Restoration of vaginal microflora after childbirth
Already from the first days after conception, the hormonal background of the expectant mother begins to change rapidly, adapting to her “interesting” position. The second hormonal surge awaits a woman after childbirth, when the body prepares for breastfeeding. Such changes cannot go unnoticed and have a significant impact on well-being and health. In some women, this is expressed in postpartum depression, others complain of weight gain after childbirth, and in some cases, hormonal imbalance provokes a violation of the vaginal microflora, which is expressed in thrush, known to many, or other manifestations of dysbiosis of intimate places.
What are the risks of vaginal dysbiosis after childbirth?
A microflora disorder is an unpleasant condition characterized by one or more symptoms:
- dryness or burning in the vagina;
- cloudy or curdled discharge;
- foul-smelling greenish or foamy discharge.
Inattention to this issue threatens complications including infertility and the transition of the disease to the chronic stage. Restoring the normal bacterial environment in the perineum should not be delayed and put off until the baby grows up. It is important to understand that the goal of treating vaginal dysbiosis is not the complete destruction of bacteria. The microflora of the vagina, like any other organ, consists of pathogenic and “good” bacteria. Both types of microorganisms can be present in a smear of an absolutely healthy woman, but the “good” bacteria should predominate. Therefore, the correct treatment tactics will be to saturate the body with the right bacteria.
Safe treatment with probiotics
Good bacteria strengthen the body, give energy, and prolong youth. Even 100 years ago, the Russian scientist Ilya Mechnikov accurately noticed that people who drink a lot of sour milk get sick less. The secret lies in the fact that fermented milk products are rich in probiotics - Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium bacteria, which have a beneficial effect on the balance of beneficial and harmful microflora. Taking probiotics with food is a very effective way to maintain your health, since the intestines provide the best conditions for the growth and reproduction of bacteria in the body.
It took 70 years before the first probiotic-fortified products hit the market. Today, stores and pharmacies have a wide range of yogurts, cereals, fruit drinks, drinking water and even cosmetics with probiotics. Not all the properties of these microorganisms have yet been studied, but researchers are finding more and more evidence of their beneficial effects.
How to relieve perineal pain after childbirth
To relieve pain in the perineum after childbirth, the doctor may recommend a warm or cold compress (depending on the situation), cream, spray, or special exercises.
What makes probiotics unique is that they are resistant to stomach acid and bile. Thanks to this feature, they safely pass the stomach and reach the intestines, where they exert their positive effects:
- produce antibiotic-like substances that prevent the development and penetration of harmful microbes into the bloodstream;
- acidify the digestive tract and thereby prevent the development of pathogenic bacteria, such as E.coli and Salmonella, as well as putrefactive microorganisms that occur naturally in the intestines, protecting against gastrointestinal infections and diarrhea;
- improve metabolism, digestion and absorption of food;
- participate in the destruction of food debris that is not digested in the small intestine;
- by accelerating peristalsis, they prevent constipation;
- participate in the metabolism of stomach acids and cholesterol, reducing its levels in the blood;
- participate in the production of vitamin K and vitamin B12;
- cleanse the body of harmful substances;
- reduce symptoms of lactose intolerance.
Infant nutrition for dysbacteriosis
How to improve the health of a newborn’s intestines and cure dysbiosis in infants using baby food? We solve the problem of dysbiosis: we discuss its signs, medical tests, treatment, nutrition and much more with the candidate of medical sciences, a doctor of the highest category, a pediatrician and the deputy head of the children's hospital on Savelovskaya Alla Anatolyevna Shcherbakova.
— Alla Anatolyevna, what is included in the concept of “dysbacteriosis in infants”?
— Dysbacteriosis is a foreign word meaning a disorder in the composition of bacteria. In our particular case, dysbiosis is considered as a disorder in the intestines, because there is skin dysbiosis, respiratory tract dysbiosis and even blood dysbiosis.
