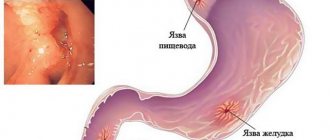
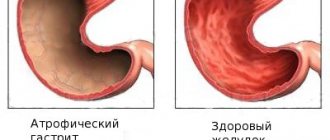
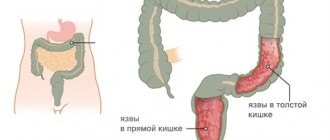
People of different genders and ages experience stomach diseases. Inflammatory processes are provoked by a variety of negative factors that affect the human body both from the outside and from the inside. Symptoms of gastritis and stomach ulcers, the signs of which we will describe below, often make human existence simply unbearable. Weak protection of body tissues appears against the background of constant irritants, due to which a person develops gastritis and stomach ulcers:
- long-term use of medications, in particular non-steroidal and painkillers;
- poor nutrition;
- abuse of bad habits;
- hereditary disposition;
- nervous disorders.
Gastroenterologist Mikhail Vasilievich:
“It is known that for the treatment of the gastrointestinal tract (ulcers, gastritis, etc.) there are special drugs that are prescribed by doctors. But we will not talk about them, but about those medicines that you can use yourself and at home...” Read more >>>
Causes of the disease
There are several prerequisites for the occurrence of ulcerative gastritis. In each case of the disease, the attending physician can determine either one or several causes of the disease. To fully get rid of the disease, it will be necessary to eliminate all negative factors, especially since treatment for ulcerative gastritis requires an integrated approach.
Causes of the disease:
- The main cause of stomach diseases is poor nutrition. It is the neglect of this important process for the body that often leads to negative consequences. Failure to follow a meal plan, an unbalanced diet, eating dry and in a hurry, insufficient chewing of food, foods of poor quality (canned and too spicy, fast food, carbonated drinks, sweets) - all this sooner or later leads to gastritis.
- Damage to the stomach by Helicobacter Pilori bacteria. Penetration of infection into the body is one of the common causes of gastritis.
- Long-term use of medications (acetylsalicylic acid, antibiotics, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs).
- Excessive consumption of alcohol, especially strong alcohol.
- Smoking.
- Prolonged stress, mental and physical stress on the body, chronic fatigue syndrome.
How does ulcerative gastritis manifest?
The peculiarity of this disease is that, under the influence of unfavorable factors, the intragastric epithelium lining the walls of the organ gradually becomes thinner. Due to aggressive hydrochloric acid, first single and then numerous tissue damage appears.
Ultimately, a stomach ulcer forms.
Experts consider it one of the most difficult to cure diseases of the gastrointestinal tract.
Signs of the disease:
- Acute pain in the epigastric region. Even external touch to the stomach becomes painful.
- A feeling of fullness of the stomach, bloating, pressure on the walls of the organ.
- Severe nausea and subsequently vomiting, possible admixture of bile or blood in the vomit. This is explained by the fact that ichor oozes from the affected areas on the walls of the stomach.
- Belching rotten air.
- Severe heartburn that cannot be treated with an antacid.
- Constant feeling of unquenchable thirst.
- Complete loss of appetite.
- Increased body temperature, general weakness, malaise.
At the first suspicion of gastritis, you should immediately consult a doctor. In no case should you ignore the manifestations of the disease, much less self-medicate. Only a doctor can determine the true cause of gastritis and prescribe treatment.
Depending on the symptoms and degree of neglect of the disease, a specialist may prescribe antispasmodics, antacids, antibiotics, enzymes, anti-nausea and diarrhea medications, and antihistamines. Timely seeking medical help will help avoid the formation of ulcers and facilitate further treatment of ulcerative gastritis.
Gastritis and stomach ulcers: symptoms, medication treatment, diet
Not everyone knows that gastritis and stomach ulcers have a lot in common in terms of symptoms and signs.
The difference lies in the time of onset of pain. Inflammation is considered a less dangerous pathology, but it can also cause complications (malignancy, ulcers, digestive disorders). These diseases are caused by poor diet (abuse of fried, spicy and pickled foods, carbonated water), Helicobacter pylori infection, smoking and alcoholism.
Prevention of gastritis and stomach ulcers is a big problem.
What is the difference between gastritis and stomach ulcers?
Symptoms of inflammation and peptic ulcer are known to all gastroenterologists. These are one of the most common diseases among the adult population.
Inflammation of the stomach can be acute and chronic, hyperacid and with reduced acidity, catarrhal and hemorrhagic. The atrophic form of the disease is often diagnosed.
Depending on the etiology, infectious and non-infectious (drug, alcohol, toxic) types of inflammation are distinguished.
The most commonly diagnosed form is catarrhal form. The causes of gastritis are the penetration of Helicobacter pylori bacteria, alcohol abuse, eating spicy food and intoxication.
The following symptoms are characteristic of catarrhal inflammation:
- general malaise;
- heaviness in the epigastric region;
- pain;
- bitter taste in the mouth;
- hypersalivation;
- nausea;
- decreased appetite.
Dizziness and weakness may occur. The first symptoms appear within half a day after exposure to the irritating factor.
Gastritis differs from a stomach ulcer in that it only inflames the mucous membrane. Ulcerative defects do not form.
The difference between gastritis and a stomach ulcer is the time at which pain occurs. With inflammation, it is observed immediately after eating, and with an ulcer - after 30-60 minutes or on an empty stomach.
The first signs of gastritis include vomiting. During it, the following are possible: tachycardia, diarrhea-type bowel movements and decreased blood pressure.
The tongue of patients is often covered with a white coating. Abdominal bloating is observed. Palpation reveals sharp pain.
Other symptoms include dry mouth and foul odor.
If left untreated, the disease can become chronic and lead to ulcers.
Symptoms of hemorrhagic inflammation
Signs of peptic ulcer and inflammation are nonspecific. The hemorrhagic form is often diagnosed.
A synonym is erosive inflammation. Only the mucous membrane is involved in the process. The size of the erosion is less than 3 mm.
If gastritis is not treated, bleeding may develop. Alcoholics are at risk.
With this pathology the following symptoms are observed:
- lack of appetite;
- dull pain in the upper abdomen;
- heartburn;
- nausea;
- vomiting with blood;
- metallic taste in the mouth;
- diarrhea or constipation;
- abdominal muscle tension;
- weakness;
- dizziness.
With massive bleeding, the stool becomes dark. Heart rate increases.
Possible depression of consciousness. In this case, you need to rule out a stomach ulcer.
Chronic gastritis may differ from acute gastritis in trophic disorders such as dry skin and brittle nails.
When bleeding occurs, a headache occurs and weakness worries you.
Symptoms of hypoacid form of inflammation
With gastritis and stomach ulcers, symptoms largely depend on acidity. The attending physician should know the signs of chronic hypoacid inflammation.
This disease is characterized by a decrease in acidity due to gland atrophy. We are talking about atrophic and autoimmune types of this pathology. The disease occurs in a relapsing form.
Pathology can develop into ulcers and cancer. This is due to mucosal atrophy and tissue dysplasia. Not everyone knows how to distinguish gastritis and ulcers.
With inflammation of the stomach with low acidity, the following symptoms are possible:
- rotten or airy belching;
- nausea;
- bitterness in the mouth;
- feeling of fullness in the stomach;
- heaviness in the stomach;
- decreased appetite;
- aching pain after eating;
- stool instability.
