Rectal polyps are benign formations, and in appearance they resemble neoplasms that arise on the intestinal mucosa. To date, the reasons why this pathology occurs have not been established, but statistics say that they are more often diagnosed in people suffering from inflammatory bowel diseases, chronic constipation, and diarrhea.
There are also no age or gender differences in intestinal polyposis - the disease is found with equal frequency in women and men; there are also hereditary forms of the disease - diffuse familial polyposis, which are detected already in adolescence.
Signs, symptoms and consequences of rectal polyps
A polyp is a growth of epithelial, glandular or connective tissue, localized in hollow internal organs. When this benign formation is formed in the rectum, the patient does not actually feel any unpleasant symptoms, but this in no way indicates that the polyp is harmless.
All rectal polyps today are classified as precancerous conditions. In most cases, their appearance is preceded by inflammatory bowel diseases, accompanied by persistent stool disorders.
The main symptoms of the pathology are:
- mucus discharge with feces;
- irregular appearance of blood in the stool;
- spasms and pain in the intestines (these symptoms appear when the polyps are large and partial intestinal obstruction occurs).
But most often, intestinal polyps are asymptomatic, i.e. clinically manifest when they reach large sizes or degenerate into intestinal cancer. In this regard, for the early diagnosis of intestinal polyps, it is recommended to perform an immunochemical stool occult blood test (for example, the ColonView test) annually.
When they appear, you need to contact a coloproctologist for a detailed examination, after which preparations will begin to remove the polyp in the rectum using one of the methods.
Possible complications
If the recommendations or individual characteristics of the body are not followed, symptoms such as:
- high body temperature;
- pain in the lower abdomen;
- edema;
- bloody discharge in the stool;
- nausea, vomiting.
Symptoms indicate the occurrence of complications or inflammation at the site of polyp removal. The reason is deviations from the doctor’s recommendations. You should immediately visit a doctor to take measures to relieve negative symptoms.
Removing polyps surgically is an effective and reliable remedy. In Moscow, the cost of the procedure is low. Ignoring the problem leads to serious consequences, including forced removal of the rectum. Eliminating complications will cost significantly more than eliminating them at an early stage. It is recommended to remove polyps immediately after detection.
Causes of polyps
There is no reliable data on the causes of polyps in the rectum, but it is known that polyps never form on an absolutely healthy intestinal mucosa. In most cases, they form after chronic or acute pathologies of the colon and rectum, after intestinal infections, as well as systematic errors in nutrition, which cause constipation. Heredity also plays an important role in their formation - polyps are often diagnosed in relatives of those who have encountered such a problem.
Restrictions
Any surgical intervention places certain demands on the body’s condition so that it can withstand the load. Surgery is not recommended for patients:
- with diabetes mellitus;
- epilepsy;
- infectious diseases;
- cardiac disorders requiring wearing a pacemaker;
- acute inflammation of the intestinal wall at the site of manipulation - this can cause end-to-end damage.
The patient must warn the attending physician about all the features of his body in order to prevent unpleasant consequences. Even a small detail can play an important role in treatment. If there are contraindications to intervention, drug therapy (tablets, ointments, suppositories) and physiotherapeutic procedures are prescribed. Sick leave is issued for the duration of treatment. If there are no contraindications, then surgery is prescribed.
Treatment methods for rectal polyp
Drug therapy for rectal polyps is not used due to ineffectiveness. When these benign neoplasms are detected, specialists prefer to remove polyps in the rectum using one of the surgical or minimally invasive methods widely used in modern proctology:
- endomicrosurgical excision of polyps;
- excision of polyps using a rectoscope or colonoscope - polypectomy;
- removal of a polyp by coagulation of its stalk (laser or argon plasma);
- resection of part of the intestine - practiced with multiple formations;
- transanal removal of polyps in the rectum
Moreover, in addition to the classic scalpel, high-tech techniques are used to remove benign formations in the intestines - laser, electrocoagulation, radio wave scalpel, as well as an “electric loop”.
