Features and mechanisms of development
Muscular fibrous structures in feces appear as a result of eating protein foods. The main source of protein in the daily diet is meat or fish. Muscle fibers are classified into three main groups:
- changed or digested (the structure of feces is unchanged, muscle fibers are without striations);
- little changed or difficult to digest (determined by muscle fibers with longitudinal striations); unchanged or indigestible (transverse pronounced striations).
Important! It is the unchanged fibers that determine the appearance of atypical structure in the stool. Such fibers have a cylindrical shape and form sharp angles when transversely striated.
Mechanisms of appearance
Normally, hydrochloric acid disrupts the structure of muscle fibrous tissue, transverse or longitudinal striations. The final digestion of fibrous tissue occurs in the duodenum. With proper digestive processes, fibrous components are not detected or are visualized under a microscope in an insignificant volume (for example, occasional consumption of too fibrous meat).
In clinical practice, the presence of unchanged muscle components in feces is called creatorrhoea. The condition is typical with a pronounced decrease in gastric juice and low levels of hydrochloric acid.
Under such conditions, meat products simply do not break down during the initial exposure to hydrochloric acid and pass into the duodenum unchanged, and appear as white fibers in the feces.
There, with reduced acidity, the production of enzymes responsible for the final digestion of meat food is simultaneously inhibited, and it descends into the lower intestines for further excretion with feces.
Note! Muscle fibers in a child’s feces are considered normal due to infantilism of the gastrointestinal tract. As the digestive processes strengthen, the striations in the stool gradually decrease.
Diagnostic features
Muscle fibers in feces are detected by laboratory microscopic examination. Adding reagents to the stool changes the color of the muscles. Eosin colors the fibers pink, methylene blue - green, Nile dye - blue. Violation of gastric digestion is manifested not only by creatorrhoea; fiber and undigested connective tissue are also present in the stool. Connective tissue fibers are differentiated using the xanthoprotenic reaction - 2 drops of concentrated nitric acid are added to the preparation. The connective tissue turns yellow.
Creatorrhea occurs as a result of impaired digestion of protein products or the lack of their absorption in the intestine. Enzyme deficiency is distinguished from absorption pathology using the Triboulet-Vishnyakov reaction. A solution of mercuric chloride is added to the aqueous emulsion of feces, which precipitates water-soluble, digested and enzyme-modified proteins. After 24 hours, the sample result is assessed. The reaction is positive when the solution is clarified, which indicates a malabsorption of proteins in the intestine.
To determine the excretory function of the pancreas, the content of elastase in the feces is studied. The enzyme breaks down elastic fibers, its concentration in the intestinal contents and feces does not change at all stages of digestion. The amount of elastase is determined by the enzyme immunoassay method. Its content in feces reflects the activity of pancreatic enzymes and the degree of disruption of the secretory function of the pancreas.
Predisposing factors for creatorrhea
If the condition persists for a long time and is accompanied by other symptoms, you should consult a specialist.
Creatorrhea is not a separate disease, but refers to the symptomatic manifestation of certain diseases and damage to the organs of the epigastric space of various natures:
- Putrid dyspepsia. The condition occurs when the protein components of food are partially or completely undigested. In this environment, the pathogenic activity of bacterial microflora rapidly increases, provoking inflammation of various parts of the intestine.
- Gastric resection. Postoperative complication after removal of part or all of the organ cavity, resulting in disruption of all digestive processes. The condition is often associated with the development of achylia (complete absence of gastric juice) and achlorhydria (lack of chlorine and hydrogen ions in hydrochloric acid).
- Accelerated expulsion of chyme. A condition in which semi-liquid contents leave the intestines quite quickly.
- Pancreatitis. A long-term disease that occurs predominantly in a chronic form. Accompanied by impaired pancreatic function and slow pancreatic secretion. Against the background of chronic pancreatitis, a violation of the external secretion of the pancreas often occurs.
- Development of hypoacid gastritis. The disease is characterized by reduced secretion of gastric juice and hydrochloric acid simultaneously with an intense inflammatory process. Hypoacid gastritis often reduces the functionality of all epigastric organs.
There are many reasons for the appearance of muscle fibers in the stool of an adult. The detection of unprocessed enzymes usually indicates the absence of important duodenal secreting enzymes, trypsin and chymotrypsin. Often the appearance of striated or non-striated protein fibrous structures indicates a violation of protein digestion (otherwise, protheliosis) and other diseases.
Digestible and indigestible fiber
Plant fiber can be digested by the human gastrointestinal tract only partially, and only a certain type. Fiber is mainly excreted unchanged in feces.
Fiber that can be partially digested is the pulp of vegetables and fruits, which contains a lot of pectin. Pectin connects plant cells together and dissolves under the influence of digestive juices. Cell walls can also be partially digested by enzymes from intestinal bacteria. For them, fiber is the main nutrient.
Indigestible fiber is the coarse fibers of plants and the cell walls of their membranes. This fiber creates volume in feces and is also a sponge that adsorbs toxins and removes them out. Coarse fiber stimulates peristalsis and improves digestion.
Possible complications
Is the presence of undigested meat particles and the appearance of white fibers in the feces so dangerous for adults and children? The main danger lies not in creatorrhoea itself, but in the disease that caused its appearance. The main complications are:
- chronic gastritis significantly increases the risk of appendicitis;
- severe pancreatitis contributes to thinning and perforation of the walls of the stomach and the lumens of the small intestine with the subsequent development of peritonitis;
- internal bleeding, development of anemia, blood infection or sepsis;
- an increase in ulcerative and erosive lesions in volume and number;
- the occurrence of malignant tumors.