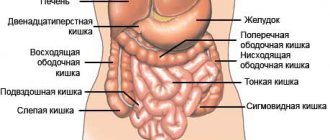
Intestinal dysbiosis in infants is a disturbance of the microbiota, the composition of the microscopic inhabitants of the gastrointestinal tract.
The concept of dysbiosis exists, but there is no such diagnosis in the international classification of diseases, just as there are no norms for the content of intestinal microbiota in a child of the first year of life. Therefore, changes in the microbiota that the laboratory gives in the results of medical tests may be a variant of the norm, but also a manifestation of an intestinal infection, and a condition after the prescription of antibiotics or probiotics. Children cannot be diagnosed with dysbacteriosis.
— Why do newborns have digestive problems and how long does dysbiosis last in a child?
— At birth, the baby switches from nutrition through the placenta to enteral nutrition with breast milk or formula. With the beginning of milk feeding, a foreign inflammatory process occurs in the intestines, which is accompanied by the formation of microbiota - “good” (bifidobacteria, lactobacilli) and opportunistic (staphylococci, klebsiella, enterococci, etc.). Opportunistic microbes can cause fermentation processes, which are considered normal during artificial and natural feeding. Therefore, treatment of opportunistic microflora is not required in 99% of cases. The natural process will end by three months, this is colic that accompanies the so-called dysbiosis.
— Do signs of dysbiosis in infants often confuse parents?
— Newborns and babies often have problems with the gastrointestinal tract - insufficient weight gain, regurgitation, constipation, diarrhea, changes in the nature and color of stool, and others. And in these situations, parents often test their baby’s stool for dysbacteriosis. And when they see differences in the results from the presented norms, they begin to get nervous and come to the appointment. But the research performed will be unfounded and uninformative, and the pediatrician will not take it into account.
— If a stool test for dysbacteriosis in an infant has no diagnostic value, how then are disorders of the digestive system diagnosed in a child under one year old?
— Today, pediatricians do not prescribe tests for dysbacteriosis. There are no norms for the content of microbes in the microbiota and dysbacteriosis in children of the first year of life.
The study is not informative, and the change in microbiota that the results show does not require any treatment or recommendations.
Fever, vomiting, diarrhea, loose stools, and abdominal pain in a child can be manifestations of an intestinal infection. Any child complaints require a preliminary examination by a doctor. If an infectious disease is suspected, a stool test for the intestinal group is prescribed - a test for enteroviruses, rotaviruses, noroviruses, which has diagnostic and therapeutic meaning.
— Are dysbacteriosis and an allergic reaction in children somehow connected? Is it necessary to treat dysbiosis in a baby with food allergies?
— Complaints about insufficient weight gain, regurgitation, constipation, changes in stool character, mucus and blood in the stool, staphylococci and Klebsiella in the stool, analysis for dysbacteriosis - most often such disturbances of the intestinal microbiota of a small child will be a secondary process against the background of food allergies. In case of food intolerance, it is necessary to prescribe therapeutic nutrition to the child, and not to fight dysbacteriosis. If you have any complaints, you should contact a gastroenterologist who provides pediatric care.
— Alla Anatolyevna, is it possible to prevent dysbiosis in infants? For example, should a newborn be given probiotics and prebiotics?
— Artificial formula is sterile unless probiotics are added to it. Breast milk contains not only prebiotics and probiotics, but also other living components that affect the baby's microbiota and the contents of his intestines. And this is a good manifestation of the interaction between mother and child. Studies have shown that the microbiota of breast milk turns into the microbiota of the baby’s intestines and is subsequently accompanied by the development of children’s immunity, promotes better absorption of nutrients, and therefore the growth and development of the child.
Probiotics given to young children may be unsafe. It is best to discuss all therapeutic decisions with your doctor. It makes no sense to prescribe probiotics to solve an existing gastrointestinal problem, because you first need to select a diet - and the dysbiosis will go away on its own.
— How to treat dysbiosis in a child and what is the importance of nutrition in infants with dysbiosis?
— Treatment of dysbiosis in infants is precisely a change in diet; treatment with bacteriophages is not prescribed. When dry milk formula is correctly selected for a bottle-fed baby or nutrition is prescribed for a breastfeeding mother, the baby should not have dysbacteriosis.