Endomicrosurgical removal of polyps
Endoscopic surgery to remove a rectal polyp using a proctoscope - an instrument inserted into the rectal cavity and equipped with a light bulb and a tube for supplying carbon dioxide. The design of the device is designed in such a way that the supplied gas expands the intestinal cavity, and the light source illuminates it, which allows the doctor to visualize the formation.
In addition, a camera is installed on the proctoscope to transmit an enlarged image to the screen. The actual operation to remove the rectal polyp is performed using surgical endoscopic instruments.
Advantages of this method:
- the ability to remove a polyp from any area and/or layer of the rectal mucosa;
- the ability to stop bleeding using coagulation;
- the ability to remove a polyp without dividing it into several parts.
The method is used for almost any type of polyp.

Polyp removal using electroexcision
Electroexcision, also known as electroloop, is performed using a proctoscope. The main instrument is a device at the end of which there is a thin metal thread in the form of a loop. During the procedure, it is draped over the polyp and tightened so that it tightly clasps the stalk of the formation, and after that the power supply is turned on so that the loop heats up. Further tightening of the loop leads to the intersection of the polyp stalk and sealing of the blood vessels.
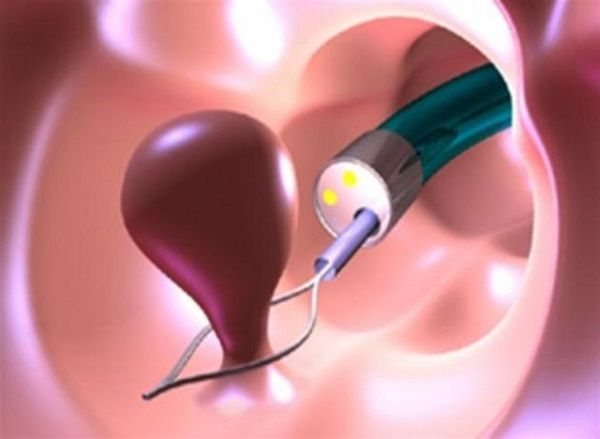
Advantages of the method:
- no or very low risk of bleeding;
- speed of the operation.
The method is suitable for removing polyps with a “pedicle” with a diameter of up to 30 mm, located at a small (up to 30 cm) distance from the anus.
Rectal resection
Direct resection is performed if the polyps show signs of becoming malignant and there is histological confirmation of the diagnosis. As a rule, such operations are performed for malignant polyps and large villous polyps. The operation is performed under general anesthesia. In recent years, laparoscopic resection of the rectum along with the polyp has become widespread.

Laser polyp removal
Removal of a rectal polyp with a laser is carried out in two ways - coagulation of the polyp or its excision. In the first case, the procedure is performed under local anesthesia, in the second - under general anesthesia.
Laser coagulation of rectal polyps is a layer-by-layer cauterization of neoplasms. Excision is a classic polypectomy using not a conventional, but a laser scalpel.
The advantages of laser removal are the low risk of bleeding.
Transanal polyp removal
The procedure is used for certain types of polyps - villous and adenomatous. The main condition for this is that they should be located at a distance of up to 10 cm from the anus. The operation is performed under general anesthesia.
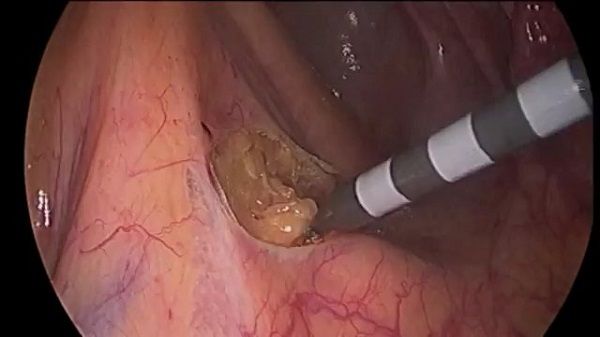
Excision of the polyp is carried out by crossing its pedicle, if the polyp has one. If it is located on a wide base, excision with an oval incision is practiced.
