Sudden onset diarrhea often does not pose a particular threat to health and goes away within a few days. However, there are cases when loose stools can be caused by very dangerous and serious diseases that require immediate treatment. Diarrhea with blood and mucus generally indicates a severe course of the disease.

What is diarrhea?
A person suffering from diarrhea experiences frequent loose stools. This condition may be accompanied by abdominal pain and an urgent urge. Diarrhea itself is not dangerous, but it can cause serious consequences, such as dehydration and imbalance of bacteria in the intestines.
With such an intestinal disorder, other symptoms sometimes occur, such as flatulence, vomiting, nausea, and increased body temperature. In addition to changes in the consistency and color of stool, blood, mucus, foam and pus may be observed in it. This condition signals the presence of a serious disease, which is often in the acute stage.
Causes of diarrhea with blood and mucus
Often, diarrhea in adults occurs due to fairly ordinary and non-serious factors:
- poisoning;
- stress, anxiety;
- alcohol abuse.
More severe conditions, when diarrhea, mucus with blood and general intoxication of the body begin, are observed with intestinal infections, diseases of the gastrointestinal tract (GIT) and other quite severe ailments. Next, we will take a closer look at the reasons that influence the occurrence of loose stools with mucus and blood.
Infectious bowel diseases
Dysentery
Dysentery or shigellosis is characterized by damage to the gastrointestinal tract (mainly the colon) and general intoxication of the body. The cause of this disease is bacteria that enter the body with dirty food and water. In addition, dysentery is a contagious disease that is also transmitted by contact from a sick person. Young children are more likely to suffer from this intestinal infection.
Basically, the disease is quite acute. It is characterized by the following symptoms:
- abdominal pain;
- the occurrence of diarrhea with mucus and blood;
- increased body temperature (38-39 ºС), chills;
- headache;
- weakness, lethargy, malaise;
- appetite worsens;
- blood, mucus and pus appear in the stool;
- blood pressure decreases.
Dysentery requires immediate treatment in a hospital. If the disease is left to chance, complications can develop, including death.
Amoebiasis
- heat;
- weakness;
- painful sensations in the abdomen.
Amebiasis is dangerous due to its complications. As the disease progresses, ulcers form on the intestinal mucosa, which sometimes leads to heavy internal bleeding. In some cases, a tumor (amoeba) may form, causing intestinal obstruction. The liver is also affected, up to an abscess.
Salmonellosis
Salmonellosis is an acute infectious disease of the gastrointestinal tract caused by Salmonella bacteria. The small intestine is mainly affected. Salmonellosis can be contracted through contact from a sick person or through food (for example, raw eggs, undercooked meat). The symptoms accompanying this disease are as follows:
- increased body temperature;
- headache;
- weakness;
- abdominal pain;
- frequent watery stools, which may contain foam with mucus;
- nausea;
- vomiting mixed with bile;
- bloating;
- streaks of blood mainly appear in severe forms if treatment is not started in a timely manner.
Sometimes the disease goes away and is asymptomatic. As a rule, this happens when a small amount of bacteria enters a strong body with good immunity.
Toxic infections
Foodborne illnesses are acute diseases caused by bacteria, which, in turn, contribute to the appearance of toxins. Most often transmitted from sick people and from animals through food (dairy and meat products). The symptoms of this disease are very similar to salmonellosis. There is an acute onset with nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, fever, chills. In some cases, inclusions of blood and mucus in the stool are observed.
Dysbacteriosis
Often, diarrhea with mucus and blood occurs after some gastrointestinal diseases, as well as as a result of treatment with strong antibiotics. Such drugs disrupt the intestinal microflora and contribute to the development of infections in the gastrointestinal tract. In this case, stool can be either mushy or watery with a large amount of mucus in it. In addition, nausea, bloating, and bad breath are observed.
Nonspecific ulcerative colitis
This disease is characterized by autoimmune inflammation of the intestinal wall, in which ulcers and scars appear on the mucous membrane. Diarrhea is mushy in nature with mucus, pus and blood. Fever, loss of appetite, and weight loss are also observed.
Principles of treatment of diarrhea with mucus and blood
After diagnosis, treatment should be started immediately. When serious illnesses, often of an infectious nature, occur, the patient is admitted to a hospital. The doctor prescribes therapy individually based on each case. Antibiotics and antibacterial drugs, as well as intestinal antiseptics, are often prescribed.