Atrophy leads to impaired absorption of nutrients and vitamins. Possible weight loss.
If you have gastritis or a stomach ulcer, their symptoms are not known to everyone. In the case of achylia (lack of hydrochloric acid), glossitis and gingivitis develop.
The tongue of patients becomes bright red. The intestines are often affected. Dysbacteriosis develops.
Persistent neurological impairment is possible. Anemia develops with internal bleeding.
The pressure drops. Pain is not a constant symptom of hemorrhagic gastritis.
Symptoms of peptic ulcer
Signs of a stomach ulcer resemble inflammation, but there are differences. The main symptom is pain.
It has the following characteristics:
- dull, piercing or cutting in nature;
- felt in the upper abdomen;
- appears on an empty stomach or 30-60 minutes after eating;
- subsides after 2 hours;
- radiates to the right hypochondrium;
- eliminated by antacids and proton pump inhibitors;
- more disturbing in autumn and spring;
- combined with dyspeptic disorders.
Gastric and duodenal ulcers differ from gastritis in that the pain syndrome depends on the location of the defect.
When the body of the organ is affected, discomfort is noted to the left of the midline.
If there is an ulcerative defect of the pyloric region, then the pain is felt on the right.
Exacerbations are more often observed in people who are accustomed to eating spicy foods.
A duodenal ulcer is different in that pain appears only after 1.5-2 hours.
Sometimes it occurs at night. Other symptoms of a stomach ulcer include a burning sensation in the chest, flatulence, and abnormal bowel movements.
Nausea and vomiting are possible. If you eat incorrectly during an ulcer, there is a high probability of bleeding and perforation of the organ wall.
In the atypical form of this pathology, pain in the lower back and heart area may occur.
How to distinguish gastritis from a stomach ulcer
Not everyone knows how to distinguish between simple gastritis and gastritis. It is impossible to do this based on the clinical picture.
An endoscopic examination (FEGDS) or radiography is required.
The signs of gastritis and stomach ulcers are similar.
The differences are:
- time of onset of pain;
- sleep disturbance;
- admixture of blood in vomit.
Gastritis and peptic ulcer have the same etiology. This makes it difficult to make a diagnosis. A distinctive feature of peptic ulcer is a decrease in pain after eating.
The reason is the enveloping of the defect with chyme, which reduces contact with the acidic contents.
Diagnosis of gastritis and stomach ulcers
Before treating a person, the diagnosis must be confirmed. Other diseases must be distinguished from ulcers and gastritis.
To do this, you will need the following research:
- determination of stomach acidity;
- FEGDS;
- biopsy;
- radiography using contrast;
- analysis for antibodies to Helicobacter;
- biochemical analysis;
- general clinical research;
- palpation of the abdomen;
- fecal occult blood test.
Treatment of gastritis and stomach ulcers with medications
If gastritis and stomach ulcers are detected, the symptoms can be eliminated with the help of medications.
There are different methods of treating ulcerative gastritis and inflammation.
Antibiotics for gastritis are used if the test results for bacteria are positive.
First-line drugs include macrolides and protected penicillins.
An excellent product is Flemoxin Solutab. The treatment regimen for gastritis and peptic ulcer includes antacids.
They help reduce acidity and reduce pain. This is the main manifestation of these pathologies of the digestive organs.
The list of drugs for gastritis and stomach ulcers is very wide. It includes medications such as Rennie, Gaviscon, Almagel, Phosphalugel.
Proton pump blockers help. The indication for their use is increased acidity.
These tablets for gastritis and ulcers block the enzyme responsible for the formation of hydrochloric acid.
These include: Sanpraz, Khairabezol, Nolpaza, Omez, Pariet. Gastroprotectors are often prescribed.
These are medicines for ulcers and hyperacid gastritis, which protect the organ mucosa from the harmful effects of acid.
The most in demand are Venter and De-Nol. All prescriptions are written by a doctor. Physiotherapy is often used to treat gastritis and stomach ulcers.
If gastritis (ulcer) is detected, hospitalization may be required. The difference is that with peptic ulcer, serious complications often develop in the form of perforation, penetration, malignancy and bleeding. In this case, the medicine will not help.
Surgery (resection or suturing) is required. In the absence of complications, surgery is not performed.
For inflammation, treatment often includes the use of gastric juice. It is indicated for achylia.
Diet for gastritis and stomach ulcers
In the treatment of gastritis and stomach ulcers, drugs are not the only remedy. All patients are prescribed a diet.
Not everyone can say what you can eat if you have gastritis. For peptic ulcer and inflammation with high acidity in the remission phase, table No. 1-b is indicated.
Special attention is paid to nutrition for gastritis and ulcers. During an exacerbation, you need to adhere to diet No. 1-a.
If a hypoacid form of stomach inflammation is detected, treatment includes following diet No. 2.
Not everyone is able to adhere to a healthy diet when suffering from gastritis and ulcers. You need will and patience.
Every gastroenterologist knows which dishes are allowed to be consumed for gastritis.
With high acidity, you need to avoid fried, spicy, pickled, salty and fatty foods. You should not eat sweet and sour fruits and vegetables.
You can drink jelly, milk, rosehip decoction, herbal infusions, water, sweet fruit juice.
The diet for gastritis and stomach ulcers prohibits drinking alcohol.
If atrophy of the glands is observed, then the diet includes extractive substances that increase appetite and juice secretion.
It is recommended to eat sweet and sour berries and fruits, rich broths. Herbs are effective for gastritis.
It is better to entrust their choice to a doctor. Sea buckthorn gives a good effect. It can be eaten fresh or in the form of jam.
Intoxic is an anthelmintic that safely removes parasites from the body. Intoxic is better than antibiotics because: 1. It kills parasites in a short time and gently removes them from the body. 2. Does not cause side effects, restores organs and reliably protects the body. 3. Has a number of medical recommendations as a safe remedy.
4. Has a completely natural composition.
Source: https://nebolitzhivot.ru/gastrita-yazvyi-zheludka.html
How to treat ulcerative gastritis
Those who are sick and their relatives should know that the sooner they see a doctor, the higher the chance of getting rid of this disease. Experts believe that gastritis, caught at the very beginning of its development, can be cured in 2-3 weeks with properly prescribed therapy.
Moreover, to avoid the formation of scars at the site of healing erosions.
If acute gastritis becomes chronic, a complete cure will no longer be possible. In place of poorly healed scars, new ones will form, periods of remission will be replaced by relapses, which will lead to constant discomfort, pain, poor digestion and, ultimately, to a general deterioration in well-being.
Since periods of calm are followed by seasonal activation of the disease, the patient will have to be treated for ulcerative gastritis in a hospital in spring and autumn, especially with acute gastroduodenitis, which often accompanies the disease.
Therefore, it is not recommended to delay visiting a doctor. A prerequisite for successfully getting rid of gastritis and pre-ulcer symptoms is changing your lifestyle. You can always try to put into practice traditional medicine recipes in addition to the drugs prescribed by a specialist. Healing fees are taken in combination with medications.
Ulcer
When folk remedies and treatment of ulcers and gastritis with medications are completed successfully, there is no need to worry about complications. However, if you do not follow the recommendations and self-medicate, a stomach ulcer may open. This disease can be defeated if the pathology phase is not advanced. It is important to immediately eliminate the factors that provoke the disease so that it does not progress. These include:
- lack of sleep;
- systematic overwork;
- abuse of cigarettes and alcohol;
- prolonged nervous tension;
- poor nutrition.