The persistent appearance of undigested muscle fibers in the feces is a reason to undergo a high-quality and comprehensive examination, and not to begin independent treatment.
How to collect stool
It is better to collect stool from an adult and a child in the morning, immediately after the morning toilet, and try to deliver it to the laboratory as quickly as possible. You need to collect material from different parts of the feces, put them in sterile containers, or special disposable plastic containers, which can be purchased at the pharmacy. Evacuation should be natural; the use of laxatives, much less enemas, is prohibited.
In infants, it is not recommended to collect feces from the diaper; it is better to use a disposable diaper or medical oilcloth if the child has loose stools.
You can collect baby feces directly from the diaper
An older child needs to prepare a potty; first wash it with laundry soap or soda.
How much feces do you need?
To carry out the analysis, you need to bring 15–20 g of material to the laboratory, which is approximately equal to 1 tsp. – this amount is quite enough to identify all the main indicators.
Is it possible to collect stool samples in the evening?
It is better to use a morning portion of feces for analysis, but if you are not sure that defecation will occur after waking up, you can collect the material in the evening; it should be stored in the refrigerator for no more than 10–12 hours, the container should be hermetically sealed.
You can store stool for analysis in the refrigerator for no more than 12 hours.
Diagnostic measures
Particles of undigested protein fibers can only be identified under a microscope. However, if you eat a lot of meat, you can see undigested fiber in your stool if you look closely. The main diagnostic criterion for creatorrhoea is a coprogram - analysis of stool for its constituent components, physical and morphological properties and chemical composition.
After confirming the diagnosis, a gastroscopic examination, colonoscopy to study the condition of the intestines, blood tests for liver and pancreas function, and ultrasound of the abdominal organs are prescribed. Examinations are prescribed based on the severity of general clinical manifestations and the patient’s medical history.
Features of the coprogram
To ensure the reliability of the results, the following rules must be observed:
- exclude any enemas 2 days before the test:
- abstain from any meat food several days before taking the sample;
- Collect feces only in a sterile container:
- Only morning stool should be collected for analysis:
- women should avoid getting vaginal secretions into the stool (it is recommended to use a tampon).
Important! For established, stable stools in children and adults, it is permissible to store the sample in the refrigerator at a temperature of +2 degrees. This temperature usually corresponds to the shelves on the refrigerator door.
General analysis data
Normally, feces have a homogeneous mixture consisting of a variety of components: fats, mucus, soaps, dietary fiber. All these components arise as a result of the secretion of various parts of the gastrointestinal tract. During a coprogram, the doctor evaluates the components as typical and atypical, according to the gender and age of the patient. The following analysis data indicate pathology:
- protein component (inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract, polyps, oncology);
- bloody spots (hidden gastric or intestinal bleeding of various nature);
- pigment stercobilin (increased pigmentation characterizes hemolytic anemia, obstruction of the bile ducts):
- bilirubin (acute inflammation or dysbiosis);
- mucous component (an increase in the volume of mucus indicates the development of acute inflammation, characteristic of dysentery, salmonellosis, and parasitic infection);
- muscle fibers (disturbance in the composition of gastric juice, painful inflammatory process).
There are many different criteria for assessing stool with coprogram, but none of them is a reliable indicator of the existing diagnosis.
Note! The final diagnosis can be made based on the totality of data from numerous studies. Using a coprogram, you can identify some parasitic infections: giardiasis, ascariasis, bovine tapeworm.
Flat and columnar epithelium
Normally, a small number of squamous and columnar epithelial cells may be present in the stool. This occurs as a result of the mechanical effect of feces on the walls of the digestive tract. With an increased number of epithelial cells, one can judge the inflammatory process of the gastrointestinal tract. Depending on what kind of epithelium is found in the stool, an assumption is made about the location of inflammation.
The detection of columnar epithelium indicates inflammation in the upper intestines; the level of inflammation helps determine other changes in the coprogram.
Treatment process

Treatment of pathological disorders in the digestion of meat foods begins with identifying the true causes. The task of official therapy is not only to eliminate the symptomatic manifestations of diseases, but also to eliminate the causes that led to the disorders.
The purpose is determined based on the totality of the diagnostic data obtained. The main drugs for treating the causes of creatorrhoea are the following:
- enzyme-containing drugs against the background of pancreatitis, acute gastritis (Festal, Creon, Mezim, Pancreatin);
- antibacterial therapy for active inflammation of various origins (Ceftriaxone, Gentamicin, Clindamycin);
- enterosorbents during the processes of decay and intoxication (Polysorb, Enterosgel, activated carbon);
- antacid drugs to reduce pain and inflammation (Almagel A with lidocaine, Maalox).
Classification of feces according to the Bristol scale
design, color, consistency, smell. It is not for nothing that doctors are so sensitive to this issue. For patients, feces are an unpleasant waste product.
But he will tell the doctor about some of the nuances of a person’s health, because how and with what he walks “in a big way” is the result of the complex biochemical processes of his body.
If something goes wrong, it is enough to determine the type of stool using the Bristol scale and change your lifestyle, eating habits, or start treatment.
Interpretation
Patients suffering from irritable bowel syndrome typically complain of abdominal cramps and constipation. In some patients, chronic constipation is interspersed with brief episodes of diarrhea; while a small number of patients with irritable bowel syndrome have only diarrhea.
