Polyps of the esophagus and stomach
Often, when a polyp is localized in the lower third of the esophagus, similar formations can also occur in the cardiac part of the stomach.
Multiple polyps of the esophagus and stomach, forming in two or more sections, are combined into the diagnosis of “polyposis”. Polyps of the esophagus and stomach are also epithelial tumors. They are benign in nature and are not morphologically distinguished from isolated esophageal polyps. Gastric polyps are most often located in the cardiac and antral regions; their shape most often resembles a mushroom or cauliflower.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=XoUy4o5aKlE
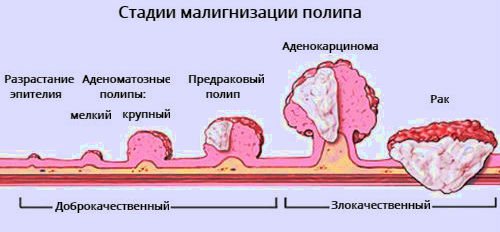
However, in the presence of multiple polyps, doctors raise the question of the possibility of their malignancy and the development of stomach cancer. Data from clinical studies and observations by pathologists confirm the possibility of malignancy.
The process of malignancy of polyps begins, as a rule, from the base. Most often, it is broad-based polyps that are susceptible to malignancy, this is especially true for large-sized neoplasms.
Contraindications
A biopsy of the esophagus is temporarily contraindicated in the presence of acute respiratory diseases that impede nasal breathing, therefore, after eliminating ARVI, a tube diagnosis is made. There are the following prohibitions on the procedure:
- Disturbances mental state that interfere with conscious swallowing of the endoscope.
- Severe cardiac and vascular pathologies. Here, manipulation is prescribed after the elimination of acute symptoms and consultation with a cardiologist.
- State of shock.
- Presence of hemorrhagic diathesis.
- Narrowing of the organ for various reasons.
- Damage to the mucous membrane of the esophagus - burns, wounds, disintegration of a malignant node.
It is important to understand that tomography or radiography using a contrast agent does not provide information about the structure of the cells of a suspicious neoplasm, therefore, after such manipulations, an accurate diagnosis is not made and the correct treatment is not prescribed.
List of allowed products after surgery
Diet plays an important role in the restoration of the body and the healing of the mucous membrane. After removal of the polyps, a wound remains on the gastric mucosa and, in order not to injure it, on the first day after the operation the patient is prescribed a full starvation diet, but with a sufficient amount of fluid calculated from body weight.
On the second day, the diet after endoscopic removal of the stomach polyp allows the patient to drink a glass of warm tea with sugar, drinking a teaspoon every 15 minutes, as well as 50 ml of rosehip decoction.
On the third day after the operation, if pain and swelling have not appeared, for rehabilitation and successful recovery the patient is prescribed diet No. 1A, with a reduced energy value due to a several-fold reduction in carbohydrates, proteins and fats.
To make it easier to imagine the patient’s diet, here is an example of a diet after removal of a gastric polyp for 1 day:
- For breakfast: cottage cheese casserole, jelly or tea, a sandwich with butter, following the norms, casserole without sugar, you can have stevia or honey.
- Snack: Baked apple with a spoon of honey, without vanilla and cinnamon.
- Lunch: Rice soup with vegetable broth, boiled chicken fillet and mashed potatoes, rose hips.
- Second snack: a glass of milk and a cracker of wheat bread.
- Dinner: fish meatball with porridge, tea.
By following the prescribed diet, the patient will get back on his feet faster, putting his stomach, gastrointestinal tract, and metabolism into full operation. Polyps in the stomach are easy to remove, but require long and strict rehabilitation. You can create a simple and very tasty menu from the permitted products. The main thing is not to go beyond the limits of permitted foods and honestly maintain water balance after surgery. If you experience discomfort in the stomach area, contact your doctor immediately.
Nutrition for gastric polyps should be gentle. It is necessary to know healthy and harmful foods for the gastrointestinal tract.
During the first month of the rehabilitation period, the menu should be based on pureed soups and slimy porridges, dishes with a high protein content, which will promote rapid cell regeneration.
Meat dishes you can eat:
- cutlets;
- dumplings;
- casseroles;
- souffle.
Fish dishes should be prepared from lean fish. The range of dishes is similar to meat dishes.
For acute and chronic pancreatitis, pumpkin is the best dietary product.
When treating gastrointestinal diseases, the menu should include the following vegetables:
- zucchini;
- eggplant;
- potato;
- carrot.
