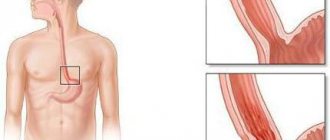
Treatment of sphincter of Oddi dysfunction
The sphincter of Oddi is a smooth muscle valve (orbicularis muscle). It regulates the flow of digestive enzymes from the pancreas and bile from the gallbladder into the duodenum. From ancient Greek, the term “sphincter” means “I squeeze.” Named after the Italian anatomist and physiologist R. Oddi. The scientist was the first to describe the physiological properties and structure of this valve. When its functions are disrupted, a person begins to suffer from indigestion and constantly feels heaviness in the abdomen.
Etiology and provoking factors
Dyskinesia of the sphincter of Oddi of the pancreatic type develops in patients due to pathological stenosis (persistent narrowing) of the sphincter or the pathogenesis is caused by impaired contractions. Pathological narrowing develops due to the inflammatory process, fibrosis, and in some clinical pictures the cause is the probable proliferation of the mucous membranes.
Inflammatory and fibrotic changes are a direct consequence of the influence of small stones that pass through the common bile duct. There is a theory according to which inflammatory transformations provoke an exacerbation of the chronic form of pancreatitis.
The separation of functional and organic disorders is quite complex, since two abnormal conditions may have the same primary source. Dysfunction is mostly detected in patients who have a history of gallbladder excision. Patients are diagnosed with insufficiency of the sphincter of Oddi, as a result of which bile continuously enters the lumen of the duodenum.
If a person is in good health, then under the influence of neuropeptide hormones the gallbladder should contract, bile penetrates the duodenum, and the sphincter of Oddi relaxes. When the gallbladder is removed, excessive sphincter tone and pathological enlargement of the bile ducts can be observed.
In some situations, after surgery, the tone decreases, so incompletely formed bile enters the gastrointestinal tract. As a result, infection of the fluid occurs, leading to severe inflammation.
Biliary-pancreatic syndrome leads to a disorder of the process during which bile repeatedly and continuously enters the intestines, as a result, a person begins to experience various symptoms of impaired digestive processes.
If bile enters the intestines irregularly, this is manifested by the following clinic:
- Disorder of enterohepatic circulation of bile acids;
- Failures in the process of digesting food, decreased absorption of nutrients;
- The bactericidal properties of duodenal contents are reduced.
A provoking factor in the development of dyskinesia is a hormonal imbalance associated with pregnancy, menopause, and the use of hormonal medications. Also chronic stress, diabetes mellitus, pathologies of the pancreas, duodenum, impaired liver function, surgical interventions in the area of the biliary tract and stomach.
What is it - sphincter of Oddi: anatomy and functions
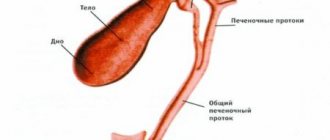
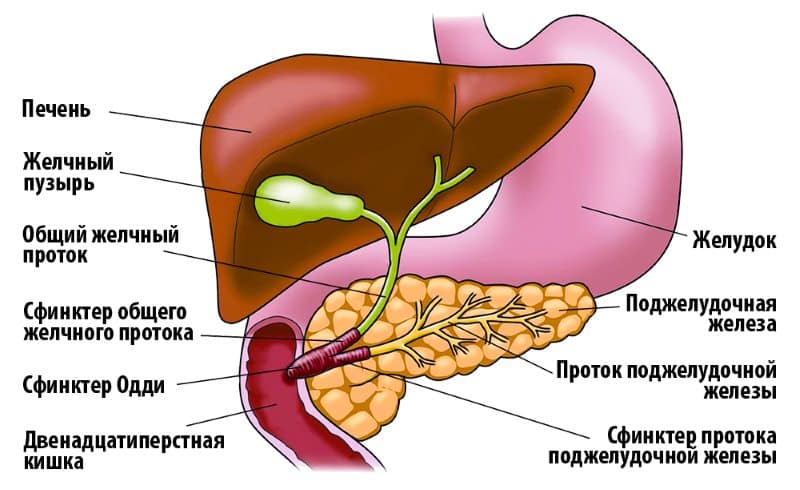
To understand the location of the sphincter, you need to know the structure of the duodenum. On its descending part, inside, there is the papilla of Vater (large duodenal). There is a shut-off valve inside it. Excretory ducts open from the bile and pancreas into the papilla of Vater. The purpose of the sphincter is to allow pancreatic juice and bile into the intestines only when the body needs to digest food, and also to prevent intestinal contents from entering the common bile and pancreatic canal.
The sphincter consists of three parts:
- The first is the rim of the end of the bile duct.
- The second one surrounds the end section of the pancreatic canal.
- The third - covers the terminal section of the common duct.