The signs of stomach ulcers and gastritis are in most cases similar. But there are still some differences. This:
- the patient develops “hunger” pains that occur between meals;
- nocturnal pain attacks;
- vomiting mixed with blood particles;
- gastritis with increased acidity.
However, it is a mistake to believe that such manifestations of stomach ulcers are most often caused by a large secretion of acid in the stomach. An ulcer can affect a patient whose acidity is almost in the normal range.
The course of this disease is long-term. Stomach ulcers occur with regular exacerbations, observed in autumn and spring. If timely and adequate treatment of stomach ulcers is not undertaken with folk remedies, the disease can lead to serious problems. It is imperative to contact a gastroenterologist and undergo examinations as soon as the first manifestations of gastritis and stomach ulcers are identified. When diagnosing a stomach ulcer and prescribing stomach treatment, patients have to perform the following studies:
- tests for the determination of H. pylori;
- general urine analysis;
- cytological examination;
- histological analysis of the mucous membrane.
This disease, like a duodenal ulcer, is treated similarly to the treatment of gastritis. The range of measures includes special nutrition, medications and some medical procedures. Also, during treatment, traditional medicine is used in the form of additional health measures, although this requires agreement with the attending physician, who will tell you how to prevent ulcers, how to distinguish it from gastritis and how to cure the pathology.
Changing your diet
When diagnosing ulcerative gastritis, the symptoms and treatment are determined by the doctor. The key to successful treatment of gastrointestinal diseases is a strict diet. Several rules must be followed:
- Meals must be fractional - 5-6 times a day in small portions.
- Fried, spicy, fatty foods, as well as canned food, smoked meats, semi-finished products, various sauces, seasonings and spices should be excluded from the menu. Vegetables with coarse fiber (turnips, radishes, rutabaga, white cabbage) are prohibited.
- It is worth excluding bread and baked goods, especially those made from rye flour. Only white bread, freshly baked or dried, and homemade crackers without seasoning are healthy.
- Patients with gastritis are very useful in liquid or pureed soups, puree soups, low-fat chicken and fish broths, milk and mucous soups.
- For cereals, it is preferable to eat semolina, buckwheat, rice, and oatmeal. Corn and pearl barley should be avoided.
- You can eat fermented milk products, but only fresh ones.
- Soft-boiled eggs and steamed omelettes are not prohibited.
- Meat - chicken, turkey, rabbit, steamed or cooked in the form of steam cutlets. Sometimes you can treat yourself to milk sausages or good quality boiled sausage.
- It is better not to eat vegetables and fruits as salads, but to chop them on a grater.
- It is better to avoid strong tea and coffee, and prefer herbal infusions, rosehip infusion, black tea with milk.
- All food should not be too hot or cold, so as not to injure the stomach.
- Completely give up fast food, semi-finished products, and canned food.
- The total calorie content of the daily diet cannot be more than 3000 kcal.
At first glance, such a diet seems bland and tasteless. However, it is always possible to prepare healthy and varied dishes even from such a limited set of products.
After all, most of those that need to be abandoned have practically no benefit for the body.
In addition to your diet, you need to change your general lifestyle. Give up bad habits, sleep more and breathe fresh air. In case of chronic stress, it is useful to consult a neurologist or psychotherapist; you may need additional drug treatment.
Ulcerative gastritis: from erosion to ulcer
The chronic course of gastritis is dangerous because permanent inflammatory processes affecting the gastric epithelium sooner or later lead to the formation of erosions - damage to the mucosa, which are in the nature of small wounds. If the disease has reached this stage, they speak of erosive gastritis. Ulcerative gastritis is the unofficial name for this pathology (if you follow the Sydney classification).
Features of ulcerative gastritis:
- erosions are well diagnosed during gastroscopy: multiple affected areas are clearly visible against the background of redness of the mucous membrane;
- erosive gastritis can develop both as a result of a long-term chronic and asymptomatic course of the disease, and after exacerbations caused by food/chemical poisoning and other one-time strong irritating effects on the stomach;
- erosions can be single, massive, covering a local area of the stomach walls or the entire surface of the mucosa;
- gastric erosions often occur against the background of activation of Helicobacter;
- treatment of erosive gastritis is quite protracted;
- serious damage to the mucous membrane, epithelium and deeper layers of the walls of the stomach, down to the muscle tissue, can lead to gastric bleeding - a complication that is quickly diagnosed and threatens very serious complications;
- why this variety is called ulcerative - because of the high risk of erosions developing into ulcers - irreversible tissue damage, in which a scar is formed in place of the mucous membrane, which does not bear any functional load for the stomach.
Causes of erosion
As in the case of superficial gastritis, the provoking factors for its development into an erosive form can be a variety of reasons. If this occurred as a result of an exacerbation of the disease, we can speak of a destructive effect on the mucous membrane of the external aggressive environment.
This can be poisoning from poor-quality food, chemical reagents (alkalis, acids), or taking a loading dose of certain medications.
Contact of such a substance on the mucous membrane leads to a burn, which heals very slowly and poorly, since it is not possible to protect the damaged area from normal irritants (food, gastric juice).
Gastric erosion occurs due to the activation of the bacterium helicobacter pylori
If ulcerative gastritis occurs against the background of a chronic disease, in many cases the responsibility for this lies with dysfunction of the secretory activity of the stomach.
As a rule, this is the result of systematic eating disorders (passion for fast food, fatty, spicy, salty foods) or internal gastrointestinal problems.
Such processes are accompanied by a decrease/increase in the production of hydrochloric acid, and the inflamed mucosa is no longer able to regenerate the affected tissues at a speed that was sufficient in a normal environment.
Treatment of ulcerative gastritis, depending on the symptoms, can last up to a year, and if the prescribed diet and drug therapy are not followed, the result of such treatment may be zero, even if most of the time the doctor’s advice was followed.
Symptoms of erosive and ulcerative gastritis
At the early stage of the occurrence of multiple erosions, it is quite difficult to identify the disease solely on the basis of patient complaints or as a result of an analysis of the clinical manifestations of the pathology - the symptoms are practically no different from non-erosive types of the disease. The only exception is the appearance of gastric bleeding, when areas of dark, almost black color are clearly visible in the stool.
All other signs that we list can only be an indirect indication that foci of erosion have begun to form in the mucous membrane:
- pain and discomfort in the epigastric region (with single lesions, pain can be quite mild, but the spread of erosion to most of the walls of the stomach may even require taking analgesics to relieve pain);
- heartburn usually occurs during the chronic course of the disease in the presence of reflux - a phenomenon in which the contents of the stomach (food along with gastric juice) are thrown back into the esophagus;
- symptoms of dyspepsia, characteristic of most types of the disease - a feeling of heaviness in the abdomen, stool disorders (constipation or diarrhea), dry mouth, belching with a rotten or sour odor;
- In case of ulcerative gastritis of the stomach, an increase in pain in the epigastrium after a long break in food intake (on an empty stomach), which is caused by the irritating effect of hydrochloric acid on pain receptors located deep in the erosive spots, can be considered characteristic.
If two such symptoms appear, it is necessary to undergo a thorough examination of the condition of the stomach as quickly as possible, combining laboratory and instrumental research methods.