Studies conducted among patients with irritable bowel syndrome, fecal incontinence, and gastrointestinal complications of HIV have used the Bristol Stool Score as a diagnostic tool that is quite easy to use.
In accordance with the latest edition of the Rome III criteria, the following clinical manifestations of IBS are defined:
- IBS with constipation (IBS-C) - hard stools * ≥25% and soft or watery stools †{amp}lt;25% of bowel movements. ‡
- IBS with diarrhea (IBS-D) - soft or watery stools ≥25% and hard stools {amp}lt;25% of bowel movements. ‡
- mixed IBS (IBS - M) - hard stools * ≥ 25% and soft or watery stools † ≥25% of bowel movements. ‡
- atypical IBS (IBS - U) - insufficient stool abnormality for IBS-C, D or M ‡
*Bristol Scale Type 1-2 †Bristol Scale Type 6-7 ‡In the absence of use of antidiarrheal or laxative drugs.
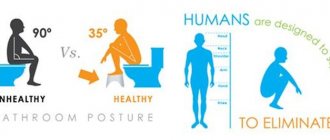
Norm or pathology
Of course, this should be done by a doctor. The patient is only required to correctly describe the appearance of his feces, the rest is the task of the specialist. Therefore, before going to see a doctor, you should try to remember how many times a day you have emptied your bowels. Did you experience discomfort, tension, pain?
According to Sophie Balzora, MD, a gastroenterologist at New York University Medical Center, everyone's normal is different.
Going to the bathroom every day is not considered a necessary indicator of good health, says Dr. Balzora.
Diet plays a very big role in not only the frequency, but also the texture, size, shape and smell. In addition to diet, gut health is affected by lifestyle, sleep, water intake, hormonal fluctuations, menopause and certain medications.
Doctors use the Bristol scale to classify bowel movements. In the table we have listed seven categories or types of stool.
- 1 and 2 indicate constipation,
- 3 and 4 are the “healthiest” types of feces,
- 5, 6 and 7 are considered diarrhea.
As a rule, most healthy people have types 3 or 4. Soft, formed stools, without effort during bowel movements, are considered normal.
Doctors say if your stool is too thick or has loose chunks of stool, it could be a sign of constipation.
A diet rich in fiber helps improve bowel function because fiber is like a sponge to retain moisture.
The American Academy of Family Physicians recommends a standard of nine servings a day of high-fiber foods, such as fruits, vegetables and legumes, to keep your bowels moving smoothly. Supplementing with additional fiber sources, such as psyllium, also helps promote soft stools that won't cause discomfort during bowel movements.
Dehydration can also play a role in constipation. The intestines need moisture, which softens the stool, improving its permeability.
Carefully! Hypersensitivity to certain foods, overgrowth of bacteria or yeast in the small intestine, and excessive consumption of red meat or alcohol may also be factors in constipation.
People with loose stools have chronic diarrhea in at least 75% of cases. The consistency may be too soft with loose edges or completely watery. As with constipation, fiber plays an important role here too.
Carefully! Potential causes of chronic diarrhea include overgrowth of bacteria and yeast in the colon, food sensitivities, excess intake of fat or fatty foods, inability to absorb certain nutrients, and chronic stress or anxiety.
It's different for everyone
The first type is characterized as sheep stool. This will not be difficult if you have ever seen a sheep or goat emptying its intestines. Their feces look like round, hard balls. But if for them this is not a problem and is associated with the peculiarities of digestion, then for a person such stool means that he is constipated.
Such feces can injure the anus and cause pain during defecation, cause hemorrhoids and even intoxication of the entire body.
What does the color of stool mean?
Massarat Zutshi, a colorectal surgeon at the Cleveland Clinic, says the color of your stool is usually related to the color of the foods you recently ate.
In some cases, color changes may indicate something more serious. This is what the color of stool can indicate.
Almost black
If you are not taking any coating, antacid or absorbent medications (which often turn the stool black), stool that is too dark may indicate bleeding in the gastrointestinal tract. Stool may also be colored as a result of stomach ulcers or high levels of iron in the body.
Some medications, such as Kaopectate, can sometimes cause pale and clayey stools.
White stool can also be caused by problems with bile getting into your gastrointestinal tract, or if your liver doesn't produce enough bile.
When the bile duct is blocked due to a stone or tumor and the bile cannot reach the intestines, the stool also turns white. This is common in liver diseases such as hepatitis and cirrhosis.
Red
Let's say your stool or urine is red. Don't panic! First, think about what you ate the day before. Dark red beet lettuce (thanks to betacyanin) may cause both your urine and stool to become colored for up to two days after consumption. In addition to beets, tomatoes, food coloring, or even cranberries may be culprits.
Yellow
Yellow stool may indicate problems with fat digestion. This may be the result of having your gallbladder removed, taking weight loss medications, or certain surgeries. Yellow, oily stools may indicate chronic pancreatitis or celiac disease.
Green
If your stool is slightly green, think about whether you've eaten any greens in the last 24 hours, because that could be the cause. If your stool is consistently green and is not related to food, consult your doctor.
Regardless of color, stool usually has a foul odor due to bacteria in the colon that digest food.
If your stool's normal odor changes to an abnormal odor, it may be due to an infection.
Another cause may be inflammation of the colon or diseases that cause malabsorption, such as celiac disease, chronic pancreatitis, cystic fibrosis or lactose intolerance.
Thick sausage-shaped feces
This type of stool also characterizes improper bowel function. This is the same as constipation, but in this case the stool contains fiber and bacteria. However, it often takes several days for a sausage of such a large diameter, exceeding the maximum open anal opening, to form.