It is recommended to grind them in a blender until the consistency of puree.
Nutrition after removal of polyps in the stomach consists of eating small amounts of the following foods:
- lean meat;
- soups from well-cooked cereals;
- porridge (except white rice);
- broths on meat (second and third broth);
- wheat crackers (unsweetened);
- boiled fish (low-fat);
- kefir;
- low-fat cottage cheese;
- butter.
It is recommended to drink black tea (strong).
Following a postoperative diet may pose a risk of relapse. Then the necessary products in the patient’s diet become:
- milk;
- dairy products;
- red fish;
- cereals;
- cabbage (helps fight pathogens in ulcers and wounds);
- vegetables and fruits;
- soups and salads with the addition of vegetable oil;
- green tea.
A balanced diet will reduce the risk of complications.
Food should contain large amounts of vitamins and minerals.
Doctors recommend eating dietary food after removal of polyps in the stomach or duodenum, and a sample menu is as follows:
- Breakfast: 2 eggs (boiled), tea.
- Second breakfast: buckwheat porridge, fruit drink.
- Lunch: fish soup, cottage cheese soufflé, bread, compote.
- Afternoon snack: 2 baked apples (can be replaced with pears), tea.
- Dinner: boiled meat, baked vegetables, juice, bread.
You can create your own menu from the list of products allowed for consumption.
Primary symptoms are rarely expressed, so patients simply do not know about the presence of a polyp in the esophageal tract. As the tumor grows, patients may notice some digestive disorders and unusual sensations when swallowing a bolus of food. Find out what causes esophageal polyps here.
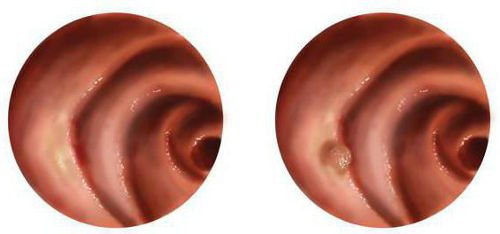
An esophageal polyp is usually small in size, but when it reaches an impressive volume, it can make swallowing difficult. The symptoms are also influenced by the location of polyps in the esophageal part of the digestive system.
The main signs of polyps in the esophagus are:
- Development of gastroesophageal reflux;
- Foreign body sensation;
- Impaired swallowing of saliva, food bolus;
- Chest pain;
- Nausea;
- Frequent attacks of vomiting after eating;
- Heartburn, feeling of heat in the throat;
- Development of iron deficiency anemia (with internal bleeding).
Polyps can fall into the stomach or pharynx, clog the lumens of the digestive tract, become pinched and twisted. The symptoms are varied, but always intense. Patients often lose weight and feel discomfort in the epigastric region and organs of the hepatobiliary system.
Considering the secondary appearance of polyps on the mucous membranes, patients often mistake the characteristic symptoms for another exacerbation of chronic gastroenterological diseases. If unpleasant symptoms appear, you should consult a doctor for a thorough diagnosis and help in solving the problem.
Why do they appear?
Polyps on the esophageal mucosa are formed as a result of any aggressive factors affecting the inner lining. The reasons may be as follows:
- A chemical burn, such as drinking strong alcohol, causes injury. And the regularity of this process leads to inflammation of the mucous membrane;
- Mechanical damage. Rough food, hot drinks, medical procedures can injure the epithelium;
- Infectious diseases. Bacteria disrupt the normal functioning of the mucous membrane;
- Esophagitis is acute or chronic inflammation of the esophagus for various reasons;
- Reflux is a pathology of the digestive tract when the contents of the stomach and intestines are thrown into the esophagus. Irritation of the inner surface occurs.

In addition to direct impact factors, general unfavorable circumstances have an impact:
- Environmental or radioactive threat;
- Poor nutrition, unhealthy foods, lack of vitamins, protein, minerals;
- Smoking;
- Decreased immunity;
- Stress, neuroses, depression;
- Serious organ pathologies;
- Endocrine disorders, such as diabetes;
- Stagnant processes due to physical inactivity.
The most important factor in the formation of polyps is hereditary predisposition. The imposition of provoking circumstances gives impetus to the growth of formations. The risk group includes anyone whose blood relatives have had cancer, polyps, or benign tumors of various organs.
Causes of esophageal polyp
There is currently no unambiguous theory of the occurrence and development of esophageal polyps. Considering the topic of “esophageal polyp causes,” several main etiological factors can be identified.
