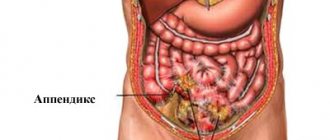
It is very difficult to recognize diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, and especially diseases associated with inflammation of the peritoneum, in a timely manner. Vague and similar symptoms, the density of organs, and individual features of the intestinal structure can interfere with [the diagnosis of acute appendicitis].
Making a diagnosis of acute or catarrhal appendicitis is critical for the patient. Even with a slight delay, there is a risk of the disease progressing to subsequent stages, which ultimately significantly complicates the course of the disease and can lead to peritonitis. Despite the minimal mortality rates, [the cecum] remains vulnerable - as a rule, patients are admitted to surgical departments already in the second phase, when inflammation of the appendix becomes phlegmonous or perforative.
Basic methods for diagnosing appendicitis
Tests for suspected appendicitis have diagnostic value as confirmation tools if there is a clear pattern of symptoms. The doctor focuses on a complex of observed factors:
characteristic pain responses to palpation and pressure at certain points;
anamnesis collected when interviewing a patient who mentions Kocher’s symptom (onset of the disease), localized pain;
rise in temperature in the afternoon, sometimes fever, chills;
the presence of vomiting, loose stools, bloating and gas accumulation
blood test data (leukocyte formula) and ultrasound confirmation.
Abdominal pain due to inflammation of the appendix
We remind you that an attack of acute appendicitis is not always accompanied by unbearable pain. The sensations may be moderate and disturbing, and the pain may resemble muscle pain. On the third or fourth day of the disease, the pain quickly subsides, the patient and those around him relax - and this leads to even greater prolongation, although it is a sign of a necrotic process when pain receptors in the membranes of the peritoneum stop working.
The result of this development of events is a periappendiceal abscess, which in a day or two turns into peritonitis. And here the chances of a favorable outcome are sharply reduced. Only an emergency and very complex operation can save the patient’s life.
A shift of leukocytes to the left confirms appendicitis
[A complete blood count] shows a noticeable increase in leukocytes, and confirmation is the same shift to the left - on the scale of the percentage of certain types of cells, an increase in band neutrophils is clearly visible. It is their growth that indicates serious inflammation. The phase of the process can be clarified by the appearance of a shift to the right - the balance shifts towards segmented leukocytes with a clear increase in their number and an increase in ESR.
A leukogram for inflammation of the appendix plays the role of not only confirmation, but also an indicator of the urgency of surgical intervention. When moving to a shift to the right, the decision is made taking into account the lack of time, since the process develops rapidly and towards the phlegmonous and perforative stages. And this is a direct threat of the occurrence of a periappendiceal abscess with transition to peritonitis.
Picture of tests for appendectomy surgery
Tests for appendicitis in adults and children differ minimally; the leukocyte formula (deciphered by type and content of cells) is considered an important indicator. If the presence in the blood is considered normal from 4 to 10x109/l, then with the development of appendicitis the concentration of leukocytes increases to 15x109/l. Statistics show that in infancy a child will have maximum levels of leukocytosis with an almost normal urine test result for appendicitis.

How is appendicitis determined by blood tests?
Is it possible to detect appendicitis using a blood test? Unfortunately, data on leukocytosis and ESR alone is clearly not enough to make a diagnosis. Any doubts are interpreted in favor of observing the patient in a hospital, sometimes this takes up to three days. High leukocytosis in combination with localized pain, Kocher's symptom (during the interview it is described by the patient himself), Shchetkin-Blumberg's symptom indicate a high probability of developing an acute catarrhal process with a transition to purulent and perforative stages. In this case, the majority of patients find themselves in a rather difficult situation and are far from being in the first stage.
Indications for prescribing a blood test
The blood sampling procedure is indicated if the following symptoms are present:
- persistently elevated temperature for more than 6–7 days;
- fever;
- loss of appetite;
- chronic constipation;
- diarrhea;
- increased fatigue;
- muscle cramps;
- periodic attacks of sharp and nagging pain on the right side of the abdominal cavity;
- nausea;
- bloating;
- painful urination;
- vomit.
We recommend reading: Exercises for constipation: gymnastics for the intestines at home
In children, it is much more difficult to determine the signs of appendicitis than in adults, since children, due to their age, are not able to indicate the exact location of the source of physiological discomfort. If a child experiences acute pain that only subsides when the body is positioned on the right side, you should seek medical help as soon as possible.
Of course, many of the listed signs indicate a wide range of diseases, but the combination of a number of symptoms is a reason for an unconditional visit to a medical facility.
Problems with ultrasound and delays in diagnosis
[Ultrasound of the abdominal cavity] is not always effective in diagnosing appendicitis. The process may be difficult to see; signs of inflammation clearly appear already at the stage of fluid accumulation around it. It is quite difficult to see the appendix on an ultrasound, and it is impossible to recognize inflammation without the whole complex of symptoms.
We remind you once again that any suspicion of appendicitis should be as alarming as possible - it does not go away on its own, it can only be treated surgically, and in the absence of help it inevitably leads to death. The disease develops quickly. rapidly passes through all stages of deterioration, and when moving to periappendiceal abscess and peritonitis poses a direct threat to the patient’s life. You can’t put pressure on your stomach yourself! - this can lead to rupture of the appendix.
Appendicitis is a fairly serious problem, since it cannot be called simply a disease. Acute or chronic inflammation of the appendix can happen to anyone, regardless of the person’s age and gender. Appendicitis requires urgent surgical intervention. If this problem is not addressed in time, inflammation can have significant consequences as regards the walls of the abdominal cavity.