Diet
Regardless of the diagnosis, when treating diarrhea with blood and mucus, you should adhere to a gentle diet. It is recommended to consume astringent products with a high tannin content, such as strong tea, blueberries, persimmons, and pomegranate. Enveloping dishes with a viscous consistency (porridge, soups, jelly) will have a beneficial effect on the irritated mucous membrane of the gastrointestinal tract. You can also eat crackers, lean steamed or boiled meat and fish. It is strictly forbidden to consume alcohol, fatty, fried, spicy and sour foods.
To prevent dehydration, you need to drink a lot of liquid, both plain water and compotes, fruit drinks, and tea. You can also use special products that restore the water-alkaline balance in the body. The most famous of them: Regidron, Re-sol, Ionica. The powder is dissolved in water at room temperature and drunk in small sips.
Drug treatment
For diarrhea, it is also advisable to take sorbents. These substances absorb and remove waste and toxins from the body, improve the functioning of the stomach and liver. Sorbents include activated carbon, Enterosgel, Smecta, and the latter drug also absorbs bacteria and viruses.
When treating food poisoning, gastric lavage is often prescribed. This is a fairly effective remedy that can quickly remove harmful microorganisms from the gastrointestinal tract. For this procedure, use clean boiled water or a weak soda solution.
If diarrhea with blood and mucus occurs as a result of dysbiosis, the use of medications that normalize the intestinal microflora is indicated. These may be Linex, Bifidumbacterin, Bifikol and others. The same drugs are also prescribed for the prevention of dysbiosis during the use of a large number of antibiotics and during the period of intestinal infections.
To fix loose stools, you can also use folk remedies. However, it is worth remembering that they will not be effective if the underlying disease is not treated. The most well-known remedies for diarrhea include jelly and other decoctions with starch. Rice decoction, decoctions of astringent medicinal herbs (oak bark, chamomile, bird cherry).
Diarrhea, accompanied by blood and mucus in adults, is a rather serious condition.
Self-medication and treatment with folk remedies rarely bring results; moreover, the disease can worsen and lead to complications. This requires consultation with a specialist, timely treatment, often with medication, and compliance with all doctor’s recommendations. Published: October 27, 2020 at 03:34
pm Diarrhea is a fairly serious ailment that always occurs suddenly and disrupts a person’s usual quality of life due to the fact that it is accompanied by very frequent liquid bowel movements. In the case where stool liquefaction does not entail additional symptoms, an adult can cope with it on his own. But if there is mucus or blood in the feces, the situation becomes extremely dangerous. In this case, the help of a specialist is needed. This type of diarrhea can be caused by various reasons. The most common are hormonal disorders, ulcerative colitis, and infectious pathogens. But no matter the reason for diarrhea with mucus and blood, it requires immediate treatment.
Patients are often interested in where mucus comes from in the digestive organs and why is it excreted along with feces? Everything is simple here. The entire inner surface of the stomach and intestines consists of it, where it plays a protective function. Moreover, its additional production constantly occurs, which increases in any pathological conditions. In this case, it is visible to the eye in the stool. This is what happens with infectious inflammation of the intestines, when diarrhea is accompanied by blood impurities. Inflammatory diarrhea that occurs in this case is called hyperexudative.
How to help a patient
Loose stools and vomiting with nausea are symptoms of diseases of serious etiology. Added to the above symptoms are high temperature, feverish condition, and loss of strength. The body aches and the bones ache. What to do if symptoms are detected: go to an ambulance, call the doctor on duty.
Before a medical professional arrives, perform a gastric lavage procedure. A person is given one and a half liters of warm boiled water to drink. If there is no natural gag reflex, press on the root of the tongue until the stomach is completely empty of contents. The first need is to provide the patient with bed rest. Provide a personal plate, cup, and cutlery (shared utensils can infect others).
If vomiting and loose stools continue for more than three days, this is an alarming sign. To prevent rapid dehydration of the body, it is recommended to take a rehydron solution. You should drink in small, frequent sips, preventing the urge to vomit. After vomiting, bring a drink to the sick person every 20 minutes. Loss of fluid from the body leads to consequences such as:
- the sick person feels dizzy;
- mild weight loss occurs;
- there is a faint state in the morning;
- body aches appear;
- the temperature rises, then drops below normal.
After the doctor makes a diagnosis and identifies the causes of the disease, treatment should begin immediately. In case of a bacterial factor, the doctor prescribes antibiotic medication for diarrhea. If the cause of vomiting and diarrhea is pancreatitis, then the lack of digestive enzymes is compensated for by taking medications such as Festal.
The doctor prescribes taking absorbents that will collect toxins in the intestines. Sorbent drugs include: activated carbon, enterosgel, polyphepan, polysorb. The product absorbs toxic substances and removes them from the body.