Endoscopy of the stomach
Diagnostics
Fibrogastroduodenoscopy (gastroscopy, FGDS) - a procedure well known as swallowing a probe, is one of the main methods for instrumentally determining the presence of erosion foci on the surface of the mucosa.
The optical device allows you to visually assess the degree of damage to the epithelium and the prevalence of erosive spots in the mucosa, and, if necessary, perform a biopsy - take a piece of the epithelium for additional laboratory tests.
In the case of hyperacid gastritis, a test is usually performed to check for the presence of Helicobacter pylori infection in the stomach.
Ulcerative hemorrhagic gastritis of the stomach
One of the serious complications of erosive gastritis is the appearance of intragastric bleeding - in this case they speak of the erosive-hemorrhagic form of the disease. This usually occurs when erosive lesions extend deep into the tissue of the gastric wall.
Particularly susceptible to this are people suffering from bleeding disorders and hypertension of any etiology, as well as patients using antiplatelet drugs, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and some analgesics in the treatment of their pathology.
Characteristic symptoms indicating the transition of gastritis to the hemorrhagic phase, in addition to the presence of blood clots in the stool, may include increased vomiting, which may also contain blood, a decrease in pain (which is associated with damage to pain receptors by erosive processes), as well as signs of anemia ( frequent dizziness, surges in blood pressure and pulse).
Treatment of ulcerative gastritis
Measures for the treatment of erosive type of disease are carried out in the following areas:
- normalizing secretory activity (in case of increased secretion, proton pump inhibitors are prescribed for this purpose);
- neutralization of the aggressive effect of hydrochloric acid on the mucosa is achieved by prescribing antacids, which have a complex effect: they reduce the acidity of the gastric environment and have an enveloping protective effect on the mucosa, promoting their speedy healing;
- gastritis with reduced acidity should be treated with enzyme preparations that stimulate secretory activity;
- since with ulcerative-erosive gastritis, destructive changes also affect muscle tissue, impaired motility of the antrum of the stomach/12 duodenum occurs. This disorder is eliminated by prescribing histamine receptor blockers;
- when diagnosing the hemorrhagic subtype of the erosive form of the pathology, hemostatic drugs are prescribed, administered intramuscularly/intravenously;
- If the presence of Helicobacter pylori bacteria in the stomach is confirmed, complex antibacterial therapy is prescribed to combat the infection, usually including two to three antibiotics.
Treatment of erosive-ulcerative gastritis can be supplemented with the use of alkaline mineral waters, which should be taken according to a certain scheme, preferably in the conditions of specialized sanatoriums under the supervision of medical staff.
Diet for ulcerative gastritis
Even with superficial gastritis, treatment using drug therapy alone will not be effective. If we talk about the ulcerative type of pathology, then strict adherence to a dietary diet is a prerequisite for a positive prognosis. Moreover, as the stage of remission is reached, in order to anticipate relapses of the disease, dietary restrictions cannot be avoided.
When treating ulcerative gastritis of the stomach in the acute stage, you will have to fast for several days, limiting yourself to drinking only, and then diet No. 1 is applied. When the symptoms of the acute course of the disease pass, you can switch to diet table No. 5. General recommendations specific to these diets are as follows:
- It is prohibited to use products that provoke an increase in secretory activity (increasing the acidity of gastric juice), as well as irritating the mucous membrane (fried, smoked, salty, fatty foods, indigestible foods);
- everything that is eaten must be fresh, cooking methods are only steamed or longer cooking than the usual recipe;
- using the principles of fractional meals (frequent and small portions);
- when preparing any dishes with solid products, they must first be crushed to a fine or mushy state;
- You only need to eat food heated to a temperature close to the temperature of the human body - this will greatly facilitate the stomach’s task of digesting the food mass; too cold/hot food is dangerous in the presence of erosions.
Compliance with dietary rules is the key to your health
Please pay attention! Brown bread should be excluded from the dietary menu, as well as any fresh baked goods, especially those made from rich flour. Prohibited are shortbread cookies, chocolate, any fatty dishes using animal products (blood milk, lean pork, lard, smoked and homemade sausages), spices, sauces and seasonings.
The permitted products include day-old white bread, bran, crackers, mashed potatoes (boiled potatoes are allowed in soups), porridge from permitted cereals cooked in water/milk without the use of fat, dietary meat (rabbit, white chicken, veal), small amount of vegetable oil. It is allowed to eat low-fat sea fish, as well as fermented milk products.
Source: https://PobediGastrit.ru/diagnost/kak-lechit-yazvennyj-gastrit.html
Folk remedies for gastritis
In the arsenal of traditional healers there are many remedies that can help get rid of the disease. However, you need to remember that home remedies need to be selected individually, and it is better to consult a doctor before using them.
- Potato juice heals minor erosions well, normalizes acidity and soothes the stomach. Before use, you need to thoroughly wash 3-4 tubers and squeeze them without peeling them. Take 0.5 cups in the morning on an empty stomach, after taking it you need to lie on your back for 20-30 minutes for the juice to have a beneficial effect. You need to be treated for at least a month.
- A simple and affordable remedy for gastritis is a honey solution. You will need high-quality natural honey, which must be diluted in lukewarm water in a proportion of 2 tbsp. l. for 1 glass of water. Drink a glass of the product for 2 weeks.
- Oatmeal jelly is considered a recognized herbal remedy for gastritis and pre-ulcer conditions. It can be prepared from either whole oats or Hercules flakes.
- Herbal decoctions help very well - chamomile, linden blossom, St. John's wort, birch bark, fennel, St. John's wort. They soothe an irritated stomach, normalize acidity, and improve digestion.
If the treatment of ulcerative gastritis is carried out comprehensively, there is always a chance for a complete recovery.
Source: MedicalOk.ru
Causes
In order for the digestive organ to maintain its functionality and be in a healthy state, it is necessary to maintain a balance of two opposing factors:
- The amount of protective mucus that coats the walls of the stomach.
- The amount of gastric juice that has aggressive properties, but is still necessary for the digestion of food.
Pre-ulcerative stomach disease develops when the amount of gastric juice increases and the hydrochloric acid contained in it begins to corrode the walls of the digestive organ. The most common cause of this is gastritis caused by the bacterium Helicobacter pylori.
In addition, a pre-ulcer condition can be caused by a violation of the diet, when the body has to produce a large amount of gastric juice to digest heavy food.
The provoking factor is stressful situations that reduce local immunity, which leads to a decrease in the production of protective mucus. As soon as unprotected areas form on the mucous membrane of the gastrointestinal tract, there is a risk of ulcers.
They cause pain in the upper abdomen, which signals the possible development of a pre-ulcerative condition.
Advice! If you have a genetic predisposition to peptic ulcer disease, you need to monitor your diet and give up bad habits.
Treatment of pre-ulcerative stomach condition – Gastrology
Gastritis in ulcerative form is an acute stage of pathology. It is characterized by the fact that first the mucous membrane is destroyed, and then the organ tissue is affected. At the same time, the person feels pain in the stomach and loses appetite.
Ulcerative gastritis is dangerous because as it progresses, it is impossible to restore the affected tissue, so a visit to the doctor should not be postponed when the first symptoms appear. If vomiting blood or pain occurs, then urgent hospitalization is necessary.
Comparison of gastritis and ulcers
The symptoms of ulcerative gastritis at the initial stage resemble those that appear with ordinary gastritis.
But at the same time, ulcerative gastritis is characterized by the following symptoms:
- Redness and inflammation appear on the mucous membrane already at the initial stage.
