Classification and varieties
It is customary to distinguish several types of intestinal hernias. Classification depends on the location of the hernial sac:
- Inguinal. Develops in the area of the inguinal canal. It can form inside, go under the skin, or be diagnosed in both places at the same time.
- Umbilical. This type of education is typical for newborn babies. Caused by an underdeveloped umbilical ring. Also, a hernia can form in women during pregnancy and after childbirth.
- Femoral. Located in the upper part of the anterior thigh. Typical for older people.
- Linea alba. In most cases, it is represented by several small hernias located in close proximity to each other.
- Ventral (postoperative). Formed in an area of thinned scar tissue.
- Sliding. Formed as a result of partial overlap of the intestine with peritoneal tissue.
Patient management tactics depend on the type of hernia
Causes and symptoms
The formation of a hernia often occurs in thinned, stretched, dystrophic areas of the abdominal wall and diaphragm. The reasons are:
- pregnancy, childbirth;
- age-related changes;
- rapid weight gain or loss;
- hacking cough;
- carrying heavy loads;
- difficulty defecating and urinating;
- diseases of the stomach and intestinal tract, accompanied by gas formation, diarrhea or constipation;
- operations in the pelvis, perineum, abdomen;
- hereditary predisposition;
- metabolic disorders due to diseases, poor nutrition and associated dysfunction of the pelvic organs.
The formation of a hernial sac in the abdomen is asymptomatic.
A noticeable sign of a hernia is a severe pain attack during abdominal tension. Along with this, digestive and defecation disorders appear:
- increased belching;
- nausea and abdominal pain;
- occasional vomiting;
- constipation.
Reducible hernias on the abdomen can be returned to their place by massage movements in a clockwise direction. The irreducible ones are constantly in relief, as they are held in place by adhesions to the surrounding tissues.
Umbilical hernia
In adult women, prolapse occurs due to stretching of the umbilical ring under intense stress on the abdomen during:
- pregnancy – repeated, two- and multiple-fetal;
- difficult childbirth;
- accumulation of a large volume of fluid in the abdomen (ascites);
- strenuous training;
- working at the limits of physical capabilities.
Fetal hernia occurs in female newborns. A sac is formed from the umbilical cord (the future wall of the peritoneum), which may contain the small and large intestines, as well as part of the liver.
Physiological hernia decreases at the 10th week of fetal development. In the absence of such retraction, the pouch on the abdomen increases, which leads to improper placement of organs and other developmental defects.
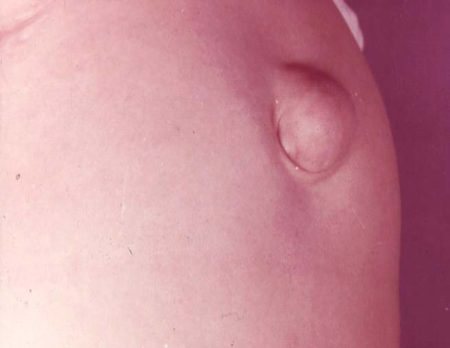
Umbilical hernia
Inguinal hernia in the lower abdomen
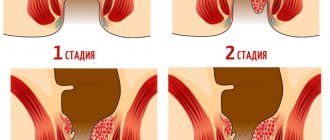
Protrusions occur in the area of the inguinal canals symmetrically on the left and right sides. There are direct hernias (through the outer canal ring), oblique (through the inner canal ring), and incomplete (within the ring). To the mentioned reasons is added a congenital anomaly of the inguinal canals.
Femoral hernia
The bag exits through the femoral canal and is visualized in the groin. Depending on the degree of extension beyond the abdomen, the formation can be complete or incomplete. Signs of its formation are not visible in the initial stage. Later, groin pain, nausea, stool retention, and pinching appear. One specific cause is hip dislocation.
