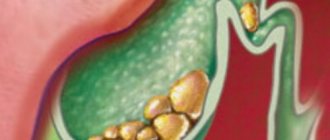
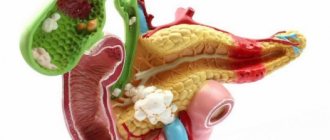
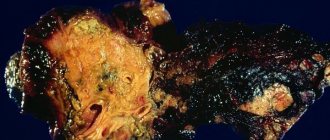
Cholestasis or cholestatic syndrome is a prolonged stagnation of bile in the gallbladder, as well as inside its ducts. It may occur due to a violation of the circulation of digestive secretions due to the presence of stones and other formations that compress the bile ducts, or the cause of the pathology is a disruption of the liver tissue. The disease is equally diagnosed in both adults and children of various age groups. Due to the long-term absence of the process of bile passing through the ducts and its entry into the cavity of the duodenum, the functioning of all organs of the gastrointestinal tract is disrupted, which negatively affects the well-being of the person faced with this disease. In this article, we will consider in more detail what causes poor outflow of bile secretions, what signs can be used to promptly detect the developing stagnation effect, and what methods exist for its treatment.
Symptoms of cholestasis
Long-term stagnation of bile in the cavity of the gallbladder provokes its deficiency in the intestines, where it is necessary for the breakdown of fats entering the gastrointestinal tract along with food. In parallel with this, a toxic effect on liver tissue occurs, since the secretion accumulates in the liver canals and has a toxic effect on its cells - hepatocytes, provoking their premature death.
All these pathological processes are expressed in the following negative symptoms:
- itching of the skin surface, which is recorded throughout the body, but is especially pronounced in the area of the feet (in women who are pregnant this is practically the only sign of the disease, and in children under 5 months of age it does not occur at all);
- a feeling of heaviness, and sometimes even aching pain in the right hypochondrium, which intensifies after eating fatty, fried, smoked foods;
- vitamins and minerals stop being absorbed by the intestines, which immediately affects a person’s body weight, which rapidly falls (if no therapeutic action is taken in a timely manner, the development of dystrophy cannot be ruled out);
- feces become white with a grayish tint (they are always liquid, voluminous with a high concentration of fat);
- urine acquires a rich dark shade and a specific smell of hay (this is due to the fact that due to prolonged stagnation of bile inside the liver tissue, or directly in the gallbladder itself and its ducts, part of this digestive secretion enters the blood, and then in the process of its purification kidneys, excreted outside the body along with urine in order to avoid severe forms of intoxication);
- the whites of the eyes and the skin acquire a jaundiced tint (in patients of the adult age group this symptom is not always diagnosed, but in children it is detected in 90% of cases);
- acute deficiency of vitamins B, A, C, D, as well as minerals such as potassium, magnesium, calcium, which manifests itself in bone fragility, blurred vision, internal and external bleeding, and impaired coordination of movements.
The most severe form of cholestasis manifests itself not only in the form of the listed symptoms, but also in the appearance of benign neoplasms in the neck, skin, chest and back. These are a kind of wen that form in the subcutaneous layer due to the fact that the natural process of assimilation of fatty foods is disrupted, which is not broken down due to the lack of a sufficient volume of bile and all fatty elements are deposited in various parts of the body, forming plaques.
Cholestasis: what is it?
Cholestasis is a condition in which the flow of bile into the duodenum is disrupted.
The occurrence of cholestasis is associated with two fundamentally different types of causes:
- reduction of bile formation in the liver;
- a violation of the excretion of bile from the liver into the intestine, which, in turn, can be divided into an intrahepatic block of excretion and an extrahepatic block.
Impaired bile formation is associated with liver diseases - viral, bacterial, toxic (including alcoholic and drug) hepatitis, cholestasis of pregnancy, benign recurrent cholestasis.
Impaired bile flow may be associated with tumor processes, cholecystitis, cholangitis, tuberculosis, sarcoidosis, lymphogranulomatosis and other diseases in which an obstruction occurs along the flow of bile.
