Gymnastics for intestinal adhesions
Physical exercise helps strengthen the abdominal wall, helps reduce adhesions in the intestines and increase their elasticity, eliminate severe pain and improve intestinal functioning. Remember that for results, gymnastics should be performed daily. Some exercises have contraindications - you should consult a specialist.
For intestinal adhesions, doctors recommend the following exercises:
- Lie on your back (preferably a hard surface), place your hands on your stomach. Slowly perform abdominal-diaphragmatic breathing: while inhaling, strain the anterior abdominal wall as much as possible, and when exhaling, pull it in. Repeat 7-10 times.
- Without changing the starting position, bend your legs at the hip joints as you exhale, and straighten as you inhale. Do it at least 7 times.
- Lying on your back, as you exhale, pull your legs towards your stomach, clasp them with your arms, then straighten them to their original position. Repeat 10–12 times.
- Sit upright, stretch your legs, slowly lean forward as much as possible, trying to grab your feet. Do it 10 times.
- Lying on your back, spread your arms to your sides, pull your legs up, bend your knees, then slowly tilt them alternately left and right. Repeat 5 times.
The gymnastic complex should be performed slowly, avoiding sudden movements. If you experience pain in the abdomen or chest, dizziness, or darkening of the eyes, you should immediately stop doing the exercises and lie down. If unpleasant symptoms persist for 15–20 minutes, consult a doctor. Important: intestinal adhesions after surgery can lead to complications, so before performing gymnastics, make sure they are absent.
Adhesions are seals formed from connective tissue. They are localized between the intestinal loops or between the layers located in the peritoneum and in the abdominal cavity (visceral and parietal, respectively).
Seals are formed under the influence of various pathophysiological processes in which epithelial cells are destroyed. Adhesions occur directly at the site of intact cells. This process is often called peritoneal scarring.
Intestinal obstruction: symptoms and treatment
Intestinal obstruction is a dangerous disease
, expressed as a disruption in the process of moving feces through the intestines.
Intestinal obstruction can happen to anyone: all ages from newborns to the elderly are susceptible to pathology, while the manifestations of the disease remain approximately the same.
If pathology develops, urgent surgical intervention is indicated, so it is important to know all the symptoms of intestinal obstruction in adults in order to promptly seek medical help.
Otherwise, the disease can lead to the death of a person.
Types of intestinal obstruction
According to the mechanism of development, mechanical and dynamic intestinal obstruction are distinguished.
Mechanical obstruction develops as a result of blockage of the intestine by various obstacles.
The causes of blockage are:
- inside - foreign bodies, balls of worms, stones, scars, tumors, other formations;
- outside - compressive formations.
All of the above options are obstructive obstruction.
If intestinal volvulus, strangulation, nodulation and, as a consequence, compression of the mesentery occur, strangulation obstruction is diagnosed.
When one part of the intestine grows into an adjacent loop, an invagination appearance develops. If the intestines are compressed by adhesions, this is the most common and frequently diagnosed adhesive intestinal obstruction.
Dynamic intestinal obstruction occurs as a result of impaired intestinal motility.
This can happen when it relaxes or spasms (overexertion). Most often, this pathology is more often diagnosed in the elderly. Its onset can be provoked by intestinal infarction or false obstruction.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=7pvP_zW0feU
According to the course, obstruction can be acute or chronic. Also, intestinal obstruction can be complete or partial.
Symptoms of intestinal obstruction
What should alert a person and prompt them to suspect intestinal obstruction:
- abdominal pain;
- flatulence;
- stool retention;
- nausea and vomiting.
- The main distinguishing sign of intestinal obstruction is pain in the intestines that appears regardless of food. The pain is cramping and very pronounced. The frequency of pain depends on intestinal motility: the pain intensifies with each wave. At the same time, signs of shock may appear on the face - cold sweat, pallor, increased heartbeat. If the pain has decreased by the end of the day, this may indicate intestinal necrosis and necrosis. With such a symptom, after 2-3 days you can expect the development of a serious complication of peritonitis, which can lead to death.
- When intestinal obstruction occurs, fecal transport stops, causing feces and gases to accumulate and stretch the walls, causing unbearable pain. Abdominal bloating is visible externally.
- A frequent companion to the pathology is vomiting. First, it occurs as a result of the movement of feces through the gastrointestinal tract. If the contents of the intestines return to the stomach, the vomit will smell like feces. In the further period of the disease, vomiting can be considered a sign of poisoning.
How to determine mechanical obstruction
In the vast majority of cases, the mechanical form of the pathology is diagnosed.
If the process develops in the small intestine, the symptoms worsen very quickly. The cramping pain around the navel begins to manifest itself. Nausea and vomiting then develop.
With complete obstruction, defecation is delayed; with partial obstruction, diarrhea occurs. In the abdomen, peristaltic sounds intensify in the wake of pain. As necrotic phenomena increase, they stop.
In the colon, pathology takes longer to develop. Initial constipation is replaced by the complete disappearance of bowel movements and flatulence. Then the pain begins, which gradually intensifies. Pain can occur in one place or spread over the entire area. Vomiting may occur once or be absent altogether.
When intestinal volvulus occurs, the disease develops quickly with severe cramping pain.
The following stages can be distinguished in the development of mechanical obstruction:
- The appearance of the initial symptoms - pain, vomiting, flatulence, etc., which is caused by distension of the intestines.
