Symptoms of the disease
polyps in the anus in the photo
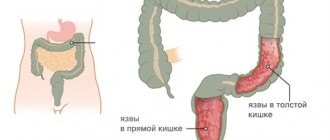
Quite often, rectal polyposis is diagnosed when benign formations form and grow on the walls of this organ. In most cases, at the initial stage of this pathology there are no symptoms at all, but from a certain point painful or simply uncomfortable sensations appear in the anus. If erosions occur in the affected areas, bleeding may develop.
Polyps in the rectum can be solitary or located in small groups. It has been established that if a person has a hereditary predisposition to the formation of such growths, then he has a fairly high probability of their malignancy.
Of great importance is timely diagnosis and implementation of a suitable treatment method for this disease, which helps prevent the development of a cancerous process in the colon.
With the pathology in question, there are no specific symptoms, and polyps can be detected during an endoscopic examination to detect other diseases. Signs of polyposis usually appear at later stages, with multiple formations on the intestinal walls, as well as with the addition of an inflammatory process or a violation of the integrity of the polyp.
Symptoms of the disease:
- The presence of blood impurities of scarlet saturated color in the stool.
- Pain in the abdominal area.
- Discharge of mucus from the anus.
- Discomfort in the anal area, sensation of the presence of a foreign object.
- Increased body temperature.
- Unreasonable constipation.
- Diarrhea occurs less frequently.
- Involuntary release of feces and gases, in particular when polyps are located directly in the anal zone.
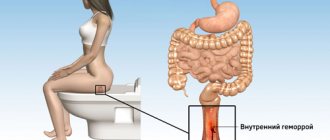
New growths in the intestine, which are attached to the wall of the organ with a kind of leg, and also located near the anus, often fall out during bowel movements and are pinched, causing pain and significant difficulty with defecation. Many people confuse such symptoms with hemorrhoids and begin to self-medicate, which is fundamentally wrong, since an incorrectly selected treatment regimen can lead to many complications.
It is important to know that the longer the polyp has existed and the larger its size, the higher the likelihood of its malignancy, so do not postpone a visit to a proctologist or gastroenterologist if the above symptoms occur.
After all, it is impossible to predict exactly when a polyp will degenerate into a cancerous tumor, immediately after its appearance or after a few years. There are very frequent cases in which the patient became aware of a fatal disease only at the last stage, when it is no longer possible to stop the development of the tumor process.
How to treat polyps in the intestines: suppositories, suppositories, and a list of medications for oral administration
Polyps in the intestines are one of the common causes of cancer. Clinicians attribute any pathological tissue growths to precancer of various parts of the intestine.
Often, intestinal polyposis accompanies major diseases of the epigastric and lower digestive organs: gastritis, peptic ulcer, increased stomach acidity, inflammation of the rectum, hemorrhoids.
Despite the fact that polyps in the intestines are treated mainly only by surgery, there are other methods when there is a ban on surgery.
Contraindications to surgical treatment
Certain factors may hinder the operation.:
- Pathologies,
- Temporary painful conditions
- Patient distress.
In some cases, surgery may be postponed for the following reasons::
- small polyps without signs of growth, strangulation, or malignancy;
- the presence of combined pathologies of internal organs or systems;
- burdened clinical history;
- pregnancy;
- exacerbation of hemorrhoids.
In some cases, a wait-and-see approach may be prescribed to assess the clinical behavior of the pathogenic tumor. Thus, in the absence of unpleasant symptoms, surgery can be performed only when a more favorable period occurs.
Note ! The intervention is contraindicated if:
- exacerbations of inflammatory or infectious diseases;
- hemorrhoidal disease;
- serious internal bleeding.
Features of non-surgical treatment
Treatment of polyps involves a wait-and-see approach with assessment of the dynamics of development of tumor-like growths of the intestinal mucosa, as well as non-invasive treatment methods.
The prescription of drug therapy and methods of alternative treatment are known, however, so far cases of complete disposal of large or multiple polyps by non-surgical methods have not been identified. Read how to take folk remedies for polyps in the intestines here. “Grandma’s” recipes can work for small and isolated growths.