Depending on the causes of the pathological process, the severity and duration of the disease, the following are distinguished:
- acute and chronic cholestasis;
- cholestasis occurring with or without signs of jaundice.
Clinical manifestations of cholestasis
The main manifestations of cholestasis include jaundice, skin itching and manifestations of malabsorption of fats in the intestines, however, none of these symptoms are early - they all appear at a fairly late stage in the development of the disease.
In the early stages, attention should be paid to the symptoms of the underlying disease, the manifestations of which can begin long before the onset of cholestasis.
In its pure form, cholestasis, unlike most diseases that affect the liver, does not cause weakness and fatigue; all symptoms of intoxication are quite specific in nature, as they are caused by the accumulation of fatty acids and bilirubin in the body.
Bile acids are likely to cause itching, which is very distressing for a person with cholestasis. The mechanism of this phenomenon is associated with the irritating effect of fatty acids on the nerve endings of the dermis and epidermis.
Due to the fact that bile acids do not reach the intestines, problems with stool appear - the absorption of fats is impaired, which appear unchanged in the stool (steatorrhea).
This pathological condition is accompanied by weight loss and a decrease in fat-soluble vitamins (A, D, K, E) in the blood.
Vitamin E is the first to decrease, which causes prolongation of blood clotting time and can manifest itself as long-term bleeding.
Long-term cholestasis leads to impaired absorption of other vitamins with the development of “night blindness”, osteodystrophy and the development of other diseases associated with hypovitaminosis.
Cholestasis can be a cause of impaired copper metabolism in the body, since normally most of this element is removed with bile. Copper accumulates in the liver and other organs, causing severe, often prognostically unfavorable conditions.
Chronic cholestasis has its own signs - xanthomas - soft, flat or slightly raised formations around the eyes, on the palmar folds, on the neck, chest, back or under the mammary glands; xanthomas in the form of nodules are located on the surface of the joints, on the buttocks and places subject to compression.
Diagnosis of cholestasis
Diagnosis of cholestasis is based on laboratory parameters: increased levels of bile acids, bilirubin (conjugated) and alkaline phosphatase in the blood. In chronic cholestasis, the level of lipids (cholesterol, triglycerides, lipoproteins, phospholipids) may be elevated.
To clarify the nature of the disease, ultrasound, endoscopic retrograde cholangiography and percutaneous transesophageal cholangiography are used.
Treatment of cholestasis
If the cause of the disease is known, then treatment should be aimed at it - formations or stones that interfere with the flow of bile are removed, medications are replaced, etc.
If the cause of cholestasis is unknown, or is known but cannot be removed, then treatment is based on diet and drug therapy. The diet involves reducing the content of animal fats in food, consuming foods with medium-chain triglycerides and adequate vitamin therapy.
The drug of choice for non-obstructive cholestasis is ursodeoxycholic acid, which displaces toxic bile acids and has a cytoprotective effect, beneficially affecting liver function. Sedatives are used to relieve itching.
Prevention of cholestasis comes down to timely detection and treatment of diseases of the liver, gall bladder and bile ducts.
Source: https://vitaportal.ru/medicine/pischevaritelnaya-sistema-i-zabolevaniya-zhkt/holestaz-chto-eto-takoe.html
Causes of bile stagnation in children, adults and pregnant women
It is believed that the general cause of the development of cholestasis is the initial damage to the liver tissue and its cellular structure by toxic substances, which led to a decrease in its functional ability to drain and pass bile secretions. Based on this, the following causes of this type of pathological condition are identified:
- alcohol abuse, drug use and chronic alcoholism;
- the presence of hepatitis C virus or other strains of this microorganism in the blood;
- work at chemical, metallurgical, coal processing industry facilities;
- long-term use of potent medications;
- imbalance of beneficial and pathogenic microflora;
- infectious infection of the gastrointestinal tract, which was not subjected to adequate drug treatment in a timely manner, or the patient initially had a severely weakened immune system;
- liver tuberculosis (this disease mainly occurs in people in contact with patients suffering from the open form of this disease);
- hormonal imbalances caused by pregnancy (in women carrying a child, this occurs in the first trimester of fetal development);
- oncological processes in the liver tissues, or in the circumference of the gallbladder and its ducts.