- By the end of the first day, intoxication of the body develops, which leads to increased vomiting, increased temperature, increasing weakness and even fainting. The pain gradually becomes less due to the onset of necrosis of the intestines.
- Peritonitis is the last stage of the disease. Necrotic foci form in the intestinal walls, which leads to perforation of the walls and the release of feces into the abdominal cavity. The pain increases many times, the stomach becomes painful. A state of shock develops. Peritonitis can develop as early as the next day from the onset of the disease.
Symptoms of the dynamic form of obstruction
The dynamic form is characterized by impaired peristalsis and is quite rare.
Contractile movements in the intestine stop most often after injury or surgery. The following stages of dynamic obstruction can be distinguished:
- vasospasm after compensatory surgery. Usually this stage is not characterized by any pronounced phenomena other than weakness;
- in the stage of organic changes, blood supply pathologies occur. The pain is spastic in nature, the abdomen is swollen, nausea intensifies, and vomiting begins;
- at the stage of morphological changes, intestinal necrosis develops. There is no pain or peristalsis. Shock develops. Surgery is required to avoid death.
Diagnosis of intestinal obstruction
During the examination, the doctor performs percussion and auscultation of the abdomen. Sklyarov's symptom is determined - the presence of surges in the area of intestinal loops.
Additionally, X-rays with a contrast agent, ultrasound, and MRI are performed. Biochemistry of blood and urine will show the general condition. If possible, a colonoscopy is performed.
Similar symptoms are produced by such common diseases as appendicitis, ulcers, cholecystitis and some gynecological diseases.
Treatment
To treat the disease in the earliest stages, drug therapy is used.
If its effectiveness is weak, in an acute condition, or in the presence of certain anatomical changes, surgery is prescribed.
The stages of condition correction consist of:
- pain relief with tablets, injections and droppers;
- administration of medications that stimulate motor skills;
- administration of medications that reduce spasms;
- restoration of electrolyte disturbances occurring as a result of intoxication of the body;
- restoring the patency of the upper section of the intestine by probing through the mouth, and the lower section by enema or surgery.
Surgery is usually effective and less traumatic.
It is used when:
- volvulus;
- closure of the lumen with gallstones;
- nodes;
- insertion of a section of intestine into a neighboring one.
In case of peritonitis, sanitation and drainage of the cavity is indicated.
After surgery, antibiotics are prescribed to prevent inflammatory processes occurring in the body. Water-salt metabolism, disturbed during illness by special medications, is also normalized.
Diet for intestinal obstruction
To restore normal functioning of the gastrointestinal tract, a therapeutic diet is required. After surgery, you should not eat at all for 12 hours to allow the intestinal walls to heal.
Further, depending on the severity of the disease and the patient’s condition, the nutrient solution can be administered intravenously.
If the operation is successful, a diet of:
- low-fat broths and vegetable broths;
- mucous decoctions of oats, flax and starch.
In the future, after suffering from intestinal obstruction, foods that cause flatulence and cause constipation are strictly prohibited.
Should be excluded from the menu:
- fatty meat and fish;
- poorly digestible cereals;
- legumes;
- smoked, spicy, salted, marinades, baked;
- coffee, alcohol, chocolate;
- rich pastries, fresh bread;
- apples;
- dairy and fermented milk products.
It is necessary to introduce rye bread and bran into the diet, and consume at least one tablespoon of vegetable oil daily. Prunes, beets, and oatmeal will be useful.
Physical exercise
For some intestinal pathologies - for example, the development of adhesive disease - physical exercise for at least half an hour daily is indicated.
Exercises such as:
- lying on your back, while exhaling, bring your knee to your head and hold it. Pull it back and repeat with the other leg. Repeat 20 times;
- Pull both knees towards your head and hold. Return it back. Repeat 10 times;
- bending one leg at the knee, reach the floor from the side of the other leg. Shoulders and back should not rise. Repeat with each leg 10 times;
- Getting out of bed, place your feet shoulder-width apart and slowly squat as you exhale, without lifting your heels from the floor. Repeat up to 10 times.
Daily simple exercises during the morning rise or an hour before bed will relieve many problems.
Prevention
Preventative measures are very simple:
- it is necessary to monitor the condition of the intestines and promptly treat all identified diseases - inguinal hernias, tumors, adhesions;
- if surgical intervention is necessary, choose laparoscopic surgery;
- switch to a healthy diet: the diet should include a variety of vegetables and spices that stimulate intestinal obstruction;
- adhere to the principles of fractional nutrition;
- drink at least 2 liters of water every day (not tea or juice, but water);
- lead an active lifestyle, if possible walk at least three kilometers a day;
- promptly treat helminthic infestations.