Drug treatment
Drug treatment is an ineffective method of antipolyposis therapy, and therefore is prescribed as symptomatic, restorative or preparatory treatment.
The main drugs are considered:
- Antibacterial drugs for the treatment of exacerbation of the inflammatory process;
- Antiseptic agents to eliminate pathogenic microflora;
- Hemostatic agents for rectal bleeding (local gels, suppositories and suppositories);
- Iron-containing preparations to increase hemoglobin levels in the blood;
- Vitamin complexes;
- Hormonal drugs for severe dysplasia of the intestinal mucosa.
Enemas with antiseptics, herbal infusions, and medicinal compounds are prescribed in case of low localization of polyps:
- rectal lumen,
- anal hole,
- lumen of the colon and rectum.
For distant localization of polypous lesions, systemic drugs for oral administration are used.
The most effective drugs against polyps are the following::
- Suppositories . Chistobolin with hemlock extract. The drug is absorbed into the circulatory system through the mucous membranes within a few minutes. The suppositories contain many herbal medicinal components that soften the mucous membranes of the rectal lumen, reduce tumors, disinfect and reduce painful syndrome.
- Phytocandles . Many patients noted high effectiveness against single polyps. Herbal components help prevent malignancy of tumor cells and reduce pain. Cocoa butter, thuja, celandine and orange maclura extracts in combination provide excellent therapeutic results. The alcoholic extracts of calendula, celandine, plantain and wormwood included in the composition have anthelmintic, antiseptic, and antitumor effects.
- Gepasolone suppositories . A combined action product that contains the hormone prednisolone, heparin, and the anesthetic lidocaine. Suppositories are used in complex therapy for painful defecation, rectal polyps, complicated by hemorrhoidal disease. The duration of treatment is no more than 14 days.
- Relief candles . A well-known drug for the treatment of hemorrhoidal disease, but it effectively eliminates the symptoms of polyposis complications in the intestines. The drug contains shark liver extract, phenylephrine, an anesthetic. Ideal for reducing the symptoms of polyps that are formed from a hemorrhoid.
For bleeding polyps, you can use such ointments:
- Heparin liniment - suitable for necrotic changes in mucous membranes;
- Hepatrombin - for active bleeding with swelling and inflammation of the intestinal mucosa;
- Heparoid Zentiva - reduction of the inflammatory process and the volume of tumors.
If there is a marked decrease in hemoglobin levels, the use of iron-containing drugs is recommended:
- Maltofer,
- Ferrum Lek,
- Aktiferrin,
- Ferlatum,
- Fenyuls.
A course of vitamin therapy is required to increase local immunity, as well as enhance regenerative processes in the intestinal mucous membranes.
Important! Although drug therapy is effective for small, single polyps, it may be used as symptomatic therapy for painful multiple polyps.
Causes of pathology
To date, the exact reasons why a person develops polyps in the rectum have not been established. There is an opinion that the pathology in question develops due to a combination of certain factors. But it is absolutely known that the formation of these formations never occurs in healthy tissues of the body.
The main causes of polyposis are often various chronic diseases, accompanied by an inflammatory process, which over time entails the aging of epithelial tissue in the colon and the appearance of pathological growths on it.
We are talking about diseases such as:
- typhoid fever;
- ulcerative colitis;
- dysentery;
- ulcerative proctosigmoiditis;
- enteritis.
In many patients, after treatment of colitis or dysentery, complete and independent disappearance of polypous growths was observed. In other cases, the culprits of the pathology were frequent constipation, leading to many health problems.
If polyps in the rectum appear against the background of normal health, then it is all a matter of hereditary predisposition. After all, this disease is often detected in young children. Other causes of polyposis:
- unhealthy diet, excess fatty foods, lack of fiber, consumption of alcohol, highly carbonated drinks, foods rich in trans fats, etc.
- sedentary, sedentary lifestyle;
- bad ecology.
Possible complications
Polyps in the rectum and anus are very dangerous for the patient’s life, since the lack of treatment can lead to the following consequences:
- Unexpected transition of a benign neoplasm to a malignant form. In most cases, pathological degeneration of villous adenomatous polyps with a branched or finger-like structure is observed. Growths on a stalk become cancerous tumors much less often than those with a wide base.