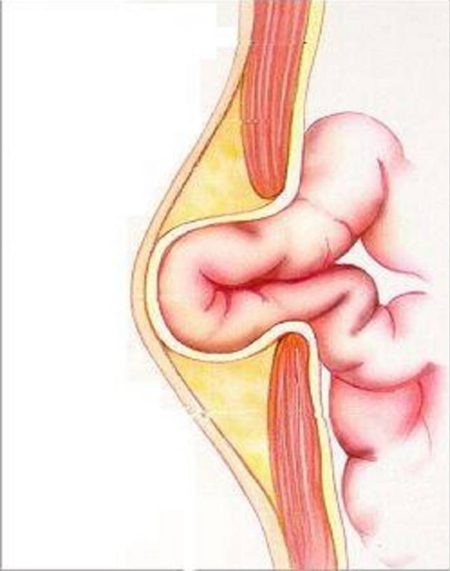
How does a hernia appear?
Hernia of the white line of the abdomen
They are found less frequently in women than in men. Protrusions on the abdomen can be:
- round;
- oval;
- single;
- multiple.
Along the vertical white line above, below or near the navel, the omentum first emerges, followed by a segment of the small intestine, and sometimes parts of the organ.
Belly after hernia removal
Ventral hernia on the abdomen
Postoperative bulging is characterized by rapid growth. The reason is purulent inflammation of the surgical wound, packing. At the same time, wide tendon plates (aponeuroses) and muscles diverge. The gap between them becomes a gateway for hernias of significant size. They can only be sutured by using transplantation at the site of damage to the abdominal area.
Diagnosis by palpation of the abdomen
Other types
Less common are perineal, obturator sciatic, and lateral hernias. Sometimes intestinal loops prolapse into intra-abdominal pouches, such as the duodenojejunal pouch of Treitz in the area of fusion of the duodenum and jejunum.
Cases have been described when a sac is formed by the wall of an organ not covered by peritoneum that has slipped from its place. Sliding hernias of the bladder appear with straight inguinal forms, and blind and large intestinal tubes - with oblique forms.
Causes
The development of pathology can be provoked by any conditions that to one degree or another affect intra-abdominal pressure, as well as thinning of the muscle layer of the anterior wall of the peritoneum or the formation of gaps in muscle tissue.
An intestinal hernia can form during the period of bearing a child as a result of the active pressure of the growing uterus on the surrounding organs; with ascites - stretching of the abdominal cavity and an increase in intra-abdominal pressure occurs due to the accumulation of a significant volume of free fluid, against the background of sudden weight loss, with physiological thinning of the walls of the abdominal cavity in as a result of age-related changes.
One of the following conditions can be a provoking factor:
- labor pains and pushing;
- pathologies of the genitourinary system;
- severe, prolonged cough;
- vomit;
- significant physical activity;
- lifting weights;
- bloating.
In some cases, the disease is caused by congenital defects in the structure of the abdominal organs.
Symptoms of the disease
At the very beginning of its formation, pathology does not announce itself in any way. And only later, as the condition worsens, characteristic symptoms appear, which gradually intensify. Typical symptoms of a hernia formation are as follows:
- the appearance of a ball-shaped protrusion on the surface of the abdomen, which disappears when lying on the back;
- pain in the area where the hernial sac appears, appearing during exercise - the pain can be dull, cramping, tingling, occur periodically or not stop at all.
It is possible that general weakness and increased body temperature may develop.
Diagnosis of pathology
When the first signs of an intestinal hernia appear, you should consult a specialized specialist. This could be a surgeon or a gastroenterologist. Diagnosis of pathology is based on the following methods:
Symptoms of hernia of the white line of the abdomen
- Patient interview. Helps to create a general picture of the disease, collect existing complaints and make a preliminary diagnosis.
- Palpation (feeling the hernia area). One of the methods to determine the presence of a hernia formation.
- MRI. The technique helps to identify pathology in the early stages, and also allows you to obtain the exact size and detailed structure of the hernia.
- Ultrasound examination. Used to determine the size of the hernial sac and its location.
- Radiography.
To get a complete picture of an intestinal hernia, the patient is prescribed a comprehensive examination (using several techniques).
