High temperature after removal of appendicitis is regarded by many people as a disease, or as a sign signaling the presence of a pathological process in the body. Doctors first of all pay attention to how the operation was performed, the characteristics of the patient’s body, what limits hyperthermia reaches and how long it lasts. It is quite natural that abdominal intervention in organs and systems is stressful and after applying the last stitch, the patient must get used to the new condition.
High fever after appendicitis surgery
It is difficult to predict how a patient will react to organ removal and how long the temperature will last after surgery, since each patient is individual and the duration of the rehabilitation process is influenced by many different factors. First of all, it is necessary to understand that hyperthermia itself, after the intervention of a surgeon, is a normal and quite expected phenomenon. The indicators are influenced by the choice of method in which the operation was performed:
- Laparoscopic - the organ is removed through an incision in the abdomen. Since the tissue is minimally damaged, the healing process will not take much time. An increase in temperature after laparoscopy can last up to 3 days and disappear spontaneously. There is no need for long-term hospitalization and recovery time is short.
- Abdominal surgery is prescribed in difficult cases, with accumulation of pus in the organ, enlargement, or looseness of the structure. After opening the incision, stitches are placed and the requirements for rehabilitation become significantly more complicated. In such cases, hyperthermia can be either low-grade or high - varying between 37 - 38 degrees. It is worth noting that it can last for a decade.
The first symptoms of appendicitis
Anatomical changes in the rudimentary appendix, its location, the form of development of the disease, the duration of the inflammatory process, the age of the patient and other conditions determine the first symptoms of appendicitis. Constant stabbing or dull pain in the abdomen, occurring suddenly without reason, in the afternoon (in most patients) is the main symptom of pathological inflammation of the appendix in its classic location.
- Potato casserole with meat: recipes with photos
- How to get rid of fungus in the cellar
- How to call a phone via the Internet for free from a mobile phone and computer
Initially, the pain occurs near the navel, then moves higher (epigastric region). Pain sensations gradually change. They become pronounced, intense, localized in the lower abdomen on the right (in the iliac region) . When walking, coughing, laughing, attacks of acute pain intensify. Positioning on the right side or on the back alleviates the patient’s condition. With an atypical location of the appendix, the symptoms are different:
- Retrocecal inflammation (the process is located behind the cecum) occurs in 6-25% of cases. The main symptom of the pathology is diarrhea with mucus and high fever. Pain may be absent or occur throughout the abdomen. In most cases, unpleasant symptoms are localized in the lumbar region. The pain radiates to the right leg.
- Pelvic localization is more common in women - 21% of cases, in men - 11%. Frequent loose stools with a lot of mucus and difficulty urinating are characteristic symptoms. Other signs of inflammation appear vaguely. Pain occurs in the lower abdomen and radiates to the umbilical area.
- The left-sided location occurs with a mirror position of the internal organs or increased intestinal motility. The clinical picture is similar to that of ordinary appendicitis, but the symptoms appear on the left side.
- The subhepatic location of the process during inflammation gives pain in the right hypochondrium.
The clinical picture of the disease is different with empyema. This is a rare form of inflammation of the appendix. Symptoms of the pathology increase slowly. Deterioration in health and increase in temperature occurs several days after the onset of the inflammatory process. In this case, mild pain in the place where the appendix is located occurs immediately.
Causes of fever
Fever is a complication that occurs after surgery in the body. Under its influence, the body's barrier functions increase the production of interferon and interleukins. The task of proteins is to ensure the phagocytic function of leukocytes.
The temperature after appendectomy stimulates the production of proteins that reduce the vital processes of bacteria and builds a connection between the immune and other systems. High temperatures enhance the functionality of anti-inflammatory proteins.
The main reason why the temperature persists after removal of appendicitis is related to the operation, but it can also be a consequence of damage to organs and systems. Fever often occurs due to complications:
- abscess formation of the wound surface;
- phlegmon in the peritoneal wall;
- accumulation of infiltrate or abscesses in the peritoneum;
- peritonitis.
In more than 80% of cases, a negative factor causing hyperthermia is a wound infection.
Etiology
The duration of manifestation of elevated body temperature in women, men and children depends on the degree of development of complications after surgery. If the unpleasant indicator persists for a week or more after surgical treatment, then this can be caused by the following factors:
- blood loss during surgery;
- injuries during surgery;
- infections of internal or external stitches;
- violation of diet rules.
Most often, fever is diagnosed by doctors precisely when providing surgical care and from damage to various organs and systems.
Temperature after surgery to remove appendicitis often manifests itself with wound and abdominal complications:
- abscess formation;
- phlegmon of the abdominal wall;
- infiltration and abscess of the cavity;
- peritonitis.