- Formation of fecal stones due to a tendency to constipation, intoxication of the body, dehydration, development of intestinal obstruction. The result of all this can be necrosis of intestinal tissue, entry of feces into the abdominal cavity, peritonitis and death.
- Ulceration of neoplasms, high risk of perforation of intestinal walls and sepsis. The patient's body temperature rises, blood is detected during bowel movements, nausea and vomiting appear.
- Serious disturbances in the functioning of the intestines, alternating occurrence of diarrhea and constipation. Diarrhea entails hypokalemia, the patient feels a deterioration in health, since insufficient potassium in the body negatively affects the normal functioning of the entire body.
- The formation of cracks in the rectum is observed due to frequent constipation, especially with unsuccessful attempts to empty the intestines. Minor bleeding and suppuration may develop.
- Pathological decrease in hemoglobin, anemia due to periodic bleeding. In this case, all the characteristic symptoms occur, weakness, dizziness, decreased performance, drowsiness and chronic fatigue.
Diagnosis of rectal polyps
Quite often, cancer occurs against the background of inflammation of polyps. However, it is worth noting that polyps grow slowly. That is why it is extremely important to diagnose their formation at an early stage. Of course, detecting a polyp at an early stage can increase the favorable prognosis of its treatment by 90%. The most effective diagnostic methods for detecting polyps include the following:
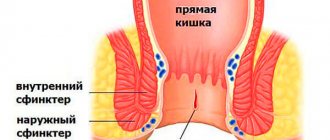
- Digital rectal examination. Using this technique, you can examine a large area of the rectum and identify neoplasms. This method is also used to diagnose rectal fistulas, hemorrhoids, and anal fissures.
- Sigmoidoscopy. One of the most effective methods of examining the rectum, which allows you to accurately and in detail assess the condition of the patient’s rectal walls. Since most polyps are often located in the sigmoid and rectum, using a proctoscope it will be quite easy to identify them.
- Irrigoscopy. This technique involves the introduction of a barium suspension into the rectum. After administering the drug, an x-ray is taken, which will reveal polyps larger than one centimeter in size.
- Colonoscopy. To carry out this diagnostic procedure, the patient should undergo a course of enemas. The technique allows you to very accurately identify even small polyps - less than one centimeter in size.
- Biopsy. This is one of the most important methods that allows you to accurately determine whether there is cancer in a given case. The technique is based on taking a suspicious area for histological examination. A biopsy can be performed during a colonoscopy or sigmoidoscopy.
- Fecal occult blood test. This technique involves examining stool for the presence of blood. However, it is worth remembering that in some cases polyps may not bleed, so this analysis may be ineffective.
- CT scan. Helps detect rectal polyps even of very small size.
Diagnostic methods
An examination by a proctologist includes several diagnostic measures, the first of which is palpation of the anorectal area. This technique allows you to find out the condition of the sphincters, the mucous epithelium of the colon, the presence or absence of polyps in this area. If necessary, sigmoidoscopy, colonoscopy, irrigoscopy, computed tomography are performed, and laboratory tests are performed. It is after palpation that it becomes possible to decide what other instrumental diagnostic procedures should be prescribed to the patient to identify the disease.
Sigmoidoscopy is performed using a special device called a rectoscope, which is used to assess the condition of the first thirty centimeters of the intestine. Proper preparation of the patient, cleansing enemas, dietary adjustments, etc. are first required. The procedure is contraindicated in cases of significant narrowing of the intestinal lumen, in the presence of fissures at the anus, severe bleeding, and also in cases of exacerbations of intestinal diseases.
Colonoscopy is one of the main diagnostic methods, which is performed using an endoscope inserted into the intestine through the anus. This procedure allows you to assess the internal state of a meter-long section of the organ.
Irrigoscopy involves the injection of a contrast agent into the intestine. Before undergoing this procedure, the patient must carefully prepare:
- Before going to bed, take a laxative;
- do an enema;
- a few days before the examination, refrain from long-digesting and gas-forming foods;
- do not eat immediately before the procedure.