Diagnostics
It is very important to immediately consult a doctor upon discovering the first symptoms of an intestinal hernia. This will not only shorten the duration of the proposed treatment, but also get rid of significant deterioration of the condition caused by complications. The examination is carried out by specialized proctologist and gynecologist if the patient is a woman.
To detect the disease, a thorough examination of the patient is carried out, followed by tests.
For detailed research, various methods are used:
- Palpation. The easiest way to determine a hernia in a patient. Perhaps already at the first request. It is a pinpoint palpation of the affected area for the purpose of further diagnosis.
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). It is one of the most accurate methods for determining the size and structure of a formation. Allows you to detect the disease even in the early stages.
- Ultrasound examination (ultrasound). Less accurate than MRI. However, it also allows you to assess the location and size of the hernia.
- Radiography. Gives an understanding of the features of the neoplasm.
To obtain a complete picture of the course of the disease, the doctor, as a rule, uses several methods in combination.
Treatment of pathology
Treatment of gastrointestinal hernias in adult patients is carried out surgically. Conservative methods do not bring the necessary therapeutic results. The exception is newborn children. As a rule, umbilical hernias are diagnosed in infants, which go away on their own by about 3–5 years of the child’s life.
Surgical treatment
The operation takes place under general anesthesia. During the procedure, the intestinal loop is reduced and the hernial orifice is sutured. In case of necrosis of the contents of the hernial sac, the dead area is removed, followed by connection of the intestine.
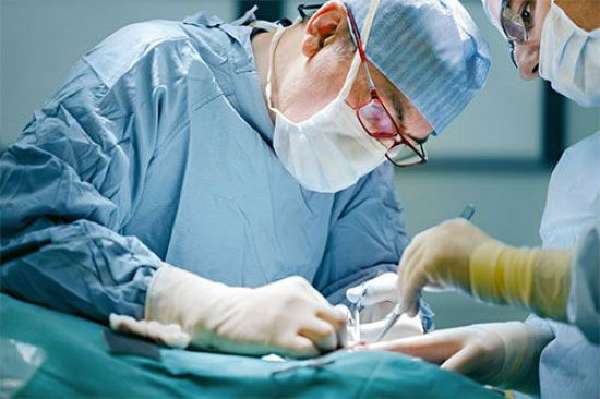
Surgeons correct the intestinal loop that has protruded beyond the anterior wall and suture the hernial orifice, preventing re-formation of the hernia
Conservative techniques
If it is impossible to perform a herniotomy operation, the following options are used:
- Wearing a bandage. The use of corrective medical underwear helps support weak muscles and slows down the progression of pathology. Each model is equipped with a solid part that provides high-quality support for the hernia.
- Physiotherapy. Effective in the early stages of pathology.
- Physiotherapy. Recommended in the initial stages.
The absence of relapse largely depends on competently performed plastic surgery. To eliminate the hernial orifice, the patient’s own tissue or a special medical mesh can be used. The second option is more functional. In addition, the body reacts positively to its material and rejection does not occur.
Traditional methods of treatment
Traditional medicine recipes help alleviate current symptoms, but cannot be an alternative to surgical treatment. The following recipes have worked well. Applying oven-baked onions to the surface of the hernia. Course duration – 3 weeks. Pour boiling water (200 ml) over horse sorrel roots (10 grams) or oak bark (10 grams) and cook for 10 minutes.
The resulting decoction is used for compresses for 10 days. The duration of the procedure is 30 minutes. This prevents the hernia from increasing in size. The following methods are also used. Wash the plantain seeds, dry until flowable and grind. Eat a pinch every day.
Nettle leaves can be applied to the surface of the hernia. The duration of treatment is no less than a calendar month. You need to take a leaf of sauerkraut and apply it to the site of the hernial sac. Or soak a piece of soft cloth in brine and use it as a compress.
Duodenal hernia symptoms and treatment
Poor environment, bad habits, predisposition, unhealthy diet and many other negative external factors negatively affect the condition and functions of the gastrointestinal tract.