- Occurs in chronic or acute form.
- It occurs due to the appearance of the bacterium Helicobacter pylori in the stomach.
- May progress over many years.
- Requires long-term treatment.
- Bleeding appears in the stomach.
As the disease progresses, the walls of the stomach are destroyed. If you seek help from doctors in a timely manner, you can prevent the development of pathology.
At the initial stage, only a small part of the mucous membrane is destroyed.
If you ignore the signs, the symptoms will become more pronounced over time. Ulcerative gastritis will spread over the entire surface of the stomach and this will complicate treatment. Only complex therapy will help restore the functionality of the organ.
Causes
The disease refers to diseases that occur due to infection with the bacteria Helicobacter pylori. But they can only show their activity when favorable factors arise.
Many patients themselves bring their body to the appearance of such a disease, as they make the following mistakes:
- Alcohol and smoking abuse.
- Poor nutrition.
- Using medications for a long time.
- Passion for spicy and fried foods.
- Constant stress.
- Large loads on the body.
Symptoms
The pathology develops quickly. After the bacterium begins to have a negative effect on the body, a person may feel unpleasant symptoms from its activity for 1-2 hours.
After 5-6 hours the symptoms become severe:
- Vomiting blood or bile.
- Nausea and loss of appetite.
- Severe abdominal pain.
- Bloating.
Symptoms may appear depending on the form of the pathology, as well as after stressful situations. At the first signs of illness, you should immediately contact the clinic.
Acidity in ulcerative gastritis
The disease leads to an increase in the secretion of glands that are responsible for the production of digestive enzymes.
In the acute stage, the acidity in the stomach increases greatly as a result of severe symptoms that last for half a month.
If the treatment is chosen correctly, the disease can be cured in two weeks. During this time, the ulcers will heal, and there will not even be any scars left.
In the chronic stage, the symptoms do not appear so clearly, but this form of the disease cannot be completely cured. From time to time, erosions scar on the walls of the stomach; with relapses, they open again. It is necessary to constantly monitor your diet. When advanced, such ulcers cause severe suffering and can lead to serious consequences.
Pre-ulcerative condition of the stomach: diagnosis and treatment
To diagnose the disease, the doctor prescribes the following tests:
- Blood analysis.
- Stool analysis.
- X-ray. It is carried out with contrast - a solution of barium sulfate. The patient is injected with contrast and several photographs are taken in different positions. Based on their data, the condition of the organ, its functionality and performance are determined.
- Biopsy. Allows you to determine the stage of development of the disease, its form, and whether there are cancerous tumors.
- Breath test to determine the presence of bacteria. The patient takes a deep breath and does not breathe for as long as possible. Next, he exhales air into a special bag. After this, drink a non-concentrated urea solution and repeat the breathing after a few minutes.
Treatment should be carried out immediately after the first symptoms appear. If this is not done, a pre-ulcerative stomach condition can cause complications.
Nutrition rules
First of all, you need to stick to your diet and eat right. The patient is assigned table No. 1, according to which:
- You can’t eat spicy, fried, smoked or fatty foods.
- Steam or boil food.
- Eat often, in small portions.
- Food should be soft and warm.
- We must give up sweets and spices.
Medicines
Drug therapy provides complex treatment. It consists of:
- Taking antibiotics that kill bacteria (Rexacillin, Nifurotel).
- To reduce and relieve pain, take antispasmodics (No-shpa, Spazmalgon).
- To reduce the urge to vomit and alleviate the patient's condition, Motilium is prescribed.
- Prescribed drugs that stabilize the excretion of feces (Duphalac, Smecta).
- Normalizing acidity in the stomach (receptor blockers: Maalox, Rennie, Gastrocepin).
- Taking drugs that restore mucous membranes (Omeprazole).
By taking these medications, the mucous membrane is restored, which will not allow acid to penetrate the stomach tissues. These medications will also help reduce acidity. Medicines can be taken in the form of tablets or syrups. When ingested, they can reduce the aggressiveness of the environment and reduce bacterial activity.
Physiotherapy
Using this procedure, you can improve the nutrition of tissues in the body, activate secretions and increase blood supply to affected tissues. This will help them regenerate faster and relieve inflammation.
Physiotherapy is prescribed:
- Ultrasound.
- Dynamic currents.
- Heat therapy.
- UHF.
- Microwave therapy.
- Pine needle baths.
- SMT.
- Electrosleep.
- Psychotherapy.
After such activities, the patient’s well-being improves. Physiotherapy can be used as an auxiliary or primary therapy.
Folk remedies
Often, when ulcerative gastritis appears, doctors recommend that their patients additionally use traditional medicine. Herbs and natural products will help and speed up the process of the main treatment. Such drugs help restore damaged cells and can be used to maintain the body after drug treatment.
The main method of treatment using folk remedies is the use of decoctions and infusions. The most common of them is cabbage leaf juice. It should be taken for a month, drinking 200 milliliters per day.
You can also use potatoes. The juice is squeezed out of the tuber and drunk, or pureed. This product should also be taken every day, 100 milligrams. It is advisable to use only fresh vegetables.
Complications
If a pre-ulcerative stomach condition is not treated on time, it can lead to serious consequences:
- Cancer.
- Bleeding.
- Pancreatitis.
Prevention
Prevention of the disease consists of establishing proper nutrition and giving up bad habits. Food should be chewed thoroughly to facilitate its absorption. By following a diet, you can avoid complications from the disease and relapses. The person will feel better and be able to return to normal life.
Source:
Pre-ulcerative condition - Treatment of gastritis
In most cases of cutting pain in the abdominal area, a stomach ulcer is to blame - a defect in the mucous membrane of the organ, surrounded by an inflammatory surface. It is most common in men aged 25 to 50 years, but recently there has been a trend towards an increase in the incidence of the disease among women.
Statistics indicate that up to 14% of the world's population suffers from peptic ulcer disease. In Russia, the percentage is slightly lower and amounts to 10%, with children accounting for 1% and teenagers 8%.
Ulcer symptoms
It often happens that in a pre-ulcerative state the stomach does not send signals about an impending illness. This occurs in about a quarter of cases and is often fatal. In this situation, you have to determine the symptoms yourself, based on the general condition and characteristics of the body.
Among the main signals of the body:
- Heartburn. It usually occurs 2–3 hours after eating and is observed in 80% of patients. The acidic contents of the stomach irritate the walls of the esophagus, which leads to severe burning.
- Pain. It is the main clinical symptom. Most often it forms in the center of the stomach, but also sometimes spreads under the right and left hypochondrium, and can extend to the back.
- Nausea. A nonspecific symptom, most often observed in the morning and sometimes accompanied by vomiting.
Also among the symptoms are: increased salivation, metallic taste in the mouth, the need for spicy and sour foods, a feeling of heaviness in the stomach, bleeding, fainting, constipation.
- IVs and other medications for stomach ulcers
- what are the causes of ulcers
Appearance also helps to identify an ulcer: increased sweating and cold hands are detected.
Appetite in peptic ulcer disease is preserved, however, due to fear of pain, patients sometimes avoid eating. The diet will help identify the most digestible foods and minimize pain.
Symptoms
Signs of a pre-ulcerative condition of the stomach, as a rule, cause discomfort and cannot go unnoticed. The main signals of developing pathology are the following symptoms:
- Constantly occurring heartburn, which appears approximately a couple of hours after eating.