In children, cholestasis most often occurs due to infection with parasites, improperly organized nutrition, and adolescence, when all physiological processes are preparing for adult life. In this case, we present those factors in the development of the disease in adults, pregnant women and children that are most often encountered in medical practice.
Causes of cholestasis
Cholestasis in pregnancy occurs in the 3rd trimester of pregnancy due to hormonal changes in the body of the expectant mother. This is considered the most harmless cause of this disease.
However, intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy, which does not cause harm to the mother, can cause serious complications in the intrauterine development of the fetus, including biliary atresia, which causes the development of cholestasis in newborns. But we’ll talk about this a little later, and now let’s return to other reasons that cause the development of this pathological condition. They may be disturbances in the formation or outflow of bile, namely:
- Cirrhosis;
- All types of toxic liver damage;
- Infectious diseases;
- Tuberculosis;
- Lymphogranulomatosis;
- Idiopathic ductopenia;
- Heart failure, etc.
There are quite a few reasons that cause the development of this dangerous condition. But the championship in frequency of occurrence, of course, belongs to its appearance during pregnancy.
As for the reasons why this disease develops in expectant mothers, they include:
- Multiple pregnancy;
- Genetic predisposition;
- History of liver disease.
Cholestasis in pregnancy requires immediate treatment. After all, this is the only way to nullify the development of possible intrauterine disorders in the unborn baby.
The cause of cholestasis in newborns in most cases is congenital biliary atresia.
Diagnostics and examinations, which doctor should I contact?
In order to determine as soon as possible that the cause of the painful state of the body is precisely stagnation of bile, you need to make an appointment with a gastroenterologist. The doctor will conduct an initial examination of the patient, palpate the abdomen on the right side, listen to complaints that bother the patient, and then, to confirm suspicions of cholestasis, write a referral for the following tests and diagnostic procedures:
- blood from a finger for its clinical examination for the percentage of vital cells and glucose levels;
- blood from a vein for biochemical analysis, determining the possible presence of cancer cells, bacterial and viral diseases, as well as other liver diseases that can be detected using this diagnostic method;
- morning urine, which is given on an empty stomach and shows the concentration of bile in urine, the level of ESR, protein, lymphocytes;
- Ultrasound diagnostics of the area of the right hypochondrium, liver tissue, gallbladder and its ducts.
In the most complex clinical cases, an MRI of the entire abdominal cavity is performed to study all organs of the gastrointestinal tract and determine the current pathology as accurately as possible. In case of oncological lesions, a liver tissue biopsy is additionally performed.
Diagnosis of cholestasis
You can suspect the development of this pathological condition based on the symptoms listed in the previous section. Laboratory tests and palpation of the liver and biliary tract can confirm cholestasis syndrome:
- General blood analysis;
- General urine analysis;
- Biochemistry analysis of blood composition;
- Liver tests;
- Coagulogram;
- Lipidogram.
New generation instrumental research methods can also help:
- Ultrasound;
- MRI;
- CT scan;
- Retrograde, transhepatic and percutaneous cholangiopancreatography.
If the presence of intrahepatic cholestasis is suspected, material is taken for a liver biopsy.
To diagnose this disease during pregnancy, exclusively laboratory methods are used. In newborns and infants, this disorder is diagnosed using cholangiography.
Effective treatment of cholestasis in adults and children
In order to treat this disease as quickly and effectively as possible, it is necessary to establish the cause of the disease. Only then will it be possible to achieve a positive result and at the same time avoid the risk of relapse of the disease. For this purpose, the following therapeutic methods are used to combat cholestasis, both in patients of the adult age group and in children:
- adherence to diet No. 5, which provides for the complete exclusion of alcohol, black tea, coffee, fatty foods, smoked foods, fruits containing organic acids (preference is given to chicken broth, vegetable salads, lean fish and meat, fermented milk products, cereal porridges, bread baked with adding bran);
- taking medications - Hofitol, Getral, Ursolfalk, Cholestyramine, Silymar, Phenobarbital (Ursosan is especially useful for pregnant women, as it has a completely natural formula and a minimum of side effects);
- performing surgery to expand the bile ducts, install a stent, remove tumors and stones that block the natural circulation of bile;
- restoration of the liver channels through which bile passes, if due to a congenital pathology the child has them completely absent (this disease is called atresia and is diagnosed in children in the first weeks after birth).