In case of advanced appendicitis, a disease such as peritonitis may occur. This consequence is more than serious, so it is better not to delay treatment and consult a doctor in time.
Causes of appendicitis:
- blockage of the appendix lumen with feces, tumors or any other foreign bodies;
- the development of various infections that provoke diseases such as tuberculosis, typhoid fever and others;
- inflammation of blood vessels that affect nearby tissues.
Leukocytes in appendicitis
It has long been established that the levels of leukocytes in the blood change in the presence of appendicitis. Therefore, almost always, if the presence of this disease is suspected, a blood test for leukocytes is taken. As a rule, the analysis should show an increase in white blood cell counts.
The upper limit reaches 18, taking into account the fact that normally this number should not exceed 9. Such tests indicate that inflammation is present and surgery must be performed immediately. In this case, you should not hesitate, because inflammation can only increase, but by itself it will not go away.
Blood test for appendicitis: types, indicators and interpretation - Gastro Portal
If acute abdominal pain occurs, it is recommended to immediately consult a doctor. In the hospital, the person will be examined and an accurate diagnosis will be made. Then treatment and recovery go smoothly and quickly. For some diseases, making an accurate diagnosis can sometimes be difficult.
Everyone knows that the symptoms of many diseases are very similar, and it will take some time to clarify the diagnosis. But sometimes there is not enough time at all when you need to immediately establish a diagnosis and determine treatment tactics. Diseases that require immediate surgery include acute appendicitis.
How can you tell if a person has appendicitis? To make an accurate diagnosis, doctors rely on symptoms of the disease, examinations and laboratory test results. In addition to the visible signs of the disease, it is a blood test for appendicitis that helps establish an accurate and final diagnosis.
This method is considered reliable and quick for making a correct diagnosis of acute appendicitis. But, unfortunately, many people with abdominal pain do not consider it necessary to see a doctor, but are treated at home and take painkillers without prescribing a specialist.
//www.youtube.com/watch?v=z3Tne5y7N3c
Taking such drugs smoothes out the clinical picture of the disease, and doctors cannot accurately determine the disease, and this leads to disastrous consequences.
All ways to determine the disease
Appendicitis is a disease in which inflammation occurs in the appendix of the cecum. This diagnosis is more often given to women, mostly young. There are 0.2 - 0.4% of deaths per year due to untimely visits, when complications of appendicitis already appear.
Purulent peritonitis is by far the most common complication, when an inflamed appendix with all the pus inside breaks into the free abdominal cavity. To prevent these complications, you need to quickly collect anamnesis and take a blood test to determine the number of white blood cells. First of all, you need to clarify what complaints the patient has.
If appendicitis is suspected, the following complaints are typical:
- Pain in the right side;
- Nausea;
- There may be constipation or diarrhea;
- Weakness, malaise;
- Fever, chills;
- Coated tongue.
In addition to determining symptoms, the patient is examined, the abdomen is palpated and some tests are performed. When palpating the abdomen, the most important sign of appendicitis is the Shchetkin-Blumberg symptom.
It is checked as follows: first, press the hand on the sore spot and sharply remove it; if the pain intensifies, then this symptom can be considered positive.
In addition, the disease is determined by other symptoms (Razdolsky, Rovzing, Voskresensky, Sitkovsky), and a detailed blood test is required.
In case of appendicitis, a general blood test is a very significant diagnostic method, since its results can be used to draw a conclusion about the condition of the appendix - whether there is inflammation or not. In adults, it is easier to determine the diagnosis than in children, because the latter cannot show the exact location of pain due to appendicitis.
Laboratory research
Many people remember very well how they took a blood test from a finger, and are more afraid of it than others who take it from a vein. Is it possible to establish a diagnosis of acute appendicitis without a blood test? No. Only from a blood test can we draw a conclusion and say for sure that this is acute appendicitis.
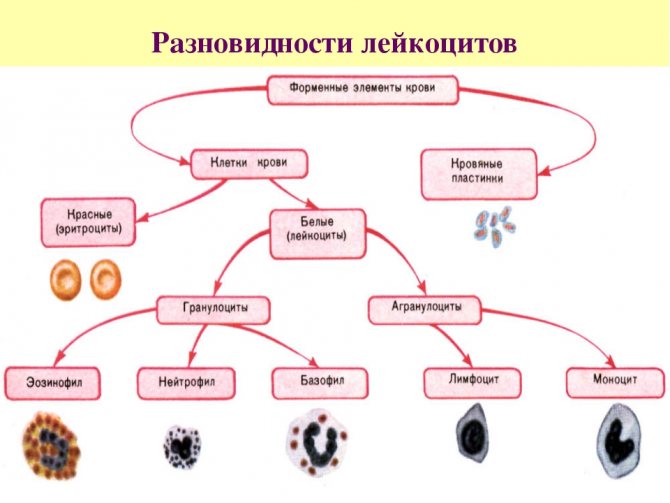
This study determines the number, volume of red blood cells, white blood cells, their percentage, platelet count and erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR). In case of appendicitis, attention is mainly paid to blood leukocytes. Leukocytes are blood elements that protect the body from pathogenic bacteria, viruses and microbes. Their norm is 4.0 – 10.0x109/l.
With appendicitis, these indicators can increase to 15.0x109/l and higher. Leukocytes are divided into 5 types:
- Neutrophils.
- Eosinophils.