Source: https://zen.yandex.ru/media/netgastritu/neprohodimost-kishechnika-simptomy-i-lechenie-5a89842e8139ba0d23cf4a1d
Reasons for education
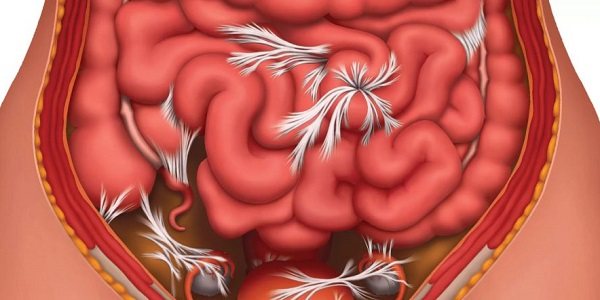
Adhesions are formed for the following reasons:
- Mechanical injuries of open and closed type. Seals can appear after a blow or knife wound, and sometimes they form over time (2 months or more). The cause of adhesions can be any trauma to the peritoneum;
- Genetics. In the case of a genetic predisposition, adhesions appear due to minor damage and mild inflammatory processes, sometimes asymptomatic;
- Female pathologies. Seals can occur against the background of female diseases of the genitourinary system. Most often, adhesions appear due to an inflammatory process in the ovary or its appendages;
- Peritonitis. A disease that occurs due to infection in the layers of the peritoneum. Pathology activates the inflammatory process, subsequently leading to damage to epithelial cells and the formation of compactions;
- Rupture of a duodenal or stomach ulcer. The ulcer is filled with exudate, pus, granulation tissue and mucus. If it ruptures, all these “components” enter the abdominal cavity, which leads to the destruction of many healthy epithelial cells. The contents of the ulcer can also enter the peritoneum through an enlarged perforation (it becomes larger as the disease progresses);
- Inflammatory pathologies localized in the intestines. As an example, patients who have had inflammation of the appendix are susceptible to the formation of compactions, which is why they are at risk. Even after removal of appendix, a person may develop adhesions;
- Congenital anomalies. As a rule, lumps form in children due to abnormalities in the structure of the intestines. These include an elongated sigmoid colon (dolichosigma), intussusception (invasion of one part of the intestine into another), coloptosis.
Most often (13-15% of all cases) compactions occur in patients during the postoperative period. Adhesions can appear after cesarean section, appendectomy and other operations performed using the open method - laparotomy (incision in the upper wall of the peritoneum). This is due to many factors, ranging from violation of the integrity of internal organs and tissues, and ending with drying out of the mucous membranes during the operation.
Reviews and results
According to patients' reviews, many years of experience in nutrition during adhesive disease allowed them to choose foods that do not cause exacerbation. A proper diet can improve bowel movements and help avoid bloating and pain. Many have rated its effectiveness and the reviews are generally positive. It is important to eat regularly and not overload the gastrointestinal tract with an abundance of difficult-to-digest foods.
- “... After appendicitis there was peritonitis, and after 10 years the adhesions suddenly showed themselves. It always gets worse after physical activity and if there is no regular bowel movement. Conclusion - do not overexert yourself physically and do not become constipated. For me, the most important medicine is grated boiled beets with olive oil. I eat it three times a day, 2-3 tbsp. l. before every meal. Baked apples are also good. Diarrhea should not be allowed, since after this the condition will also worsen. Moderation in food is also important. I don’t eat anything spicy or fatty or anything that causes bloating. Such simple rules help maintain a normal state”;
- “... Adhesions appeared after an abdominal injury and forced surgery. I never overeat, I keep a routine. My diet contains little sweets, dough and fatty foods; if I do eat these, I always take Mezim. I eat vegetables and fruits without peeling, and have almost switched to seafood. I do breathing exercises, walk or swim a lot, and do hoops. In this way, I keep myself in a normal state”;
- “...I know this condition. Over the course of 6 years, she underwent 7 operations, and was in the department several times a year with exacerbations. I suffered from pain, gas began to accumulate, and constipation appeared. I couldn’t even eat an apple, not to mention cabbage, salads and radishes. Of course, I have to exclude all this, and I only eat boiled vegetables. My health improved, but I began to feel great after the sanatorium treatment (mud with electrophoresis, mineral water, nutrition, etc.). I’ve been traveling for three years in a row, and I haven’t been to the hospital, I’m in excellent condition.”
Symptoms of the disease
Many patients turn to specialists as a last resort because they do not experience significant symptoms of adhesions. Signs that lumps have formed in the intestines appear too late or do not appear at all.
Therefore, the first thing people at risk need to focus on is frequent pain localized in the abdomen and pelvis.
Full symptoms of intestinal adhesions:
- Pain. It becomes more intense after a heavy meal, as well as during physical exercise and long walking. The pain can have a different character, but most often it is felt as a pulling sensation. Experts note that with adhesions and appendicitis, patients feel discomfort of approximately the same intensity;
- Dyspeptic syndrome. Patients usually feel bloated in the abdomen. Also, many patients experience rumbling that is not associated with a feeling of hunger. All these symptoms are associated with intestinal dysfunction. They may be expressed differently depending on the stage of development of the disease;
- Constipation. Problems with stool occur frequently and last an average of 2 days. Food cannot be properly digested and move through the intestines, so the patient feels severe discomfort. Sometimes a person does not even have the desire to go to the toilet, but at the same time he feels nauseous.
Symptoms of the formation of adhesions in the intestines
The adhesive process does not occur in the abdominal organs in one day. And, as a rule, the clinical picture does not appear immediately, so patients often seek medical help only when the disease is at a stage that requires urgent surgical intervention.