The disadvantage of this method is the high risk of bleeding, which can be reduced by additional procedures, in particular vascular coagulation and suturing.
Polyp in the intestines: removal or not?
After detecting a small polyp, doctors may resort to watchful waiting. Its essence lies in dynamic control over the size of the tumor and influence on symptomatic manifestations.
- If the polyp does not exceed 1 cm, does not disturb the patient’s condition, or does not affect the functionality of the intestines, then periodic examinations of the tumor are carried out after a certain period of time.
- If the growth remains stable, does not grow, its structure does not change, and new polypous foci do not appear, then the operation is postponed.
The key criterion for the need for removal is considered to be any change in polypous lesions.
Such changes are the main indications for removal:
- Hidden and obvious bleeding (up to the development of anemia);
- Symptoms of obstruction due to a growing polyp;
- Deterioration of intestinal motility in the area of the polypous lesion;
- Constipation, diarrhea, stool instability;
- Copious discharge of mucous secretion from the anal canal;
- Pain during defecation, in the peritoneal area.
Doctors also take into account the psychology of patients. Having heard the news about the stability of the pathological growth and the absence of a threat to life, many forget about the recommended regular examinations. They often seek help at an advanced stage of cancer or with serious symptoms, when emergency intervention is required. In this case, doctors warn patients about the danger and recommend timely removal. What will happen if you do not remove the polyp in the intestines? Read more here.
Unfortunately, conservative medicine is ineffective in treating polyps, and therefore no traditional medicine methods or medicine for intestinal polyps can completely cure the intestinal mucosa. At best, such tumors will decrease slightly in size.
Preparing to remove rectal polyps
Before removal of rectal polyps, patients are advised to follow a special diet that excludes fiber-rich foods to reduce intestinal volume. The day before the treatment, it is recommended to drink more water and use a cleansing enema to completely cleanse the intestines of feces. Your doctor may also recommend taking laxatives. To do this, you can use regular enemas, or special medicinal ones: Microlax, Enema wedge. Sometimes, to completely cleanse the colon, the doctor may recommend taking special laxatives - Fortrans, Lavacol, Endofalk.
Preparatory stage
Before the procedure, it is necessary to remove all remaining food from the intestines. This is achieved in several ways:
- Two days before the operation, nutrition is carried out on a slag-free diet.
- You need to take castor oil one day before.
- Before going to bed, an enema is done with two liters of water.
- On the morning of the procedure, 3 enemas are given with a half-hour break. It is strictly forbidden to eat food. 1 glass of tea or juice is allowed.
- Cleansing with laxatives. It is selected by the attending physician based on the individual characteristics of the body. It is not recommended to choose on your own.
It is worth preparing under medical supervision to control the body’s reaction. Preparation requires attention; violation of recommendations will lead to complications during surgery.
Postoperative period
Complete restoration of the mucosa after removal of a polyp in the rectum occurs after 2 or more weeks, depending on the type of procedure used. During this period, it is necessary to follow a special diet that will help prevent constipation.
Also, during the recovery period, it is not recommended to drive a car, lift heavy objects, or eat irregularly and in large portions. It is worth excluding spicy and salty foods, as well as alcohol, from the menu. In the first week after surgery, it is recommended to exclude vegetables and fruits from the menu - they contain coarse fiber, which can injure the unhealed mucous membrane. Preference should be given to slimy soups and porridges.

The onset of complications may be indicated by:
- bleeding from the rectum;
- vomit;
- dizziness and general weakness;
- temperature increase;
- swelling and/or pain in the legs;
- cough.
If they appear, it is recommended to immediately consult a doctor.
Features of the diet after surgery
Special dietary nutrition after rectal surgery completely determines the effectiveness of the rehabilitation process. The time frame for restoration of damaged intestinal mucous tissue depends on certain diet rules, changes in which must take place in stages.