As for laboratory tests, it is necessary to donate blood for general and biochemical tests, which complement the overall picture of the disease, providing information, for example, about the level of hemoglobin, which may be reduced, and other vital signs. Examination of stool makes it possible to determine the presence of hidden blood, mucus or undigested food debris in it, as well as to establish the characteristics of the course of the pathology.
The most reliable and painless diagnostic method is computed tomography, which can be used to determine the size and shape of tumors in the intestine, without the need to enter the organ through the anus.
Treatment of polyps in the intestines without surgery -
» Treatment of polyps in the intestines without surgery
Intestinal polyps are small, benign growths that grow asymptomatically on the inner mucosa. This pathology is considered common. It affects 15 to 20% of people. It is asymptomatic.
On average, the size of polyps reaches 1 centimeter. In rare cases, they reach several centimeters. In the intestines, polyps grow both in groups and alone. They look like small cones and may have a thin or thick compacted stem in the shape of a bunch of grapes or a mushroom.
The polyps themselves are considered benign formations that rarely affect a person’s well-being. But they also transform into malignant tumors that are difficult to treat. If intestinal polyps are detected, they are recommended to be removed.
Only a doctor can diagnose intestinal polyps. They occur in people of any race, gender and age. They are more common among representatives of the stronger half of humanity. People 50 years and older are at risk. People of the Negroid race are more prone to the formation of polyps and their malignant degeneration than Caucasians.
Types of polyps
There are three types of polyps:
- The first type, adenomatous, is considered the most common. This species can malignize and degenerate into cancerous tumors.
- The second type is serrated. Depending on the location and size, they have a different probability of malignancy. Large polyps, which are still flat (sessile), located in the upper part of the intestine, most often transform. But small formations that are located in the lower part of the colon, also called hyperplastic polyps, rarely turn into cancerous tumors.
- The third type is inflammatory. These polyps occur after inflammatory bowel diseases such as ulcerative colitis and Crohn's disease. Also prone to malignant degeneration.
As already mentioned, polyps are mainly discovered during a routine examination of the large intestine.
This is due to the fact that the disease is asymptomatic or the symptoms are characteristic of many pathologies, such as hemorrhoids, inflammatory bowel diseases, and peptic ulcers. Large polyps can only be detected with MRI or CT.
Both methods are convenient and painless, but they do not detect small tumors. Therefore, if polyps are suspected, doctors refer patients for examinations such as colonoscopy and flexible sigmoidoscopy.
Colonoscopy is the most sensitive test that uses an endoscope to examine the inside of the intestines.
The endoscope is inserted through the anus into the rectum, and the entire surface of the colon is displayed on a large screen to the doctor. In addition to the video camera, it is also equipped with micro-instruments.
Therefore, tumors can be removed directly during diagnosis.
The doctor may also take a piece of intestine from a suspicious area for histological analysis. Flexible sigmoidoscopy is considered a shortened version of colonoscopy. Using a flexible tube with a video camera, only the rectum and partially the sigmoid colon are examined.
Treatment of polyps in the intestines without surgery
Treatment of intestinal polyps without surgery is carried out through the use of tinctures, healing mixtures, microenemas and decoctions.
The probability of success of home therapy is quite high in cases where the tumor is small in size and the presence of cancer cells is not detected in the polyps.
Mandatory preliminary agreement with the proctologist, as well as systematic monitoring of the patient’s general condition, require events of this kind.
To reduce the risk of degeneration into a malignant tumor, any type of tumor should be removed immediately. Folk remedies are also used to treat polyps in the intestines.
Alternative therapy reduces the risk of tumor regrowth, as opposed to surgical removal. However, such treatment requires long courses.
The course of treatment should be prescribed by the attending proctologist.
Treatment of intestinal polyps without surgery will give positive results if neoplasms are diagnosed in a timely manner. You should resort to medication if the disease is in an advanced form. Adherence to a proper diet, as well as the use of traditional medicine, will help cure the proliferation of intestinal epithelium or reduce this process.
Traditional methods
Traditional methods of treating polyps are:
- oils and ointments (iodine, honey, sea buckthorn, camphor oil);
- decoctions (pine needles, celandine, sage);
- tinctures (viburnum, celandine, walnuts);
- enemas and compresses from plant extracts, their leaves, fruits and stems.