The intestinal muscle tissue is especially affected, causing hernias to appear. Due to a sharp increase in tone, the walls expand with the formation of small protrusions that look like pouches. If they are formed behind the stomach, in the first section of the intestine, a duodenal diverticulum (DDC) develops.
If there are many such protrusions and they become inflamed, diverticulosis develops.
IT IS IMPORTANT TO KNOW! Even a “neglected” gastrointestinal tract can be cured at home, without surgery or hospitals. Just read what Galina Savina says and read the recommendation.
Description
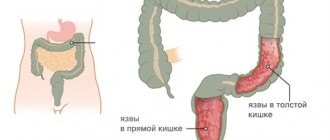
A diverticulum is a sac-shaped process protruding from the walls of hollow, tubular organs. Typically, single diverticula form in the duodenum, but multiple formations are also possible. Diverticular disease is characterized by three conditions:
- diverticulosis;
- diverticulitis;
- bleeding from a protrusion.
The last two terms are considered to be complications of diverticulosis.
Causes
Provoking factors are:
- genetic weakness of the wall of the duodenum;
- hernia of the diaphragm, in the groin or navel;
- inflammation developing in nearby organs: pancreatitis, peritonitis, necrosis of the head of the pancreas, pericholecystitis;
- improper diet and diet;
- tissue changes according to age;
- a sharp increase in pressure in the organ;
- creation of adhesions with surrounding tissues.
Symptoms
Diverticulum is often asymptomatic. Sometimes after eating there is mild pain, heaviness, and discomfort in the right side. Possible nausea . Obstructive jaundice occurs less frequently if the diverticulum affects the gallbladder. This is possible due to the proximity of the duodenal and bile-producing organs.
Severe pain occurs when the protrusion becomes inflamed. Along with pain, the inflammatory process in the diverticulum contributes to the appearance of other symptoms:
- severe bleeding;
- the appearance of blood clots in the stool;
- severe flatulence, bloating;
- heat - up to 38-39°C;
- nausea;
- stool variability.
Classification
Diverticula are included in three groups, formed based on the characteristics of the protrusions:
- by the number of defects in the wall of the duodenal organ: single, when only one protrusion appears; multiple, when many diverticula affect large areas of the intestine;
- by location: protrusions in the lower part; diverticula in the upper part. 3. By size and etiological factor: full-time; correspondence
- true diverticula, which cover all layers of the intestinal wall;
- pseudodiverticula or false protrusions are formed by the mucous layer of the wall;
- congenital;
- acquired.
Correspondence
Diverticulum is distinguished by its rarity of occurrence and the possibility of growing to large sizes. Usually located in the area of the major papilla of the duodenal organ, that is, at the entry point of the bile and pancreas into the duodenum.
THIS IS REALLY IMPORTANT! The gastrointestinal tract cannot be neglected - this risks cancer. Cheap product No. 1 against stomach pain. FIND OUT >>
The cause of the formation of absentee protrusion is a noncongenital pathology. A diverticulum is formed due to loss of elasticity of the wall, that is, at the weakest point of the intestine.
Full-time
A diverticulum forms in the lumen of the organ, which is responsible for transporting and neutralizing the digestion of food in the stomach. The pathology is congenital in nature and is explained by underdevelopment of the gastrointestinal tract in the fetus during the embryonic period.
Diagnostics
The examination is carried out in several stages:
- Examination by a therapist, gastroenterologist, surgeon. The symptoms are assessed to determine the cause of occurrence, the mechanism of development, the type and form of the disease.
- Ultrasound. The method allows you to identify structural changes in the organ, hernias, exclude malignant tumors, and select a therapeutic method.
- X-ray with contrast. The method allows you to determine the functional characteristics of the intestine over time, the degree of tissue damage and the nature of the disease.
- Irrigoscopy, colonoscopy. Using the method, the intestinal walls are carefully examined to determine the exact location and number of diverticula.
- NMR and CT are performed as necessary.
