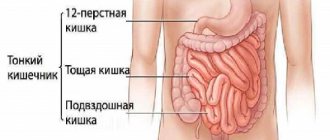
Surgical excision of an inflamed appendix does not yet indicate that this appendix will not have to be dealt with in the future. A sluggish inflammatory process that does not acquire acute forms can last for several years, and this is most often observed in older people. How does chronic appendicitis proceed, symptoms in women, diagnosis and treatment of a rather painful disease?
Does chronic appendicitis occur in women?
When asked whether chronic appendicitis occurs in women, every surgeon will confidently answer that this disease most often occurs in the fairer sex . There are many reasons for this, but there is only one way out - immediate contact with a doctor for further treatment, usually surgical.
Often, women do not pay attention to alarming symptoms, attributing everything to malaise or even the beginning of menstruation, which may have similar symptoms. You should not be careless about the body’s signals, which may not be similar to ordinary weakness - only a visit to the doctor with a detailed, thorough examination and accurate diagnosis will help you begin immediate treatment.
If there is any doubt that this is chronic appendicitis, symptoms in women that are promptly noticed will help prevent complications and exacerbation of the disease. Even if not all the signs indicating the disease are present, you should not try to get rid of the pain on your own - these actions can lead to significant health complications.
Analyzes
However, the clinical picture of the disease is not always clear enough. In this case, the doctor will need laboratory results. And, first of all, he will prescribe a blood test for appendicitis. Here he will look at the results of the following studies:
- general blood analysis;
- ESR;
- leukocyte formula;
- hCG level;
- C-reactive protein;
- You may also need a general urine test to rule out the possibility of urinary tract inflammation or kidney stones.
Symptoms of chronic appendicitis in women
Is it possible to independently recognize the symptoms of chronic appendicitis in women? This is not as difficult as victims of the disease may think, because in most cases the disease has similar symptoms. The most basic symptom that is observed in almost everyone is abdominal pain . They can be localized both on the right side and near the navel itself or even on the left . The nature of the pain can also differ - it can be unpleasant and aching, or occur in sharp outbreaks.
Additional signs indicating the development of the disease:
- intestinal disorders (usually prolonged constipation);
- nausea, almost always turning into vomiting;
- frequent urination, accompanied by attacks of pain;
- At night the temperature usually rises significantly;
- if you press on the alarming side of the abdomen, a flash of severe pain is felt.
Often in women, such signs are associated with most gastric diseases, so it is quite difficult to say for sure that this is inflammation of the appendix. Only an immediate visit to the doctor with subsequent examination will help determine the cause of the pain and respond to this alarming manifestation. You should not be afraid of the diagnosis of chronic appendicitis; symptoms in women can often indicate a milder illness; the main thing is not to treat these signs carelessly.

How to recognize an attack yourself
The sooner appendicitis is detected, the easier the operation will be. If you suspect a disease, you must call an ambulance. You can determine appendicitis at home using special tests that doctors use. Palpation is carried out carefully, without sharp pressure.
To check for appendicitis, you need to:
- Place the child or adult on their back. The surface for the test is chosen to be flat.
- Feel the lower right rib. Using your fingertips, gently tap the area just below the bone.
- Assess palpation. If a person feels pain while pressing, this will confirm the suspicion.
You can check for appendicitis by observing the nature of the pain. When the appendix is inflamed, children and adults feel relief by adopting the fetal position on the right side. You can understand that the pain is associated with appendicitis if a person complains of pain when changing position. A forced posture will help to recognize the source of inflammation, distinguishing it from renal colic and gastrointestinal diseases.
To independently determine whether the discomfort is associated with appendicitis, apply pressure to the place where it hurts the most. Feel this area with the middle and index fingers. When pressed, the unpleasant sensations subside. After the test, the pain increases sharply.
You can detect inflammation of the appendix at home using clinical symptoms of abdominal wall irritation:
- Starting position – lying on your back. Raise your right leg. Appendicitis is confirmed if sharp pain is felt in this position.
- Walk around the room. Appendicitis manifests itself as increased pain with every step.
- Press your fingertips onto your stomach. When pain is associated with appendicitis, the abdominal wall is very tense.
If self-diagnosis and observations do not confirm suspicions, you need to visit a doctor. A specialist will help determine the cause of the pain and prescribe appropriate treatment.
It is difficult to detect appendicitis at home without medical help, since the disease manifests itself with symptoms characteristic of many pathologies. Severe pain, along with other signs, indicates serious disorders that also require urgent hospitalization.
Diagnosis of chronic appendicitis - how it is carried out
How is chronic appendicitis diagnosed and is it possible to make mistakes in determining the disease? If a woman’s medical history already includes acute appendicitis, then first of all the doctor will suspect its chronic form, and will focus on symptoms that can confirm this. Just one glance at the patient’s stomach will be enough to make sure that the cause of the malaise is the appendix. This is easy to determine - this side of the abdomen will be softer, with loose skin.
You should not assume that the doctor will get by with just an external examination - an ultrasound of the abdominal cavity , which will most likely prove that the doctor’s suspicions are not groundless.
