Various tests are an excellent option to find out something about a person’s health. After all, if they read their results correctly, doctors may well be able to recognize the disease. This skill is especially important in situations where they are talking about hidden pathologies such as appendicitis. In this case, a blood test for appendicitis will be especially informative. Moreover, there will be no difference whether someone has appendicitis - an adult or a child.
When is it prescribed?
Some symptoms are considered typical for inflammation of the appendix. Half of the patients who go to the doctor with acute abdominal pain suspect appendicitis and find symptoms characteristic of this disease. The rest talk about other symptoms, which may well be manifestations of other diseases. It happens, and vice versa - with manifestations of seemingly typical appendicitis, but the final diagnosis reflects the problem of another organ.
Important! Symptoms of an inflamed appendix depend on its location.
The disease occurs atypically in the following categories of patients:
- aged people;
- patients with reduced immunity;
- pregnant and lactating women;
- children.
It is recommended to do an ultrasound of the appendix in the following cases:
- With atypical localization of the appendix. This leads to a change in symptoms and without an ultrasound examination it becomes problematic to make a correct diagnosis.
- If the disease proceeds non-standardly.
- If appendicitis is complicated and requires immediate surgical intervention. In this case, ultrasound is used as the most accurate and fastest way to find out all the necessary information.
- If the doctor suspects inflammation of the appendix, but the symptoms are mild, ultrasound can help quickly make a diagnosis.
- If a blood test shows a shift in the formula with an increase in the number of leukocytes.
- If it is necessary to exclude that the appendix of the cecum is inflamed against the background of implicit, vague symptoms of the disease.
Blood test for appendicitis: exceptions to the rules
It is worth considering that since people are individual, their test results may be different. For example, it is rare, but it also happens that a person has very severe inflammation, and the tests are quite good.
In this case, one should look at the formal severity of the process. So, for example, if the number of leukocytes is not so much higher than normal, but a person cannot get out of bed due to pain, he should be hospitalized as quickly as possible.
It is also worth understanding that after surgery to remove appendicitis, leukocytes do not immediately return to normal. The immune system takes some time to recover. Therefore, the number of leukocytes may well be slightly elevated after surgery for a certain period.
What will the study show?
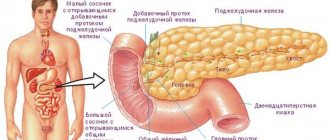
Initially, the specialist searches for the appendix, after which it is checked for the presence of an inflammatory process. During such an audit, the goal is to determine:
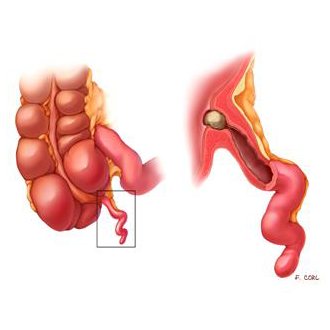
- size of the appendix and its location;
- availability of content, its nature and volume;
- thickness of the walls of the process;
- location of the appendix and the condition of adjacent tissues;
- condition of nearby organs.
Ultrasound examination of the appendix in adults and children includes several stages:
- examination of the upper rectum;
- search for iliac vessels;
- examination of the iliacus muscle, as well as the space behind the ileum;
- examination of the area located behind the cecum;
- examination of the small pelvis, rectouterine cavity and right ovary.
Diagnosis in women
The physiology of the female body does not always make it possible to understand the real cause of abdominal pain.
Important! Symptoms of appendicitis can be mistaken for signs of an ectopic pregnancy or inflammation in the pelvic organs.
Appendicitis occurs more often in the fair sex, and this is due to physiological differences between male and female bodies. The reason is that the female genital organs are almost adjacent to the organs of the gastrointestinal tract.
Reference! During regular female bleeding, blood circulation in the pelvic organs increases and the uterus enlarges. It can put pressure on nearby organs, including the appendix.
Typically, an ultrasound of the appendix is performed through the abdominal wall, but it happens that women are examined using a transvaginal probe. In this way, the examination better shows the appendix.
In pregnant women
During pregnancy, the appendix undergoes mandatory examination. There is an opinion that gestation can be an impetus for the development of appendicitis.
Reference! The growing uterus displaces nearby organs, and the appendix becomes pressed against the intestines.
If the appendix is crushed, its blood circulation is impaired and the risk of inflammation increases. Statistics say that most often an inflamed appendix is removed during pregnancy; the risk of inflammation is especially high in the later stages of gestation.