If the baby's only complaints are colic, a formula containing MAMAKO® goat's milk may be prescribed. Goat milk formulas, among other milk formulas, are closest to mother's breast milk in terms of protein profile. MAMAKO® Premium does not contain palm oil, which many mothers are afraid of. The food is designed to feed healthy babies, prevent colic and other digestive problems.
— When changing the artificial mixture, how quickly will the results be visible and what are the signs that indicate that the problem has subsided?
— When changing infant formula, the first changes in the child’s condition may be visible after 5-7 days. For example, if a baby experiences colic, bloating, flatulence, pain during feeding, mucus, blood, undigested pieces, and cheesy clots appear in his stool, then with positive dynamics on the new diet he will feel better. Pediatricians promise parents obvious changes in health in 2-4 weeks, when there should definitely be results and favorable changes. One month is the period when you can tell whether the condition of the gastrointestinal tract has changed, whether the child’s stool has changed, whether there are positive dynamics.
— Why is goat formula not suitable for all children?
— Goat milk formula is a product for healthy children and comfortable digestion. If the baby is premature and was born with a low birth weight, then the priority for him is a formula labeled PRE with a high protein content, which corresponds to colostrum.
Rash, dryness, redness, itching of the skin or regurgitation, insufficient weight gain, diarrhea, mucus and blood in the stool, increased values of leukocytes and red blood cells in the coprogram, a positive reaction to protein and occult blood in the stool - all these are signs of cutaneous and gastrointestinal forms of allergy to food for which special medicinal mixtures based on hydrolysates or amino acids are prescribed.
Dysbacteriosis in translation means a violation of the microbiota, but there is no such disease in the international classification of diseases. Problems in a child with the gastrointestinal tract are always a reason to consult a doctor, change the diet and prescribe specialized treatment.
Pediatrician Alla Anatolyevna Shcherbakova
*The ideal food for an infant is mother's milk. WHO recommends exclusive breastfeeding for the first 6 months. MAMAKO® supports this recommendation. Before introducing new foods into your baby’s diet, consult a specialist.
Probiotics for Women's Health
Also, some time ago, doctors began to use probiotics in female gynecology. After all, it is probiotics, entering the female body locally and coming into contact with tissues and mucous membranes, that trigger natural regenerative processes aimed at combating various types of infections, fungal infections, disturbances of the vaginal microflora and other inflammatory processes. To do this, antenatal clinic specialists prescribe suppositories, vaginal tablets or sprays with probiotics to their patients.
As an additional remedy in the treatment of gynecological diseases, it is recommended to use special sanitary pads containing a probiotic. Such pads are good not only during therapy and recovery from vaginal dysbiosis, but also as a daily means of maintaining healthy microflora in intimate places. It's natural and simple, and it also provides the problem area with essential probiotics throughout the day. And most importantly, it is completely safe for mother and baby. You can learn about all the mechanisms of action and participation of probiotics in feminine intimate hygiene from this article.
Causes of dysbiosis after childbirth
Dysbacteriosis is not an independent disease, but a consequence of other changes in the body.
The causes of this syndrome may be:
• acute or chronic diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, namely: gastritis, duodenitis, pancreatitis;
• intestinal infections caused by salmonella, shigella, pathogenic E. coli;
• various diets that women begin to use after childbirth to return to their previous shape;
• intestinal or liver parasites – lamblia, pinworms, roundworms.
Often dysbiosis after childbirth occurs in a mother after a cesarean section. This happens because after the operation, doctors prescribe a course of antibacterial therapy, which can cause dysbacteriosis. Taking antibiotics can lead not only to intestinal dysbiosis, but also to vaginal dysbiosis, which also needs to be treated.
How to get tested for dysbiosis in children
The lack of reliable analysis of the composition of the intestinal microflora contributes to disbelief in dysbiosis. Since it is possible to examine only human feces, testing for dysbacteriosis is reminiscent of fortune telling using tea leaves.