If necessary, the attending physician can select other therapeutic methods that, in his opinion, will be the most effective in a particular clinical case.
Folk remedies for treating liver cholestasis

Cholestasis syndrome is treated comprehensively, including using traditional medicine. Decoctions used as additional therapy during drug treatment have proven themselves well. The most effective of them:
- A decoction of corn silk, dry collection of St. John's wort and immortelle flowers;
- A decoction of stinging nettle leaves and rose hips;
- A decoction of green catkins of Canadian maple.
Recipes for preparing decoctions can be found in traditional medicine reference books or on the Internet. Folk remedies are not used to treat newborns.
Possible complications and consequences
In the absence of adequate treatment or an incorrectly formed course of therapy, the following health problems may develop:
- intoxication of the body with excessive concentration of bile in the liver tissues, which will lead to loss of appetite, constant nausea, vomiting, physical weakness and loss of strength;
- fragility of bones, nail plates and hair (occurs due to a lack of vitamins and minerals, which simply cease to be absorbed by the intestines);
- frequent internal and external bleeding;
- destruction of liver cells - hepatocytes, which ultimately leads to cirrhosis;
- the formation of stones inside the ducts, which are constantly filled with bile, since there is no stable outflow;
- malignant tumors that have formed against the background of impaired metabolism, chronic poisoning of not only liver tissue, but the entire body as a whole;
- the development of secondary diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, which suffer due to the lack of normal functioning of the digestive system, since most of the fatty acids are simply not broken down in the intestinal cavity.
All these negative complications and consequences can be easily eliminated through timely preventive measures and the organization of proper nutrition with periodic examinations by a gastroenterologist. Especially if one of your close relatives suffered from cholestasis. This dysfunction of the liver and gallbladder can be inherited along with genetic information.
Similar articles:
Types of cholestasis
Based on the location of bile stagnation, this pathology is usually divided into intrahepatic and extrahepatic. Intrahepatic cholestasis, in turn, is divided into the following types:
- Functional;
- Morphological;
- Clinical.
All of its types occur in the absence of obstruction of the bile ducts, while the extrahepatic form of cholestasis develops exclusively in its presence. Intrahepatic cholestasis is dangerous due to excessive accumulation of bile acids in the tissues of the body, while in the duodenum there is an acute deficiency. This type is most often diagnosed in newborns.
According to the mechanism of occurrence, the following types of cholestasis are divided:
- Partial, characterized by a decrease in bile secretion;
- Dissociative, when during the normal secretion of bile some components are missing in its composition;
- Total, when an insufficient amount of bile enters the duodenum.
Depending on the severity, cholestasis can be:
- Acute – with pronounced symptoms;
- Chronic – with a blurred clinical picture.
In addition, this disease can be icteric or anicteric, and also provoke cell destruction or not. A separate form of cholestasis of newborns is distinguished.
Stagnation of bile - what to do
Exercises for bile stagnation
It turns out that there are special physical exercises that can improve the flow of bile from the gallbladder. This method of treatment is usually used during the period of improvement to consolidate the result and for prevention. Here are some effective exercises that you can do at home:
- stand straight with your feet shoulder-width apart. Perform slow bends of the torso forward, gradually supplementing them with bends with rotation of the torso;
- Lie on your stomach and do the boat exercise. Lift your arms and legs extended forward from the floor and stay in this position. You can also alternate with raising your legs and performing cross movements in a raised position;
- regular walking in place and walking with high legs;
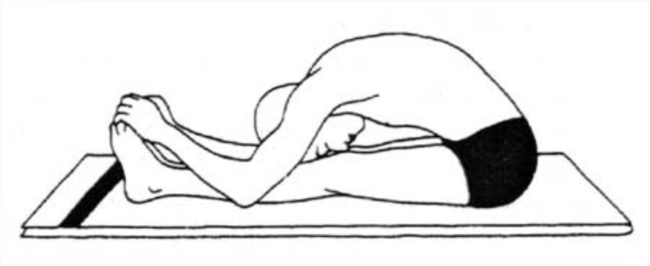
- lie on the floor on your back. Slowly pull your legs towards you, sliding your feet along the floor. Wrap your arms around your knees and press your forehead against them.