You can suspect the presence of adhesive processes if you find:
- Pain in the abdomen of a pulling nature, which intensifies after prolonged physical exertion associated with sharp bends and turns of the body, as well as with an increase in pressure inside the abdominal cavity. As a rule, they are localized at the site of a postoperative scar;
- Dyspeptic symptoms, manifested in the form of constipation, less often diarrhea, bloating, a feeling of fullness in the umbilical area;
- Defecation disorders associated with difficulty passing a bolus of food through a section of the intestine that is pinched by adhesions;
- A sign of complete intestinal obstruction when there is no stool for more than two days. In this case, it is necessary to urgently seek medical help.
Complications
Intestinal adhesions can be fatal. Of course, deaths due to this disease are rare, but they do happen. As a rule, complications require timely surgical intervention, in the absence of which the person may die.
Neoplasms can affect other organs, stretching and bending them. In such situations, the consequences are unpredictable, since they depend solely on which organ was damaged. Naturally, the seals stretch some parts of the intestine. Due to adhesions, acute intestinal obstruction may occur, in which the organ increases in size.
Internal scarring interferes with the normal functioning of the digestive organs, causing food to accumulate and decompose, causing intoxication. Due to constant constipation, a person may develop an inflammatory process in the colon, which will cause the emergence of new diseases.
A large number of adhesions in the intestine often leads to tissue necrosis. This occurs because the tumors compress the arteries, thereby blocking the blood supply. As a rule, the intestinal walls are affected, and subsequently the dead part of the intestine is simply removed.
Diagnostics
What diagnostic procedures help identify intestinal adhesions? The most accurate method is diagnostic surgery (laparoscopy), in which the patient makes a small incision (up to 1.5 cm). Subsequently, specialists place a miniature camera in this incision and examine the condition of the internal organs for the presence of tumors. Not every patient will agree to this method, so it is often carried out at the very end, after other diagnostic procedures (if they did not produce results).
What non-surgical methods are used for diagnosis? First of all, ultrasound (ultrasound examination) of the gastrointestinal tract (gastrointestinal tract). The result of such a diagnosis depends on the location of the adhesions. It is worth noting that ultrasound does not always show tumors.
Another diagnostic method that you can turn to is an X-ray of the intestines. And here, again, the result will not be one hundred percent.
In some cases, the doctor may suspect the development of an internal inflammatory process and refer the patient to donate blood.
Diagnosis of the disease
If the patient has had abdominal injuries or surgery on the abdominal organs in the past, then diagnostics for the presence of adhesions includes laboratory and instrumental examination methods:
- Complete blood count - shows the presence of inflammation in the body (increased erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) and increased leukocytes);
- Ultrasound of the abdominal organs - performed after bowel preparation;
- X-ray with barium - based on the presence of defects in intestinal filling, the adhesive process is assessed;
- Laparoscopy - allows you to enter the abdominal cavity and, using a laparoscopic camera, examine the condition of the intestinal loops and determine the presence of adhesions. If an adhesive process is detected, they are dissected.
Diagnostics and treatment can be carried out in Russia, in Germany https://emex-medical.ru/, and in other countries.
Traditional Treatments
In this case, you do not need to rely on medications or any therapeutic procedures. When adhesions are just forming, a person cannot feel it due to mild or complete absence of symptoms.
When internal scars have already formed, it is useless to take “absorbable medications”, since they will not give the desired result.
There are isolated cases when adhesions are found by chance during a general examination. This often happens to pregnant women, as they are advised to undergo regular abdominal diagnostics.
At the moment, modern medicine (in particular foreign medicine) suggests only a surgical method for removing adhesions. The operation allows you to immediately get rid of all the seals, as well as prevent the development of complications.
There are 3 ways to remove internal scars:
- surgery with a large incision (laparotomy) - performed when there are a large number of adhesions;
- surgery with a small incision (laparoscopy) - performed when a small number of lumps are detected;
- minimally invasive laser removal - is carried out in the presence of several neoplasms of different localization.
The exact method of operation is selected by a specialist after the patient undergoes all the necessary diagnostic procedures. Removal of thickened and compacted scars is in any case carried out through open surgery.
Drugs used after surgery to prevent complications: Heparin (anticoagulant, administered twice during the day after surgery), Hydrocortisone (corticosteroid, despite the fact that it is contraindicated in the postoperative period, it is still administered 4 times within 1 day).
For severe abdominal pain, you can take No-Shpu, Paracetamol. Maximum dose of drugs: 3 tablets per day (in 2-3 doses). It is also recommended to drink Spazmalgon for spasms.
Patients are recommended to take folic acid, as well as vitamin and mineral complexes (both before and after surgery). You can drink Complivit, Aevit, or inject some vitamins separately if they are deficient.
Ready-made menu for a week in the postoperative period
In the first 6-8 weeks, a diet that is as gentle as possible on the digestive system is required. The diet should not contain food high in indigestible residues (mainly fiber).
Fiber is great for prevention, but should be avoided as much as possible during healing after adhesions have been removed.
After restoration of intestinal function, a liquid diet is prescribed, then a porridge diet. Gradually, the patient switches to a nutritious diet in accordance with the dietary rules recommended by the doctor.
In case of vomiting after surgery to remove adhesions, total parenteral nutrition (into a vein) is administered.
After surgery, the extent of the procedure, the method of intestinal repair, and the degree of risk of complications during healing should be taken into account.