The valve of Oddi is formed from multidirectional muscle fibers and connective tissue. Due to the contraction of the muscle structure, the common duct into the initial section of the small intestine closes and opens.
What is the sphincter of Oddi?
In 1681, the first described the sphincter of Oddi. This was done by the British doctor Francis Glisson, but the sphincter received its name thanks to the Italian scientist Oddi Ruggiero. It was he who published scientific works on the morphological structure in 1888, and also for the first time carried out manometry of the biliary tract.
Also, the Italian physiologist was the first to describe the dilation of the main duct after resection of the gallbladder (cholecystectomy).
The sphincter of Oddi is located in the major duodenal papilla. In appearance it is a smooth muscle, the functionality of which is to regulate the flow of pancreatic juice and bile into the duodenum. It also prevents contents from the duodenum from entering the ducts.
Classification of sphincter of Oddi dysfunctions
Malfunction of the valve of Oddi is an acquired disorder of its motility, which is classified into stenosis (swelling, narrowing) and primary functional dyskinesia (improper contraction). In both cases, the pathology leads to the uncontrolled flow of bile and pancreatic secretions into the duodenum.

With timely initiation of pharmacotherapy, the symptoms of sphincter of Oddi dysfunction are leveled out in a short time. The effectiveness of invasive treatment methods exceeds 90%.
Primary and secondary dysfunction can be caused by the same factors.
Due to illness
Pathological disorder of smooth muscle valve motility in some people occurs due to precursor diseases. The cause of secondary Oddi dysfunction can be recurrent pancreatitis, inflammation of the walls of the gallbladder, small stones in the bile ducts.
According to functional status
Smooth muscle valve insufficiency is divided into:
Sphincter hypertonicity occurs when spasm engulfs muscle fibers. Pathology leads to increased pressure in the duct system. This makes it impossible for the required amount of bile and digestive enzymes to enter the duodenum. Hypofunction, on the contrary, is characterized by a strong relaxation of the sphincter muscle fibers, which leads to the uncontrolled flow of hepatic and pancreatic secretions into the intestines.
According to Roman criteria
The Rome Agreement of 1999 provides for three violations of the biliary type (relating to the liver and bile) and 1 violation of the pancreatic type (pathology related to the pancreas and its secretions). In biliary conditions there are:
- Type I - recurrent moderate or severe pain on the right under the ribs, in the epigastric region. Lasts at least 20 minutes. Dilation of the common duct, slow release of contrast on X-rays, and a 2-fold increase in the number of liver enzymes are diagnosed.
- Type II is a classic pain syndrome for a biliary attack (radiates to the back). Increased liver enzymes or delayed contrast release during special x-ray diagnostics.
- Type III - isolated pain without other symptoms.
The pancreatic type is characterized by pain on the right under the ribs and increased levels of digestive enzymes.
Sphincter of Oddi: its role in the body
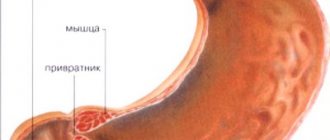
There are three main sections of the sphincter:
- Segment of the common bile duct.
- Pancreatic duct segment.
- The ampulla surrounding the confluence of the bile duct and the pancreatic duct.
What is the sphincter of Oddi used for?
- Control of the flow of bile and pancreatic juice into the duodenum.
- Prevents the development of reflux of duodenal contents into the common bile or pancreatic duct.
- Guarantees the accumulation of hepatic bile in the gallbladder.
Symptoms of the disease
Signs of sphincter spasm are the following clinical conditions:
- Repeated half-hour pain on the right side under the ribs or in the epigastric region. During a painful attack, pain occurs in the area of the shoulder blade or spreads to the back. Does not disappear after taking analgesics or changing body position. Painful sensations are accompanied by nausea and bouts of vomiting.
- 2-3 hours after eating fatty foods, a person experiences a feeling of heaviness and pain in the right side. Pain syndrome often occurs at night.
Any pathology of the hepatobiliary system (liver, gall bladder, ducts) provokes a condition in which changes occur in the composition of the intestinal microflora. This leads to an inflammatory process in the intestines.
Diagnostic methods
Sphincter of Oddi dyskinesia is diagnosed based on research results.
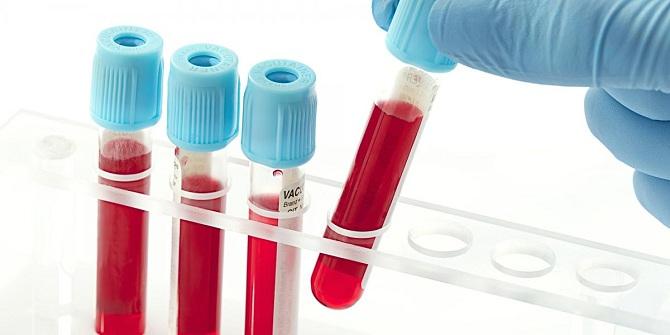
To determine the presence of sphincter dysfunction, doctors prescribe a laboratory blood test, which is performed during the pain syndrome or within 6 hours after it.