- Pain in the upper abdomen that occurs on an empty stomach. They can intensify due to stress and physical activity.
- Periodically occurring constipation and diarrhea not related to the quality of food. They are accompanied by belching of air and increased gas formation.
- Nausea due to reflux, that is, when gastric juice enters the esophagus. This factor provokes heartburn, which persists for a long time.
With a pre-ulcerative condition of the stomach after eating, there is always heaviness in the epigastric region. In this case, saturation occurs very quickly, but soon a feeling of hunger may arise. Against the background of constant discomfort in the abdomen, there may be a lack of appetite.
Diagnostics
To confirm a pre-ulcerative condition, it is necessary to conduct laboratory and instrumental diagnostics. At the first appointment, the doctor will definitely clarify the symptoms that prompted your visit.
Among laboratory tests, the most revealing is a blood test. Deviations of certain indicators from the norm indicate an inflammatory process.
In addition, the study is necessary in order to confirm or refute the presence of Helicobacter pylori infection. To make a diagnosis, the following instrumental studies are required:
- X-ray using contrast agent. In this way, it is possible to confirm the signs that indicate a pre-ulcerative condition.
- Endoscopy. With its help, it is possible to determine the location of damaged areas and their size.
- Ultrasound of the abdominal organs, which allows you to assess the general condition of the patient.
- Probing the stomach to determine the acidity of gastric juice.
Treatment
A timely diagnosis allows for effective treatment that will promote healing of damaged areas. This means that the risks of developing peptic ulcers will be significantly reduced.
The goal of therapy when a pre-ulcerative condition is confirmed is to reduce the acidity of the stomach and destroy the Helicobacter pylori bacterium. In order for treatment to be effective, the patient must comply with all medical instructions.
A healthy lifestyle and giving up bad habits will strengthen local immunity, which will contribute to a faster restoration of the mucous membrane of the digestive organ.
Medicines
If the presence of a bacterial infection is confirmed, the doctor must prescribe antibiotics. Various treatment regimens with antibacterial drugs are used, but the following drugs are most often used:
- Macrolides. Clarithromycin 500 mg may be prescribed morning and evening.
- Penicillins. The most effective is amoxicillin, which is indicated for taking 500 mg four times a day.
- Nitroimidazoles. Metronidazole has proven itself well, which is recommended to be taken after meals, 500 mg three times a day.
In addition, other medications can be used to relieve pre-ulcerative conditions:
- Antisecretory agents that reduce the production of gastric juice.
- Bismuth preparations that have a detrimental effect on the bacterium Helicobacter pylori.
- Medicines that improve gastric motility.
- Antacids that minimize the discomfort of the disease.
Folk remedies
It is impossible to cure a pre-ulcerative condition with folk remedies, but they can significantly increase the effectiveness of traditional treatment methods. This is a recognized fact, which is why most doctors recommend additionally using time-tested recipes. In particular, taking potato and cabbage juice is indicated. The following herbal remedies are also considered effective:
- An infusion of yarrow and buckthorn can normalize the digestion process. One spoon of each herb is placed in a thermos, poured with a liter of boiling water and infused for a couple of hours. You need to take the product one glass in the morning and evening.
- Licorice root infusion reduces stomach acidity. Ten grams of crushed root are poured into a thermos with a liter of boiling water and left for a day. Take 100 ml each time before meals.
Advice! The use of folk remedies and the duration of their use must be agreed with the doctor.
Diet
When treating a pre-ulcer condition, an important condition is to follow the diet regimen prescribed by the treating doctor. The diet should include foods that are gentle on the mucous membrane to minimize pain by reducing the load on the stomach.
This is primarily achieved by fractional nutrition. That is, you need to eat often, but the portions should be small. All spicy, fatty and fried foods are removed from the menu during the treatment period. Food should be cooked by boiling or steaming.
It is also possible to use an oven for cooking. It is necessary to monitor the temperature of the food you eat. It should be warm; too hot and cold dishes have an irritating effect on a sore stomach.
Treatment method for erosive gastritis
The treatment regimen for gastritis is aimed at combating the root cause. At the first appointment, the doctor uses endoscopy to determine the type and severity of the disease. You may have a blood test, tissue biopsy, or stool test to check for occult blood. Research will help establish the exact localization of erosions. Then specific drug treatments for gastritis are taken:
- If an infection with Helicobacter bacteria is detected in the body, antibiotics are required. They will help neutralize and quickly destroy pathogens. Tetracycline drugs, amoxicillin and others are often prescribed. It is important to strictly follow the doctor’s prescription and not interrupt the course of antibiotic therapy, otherwise the treatment will not work and the bacteria will become resistant to the antibiotic.
- If the diagnosis reveals an increased pH level in the stomach, the doctor will prescribe medications that reduce acidity in the body. The gastric mucosa needs protection and restoration of aggressive acids; a wide range of drugs with a similar effect will help: Rennie, magnesium hydroxide, Maalox. You cannot change medications on your own without a doctor's prescription. In an individual case, the medicine is prescribed based on the characteristic symptoms.
- Medicines that reduce acidity impair the production of gastric juice, which is necessary for proper digestion of food. In addition to antacid therapy, synthetic pancreatic enzymes are prescribed. They are designed to improve food processing and its proper absorption.
- To relieve stomach pain that interferes with normal life, medications that relieve spasms are prescribed. Among the famous ones are no-shpa and others.
- The last stage is stimulation of regeneration of damaged tissues. Products that increase blood circulation and have healing properties will help. For example, trental.
Folk remedies
Perhaps this is a rare disease when the attending physician will advise you to turn to the resources of traditional medicine. The power of herbs and natural products has long been known. Folk remedies can help in the regeneration of damaged membranes, after drug treatment, as maintenance therapy.
Traditional healers will advise using juice from young cabbage leaves. Should be taken for 1 month, weekly method:
- 1 week – mix 200 ml of fresh juice with 200 ml of water at room temperature and drink 1/2 cup before meals.
- Week 2 – 400 ml of cabbage juice per 200 ml of warm water, drink a whole glass before meals.
- Week 3 – 600 ml of freshly squeezed cabbage juice, diluted with 200 ml of water and drink 2 glasses – the first before meals, the second after meals.
- Week 4 – drink 800 ml of juice with 200 ml of water according to the scheme, gradually returning to the original dose.
A simple, accessible remedy will help with difficulties in choosing traditional therapy.
A proven vegetable used for gastritis is potatoes. The juice is squeezed out of the tubers; just grate the potatoes. Required:
- Wash, peel and grate several potatoes;
- squeeze the resulting mass through cheesecloth;
- drink half a glass of juice on an empty stomach until the symptoms of gastritis completely disappear;
- Do not store the finished juice, squeeze it into a single serving, the juice loses its healing properties if it is not fresh.
Prevention
The main recommendation for preventing the occurrence of pre-ulcerative conditions is that you need to monitor your diet and lead a healthy lifestyle. In addition, you should take great responsibility for your dental health.
Poorly chewed food increases the load on the digestive organ, and, therefore, can cause the development of a pre-ulcerative condition. If you are lactose intolerant, you should definitely include milk in your diet. This product contains many useful substances that accelerate the restoration of the mucous membrane.
It is also important to avoid nervous tension and stress. A calm, measured life filled with positive emotions helps strengthen local immunity, which means it significantly reduces the risk of developing a pre-ulcerative condition.