Intestinal function resumes after diarrhea and vomiting if you strictly follow the doctor’s recommendations. To restore the natural microflora, a medicine containing bifidobacteria and lactobacilli will help. You cannot and should not cure the symptoms of the disease on your own. Your doctor will determine the appropriate treatment for nausea, vomiting and diarrhea.
Diet
In case of poisoning from overeating and after alcohol abuse, rinsing is done. Taking antiemetic medications helps control vomiting. Subsequently, a gentle diet is followed. The menu includes white crackers, slimy soups, jelly, and rice water. Fresh vegetables and fruits are prohibited. You can only eat bananas. After a day or two, boiled lean meats, poultry and fish are added. The first day, if possible, treat the patient with hunger.
To avoid abdominal pain, fatty, spicy, fried foods are removed from the usual diet. Fiber is the best food for provoking intestinal motility. You should not drink milk or sweet carbonated drinks: they simultaneously cause bloating and fermentation in the intestines.
The quality of feces, like the process of defecation itself, is an indicator of human health. Ideally, everything should happen every day, at approximately the same time, quickly and without causing discomfort.
Any inclusions in the stool - blood, mucus, undigested pieces of food - a change in color should alert the patient. If the temperature rises, vomiting occurs and the general condition worsens, self-medication and self-diagnosis are inappropriate.
Causes of diarrhea with blood and mucus
This type of loose stool is caused by internal ulceration of the intestine or hemorrhagic inflammation. It usually occurs with the following pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract:
All patients are interested in what actions need to be taken in case of this pathology? If a person’s diarrhea with mucus and blood does not stop for more than a day and there is pain in the abdominal cavity, urgent medical attention is needed. First of all, you should undergo appropriate diagnostics to identify the disease or infectious agent that provoked it. For this purpose, laboratory and instrumental studies are carried out.
If neither the disease that caused such symptoms nor the infection are identified, attention should be paid to nutrition. The cause of diarrhea with blood and mucus may well be expired or poor quality products. Also, due to the fact that with this pathology fluid is very quickly lost from the body, it should be replenished. In order to correct the disturbed water-salt balance, experts recommend taking carbohydrate-electrolyte solutions. You can prepare them yourself, or buy them without a recipe.
Everyone has experienced the intestinal disorder we know as diarrhea. A peculiarity of this condition is an increase in the release of liquid feces that are uncontrollable. Basically, diarrhea is an indicator of intestinal disease. Diarrhea with blood in an adult is of particular concern, the causes of which we will consider.
Diarrhea manifests itself as frequent loose stools, accompanied by bloating, transfusion in the peritoneum, and pain. This phenomenon is characterized by increased peristalsis, which is why the movement of masses through the intestinal tract accelerates. Also, with diarrhea in the large intestine, the absorption of water is impaired and a large amount of inflammatory secretion is observed from its walls.
The following are the causes of diarrhea:
Bloody diarrhea is a symptom of diseases such as:
- dysentery;
- ulcerative colitis;
- intestinal tumors;
- haemorrhoids;
- anal fissure.
Prevention
To prevent the appearance of mucous feces with blood in adults and children, it is enough to adhere to the following rules:
- Always wash vegetables and fruits, even if they are collected at your own dacha.
- Follow food storage rules and do not consume them after the expiration date.
- “Proper” food should not contain dyes or preservatives.
- The temperature and cooking time should be maintained for dishes made from meat, fish, and eggs. Thorough heat treatment will help avoid helminthiasis, salmonellosis and other diseases.
- It is necessary to strengthen the immune system. It is he who stands guard over infectious diseases. Swimming in sea water, hardening procedures, sunbathing, an abundance of vitamin-rich vegetables and fruits are the key to good health and proper functioning of the gastrointestinal tract.
- Swim only in specially equipped reservoirs.
- Hygiene requirements must not be neglected. Both children and adults are taught to wash their hands.
- If one of your household members is sick, contact of small children should be excluded.
- Pets can also cause diarrhea. It is necessary to explain to the child that after playing with animals it is necessary to wash his hands. Every child should learn that eating from a cat’s bowl is dangerous, and kissing a four-legged friend is not recommended.
What to do when loose stools contain blood?
If you have loose stools with blood, you should not delay a visit to the doctor, who needs to be told in detail about all the symptoms. To determine an accurate diagnosis, a number of tests may be performed after a physical examination. Blood and urine samples will be required, as well as an examination of the rectum and an ultrasound examination of the abdominal organs.
Additional diagnostics are also possible:
- Gastroscopy - insertion of an endoscope through the mouth, esophagus into the stomach and duodenum. The doctor can use it to find the source of bleeding and take samples for a biopsy.
- Colonoscopy is a procedure similar to gastroscopy except that an endoscope is inserted through the rectum to view the large intestine.