The most effective diagnostic methods:
- Laboratory blood test - used to study the activity of digestive enzymes. The method helps determine whether bilirubin levels are elevated, which would indicate abnormal liver function.
- Computed tomography allows you to see how dilated the bile duct, pancreatic or common duct is.
- Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) helps evaluate valve function. Diagnosis of sphincter dysfunction is carried out using a contrast agent and an optical device (duodenoscope).
- Endoscopic manometry is prescribed to determine the pressure in the common duct and assess the motor activity of the valve.
Diagnostics
- Clinical studies do not provide a complete, reliable picture and are not sufficient to make an accurate diagnosis.
- Laboratory tests provide reliable information only immediately after or after the pain syndrome.
- Non-invasive tests - use ultrasound to determine the size of the bile or pancreatic duct.
- Hepatobiliary scintigraphy - determines how long it takes the isotope with bile to travel from the liver to the duodenum.
- Invasive methods - endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) - can reject other diagnoses.
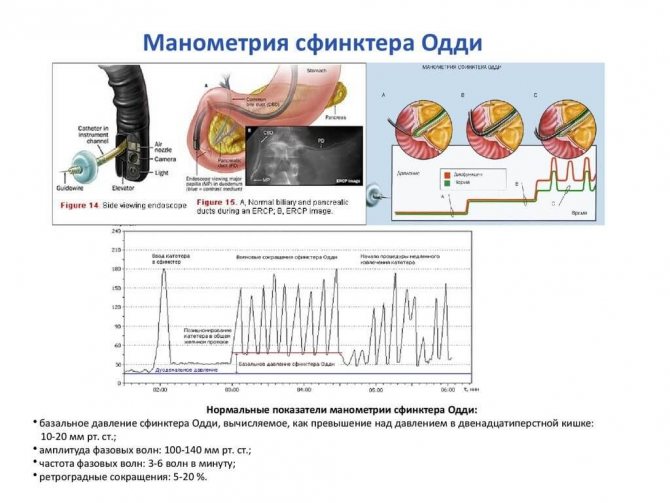
Endoscopic manometry of the sphincter of Oddi is recognized as the most accurate method - sphincter pressure is measured using a catheter. Based on the obtained indicators, an accurate clinical picture is formed.
Treatment methods
Treatment of sphincter of Oddi dysfunction is carried out on an outpatient basis. Patients with severe pain are hospitalized to rule out complications and undergo further examination. Therapy for Oddi valve dysfunction is aimed at relaxing its smooth muscle structure, eliminating pain and normalizing the outflow of pancreatic and hepatic secretions.
Diet therapy
For dysfunction of the sphincter of Oddi, dietary nutrition is indicated. Fatty, fried foods, spicy dressings, smoked foods and pickles are excluded from the patient’s menu. Fresh vegetables and fruits are prohibited; they are consumed only after heat treatment. Allowed products are prepared by steaming, boiling or baking. Meals are fractional, the patient should eat up to 7 times a day, but in small portions.
In addition to an unhealthy diet, spasm of the sphincter of Oddi can be caused by smoking. Doctors recommend that their patients either give up cigarettes completely or reduce the amount they smoke per day.
Drug treatment
Disorders of the Oddi valve, including mixed type DSO, are eliminated with the help of the following drugs:
- Nitroglycerin, Nitromax - relieve attacks of pain.
- Akineton, Parkopan - relieve muscle spasms, relax the sphincter.
- No-shpa, Papaverine - are prescribed to relieve pain and spasms throughout the body.
- Mebeverine, Niaspam - indicated for increased tone of the valve of Oddi.
- Gimecromon, Odeston - provide a choleretic effect, normalize the functioning of the sphincter muscles.
- Ursofalk, Ursosan - improve the functioning of the biliary system.
When biliary pathology is complicated by a bacterial infection, the patient is prescribed antimicrobial drugs (Enterofuril, Rifaximin). To normalize intestinal functions, the drug Hilak Forte is prescribed.