Abnormal esophageal motility may also indicate certain health conditions
Some digestive disorders, such as irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), Crohn's disease, and ulcerative colitis, can affect your stool when certain problems occur along with other symptoms. For example, bouts of diarrhea or constipation (or alternating between them), as well as abdominal pain and excess gas, are the primary signs of IBS, a common colon disorder.
Crohn's disease, a chronic disease characterized by inflammation of the intestines, includes chronic diarrhea, as well as weight loss, fever and lower abdominal pain.
Ulcerative colitis is an inflammatory disease similar to Crohn's disease that begins in the rectum and spreads to other areas of the colon.
Chronic diarrhea, sometimes bloody, is a key indicator of ulcerative colitis.
Sausage with cracks
The Bristol scale defines the third type of feces. The chair looks like a sausage with cracks. A person who has it is definitely constipated. Although he may not think so. After all, the contents of the intestines leave it quite quickly.
But don't rejoice. There are still problems with digestion. In order to have a bowel movement, you have to strain, which means there is a danger of hemorrhoids and anal fissures. Most likely, you have irritable bowel syndrome.
The diameter of such a “sausage” can be 2-3.5 cm.
Who came up with this method for diagnosing constipation?
The method, as its name suggests, was developed by scientists from the University of Bristol, which is located in the UK. It was first published and proposed for the diagnosis of constipation and other disorders in 1997.
Since then, the Bristol scale has been used all over the world - doctors have recognized it as a very effective and important diagnostic method.
- The Bristol scale helps to evaluate only the shape of stool. It does not take into account other indicators, such as color, blood, mucus, undigested particles, etc.
- This method will not help detect many serious health problems, especially in people who have chronic diseases.
- And even more so, you cannot, based only on this scale, independently, without a doctor, diagnose yourself.
However, by the consistency of the stool you can assess the general condition of the intestines and, if necessary, take a laxative to quickly cope with the problem. For example, with functional constipation not associated with serious diseases, the drug Microlax® helps.
Some medications can cause problems with bowel movements. If you start taking any medication and notice a change in the consistency of your stool, you should immediately tell your doctor. Your doctor may stop the medication, prescribe a substitute that doesn't have this side effect, change the dosage, or recommend taking laxatives while you are undergoing treatment.
If you know what types of stool there are and know how to use the Bristol scale, you speak the same language with your doctor. Of course, this will help the doctor more correctly assess your condition and prescribe the most effective treatment.
Type 1 stool spent the longest time in the colon, and type 7 stool spent the shortest time.
Lumpy type feces (1 and 2) are difficult to pass and require straining.
Loose or watery stool passes too quickly and can cause problems.
What type of chair is ideal?
The feeling that you need to have a bowel movement is clear, but not urgent. When you are already sitting on the toilet, there is no delay. No special effort or strain is required. The feces come out smoothly and smoothly. Afterwards, only a pleasant feeling of relief remains.
This corresponds to stool type 4 on the Bristol Stool Scale
Read a more detailed article about constipation in children HERE
About feces in children
Goat pellets in the stool - lack of fluid in the stool and intestinal spasticity (feces are thrown out in portions) Green color - bacteria Sour smell - candida, Yeast-like stool, with candida spores, airy, porous, sour Slurry - bacteria, poor breakdown of complex carbohydrates
Stool color is also important
darker indicates pronounced rotting; lighter indicates fermentation (or takes on the color of the food eaten)
Unshaped chair
The next type, as shown by the Bristol scale, has no shape. But at the same time, it is not liquid, but consists of several soft parts with torn edges. This is not diarrhea yet, but already a condition close to it. This form of feces can be caused by taking laxatives, large amounts of spices, drinking water with a high content of minerals, and high blood pressure.
What do muscle fibers in feces mean?
This means that protein food is digested in insufficient volume and at a minimum speed . This may be a consequence of many pathologies, which will be discussed below.
In turn, muscle fibers in feces can be divided based on the absence or presence of striations. It is important to understand what exactly this or that sign means and why creatorrhea develops.
With striations
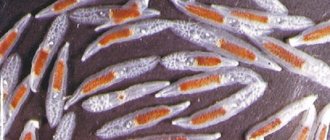
Each coprogram has a special column for muscle fibers, defining them by the degree of striation or lack thereof. In the first case, we are talking about the presence of inclusions of meat food, which was partially processed in the stomach or intestines. Muscle fibers with striations in the feces look like elongated cylindrical formations, which are characterized by smoothed corners.
Without striations
Speaking about fibers that do not have striations, pay attention to the fact that:
- they are small-sized lumps;
- normally, the presented indicator should disappear in the stomach area - under the influence of its juice;
- however, this does not happen, which may indicate abnormalities in the functioning of the digestive system and, in particular, the pancreas.
That is why the very fact of the appearance of muscle fibers without striations in feces should in no case be ignored.
What is creatorrhoea?
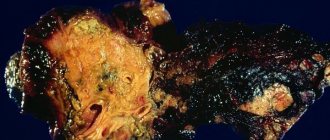
Meat consists of proteins - long chains of sequentially connected amino acids and the connective tissue that holds them together. Under a microscope it looks like a fiber with transverse whitish layers. Digestion of meat, turning it into the final product - individual amino acids that are absorbed in the intestines into the blood - is a complex multi-stage process. Chewing, the mechanical breaking up of a bolus of food in the mouth, prepares the product for digestion. Pepsin, the main enzyme in the stomach, works in a very acidic environment. Its function is to break down collagen, the protein that makes up connective tissue. Destruction of the bridges between amino acid chains leads to loss of cross-striation of the muscle fiber.