Oral food intake after restoration of the intestinal tract is prescribed from the 3rd to the 4th postoperative day; it is necessary that the doses of food be small and frequent (up to 7 times a day).
A common consequence of surgery for adhesive disease is diarrhea due to insufficient water absorption or fiber absorption. Therefore, it is necessary to adjust the diet or, if necessary, influence the disorder by taking medications.
Although the spike diet has many rules, it focuses on easily digestible foods and can be fun and tasty.
Day 1:
- Breakfast: omelet with salmon.
- Appetizer: peach compote.
- Lunch: baked potatoes with ham and cheese.
- Snack: grated apple.
- Dinner: Chicken broth with root vegetables.
Day 2:
- Breakfast: bread with melted butter, apricot jam.
- Snack: kefir or acidophilus milk.
- Lunch: potato pancakes.
- Snack: cottage cheese.
- Dinner: tomato soup with cheese.
Day 3:
- Breakfast: bread with ham, cheese.
- Snack: kefir smoothie with banana.
- Lunch: tagliattele with salmon.
- Snack: banana.
- Dinner: creamy zucchini soup.
Postoperative recovery of the body
After surgery, it is very important for the patient to remain in bed and completely avoid physical activity and sports. If a person has undergone laparotomy, then he needs to rest for a week, and if he has undergone laparoscopy, then 3 days. If severe pain occurs during movement, bed rest should be extended.
You also need to adhere to a special diet:
- On the first day after surgery, a person eats a “surgical” diet - it involves seven feedings of 200-300 kcal at a time, carried out in the hospital. This diet completely excludes foods that are difficult and take a long time to digest. At the same time, the diet is quite complete, since during it the human body receives 2000-3000 kcal, 100 grams of proteins and fats, as well as 400 grams of carbohydrates;
- On the second day and beyond, the main diet consists of soups and cereals, which do not burden the gastrointestinal tract. Preference is given to light, but satisfying and healthy food;
- From day 5-6, the menu includes an increasing number of products, in particular lean meat and fish. In this case, the patient should not eat spicy, fried, smoked and excessively salty foods.
Fully or partially limited products
- You should not eat rye bread, yeast and puff pastries. Chocolate, fatty cookies, products with cream, cakes and pastries, which increase constipation, are not allowed.
- Jelly made from bird cherry, quince, blueberry, pear, dogwood, strong tea, cocoa, coffee, as they contain tannins.
- Difficult to digest fatty meats, poultry and fish, canned food, fried foods, smoked foods, hard-boiled eggs are excluded - all this causes constipation.
- Dishes with a viscous consistency (mucoid soups, mashed potatoes, jelly, jelly, pureed porridge), as they slow down intestinal motility.
- Legumes, grapes, pears, cherries, white cabbage (fresh and pickled cabbage equally cause bloating), corn (fresh and canned), fresh onions, radishes, turnips.
- Hot sauces, horseradish, adjika, mustard, mushrooms, rice, noodles, sago, semolina, noodles should be limited.
- Kvass, carbonated drinks.
Table of prohibited products
| Proteins, g | Fats, g | Carbohydrates, g | Calories, kcal | |
Vegetables and greens | ||||
| sauerkraut | 1,8 | 0,1 | 4,4 | 19 |
| corn | 3,5 | 2,8 | 15,6 | 101 |
| bulb onions | 1,4 | 0,0 | 10,4 | 41 |
| pickles | 0,8 | 0,1 | 1,7 | 11 |
| radish | 1,2 | 0,1 | 3,4 | 19 |
| white radish | 1,4 | 0,0 | 4,1 | 21 |
| turnip | 1,5 | 0,1 | 6,2 | 30 |
| horseradish | 3,2 | 0,4 | 10,5 | 56 |
| garlic | 6,5 | 0,5 | 29,9 | 143 |
Fruits | ||||
| quince | 0,6 | 0,5 | 9,8 | 40 |
| cherry | 0,8 | 0,5 | 11,3 | 52 |
| pears | 0,4 | 0,3 | 10,9 | 42 |
| dogwood | 1,0 | 0,0 | 10,5 | 44 |
| persimmon | 0,5 | 0,3 | 15,3 | 66 |
| apples | 0,4 | 0,4 | 9,8 | 47 |
Berries | ||||
| grape | 0,6 | 0,2 | 16,8 | 65 |
| blueberry | 1,1 | 0,4 | 7,6 | 44 |
Mushrooms | ||||
| mushrooms | 3,5 | 2,0 | 2,5 | 30 |
Cereals and porridges | ||||
| semolina | 10,3 | 1,0 | 73,3 | 328 |