Currently, clinicians identify the following causes of esophageal polyp:
- Chronic inflammatory diseases of the mucous membrane (esophagitis of various etiologies);
- Periodic microtraumas of the wall of the esophagus (may be associated with regular intake of rough or chemically aggressive food, attempts to ingest chemicals);
- Reflux of gastric juice due to insufficiency of the esophageal-cardiac sphincter;
- Alcohol abuse;
- Genetic predisposition.
Also, certain general factors that increase the risk of developing polyps are physical inactivity, unbalanced nutrition, unfavorable environmental conditions, and stress.
When making a diagnosis, the specific causes of the esophageal polyp are clarified from the patient during the collection of anamnesis. This is necessary to eliminate etiological factors and reduce the risk of new formations.
There is no specific reason for the formation of polypous growths in the esophagus. Gastroenterologists identify several factors that cause esophageal polyps:
- chronic inflammatory process in the mucous membrane – esophagitis;
- frequent injuries to the mucous membrane - rough and irritating food, alcoholic drinks, foreign bodies;
- reverse reflux of acidic gastric juice;
- frequent vomiting;
- hereditary factor.
Frequent stress, poor nutrition, and poor environment increase the risk of developing polypous formations.
Possible complications, prevention
The long course of the pathology is associated with an increased risk of ulcerations and erosions due to the constant maceration of the formations by the food consumed. It should be taken into account that possible massive bleeding from the esophageal vessels poses a threat to the patient’s life.
With repeated low-intensity blood loss, iron deficiency hyporegenerative anemia occurs, accompanied by dizziness, general weakness, paleness of the skin and mucous membranes, and flickering of spots before the eyes.
The most dangerous complication of esophageal tumors is their malignancy with the formation of adenocarcinoma or esophageal cancer. Most often, malignancy is observed in adenomatous growths, in 0.25–7.1% of cases – hyperplastic ones.
In the later stages of the disease, due to the impossibility of adequate enteral nutrition, many patients may develop cachexia.
Specific measures to prevent the disease have not been developed. In order to prevent polyposis, it is recommended to promptly diagnose and treat esophageal pathologies, chew food well, avoid eating rough foods and limit alcohol consumption.
Diet duration
For the first week or ten days, depending on the speed of recovery of the body, the patient eats liquid, pureed food from quickly digestible, light foods. Any dairy products are excluded from the diet in order to avoid fermentation processes in the body. Types of foods that stimulate secretion and irritate the walls of the stomach are also prohibited. Salt intake is reduced to a minimum; it is advisable to completely exclude it from the diet so as not to harm healing wounds.
In the first days after surgery, the patient actively loses fluid, so there is a need for constant replenishment. The water regime is from 2 to 2.5 liters of water. If the patient develops a fever or characteristic symptoms of intoxication, then the daily intake of clean water increases by 1 liter.
It is especially important to pay attention to the water regime, drinking at least the established norms. Also, tea, juice, compote, water with added fruits, syrups, and so on are not considered water. The diet after surgery to remove a polyp in the stomach strictly prohibits sour juices and water with lemon, tea with lemon. Only pure, distilled water.
7-10 days after the operation, to enable regeneration of the operated mucosa, the patient is transferred to a diet of group 1B, according to Pevzner. It is just as strict, has restrictions on carbohydrates and the content of proteins and fats in selected products and ready-made dishes, but is closer to the norm. Vegetable soups and purees are prepared for the patient.
The basic principle of nutrition on this diet is the mechanical consumption of foods, at low temperatures and with a gentle chemical composition. The diet after removal of a polyp from the stomach and esophagus must comply with the main requirements of diet No. 1 according to Pevzner. From its norms it follows that for the patient’s successful recovery, the patient’s food for the next few weeks should be:
- Approximately 36-37 degrees, so that it is pleasant to eat, without damaging the delicate walls of the operated stomach.
- The patient's food should have a liquid, semi-liquid, delicate consistency and should resemble an ideal, tender puree.
- Methods of preparing food for the patient include boiling, stewing, steaming and oven baking. When baking vegetables and meat, it is advisable to use foil, sleeves, and cooking in pots. When baking a dish on a baking sheet, remove the hard crust from it.
- The number of meals per day should be at least 5-6 times to start the gastrointestinal tract and metabolism.
- The intervals between meals should not exceed 3 hours; the patient should not experience a feeling of hunger, since this causes the body to produce hydrochloric acid. Increased acidity destroys polyps, which can lead to hyperplasia of the delicate mucosa.