Nutrition for bile stagnation
Diet for bile stagnation
If there is stagnation of bile in the gallbladder, the doctor will definitely prescribe a diet, the observance of which will significantly alleviate the patient’s condition. Here are some basic nutritional recommendations for bile stagnation:
- go to 5-6 meals a day, avoid long periods between meals;
- Do not eat cold food or cold drinks;
- forget about fried foods and foods high in fat, fast food;
- When choosing a cooking method, give preference to steaming, baking and boiling.

Products for bile stagnation that can be consumed
If there is stagnation of bile in the gallbladder, the following types of foods are allowed to eat:
- milk, kefir, yoghurts and other low-fat dairy and fermented milk products;
- fresh vegetables and fruits;
- cereals;
- bakery products made from whole grain flour;
- low fat meat and fish;
- marshmallows, marshmallows, sweets without chocolate in moderation;
- juices, compotes, teas.
Foods for bile stagnation that should not be consumed
There is also a list of foods that you will have to avoid eating if there is stagnation of bile in the gallbladder:
- strong coffee;
- pickles;
- baked goods;
- sweets;
- mushrooms;
- sorrel;
- green onions;
- fatty meat, mushroom, fish broths;
- cocoa and chocolate.
Sample menu for one day for bile stagnation
- Breakfast: oatmeal with low-fat milk, cottage cheese, tea.
- 2nd breakfast: apple, banana.
- Lunch: vegetable soup, brown rice with chicken breast, cabbage salad, compote, whole grain bread.
- Afternoon snack: tea, pastille.
- Dinner: vegetable stew with fish, cottage cheese, tea.
Medication methods
If the patient has severe symptoms of the disease, the doctor first conducts all the necessary examinations. This helps to make a diagnosis with high accuracy, after which you can begin to choose the right treatment tactics.
When selecting a particular drug, the gastroenterologist takes into account the patient’s health condition. It is important that all painful symptoms of stagnation are completely eliminated in a short period of time. You also need to understand the reasons that led to the development of the disease. All treatment takes place at home, but in advanced cases, urgent hospitalization is recommended. This depends on the speed of development of the pathology and the need for surgical intervention.
Treatment of biliary stagnation is carried out with medication, but at the same time the doctor must develop a diet for the patient. Of course, modern specialists are not always against traditional medicine. It is permissible to take medications and herbs at the same time to help remove bile. This set of measures easily eliminates the resulting pathology. Thanks to the correct selection of drugs, a specialist must solve several main problems at once:
- completely eliminate skin itching and remove all rashes;
- ensure normal flow of bile to avoid stagnation;
- maintain the functioning of the liver, and, if necessary, improve its functioning.
Patients with cholestasis suffer from severe itching, which is relieved with creams and ointments. Antihistamines or corticosteroids are also suitable. In addition, the patient must take medications to normalize the flow of bile and reduce acidity levels.
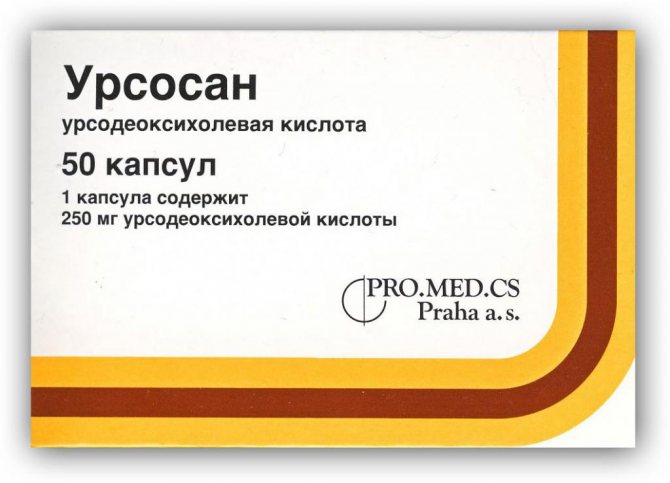
If we talk about means for the treatment of bile stagnation with a choleretic effect, then we can highlight “Holacid” and “Ursosan”. They not only perform their main function, but also eliminate the presence of dense clots. Their regular use contributes to the complete dissolution of stones.