As a rule, the therapeutic course is designed for a long time, so it will not cause harm to the human body. Before treatment, you need to make sure whether the patient has allergic reactions to certain plants. Treatment of intestinal polyps with folk remedies has a number of advantages. We include:
- environmentally friendly drugs;
- strengthening the immune system;
- subject to dosage, no side effects;
- simultaneous use of several drugs;
- 100% result, proven over centuries;
- during treatment, the body receives vitamins, minerals and other beneficial substances;
- there are no negative effects on internal organs and systems.
Compliance with general useful recommendations involves treating polyps with folk remedies. Therapy is carried out over a certain period of time. It is not recommended to interrupt it. Plants and herbs must be collected at a distance of at least 5 km from the city or highway. To preserve more useful substances, it is recommended to prepare medicines in a water bath.
Medicines can be combined with herbal natural preparations. But before this, you should consult your doctor. It is recommended to use toxic herbs with strong effects carefully. In case of side effects, stop the course and contact your doctor to find a different prescription.
Source: https://proctolog81.ru/lechenie-polipov-v-kishechnike-bez-operacii/
Treatment
Unfortunately, it is impossible to get rid of polyps with medication, since there are no drugs that can have a destructive effect on them or at least reduce them in size. Only antispasmodics can be prescribed to eliminate pain, as well as medications that reduce gas formation. Polyps can only be removed through surgery; the type of surgery depends on the type of growths and their number.
For single polyps, endoscopic surgery is used, which involves grasping, pinching and cutting off the stalk of the polyp. Electrocoagulation is used to cauterize pathological growths. The main advantages of this treatment are the absence of the need for general anesthesia, a quick recovery period, and minimal trauma to the intestine.
Multiple formations require abdominal surgery, in which a section of the large intestine is removed. After this, the patient requires complex treatment and hospital stay. The material obtained after the removal of polyps is sent for histological examination to determine the presence or absence of atypical cells in it.
If a patient has had multiple polyps larger than two centimeters in size removed, then it is very important to undergo annual preventive examinations, since they are likely to reoccur. According to statistics, in thirteen percent of patients, growths appear in the same place where they were before, and in seven percent in other areas of the rectum.
Prognosis for rectal polyps
With timely detection and removal of polyps, a complete recovery of the patient is quite likely. However, in some cases it is not possible to prevent a recurrence of the disease. Such relapses often occur several years after the removal of polyps. To prevent the return of the pathological process, a colonoscopy is performed a year after the operation. In addition, it is advisable for the patient to undergo endoscopic examination every couple of years. It is worth noting that the size and number of tumors play a large role in the development of cancer. Therefore, large multiple polyps are most susceptible to malignancy. The most dangerous type of rectal polyps is considered diffuse, which most often degenerates into cancer.
Traditional methods of treatment
Alternative medicine involves the use of decoctions and infusions of various medicinal plants to eliminate the symptoms of many diseases. The pathology in question can be successfully treated with celandine. The best effect is obtained from enemas made from a decoction of this dried herb.
Recipes against polyps:
- Pour boiling water over the herb celandine, calendula, yarrow, add vegetable oil and do a therapeutic enema after preliminary cleansing of the intestines.
- Take orally a decoction of viburnum, which prevents and suppresses the pathological growth of growths in the rectum, and also prevents the development of the oncological process.
- Use horseradish and honey in equal parts.
- Make an alcohol tincture from the golden mustache and take it for fourteen days.
- Mix propolis, a glass of milk and a small amount of butter. Use three times a day.
The use of all traditional methods must be agreed with the attending physician.
Prevention
Any disease is much easier to prevent than to treat, so prevention is necessary. It is important to maintain normal activity of the gastrointestinal tract, eat healthy and balanced, promptly treat existing diseases, and fight constipation. After reaching the age of fifty, it is recommended to undergo regular preventive examinations and examinations in order to promptly detect and eliminate existing polyps in the intestines. This is especially true for those people who have a hereditary predisposition, or among close relatives there are people suffering from polyposis.