- Portions are significantly reduced from usual. In the first days after surgery, eat 1-2 tablespoons of each dish. Active and frequent overeating leads to expansion of the stomach, which is unacceptable during the period of nutrition after removal of a polyp in the stomach; there is a risk of harming the wounds and worsening the process of assimilation of foods.
- When on a diet, it is imperative to maintain a water regime; for a speedy recovery, it is recommended to drink slightly cold or room temperature water without ice or additives, in small sips between meals.

The duration of the diet after surgery does not have a specific time frame; it is removed by the doctor after examining the patient for complications and asking about his general well-being. If your doctor confirms that the wounds from the polyps have healed successfully, you can gradually introduce your favorite foods into your diet.
Honest adherence to the prescribed diet is the prevention of relapse. The main task of the diet in the postoperative period is to reduce the load on the digestive processes in the gastrointestinal tract.
Diet No. 1 must include a sufficient amount of protein to restore blood lost during surgery.
To eliminate metabolic acidosis, new food products are gradually added to the menu in small portions without additives or preservatives.
Fruits are fast carbohydrates, and they also make an excellent puree. The best fruits for a sick person are banana, peeled pears, apples, boiled or in compote, persimmons, cherries, strawberries and avocados.
Fruits and berries can also be added in small portions to cottage cheese and kefir to diversify the patient’s taste of familiar dishes.
Polyps can be detected both in the stomach and intestines (colonoscopy determines their presence).
The peculiarities of the diet are that it is necessary to exclude from the diet those foods that can harm the mucous membranes of the digestive tract. They should also be prevented from being exposed to irritating factors (mechanical, thermal or chemical).
The diet after removal of the stomach polyp and other formations on the mucous membrane should ease the burden on the digestive organs. If you do not follow it, the recovery processes in the body will be disrupted. This operation involves removing part of the mucous membrane.
Large pieces of food can take a long time to digest, resulting in fermentation and rotting processes in the stomach. You should not eat food in large portions, because... this contributes to the release of a large number of enzymes, which complicates the functioning of the digestive tract.
The level of stomach acidity plays an important role when choosing dietary nutrition. With low acidity, the diet should contain foods that stimulate the production of gastric juice: first and second courses cooked in concentrated meat or mushroom broths, as well as ham, vegetables, cheese, pasta, sausage (boiled), spicy seasonings.
With high acidity, the diet should consist of lean dishes: soups with meat or vegetable broths, mashed potatoes, slimy porridges (except corn, wheat and barley).
For the first 2 weeks after surgery, it is recommended to adhere to a gentle diet to avoid exacerbation. Most often, at the initial stage of recovery, the acidity level is elevated. It can be corrected with a diet of lean dishes.
Food must be subjected to minimal heat treatment. The most suitable cooking methods are baking and boiling. But in the first 15 days after surgery, doctors recommend eating steamed dishes. Ingredients that will be steamed should be chopped as finely as possible. For preparing meat dishes, it is best to use minced meat.
It is allowed to consume vegetable soups in meat broth with the addition of cereals and lean meat. During the first 10 days of the postoperative period, you can eat meat broths (when preparing them, the water must be drained 3 times). Vegetables should be present in the soup in grated form.
Regardless of the method of preparing dishes, salt should be present in a minimum amount. For various diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, the maximum amount of salt consumed per day should be no more than 10 g. The situation is similar with sugar. It is not recommended to consume more than 1 tsp. sugar per day. If you can’t completely eliminate sugar, you can replace it with honey, but not more than 1 tsp. in a day.
The use of hot seasonings is prohibited, because... they increase the production of enzymes, which negatively affects the mucous membrane.
You should limit your consumption of low-fat foods and dishes so as not to provoke irritation of the mucous membranes of the digestive organs.
The diet can be supplemented with enzyme preparations as prescribed by a doctor.
For patients diagnosed with polyposis, special therapeutic nutrition is recommended. Let us consider the issue of “esophageal polyp diet” in more detail.
Nutrition for this disease has many restrictions and nuances. Food must be processed and have such a consistency as to minimize the risk of injury to the esophageal mucosa. All dishes are steamed and brought to a puree-like consistency.
The diet for esophageal polyp consists of limiting foods high in coarse fibers, stringy coarse meat, game, bread made from coarse flour, hard vegetables, okroshka, mushrooms, coarse porridges, pasta, alcoholic and carbonated drinks.
Spicy, salty, fatty foods are strictly prohibited to minimize the risk of gastroesophageal reflux.
Meals should be frequent and small, with at least one and a half liters of liquid consumed per day.