- Enteroscopy is a procedure similar to gastroscopy and colonoscopy, used to examine parts of the small intestine. In some cases, it involves swallowing a capsule with a tiny camera inside that transmits an image to a video screen as it moves through the digestive tract.
- Radionuclide testing involves injecting small amounts of radioactive material into a vein and then using a special camera to monitor images of blood flow in the digestive tract.
- Angiography is a procedure that involves injecting a special contrast agent into a vein, making the blood vessels visible on X-rays or a CT scan.
- Laparoscopy is a procedure in which an endoscope is inserted into the abdominal cavity through a puncture in its wall.
The doctor uses these examination methods to make an accurate diagnosis and decide on conservative or surgical treatment. Therapy sometimes includes simple methods that the patient can perform independently. This applies to dietary compliance.
Many mothers know that baby formula has its own characteristics: it has a more liquid consistency, sometimes there may be lumps and small mucous patches. Content:
Survey
The patient is examined by a gastroenterologist; in the case of massive hemorrhage, a consultation with a surgeon is required. The diagnostic search in the presence of melena is aimed at quickly identifying the source of bleeding, and, if possible, eliminating it. A complex of instrumental and laboratory methods is used, which are necessary to study the state of the digestive tract, assess the severity of the patient’s condition and the degree of hemodynamic disorders. The most valuable for diagnostics are:
- X-ray examination
. A series of radiographs with oral contrast of the gastrointestinal tract with barium sulfate is an alternative to the endoscopic examination method. Using radiography, in 80-85% of cases it is possible to determine the location of the damage, but the technique is not always informative for establishing the etiology. - Endoscopy
. Endoscopy using a flexible probe is used not only to detect the site of hemorrhage, but also as a therapeutic method - special tools allow you to “cauterize” the bleeding vessel. In doubtful cases, a biopsy of altered areas of the mucosa is performed to verify the causes of melena. - Stool analysis
. In order to confirm the presence of blood in the stool, a three-fold Gregersen reaction is performed, which detects even a small amount of blood pigments. A standard coprogram must be performed, and bacteriological examination of stool is prescribed according to indications. - Coagulogram.
The results of the analysis of coagulation ability, the activity of the internal and external components of hemostasis are indicative of suspected hereditary hemorrhagic pathologies with impaired coagulation. To monitor the dynamics of the patient's condition, the study is done several times. - Blood tests
. All patients with melena are recommended to have a general blood test, which provides a rough estimate of the degree of blood loss for the development of further treatment tactics. To exclude concomitant diseases, a biochemical blood test and liver tests are necessary.
In case of massive bleeding and the impossibility of conducting a high-quality endoscopic examination, selective mesenteric arteriography is prescribed to visualize the exact location of the vessel damage. As a screening test for unclear etiology of melena, the radionuclide scanning method with labeled red blood cells is used.
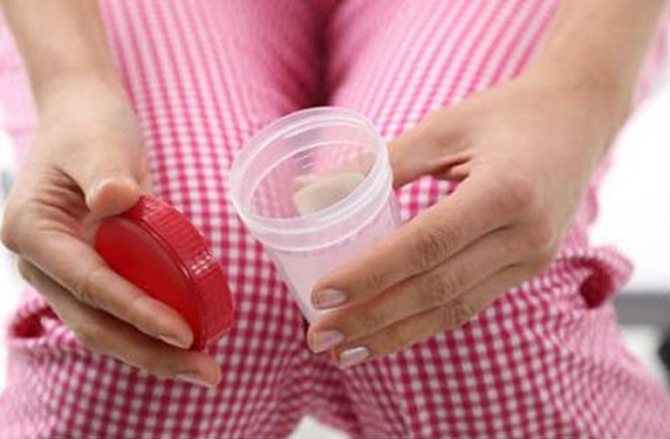

To detect traces of blood in the stool, a stool occult blood test is prescribed.
The child has diarrhea with blood and mucus. Causes
As a rule, a baby's stool has an unformed appearance, because it feeds mainly on mother's milk or an adapted formula. With the start of complementary feeding, the baby also receives “baby” food in the form of vegetable or fruit purees.
From here we can draw a simple conclusion: the stool of children under 10-12 months has a liquid consistency from light yellow to brown, and the stool of a baby over a year old has a formed mass (like that of an adult). The presence of a small amount of mucus is also considered normal if it does not happen often and the child feels normal.
Not everything goes as smoothly as we want. It also happens that the child suddenly defecates differently than usual and a sensitive mother may notice watery feces with blood and mucus in diapers or panties. What could this be and what needs to be done in this case? Let's figure it out!