Operation
If drug therapy fails, the sphincter can be treated surgically:
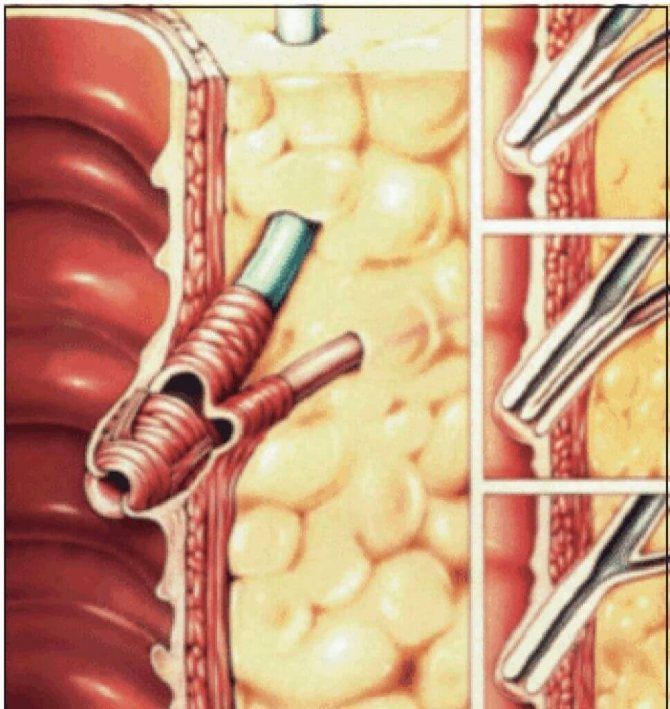
- Endoscopic papillosphincterotomy. The method involves incision of the papilla of Vater with a single-edged loop-shaped instrument, which is necessary for the outflow of bile and the establishment of sphincter function.
- Endoscopic dilatation of the duct. It is carried out through the introduction, followed by removal, of a special cylinder. It widens the duct to accommodate a stent (a thin metal tube).
Massage
Folk remedies
It is impossible to restore the functioning of the biliary system using folk remedies alone. Doctors recommend using them as auxiliary ones.
Corn silk infusion
How to prepare: pour 20 g of raw materials into a thermos, pour a glass of boiling water, strain after 1 hour.
How to take: 40 ml during the day. The course of treatment can last 1-3 months.
Result: the infusion provides a gentle choleretic and anti-inflammatory effect.
St. John's wort decoction
How to cook: 1 tbsp. l. Brew dry St. John's wort herb with a glass of boiling water, bring to a boil over medium heat, strain after 1 hour.
Sphincteritis, fissure and itching of the anus
Sphincteritis
– inflammation of the sphincter of the hepatic pancreatic ampulla (sphincter of Oddi). More often it occurs secondarily as a complication of cholelithiasis, chronic cholecystitis, cholangitis, and after surgery on the biliary tract (due to technical errors in their implementation). Less commonly, it is a consequence of hypertonicity and prolonged spasm of the sphincter of Oddi of a functional nature or occurring reflexively in chronic pancreatitis, doudenitis, or duodenal ulcer. The development of sphincteritis is accompanied by impaired function of the sphincter of Oddi, difficulty in the entry of bile and pancreatic secretions into the duodenum, and increased pressure in the bile and pancreatic ducts.
Clinical manifestations are not specific.
There are paroxysmal (like hepatic colic) or constant aching pain in the right hypochondrium and (or) in the epigastric region, intensifying after eating, nausea, vomiting of bile, bitterness in the mouth; jaundice develops, which is transient in nature, which is accompanied by itching, darkening of urine, and discoloration of feces; with concomitant cholangitis, fever and chills appear.
Long-term sphincteritis leads to cicatricial stenosis of the major duodenal papilla, resulting in persistent obstructive jaundice, cholestatic hepatitis, and chronic recurrent pancreatitis.
Treatment
aimed at eliminating inflammation and spasm of the sphincter of Oddi, improving the outflow of bile. Antibacterial, spasmodic and choleretic agents are used. If conservative treatment is ineffective and cicatricial stenosis of the major duodenal papilla develops, surgical intervention is resorted to.
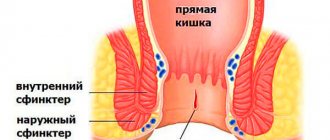
Crack in the anus.
An anal fissure is a rupture of the linear, triangular or oval shape of the rectal mucosa. The crack can be small, up to 1 cm in length and located near the anus, or it can extend into the anal canal. A single defect is more common - along the back wall. But sometimes there are two – in this case they are located opposite each other (“mirror” or “kissing” cracks).
Causes of anal fissures.
An anal fissure very often appears due to mechanical trauma to the mucous membrane with very dense feces (constipation), in the presence of undigested sharp particles in the feces (for example, sunflower seed husks), and during rough anal sex without the use of lubricants. Diarrhea can also cause anal fissure.
Often an anal fissure occurs against the background of gastritis, enterocolitis, cholecystitis, and peptic ulcers of the gastrointestinal tract. But most often anal fissure is accompanied by hemorrhoids.
Symptoms.