Useful video
If there are polyps in the esophagus, the symptoms and treatment of which are clear, their removal is not so traumatic, as can be seen in this video.
If the growth is removed in a timely manner, the postoperative wound heals within 4-5 days, and the functions of the esophageal canal are restored after a short rehabilitation period. The postoperative prognosis is usually good, relapses and complications are practically excluded.
If there is a polyp of the esophagus, treatment with folk remedies is very effective, but only at the initial stages of the development of the pathology, and also as preventive measures.
Recipe No. 1. Burdock juice.
A useful remedy used for neoplasms on the mucous membranes of internal organs. Preference should be given to young burdock leaves, then cut them off, wash and dry. Next, we pass the burdock leaves through a juicer, and put the resulting nectar in a cool place. It is recommended to drink juice 2-3 times a day, a teaspoon, after meals. The course of treatment is 1 month, after which you need to take a two-week break.
Recipe No. 2. A decoction of hop cones and spruce needles.
This drug will help eliminate the unpleasant symptoms of growths in the gastrointestinal tract, as well as completely rid the body of small growths. To prepare a healing decoction, you need to pour 3 tablespoons of spruce needles with boiling water and let it brew for 20 minutes.
Then you need to add a small spoon of dry raw material from hop cones to the broth and bring everything to a boil, and then strain. You need to take the decoction internally, 1 glass per day, for 3 days, after which it is important to take a 5-day break. In total you need to take 3 courses.
Source: GastrituNet.online
Esophageal polyp symptoms

The clinical picture of the pathology is nonspecific; symptoms and treatment of a polyp in the esophagus are determined by its location and size.
When the tumor reaches a sufficiently large size, symptoms are caused by compression of adjacent organs.
If the polyp is located in the upper third of the organ, the following symptoms occur:
- difficulty breathing;
- cough;
- choking on food and water.
The location of the tumor in the lower third of the organ causes pain during eating and when bending over. The location of the tumor directly in the cardia leads to disruption of the esophagogastric sphincter. Then the disease manifests itself with frequent belching and heartburn.
The degeneration of a benign tumor into a malignant form leads to the development of intoxication and exhaustion. A person loses his appetite and quickly loses weight. He is bothered by frequent nausea and vomiting.
The clinical question “esophageal polyp symptoms” is quite extensive. The clinical picture of a polyp largely depends on its location and size.
If there are small polyps in the cardiac region, if they are pinched or fall out into the pharyngeal cavity, pain, heartburn, a sensation of a “lump in the throat,” a feeling of pressure behind the sternum may occur, and the swallowing process may be disrupted or become painful.
Small polyps of other locations, as a rule, do not cause any subjective sensations in the patient and do not affect his condition. They may not be detected at all or may be an accidental finding during examination or postmortem examination.
Symptoms of an esophageal polyp become more pronounced when it reaches a large size.
The first alarming sign is dysphagia - a violation of the act of swallowing when the lumen of the esophagus is reduced by the body of the polyp.
In addition, the patient is bothered by pain and discomfort in the chest, a feeling of nausea, periodic vomiting, and pain when eating.
Esophageal polyps, unlike cancer, do not have a tendency to rapid progressive growth, which is reflected in the preservation of these sensations without a tendency to worsen for a long time.
Situations may arise when spasm of the esophageal wall in the area of the polyp decreases, and then the patient notes a temporary spontaneous improvement in the condition and a decrease in the intensity of symptoms.
General symptoms of an esophageal polyp include some loss of appetite, weight loss associated with eating disorders, irritability and anxiety of the patient.
Possible complications and prognosis for recovery
After removal of polyps, if the patient seeks medical help in a timely manner, he can return to his usual rhythm of life within a month. To exclude relapses, it is recommended to undergo a preventive examination once a year.
Despite its practically asymptomatic course, the disease is a serious problem for any person. In some cases, complications may develop. Among them, the most dangerous is the malignancy of the pathological process. For hyperplastic polyps, unlike adenomatous formations, such a complication is not typical. Rapidly developing cancer significantly worsens the prognosis for recovery for the patient.
Lack of treatment and non-compliance with diet can lead to damage to the surface of the growth. This, in turn, entails bleeding with a high probability of developing chronic anemia.
Esophageal polyp treatment
Traditional methods of treatment are not basic, but may well be used if:
- The neoplasms are small;
- There are no risks of tumor malignancy;
- Doctors chose a wait-and-see approach;
- There is no possibility for surgical manipulation.