Every parent knows that any distortions and pathological impurities in the stool indicate some kind of malfunction or disease. Diarrhea is a protective reaction of the body that helps to overcome the cause that interferes with the normal functioning of internal organs.
Causes of diarrhea with blood and mucus:
- the reaction of the digestive system to toxic substances that enter the body;
- pathogens in the gastrointestinal tract;
- diseases (dysentery, salmonellosis, gastroenteritis, colitis, rotavirus infection);
- poor quality food containing E. coli.
In addition, one should not exclude other reasons that can cause pathological stool. This could be: stressful situations, inflammatory changes in the mucous membrane of the intestines, stomach and stomach, abundant consumption of vegetables or fruits that have a laxative effect, an allergic reaction to the consumption of certain foods, enzyme and lactose deficiency.
Bloody streaks in the stool may also indicate the presence of internal hemorrhoids. With this disease, there is itching and burning of the anus after defecation.
Light and bright scarlet bloody impurities can indicate colitis or dysentery. If there are dark bloody spots, a gastric or duodenal ulcer is suspected.
Do not forget that benign and malignant tumors (especially at the stage of active growth) can also cause minor internal bleeding, which can be seen as a result of bowel movements.
If liquid feces with red impurities are found in the diaper of a small child, then it is necessary to prevent the ingestion of small parts of toys that could injure the mucous membrane (small construction toys, toys from three years old) or household items (coins, pins, etc.). ).
The child has diarrhea with blood and mucus and a fever
If you have bloody stools with mucus, you can suspect a number of different diseases. However, if at the same time the body temperature rises (low-grade or hyperthermia), then in this case it is highly likely that they are talking about intestinal ones, which can cause enormous damage to health if left untreated.
Intestinal infections very often develop as a result of eating low-quality or expired food. Poisoning occurs from several hours to a day after eating unfavorable food.
Intoxication develops acutely and very often has the following manifestations:
- high body temperature (38-40 degrees);
- lethargy;
- headache;
- epigastric pain;
- vomit;
- loose stools (possible admixtures of blood and mucus) - up to 15-20 times;
- stool may be green in color with a pungent odor.
However, loose stools with fever can also occur with other intestinal disorders. This may be an inflammatory change in the pancreas due to a long and incorrect diet, unhealthy diet, disorders of the internal organs as a result of heavy and poorly digestible food, alcohol.
Usually this condition goes away either on its own or under the influence of artificial enzymes. The temperature may be subfebrile (37.2-37.5) and will not rise above 38 degrees.
A high body temperature, which is combined with a gastrointestinal tract disorder, can also indicate a rotavirus infection. Stool with this disease may have copious mucus and a strong odor. It is not recommended to treat this condition on your own, since after a few days the condition of the sick child may worsen. With this, after a few days, other symptoms are added: sore throat, migraine, runny nose, lethargy.
The child has diarrhea with blood and mucus. Danger
The most dangerous thing a child can experience with diarrhea with blood and mucus is self-medication and late medical consultation, when the disease rages and is then difficult to treat.
Modern medicine has long learned to deal with all infectious problems of the stomach and intestines, so at the first sign you should not ask a neighbor or friend how they treated their child with similar symptoms.
Each disease has its own management and treatment characteristics. Now only a doctor can figure out what exactly your child needs, and only during inpatient treatment in an infectious diseases hospital. So, let's figure out what the danger is if the baby suddenly has blood streaks in his stool.
In parallel with diarrhea, the child may also experience frequent, profuse vomiting. Against the background of severe intoxication, all this can lead to severe dehydration, which is very dangerous for the human body. A child's body has less body weight and, accordingly, less fluid content in the blood and internal organs. Therefore, under such circumstances, dehydration can occur very quickly, which can lead to negative results.
In addition, in children under three years of age, the fluid control system has not yet been improved, so they are at risk and urgently need medical supervision.
When internal organs and their systems are in critical condition due to an acute lack of fluid, a disruption of the metabolic process occurs, which can lead to loss of consciousness. It is important to know that a loss of water of 20-25% of the norm leads to death, and a loss of 10-15% leads to long and grueling treatment, which in some cases does not help the patient.
As we see, dehydration occurs sharply and acutely and develops rapidly. Medical treatment does not immediately give a positive result (stopping vomiting and diarrhea), so it is important to contact a doctor as early as possible.
Diagnostics
To eliminate the symptoms, it is important to understand what disease led to the occurrence. To do this, diagnostics are carried out using the following methods:
- ultrasonography;
- endoscopy – examination of the internal state of the stomach;
- urine and stool analysis;
- enteroscopy – examination of the abdominal cavity;
- sigmoidoscopy - examination of the condition of the rectum.