- Basophils.
- Lymphocytes.
- Monocytes.
The white blood cell count can sometimes increase or decrease, depending on the underlying disease.
An increase in leukocytes is observed in infectious diseases, inflammatory processes in any organ, cancer, operations, bleeding, etc.
A decrease in white blood cells can be found with influenza, rubella, typhoid fever, measles, malaria and AIDS. Since appendicitis is an inflammatory disease, white blood cells are elevated in blood tests.
Leukocytosis with a shift to the left
In case of appendicitis, the patient undergoes a detailed blood test, during which the leukocyte formula is determined. A leukogram is the percentage of all leukocytes. Only neutrophils determine the state of inflammation in the diseased organ.
In medicine, the term “leukocyte shift to the left” is used when a large number of band neutrophils are found in the blood. This indicates that an inflammatory process is developing in the body. There are 3 types of neutrophils: young, band and segmented.
It is during acute appendicitis that band neutrophils increase, and this indicator is used to clarify the diagnosis of acute appendicitis. If segmented neutrophils increase in the blood, this is called a “shift of leukocytes to the right.”
A blood test helps determine the state of the inflammatory process in the appendix (appendix) in order to decide on surgical intervention.
The level of leukocytes in the blood is different for everyone
You should not think that everyone’s test results are the same, that is, if leukocytes are elevated, it means there is appendicitis. This is absolutely not true. In young people, the indicators may, on the contrary, be reduced, and in the elderly they may be completely absent. It is also worth considering the fact that after the operation the level of leukocytes does not immediately return to normal, but a certain time must pass. In this case, the doctor prescribes certain medications for recovery, as well as appropriate nutrition. This is explained by the fact that there is also an inflamed wound, which, despite all treatments, still becomes inflamed. Everything happens gradually, so leukocytes are restored only when the wound is completely healed and, accordingly, when the body’s condition is restored.
If a leukocyte level of more than 9 was detected during appendicitis, then at the time of discharge this figure should not exceed itself. The patient may be left in the hospital until complete recovery if leukocytosis continues and the levels do not decrease. In this case, additional treatment is prescribed, followed by a repeat blood test. The main thing to remember is that the presence of elevated white blood cells is the first sign of inflammation in the body, and this cannot simply be left alone.

Norm of leukocytes in the blood
During treatment of appendicitis and after surgery, it is necessary to accurately count white blood cells. In this case, testing is simply necessary - blood and urine. Normally, the amount should range from 8 to 10. Sometimes doctors do nothing when the indicators even reach 20, considering this to be the norm. But it is worth noting that such a doctor should no longer be trusted. Any leukocyte level in the blood greater than 18 should not be ignored. It’s better to get checked right away or get re-tested. If, even with other symptoms of appendicitis, the indicators are not elevated, then this is simply an individual characteristic of the body. Therefore, you can do an ultrasound of the abdominal cavity and undergo additional examination.
What parameters indicate appendicitis?
A comprehensive examination and analysis of the results will allow you to make a diagnosis with great accuracy. What do these studies provide, and what parameters will be of interest to the doctor?
If the indicator reaches 18 units or more, then there is a high probability of developing appendicitis. If the value is above 20.0, the doctor may suspect intestinal perforation and the onset of peritonitis. This may be the basis for urgent surgical intervention.
The greater the number of leukocytes in the blood, the more extensive and intense the inflammation. And more dangerous. However, it must be remembered that in pregnant women the number of leukocytes is always increased, so OAC will not be a faithful assistant here.
Also, this analysis will be ineffective in diagnosing the disease in older people, since their leukocyte levels, as a rule, do not rise. Or shows a slight increase.
The presence of inflammation is indicated by an increased erythrocyte sedimentation rate. However, this is not a specific indicator. And again, in pregnant women this parameter is always higher than normal due to physiological reasons.
In addition to the total number of leukocytes, it is necessary to establish which type of white blood cells predominates. The fact is that with appendicitis the content of neutrophilic leukocytes increases significantly.
C-reactive protein is another marker of the presence of an inflammatory process in the body. If this parameter is normal, then appendicitis is unlikely. However, an elevated level does not specifically indicate appendicitis, but only informs about the presence of some kind of inflammation.
HCG levels are checked in women. This will eliminate the possibility of an ectopic pregnancy and associated complications. In case of appendicitis, leukocytes will also appear in the urine, which will also suggest the presence of severe inflammation.
Timely and high-quality diagnostics will allow timely detection of the disease and initiation of treatment. Therefore, if a doctor prescribes any tests, there is no need to argue with him. It is better to go through them and find out for sure what is happening in the body. This will help avoid misdiagnosis. You should always remember that appendicitis is dangerous due to its complications and can lead to death if the inflamed appendage of the cecum is not removed in time.
Watch a video about how to treat gastritis, why it occurs, and what measures need to be taken.
Urine indicators for appendicitis
A urine test is taken to differentiate appendicitis, so its significance is also quite important. In this case, it is worth remembering that an increase or significant decrease in red blood cells and granular casts may be observed in the blood.
White blood cells increase when the inflamed appendix comes into contact with the bladder. In this case, clinical manifestations occur as with ordinary cystitis and sometimes it is quite difficult to determine the presence of appendicitis. Almost 48% of cases are noted by the fact that in acute appendicitis there may be no significant increase in leukocytes, which is also explained by the contact of internal organs with the appendix. This is a kind of hidden form that is very difficult to identify in time. Such people most often suffer from an acute form of appendicitis and already during a critical situation (severe pain) end up on the surgical table.