Only a proctologist or surgeon can correctly diagnose this disease. Pain in the anal area is intense and continues for several hours after defecation (or attempted defecation). However, such pain can also occur with hemorrhoids, inflammation of the rectum, paraproctitis and fistula.
(“Posterior Crack”).
An anal fissure (“anal fissure”) is a minor defect in the mucosa at the very beginning of the anal canal. The length of this defect rarely exceeds 1 cm. The disease seems to be “small”, but the problems are quite serious. The main symptom of this disease is pain and blood during or after bowel movements. The intensity of pain in some cases may be insignificant, but more often it is quite strong, lasting from several minutes to several hours after stool. Sometimes the pain is so strong that it causes fear. And the fear of stool makes you use all possible means to “delay” or delay defecation.
Causes of anal fissure.
There are many reasons that cause anal fissure (fissure in the anus): constipation, diarrhea, heavy physical work, prolonged sitting, eating spicy food, alcohol, anal sex, etc.
Often an anal fissure occurs against the background of gastritis, enterocolitis, cholecystitis, and peptic ulcers of the gastrointestinal tract.
The reason for severe pain with anal fissure is that a small wound in the anal canal causes a strong spasm of the anal sphincter (the main muscle that holds feces). The spasm, in turn, causes pain and does not allow the crack to heal. A “vicious circle” arises. This explains the duration of the disease and the difficulties in its treatment. If the duration of the disease is up to 1 month, we are usually talking about an acute fissure. After this period, the fissure usually becomes chronic with the formation of external and internal (in the anal canal) tubercles. This is important to know because acute anal fissure can be treated with conservative methods. It is almost impossible to cure a chronic fissure using a conservative method.
Treatment of acute anal fissures.
Patients with acute anal fissure can be treated conservatively. Spicy foods and alcohol are excluded. First of all, it is necessary to improve the functioning of the intestines, to “soften” the feces in order to minimize injury to the anal canal and the fissure itself. For this purpose, it is good to use the so-called before the chair. “counter” oil microenemas (50g sunflower oil + 150g warm water in a 200ml enema bulb for 10-15 days). This method, unlike laxatives, allows you to soften the lowest lump of feces, which most traumatizes the fissure. Laxatives can also be used.
Thermal procedures of all types are very useful: warm sitz baths, heating pads on the perineum. Heat relaxes the muscles, thereby reducing sphincter spasm and pain subsiding. There is a belief that the specific gravity of heat as a healing factor for cracks is higher than that of ointment candles. Therefore, immediately after bowel movements and perineal hygiene, the patient takes a warm bath for 20-30 minutes, which it is advisable to repeat in the evening. After the bath, candles are used, the choice of which is wide today. Suppositories are usually administered 2 times a day, morning and evening. It is important to know the general rule: before use, it is advisable to knead the candle in your hands and, after inserting it into the anus, do not immediately push it, but hold it at the level of the anus for 2-3 minutes and only then push the rest of the candle into the anal canal.
Treatment of chronic anal fissures.
For patients with chronic anal fissure, it is better to have surgery immediately. Conservative therapy, even in combination with blockades, can relieve exacerbation and reduce pain, but the effect is usually temporary. Constipation, heaviness, and feasting provoke another exacerbation, “knocking out” a person for 2-3 weeks.
Surgical intervention in the classical version involves excision of the crack, etc. sphincterotomy. The latter means partial dissection of the sphincter in one way or another in order to relieve sphincter spasm in order to relieve sphincter spasm. Otherwise, the crack will take a very long time to heal or may not heal. But sphincteromy itself does not completely relieve the spasm and leads to a relapse of the disease, and excessive sphincteromy can lead to insufficiency (weakness) of the anal sphincter.
What is sphincter of Oddi dysfunction?
Not everyone knows the location of the sphincter of Oddi, formed by connective tissue elements and muscle fibers. This structural element surrounds the end sections of the ducts of the gallbladder and pancreas, which allows you to regulate the release of digestive secretions, prevents the reflux of intestinal contents into the organs, increases the pressure in the duct, and accelerates the filling of the gallbladder.
Dysfunction of the sphincter of Oddi occurs when the tone of the organ increases, so the ducts expand, and unregulated secretion into the duodenum is noted. In this case, the concentration of bile may not reach normal values, which provokes infection and the development of symptoms of inflammation.
As a result, the following violations occur:
- Changes in the composition of intestinal microflora;
- Intestinal secretions lose their bactericidal activity;
- The process of breakdown and absorption of fats is disrupted;
- The normal circulation of fatty acids is altered.
Sphincter of Oddi insufficiency occurs when the organ loses its ability to maintain pressure. In such situations, bile secretion is continuously released into the intestinal lumen, which provokes the development of hologenic diarrhea. Over time, this pathology provokes damage to the intestinal mucosa and stomach, which causes the appearance of dyspepsia.