When the first discomfort symptoms appear after eating and even the slightest pain in the stomach occurs, you should definitely undergo an examination. If a pre-ulcerative condition is detected in a timely manner after appropriate treatment, the prognosis is always positive.
Source: vnorg.ru
Treatment of stomach diseases with folk remedies
Treatment of any gastrointestinal pathology should begin with diet. Proper nutrition not only prevents the development of diseases, but also helps fight them.
Basic principles of proper nutrition:
- Each meal should last at least an hour.
- At least once a day you need to eat hot food: natural soups or broths.
- Complete exclusion of alcoholic beverages from the diet.
- You should give up coffee, and if this is not possible, then under no circumstances drink it on an empty stomach. This creates favorable conditions for the development of gastritis, and subsequently gastric ulcers.
- You should not eat salty or spicy foods: salt and pepper are excellent stimulants of the disease.
- Food that is too cold or too hot can cause muscle spasms.
Source: www.wmj.ru
Complication of pathology
If the deep layers of the organ are damaged, bleeding may begin, and then the disease is already classified as erosive-hemorrhagic gastritis. Superficial erosions located on the anterior or posterior wall of the stomach or on its bottom rarely bleed. Bleeding from several or large lesions is dangerous. If the wound is close to blood vessels, serious gastric bleeding may occur.
The symptoms of gastritis and stomach ulcers are very similar. The only difference is that with a peptic ulcer, the pain syndrome is much more intense, since the ulceration is deep. The pain can radiate to the left side of the chest, lower back, shoulder blade, and spine. The symptom occurs after eating and intensifies within an hour; “hunger” pain may appear.
As with erosive gastritis, nausea, vomiting, flatulence, bowel dysfunction, and heartburn are possible. A sign of a perforated stomach ulcer is an “acute abdomen.” With a peptic ulcer, the intestinal walls are often affected, so you need to start treating gastritis, and not wait until it develops to the point of perforation and inflammation affects neighboring organs.
Symptoms and signs of peptic ulcer
Symptoms and disturbances in motor-evacuation functions in pre-ulcerative condition and peptic ulcer disease are similar. There are many studies on the basis of which it can be argued that the pre-ulcer stage is most often characterized by typical signs of the disease itself.
It should be remembered that the acute form of the disease without proper treatment can lead to serious consequences. Stomach disease, especially if it is accompanied by bleeding, can lead to the development of an infiltrative oncological ulcer.
The clinical picture of peptic ulcer disease has one important feature - the presence of frequently manifested pain. They arise due to disorders associated with the motor function of the stomach, as a result of which its muscles contract convulsively. The appearance of pain is possible due to the irritating effect of gastric juice on the defective surface, as well as due to inflammatory processes.
One of the characteristic features of pain is its relationship with the process of eating. When the lesion is located in the stomach area, painful cramps occur a short time after eating. Often, patients' complaints indicate increased pain in the late afternoon, which forces them to skip dinner. Sometimes the pain is constant and can be quite intense or become unbearable. At the highest level of pain, vomiting is possible. The course of peptic ulcer disease can occur secretly. In this case, there is no pain syndrome.
When adhesions form, physical activity or walking can cause increased pain. Often, patients take a characteristic position: lying on their side with their legs pulled up to their stomach. This allows you to experience relief. Using a warm heating pad has a similar effect.
Other characteristic symptoms of peptic ulcer disease include:
- Frequent heartburn. Often its manifestation occurs even earlier than the onset of pain. Sometimes heartburn occurs after eating. This initial manifestation is then accompanied by pain.
- Vomiting, which often occurs without previous symptoms of nausea and goes away quite easily. The vomit contains a large amount of acidic contents, the admixture of food is small. Vomiting often brings relief, and the pain becomes less severe or disappears for a certain period. If the evacuation activity of the stomach is disrupted, a fairly large amount of food is present in the vomit. It is also possible to diagnose the presence of bleeding by the appearance of these masses. In this case, they look like coffee grounds.
- Constipation, often accompanied by bloating. Sometimes it is possible to alternate between constipation and diarrhea. Tarry stools are a sign of internal bleeding.
- The manifestation of excessive sweating against the background of wet and cold hands.
- The patient is afraid to even touch food because of the expectation of subsequent pain.
Symptoms and treatment of pre-ulcerative condition
A pre-ulcerative or pre-ulcerative condition of the stomach mainly manifests itself in the form of gastritis or duodenitis and precedes the onset of an ulcer.
Small defects form on the mucous membrane of the gastrointestinal tract due to exposure to a number of aggressive factors, for example, hydrochloric acid.
Patients complain of severe pain, which most often occurs after eating food.
Why is it developing?
Predominantly, the pre-ulcerative condition of the stomach is caused by infection with the bacterium Helicobacter pylori. The microorganism is found in many people, but not everyone causes gastritis or ulcerative lesions. In addition, damage to the gastrointestinal mucosa can also occur when exposed to the following factors:
- genetic predisposition;
- unhealthy and unbalanced diet;
- use of certain pharmaceuticals, for example, corticosteroids;
- bad habits;
- abuse of caffeinated drinks;
- constant nervous tension and stressful situations.
How the pathology manifests itself: symptoms
The symptoms of pre-ulcer and peptic ulcer are similar. The main symptom is pain associated with eating. After eating, the pain appears after a short period of time. In addition, patients note that the discomfort increases in the evening, which is why many patients refuse dinner. In some situations, the pain is constant.
Heartburn may be a symptom of pre-ulcer pathology of the digestive organ.
The following symptoms are characteristic of a pre-ulcerative condition of the stomach:
- heartburn;
- attacks of nausea and vomiting;
- constipation;
- diarrhea;
- darkening of stool.
Diagnostic measures
If a person begins to frequently experience pain in the stomach, it is important to visit a medical facility as soon as possible.
First of all, the doctor conducts a survey of the patient, during which he finds out what symptoms are bothering the patient, whether close relatives suffered from ulcerative lesions of the gastrointestinal tract.
Then the doctor begins to palpate the abdomen, which reveals tension in the abdominal wall in the epigastric zone. To make an accurate diagnosis, a person is sent for the following examinations:
- A blood test that detects the presence of Helicobacter pylori.
- Probing of the stomach. Allows you to determine the acidity of gastric juice.
- X-ray examination. Shows signs that are characteristic of a pre-ulcerative condition.
- Endoscopy. Makes it possible to detect the location of the lesion in the mucous membrane and the size of the defect.
Drug therapy
Antibacterial drugs are prescribed to combat the microorganism Helicobacter pylori.
If a pre-ulcerative condition of the stomach is caused by infection with the bacterium Helicobacter pylori, treatment necessarily involves the use of antibacterial drugs. Most often they resort to the following groups of medications:
- Macrolides. Clarithromycin is prescribed 500 mg in the morning and evening.
- Penicillins. Amoxicillin is prescribed 500 mg taken 4 times a day after meals.
- Nitroimidazoles. Metronidazole is used in an amount of 500 mg three times a day after meals.
To reduce stomach acidity, get rid of heartburn and relieve pain, the following medications are prescribed:
- Proton pump inhibitors - Omeprazole. Take 20 mg 2 times a day before meals.
- H2 receptor inhibitors - Ranitidine. Prescribed in an amount of 150 mg, taken twice a day before meals.
- Antacids - "Almagel". A tablespoon of the medicine is drunk half an hour before eating.