It is also worth noting that the number of leukocytes and erythrocytes can change in different forms of the disease. For example, with a retrocecal location of the appendix, the indicators may not increase significantly, and not everyone can immediately detect the problem. In addition, you should pay attention to the indicators of sialic acids. The higher their level, the more pronounced the inflammatory process in the body. This means urgent treatment, or rather surgical intervention, is necessary.

It is possible to determine appendicitis using a blood test, but additional research will be required. An analysis is prescribed if difficulties arise during diagnosis. The main indicator that indicates the development of the inflammatory process is an increased level of leukocytes (elements of the immune system), which detect, attack and eliminate viruses.
Acute appendicitis
Appendicitis is an acute inflammation of the inner lining of the appendix. It is the most common cause of acute surgical interventions and most often occurs between 10 and 30 years of age.
The pain usually starts in the center of the abdomen, then moves down to the lower right side. As a rule, it intensifies within 12-18 hours and becomes very pronounced.
Treatment for appendicitis involves immediate surgical removal of the appendix. Without surgery, it leads to serious complications.
Synonyms Russian
Inflammation of the appendix.
English synonyms
Appendicitis.
Symptoms
- Aching pain in the abdomen that begins in the navel area and then usually moves to the lower right side of the abdomen.
- Short-term nausea, vomiting.
- Loss of appetite, constipation.
- Abdominal pain that gets worse over several hours.
- Acute pain in the lower right part of the abdomen, which occurs when pressure suddenly decreases during palpation.
- Abdominal pain, aggravated by coughing, walking, or sudden movements.
- Pain in the lower right abdomen when palpated.
- Increase in body temperature to 37.7-38.3 °C.
- In children under 3 years of age, behavior changes and refusal to eat, as well as diarrhea and vomiting.
- In elderly patients, symptoms may not be expressed.
The difficulty lies in the fact that typical symptoms are characteristic of only 50% of patients. Sometimes abdominal pain may be absent, not localized to the right side, etc. Atypical symptoms are usually observed in older people and pregnant women.
General information about the disease
Appendicitis is an acute inflammation of the inner lining of the appendix - the vermiform appendix of the cecum (the cecum is the initial section of the large intestine in the lower right part of the abdomen; the appendix is a small appendix of the cecum, the function of which in the body has not yet been precisely established). It is the most common cause of acute surgical interventions and most often occurs between 10 and 30 years of age.
Inflammation of the appendix is caused by its blockage, which may be associated with increased pressure in the intestinal lumen. This may happen due to:
- lymphoid hyperplasia - an increase in lymphoid tissue located fragmentarily along the intestinal wall;
- fecal stones (fragments of hardened feces);
- parasites;
- foreign bodies, tumors.
The blockage leads to expansion of the process and infection. As a result, the outflow of venous blood from the appendix is disrupted, which causes oxygen starvation of its tissues.
Also, in some cases, appendicitis is a consequence of inflammatory or infectious bowel diseases.
The following types of appendicitis are distinguished.
- Catarrhal (simple). It occurs most easily and is characterized by minimal inflammation of the appendix. In this case, suppuration does not occur.
- Phlegmonous. The appendix ulcerates, becomes inflamed and suppurates.
- Gangrenous. It is a consequence of thrombosis of the vessels feeding the appendix, resulting in tissue necrosis, which leads to peritonitis - inflammation of the peritoneum (the membrane covering all organs of the abdominal cavity). This type of appendicitis is extremely dangerous.
- Perforated. When it occurs, suppuration of the appendix occurs, followed by melting of the tissues, a hole is formed in the appendix and its contents enter the abdominal cavity. This causes inflammation of the peritoneum, which is accompanied by systemic inflammation of the entire body. Accompanied by severe pain.
The appendix may be located in an atypical location: behind the cecum, in the pelvis, close to the liver.
In this case, the symptoms will differ significantly from the classic ones and resemble the signs of other diseases. Making a diagnosis with an atypical location of the appendix can be difficult.
In addition, the position of the appendix changes during pregnancy, which can also complicate diagnosis.
Appendicitis can lead to the following complications.
- Appendicular infiltrate is a formation consisting of the cecum, appendix, loops of the large intestine and omentum. It is formed at the location of the appendix on the 3-5th day from the onset of acute appendicitis and usually resolves on its own within a month. In some cases, it may suppurate with the formation of a periappendiceal abscess.
- Peritonitis is an inflammation of the peritoneum, the membrane that covers all organs of the abdominal cavity from the outside.
- Periappendicular abscess is a purulent inflammation of tissues, their melting and the formation of a purulent cavity. The appearance of an abscess requires its surgical removal.
Who is at risk?
- People aged 10-30 years.
- Suffering from inflammatory bowel disease.
- Suffering from parasitic intestinal diseases.
- Pregnant women.
Diagnostics
If classic symptoms are present, the diagnosis of appendicitis is usually not in doubt. In case of atypical or erased symptoms, additional research is required to diagnose it.
Laboratory research
- Complete blood count (without leukocyte formula and ESR). In 80-85% of patients with appendicitis, the level of white blood cells increases. At the same time, their normal number does not exclude the presence of appendicitis. Since during pregnancy there is a physiological increase in the level of leukocytes, a general blood test in this case does not help in diagnosing the disease.
- Leukocyte formula. Determines the ratio of different types of leukocytes as a percentage. With appendicitis, a significant predominance of neutrophilic leukocytes can be observed.