Study in children
Diagnosis of appendicitis in children is complicated by the fact that young patients cannot always accurately describe the nature of the pain and its location. They simply cry and often assume the “fetal position,” often preventing normal palpation of the painful area.
There are many cases of inflammation of the appendix in schoolchildren.
Reference! Due to physiological characteristics, inflammatory processes in the appendix are accompanied by complex inflammation of adjacent organs.
This can lead to a dangerous complication - appendiceal peritonitis, that is, inflammation of the abdominal cavity. The cause of the pathological process can be:
- previous infectious or viral disease;
- the presence of stool or foreign body in the appendix;
- heredity.
The disease is more severe in children than in adults. The impetus for the development of the inflammatory process in children can be a common cold, diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, measles or sore throat. If you do not start the necessary treatment in time and start the process, then inflammation develops quickly and delay is unacceptable.
What will be seen during the study? An ultrasound will make it possible to assess the condition of the appendix, help determine the cause of inflammation and show the functioning of other organs for further comprehensive treatment.

Is it possible to remove appendicitis in advance?
The appendix is not removed without indications. There are indications for appendectomy: acute inflammation of the appendix, complications: loose appendiceal infiltrate, peritonitis, abscess of the periappendiceal region, neoplasms of the appendix.
The vermiform appendix cannot be removed without indications. This organ is considered immune. There have been studies that prove that after removal of the appendix, a person begins to get sick more often.
Appendicitis should be treated promptly. To do this, the patient must contact the clinic 6-12 hours after the onset of the disease. Such timing is due to the rapid development of appendiceal infiltrate, abscess formation and peritonitis due to a breakthrough of the abscess.
Take care of yourself!
[Total: 1 Average: 5/5]
Preparation
For appendicitis, no special preparation is required from the patient. In addition, ultrasound is usually performed on an emergency basis. When a patient admitted to the hospital experiences an acute phase of appendicitis, the diagnosis can only be quickly clarified using ultrasound.
During a routine examination, the patient must adhere to several simple rules:
- do not overeat;
- do not eat foods that cause flatulence;
- Do not come to the procedure hungry.
Norms and interpretation of results
The condition of the appendix is assessed based on the results of an ultrasound examination.
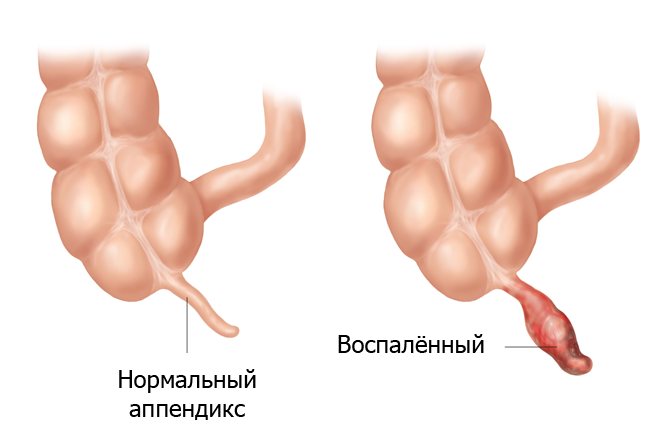
A normal appendix should have the following features:
- curved shape and tubular structure consisting of several layers of fabric;
- round section;
- blind ending;
- absence of contractions of the walls and contents;
- wall diameter – up to 6 mm, thickness – up to 3 mm.
An inflamed appendix manifests itself on ultrasound as follows:
- tubular structure ending blindly;
- cross section similar to the target;
- impossibility of compression;
- increased wall thickness and diameter;
- In the lumen of the appendix, it is possible to detect a fecal stone with a diameter of no more than 1 cm.
An ultrasound may reveal signs of a violation of the integrity of the appendix:
- abrupt and layered structure of uneven walls of the process;
- increasing the density and echogenicity of the omentum due to its inflammation;
- effusion in the peritoneum and in the area where the appendix is located;
- abscesses of intestinal loops.
It happens that it is not possible to identify the appendix during the examination and signs of inflammation are not visible - this means that we are talking about a negative result. Visualization of the appendix without signs of inflammation indicates a true negative result. If the appendix is present, but the symptoms of inflammation are blurred or few are detected, then the result of the examination is considered to be doubtful.
If the doctor diagnoses “acute appendicitis,” the following examinations may be prescribed in addition to ultrasound to confirm it:
- clinical urine and blood tests;
- laparoscopy
- X-ray examination;
- CT scan.