The next stage of the examination, which will help determine the size of the inflammation and the structure of the appendix, is an x-ray . Computed tomography is rarely prescribed and only in cases where there is a suspicion that this is not an inflammatory process, but just one of the gastric diseases. A general blood test must also be performed. The research results will help determine the development of inflammation.
Diagnosis of the disease
Indirect manifestations of chronic appendicitis can be identified by palpation of the abdomen. We can talk about local pain in the right iliac region, as well as a positive Obraztsov’s symptom and, quite rarely, positive symptoms of Rovsing or Sitkovsky. Experts draw patients' attention to the following:
- To identify a condition such as chronic appendicitis, it is strongly recommended to perform X-ray contrast irrigoscopy in the area of the large intestine. The presented examination makes it possible to identify the absence or partial filling of the appendix with barium, the slowdown in its emptying, which is direct evidence of changes in the shape of the appendix, narrowing in the area of its lumen;
- Colonoscopy makes it possible to reject the presence of any neoplasms in problem areas in men and women. Carrying out plain radiography and ultrasound allows one to achieve similar visualization in relation to the abdominal region;
- clinical tests of the patient’s blood and urine in the presence of chronic appendicitis, in the vast majority of cases, are not associated with any pronounced changes.
How long does the postoperative period of gangrenous appendicitis last?
In the primary chronic form of appendicitis, the diagnosis is determined by excluding other possible diseases of the peritoneal organs, which are characterized by similar symptoms. It is necessary to carry out differential diagnosis of the presented pathological condition with the following diseases: stomach ulcer, Crohn's disease, irritable bowel syndrome, chronic cholecystitis, spastic colitis.
In addition, speaking about differential diagnosis, I would like to draw attention to abdominal toad, yersinioso and many other diseases, including gynecological in women and helminthic infestations in children. It is important to consider that the diagnostic examination should include a complete list of procedures so that the diagnosis remains as correct as possible. Also, in some cases, a re-examination may be required to determine certain features of the pathological condition and why signs of chronic appendicitis have formed.
Treatment of chronic appendicitis - how does it happen?
If the disease becomes threatening and the pain continues for a long time, treatment of chronic appendicitis is carried out by only one method - surgery. At the same time, studies are carried out on internal organs and the possibility of spreading to healthy tissue. It is possible that the inflammatory process in the appendix has caused damage to neighboring important organs and treatment will require a longer period of time.
If the inflammation of the appendix does not threaten anything and there are no signs of exacerbations, it is quite possible that surgical intervention will not be needed. To influence the disease, a course of taking antispasmodics or special physical therapy is sufficient.
Despite the fact that the disease is not always of a threatening nature, only an experienced doctor can determine the degree of its development, who will prescribe the necessary method of influence. Trying to do anything on your own with a rather dangerous illness is strictly prohibited - complications in this case are guaranteed.
Features of treatment
Particular attention is paid to how exactly chronic appendicitis should be treated. In particular, if the diagnosis has already been confirmed and the painful syndrome is persistent, it is strongly recommended to consider surgical treatment. We are talking about removing the caecum, which can be done using an open appendectomy or laparoscopic method. As part of the surgical intervention, a full examination of the condition of the peritoneal organs is also carried out to identify other probable causes of pain in the right iliac region.
The period after surgery must necessarily be associated with antibiotic therapy. Long-term results after surgery for chronic appendicitis are assessed as more problematic than, for example, after acute appendicitis. This is due to the development of adhesion algorithms.
In the case where mild symptoms are identified in a patient with a chronic form of appendicitis, conservative treatment is resorted to.
We are talking about the use of antispasmodic medicinal components, the introduction of physiotherapeutic procedures, and the elimination of intestinal disorders.
Macroscopic changes in the area of the appendix in the chronic form of appendicitis can remain so blurred that they can be identified only by conducting a morphological examination of the most distant appendix. In the event that in women or men the caecum remains without any changes, there is a possibility that surgery may further aggravate the already existing painful syndrome. As you know, it is this that is the basis for appendectomy.
Is it possible to cure hemorrhoids and get rid of them forever?
The operation is extremely rarely associated with complications, however, for optimal recovery of the body, it is advisable to spend some time in a hospital under the supervision of specialists. Special procedures and the use of medicinal components make it possible to speed up the recovery process and minimize pain . In order for recovery to be even faster and the likelihood of complications to be minimized, it is necessary to resort to certain preventive measures.
When should you not hesitate?
As mentioned above, inflammation of the appendix can cause death due to the development of peritonitis. A real threat to the patient’s life can be suspected if:
- pain subsides for several hours, which is caused by rupture of the wall of the appendix, and its subsequent return, but now greatly intensified;
- the presence of constant vomiting or the urge to vomit;
- a sharp increase or, conversely, a decrease in temperature to critical levels;
- tension of the abdominal muscles, which is accompanied by acute pain upon palpation and the slightest touch to the skin;
- the appearance of confusion, delirium, etc.
Attention! The appearance of at least one of these signs is a reason to immediately call an ambulance.
Article on the topic: Bifidumbacterin for newborns: detailed instructions for use