- C-reactive protein. It is a protein produced in the liver that quickly responds to active inflammation. A normal CRP level practically excludes the diagnosis of appendicitis, but an increase in its level is not specific for appendicitis. The test is especially reliable in combination with determining the level of leukocytes.
- General urine analysis. This is done to rule out urinary tract infections and kidney stones.
- Determination of hCG level. The study is prescribed to women to exclude ectopic pregnancy.
To exclude diseases of the liver and pancreas, the following tests are performed:
Other research methods
- Ultrasound (US) or computed tomography (CT) of the abdominal cavity. They allow you to evaluate the condition of the appendix and confirm appendicitis or detect other causes of abdominal pain.
- Laparoscopy. A method in which the examination of internal organs is performed through small holes in the abdominal wall using special equipment. In some cases, especially in women with mild pain in the lower abdomen, only laparoscopy can make an accurate diagnosis.
Treatment
Treatment for appendicitis involves immediate removal of the inflamed appendix. Currently, the mortality rate for appendicitis does not exceed 1%. If treatment is delayed, the risk of death increases.
In most cases, surgery can be performed in a low-traumatic manner through a small incision in the right lower abdomen. Antibiotics are recommended before surgery. In case of purulent complications, the scope of the operation can be expanded.
After appendix removal, the following safety precautions should be followed for several weeks to speed up healing:
- avoid physical activity, support your stomach (with your hand) when coughing and laughing so that the stitches do not come apart;
- activity should be increased gradually.
Prevention
There are currently no preventive measures for appendicitis.
Recommended tests
Literature
- Dan L. Longo, Dennis L. Kasper, J. Larry Jameson, Anthony S. Fauci, Harrison's principles of internal medicine (18th ed.). New York: McGraw-Hill Medical Publishing Division, 2011.
Source: //helix.ru/kb/item/904
Laboratory analysis – for what?
Symptoms of inflammation of the appendix:
- pain in the right hypochondrium;
- temperature increase;
- attacks of nausea.
Sometimes the symptoms are vague, which is why inflammation of appendicitis is mistaken for other pathologies of the abdominal cavity or diseases of the genitourinary system. A blood test for appendicitis in adults and children is a method that will allow you to make a correct diagnosis in time for latent symptoms or atypical forms of the disease.

A blood test for appendicitis will help make an accurate diagnosis if the symptoms are vague.
In older people, it is more difficult to detect inflammation of appendicitis using a blood test, since their leukocyte levels are slightly elevated. Your doctor will tell you in detail how to determine appendicitis using a blood test.
Symptoms of appendicitis
The sooner the disease can be identified, the better for the patient. Inflammation of the appendix of the cecum has a number of characteristic signs that will help you navigate and seek medical help in time. The symptoms of this disease are as follows:
- nausea, vomiting;
- abdominal pain that intensifies over several hours;
- weakness;
- soreness of the lower abdomen on the right side, discomfort increases with palpation;
- loose stools or constipation;
- abdominal pain begins in the middle and then moves to the right iliac region;
- loss of appetite;
- pain intensifies with any activity (walking, coughing, sharp turns);
- the most comfortable position is lying on your right side with your knees bent;
- high temperature, up to 38 °C and above;
- possible increased heart rate;
- in young children, their behavior changes sharply, they become capricious, refuse to eat, and they may also develop diarrhea and vomiting;
- In older people, appendicitis does not manifest itself so clearly, the pain is often moderate, and there may be no fever.
It is not necessary that the patient will have all the symptoms; an experienced doctor will only need a few of them to correctly diagnose and refer the patient for surgery. If appendicitis manifests itself clearly, then additional studies to clarify the diagnosis will not appear.
Signs of inflammation in a blood test
After a blood test, the doctor pays attention to the content of formed elements in the composition. The number of leukocytes in appendicitis is 18 units.
Leukocytes in appendicitis in a child and an adult, exceeding the normal level by 2 or more times, indicate the stage of tissue breakdown, which is dangerous due to general blood infection. The remains of dead leukocytes in the form of purulent masses become a source of intoxication.
In addition to the level of formed elements, the specialist also pays attention to the percentage of leukocytes. They are divided into 5 types:
Neutrophils are divided into band, young and segmented. The predominance of band leukocytes indicates the development of acute appendicitis.
With appendicitis in an adult, the level of not only leukocytes changes. The presence of appendicitis can be determined by markers such as:
- The level of red blood cells - blood cells that transport oxygen and carbon dioxide.
- CRP (C-reactive protein). The element is synthesized by the liver after the appearance of inflammation in the body. The purpose of the protein is to suppress latent infection.
- ESR (erythrocyte sedimentation rate). The indicator determines the intensity of the inflammatory process. The faster the red blood cells settle, the more widespread the inflammation. If this indicator increases along with an increase in the proportion of leukocytes in the blood, then this indicates an aggravated inflammatory process.
Blood test for appendicitis: interpretation, indicators in adults and children
With appendicitis, discomfort is localized in the lower right part of the abdominal cavity. But pain in the right side during physical activity is not the main sign of the disease. Most often this is a consequence of muscle spasm or neuralgia.
If painful sensations are accompanied by a thickening of the abdomen, which is located below and to the right of the navel, an increase in body temperature, and vomiting, this is a sure sign of a serious intestinal disease. Doctors consider a chemical study of blood composition to be the main indicator of the general condition of the body.
A blood test for appendicitis is the main indicator of the presence or absence of this disease.