Acute peritonitis
An increase in temperature can also be caused by a decrease in immunity. Surgical assistance is quite a serious stress for the patient’s body, and subsequent rehabilitation depends on the characteristics of the patient’s body. During the recovery period, the body directs all its strength and reserves to eliminating the infection. With a reduced level of immunity, the patient begins to experience inflammatory processes that need to be eliminated only with medication.
Also, the cause of an increase in body temperature after appendicitis may be the installation of drainage. The patient will continue to have a high fever until the drainage tubes are removed. To prevent infection of a patient's wound, doctors prescribe antibiotics.
Classification of fever
To determine what exactly caused the system dysfunction, fever is classified:
- temperature 37 – 38 degrees – subfebrile;
- from 38 to 39 – febrile;
- from 39 to 40 – pyretic;
- from 40 and above – hyperpyretic.
To determine the graph of temperature fluctuations after removal of appendicitis, on the first day, drugs with antipyretic effects are not prescribed.
According to the type of fluctuations, hyperthermia is:
- constant (balancing within 1 degree);
- laxative (values are not stable, fluctuate by 1 – 2 degrees);
- intermittent – varies between low temperatures of 38 – 39 degrees;
- return – high numbers after a couple of days, decrease to normal limits;
- hectic - fever occurs with sudden temperature changes of 3 - 5 degrees;
- wavy - there is a smooth increase, decreasing to subfebrile values, with a smooth transition to normal limits;
- atypical – causeless increase;
- perverted - when the temperature rises in the morning, and in the evening there are no deviations from the norm;
- wavy in an acute form - short jerks without breaks between lifts;
- recurrent – after remissions, the fever returns.
Duration of hyperthermia
The duration of temperature after surgery for appendicitis is above normal limits and should not exceed a decade, but if all signs indicate that the body is not recovering, it is worth focusing the doctor’s attention on this, since there is a more serious danger of developing postoperative pathology.
Reasons why the temperature does not stabilize after appendicitis removal a week later:
- large blood losses during removal of appendicitis;
- injuries to nearby organs;
- infection during surgery;
- against a background of suppressed immunity, acquisition of respiratory diseases;
- inflammation in the postoperative wound;
- if after surgery a drainage is placed in the wound;
- non-compliance with the recommended diet - adherence to the correct diet speeds up the healing process.
It is worth noting that if the drainage is in the wound for a long time, the temperature can persist for more than 10 days.
More serious causes are usually accompanied by additional symptoms:
- bowel dysfunction – mainly constipation;
- abdominal cramp;
- bouts of vomiting;
- excessive sweating;
- loss of consciousness.
Complications that maintain high temperature in the body can be caused by the negligence of medical personnel and insufficient competence of doctors. Before you decide to take a responsible step, you should familiarize yourself with the reputation of the clinic and doctor. Lack of sterility, improper dressing, earlier removal of sutures, drainage forgotten in the wound - reasons that can not only increase the readings on the thermometer, but also lead to more serious consequences.
Reasons for rising temperature
Treatment of acute appendicitis is always a surgical operation to remove the appendix. Intervention in the body, its integrity, is an unnatural process that disrupts the functioning of organs and cells. The body reacts by increasing its temperature.
In most cases, such a reaction is a variant of the norm, since the immune system after surgery for appendicitis begins to produce a large number of leukocytes to neutralize possible viruses and pathological conditions. As a rule, when damaged tissues heal, a reaction in the form of an increase in temperature is considered normal.
It is not recommended to lower the temperature below 38C, so as not to disrupt the body’s healing process. Moreover, doctors are concerned when a person’s body temperature does not increase. This indicates that the immune system is very weak, which means that adverse reactions, complications, and inflammatory diseases are possible. The absence of hyperthermia after abdominal surgery can especially lead to serious health problems.
Experts note that overheating in the human body begins at the stage of the inflammatory process in the appendix of the cecum. This is a symptom indicating an inflammatory process, acute appendicitis. Therefore, after removal, the symptom persists for several days.
But in some cases, long-term persistence of fever indicates pathology.
- A strong temperature jump over a short period of time for no apparent reason. Sometimes such a reaction indicates an allergic reaction when introducing certain drugs or the ingress of pathogenic microflora that is actively reproducing.
- Hyperthermia as an immune response to the introduction of a drainage system after surgery. If it goes beyond a certain time, it is considered a pathology and requires drug treatment.
- Complications during surgery resulting in damage to internal organs.
- Excessive blood loss during surgery.
- Infection during surgery.
- A patient with ARVI during the postoperative period. The patient's body's defenses after removal of the appendix are aimed at recovery. Against the background of reduced immunity, any ARVI is tolerated more severely by the patient, longer, and longer treatment is required.

- The patient does not follow a diet after the appendix has been excised. If you ignore the diet prescribed by the doctor, disturbances in the functioning of the intestines, and even inflammatory processes, are possible.