Immediately after surgery, the patient should be on a “starvation diet” for 24 hours. Only after such an interval can you take a couple of sips of water (up to 50 ml), dried fruit compote (without sugar) or vegetable broth. After a 12-hour break, the first meal is allowed. The diet may consist of a small amount of weak meat broth, rice water, jelly, or rosehip infusion.
Such “strictness” is due to the need to eliminate intestinal peristalsis as much as possible (contraction of the intestinal walls to move food through it) and reduce their enzymatic functions (secreted digestive enzymes and bile can have a detrimental effect on damaged tissues and sutures).
- If the patient’s condition is normal, on the third day after removal of the polyps, the diet can be expanded to include: liquid porridges (rice, oatmeal, millet), soufflés made from lean meats, and soups with a mucous consistency. At the same time, the patient's condition must be monitored. If there are signs of bloating or pain from the product that provoked these symptoms, you should refuse. The load on the intestines should occur gradually. The main thing is to restore normal stool.
- For the next 4 months, the patient should adhere to a light diet. And adhere to certain rules.
Benefits of laser removal
Laser removal of anal polyps has several significant advantages:
- Simultaneous antiseptic treatment of the wound surface: coagulation of blood vessels, antimicrobial effect of the laser beam. This eliminates bleeding, inflammatory processes, and reduces the likelihood of infectious complications.
- Speed of intervention: the operation will take less time than intervention with a scalpel.
- Low-traumatic: when exposed to laser, healthy areas of the mucous membranes are not affected, and the ability to regulate the depth of penetration of the beam eliminates damage and burns.
- The ability to remove several polyps at once in one operation.
How to recognize a polyp
In most cases the disease is asymptomatic, but some patients may experience certain symptoms, e.g.
- pain - aching, bursting, cramping, localized in the lower or lateral part of the abdomen; after defecation, the intensity of the manifestations weakens or disappears;
- digestive dysfunction - constipation alternates with diarrhea;
- mucus or blood in the stool - this sign is characteristic of villous polyps located in the lower intestines.
Large polyps can block the intestinal lumen, which causes intestinal obstruction. The patient experiences intense pain, nausea, vomiting, lack of stool and passing gas. With this development of events, the patient needs urgent help from a surgeon.
To determine the type of polyp, its location and indications for surgery, as well as select the correct surgical treatment tactics, you must send me a complete description of the colonoscopy, histology data, and, if possible, MSCT data of the cavity with contrast, by email to my personal email address, indicate your age and main complaints. Then I will be able to give a more accurate answer to your situation.
What the patient needs to know
- Maintain a consistent diet. This stabilizes digestive processes and regenerative (restorative) intestinal functions.
- Frequent (up to 5 times) food, divided into small portions, helps improve intestinal motor functions and reduces the load on it.
- Some foods promote fermentation processes, which can cause the development of inflammatory processes in the peritoneum (peritonitis). The following items are prohibited: products with nuts, dishes with mushrooms and asparagus.
- To prevent delays in bowel movements (the development of constipation), the diet must include liquid dishes (first courses, jelly, compotes, teas, decoctions, etc.) - up to 3 liters of the total daily volume.
- A delay in regenerative processes occurs due to excessive secretion of bile, which is caused by the presence of fatty foods in the diet. It must be excluded.
- Protein foods contribute to tissue restoration - dishes with the addition of eggs, lean meat, and dairy products.
- Prepared dishes should be well baked or boiled, since rough food can injure already damaged intestinal walls.
An important aspect of the diet is the exclusion from the diet of foods that contribute to intestinal irritation (fried foods, spicy or sour).
Not a single, even brilliantly performed surgical intervention on intestinal polyps guarantees complete relief from the pathology. The main aspect is the prevention of relapse of pathology. The patient should know that treatment does not stop there and he must be under constant medical supervision.
0 0 vote
Article Rating