To eliminate the manifestations, symptomatic and primary therapy is selected against the cause of the disease.
To prevent dehydration, make a “Rehydron” solution and consume 1 or more liters per day. You can make the remedy yourself by adding 4 tablespoons of sugar and salt to 1 liter of water.
Gastritis and ulcers are treated with drugs:
- De-Nol – 1 tablet 4 times a day and wash down with plenty of water;
- Mezim - 1-3 tablets before meals, the course is selected individually.
Infections and bacteria that provoke bloody vomiting are eliminated with antibacterial drugs:
- Nifuroxazide – 2 tablets 4 times a day or syrup 10-15 mg 4 times a day;
- Levomycetin – 1 tablet up to 4 times a day, duration of use no more than 10 days;
- Ofloxacin – 1 tablet 2 to 4 times a day.
For food poisoning, absorbents and astringents are used:
- activated carbon – 1 g every day 3 times, the course of treatment of acute diseases is 5 days;
- Smecta - 1 sachet diluted in 50 g of water and used 3 times a day an hour before meals;
- Polysorb - 1 teaspoon diluted in 50 g of water, taken 3 times a day an hour before meals;
- Atoxil - 2 g diluted in 150 ml of warm water, taken 5 times a day an hour before meals.
The intestinal microflora is restored with the help of:
- Linex – 2 capsules 3 times a day, duration individual;
- Acipol – 1 capsule 4 times a day 20 minutes before meals, for a course of 7 days;
- Bifidumbacterin - 2 sachets diluted in 50 ml of water and drunk 3-4 times a day 25 minutes before meals.
- Duphalac – 10 ml 3 times a day before meals, course up to 7 days;
- Lactusan – 10 ml 2 times a day or before meals 2 tablets 5 times a day;
- Normaze – 10 ml 2-3 times a day.
If there are neoplasms in the gastrointestinal tract, chemotherapy or surgical removal is prescribed according to indications. Self-medication for bloody vomiting and diarrhea is excluded in order to prevent the situation from worsening. A qualified specialist prescribes therapy and medication.
The risk group includes:
- children under 5 years old;
- people over 60.
Immediate consultation with a doctor occurs:
- if the pain rapidly intensifies;
- a large volume of blood appears in the vomit.
When bloody vomiting and diarrhea last more than a day, you should immediately go to the hospital. Prolonged presence of the symptom leads to dehydration and may indicate a serious illness.
Learn more about intestinal infections that can cause vomiting and bloody diarrhea.
The appearance of vomiting and diarrhea when there is blood in them is a dangerous situation. It means the presence of internal bleeding due to pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract. Correct treatment is prescribed only by a gastroenterologist, based on examination data.
An infection or bacteria that enters the body causes vomiting and intestinal upset. The latent period of development of symptoms of the disease takes from several hours to several days. Delay in eliminating symptoms causes severe dehydration and exacerbation of chronic diseases in an adult.
The child has diarrhea with blood and mucus. How to treat?
Self-treatment, as a rule, does not bring any benefit, but only allows the disease to progress and torment the body. If you notice that the child is passing a “big” liquid, mucous and bloody consistency, then the first thing you should do is call your doctor (or an ambulance if there is a parallel increase in temperature and vomiting). What should parents do to provide pre-medical assistance?
- calling a doctor. If there are bowel movements in the potty, you should leave them to show the doctor;
- The child will most likely have no appetite. Do not force anyone to take any food;
- Due to the sudden loss of fluid, it needs to be replenished. The child needs to be soldered, but at the same time given a portioned amount of water (for example, 10-20 ml) every 3-5 minutes. It is not recommended to offer your child a lot of water at once, as due to the inflammatory condition of the stomach, vomiting may occur;
- for desoldering, you can prepare it yourself (a teaspoon of salt and sugar per liter of warm water) or use a special powder to replenish liquid (Regidron, Orolit);
- with increased body temperature and chills - antipyretic drugs;
- In case of diarrhea, it is recommended to wash the child after each trip to the toilet, since excessive stool causes irritation of the anus.
Diarrhea with mucus and blood is dangerous, so it is necessary to treat the baby only under medical supervision, strictly following all recommendations. The development of medicine has gone so far that such symptoms can be treated simply and quickly, remove intoxication in a matter of days and significantly improve the patient’s well-being.
After watching the video, you can learn about the tests that are done for diarrhea.
You should not be “stubborn” and treat the child yourself, because this can greatly undermine his health and in the future “come back to haunt” him under the guise of chronic digestive diseases.