Main signs of appendicitis
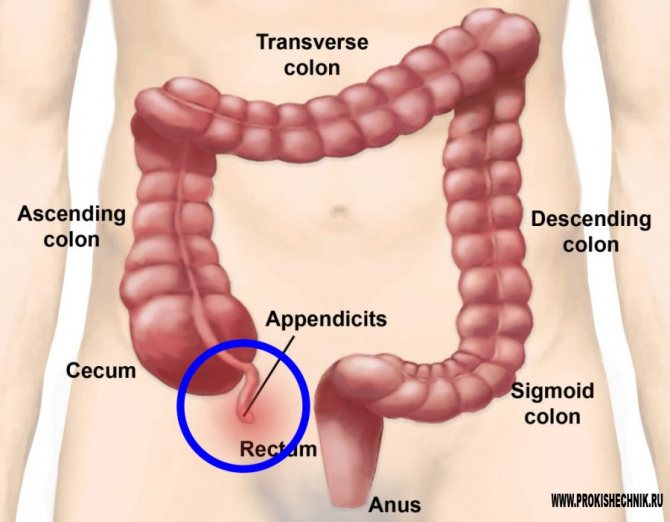
Main signs of appendicitis
If the disease develops typically, then the classic precursor to appendicitis, according to ProKishechnikRu, is pain near the navel, then a single loose stool, after which all sensations shift to the right, to the lower abdomen.
In acute form
In acute form
In acute cases, symptoms of appendicitis include:
- Increased pain when pressing on the abdomen;
- Body temperature 37-38o C, symptoms of intoxication, signs of inflammation: dry mouth, rapid pulse, pointed facial features;
- A characteristic symptom is the “shirt”, in which even touching the clothes above the stomach with your hand causes discomfort;
- The patient cannot lie on his left side;
- Lying on his back, the patient cannot raise his right leg straightened at the knee;
- Tension of the abdominal muscles does not allow you to feel the stomach;
- Trying to cough and strain causes increased pain.
In chronic form
In a chronic course, notes ProKishechnikRu, pain and a feeling of heaviness in the lower abdomen on the right regularly occur after physical activity or errors in diet. There is a tendency to constipation or loose stools. Body temperature is normal, or occasionally rises slightly to 37.0-37.2 o C in the evening. Blood and urine tests change only during exacerbation; there are no changes between attacks.
The chronic form can be a consequence of the acute form, or occur as an independent disease. With untimely diagnosis, improper treatment, and unmotivated prescription of antibiotics, inflammation becomes chronic with periodic exacerbations.
Video about appendicitis symptoms
The video lists important symptoms that should not be missed.
How do they do it?
Ultrasound examination of the appendix will be informative regardless of whether the intestine is empty or not. The patient does not need to fast before the procedure or use a cleansing enema, which is very important for intense pain.
During an ultrasound, the appendix is examined using a high-frequency probe that is pressed against the skin of the abdomen and moved to visualize the organs. First of all, they establish the location of the appendix, and then look for signs of inflammation in it. All manipulations may take several minutes, or maybe half an hour, depending on the doctor’s experience and the location of the process.
What can interfere?
Difficulties in detecting the appendix may occur:
- in pregnant women;
- in obese people whose body weight significantly exceeds the norm;
- in patients suffering from flatulence.
Advantages and disadvantages
Ultrasound examination is highly accurate: with its help, a doctor can determine the disease with a 90% probability.
The technique also has a number of advantages over x-ray examination:
- The patient does not experience radiation exposure.
- Diagnostics are available to both doctors and patients.
- The examination does not cause discomfort to the patient.
- There is a chance to detect all the causes of pain in the area being studied.
- High speed of obtaining information.
- Relatively low cost of the procedure.
An abdominal ultrasound shows the area that is the source of pain. This is an important nuance when studying an abnormally located process and detecting concomitant pathologies.
How does acute appendicitis manifest in adults?
In order to contact the clinic in a timely manner, you should know the symptoms of the disease. There are early and late signs of the disease. Early symptoms are important for the patient.
Only a doctor can make a correct diagnosis. Don't self-medicate!
How to determine appendicitis at home:
- Sudden onset of pain.
- First, pain occurs in the umbilical or epigastric region, after 2 hours it moves to the right iliac region.
- Nausea, single or double vomiting at the onset of the disease.
- Severe weight loss.
- Dryness in the mouth area.
Over time, chills occur, the temperature rises to 39ᵒC, the general condition worsens, and hallucinations are possible against the background of the temperature.