic microorganisms, which simultaneously cause spasm and pain. Protecting itself, the pancreas produces and releases interleukin into the blood, an enzyme that signals the presence of foreign cells in the body’s tissues. The blood carries them to the brain, where the hypothalamus turns on the body to fight foreign agents and gives the command to produce phagocytes, which include lysozyme, white blood cells and other substances responsible for the destruction and removal of foreign cells and microorganisms from the body.

The temperature with pancreatitis often reaches subfebrile values
The process is accompanied by the release of energy, the temperature rises, accompanied by dry skin without sweating. Heat exchange is regulated by small tremors - chills. Poor nutrition of the brain causes headaches.
To normalize the temperature, it is necessary to relieve the spasm and treat the pancreas. To do this, you need to take an analgin tablet or even half of it and lie down. The pancreas loves peace. To treat chronic pancreatitis and reduce the temperature to a normal level, you need a diet and adherence to a nutritional schedule.
If for gastritis and ulcers you need to eat small portions every 2-3 hours, then for pancreatitis the daily norm of the product is divided into 4 times. Snacks are excluded. Each meal causes the organ to turn on and produce enzymes. Simply put, every bite, especially eaten on the go, loads the pancreas, causing it to produce enzymes and release interleukins into the blood and brain.
Low-grade fever and dry skin require additional hydration of the skin and tissues of internal organs. Therefore, you need to drink 40–50 grams of highly alkaline mineral water 20 minutes before each meal. You need to open the bottle in advance so that the gases escape and keep it in the room. Then the water temperature will be optimal for consumption. At the same time, it is necessary to increase the rate of consumption of ordinary water, which removes waste and toxins from the body. It cannot be replaced with tea and juices.
Dietary nutrition for pancreatitis with fever primarily excludes the consumption of fats, sugar and chocolate. Smoking, especially on an empty stomach, has a more aggressive effect on the pancreas than alcohol. Therefore, both irritants should be avoided.
What happens?
Depending on the severity and form of the disease, the temperature in patients varies:
- Low (about 35 degrees). In case of vascular collapse due to acute pancreatitis with severe intoxication and complications.
- Subfebrile (37–38 degrees). This temperature is observed in patients with a mild acute form of the disease or with a chronic form.
- High (38–40 degrees). A significant increase in this indicator in a patient indicates a moderate to severe degree of the disease in acute form. Such heat often accompanies the development of complications and damage to nearby organs and tissues by the inflammatory process.
Treatment
Doctors, speaking about what to do at high temperatures with pancreatitis, note the undesirability of self-treatment . If hyperthermia develops, the patient is advised to call an ambulance. Specialists will conduct the necessary examination and determine further treatment tactics.
If the temperature does not exceed 38°C and is not accompanied by severe abdominal pain, the patient is allowed to take antipyretic drugs: Paracetamol, Ibuprofen, etc. They help cope with hyperthermia and alleviate the person’s condition.
In case of chronic pancreatitis and symptoms of its exacerbation (severe pain, vomiting), antipyretic and anti-inflammatory drugs cannot be used. Eliminating pain will prevent the doctor from examining the patient and determining the cause of the discomfort.
To alleviate the condition, the patient can independently use the following groups of medications:
- antispasmodic medications (“No-shpa”, “Drotaverine”, etc.), eliminating spasm of the pancreatic duct and ensuring the removal of active enzymes from the pancreas. This will reduce pain and prevent the development of pancreatic necrosis;
- enzyme agents if symptoms develop after ingesting large amounts of food or fatty foods. Doctors recommend using Festal, Gastal and their analogues.
In addition to medications, therapeutic fasting is indicated: a person should not take food, carbonated drinks, etc. It is allowed to drink plain water in small portions.
While waiting for an ambulance, the patient is prohibited from:
- use traditional medicine or homeopathic medicines. They do not have proven safety and effectiveness, and therefore can lead to progression of the disease or the development of complications;
- take any food. When products enter the gastrointestinal tract, the formation and secretion of pancreatic juice, rich in enzymes, increases. In this regard, the degree of damage to the pancreas during exacerbation of the disease increases;
- drink alcohol or smoke;
- independently use antibacterial agents or painkillers;
- induce vomiting, expecting relief.
It is important for patients to know whether the temperature rises with pancreatitis. Understanding that hyperthermia is a symptom of an exacerbation of the disease allows patients to seek medical help in a timely manner.
Surgery
After surgery for pancreatic necrosis, the patient is in the intensive care unit. His temperature may be high for the first few days. If there are positive changes in the tests, there is nothing to worry about. A healthy body always reacts with fever to inflammatory phenomena and severe interventions. On the second or third day the temperature returns to normal. After the operation it should be at 37.5⁰C. This is not a contraindication for transfer to the general surgical department.
Operations are difficult to tolerate for this category of patients. Mortality after surgery reaches high figures. Therefore, doctors try to avoid surgery in all possible cases. In the acute period, it is better to replace them with the technique of establishing drainage under ultrasound control.
If after surgery for pancreatic necrosis, the fever does not subside for more than 1 week, this is a poor prognostic sign. As a rule, such symptoms indicate that the revision of the abdominal cavity was not completed. An abscess may remain somewhere, which causes high fever and intoxication.