Honey and bee products help effectively eliminate unpleasant symptoms associated with irritation of the gastric mucosa. Honey goes well with various food ingredients and is included in many traditional medicine recipes.
It is important to understand that honey is a highly allergenic product and in the presence of allergic reactions, it can only aggravate the general condition.
Here is a list of effective recipes:
- Recipe No. 1. To prepare, you will need to melt 0.5 kg of butter over low heat and add 0.5 kg of honey. The composition is brought to a thick consistency over low heat for about 30 minutes. It is important that the composition simmers and not boils. When honey boils, it loses all its beneficial qualities. The finished mass can be stored in the refrigerator. The course of treatment is 14 days with a break of 4-5 days. You need to take the composition on an empty stomach every morning, 1-2 tbsp. spoons.
- Recipe No. 2. The juice of 2 lemons, 0.5 kg of honey and 0.5 kg of olive oil are mixed together. To improve stirring, you can warm the honey a little. The finished composition is placed in the refrigerator and consumed 2 tbsp. spoons on an empty stomach. The general course of treatment is 20 days, after which a break of 5 days should be taken.
- Recipe No. 3. To prepare, grind 15 g of propolis into powder, combine with 200 g of butter and heat in a water bath for about 15-20 minutes. The resulting composition is drunk with warm milk on an empty stomach in the morning and at night (for example, 200 ml of milk and 1 teaspoon of the composition). The mixture can be stored in the refrigerator for no more than 5 days.
- Recipe No. 4. Bee propolis (about 100 g) is poured into 0.5 liters of vodka and placed in a dark place for a week. The infusion is shaken periodically. The composition must be heated before use. One serving - 50 ml before meals. The daily dose should not exceed 200 g per day.

Honey can be eaten plain without diluting with any additional ingredients. Tart varieties of honey are better suited for these purposes.
If a polyp of the esophagus is detected, treatment is carried out only by surgery. Medicines and folk remedies cannot remove tissue growth. Before surgery is scheduled, the polyp is treated with medication only for the purpose of temporarily eliminating symptoms.
Typically, removal of polypous formations is carried out as planned, after the necessary examination and preparation of the patient. Elective surgeries are performed for small hyperplastic polyps.
Urgent operations are prescribed for:
- rapid growth of education;
- bleeding caused by a polyp (urgent surgery);
- high risk of malignancy.
In such cases, the tumor must be removed as quickly as possible.
The use of folk remedies, like medications, has only symptomatic effectiveness. Reducing discomfort with the help of folk recipes is possible only in the early stages of the disease.
- Honey with butter: take 1 kg of butter, melt it in a water bath. Mix with 1 kg of liquid honey. The mixture is taken one tablespoon before meals.
- Celandine decoction: 20 grams of dry or fresh plant, pour half a liter of boiling water, bring to a boil. Take a tablespoon of decoction in the morning.
- Pine decoction: take 50 grams of pine needles, pour boiling water over it, cook for 10 minutes. Then add 50 grams of hop cones and let it brew. Take 50 ml in the morning.
Attention! You should consult a specialist about the possibility of using folk remedies.
Medical nutrition
To reduce discomfort while eating, you must follow a special diet. Its purpose is to reduce trauma to the mucous membrane and improve peristalsis of the organ.
The following foods should not be eaten:
- high in fiber - fresh fruits, legumes;
- canned food;
- stringy meat;
- baking;
- coarse cereals - pearl barley, buckwheat, rice.
It is necessary to establish a strict diet. Take food at the same time, in small portions. The frequency of meals is 5-6 times during the day. Dinner should be no later than two hours before bedtime.
The type of surgical intervention to remove polypous growth depends on its characteristics - size, location, structure.
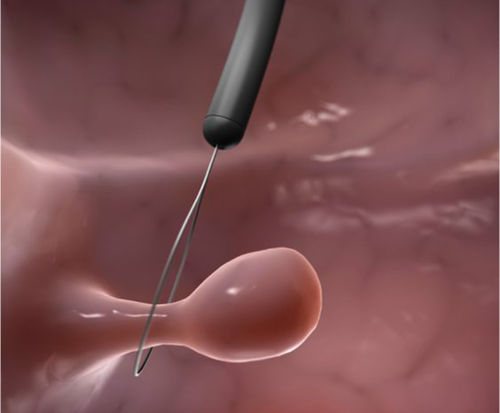
- Endoscopic removal of a polyp in the esophagus is possible if the formation is pedunculated, small in size, and located in an area accessible to the endoscope. The surgeon uses an esophagoscope to remove the tumor and cauterize the vessels with a coagulator. The operation lasts only a few minutes, and after 2-3 days the mucous membrane is restored.