With feces, the body is freed from excess or pathogenic microorganisms, that is, it gets rid of unnecessary things. Based on such an analysis, one cannot draw conclusions about the microflora inside the body.
There is no test for dysbacteriosis. There is only an analysis for the presence of pathogenic microorganisms.
This is the type of study that is carried out when identifying symptoms of dysbiosis.
What can dysbiosis lead to after childbirth?
The consequences of dysbacteriosis are very extensive and dangerous. 1 ml of intestinal contents contains from 100 thousand to 1 million different microorganisms. Among them, 90% are bifidobacteria, the rest are lactic acid bacteria, staphylococci, fungi, and E. coli. If this indicator is violated, a putrefactive and fermentative environment develops in the intestine, which contributes to the appearance of various inflammatory reactions. A woman's immunity is weakened, which leads to various infections.
Another negative is that at the same time the absorption of nutrients in a woman’s body decreases; this, of course, is passed on to the baby. With a lack of vitamins and minerals, the process of growth and development of the child is disrupted. This syndrome leads to the development of local inflammatory reactions and the baby’s immunity is weakened. Dysbacteriosis in the mother can cause the development of chronic foci of infection in the child and, as a consequence, the development of anemia.
Dysbacteriosis in infants: what is it?
Normally, a baby's intestines should be populated by certain types of bacteria. A disturbance in the composition of the microflora may not manifest itself in any way, but it can also lead to unpleasant phenomena.
At birth, the baby's intestines are sterile. However, then the gastrointestinal tract gradually begins to be populated by bacteria entering it from the environment. This happens, first of all, during the feeding of the baby, during contact with the mother, etc. By the age of one year, the intestinal environment has stabilized.
Two groups of bacteria are recognized as the most important and beneficial microorganisms among all intestinal microflora - bifidobacteria and lactobacilli. They normally make up up to 90% of the contents of the large intestine. The remaining bacteria occupy a neutral position. These are streptococci, enterococci, E. coli. They are called opportunistic because under normal conditions they are not dangerous. The set and ratio of types of neutral microflora are unique for each child.
The intestinal microflora is involved in the production of some useful substances and promotes the regeneration of the intestinal mucosa. However, the main function of beneficial intestinal microflora is protective.
A decrease in the number of beneficial microflora makes it possible for pathogenic bacteria to take their place. These can be either opportunistic microorganisms that previously lived in the gastrointestinal tract, or those that have penetrated the intestines from the outside. Pathogenic bacteria produce a large amount of toxins, which can partially enter the blood. At the same time, immunity decreases, stool formation is disrupted, and general intoxication can occur.
Treatment of dysbiosis after childbirth
Only a doctor can decide how to treat dysbiosis after childbirth in a woman. Treatment must be selected adequately in relation to both mother and child. First of all, a special diet is prescribed to help improve the atmosphere in the intestines. All gas-forming products containing yeast are prohibited. Undoubtedly, fermented milk, natural products will be very useful.
General therapy
To restore the intestinal microflora, experts prescribe prebiotics, preparations with bifido- and lactobacilli, for example, Lactobacterin or Bifidumbacterin, as well as preparations containing bifido- and lactobacilli, for example, bifiform.
Lactobacilli ensure that the number of harmful bacteria does not exceed acceptable limits and control the restoration of the intestinal mucosa. The drug Lactobacterin has an antibacterial effect, its function is to restore intestinal microflora and normalize the activity of the gastrointestinal tract. Lactobacilli colonize the intestines and leave no room for pathogenic microorganisms to colonize. Lactobacilli are contraindicated in people with lactose intolerance.
Bifidobacteria create a protective layer against harmful microbes that enter the body with food, water, and air. The drug Bifidumbacterin, due to the large number of bifidobacteria, activates the functions of the gastrointestinal tract, the digestion process, and the synthesis of vitamins. The drug fights various pathogens: E. coli, staphylococci, some types of fungi, preventing them from taking root in the intestines.