The health of children is of paramount importance to parents. There are a lot of cases when a lightning-fast reaction is required from parents. These include a situation in which a child has diarrhea with blood. This can indicate either minor problems in the functioning of organs or a serious malfunction.
Before taking action, parents must understand why this condition occurred. And this needs to be done as soon as possible in order to provide timely and adequate assistance. So, not every parent will immediately realize that if you do not pay attention to diarrhea, the child may become dehydrated. And for a child’s body this is much more dangerous than for an adult.
In addition, a delay in treatment inevitably leads to irritable bowel syndrome in a child, which can last three weeks or more. But blood in the stool can also be due to a fissure in the anus; it does not have to be an infection. In any case, the appearance of such a sign is a serious reason to go to the hospital.
Rarely, diarrhea with blood and mucus in a child is associated with a single malnutrition. Most often this is a consequence of some kind of internal disease - acute or chronic. If such a symptom is associated with nutrition, then most likely there is poisoning with poor-quality food or uncontrolled consumption of plant fiber, which has a laxative effect. With internal diseases the situation is much more serious.
Before your baby turns 1 year old, it is normal for him to have mucus-filled stools. The functioning of his gastrointestinal tract has not yet been established, so there is no need to be alarmed. But the blood should not be normal.
The appearance of mucus in the stool is often a sign of a previous viral infection. It will manifest itself only after a few days with visible symptoms similar to a cold.
Why does a child have bloody diarrhea? Possible reasons:
- Pathogenic microflora in the intestines.
- Diseases of an infectious nature.
- Inflammatory process in the mucous membranes of the gastrointestinal tract.
- Congenital form of hemorrhoids.
- Food allergies to certain foods.
- Lack of beneficial microorganisms.
- Ulcerative lesion of the stomach.
- Lack of enzymes or lactose.
- Oncological diseases.
- Helminthiasis.
There is a rare disease called Brainerd's diarrhea (named after the city where it was first reported). Diarrhea lasts for several months. If left untreated, it leads to the death of the child due to increasing dehydration.
As you can see, some of these situations are easily correctable, while others require a lot of time, effort and money to treat, so the parents’ reaction must be lightning fast. Loose stool in a child mixed with blood can also be caused by stress, a poorly performed operation, foreign bodies entering the stomach, or intolerance to certain medications. In the latter case, the child’s diarrhea with mucus and blood will go away with the abolition of the causative pills.
Non-infectious
In a child, diarrhea with mucus and streaks of blood occurs as a result of inflammatory processes in the rectum. The pathological condition is possible due to unsuccessful surgery.
Emotional experiences, stress, side effects of taking medications and allergic manifestations are the sources of the disease. Getting small objects into a baby's stomach can have serious consequences.
Such elements injure the mucous membrane of the digestive organ.
We list a number of non-infectious causes that cause diarrhea:
- Food poisoning.
- Colonization of the suction organ by pathogenic structures.
- Deficiency in enzymes, lactose.
- Ulcerative colitis.
- Activity of helminths in the baby’s digestive system.
- Inflammation of the gastric mucosa.
- Crohn's disease.
- Development of hemorrhoids.
- Oncological diseases.
Modern medicine distinguishes Brainerd's diarrhea among others. Loose stools last for about 60 days, causing dehydration. If the disorder is not promptly eliminated, the child’s life is in serious danger. A critical lack of water in the body leads to loss of consciousness and death. Already the first signs of the disease require prompt action from parents and doctors.
Diagnostic search
It is important to take into account all the factors that may have influenced the little person, then the diagnosis will be correct. It is a myth that a baby’s diarrhea will go away on its own. Like any other pathological condition, it requires treatment. Before coming to the doctor, parents can examine the baby themselves. The color, smell and consistency of stool can tell a lot.
Characteristics of feces
If a child has diarrhea with blood streaks, then their color is important for diagnosis. The presence of scarlet veins indicates dysentery or damage to the large intestine, such as in dysentery. It is often accompanied by a false urge to defecate. Vomiting and fever are also not uncommon for this disease. In addition to a small amount of blood in the stool during dysentery, you can find mucus collected in lumps.
Dark veins indicate the possible presence of an ulcer, which is very rare at this age.
With a bacterial infection, the stool often has a green tint and a strong odor. A greenish color to the stool may also appear if the child eats a lot of foods that contain dyes, as well as fresh herbs. Diarrhea mixed with blood may be green if carbohydrates are poorly absorbed and hemoglobin is high. If the condition is without fever, then the danger of infection or inflammation is very small.
Intoxication
If the condition is with fever, then we can talk about infection. In addition to loose stools, the child will have weakness, abdominal pain and possibly a headache.