- Wide-based polyps are usually located in the upper part of the esophagus. It is impossible to remove them endoscopically; open access is required. An incision is made along the side of the neck, then the esophageal tube is opened, and a section of tissue with a polypous growth is excised. The defect is sutured. Recovery takes 7-10 days.
- Laparotomy surgery. An incision along the anterior abdominal wall is made if the neoplasm is located near the entrance to the stomach, 3-5 mm from it. The operation is carried out extremely carefully, and the extracted polyp is sent for urgent histological examination, since tumors with a similar location often turn out to be malignant. Recovery takes 10-14 days.
- Resection of the esophagus. Required if the malignant nature of the tumor has been confirmed. The organ wall is excised at a distance of 2 cm around the tumor. After this, radiation or chemotherapy is prescribed.
After any operation, a strict diet is required for at least 2 weeks. Working capacity is limited for 7-21 days depending on the type of surgery.
The appearance of symptoms allows the doctor to suspect a characteristic pathology of the esophagus. The final diagnosis is made solely on the basis of endoscopic and X-ray examination of the esophagus with contrast.
After the final diagnosis has been established, the issue of treatment for the esophageal polyp is decided.
Treatment of esophageal polyp is only possible with surgery.
The possibility of malignancy of the neoplasm requires its unquestioning removal.
Delay in treatment can lead not only to degeneration into cancer, but also to esophageal bleeding. Also, polyposis can spread to other parts of the gastrointestinal tract, causing related pathology.
When planning treatment tactics for a polyp, it is necessary to remember that the nature of the neoplasm can be definitively established only after a histological examination of the tumor. Therefore, all operations are carried out with caution, eliminating the risk of colonization of surrounding tissues with polyp cells. Surgical treatment in the early stages of the disease eliminates the need for more extensive surgical intervention in the future.
When a diagnosis is made and the doctor explains the treatment tactics, many patients cannot decide to undergo surgery for a long time.
Currently, there are many known ways to treat esophageal polyp with folk remedies.
Some recipes are based on taking medicinal mixtures of honey and butter, others describe methods for preparing herbal medicinal mixtures or using sea buckthorn oil.
Internet content is full of recipes of various properties and contents.
It is difficult to confirm or deny the effectiveness of the described methods of self-treatment of polyps. However, it must be remembered that by choosing treatment for an esophageal polyp with folk remedies and refusing qualified medical care, the patient exposes himself to the risk of developing oncology and other complex conditions that threaten his life and health.
For high-quality and correct treatment, without the possibility of causing harm to other organs, you need to contact a specialist, whom you can choose on the website (list of doctors to the left of the article), also for your convenience, you can fill out the form to search for the doctor you need (form at the top of the article), or choose a clinic yourself and make an appointment to receive qualified assistance. Be healthy!
How to detect esophageal pathology?
Taking an anamnesis helps suggest the direction in which to look for the problem, but does not provide a basis for making a diagnosis. The presence of internal bleeding, as indicated by blood in the stool sample and the patient’s low hemoglobin level, may be a cause of concern. Next, effective methods of instrumental diagnostics come into play:
- Endoscopic examination. Using this device, a specialist examines the entire surface of the esophageal mucosa. If a polyp is detected, it is possible to take a piece of tissue for histology.
- Radiography. The image will show the structure of the inner membrane if the patient drinks a coloring liquid before the procedure.
- Ultrasound is a very informative method of research.
- MRI and CT are the most reliable methods, along with endoscopy, and do not cause discomfort. The type of tissue, size, and condition of the surrounding area of the organ are determined. Disadvantages: does not provide material for histology, high price.
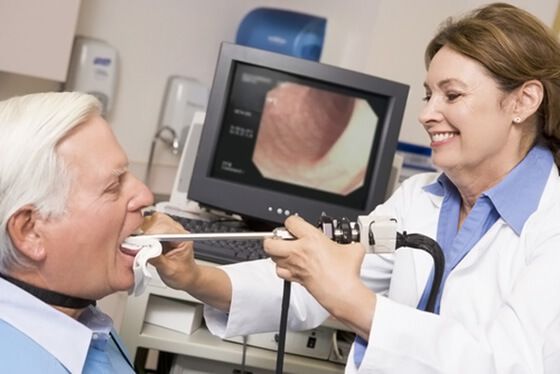
Attention! Diagnostic procedures also have their contraindications!