Sometimes doctors resort to prescribing bacteriophages; they suppress and destroy harmful microflora. Antibacterial therapy is prescribed extremely rarely, since it itself causes dysbacteriosis.
Traditional methods
Traditional medicine also offers its own recipes for recovery. One of them: put sour milk on low heat, after which you need to wait until the curd separates from the whey. The serum is taken to treat dysbiosis. The recipe has no contraindications for women and children.
Undoubtedly, strengthening the general strength of the body and increasing the body's immune defense are of great importance in treatment. Experts recommend taking multivitamins and minerals and hardening procedures.
In order to prevent the occurrence of dysbiosis after pregnancy, women should monitor their diet and promptly treat all acute diseases and exacerbations of chronic processes.
Preparations and means for the treatment of dysbiosis in children
Despite the openly negative attitude of doctors towards the existence of dysbiosis as an independent disease, they do not forbid parents to actively fight against dysbiosis, even with the help of pharmacological agents.
All kinds of probiotics, according to pharmacological companies, contain beneficial lacto- and bifidobacteria. But doctors warn that saliva, gastric juice, bile and other gastric tract fluids completely dissolve and neutralize these microorganisms. However, this has not been proven.
Accordingly, they cannot cause any harm or benefit to the body.

In most countries, probiotics are classified as “potentially harmless drugs.” Roughly speaking, these are the same dietary supplements, only in profile.
Pharmacies provide several preparations containing lactobacilli : Lactobacterin in tablet form and Biobacton or Acylact in powder form.
Beneficial bifidobacteria are contained in the following preparations : Bifidumbacterin, available in tablet form, not recommended for children under 3 years of age. Rectal suppositories are produced under the same name.
Causes
Microbial imbalance often occurs during pregnancy, but is no less often recorded after childbirth during breastfeeding. There are no specific reasons for the occurrence of dysbiosis during this period, and they can be very diverse.
These can be various acute or chronic diseases of the digestive tract, or “female” diseases. In addition, often when breastfeeding, mothers begin to diet and limit themselves in food for various purposes - not to harm the newborn or to lose weight.
Parasitic diseases and intestinal infections cannot be ruled out.
Dysbacteriosis after cesarean section deserves special attention. On the one hand, dysbiosis can develop after an infection that has spread throughout the intestinal tract; on the other hand, after surgery, drug treatment is often prescribed to prevent complications. And as you know, taking certain medications can cause the development of disturbances in the intestinal microflora.
Symptoms
The first signs of dysbiosis in nursing mothers will be the appearance of constipation or diarrhea, often these conditions replace each other. The appearance of symptoms such as increased fatigue and weakness is often attributed to the postpartum period and general fatigue, a change in daily routine and caring for a newborn. Also, a symptom of dysbiosis can be considered a feeling of incomplete bowel movement and the periodic occurrence of false urges to defecate.
But still, most often, the symptoms of dysbiosis go away in an erased form, and even emerging symptoms are attributed to dietary errors, exacerbations of chronic diseases, etc.
Diagnosis of intestinal dysbiosis in nursing mothers
Diagnosis of the disease occurs only based on the results of laboratory testing. The most popular and most frequently used method is bacteriological examination of stool.
Based on its results, it is possible to estimate the ratio of microorganisms, determine the prevailing group and assess the microbial landscape. Despite all the advantages, this research method also has a number of disadvantages. Its results will largely depend on the method of collecting the material, whether the collection technique was violated, how long it took to deliver it to the laboratory, and how soon the study began. If the test material reaches the laboratory in more than 2 hours, it is difficult to talk about reliable results, as colonization of external flora may occur. Moreover, it is important to use sterile instruments.
Symptoms of dysbiosis in infants
Externally, dysbiosis in infants can manifest itself in different ways. The main symptoms are stool disorders. The stool changes color and consistency, and mucus appears in the stool. Normal baby stool is yellow in color and the consistency of sour cream. A small amount of mucus and foam are not always signs of dysbiosis; this may be a variant of the norm. But if there is an increase in bowel movements, this may be a cause for concern. Sometimes, on the contrary, constipation is observed.