Treatment
In most cases, conservative measures are used aimed at curing and preventing pathology.
If diverticulitis constantly recurs, complications develop, and the protrusions grow to large sizes, surgical intervention is recommended.
To accurately detect a diverticulum, insufflation of air introduced by probing is used. The small defect is immersed and sutured. If the protrusion is large, organ resection is possible.
Medication
Drug therapy is selected depending on the severity of the pathology:
- Early asymptomatic diverticula, discovered by chance, are treated: Drug therapy includes the prescription of drugs of various effects, taking into account the severity of the disease
diet; probiotics (similar in action to Linex), enzyme agents; anti-flatulence medications;
- in case of inflammation of the diverticulum without serious complications, along with the diet, the following are prescribed: laxatives or stool-stabilizing drugs (Duphalac, Poslabin, Lactulose Poly, Normaze); broad-spectrum antibiotics for at least 5-10 days; enzymes that promote digestion; medicines based on 5-aminosalicylic acid; stimulants of gastrointestinal motility (Metoclopramide, Dromperidone, Motilak, Motilium); antispasmodics (“Spazmol”, “No-shpa”, “Spazmonet”); hemostatic and hemostatic.
- severe complications leading to a threat to life, such as heavy bleeding, perforation, peritonitis, obstruction;
- formation of fistula tracts;
- infiltration of the wall, threatening the development of a malignant tumor;
- duodenal stasis;
- obstruction of the pancreatic or common bile duct;
- frequent relapses of diverticulosis.
An important step is to stabilize the stool and achieve regular bowel movements without the use of strong laxatives. For high acidity, long-acting antacids are recommended. At the same time, therapy and prevention of underlying diseases are carried out.
The doctor and the patient select a position in which the pocket on the duodenal wall is better emptied. The patient should take this position every evening before going to bed to eliminate the risk of clogging and stagnation of food in the bag. A light massage is indicated.
Surgery
Indications for surgical intervention when a diverticulum is detected:
Today, it is becoming more common to operate on uncomplicated forms of pathology, which are accompanied by severe symptoms that reduce a person’s quality of life.
Traditional methods
To treat diverticula with traditional methods, tinctures and decoctions of medicinal plants and their fruits, such as dill, rose hips, motherwort, nettle, and chamomile, are used. They can be consumed in pure form or combined in a collection. To do this, take a 1:1 proportion of each plant and pour in 250 ml of boiling water. You need to take 100 ml twice a day (morning and evening) after meals. The course of treatment is 1 month.
The use of folk remedies is effective only when combined with standard therapeutic methods using drugs. Treatment of complicated diverticulosis is carried out under the supervision of a physician.
Complications
- inflammation of the gallbladder (cholecystitis);
- bacterial infection;
- cholelithiasis;
- obstruction of pancreatic and bile ducts;
- inflammation of the pancreas (pancreatitis);
- perforation of the walls of the duodenal organ;
- intestinal obstruction;
- development of internal bleeding;
- hiatus hernia.
People with diverticula in the duodenal process experience sagging skin, weakness of the muscle fibers of the anterior peritoneum, umbilical and inguinal hernias.
Diet
If pouch-like protrusions are detected in the duodenum, it is necessary to adhere to a therapeutic diet. This will reduce the risk of complications and effectively combat the disease. Nutrition principles:
Source: https://tsitologiya.su/zheludok/gryzha-dvenadcatiperstnoj-kishki-simptomy-i
Is wearing a bandage justified?
The use of a bandage for a diagnosed intestinal hernia is mandatory during pregnancy, since surgical intervention during this period is completely contraindicated for a woman. The use of a bandage shows good results at the initial stage of pathology and prevents strangulation of the hernial sac. You need to put it on while lying down and be sure to take it off before going to bed.
Contraindications to use of the product are:
- the presence of any type of damage on the surface of the skin;
- dermatitis and other skin diseases;
- strangulated hernia;
- heart pathologies that occur in severe form.