Clinical picture of biochemical studies in inflammation of internal organs
The chemical composition of human blood is a constant value. They donate blood for analysis in order to find out the quantitative relationships of its components. If the levels of white and red blood cells are increased, the composition of the plasma has changed, then you need to start treatment without delay.
A mandatory laboratory test for the presence of leukocytes in the blood is prescribed if inflammation of the appendix is suspected. During acute inflammatory processes, the composition of human blood changes due to the ingress of bacterial metabolic products into it. Leukocytes with appendicitis increase in size and number.
They are the main tool of immunity, but at the first stage of inflammation this increase is imperceptible. The state of red blood cells also changes. Their number is not subject to strong fluctuations, but inflammation shortens the lifespan of the red blood cell.
Urine also changes its composition, which correlates with the type of disease. The amount of dead leukocytes and red blood cells in it increases, the alkaline reaction changes, and the most severe cases are accompanied by the appearance of protein. To determine appendicitis using a blood test, it must be taken early in the morning on an empty stomach.
Differences between blood tests in adults and children
Blood tests for children are highly dependent on the individual condition of each child. The metabolic rate of a child's body is much higher than that of an adult. The leukocyte is actively involved in metabolism. Their amount in the blood of children significantly exceeds the proportions for older people.
The correct indicators for a mature person in relative values of leukocytes are from 4 to 8 units. In children they can reach 17. During pregnancy – 12-18.
If leukocytes exceed 20, then there is a suspicion of peritonitis - a severe form of appendicitis that requires urgent surgical intervention. The decision about the severity of the disease should be made by specialized specialists - a pediatrician and a gastroenterologist.
Since in acute peritonitis the patient’s death is likely due to blood poisoning, it is important not to miss the moment.
Other signs of appendicitis:
- Physiological signs. An increase in temperature, painful lumps in the lower abdomen, vomiting, and loose stools are the first external signs. If the disease has progressed, bloody discharge may appear in the stool and urine. In particularly difficult cases, a fistula develops with access to the skin.
- Changes in the composition of urine. The vital activity of pathogenic microorganisms is reflected in all body secretions. The kidneys separate metabolic products, signaling the onset of the disease by the changed chemical composition of the filtrate. If proteins appear in the general urine analysis, the bacterial background is increased, and its color takes on an unhealthy, cloudy appearance, this is a sure sign of internal inflammation.
- ESR. An ESR (erythrocyte sedimentation rate) analysis is designed to show what stage the disease is at. The activity of red blood cells varies depending on the state of the body. The inflammatory process provokes red blood cells to increase the consumption of their resources. ESR shows how long these cells live. Expressed in the height of the plasma layer and measured in millimeters per unit of time. In a healthy man it is 1-10 millimeters per hour, in a woman 3-15, in a child 12-17, in a newborn 0-2.
- However, only the results of a comprehensive examination, taking into account the total number of leukocytes and erythrocytes, will help to draw a conclusion about the nature of the disease.
The initial period of appendicitis
Children are more susceptible to changes in blood composition. This makes it difficult to diagnose appendicitis in a timely manner. A child's blood contains a much larger number of leukocytes. Because of this, in children the disease at an early stage is easy to miss. It is accompanied by a relatively unnoticeable change in laboratory test results or is not diagnosed at all.
Pain syndrome is attributed to physical activity, general malaise to a cold, digestive problems to stress, and so on. If these signs are present, it is necessary to submit samples of discharge for testing for general composition. Sampling should only be done in the absence of stimuli. A comprehensive blood and urine test is designed to help identify the disease at this stage.
Beginning of the acute phase of inflammation
The cecum performs the function of storing enzymes necessary for digestion and immune function. It is isolated from the intestines, and this causes suppuration when the immune system is weakened.
Diagnosis based on a high white blood cell count clearly indicates inflammation. This condition is called leukocytosis. It is necessary to determine whether an acute inflammatory process has begun in cases of suspected appendicitis as quickly as possible! This disease is dangerous with complications.
Prompt treatment with modern antibiotics and close clinical supervision can completely stop the disease at this stage.
Strict adherence to the recommendations guarantees complete recovery, and failure to comply will lead the disease to the chronic stage.
Pathological stage
The transition to this stage will show that the permissible level of leukocytes is many times exceeded (by 2 or more times). The beginning of tissue breakdown threatens general blood poisoning. The accumulating liquid containing the remains of dead leukocytes in the form of suppuration becomes a source of intoxication.
It can cause severe anaphylactic shock and coma. The proximity of the appendix to the lymph nodes poses a particular danger. Only urgent surgery will save a patient with this form of the disease. Drug treatment cannot help in this case.
People often die from medical errors when treating peritonitis.
Prevention of appendicitis
At a time when human internal organs remained poorly understood, doctors were not able to localize inflammation. Dissection of corpses was prohibited by medieval religion.
Diseases of the cecum were studied by ancient scientists. Hippocrates wrote about severe intestinal suppuration, but did not know its causes. Cases of cure were rare. The cause of appendicitis was discovered only in the 16th century. The treatment methods offered were wild by modern standards. For example, doctors advised swallowing small lead balls to clear the cecal valve.
Until the beginning of the 20th century, the causative agents of appendicitis were considered to be foreign bodies that had no way out of it, since there is no through passage through the cecum. Popular superstitions still contain advice on prohibiting the consumption of small, difficult-to-digest foods, for example, sunflower cake.
In the 20th century, medicine achieved great development and refuted such misconceptions.