Symptoms such as flatulence, colic, and increased regurgitation are also typical. The baby's belly may be swollen. A white coating appears on the tongue. Sleep and appetite worsen. Frequent signs of dysbacteriosis are allergic rashes. With prolonged gastrointestinal disorder, the child stops growing and does not gain weight, and cries a lot. Often, when switching from natural milk feeding to artificial milk, short-term transient gastrointestinal disorders are possible that do not require treatment.
Treatment
What can you do
When prescribing treatment for any pathology during pregnancy and breastfeeding, it is necessary to assess and take into account the risks to the fetus and infant. Dysbacteriosis does not tolerate amateur activity, and is not a diagnosis - it is just a symptom of a concomitant pathology. Based on this, only a doctor can prescribe adequate therapy based on the results of the study and calculation of the cause of its development.
But in all cases of dysbiosis, nursing mothers are prescribed a diet that will help restore microbial balance. Diet restrictions apply only to gas-forming products that contain yeast. In general, it is necessary to adhere to the principles of a healthy diet and monitor the complete composition of vitamins and minerals. Fermented milk products, natural, without any additives, will be beneficial.
What does a doctor do
The main emphasis in treatment is therapy of the underlying disease, these can be diseases of the digestive tract, infections, etc. To relieve the symptoms of dysbiosis and quickly restore the balance of the flora, prebiotics and preparations with bifidobacteria and lactobacilli are prescribed. In some cases, according to indications, bacteriophages are prescribed, which suppress growth and destroy “bad” microflora.
Only in the case of a complicated form of dysbacteriosis, appropriate drugs can be prescribed to suppress the growth of pathogenic microflora based on the antibiotic sensitivity of the main group.
Strengthening the body’s own strength – increasing the functioning of the immune defense – is also important in treatment. These goals can be achieved by adjusting the diet, taking multivitamins and minerals, and hardening procedures. In rare cases, and in cases of severe immunodeficiency, stimulant drugs are prescribed.
After a cesarean section, in order to prevent postoperative consequences, a special course of therapy is prescribed, as a rule, these are antibiotics and drugs for the prevention of thrush and dysbacteriosis - biotics.
Restoration of vaginal microflora after childbirth
Already from the first days after conception, the hormonal background of the expectant mother begins to change rapidly, adapting to her “interesting” position. The second hormonal surge awaits a woman after childbirth, when the body prepares for breastfeeding. Such changes cannot go unnoticed and have a significant impact on well-being and health. In some women, this is expressed in postpartum depression, others complain of weight gain after childbirth, and in some cases, hormonal imbalance provokes a violation of the vaginal microflora, which is expressed in thrush, known to many, or other manifestations of dysbiosis of intimate places.
How is it diagnosed?
To identify or confirm the diagnosis of dysbiosis, standard diagnostic methods are used:
- Coprogram.
- Stool culture.
Feces should be collected from the infant before taking antibacterial agents or more than 12 hours after they are discontinued. When undergoing therapy for any pathologies with probiotics, analysis can be taken only 30 days after their discontinuation.
Symptoms of lactose deficiency and methods of treating the disease.
How to treat intestinal disorders (diarrhea and constipation)? Read in this article.
What are the risks of vaginal dysbiosis after childbirth?
A microflora disorder is an unpleasant condition characterized by one or more symptoms:
- dryness or burning in the vagina;
- cloudy or curdled discharge;
- foul-smelling greenish or foamy discharge.
Inattention to this issue threatens complications including infertility and the transition of the disease to the chronic stage. Restoring the normal bacterial environment in the perineum should not be delayed and put off until the baby grows up. It is important to understand that the goal of treating vaginal dysbiosis is not the complete destruction of bacteria. The microflora of the vagina, like any other organ, consists of pathogenic and “good” bacteria. Both types of microorganisms can be present in a smear of an absolutely healthy woman, but the “good” bacteria should predominate. Therefore, the correct treatment tactics will be to saturate the body with the right bacteria.