Prohibited Products
The diet after surgery on the stomach and gastrointestinal tract is very strict, however, the patient’s diet must contain all useful elements, nutrients, vitamins and minerals. In this case, the daily calorie intake should not exceed 3000 kcal. The list of prohibitions on the diet is huge, but this does not mean that the patient will have nothing to eat. He will definitely find a product to his liking on the list of approved ones. What to eat after removal of polyps in the stomach?
- Well-cooked cereals - buckwheat, rice, semolina.
- Lean meat - veal, poultry and rabbit.
- Low-fat sea fish: hake, pollock, baked or boiled.
- It is not only possible, but also necessary, to eat soups in low-fat or vegetable broth.
- At the second stage of the recovery diet, you can start eating low-calorie cottage cheese and drinking kefir.
- On a diet, you are allowed to eat no more than 30 g of butter per day.
- Soft-boiled eggs or steamed omelet.
- Galette cookies.
- Weak tea, rosehip infusion, homemade jelly.
- Jelly and mousse.
- It is recommended to limit consumption, but still not prohibited: honey, sugar, jam and marshmallows.
On a diet you cannot:
- Sausage, smoked sausages;
- Pork, duck, lamb;
- Canned food in oil;
- Mayonnaise and ketchup;
- Fatty fish;
- Mushrooms;
- Nuts and seeds;
- Confectionery;
- Alcohol and soda;
- Sour dishes – cabbage soup, okroshka;
- Flour - pies, pies, buns.
In addition, the menu has a huge list of prohibited vegetables. So on a diet you cannot eat vegetables containing coarse fiber, these are radishes, turnips, horseradish and garlic, onions, sour sorrel and white cabbage.
Diet for polyps in the stomach and in the postoperative period is an effective and necessary factor for the restoration of the body.
In this regard, you should avoid the following foods and drinks:
- spicy, salty and fried foods;
- smoked meats;
- bread and bakery products (butter);
- white cabbage;
- peas;
- seasonings and spices;
- milk (fresh);
- carbonated drinks;
- juices (in packages);
- coffee;
- alcohol.
It is undesirable to use these products for any diseases of the gastrointestinal tract.
How to avoid polyps?
You can protect yourself from the primary or repeated formation of esophageal pathology if you take a number of measures recommended by WHO:
- Follow the rules of healthy eating. A postoperative diet will help you understand the principles of subsequent eating behavior.
- Avoid alcohol, smoking, drinking coffee and energy drinks.
- Move more, stay in the fresh air.
- Treat any emerging pathologies under the supervision of a doctor.
- Do regular diagnostics of the whole body.

The basis for preventing esophageal formations is nutrition. Not only the rejection of harmful foods and cooking methods. You need to eat often, calmly and little by little. The consistency of the dish, temperature, as well as balance and nutritional value are important.
Diagnostics
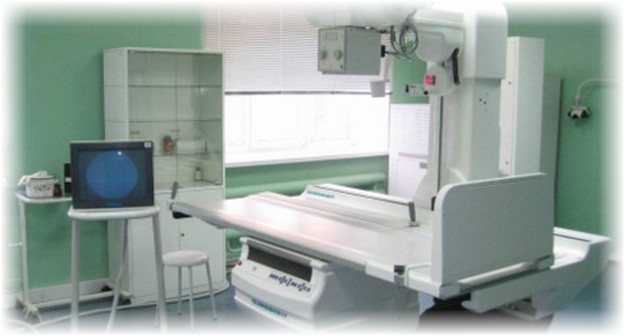
Before you begin to fully treat the polyp, you must undergo a detailed examination. To fully diagnose such a diagnosis according to ICD 10 as a polyp, the patient is prescribed two fundamental procedures for a full study of the problem:
- X-ray of the chest area.
- Endoscopy.
Additional diagnostics exist and are quite common in medical practice. So, the patient may be prescribed a biopsy and histology. These procedures are necessary to study polyp cells. Based on the data obtained, the doctor can determine whether there are any malignant elements in the tumor. In rare cases, malignant cells may appear in children.
Important: Even if the polyp is a very small neoplasm that does not affect the patient’s general condition in any way, it should be removed. Otherwise, over time, an ordinary polyp can develop into a full-fledged tumor and even cancer, as mentioned in ICD 10.
X-rays are very important in the study of this disease. It is on the basis of the images obtained that the doctor can say with complete confidence in which part of the esophagus the polyp is located and whether the existing symptoms are dangerous. The obtained data on the location of the tumor afterward is necessary for its excision and biopsy.