| corn grits | 8,3 | 1,2 | 75,0 | 337 |
| millet cereal | 11,5 | 3,3 | 69,3 | 348 |
| rice | 6,7 | 0,7 | 78,9 | 344 |
| sago | 1,0 | 0,7 | 85,0 | 350 |
Flour and pasta | ||||
| pasta | 10,4 | 1,1 | 69,7 | 337 |
| noodles | 12,0 | 3,7 | 60,1 | 322 |
Bakery products | ||||
| Rye bread | 6,6 | 1,2 | 34,2 | 165 |
Confectionery | ||||
| pastry cream | 0,2 | 26,0 | 16,5 | 300 |
Chocolate | ||||
| chocolate | 5,4 | 35,3 | 56,5 | 544 |
Raw materials and seasonings | ||||
| mustard | 5,7 | 6,4 | 22,0 | 162 |
| mayonnaise | 2,4 | 67,0 | 3,9 | 627 |
Meat products | ||||
| pork | 16,0 | 21,6 | 0,0 | 259 |
| salo | 2,4 | 89,0 | 0,0 | 797 |
Sausages | ||||
| dry-cured sausage | 24,1 | 38,3 | 1,0 | 455 |
Bird | ||||
| smoked chicken | 27,5 | 8,2 | 0,0 | 184 |
| duck | 16,5 | 61,2 | 0,0 | 346 |
| smoked duck | 19,0 | 28,4 | 0,0 | 337 |
| goose | 16,1 | 33,3 | 0,0 | 364 |
Fish and seafood | ||||
| smoked fish | 26,8 | 9,9 | 0,0 | 196 |
| canned fish | 17,5 | 2,0 | 0,0 | 88 |
Oils and fats | ||||
| animal fat | 0,0 | 99,7 | 0,0 | 897 |
| cooking fat | 0,0 | 99,7 | 0,0 | 897 |
Non-alcoholic drinks | ||||
| mineral water | 0,0 | 0,0 | 0,0 | — |
| instant coffee dry | 15,0 | 3,5 | 0,0 | 94 |
| black tea | 20,0 | 5,1 | 6,9 | 152 |
Juices and compotes | ||||
| jelly | 0,2 | 0,0 | 16,7 | 68 |
| * data is per 100 g of product | ||||
Treatment with folk remedies
No normal doctor would recommend using “grandmother’s” methods or homeopathic medicines for treatment.
If a patient turns to alternative medicine, then all further responsibility for his own health falls entirely on his shoulders.
An alternative therapeutic method, which is sadly approved by modern medicine, is leeches. The thing is that the saliva of these annelids contains hirudin, a substance that is a very effective anticoagulant.
The patient can also use natural, preferably unfiltered oil (vegetable, olive). This product contains a large amount of omega acids, which have a positive effect on the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract. What does oil help with? Mainly for constipation, as it speeds up the movement of feces through the intestines. The oil also protects mucous membranes from damage.
Other methods (chamomile infusions, thyme decoctions, magic herbal tablets) are ineffective. It is worth considering that all folk methods of this nature, if they have a positive effect, then only in a cumulative form.
Authorized Products
- Soups are prepared with weak meat or vegetable broth. You should prepare more vegetable soups, given that you need to get more plant fiber.
- The diet should include all vegetables and use them raw (in the absence of flatulence), boiled or stewed. It is good to add seaweed to vegetable dishes, which has a positive effect on digestion.
- Considering that meat dishes are difficult to digest, it is not advisable to consume them daily.
- You can replenish the protein composition of your diet with low-fat fish (hake, blue whiting, pollock, pike perch), since fatty fish can cause constipation. When preparing meat dishes, prefer dietary varieties (chicken, beef, turkey). Meat and fish dishes are eaten boiled or baked.
- You can prepare crumbly porridges and casseroles from cereals. Dried fruits can be added to sweet porridges.
- Fermented milk drinks are very useful for constipation and intestinal problems. Choose low-fat fermented milk products and be sure to be fresh. Three-day kefir will cause constipation. You can make kefir and yogurt at home from healthy starter cultures.
- Whole milk most often causes bloating, so it is allowed only in dishes; cottage cheese and cheeses should be consumed sparingly, as they can be strong.
- The diet should contain soaked dried fruits every day, which can be added to porridge, cottage cheese, vegetable salads or kefir.
- It is better to eat gray bread or with bran (Doctorsky). Remember that fresh bread and yeast baked goods cause bloating, so all bread products must be dried.
- You can drink weak tea, herbal teas, juices (plum, potato, carrot, beet, apricot, tomato), rosehip infusion.