Intestinal diseases are affected by the following reasons:
- Poor nutrition;
- Bad habits such as smoking and alcohol;
- Harmful working conditions associated with toxins;
- Lack of food hygiene.
Once these factors are eliminated, the risk of appendicitis will decrease.
Source: //GastroTract.ru/appenditsit/analiz-krovi-pri-appenditsite.html
Table of blood marker norms depending on age
| Age | Red blood cells | Leukocytes | ESR | S-RB | Neutrophils |
| 6-12 months | 3,4-5,2 | 7-32 | 3-10 mm/h | 0-5 mg/l | 2-7 |
| 2-5 years | 3,7-5 | 5-15,5 | 5-11 | 0-5 | 1-6 |
| 6-14 years | 3,5-5,5 | 4,5-13,5 | 4-12 | 0-5 | 1-5 |
| 15-17 years old | 3-5.5 (girls), 3.9-5.6 (boys) | 4,5-11 | 2-15 (girls), 1-10 (boys) | 0-5 | 1-6 (girls), 1-7 (boys) |
| 18-30 years old | 3-5.5 (women), 4.2-5.6 (men) | 4-10.5 (women), 4.2-9 (men) | 8-15 (women), 2-10 (men) | 0-5 | 1-6 (women), 1-7 (men) |
| 30-60 years | 3.5-5.1 (w), 4-5.6 (m) | 4-10.5 (w), 4.2-9 (m) | 8-20 (w), 2-10 (m) | 0-5 | 1-6 (w), 1-7 (m) |
| 60 years and older | 3.4-5.2 (w), 3.1-5.7 (m) | 3.7-9 (w), 3.9-8.5 (m) | 8-20 (w), 2-15 (m) | 0-5 | 1-6 (w), 1-7 (m) |
If it was found that the number of red blood cells has reached a minimum level, while the content of CRP, leukocytes and neutrophils is increased, as is ESR, then this indicates progressive appendicitis.
Some symptoms of inflammation of the appendix resemble the clinical picture of an ectopic pregnancy, so women are sometimes prescribed a blood test for hCG (human chorionic gonadotropin, a hormone secreted by the placenta during pregnancy).
If the blood test for hCG for appendicitis in adult women does not exceed 0-5.3 mIU/ml, then pregnancy is excluded.
Blood test indicators for appendicitis in children depend on the individual condition of the body. The metabolic rate of a child is much higher than that of an adult. Since leukocytes actively participate in metabolic processes, their content in the blood significantly exceeds the number of these formed elements in the body of an adult.
A blood test for appendicitis in children is not the only diagnostic measure. To confirm inflammation, a urine test is additionally prescribed. This eliminates inflammation of the urinary tract or excrement in the kidneys.
In addition to blood and urine tests, to detect appendicitis the following are prescribed:
- Ultrasound of the appendix.
- Computer or magnetic resonance imaging.
- Laparoscopy.
The laparoscopic method is the most informative. Allows you to accurately determine the type of inflammation in the abdominal cavity. If necessary, proceeds to surgery to remove appendicitis.
What does a blood test show for appendicitis?
Appendicitis is an inflammation of the appendix of the cecum.
Untimely removal of the appendage leads to the development of complications: intestinal perforation and the onset of peritonitis. The most dangerous consequence of the pathology is death.
In the absence of pronounced symptomatic signs in elderly people and children, laboratory tests of blood, urine and instrumental examination can determine possible inflammation of the appendix.
Causes
The occurrence of the disease has a different nature of origin:
- mechanical: penetration of parasites, pathogenic bacteria;
- fecal stones;
- an increase in lymphatic follicles in the area of the cecal appendage;
- entry of a foreign object;
- chronic diseases of the pelvic organs;
- inflammation of blood vessels;
- infectious diseases: typhoid fever, tuberculosis, amoebiasis;
- pathologies of the endocrine and immune systems.
The main cause of inflammation is blockage of the appendix, which leads to the destruction of the internal microflora of the cecal appendage, compression of blood vessels and lymph nodes. In children, exacerbation of appendicitis occurs due to reduced immunity in winter and spring, and foreign objects entering the body.
Symptoms of appendicitis
The first symptomatic signs of an inflamed appendix are:
- nausea;
- vomiting;
- prolonged severe pain in the right side of the abdomen;
- increased spasms during palpation of the area of the vermiform appendage of the cecum, physical exercise, changes in body position;
- stool irregularity;
- decreased appetite;
- weakness;
- increased body temperature;
- cardiopalmus;
- tearfulness in young children.
With inflammation of the appendix of the cecum, only some symptomatic signs may be observed for 6-8 hours. In older people, in accordance with age characteristics, appendicitis does not have pronounced manifestations. The main symptoms of the pathology in young children are diarrhea, vomiting, tearfulness, and lack of appetite.
Diagnostic methods
For inflammation of the appendix, the main diagnostic methods are prescribed:
- primary examination - palpation;
- lab tests:
- blood;
- urine;
- instrumental research:
- computer, magnetic resonance imaging;
- ultrasound examination of the abdominal organs;
- medical thermography;
- laparoscopy;
- radiography.
Diagnostics allows you to detect the disease in a timely manner, prescribe effective treatment, and eliminate the pathology.
Initial examination
The first diagnostic method is an initial examination with palpation of the abdominal area. If the blood supply to the appendix is disrupted, strong, sharp pain is observed when pressing on the iliac region on the right side.
In some clinical cases, the doctor may feel the inflamed appendage. The basic rule of palpation is to sharply release the hands after pressing on the abdomen.