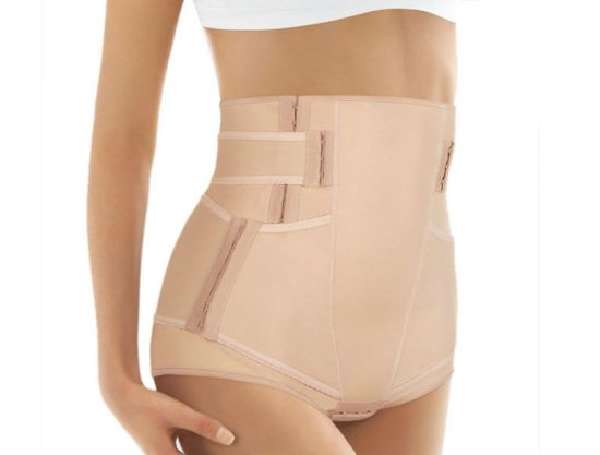
Wearing a special bandage will help prevent the formation of a postoperative intestinal hernia after intervention on the abdominal organs. It looks like an elastic belt and provides reliable support for the anterior abdominal wall.
Intestinal hernia in children
The main symptom indicating the development of an intestinal hernia in a child is the appearance of a pathological protrusion. The size of the formation may be different, since they depend on the size of the intestinal loop trapped in the hernial sac. There are three types of intestinal hernias:
- Reducible. If, when lying on your back or pressing a finger on the surface of the formation, it decreases in size or completely disappears, then this is a reducible hernia.
- Unfolded, unguided. In the absence of pain, but the impossibility of reducing the hernia, we are talking about an uncomplicated unreducible form.
- Disadvantaged.
Uncomplicated unreducible hernias may be accompanied by the following symptoms: aching pain, disruption of the digestive system - nausea, vomiting, constipation or diarrhea, difficulty urinating. The greatest danger is a strangulated hernia. Its signs are the development of sharp pain in the area where the hernial sac is located, a rapid rise in body temperature, the development of vomiting, the hernia cannot be reduced, becomes painful to the touch and tense.
The use of conservative treatment methods is possible only for umbilical hernias, since they tend to heal on their own. Other types of formations are operated on as planned. Temporary contraindications include inflammation of the skin, periods of exacerbation of chronic diseases, acute respiratory viral infections and colds.
Emergency surgery is performed when symptoms of strangulation of the hernial sac appear.
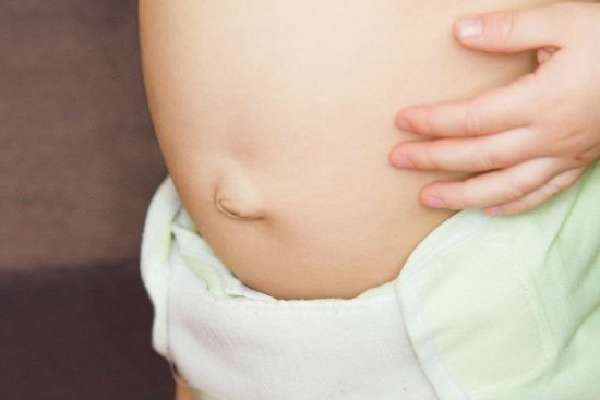

Umbilical hernia in a child
Hernia of the 12 duodenum. Symptoms and treatment of duodenal diverticulum
The causes of duodenal hernia are very diverse, but among them there are several main groups that are most often encountered in medical practice:
- eating disorder. 12 the intestine does not cope well with the process of neutralizing acid to the extent it should;
- excessive physical activity;
- inflammatory processes that occur in various parts of the digestive system;
- weakening of connective tissues;
- loss of intestinal muscle tone;
- disruption of regulatory processes, the cause of which may be organic pathology.
The most common complaint of patients with a hernia of the duodenum is heartburn, which worsens at night, after eating and exercise, and also as a result of injuries.
Since this pathology relates to internal hernias, the symptoms are subtle.
The internal type of hernia exhibits symptoms characteristic of diseases and disorders of the gastrointestinal tract, while external prolapses can be diagnosed based on signs such as bloating, protrusion, and others.