Table of permitted products
| Proteins, g | Fats, g | Carbohydrates, g | Calories, kcal | |
Vegetables and greens | ||||
| zucchini | 0,6 | 0,3 | 4,6 | 24 |
| Brussels sprouts | 4,8 | 0,0 | 8,0 | 43 |
| cauliflower | 2,5 | 0,3 | 5,4 | 30 |
| carrot | 1,3 | 0,1 | 6,9 | 32 |
| beet | 1,5 | 0,1 | 8,8 | 40 |
| tomatoes | 0,6 | 0,2 | 4,2 | 20 |
| pumpkin | 1,3 | 0,3 | 7,7 | 28 |
Fruits | ||||
| apricots | 0,9 | 0,1 | 10,8 | 41 |
| watermelon | 0,6 | 0,1 | 5,8 | 25 |
| bananas | 1,5 | 0,2 | 21,8 | 95 |
| melon | 0,6 | 0,3 | 7,4 | 33 |
| nectarine | 0,9 | 0,2 | 11,8 | 48 |
| peaches | 0,9 | 0,1 | 11,3 | 46 |
| plums | 0,8 | 0,3 | 9,6 | 42 |
| apples | 0,4 | 0,4 | 9,8 | 47 |
Nuts and dried fruits | ||||
| dried figs | 3,1 | 0,8 | 57,9 | 257 |
| dried apricots | 5,2 | 0,3 | 51,0 | 215 |
| dried apricots | 5,0 | 0,4 | 50,6 | 213 |
| prunes | 2,3 | 0,7 | 57,5 | 231 |
Cereals and porridges | ||||
| buckwheat (kernel) | 12,6 | 3,3 | 62,1 | 313 |
| oat groats | 12,3 | 6,1 | 59,5 | 342 |
| pearl barley | 9,3 | 1,1 | 73,7 | 320 |
| barley grits | 10,4 | 1,3 | 66,3 | 324 |
Bakery products | ||||
| wheat bread | 8,1 | 1,0 | 48,8 | 242 |
Confectionery | ||||
| jam | 0,3 | 0,2 | 63,0 | 263 |
| marshmallows | 0,8 | 0,0 | 78,5 | 304 |
| fruit and berry marmalade | 0,4 | 0,0 | 76,6 | 293 |
| paste | 0,5 | 0,0 | 80,8 | 310 |
| Maria cookies | 8,7 | 8,8 | 70,9 | 400 |
| oatmeal cookies | 6,5 | 14,4 | 71,8 | 437 |
Raw materials and seasonings | ||||
| honey | 0,8 | 0,0 | 81,5 | 329 |
| sugar | 0,0 | 0,0 | 99,7 | 398 |
Dairy | ||||
| kefir | 3,4 | 2,0 | 4,7 | 51 |
| sour cream | 2,8 | 20,0 | 3,2 | 206 |
| curdled milk | 2,9 | 2,5 | 4,1 | 53 |
| acidophilus | 2,8 | 3,2 | 3,8 | 57 |
| yogurt | 4,3 | 2,0 | 6,2 | 60 |
Cheeses and cottage cheese | ||||
| cottage cheese | 17,2 | 5,0 | 1,8 | 121 |
Meat products | ||||
| beef | 18,9 | 19,4 | 0,0 | 187 |
| beef liver | 17,4 | 3,1 | 0,0 | 98 |
| beef tongue | 13,6 | 12,1 | 0,0 | 163 |
| veal | 19,7 | 1,2 | 0,0 | 90 |
| rabbit | 21,0 | 8,0 | 0,0 | 156 |
Bird | ||||
| chicken | 16,0 | 14,0 | 0,0 | 190 |
| turkey | 19,2 | 0,7 | 0,0 | 84 |
Eggs | ||||
| chicken eggs | 12,7 | 10,9 | 0,7 | 157 |
Oils and fats | ||||
| butter | 0,5 | 82,5 | 0,8 | 748 |
| corn oil | 0,0 | 99,9 | 0,0 | 899 |
| olive oil | 0,0 | 99,8 | 0,0 | 898 |
| sunflower oil | 0,0 | 99,9 | 0,0 | 899 |
Non-alcoholic drinks | ||||
| instant chicory | 0,1 | 0,0 | 2,8 | 11 |
Juices and compotes | ||||
| apricot juice | 0,9 | 0,1 | 9,0 | 38 |
| carrot juice | 1,1 | 0,1 | 6,4 | 28 |
| plum juice | 0,8 | 0,0 | 9,6 | 39 |
| tomato juice | 1,1 | 0,2 | 3,8 | 21 |
| pumpkin juice | 0,0 | 0,0 | 9,0 | 38 |
| rose hip juice | 0,1 | 0,0 | 17,6 | 70 |
| * data is per 100 g of product | ||||
Preventive measures
There are too many reasons for the formation of adhesions, so there is no basic preventative advice on this matter. You can try not to hit your stomach and treat other abdominal diseases, including inflammatory and infectious ones, in a timely manner.
A good, but quite expensive and complex preventive method is the installation of a special (biodegradable) film through surgery. It does not need to be removed later, as it dissolves independently in the body. The film reduces the risk of seals by approximately 2 times.
Intestinal adhesions are a common and quite dangerous disease, which today does not have the best prognosis. This is associated with a large number of relapses and the likelihood of death in the absence of timely treatment. So, if you suspect adhesions, you should try to get diagnosed immediately, and if neoplasms are detected, it is best to consult a surgeon.
We bring to your attention a video in which a specialist explains what intestinal adhesions are and how the disease is treated:
Adhesive disease of the pelvis is the formation of connective tissue cords covering the surface of the pelvic organs and connecting them to each other. Its peculiarity is the hidden nature of the course, problematic diagnosis. The painful sensations characteristic of the disease can easily be confused with PMS and physical fatigue. When planning a child in the future, the pathology is fraught with miscarriage or infertility. One of the most effective methods of prevention and rehabilitation is a special set of exercises against adhesions in the pelvis. However, in the later stages of the disease, surgical intervention and drug therapy cannot be avoided.
Basic principles of proper nutrition
Nutrition for adhesive bowel disease has several general rules:
- The diet for adhesions should not be fatty , irritating, food should not leave undigested residues in the body.
- The menu should contain more protein than the diet of a healthy person, special attention is paid to taking vitamin C.
- For intestinal adhesions, regular eating is important - 5-6 times a day in small portions.
- When preparing food for a person with adhesive disease, grains, peels, and crusts are removed from the food.
- The most suitable processing is stewing, cooking, including steaming.
The benefits of exercises for adhesions in the pelvis
Exercises aimed at normalizing the body’s condition are called therapeutic exercises. The main goal of the classes is to prevent further development of the disease or speed up the recovery process after surgery. Also, an individually developed complex can be used as an adjuvant therapy to conservative treatment.