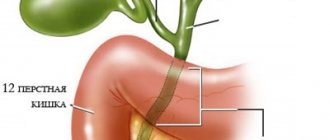
The next stage is the digestion of meat in the duodenum by proteolytic enzymes of the pancreas - trypsin, chymotrypsin, elastase. They split long protein chains into short sections of two or three amino acids. Digestion of meat is completed in the small intestine, the walls of which consist of enterocytes. These cells contain peptidases, intestinal enzymes that break down proteins into individual amino acids, which enter the blood through the intestinal wall.
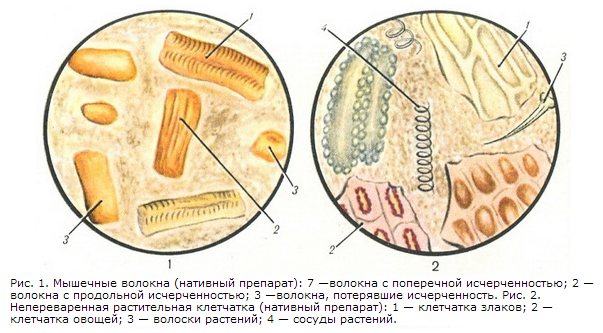
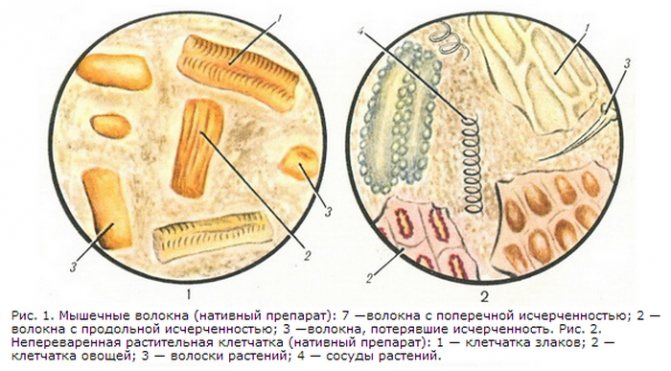
During stool microscopy, the nature of the pathology is determined by the appearance of the remains of undigested meat and the presence of connective tissue. Bundles of muscle tissue with sharp corners and striations indicate a stomach disease. Oval, without striations indicate insufficient activity of intestinal enzymes.
Causes of deviations and normal muscle fibers in feces
The factors causing the presented deviations in children and adults must be considered separately. This will allow us to fully study the etiology of each process.
The child has
In children under 12 months of age who have already started eating meat, it is possible and acceptable to have a high ratio of muscle fibers in the feces. Such reactions are identified due to the immaturity of the gastrointestinal tract in general and digestive functions in particular.
As you grow older, these processes will improve, and food will begin to be absorbed almost completely.
At the same time, if muscle fibers are identified in a child’s stool in large quantities or numerous negative symptoms are noted, the reasons for such deviations are very serious. This list may include:
- Forced release of food semi-liquid contents from the intestinal region called chyme. The pathology is often found in children and leads to the fact that food does not have the opportunity to be digested to its full extent.
- Disruption of the pancreas, associated with malfunctions of external secretions. The condition can be congenital or acquired, but treatment is necessary regardless of developmental conditions.
- Complex forms of gastritis, for example, hypoacid, in which an aggravated secretion of hydrochloric acid is identified. As a result, the digestive abilities of the stomach are reduced. In addition, hypoacid gastritis is associated with inflammatory damage to the gastric mucosa, which also affects the appearance of undigested muscle fibers in the feces.
If there is any suspicion of any of the presented diagnoses, as well as with confirmed creatorrhea in a child, it is important not only to start treatment on time, but also to carry out a coprogram every six months. This will allow you to monitor the healing process and eliminate the development of complications, which will be discussed below.
In an adult
The appearance of muscle fibers in the feces of an adult is possible due to a lack of bile, ulcerative colitis, as well as a form of this disease that is accompanied by constipation. The list of provoking factors is supplemented by:
- a chronic form of pancreatitis, in which the production of enzymes essential for the breakdown of proteins is reduced;
- chronic atrophic gastritis;
- hepatitis or gallstone disease;
- dysbacteriosis, namely putrefactive or fermentative dyspepsia.
Experts call gastrectomy another predictable factor. This can also be affected by pathologies that are accompanied by a lack of gastric juice secretion (achilya) or a lack of components that form hydrochloric acid. We are talking about chlorine and hydrogen ions, and their absence is called achlorhydria. Having determined the specific reason why muscle fibers are found in the stool, it is necessary to begin treatment.
Causes of creatorrhea, steatorrhea and amilorrhea
Many patients are interested in what these signs mean and why they appear. The most common disease in which they are detected in scatological analysis of stool is chronic enteritis. Also, in addition to them, with this pathology, the material under study contains many pieces of undigested food. In the event that a disease caused by a digestive disorder takes a severe course, the presence of abnormal inclusions in the stool appears in large quantities:
- A symptom of pathology, such as amilorrhea, is manifested by an excess content of starch in the feces under study, which, if digestion is impaired, cannot be broken down into sugars, as happens in a healthy body. Also, unsplit starch grains, indicating the presence of pathology, indicate that the patient has impaired carbohydrate breakdown. This suggests that amilorrhea is also possible with pancreatic insufficiency;
- Steatorrhea discovered during the study occurs as a consequence of the fact that the breakdown and absorption of fats is impaired in the intestines;
- Creatorrhea, like steatorrhea or amilorrhea, occurs due to the fact that due to a decrease in the activity and concentration of enzymes in the digestive organs, complete breakdown of muscle fibers is not ensured. This happens due to the fact that the patient has impaired digestion.