For bile stagnation in children and adults, doctors recommend purchasing medications that will help remove it from the body. They usually contain a herbal component that has a beneficial effect on the condition of the liver. The most popular are “Hofitol”, “Allohol” and “Hepatosan”. In some cases, the patient is offered to undergo blind tubing, but before this it is important to make sure that there are no contraindications.
If an examination inside the gallbladder reveals an inflammatory process, you will have to take a course of antibiotics. Thanks to their action, bacteria will stop multiplying and die. When bile stagnates, the mucous membrane of the organ becomes thinner, so pathogenic microorganisms begin to actively act. Usually a course of 7 to 10 days helps.
The chosen remedy does not always give the desired result, so the doctor may prescribe a different type of antibiotic. They are available in the form of tablets or capsules, and sometimes it is recommended to give injections, as they are more effective and help you recover faster.
Of course, you should not prescribe various medications for yourself, especially without having test results on hand. All medications must be taken under the strict supervision of the attending physician. Only a specialist can correctly select one or another treatment option that will not harm the patient’s health, but, on the contrary, will give a positive result.

Stagnation of bile - treatment
In the arsenal of doctors in the fight against bile stagnation, there are both conservative and surgical treatment methods. It is very important to consult a doctor as early as possible when you notice the very first symptoms. Stagnation of bile in such cases is successfully eliminated by conservative methods. But if the disease drags on, with prolonged self-medication that does not bring results, the intervention of a surgeon cannot be avoided. Using conservative treatment methods, the doctor may prescribe:
- following a special diet aimed at preventing bile stagnation;
- prescribing various medications - choleretic agents, hepatoprotectors, drugs to eliminate itching, enzymes to improve digestive activity, vitamin preparations;
- prescription of physiotherapeutic research methods. This method of treatment is used outside the acute phase of stagnation of bile in the gallbladder.
If conservative treatment methods have shown ineffectiveness, the doctor may begin to consider the option of surgical intervention. If the outflow of bile is interfered with by stones or parasites, then the operation will be aimed at removing them and restoring the patency of the bile ducts. If the problem is much more serious, then even a liver transplant may be considered. It is worth understanding that stagnation of bile in the gallbladder is not an independent disease. This is a signal that there are serious problems in the human body.
Additional symptoms
Additional signs of the disease:
- causeless rashes appear;
- feces change color;
- urine darkens;
- a person experiences constant thirst;
- itching of varying degrees appears;
- the skin changes color.
The entire list of symptoms applies not only to adults, but also to children. Therefore, if any deviation from the norm is detected, discomfort or pain occurs, it is necessary to contact a specialist to make an accurate diagnosis.
Treatment and symptoms of bile stagnation in adults are closely related. More on this later.

How does cholestasis manifest in a person? Symptoms and main signs of bile stagnation.
Cholestasis - symptoms and treatment photos It is quite simple to determine the symptoms of cholestasis. Often the patient begins to experience dull pain in the hypochondrium (on the right side). In addition, the patient’s liver enlarges, the skin and whites of the eyes become yellowish. Also, symptoms of cholestasis manifest themselves in the form of chronic fatigue, lethargy, constant drowsiness and poor health.
The patient has vitamin deficiency, bitterness appears in the mouth, all this is accompanied by constant belching, vomiting, nausea and itchy skin. Quite often, bowel problems such as constipation or diarrhea may occur. If the patient has the above symptoms, it is imperative to consult a doctor and undergo a full diagnosis. This will help to avoid all sorts of dangerous complications in the future.