One of the main signs of a possible hernia is gastroesophageal reflux. This is the return of food along with gastric juice from the duodenum 12 into the esophagus. In case of complications (which are extremely rare), a symptom of protrusion may be internal bleeding. It must be taken into account that in this case the only symptom is progressive anemia.
How is the disease classified?
This pathology affects the human body in three types:
- A hernia of a floating nature, it begins to be born in the area of the esophagus, it is also called sliding or floating. It is characterized by the fact that it can move to the upper gastric part, that is, to the esophageal region. Detection of such a pathology is possible when a person changes the posture of his body.
- Near the esophageal view, then the curvature of the stomach protrudes into the thoracic region through the diaphragmatic opening.
- Mixed type, that is, the pathology combines the characteristics of the first two types.
The patient is examined by specialized specialists, such as a gynecologist (for women) and a proctologist. To make the correct diagnosis, the patient is carefully examined and the necessary tests are prescribed.
For a detailed study, the following methods are used:
- Palpation. It consists of pinpoint probing of the diseased area with your fingers.
- Ultrasonography. Helps assess the size and location of the hernia.
- Magnetic resonance imaging. The most accurate way to determine the size of the hernia and its structure. With its help, the disease can be detected in the early stages.
- Radiography. Helps to find out the features of a hernia.
If necessary, the doctor can use several methods at once.
Symptoms and complications
The disease has no clinical manifestations for a long time. A person feels dangerous signs at an advanced stage of development. Constipation, nagging pain in the lower abdomen (can be constant or appear periodically), and flatulence are also noted.
With inflammatory changes in the duodenum, the following symptoms are observed:
- increase in body temperature;
- false urge to have a bowel movement;
- subsidence of pain after defecation;
- loss of appetite;
- metabolic disorder;
- nervousness, irritability;
- intense bleeding or the formation of a blood clot in the stool;
- alternating diarrhea and constipation;
- feeling of incomplete bowel movement;
- feces with mucus.
Upon palpation, the specialist identifies pain in the epigastric zone of the abdomen and increased gas formation. If the diverticulum is located near the nipple of Vater, there is a possibility of gallstones.
Often it becomes inflamed and cholecystitis occurs. Pathogenic microorganisms located along the channels lead to an intense inflammatory process.
Complications of diverticulitis in a patient may include pancreatitis and biliary colic.
Intact diverticula are associated with blockage (duodenal obstruction), which has the following symptoms:
- diarrhea or constipation;
- decreased appetite;
- one-time or multiple vomiting;
- fever;
- constant feeling of pain.
If you have such signs, you need to consult a doctor for medical help; self-medication is unacceptable here.
How does diverticular disease manifest?
In many patients, diverticula are discovered incidentally during tests for another reason, since the disease often does not cause any symptoms. Pain and other symptoms appear periodically. They are caused by the accumulation of food or feces, which decompose in the appendix.
The clinical picture of diverticulosis is progressive. With a long course of the disease, complications are added to it: inflammation, perforation of the intestine. All this is dangerous for the development of oncology. Characteristic symptoms of diverticulosis:
- increased gas formation;
- feeling of incomplete bowel movement;
- alternating constipation and diarrhea;
- loss of appetite;
- tachycardia;
- elevated temperature.
Main symptoms
A characteristic sign of diverticular disease is sharp or aching spasmodic pain in the abdomen without signs of inflammation. It increases after eating and decreases after bowel movements or passing gas. During the acute stage, pain appears on the left in the iliac fossa.
Functional disorders
Symptoms of diverticular disease are nonspecific. They can also occur in other pathologies. With a long course of the disease, signs of functional disorders of the entire gastrointestinal tract appear:
- intestinal bleeding;
- stomach upset;
- flatulence;
- bouts of vomiting;
- mucus in stool;
- intestinal bleeding;
- pain in the left side of the abdomen;
- frequent urge to defecate;
- blood impurities in stool.