In addition, in such a pathological symptom as creatorrhea, the causes of development are the result of insufficient intake of chymotrypsin and trypsin, as well as other proteolytic enzymes, into the duodenum. Injuries or tumors of the pancreas, alcohol abuse, and toxic substances entering the gastrointestinal tract can also contribute to the appearance of this symptom. But, despite what caused creatorrhoea, the accompanying symptoms will be expressed in pain, nausea, vomiting and the presence of undigested muscle fibers in the stool.
Treatment of creatorrhea
The choice of treatment for this pathological symptom depends on what particular disease caused it, since first of all it is necessary to eliminate the root cause. But in any case, creative rhea, as well as the disease that caused it, require complex treatment. If the pathology is in the acute stage, all therapeutic measures are carried out only in a hospital setting.
During the period of remission of the disease that contributed to the development of creatororrhea, attention should be paid to treating the pathology and its symptoms with folk remedies. In medical practice, there is information about a large number of cases where, thanks to them, patients were able to cure the disease completely. Also, during therapy aimed at ridding the patient of such a symptom as creatorrhoea, it is necessary to follow an appropriate diet, which is selected by a specialist. It should contain a high protein content.

Muscle fibers in the stool are not the main sign of dysfunction of the gastrointestinal tract; they are accompanied by visible striations of the stool in the longitudinal or transverse direction. Fibrous structures can be painted white, brown or black, which characterizes the course of the underlying disease. If an alarming sign appears, you should consult your doctor.
What to do if there is a deviation from the norm in the analysis
The rehabilitation course must be comprehensive. Outpatient treatment is usually prescribed, while hospitalization and other more serious interventions are relevant only for the most complex cases. The main methods of treatment are the use of digestive enzymes, diet, and the use of antibiotics. Surgery may also be required.
Speaking about digestive enzymes, which may be required for muscle fibers, pay attention to the fact that their use is relevant for inflammation of the pancreas and certain forms of gastritis. Please note that:
- such names as Pancreatin, Festal, Mezim and some others are accepted;
- each of the drugs allows you to relieve the load on the pancreas, improves the complete digestion of food, and also neutralizes the feeling of heaviness in the stomach;
- use is possible after consultation with a specialist as part of long courses during or after eating.
The next step is following a diet. As you know, any disease of the digestive system will be cured only if you change your diet. Thus, it is very important for the patient to stop eating indigestible foods, spicy foods, and rich baked goods.
Fast food, alcoholic drinks, as well as strong tea and coffee are prohibited. During periods of deterioration of the general condition, we can talk about complete fasting.
As noted earlier, if a poor stool test for muscle fibers was obtained, antibiotics, along with other methods, will help to cope with this. They are prescribed mainly for ulcerative lesions, gastritis, as well as in the most complex cases of pancreatitis. Along with antibiotics, it is advisable to use probiotics, which will help maintain and improve the condition of the intestinal microflora.
In some cases, surgical intervention is not possible. Experts point out that with creatorrhoea:
- The operation is performed only in extremely severe cases, when the pathology rapidly progresses or the main treatment is ineffective over a long period of time.
- The intervention is carried out in case of perforation of a gastric ulcer or blockage of the bile ducts. This may also be necessary for serious complications of cholecystitis and inflammatory processes in the pancreas.
- Whenever possible, specialists try to perform laparoscopy. This will eliminate significant blood loss, as well as complications after surgery.
How long does a stool test take?
A person can receive a transcript of the analysis 1-2 days after submitting the material. How much coprogram is done depends on the workload of the laboratory. The patient receives the results of a chemical, micro- and macroscopic examination of the stool. The characteristics (deciphering) of the coprogram are compiled by the doctor, who can also identify the identified pathologies. Deviations from the norm in the composition of feces may indicate the onset of development or the presence of pathology of a certain organ.
The site provides reference information for informational purposes only. Diagnosis and treatment of diseases must be carried out under the supervision of a specialist. All drugs have contraindications. Consultation with a specialist is required!
Can there be complications?
In some cases, when a patient has many muscle fibers in the feces, the presented pathology does not go away without complications. Bleeding and even neoplasms are likely to occur if gastritis, and later a stomach ulcer, are not treated on time. In addition, peritonitis and inflammation of the appendix are considered serious complications of the pathology.
Such complications of creatorrhoea in children and adults can be avoided if diseases of the digestive system are treated in a timely manner, as well as preventive examinations are carried out. The ideal prevention of pathology is a proper diet, a healthy lifestyle, as well as physical activity and the elimination of bad habits.
A coprogram is a comprehensive study of human feces, its physical, chemical properties and various inclusions.
The coprogram allows you to evaluate the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract, detect dysfunction of the liver and pancreas, identify helminths in the intestines or diagnose inflammatory changes in the digestive tract.
Coprogram - why do it?