A patient after surgery for pancreatic necrosis receives high doses of antibacterial drugs. However, if the drugs are chosen incorrectly, there is a risk of infectious diseases of other organs. Most often after surgery, the lungs are affected. High temperatures may indicate pneumonia, which has developed due to weakened immunity. During the operation, a machine breathes for the patient. Artificial ventilation is sometimes performed in the intensive care unit. This is an additional point that provokes the development of complications.
Why is it dangerous?
Changes in temperature during pancreatitis in themselves are not so dangerous. However, the reasons for this change are dangerous:
- Thus, a significant and sharp increase in it is promoted by an extensive inflammatory process with possible suppuration or tissue necrosis, as well as damage to nearby organs.
- A drop in temperature below 36 degrees indicates the onset of vascular collapse due to severe intoxication and the need for urgent medical attention.
- Subfebrile values over a long period of time allow us to judge the possible onset of oncology.
Overheating of the body itself poses the following dangers:
- cardiopulmonary failure;
- convulsions;
- blood viscosity increases;
- dehydration;
- folding of proteins in the structure of cells.
Changes in temperature help indirectly monitor the patient’s condition and the development of his disease. This is why it is so important to quickly respond to all temperature fluctuations.
How to normalize temperature in chronic pancreatitis
Patients who have been diagnosed with pancreatic disease are often interested in whether the temperature with pancreatitis is chronic and how it can be brought down. To do this, you need to relieve the spasm and be able to restore normal functioning of the gland with the help of foods, diet and folk remedies. Medications:
- Baralgin;
- Drotaverine;
- No-shpa.
Among the folk remedies, pharmacies sell the Monastic herbal collection - tea. It should be drunk warm, morning and evening, instead of regular tea and coffee for 3 weeks. Changing the herbal composition or taking a break of 10 days will help avoid the body getting used to the product.
The easiest way to deal with a temperature that rises immediately after a person eats food is around 37 degrees. If it lasts an hour or less, then the reason is overeating. Too much food has entered the stomach and the pancreas works overtime to produce the required amount of enzymes to break it down. Portions should be reduced and fatty meat should be excluded for several months.
With pancreatitis, discomfort and periodically rising temperature can relieve a glass of warm milk and a banana for dinner. Pain and low-grade fever often occur at night in chronic pancreatitis. This dinner will prevent them.
External signs
When the temperature rises, weakness and general malaise occur, as well as:
- pain syndrome;
- weight loss;
- diarrhea;
- nausea.
The higher the value, the worse the person feels. The heat is accompanied by a feeling of coldness and trembling. If chills cause serious discomfort, antipyretics are used.
No less important information about pancreatitis during pregnancy - treatment methods, possible complications
Of course, a high temperature in itself is already a cause for concern. But there are symptoms that cannot be ignored - and if they are combined with an increase in febrile reaction during pancreatitis, urgent medical attention is required. "Warning signs" include:
- sharp increase in abdominal pain;
- the appearance of pronounced tension in the muscles of the abdominal wall;
- convulsions;
- bleeding of their upper or lower gastrointestinal tract;
- shortness of breath with paleness and/or cyanosis of the skin, dizziness and a feeling of suffocation;
- attack of cough with moist wheezing in the lungs;
- extreme thirst or, conversely, loss of the ability to drink fluids with frequent vomiting, diarrhea and fever (this can lead to shock due to dehydration).
With severe intoxication, confusion and disorientation in space often occur. Therefore, fainting or the patient’s indifference to what is happening around him, lack of response to stimuli (questions, touching the hand, etc.) is a truly alarming symptom: the nervous system is suffering, help is needed immediately. It may also be a sign of collapse (a sudden drop in blood pressure) and shock.
What to do and how to reduce the fever?
If a patient with pancreatitis has a fever, then, regardless of the form of the disease and the magnitude of the indicator, it is recommended to immediately consult a doctor.
Such changes most often accompany worsening of the inflammatory process in the body.
With a slight increase, if it does not cause discomfort, the temperature is not reduced at all or resort to the help of herbal remedies. So, decoctions of rosehip or mint can reduce fever. However, traditional medicine recipes are not suitable for all patients, as they cause allergies.
When the thermometer reaches 38 degrees, it is recommended to begin antipyretic therapy . Drugs such as Paracetamol and Aspirin help with this. The drugs are not intended for self-administration, and therefore the patient waits for the doctor to assess his condition and prescribe appropriate treatment.
Until the doctor arrives, keep the patient quiet and drink plenty of fluids to prevent dehydration.
Fever is an optional symptom of inflammation of the pancreas. At the same time, any change in the body temperature of a patient suffering from pancreatitis indicates the development of the disease, its aggravation or the appearance of complications. Therefore, it is important to monitor how the temperature changes and, at the slightest suspicion of a worsening condition, consult a doctor.
Characteristic
Exacerbation of pancreatitis is accompanied by high fever: 39-40 degrees. If there is a combination of fever and aching pain in the left side of the abdomen, call an ambulance. Acute damage to the gland poses a threat to human life. It must be treated in a hospital setting.
Thermometer for measuring body temperature
It’s not a good idea to take an antipyretic before seeing a doctor; it can complicate the diagnosis. If a diagnosis has already been made, the doctor may prescribe antipyretic medications. When treating indolent lesions, a person does not need to be given antipyretic drugs if the therapy regimen has been drawn up correctly and the diet is followed.