Benefits of exercise therapy for women:
- physiological;
- acceleration of regeneration processes;
- restoration of muscle tone;
- reduction of pain and discomfort;
- improved blood circulation;
- increasing resistance to viruses and bacteria.
Also, with proper training, the body becomes more resistant to temperature changes, cells and tissues are enriched with oxygen, and the flow of nutrients to them increases.
Despite all the advantages, sports activities are not a complete replacement for traditional treatment of adhesions in the pelvis.
The basis for a therapeutic set of exercises can be taken from yoga asanas, breathing techniques from bodyflex, and stretching methods. For pelvic pathology, the use of exercise equipment is allowed.
Contraindications to classes
Before you start playing sports with adhesions in the pelvic area, read the list of contraindications. These include:
- fever, vomiting, general malaise;
- the presence of blood clots in the vessels;
- threat of internal or external bleeding;
- severe pain syndrome;
- acute inflammatory and infectious diseases;
- progression of existing pathology;
- presence of metastases;
- late stages of oncology;
- the presence of foreign bodies near blood vessels and nerve trunks.
General principles of exercise therapy for adhesions in the pelvis
Properly organized therapeutic exercises will help you get in shape after gynecological operations and prevent possible complications and relapses of the disease. You can start doing exercises on the second day of your hospital stay. Basic principles of exercise therapy:
- The total duration of the session is 25-30 minutes.
- Start your workout with a warm-up and end with a cool-down.
- Exercise 3-4 hours after eating and 30-40 minutes before your next snack.
- Repeat each exercise at least 3-4 times.
- During physical activity, do not forget to breathe. It should be deep and even.
- If pain occurs, exercise should be stopped.
It is useful to combine physical therapy with walking, swimming, air baths, outdoor games, and massage sessions. Such an integrated approach will provide reliable protection against the formation of adhesions, have a beneficial effect on hormonal levels and relieve blood stagnation in the pelvis.
Types and techniques of exercises
There are many options for exercise therapy for adhesions. The standard complex includes 6-7 exercises in combination with breathing practice. To conduct classes at home, a special rug or blanket and light, cotton clothes are enough.
Physiotherapy
Exercises against adhesions in the pelvic area are safe and effective for any gynecological diseases. They should be performed slowly, in several approaches.
- Lie on your back and extend your arms along your torso. Straighten your legs. On the count of 1-2, raise your hands and take a deep breath through your nose. Then, as you exhale, lower your arms down.
- While still lying on your back, bend your arms and clench your fingers into fists. Keep your legs straight with your toes pulled up. On the count of 1, unclench your fingers and pull your toes towards you. On the count of 2, return to the starting position.
- Relax while lying on your back. At the count of 1-2, gradually bend your knees, and at the count of 3-4, return them to their original position. Don't lift your heels off the floor.
- Bend your knees, bringing your heels as close to your pelvis as possible. On a count of 1-2, lift your pelvis and hold it in the air. On the count of 3-4, return to the starting position. It is recommended to perform the exercise no earlier than 3 days after surgery.
- Take a traditional lying position. On a count of 1-2, slowly move your right foot to the edge of the mat. Then return it to its place. Repeat the same with your left leg.
If you have an orthopedic bed, you can do the complex in the morning, instead of morning exercises.
Yoga for adhesions in the pelvis
To normalize the functioning of the pelvic organs, eliminate adhesions, relax muscles and pacify, special asanas (postures) are used. How to do them correctly:
- Vrikshasana (tree pose). Stand up straight against a secure support (chair or wall). Take a few deep breaths in and out. Bend your left leg and place its mark on your crotch. The foot should rest completely on the right thigh, toes pointing down. Move your knee to the side to open your pelvis. Your arms can be folded over your head or on your chest. Hold the pose for as long as possible.
- Marjariasana (cat pose). Get on your knees. Place your palms on the floor, opposite your knees. As you exhale, arch your back upward to form a hump. Pull your stomach in and lower your head between your hands. As you inhale, slowly change your position: lower your back and bend down, and throw your head up.
- Adho mukha svanasana (downward facing dog). Get on all fours with your hands and feet shoulder-width apart. As you exhale, bend at the waist, pushing up with your hands and lifting your buttocks. Stretch each limb. Press your heels to the floor. Hold the pose for about 1 minute, then relax and return to the starting position.
Janu Shirshasana, Baja Konasana, Urdhva Mukha Svanasana and Kandharasana poses are also beneficial for women’s health.
With the help of yoga, female reproductive function is improved, the likelihood of miscarriage is reduced and the risk of varicose veins and blood stagnation in the pelvis is reduced.
Bodyflex for women's health
Bodyflex is, first of all, breathing exercises. It can be combined with a standard exercise therapy complex or yoga. If desired, you can resort to technology while walking, during breaks between work. Main types of exercises:
- exhale completely through the mouth to the letter “u”;
- take a deep and quick breath through your nose;
- exhale sharply through the mouth, without stretching the lips;
- holding your breath with your head down and your stomach pulled in;
- relaxed inhalation through the nose in an open position.
At first, the practice may make you feel dizzy or cause a cough. This is completely normal and will go away with time. This is how lungs that are not accustomed to hyperventilation react.