The coprogram will also show crystals of salts, in particular oxalates
Diagnosis of gastrointestinal diseases, pathologies of the kidneys and ureter in a small child is a problem. Determining diseases is often impossible using techniques used for adults, so laboratory diagnostics remains one of the most productive methods. When collecting stool for analysis, mothers themselves do not always expect the results that are revealed. For example, the presence of oxalate crystals is frightening, alarming and forces you to immediately seek the best treatment.
What does a stool test provide:
- identification of disorders of acid-forming and enzymatic activity of the stomach, intestines, and pancreas;
- liver function failure;
- instability of juice evacuation from the stomach/intestines;
- the presence of inflammatory processes;
- disturbances in the state of intestinal and stomach microflora;
- the presence of inflammatory processes in internal organs.
With this analysis, it is easy to identify whether there are crystals, what kind they are, what they are associated with, and choose the desired treatment option. During normal life processes, there should be no oxalate crystals in the feces.
Deviations from the norm
Form
Hard, small feces are characteristic of constipation due to colitis, stomach or duodenal ulcers.
Consistency
An ointment-like consistency is characteristic of pancreatic diseases.
Liquid feces are a sign of enteritis or dyspepsia.
Pasty feces occur with colitis.
Color
Changed color of stool is associated with the consumption of certain foods or medications, or is associated with impaired circulation of bile and its derivatives in the body.
Light yellow feces - found in dairy product lovers.
A bright yellow color is a sign of accelerated evacuation of food from the intestines, when bilirubin does not have time to transform into the form of hydrobilirubin.
Dark brown feces are characteristic of predominantly meat-based foods in the body.
Intensely dark brown feces occur when there is a sudden large intake of bilirubin into the intestines, when the reason blocking its movement is eliminated (destruction of a bile duct stone, tumor disintegration).
Black (tarry) stool is a sign of bleeding from the upper gastrointestinal tract, since blood turns black when it interacts with hydrochloric acid in the stomach. This could be a stomach ulcer, bleeding from dilated veins of the esophagus with cirrhosis of the liver. Preparations of iron, bismuth, and carbolene also color stool black.
Blueberries, cherries, and chokeberries give the stool a blackish tint.
Acholic discolored feces are a consequence of the cessation of bilirubin entering the intestines. It occurs when the bile duct is blocked by a stone, with cancer of the head of the pancreas or when the liver tissue is damaged due to hepatitis A, chronic hepatitis, or cirrhosis of the liver.
Light-colored stool is a sign of increased fat content and is observed in cases of impaired pancreatic function (pancreatitis, pancreatic cancer).
Smell
The pungent odor of feces indicates the advantage of meat products in the diet. Sour appears with excessive consumption of carbohydrates (sugar, fruits, flour, peas and cabbage). Foul-smelling feces occur when the secretion of pancreatic enzymes is impaired or when bile does not enter the intestinal lumen.
Reaction
An alkaline reaction of feces is observed when putrefactive processes predominate. When the intestines intensify the putrefaction of proteins that are not digested in the small intestine, ammonia is released. It causes an alkaline reaction.
An acid reaction is a consequence of fermentation processes that release carbon dioxide, the predominance of carbohydrate foods in the diet, and the excessive formation of fatty acids.
Connective tissue
Connective tissue is the remains of meat food that are not sufficiently digested in the gastrointestinal tract and end up in the feces. When examined microscopically, connective tissue appears as white-gray elements with a fibrous structure. They differ from mucus in their high density and clear contours.
Connective tissue in the stool indicates a violation of the digestion of food in the stomach, since hydrochloric acid is needed to destroy its fibers. Undigested connective tissue fibers are a sign of low acidity of gastric juice.
The second reason for the appearance of connective tissue fibers is a lack of pancreatic enzymes. A change in the composition of pancreatic juice leads to incomplete digestion of meat food and the release of its remains in feces.
Muscle fibers
Muscle fibers in feces are a consequence of insufficient digestion of protein foods (meat products or fish), the remains of which end up in feces. Muscle fibers are divided into digestible (changed) and indigestible (unchanged). Indigestible muscle fibers are cylindrical in shape, with clearly defined transverse striations. Digestible muscle fibers are small oval-shaped lumps without pronounced striations.
Hydrochloric acid in the stomach destroys muscle fibers and their striations disappear. The final digestion of muscle fibers occurs in the duodenum under the influence of pancreatic enzymes.
The presence of a large number of muscle fibers in the stool is called creatorrhea. It occurs with reduced acidity of gastric juice or with insufficiency of pancreatic enzymes responsible for the breakdown of proteins.
The appearance of muscle fibers in the feces of children under 1 year is allowed. This is due to the immaturity of the digestive system. As the child grows up, meat food is completely digested.
Neutral fat, fatty acids, soaps
Fatty acids and soaps are a product of the breakdown of neutral fat.
The appearance of neutral fat, fatty acids or soap in the stool is called steatorrhea. Insufficient digestion of fats and their appearance in feces is typical for the following conditions:
1. Diseases of the pancreas (chronic pancreatitis, pancreatic cancer).
The pancreas produces lipase. This is an enzyme that breaks down fats. If it is not enough, then food fats are not absorbed, and neutral fat appears in the feces. Moreover, a sign of pancreatic disease is persistent steatorrhea - confirmation of the result in several stool tests.
2. Impaired flow of bile into the intestines (obstructive jaundice).
In a healthy body, bile is involved in the breakdown of fats; its absence disrupts the digestion of fats.
3. Impaired absorption of fats in the intestine (intestinal amyloidosis) or accelerated excretion of intestinal contents from the rectum.