Safe treatment with probiotics
Good bacteria strengthen the body, give energy, and prolong youth. Even 100 years ago, the Russian scientist Ilya Mechnikov accurately noticed that people who drink a lot of sour milk get sick less. The secret lies in the fact that fermented milk products are rich in probiotics - Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium bacteria, which have a beneficial effect on the balance of beneficial and harmful microflora. Taking probiotics with food is a very effective way to maintain your health, since the intestines provide the best conditions for the growth and reproduction of bacteria in the body.
It took 70 years before the first probiotic-fortified products hit the market. Today, stores and pharmacies have a wide range of yogurts, cereals, fruit drinks, drinking water and even cosmetics with probiotics. Not all the properties of these microorganisms have yet been studied, but researchers are finding more and more evidence of their beneficial effects.
How to relieve perineal pain after childbirth
To relieve pain in the perineum after childbirth, the doctor may recommend a warm or cold compress (depending on the situation), cream, spray, or special exercises.
What makes probiotics unique is that they are resistant to stomach acid and bile. Thanks to this feature, they safely pass the stomach and reach the intestines, where they exert their positive effects:
- produce antibiotic-like substances that prevent the development and penetration of harmful microbes into the bloodstream;
- acidify the digestive tract and thereby prevent the development of pathogenic bacteria, such as E.coli and Salmonella, as well as putrefactive microorganisms that occur naturally in the intestines, protecting against gastrointestinal infections and diarrhea;
- improve metabolism, digestion and absorption of food;
- participate in the destruction of food debris that is not digested in the small intestine;
- by accelerating peristalsis, they prevent constipation;
- participate in the metabolism of stomach acids and cholesterol, reducing its levels in the blood;
- participate in the production of vitamin K and vitamin B12;
- cleanse the body of harmful substances;
- reduce symptoms of lactose intolerance.
The use of folk remedies
Traditional treatment of dysbiosis in infants or older children can be combined with the use of safe traditional medicine.
- An effective remedy for diarrhea is a decoction of oak bark. The compounds present in its composition have antibacterial, astringent and anti-inflammatory properties. To prepare the decoction, add crushed oak bark (1 tbsp) to boiling water (300 ml). Boil the mixture for 5 minutes, keep warm for about an hour, filter thoroughly through sterile gauze. Each time before meals, the infant should drink 1 tsp. received funds.
- To normalize the composition of the intestinal microflora in children, you can use berry fruit drinks that have bactericidal properties. You can offer your baby decoctions and infusions made from strawberries, cranberries, rose hips, blueberries, and raspberries. The listed funds can be used without restrictions. The only contraindication to the use of this technique is if the baby is allergic to the listed products.
- To combat intestinal dysbiosis in children, you can use onion infusion . This drink contains substances that can destroy pathogenic microflora and increase the secretory activity of the digestive tract. To prepare the medicine, you need to chop the onion and pour 1.5 cups of cool boiled water over the vegetable mixture. After 12 hours, filter the drink and put it in the refrigerator. Give the ready-made infusion to your baby instead of drinking water.
- Another affordable and safe remedy that allows you to effectively treat childhood dysbiosis is a decoction of cinquefoil bush. A drink made from the herb of the above-mentioned plant has antibacterial, soothing, anti-inflammatory, and immunomodulatory properties. The recipe for the decoction is relatively simple: dried cinquefoil (1 g per 1 kg of baby’s weight) must be poured with water (10 g for each gram of plant material) and boiled for 4 minutes. Cool the finished tea, filter and ensure that the child drinks it within 24 hours.
- An effective disinfectant, astringent and soothing agent is a decoction prepared from a collection of bird cherry and blueberries, chamomile inflorescences, blueberry leaves, and caraway seeds. All components for collection should be taken in equal proportions. To prepare this healing drink, you need to pour 2 tbsp into boiling water (400-450 ml). l. vegetable mixture and simmer over low heat for 13-15 minutes. Herbal tea prepared according to the given recipe can be given to your baby without restrictions.