An increase in temperature after removal of the appendix lasts about a week and is considered normal and part of the recovery phase. But if the time frame is not met and the fever persists after a week, additional blood, urine and other tests are necessary, at the discretion of the specialist. Tests are necessary to establish the exact cause of fever, diagnosis, and timely treatment.
Diagnostics
If after appendicitis the temperature persists for more than a decade, the reasons for this phenomenon are determined using diagnostic methods.
The purpose of the measures is to identify additional infections in the body. The doctor examines the suture site in detail. Draws attention to possible suppuration and the presence of foci of hyperemia.
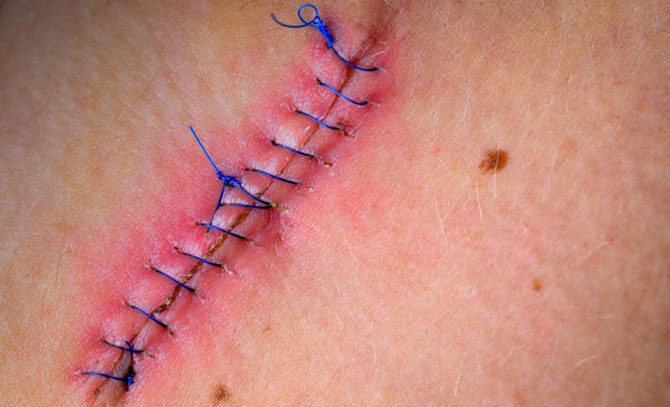
The addition of putrefactive microflora is detected by laboratory methods:
- general analysis of urine and blood - you can notice the dynamics of the disease;
- ultrasound allows you to study the condition of the abdominal cavity and the picture at the site of surgical intervention;
- when pus and blood particles are released, a laparotomy is performed for therapeutic purposes.
Blood analysis
Acceptable limits:
| Components in the structure of blood | Values for the younger age group | Man | Woman | ||
| 1 — 6 | 7 — 12 | 13 — 15 | |||
| Hemoglobin | 110-140 | 110-145 | 115-145 | 130-160 | 120-140 |
| Red blood cells | 3,5-4,5 | 3,3-4,7 | 3,6-5,1 | 4-5,1 | 3,7-4,7 |
| Lymphocytes | 26-60 | 24 — 54 | 25 — 50 | 18-40 | |
| Platelets | 160-390 | 160-380 | 160-360 | 180-320 | |
| ESR | 4-12 | 4-15 | 1-10 | 2-15 | |
| Leukocytes | 5-12 | 4,5-10 | 4,3-9,5 | 4-9 | 4,9 |
| Color index, % | 0,85-1,15 | ||||
| Eosinophils | 0,5-7 | 0,5-7 | 0,5-6 | 0-5 | 0-5 |
| Basophils | 0-1 | ||||
| Reticulocytes | 3-12 | 2-11 | 0,2-1,2 | ||
| Monocytes, % | 2-10 | 2-9 | |||
| Bands, % | 0,5-5 | 0,5-6 | 1,6 | ||
| Segmented, % | 25-60 | 35-65 | 40-65 | 47-72 | |
Deviations from the data indicate a disease, source of infection, pathological process. Typically, the data have some physiological differences, depending on age and gender.
In women, the indicators may be wider due to hormonal changes during puberty, pregnancy, lactation, menstruation, and menopause.
In children, a general blood test is performed before surgery and a week after the surgeons’ manipulations. Instability of the body's barrier functions can allow infection into a weakened body. Temperature after appendicitis in a child may indicate more than just the recovery period. Often high rates confirm the addition of acute respiratory infections and acute respiratory viral infections.
In blood tests, not only normal limits are important, but also compliance with proportions. An imbalance indicates inflammation. If a child has a fever, there is no room for confusion - you should immediately show the patient to a doctor.
How to react to test results
If any indicator indicates a health problem, the temperature has risen, you should not delay treatment. Inflammation and infection negatively affect systems and organs. The analysis must be deciphered by the attending physician. Medical specialists also decide on treatment methods.
How does an attack of appendicitis manifest?
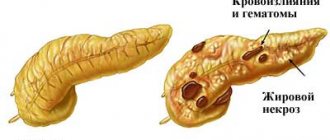
The development of inflammation of the appendix occurs within 48 hours and goes through three stages, during which the form of the disease changes:
- The initial stage of inflammation of the appendix is the catarrhal form. The symptoms of the disease are hidden. The duration of the initial stage is the first 12 hours of the attack.
- During the second stage, a phlegmonous form develops. Lasts 36 hours. The main symptoms of the disease appear . Removing the appendix at this stage does not lead to serious complications.
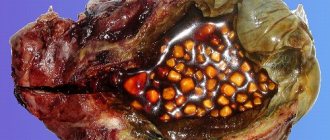
- The third is the advanced, destructive stage. A gangrenous form develops. Without surgical intervention, death occurs.