A description of associated symptomatic signs is an important part of the purpose of additional studies.
Lab tests
Submitting biological material for laboratory testing is important to determine further treatment for appendicitis.
The exception is clinical cases when there is a serious complication that requires immediate surgical intervention to avoid the death of the patient.
Based on the results of laboratory tests of blood and urine, it is possible to determine the cause of inflammation and eliminate possible problems with urination.
Biological material is collected to carry out the necessary tests:
- general blood and urine analysis if appendicitis is suspected;
- measuring the level of red blood cells, leukocytes;
- establishing the reactive protein indicator;
- determination of hCG level.
Establishing the number of leukocytes and erythrocytes contained in the blood allows us to identify the internal inflammatory process. Urine examination makes it possible to exclude diseases of the urinary system and determine the presence of pathogenic bacteria, infections, and viruses.
An increase in the number of leukocytes and red blood cells indicates the effect of an inflamed appendix on the urinary system. An indirect sign of damage to the vermiform appendage of the cecum is intense, dark color of urine.
Required parameters
The main indicator in laboratory analysis is the level of leukocytes in the blood. It indicates the presence of an internal inflammatory process and the nature of the pathology. Leukocytes in appendicitis have an indicator of 11-15 units in children, more than 18 in adults.
High indices are grounds for emergency hospitalization and surgery. The predominance of the neutrophilic variety of leukocytes indicates that the inflammation becomes acute.
Each person’s blood circulation is individual, therefore, to avoid inaccuracies, biological material is collected several times throughout the day.
Tests to determine inflammation of appendicitis involve determining the erythrocyte sedimentation rate. An increase in the indicator indicates an exacerbation of the pathology. Changes in hormonal balance during pregnancy in women are the cause of an unstable erythrocyte sedimentation rate index, as well as a possible slight increase in the level of white blood cells.
Signs of the inflammatory process are directly related to the level of reactive protein.
Therefore, this indicator is not an infallible method for determining appendicitis, as it indicates a change in the functioning of any body system.
For women, a blood test is required to determine the level of human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) to distinguish appendicitis from signs of ectopic pregnancy. The accuracy of the result is ensured by the regularity and dynamism of the procedure.
Established standards
A blood test to determine appendicitis involves establishing the level of leukocytes in accordance with standardized indicators for age categories:
- infants and children under 3 years old – 6-17 units;
- 3-6 years – 5-12;
- 6-10 years – 6-11;
- more than 11 years – 4-9.
Each person’s body is individual, therefore, when obtaining the results of a blood test for appendicitis, it is necessary to take into account the peculiarities of physiology.
A normal phenomenon is increased levels of leukocytes in pregnant women and the elderly, and a decrease in the index in male adolescents.
After appendectomy surgery, your white blood cell levels will stabilize after a certain amount of time.
There are standards for erythrocyte sedimentation rate in accordance with gender characteristics: for women the rate should be 2-15 mm/h, for men – 8-15 mm/h, for children and adolescents – 3-12 mm/h. The standard C-reactive protein index is less than 10 mg/l.
Instrumental examination
Instrumental examination methods are auxiliary methods for determining inflammation of the appendage of the cecum, necessary for an accurate diagnosis during pregnancy and medical contraindications to surgical intervention.
Magnetic resonance imaging and ultrasound examination of the abdominal cavity allows you to visually examine areas of the cecum. Availability and absence of contraindications make it possible to conduct research on newborns and pregnant women.
Measuring local temperature (medical thermography) is aimed at identifying the location of inflammation, where a significant excess of indicators is observed.
The laparoscopic method allows you to determine the nature of appendicitis, as well as perform an appendectomy - emergency removal of the appendix.
Treatment methods for the disease depend on the form of the disease. Blood and urine tests for appendicitis can reveal the nature of the inflammatory process.
Instrumental examination determines the influence of pathology on the functioning of the abdominal and pelvic organs. By submitting biological material for suspected appendicitis, you can establish the level of leukocytes and erythrocytes, indicating the degree of inflammation.
Elimination of the affected process, as well as removal of the adenoids for adenoiditis, is the main method of treating the disease.
The information on our website is provided by qualified doctors and is for informational purposes only. Don't self-medicate! Be sure to consult a specialist!
Rumyantsev V. G. Experience 34 years.
Gastroenterologist, professor, doctor of medical sciences. Prescribes diagnostics and carries out treatment. Expert of the group for the study of inflammatory diseases. Author of more than 300 scientific papers.
doctor
Source: //gastrot.ru/kishechnik/analiz-krovi-pri-appenditsite
Leukocyte formula shift
When assessing blood test results, the doctor examines not only the number of formed elements, but also estimates the proportion of each type of cell. The percentage of leukocytes is called the leukocyte formula, or leukogram.
A microscope is used to count the number of white blood cells. With its help, 100-200 blood cells are counted and their numbers are arranged in a special table. Then the percentage is calculated for each type. This is a leukogram. Under the influence of certain factors, it changes, moving left or right.
A shift in the leukocyte formula to the left is changes associated with an increase in the number of immature (young) neutrophils. This clinical picture indicates a severe degree of intoxication, as well as infectious processes.
A shift of the leukogram to the right occurs with an increase in the number of mature neutrophils, in other words, due to blood aging. Such a change indicates chronic pathologies of internal organs.
No surgery is performed until the results of the blood test are received. After receiving the necessary information, the doctor assesses the patient’s condition and, if the diagnosis is confirmed, prescribes surgery.