Functioning of the sphincter of Oddi
The sphincter of Oddi helps to increase pressure in the common bile duct. The tone of the sphincter of Oddi outside of digestion is increased, which limits the release of bile into the intestine.
During the period of activity of the stomach and duodenum, the sphincter of Oddi works as a fast pump, ensuring the release of bile in a continuous stream with a duration of several seconds to 1 minute. In the resting phase, the release of bile into the duodenum also occurs, but sporadically, approximately 18 drops per minute.
The sphincter of Oddi, being in a state of activity almost all the time, makes slow movements, as if squeezing out bile and passing it into the duodenum (working like a slow pump).
In healthy people, the basal pressure of the sphincter of Oddi is 10-40 mmHg. Basal pressure values above 40 mm Hg. Art. are considered pathological.
Causes of pathology
Spasm of the sphincter of Oddi is an acquired disease, the main cause of which is muscular dyskinesia. The following factors provoke the pathological condition:
- Changes in the composition and rheological characteristics of bile;
- Passage violation;
- Intestinal dysbiosis;
- Surgical interventions;
- Structural changes in the sphincter that provoke the development of stenosis;
- Duodenitis.
Diseases of the gallbladder and sphincter of Oddi occur in patients at risk:
- Women during menopause, pregnancy, during treatment with hormonal drugs;
- Asthenic people;
- Development of emotional lability in young people;
- People whose work or life involves frequent stress;
- Patients after cholecystectomy (removal of the gallbladder);
- Patients with a history of diabetes mellitus;
- People with pathologies of the hepatobiliary system;
- Patients who underwent surgical treatment of the digestive organs.
There is this connection and the connection is very close!
The sphincter of Oddi is a circular layer of muscle. This layer is located in the very terminal section of the common bile duct. More precisely, exactly in the place where the common bile duct flows into the duodenum.
When the sphincter of Oddi muscles contract, they close the exit of the duct. And when they relax, the exit opens.
That is, the sphincter of Oddi is the guard that stands at the door from the bile ducts to the intestines. And it is this guard who “decides” when to let the flow of bile into the duodenum and when to stop this flow.
From the above, it becomes clear that the location of the sphincter of Oddi should be somewhere on the border between the bile ducts and the intestines, isn’t it?
Gastroenterologists in Moscow
Gastroenterologists of the Moscow region
Detailed information about each doctor, photo, rating, reviews, quick and convenient appointment.
This is where it is located - in the place where the common bile duct flows into the duodenum.
And, imagine, it’s not at all difficult to see it here. And all because in this place on the wall of the intestine there is a tubercle called the nipple of Vater!
As you can see, these tiny formations are closely related to each other!
Good functioning of the Vater nipple and sphincter of Oddi is very important for any person. But for a person who has undergone surgery to remove the gallbladder, it is doubly important. Because a person’s well-being after surgery depends on their behavior, on how quickly they can adapt to the current situation. Will there be pain? Will he be able to eat normally?
Types of pathology
According to the modern classification, dysfunction of the sphincter of Oddi can take the following forms:
- Biliary type I. This usually includes disorders that provoke the occurrence of severe pain in the right hypochondrium. The duration of attacks does not exceed 20 minutes. ERCP reveals a decrease in the rate of removal of contrast, the following indicators increase: AST, alkaline phosphatase;
- Biliary type II. With this form of dysfunction of the sphincter of Oddi of the biliary type, characteristic painful sensations appear, 1-2 symptoms characteristic of type I pathology;
- Biliary type III. Only pain syndrome appears, there are no other symptoms.
- Pancreatic type. Spasm of the sphincter of Oddi causes pain in the epigastric region, which radiates to the back. Painful sensations decrease while bending the body forward. An increase in amylase or lipase is characteristic.
Clinical picture
Spasm of the sphincter of Oddi is characterized by the development of severe recurrent pain syndrome, which is localized in the area of the right hypochondrium, epigastrium. The pain usually radiates to the back or right shoulder blade. The duration of pain rarely exceeds 30 minutes. The pain syndrome can have varying intensity and often brings suffering to the patient.
Pain syndrome is often accompanied by the following symptoms:
- Nausea and vomiting;
- Bitter taste in the mouth;
- Belching air;
- There may be a slight increase in body temperature;
- The appearance of a feeling of heaviness.
The listed symptoms usually worsen after eating fatty and spicy foods.
Clinical symptoms of sphincter of Oddi dysfunction include:
- Increased liver enzymes;
- Slowing down the evacuation of contrast agent during ERCP;
- Expansion of the common bile duct.
Often dysfunction develops within 3-5 years after cholecystectomy. In this case, patients note an increase in pain, which is associated with the removal of the bile reservoir.