The clinical picture of an acute inflammatory process changes hourly. Characteristic signs of the disease appear as follows:
| Sign | Stage I | Stage II | Stage III |
| Appetite and general condition | Loss of appetite, general discomfort | No appetite. The patient can only lie down (on the right side or on the back) | The condition is similar to severe food intoxication |
| Pain | Weak (strong occurs with thrombosis of the appendicular artery) | Gain | Very strong |
| Weakness | Small | Stronger | Complete lack of performance, possible loss of consciousness |
| Temperature | Normal or 37.3-37.5°C | Increase to 38°C | 38°C-40°C, hyperthermia, fever |
| Language | Specific white coating at the base, no dryness | All white, not dry | All white, dry |
| Nausea, vomiting | Appear 6 hours after the onset of the attack | Vomiting occurs 1-2 times, is the body’s reaction to pain, does not bring relief | |
| Chair | Defecation disorder (diarrhea, constipation, excessive gas) | ||
| Pulse | Violation in the presence of concomitant diseases | 80-85 beats per minute | Tachycardia |
| Arterial pressure | Increases in the presence of concomitant diseases | Increased | |
Chronic appendicitis occurs in 1% of cases. Most patients with this diagnosis are young women. The disease develops slowly over several years. The main symptom is increased pain in the right side of the abdomen during exercise, coughing, during bowel movements, and in situations where the abdominal muscles tense. Periodically, the disease worsens. Nausea, vomiting, stool upset, and other symptoms of acute appendicitis occur.
In children
The vestigial organ becomes inflamed in children of different ages. Newborns and infants rarely get sick. This is due to the anatomy of the appendix and the peculiarities of their nutrition. The incidence begins to increase from 2 years of age. The clinical picture of appendicitis in children does not differ from that in adults. It is difficult to diagnose the disease in children 5-7 years old. Because of the fear of surgery, they hide the worsening condition. The doctor must demonstrate certain skills in order to win over the child.
Features of the mental development of children aged 6 months to 5 years make diagnosis difficult. Kids cannot clearly tell and show where and how it hurts. The disease in most young patients begins acutely. The increase in temperature during appendicitis reaches 38.5°C-39.5°C . The child becomes restless due to severe abdominal pain, repeated bouts of vomiting, and loose stools appear. These are symptoms of a late stage of the disease.
Any deviations in the child’s behavior and condition should alert parents. Restless sleep, unmotivated whims during the day, sudden squatting with crying during play, poor appetite, fever up to 37.3°C-37.5°C - all these signs indicate possible inflammation of the appendix and are a reason for immediate treatment for medical help.
In older people
The clinical picture of appendicitis in elderly and senile patients is not pronounced and does not correspond to destructive changes in the appendix . Early diagnosis of the disease is difficult. Patients indicate mild abdominal pain, the localization of which is absent. The abdomen is soft, even with rough palpation the pain in the right iliac region is moderate. Appendicitis without fever and an acceptable number of leukocytes make it difficult to diagnose the pathology.
A decisive role in determining inflammation of the appendix is played by hardware techniques - ultrasound (ultrasound), X-ray, computed tomography (CT). Most elderly patients have comorbidities. Against the background of inflammation of the appendix, they worsen. For example, diabetes mellitus decompensates, heart failure increases, and hypertensive crises occur. All this must be taken into account when preparing the patient for surgery and prescribing therapy in the postoperative period.
- The best antioxidants
- Silicone shoe pads: anti-chafing inserts
- Fungus between the toes: effective treatments
In pregnant women
In the first and second trimesters of pregnancy, appendicitis occurs without characteristic features. In the third trimester, when the uterus greatly increases in size and the appendix moves, diagnosing the disease becomes difficult. The attack begins with severe cramping pain in the right side of the abdomen, so initial hospitalization occurs in the gynecological or obstetric department. After 6-12 hours, the pain is localized in the right hypochondrium; after 12-24 hours, pregnant women complain of poor sleep due to aching, constant pain.
In the second half of pregnancy, to determine the pathology, it is necessary to carefully analyze the clinical picture and resort to additional research methods. Using ultrasound, the early stage of inflammation of the appendix is diagnosed; this is the safest method that can be used at any stage of pregnancy. X-ray and laparoscopy have contraindications. All prescribed additional studies should be carried out as carefully as possible and in the shortest possible time.
How to treat postoperative inflammation
A high temperature after appendicitis associated with a complication puts especially strain on the functioning of the kidneys and liver. If the organs had pathological changes before the operation, then the additional load can cause an exacerbation.
In some cases, a general blood test indicates the development of a purulent process. It is important to correct the situation in a timely manner. Fever after purulent appendicitis consistently leads to repeat surgery. Excess inclusions are removed, local antibiotic therapy is carried out, and drainage is installed.