If a patient has a severe functional disorder of intestinal digestion, which is accompanied by nausea and vomiting, medications are prescribed not in tablet form, but in the form of injections.
Medicines and the duration of their use have the right to be prescribed exclusively by a doctor, who takes into account the individual characteristics of the patient and the severity of the pre-ulcerative condition.
On average, the duration of treatment is about 2 weeks.
Diet
The diet involves avoiding spicy foods.
Diet is one of the main elements of treatment for both gastritis and pre-ulcer pathology. First of all, the patient will need to give up foods that irritate the mucous membrane of the gastrointestinal tract.
It is important to remove fatty, fried, bitter, spicy and overly salty foods from the menu. You will also need to monitor the temperature of the prepared dishes. They should not be too hot or cold. In addition, doctors recommend avoiding foods that increase the secretion of gastric juice.
Food should be prepared using a double boiler, boiled or baked in the oven. The patient will need to create a diet and eat small portions at least 5 times a day.
Daily calorie content varies within 2000 kilocalories. It is recommended to start the morning with a glass of milk, which has an astringent effect.
Hydrocarbonate mineral waters, which should be consumed daily, have similar properties.
The drinking regime may also include soothing teas, for example, mint.
The main dishes on the menu should contain protein, as well as a sufficient amount of vegetables and fruits. Fermented milk products regulate recovery processes in the body, so low-fat cottage cheese, sour cream, and kefir should be added to the diet.
As for meat and fish, patients are allowed to eat low-fat types, for example, chicken fillet, rabbit, hake and pike perch. In order for ulcerative lesions of the mucous membrane to heal faster, the diet is enriched with vegetable fats. Sea buckthorn and olive oil are well suited for these purposes.
Breakfast should be hearty, so you should start your morning with cereals, such as buckwheat or oatmeal.
Preventive actions
To prevent problems with the gastrointestinal tract, you need to stop eating fast food.
To prevent stomach problems, a person will need to monitor their diet. It is important to avoid snacking on the go and eating fast food. Doctors recommend creating a diet and eating food at the same time every day.
At the same time, it is better to do this in small portions and distribute meals over 5 times. Smoked, spicy, salty, sour and fried foods should be excluded from the diet.
The diet also involves avoiding eating excessively hot or cold foods, which can provoke not only pre-ulcer syndrome, but also cancer of the gastrointestinal tract.
Doctors recommend giving up alcoholic and carbonated drinks, coffee, and smoking. This is due to their irritating effect on the mucous membrane of the digestive organs.
An important preventative measure is the careful use of medications.
If a person is prescribed non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, it is important to strictly follow all the doctor’s recommendations and not exceed the dosage, since medications from this group have a detrimental effect on the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract.
Source: https://EtoZheludok.ru/zabolevania/esche/predyazvennoe-sostoyanie-zheludka.html
Causes of the disease
The functioning of the stomach is ensured by the interaction of two opposing factors. The protective function includes the production of a small amount of mucus, which prevents the possibility of destruction of the gastric mucosa. The second, destructive factor is the presence of gastric juice. It contains hydrochloric acid and pepsin - a substance due to which protein compounds are digested. A destructive factor is also the presence of bacteria in the stomach, such as Helicobacter pylori. In this regard, it is impossible to do without antibiotics when treating the disease.
Ulcerative manifestations occur when the second factors prevail over the first. It is their correction that the treatment of the disease is aimed at.
Many manifestations of gastritis and ulcerative lesions are directly related to the presence and development of a microorganism called Helicobacter pylori in the gastrointestinal tract. This spiral-shaped bacterium is able to survive even in such an aggressive environment as gastric juice. The habitat of this parasite is the mucous membranes of internal organs. This bacterium is detected in many people, but only some carriers develop gastritis or ulcerative lesions.
The symptoms of pre-ulcerative conditions are very diverse, which is why further treatment requires a detailed examination of such patients. Test data and direct complaints from patients are of significant importance in diagnosing the disease.
Other causes of pathological development of the mucous membranes of the stomach include:
- Hereditary factors resulting in biological defects.
- Irrational and unhealthy diet. Violations of the regime, consumption of products that have a soda effect. These are bitter, sour, spicy and salty dishes. The cause of a pre-ulcerative state of the stomach may be fresh baked goods, the habit of eating a lot of food, eating dry food, or a love of cold or very hot dishes.
- Long-term use of corticosteroids or acetylsalicylic acid has an irritating effect on the gastric mucosa.
- Abuse of alcoholic beverages, excessive coffee consumption, as well as smoking, especially on an empty stomach, leads to a pre-ulcerative condition.
- Harmful effects. Working in a hot shop, vibration or exposure to microwave radiation while performing official duties.
And of course, nervous tension, prolonged stressful situations and constant anxiety have a negative effect on the digestive organs.
Diet
The right approach to nutrition is perhaps the most important step to a healthy life without exacerbations. In the first days after the onset of exacerbation of ulcerative gastritis, fasting is a necessary measure, but later the patient requires a lifelong gentle diet. After an attack, you need to gradually introduce new foods into your diet. Starting 3 days after the onset of an exacerbation, you can eat light foods. During this period, it is recommended to consume pureed vegetable soups, non-rich broths, semolina porridge and jelly. Starting from days 5–6, the diet may include lean varieties of fish and boiled meat. It is necessary to remove the skin and tendons from such products in advance. In the future, the diet for ulcerative gastritis completely excludes the use of:
- fresh bread and baked goods;
- fried foods;
- bloodlettings;
- lard;
- pork;
- chocolates;
- sausage with spices;
- semi-finished products.
In diets developed for people with similar stomach disorders, all dishes should be served exclusively warm. It is best to eat porridge and liquid foods in the first few months after an attack of exacerbation of the condition. Despite significant restrictions, the diet for ulcerative gastritis requires adequate nutrition. Authorized products include:
- fermented milk dishes;
- stale and black bread;
- mashed potatoes;
- low-fat soups;
- all porridges, except barley and millet;
- butter and vegetable oil
- rabbit meat;
- veal;
- chicken;
- lean fish.
A properly composed diet will make existing restrictions invisible. A diet consisting of gentle dishes promotes faster restoration of damaged gastric mucosa. It is worth adhering to it throughout your entire life. This will help significantly reduce the risk of exacerbations and unwanted complications.
The importance of the personal factor in the development of the disease
Many studies indicate that personal qualities play an important role in the development of the pre-ulcer stage of the disease. Thus, it has been reliably established that with such pathology, patients exhibit a high degree of anxiety, which is more pronounced than situational. It is permanent. Such patients often tend to blame others when any difficulties arise on the way to their goal. They also experience low mood. Men with this disease are characterized by a decreased need to achieve success.
A slightly different picture is observed when examining children with gastric functional disorders, which can be considered as a pre-ulcerative condition. In half of the cases, young patients are withdrawn and distrustful, they have increased anxiety and quite pronounced negative emotions. Many of the children examined had psychological trauma of an acute or chronic nature, which was associated with family troubles, and somewhat less frequently, with problems at school. Such patients depend on others, are not confident in themselves, they exhibit increased excitability, and they often express pessimism about the possibility of recovery.
In patients with the pre-ulcer stage, the psychological characteristics are similar to those found in patients with a reliably diagnosed peptic ulcer.
Based on many studies, we can conclude that gastric ulcer is a multifactorial pathology. For effective treatment, it is necessary to take into account all factors, including psychological ones.
Source: 1zhkt.ru