Important! The pain usually develops at night and cannot be relieved by taking painkillers or changing body position.
Symptoms and consequences of hypertonicity of the sphincter of Oddi
Dysfunction of this valve leads to diseases of the liver, gall bladder, pancreas, intestines and disorders throughout the digestive system. Digestion and assimilation of food does not occur properly or is impossible at all, depending on the form of hypertonicity and its degree.
Malfunctions of the sphincter of Oddi are classified into three biliary types and one pancreatic type, associated with the liver and pancreas, respectively.
Due to dysfunction of the sphincter of Oddi, the following diseases and conditions occur:
- cholecystitis;
- pancreatitis;
- duodenal ulcer;
- diarrhea;
- nausea and vomiting;
- pain in the epigastric region that lasts more than 20 minutes and occurs several times a day;
- fever;
- loss of appetite, vomiting when eating food, etc.
Diagnostic measures
To determine the presence of sphincter dysfunction, doctors prescribe a laboratory blood test, which is performed during the development of pain or within 6 hours after it. This reveals elevated levels of amylase and lipase, aspartate aminotransferase, alkaline phosphatase and gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase.
Clinical symptoms may indicate the development of other diseases of the digestive tract caused by obstruction of the bile ducts. Therefore, the following instrumental diagnostic methods are widely used to confirm the diagnosis:
- Ultrasound. The scan is carried out while taking provocative agents, which makes it possible to assess the exchange of ducts. If normal values increase by 2 mm, incomplete blockage of the bile ducts can be suspected;
- Cholescintigraphy. The method allows you to determine sphincter motility disorders by the speed of movement of the injected isotope from the liver to the upper intestine;
- Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP). The technique involves the introduction of duodenoscopes with lateral optics to assess the diameter of the ducts and determine the rate of their emptying;
- Manometry. The technique is based on the insertion of a triple-lumen catheter through a duodenoscope into the ducts to measure sphincter pressure.
Features of therapy
Treatment of sphincter of Oddi dysfunction involves relieving pain and other symptoms, normalizing organ motility and removing digestive secretions. With the development of inflammation and dysbiosis, it will be necessary to eliminate the bacterial infection and normalize the intestinal biocenosis. For this purpose, drug therapy, diet therapy, endoscopy and surgical treatment are widely used.
Drug therapy
The following groups of drugs are widely used to eliminate dysfunction:
- Nitrates (Nitrosorbide, Nitroglycerin). The drugs help reduce the severity of pain;
- Anticholinergics (Biperiden, Akineton) help eliminate muscle spasm;
- Calcium channel blockers relax the sphincter of Oddi. Often cause adverse reactions, so they are rarely used;
- Antispasmodics (Papaverine, Pinaveria bromide, Drotaverine) eliminate spasms and pain;
- Myotropic antispasmodics. Mebeverine reduces sphincter tone and smooth muscle mobility. Gimecromone eliminates spasms and has a pronounced choleretic effect;
- To eliminate bacterial infection and dysbiosis, intestinal antibacterial drugs (Rifaximin, Enterofuril, fluoroquinolones), prebiotics and probiotics (Lactulose, Bifiform, Hilak forte) are used;
- Products based on ursodeoxycholic acid (Ursosan, Ursofalk) can eliminate biliary insufficiency.
Medical nutrition
Effective treatment of diseases of the digestive tract is impossible without following a special diet. If the sphincter of Oddi is malfunctioning, nutritionists recommend completely abstaining from fatty, spicy foods and fast food. The dishes consumed should be enriched with coarse fiber, which helps to normalize the motility of the digestive organs.
You should avoid eating fresh vegetables and fruits - the products must undergo heat treatment. Dishes should be boiled, stewed, baked, steamed. The daily diet should be divided into equal 6-7 servings, which are recommended to be taken every 3-3.5 hours.
Important! Having a late dinner just before bedtime helps avoid bile stagnation.
Traditional medicine recipes
To increase the effectiveness of drug therapy, you can be treated with folk remedies. However, the use of traditional medicine recipes is possible only after consultation with a specialist. To normalize the functioning of the sphincter, the following medicinal raw materials are widely used:
- Corn silk. The plant is used to treat numerous pathologies of the hepatobiliary system. The raw material has pronounced choleretic and anti-inflammatory effects. To prepare the infusion, simply pour 20 g of corn silk into 200 ml of boiling water and leave the mixture for 1 hour. The product is taken 40 ml up to 5 times a day;
- St. John's wort herb. The raw materials are used to normalize the functioning of the liver and gall bladder, and to treat dyskinesia. To prepare a decoction, simply grind 1 tablespoon of the raw material and pour 250 ml of boiling water over the resulting mixture. The product is brought to a boil in a water bath and left for 1 hour. The decoction is taken 50 ml up to 3 times a day;
- Immortelle flowers. The plant is widely used to treat bile stagnation, hepatitis, and cirrhosis. To prepare the medicine, simply pour 2 tablespoons of crushed flowers into 250 ml of boiling water. The mixture is boiled for 10 minutes, cooled, and filtered. For the treatment of pathologies of the hepatobiliary system, it is recommended to take 50 ml of decoction 30 minutes before meals three times a day;
- Agrimony grass. Raw materials can alleviate acute and chronic hepatitis, cirrhosis, cholecystitis, and biliary dyskinesia. To prepare the infusion, simply pour 200 ml of boiling water into 1 tablespoon of crushed raw materials. The composition is infused for 2 hours, after which 100 ml are taken three times a day.