4. Excessive intake of fats from food or use of medications containing fats (use of rectal suppositories or castor oil).
Cellulose
Fiber is a complex carbohydrate that forms the cell wall of plants. It enters the body with vegetables and fruits, with cereals and legumes.
In the digestive tract of a healthy person, fiber is practically not digested due to the lack of special enzymes that can break it down. Only partially can it be broken down by the intestinal microflora.
Fiber is a source of nutrients for normal intestinal microflora, which “prefers” coarse dietary fiber. In addition, it is a stimulator of peristalsis (normal contractility of the intestine), it mechanically irritates the nerve endings of the intestinal wall and accelerates its contractions. Thanks to this, food moves evenly through the digestive tract.
Indications for taking a coprogram
A stool test should be taken as part of an annual preventive examination in order to recognize problems with the digestive tract in time and begin treatment.
When is scatology prescribed:
- inflammation of the digestive system in acute and chronic form;
- hemorrhoids, fissures in the anus, chronic constipation;
- cirrhosis of the liver;
- irritable bowel syndrome;
- neoplasms in the gastrointestinal tract;
- poisoning;
- suspicion of helminthic infestation, amoebic dysentery;
- assessment of the effectiveness of drug treatment;
- before conducting instrumental diagnostics of the gastrointestinal tract and surgical interventions.
A stool test should be taken if tumors appear in the intestines.
How is a patient examined?
Laboratory analysis is considered the most reliable test. Tests involve studying the content of fatty acids, soap, and triglycerides in feces.
If the total fat mass in the stool is 5 g or more, then the patient suffers from steatorrhea.
To make a diagnosis and prescribe the correct treatment, it is not enough to take only one laboratory test.
The doctor must examine the patient, assess his general condition and find out how other organs work. First of all, a conversation should be held with the patient, during which an anamnesis of the disease is compiled.
The next stage is examining the patient. To do this, it is necessary to palpate the left side of the patient’s abdomen. Such actions will cause rumbling or a sensation of overflowing contents in the left side.
To complete the picture, the patient may be prescribed an X-ray examination. The patient's diagnosis will be confirmed if there is swelling of the intestinal mucosa.
To carry out a more detailed diagnosis, it is necessary to undergo a radioisotope study. This method involves filling the patient’s digestive tract with radioactive isotopes.
After their accumulation, the doctor studies how the organs work. A biopsy can be done to confirm the diagnosis.
Before prescribing medications, macroscopic and microscopic assessment of stool contents must be performed.
Only after the exact amount of neutral fats, fatty acids and soaps in the stool is known can the correct treatment be prescribed.
It is important to undergo all tests in a timely manner at the first signs of the disease. If steatorrhea is not treated, serious illnesses may develop, such as leukopenia, hypolipemia, hypochromia and others.
An advanced disease can lead to complications:
- the functioning of internal organs will be disrupted;
- hypovitaminosis will develop;
- the water-salt balance will be disturbed, the patient will develop edema;
- the patient will suffer from protein deficiency;
- performance will decrease;
- the patient will develop mental abnormalities.
The initial form of the disease does not threaten the patient’s health and is treatable.
Diagnosis and treatment of fatty stools
If you suspect fatty acids in the stool of an adult, contact a gastroenterologist. The main test for diagnosing steatorrhea is a coprogram. Stool analysis in the laboratory evaluates the physical properties and composition of feces. Before the examination, you should not use anal suppositories, enemas, or take bismuth or iron supplements or laxatives. Together with the coprogram, one or more of the following diagnostic methods are carried out:
- collecting anamnesis (questioning the patient about his healthy lifestyle, nutrition, hereditary problems);
- general urine analysis;
- Ultrasound;
- colonoscopy;
- X-ray;
- biopsy;
- radioisotope survey.
Treatment aims to eliminate symptoms.
Enzymes are designed to improve digestion and the overall functioning of the gastrointestinal tract (Creon, Pancreatin, Pancitrate). Antacids (Gastal, Phosphalugel, Almagel) cope with high fat content. They reduce the amount of gastric juice, which enhances the effect of enzymes. You can improve digestion and reduce bloating with the help of adsorbents (Enterosgel, Smecta, Atoxil). The patient needs a diet during treatment.
The diet should include lean meat, lean fish, milk, vitamins A, D, E, K, and folic acid. Exclude salted, fried, smoked, alcohol, vegetable fats, legumes, and semi-finished products.
Hot soup or broth in the daily menu will help the gastrointestinal tract absorb fats. You can prevent fatty stools by following proper nutrition and giving up bad habits.
Researcher at the Laboratory for the Prevention of Reproductive Health Disorders of Workers at the Research Institute of Occupational Medicine named after. N.F. Izmerova.
A coprogram can indicate the development of quite dangerous pathologies and conditions. What does the presence of fatty acid salts in feces indicate? This means that fats are not fully absorbed by the body. And it indicates the development of a certain pathology. This state of affairs, when fat and fatty acids are found in the stool, is called steatorrhea. The disease has its own causes, symptoms, varieties, methods of diagnosis and treatment. In this article we will take a closer look at them.
Normal indicators
What is the normal level of fatty acid salts in feces? A healthy body absorbs 90-98% of all fat that enters the body as part of food. As for the norm, feces should not contain triglycerides (neutral fat) or fatty acids. Some residual inclusions can be found in feces in the form of soaps.
Salts of fatty acids in feces can be detected using a special laboratory test - a lipogram. Here the presence in feces of both neutral fat and fatty acids and their soaps (salts) is checked. Research is being carried out in the laboratory.