- An effective and safe remedy for constipation that occurs in children due to disturbances in the quantitative and qualitative structure of the intestinal microflora is an infusion prepared from a collection of chamomile inflorescences, dill fruits (1 part each) and caraway seeds (2 parts). In a half-liter jar you need to add 2 tbsp. l. medicinal raw materials, fill it to the top with boiled water, close the lid, keep warm for 2 hours. Give the strained infusion to the baby before meals. Single dose for administration - 1 tsp.
- The most powerful natural antiseptic that can quickly cure dysbiosis in infants is a decoction of chamomile. This universal remedy contains substances that have antibacterial activity, weaken intestinal spasms, reduce the formation of gases in the intestines, block the spread of inflammatory processes, and strengthen local immunity. To prepare the decoction, add dried chamomile flower baskets (1 tablespoon) to boiling water (900 ml) and boil them for 4-5 minutes. Ready-made chamomile tea can be given to your baby without any restrictions on volume.
- An effective remedy is an infusion prepared from a collection of agrimony herbs, St. John's wort (1 part each), peppermint leaves, plantain and chamomile inflorescences (2 parts each). This drink contains compounds that normalize the biocenosis and secretory activity of the digestive tract, promote the removal of toxins from the body, and have astringent, anti-inflammatory and disinfectant properties. To prepare a medicinal infusion, you need to pour 1 tbsp into a half-liter jar. l. collection, fill it to the brim with boiling water and let it brew for at least an hour. Pass the resulting tea through sterile gauze and give it to the baby without any restrictions on quantity.
- Traditional healers recommend treating intestinal dysbiosis in infants using regular kefir. Rub the drink (10 g per 1 kg of baby weight) through a fine-mesh sieve and heat slightly in a water bath. Use the resulting product to prepare a therapeutic enema.
- As an enveloping agent, you can use a decoction of oat grains or flax seeds . It protects the tissues of children's intestines from irritation, prevents the spread of inflammatory processes in the digestive tract and has a nonspecific analgesic effect in colic caused by dysbacteriosis. To prepare it, add a large handful of plant material to boiling water (900 ml) and cook, stirring, for 7-10 minutes. Pass the finished mixture through cheesecloth and give to the baby in unlimited quantities.
- An infusion of pomegranate peels is an effective remedy for diarrhea. This healing drink contains compounds that normalize the functioning of the digestive system and help eliminate toxins from the child’s body. To prepare a healing infusion you need 1 tsp. Brew the crushed peels into powder with boiling water (350-400 ml) and leave for 50 minutes. Give the product to the baby before meals. Single dose of infusion - 1 tsp.
- To strengthen the baby’s immune forces, it is advisable to use a decoction prepared from a collection of senna grass and buckthorn root. Pour 1 tbsp into a half-liter jar. l. each component and fill it to the brim with water brought to a boil. Close the container with the mixture with a lid, wrap it with a thick cloth and leave for 4 hours. Filter the infusion prepared according to the given recipe through a tea sieve and give 1 tsp to the baby before meals.
It is important to understand that many folk remedies have contraindications and side effects. They can be used in the treatment of dysbiosis in infants or older children only after obtaining the appropriate permission from a pediatrician or an experienced herbalist.
Probiotics for Women's Health
Also, some time ago, doctors began to use probiotics in female gynecology. After all, it is probiotics, entering the female body locally and coming into contact with tissues and mucous membranes, that trigger natural regenerative processes aimed at combating various types of infections, fungal infections, disturbances of the vaginal microflora and other inflammatory processes. To do this, antenatal clinic specialists prescribe suppositories, vaginal tablets or sprays with probiotics to their patients.
As an additional remedy in the treatment of gynecological diseases, it is recommended to use special sanitary pads containing a probiotic. Such pads are good not only during therapy and recovery from vaginal dysbiosis, but also as a daily means of maintaining healthy microflora in intimate places. It's natural and simple, and it also provides the problem area with essential probiotics throughout the day. And most importantly, it is completely safe for mother and baby. You can learn about all the mechanisms of action and participation of probiotics in feminine intimate hygiene from this article.