Local manifestations
Itching after bowel movements may indicate internal hemorrhoids. An external hemorrhoid may be tiny and bleed. Although this disease is rare for a baby, it is important not to rule it out until the doctor examines the little patient. Anal fissures in children are not so rare, since their skin in this area is very thin. After bowel movements, the baby may feel a burning sensation and pain, and there may be blood in the stool. This pathology often occurs due to a tendency to constipation.
By type of diarrhea
By examining the appearance of the bloody discharge, you can roughly determine what is bothering the baby:
- Melena. Tarry stools, black or burgundy. It occurs due to problems with the esophagus, stomach, small intestine, and large intestine.
- Streaks of fresh blood. They may indicate diseases of the colon. It is located lower along the tract where food enters after fermentation. In this case, the blood comes out naturally in the stool.
- Drops on the surface of stool. Such discharge is the result of damage to the rectum, hemorrhoids. Similar conclusions can be drawn with smudges and blood prints.
- Green diarrhea and mucous structure of blood in stool. So-called “fatty” blood indicates an infectious infection or chronic inflammation of the intestines. The mucous base is the result of the child’s immune resistance.
First aid and treatment
An accurate diagnosis established on time will help avoid the consequences of improper treatment. Antibiotic therapy is prescribed if bloody diarrhea is caused by a bacterial infection. This treatment lasts no more than two weeks. It is not advisable to communicate with other children at this time, so as not to infect anyone or to prevent another infection from entering the weakened body of a sick child.
At this time, it is important to take care of restoring water and salt balance. Colon inflammation is treated with anti-inflammatory bowel medications. Regardless of the nature of diarrhea, doctors advise drinking a lot to avoid dehydration.
If an infant has diarrhea, he or she should be put on a diet. It is very undesirable to feed him before being examined by a specialist. The diet prescribed by the doctor consists of easily digestible foods. You cannot give:
- raw fruits;
- vegetables;
- berries;
- juices;
- puree or smoothie.
Fatty, fried or salty foods, as well as meat with veins, are also prohibited. Ripe bananas are allowed as fruit. In addition, you can eat boiled potatoes, crackers and rice water.
You should only drink boiled water or a weak infusion of tea. If the temperature is high (more than 39°C), before the ambulance arrives, you can give the child Ibuprofen or paracetamol to reduce it. Give your baby something to drink after each bowel movement to prevent dehydration.
Regidron or Humana solution will help replenish the loss of minerals. If these drugs are not at hand, then you can prepare a solution of similar properties yourself. To do this, you need to take a liter of cold boiling water, add two tablespoons of sugar and a teaspoon each of soda and salt. To prevent vomiting, you need to give your child two small spoons of this solution every ten minutes.
In case of infectious diseases, it is necessary to introduce water into the child’s body, even if you have to do this with the help of droppers (this method, of course, is used only in a hospital). Antibiotics can only do harm, since their use will also lead to dysbiosis in addition to an infectious disease. At this time, bed rest and liquid nutrition are important. When the condition returns to normal, you can switch to regular food, but limit the consumption of dairy, fatty products and vegetables that cause fermentation in the intestines, as well as black bread.
Inpatient treatment is indicated only for severe and prolonged forms of diarrhea or if there are no conditions for proper treatment at home. If dysbacteriosis occurs, you can feed your child carrots, blueberries and raspberries in small quantities, as well as fermented milk products. A rosehip decoction will be useful for drinking. These products will help restore microflora.
Vomiting during an intestinal infection is a protective reaction, as the body seeks to rid itself of toxins. Therefore, there is no need to stop it on the first day.
It's better to prevent than to treat later
In order not to blame themselves for their child’s illness, it is important for parents to monitor their personal hygiene and proper nutrition. Of course, we all understand that living water is healthier than boiled water, but for a baby, boiling water is a good preventive measure against diarrhea. When he grows up and his body gets stronger, let him drink clean, raw water.
Not only water, but also all foods that the child eats need to be heat treated. They must be stored at the correct temperature, which is indicated at the factory. Be sure to wash all fruits and vegetables thoroughly. Toys should also be washed, since children put everything in their mouth. To prevent a foreign body from damaging the baby’s mucous membrane, it is important to ensure that he does not put small objects in his mouth and, accordingly, do not buy small toys, such as Kindersurprise, for example.
Parents should not panic immediately as soon as they see red spots in the child’s stool. They may just be tomato skins or the remains of undigested beets, but you shouldn’t leave everything to chance either. A balanced approach will help you conscientiously monitor your baby’s health without shaking your nervous system, and your doctor will tell you what to do.
What to do if a child has diarrhea with blood or mucus updated: July 14, 2020 by: admin