Endoscopic and surgical therapy
If conservative treatment does not bring positive results, then the following methods are used:
- Endoscopic papillosphincterotomy. The method involves dissection of the large duodenal papilla;
- Balloon dilatation of the sphincter with installation of temporary stents;
- Transduodenal sphincteroplasty;
- Injections of botulinum toxin into the area of the duodenal papilla. The therapeutic effect of the drug lasts for 3-4 months, after which the substance is completely eliminated from the body.
Treatment
Treatment of the disease begins with a visit to a specialist who, based on the patient’s complaints and conducting certain studies (ultrasound, manometry, cholescintigraphy), establishes an accurate diagnosis and selects an effective therapeutic regimen.
Reference. Therapy involves eliminating symptoms, normalizing organ motility and removing digestive secretions.
Treatment of functional disorders of the sphincter of Oddi of various origins includes the use of both conservative and surgical techniques (presented in the table below).
| Therapy | Techniques | |
| Conservative | Diet |
|
| Medicines |
| |
| Surgical |
| |
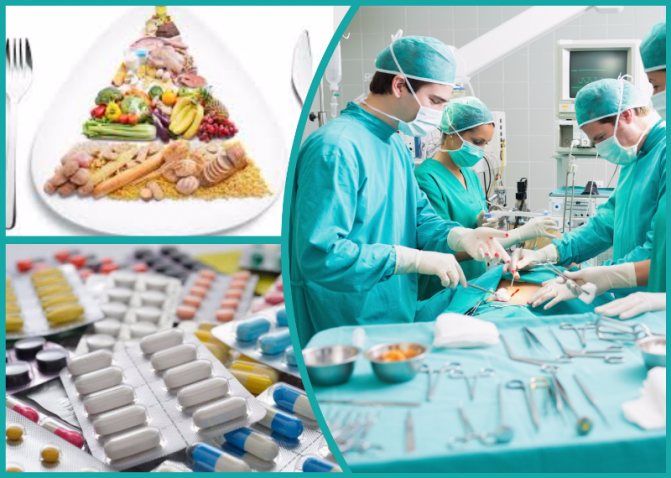

Main directions of treatment of dysfunction
It is worth noting that surgical intervention is resorted to only in situations where conservative therapy has proven ineffective.
Traditional treatment
To increase the effectiveness of official treatment, various non-traditional methods can be used as a supplement.
Treatment of the sphincter of Oddi with folk remedies involves the use of the following recipes:
Traditional treatment involves taking various infusions and decoctions
- St. John's wort decoction - normalizes the functioning of the liver, gall bladder, and eliminates dyskinesia. For cooking you need 1 tbsp. Steam a spoonful of herbs with a glass of hot water, bring to a boil and leave for an hour. Drink 50 ml 3 times a day.
- Corn silk tincture has anti-inflammatory and choleretic effects. Measure out 20 grams. raw materials and add 200 ml of water. Leave for 60 minutes. Drink 40 ml up to 5 times a day.
- Immortelle decoction (flowers) - used to eliminate stagnation of bile. Take 2 tbsp. Steam spoons of raw material with 250 ml of hot water, boil for 10 minutes, then cool and strain. Drink 50 ml half an hour before meals three times a day.
It is worth noting that treatment of sphincter of Oddi dysfunction with folk remedies should only be started with the permission of a doctor in order to avoid worsening the condition.
Forecast and preventive measures
Dysfunction of the sphincter of Oddi is characterized by a favorable prognosis. With adequate long-term conservative treatment, it is possible to completely eliminate the unpleasant symptoms of the disease.
There is no specific prevention of pathology. However, to prevent disturbances in the motility of the digestive organs, gastroenterologists recommend adhering to a balanced diet, maintaining optimal body weight, and exercising regularly.
The sphincter of Oddi is an important element of the hepatobiliary system. If its functioning is disrupted, serious pathologies of the digestive organs develop. Therefore, it is important to adhere to a healthy lifestyle, and at the first symptoms of pathology, seek help from a specialist.