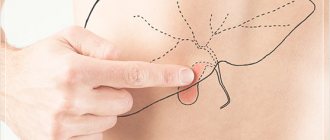
According to statistics, about 5% of patients who have undergone cholecystectomy experience such a symptom as stomach pain after removal of the gallbladder. It is important to pay attention to additional symptoms and be able to provide yourself with the necessary help in a timely manner.
Gallbladder removal
Despite the fact that currently there is an active development of various methods of treating cholelithiasis without surgery, most specialists trust the cholecystectomy method. It is a radical solution to the problem when a huge number of insoluble stones or one huge stone accumulates in the bladder cavity, and removal of this organ can not only improve the patient’s health, but also save his life.
The accumulation of a large number of stones in the cavity of the gallbladder contributes to disruption of the functioning of this organ and bile ducts, and also provokes the development of organic dysfunctions near the located organs. This problem must be solved only in radical ways, therefore, in most cases, cholecystectomy is the only correct solution. The affected organ is removed through a 12-mm laparoscopic incision, into which the laparoscope itself is inserted and the gallbladder is removed.
This method of surgery will allow the patient to recover as quickly as possible after the operation and spend a minimum amount of time in the hospital.
Also, do not forget about possible complications that appear after removal of the gallbladder, the main of which will be discussed below.
Postcholecystectomy syndrome and adhesions
The development of postcholecystectomy syndrome is a dependent pathology that occurs against the background of disruption of bile circulation processes due to poor diet and consumption of alcoholic beverages.
This disease manifests itself with the following symptoms:
- the appearance of pain in the right side, abdomen and gastric cavity;
- development of flatulence;
- the appearance of a feeling of heartburn;
- rise in body temperature to subfebrile limits;
- development of diarrhea;
- the appearance of constipation, which contributes to the formation of hemorrhoids;
- feeling of nausea and vomiting;
- the appearance of belching with a bitter aftertaste;
- yellowness of the skin and sclera.
Symptomatic signs may not appear in every case, but the main characteristic of postcholecystectomy syndrome is the development of flatulence and painful symptoms. What to do in such situations?
To eliminate this pathology, immediately after the first painful sensations, it is necessary to seek qualified medical care and prescribe appropriate treatment, which consists of the use of enzymatic agents, as well as antispasmodic drugs with a choleretic effect. In some cases, repeated surgery may be prescribed to correct the changes that have occurred.
In order to prevent the development of such a complication, after cholecystectomy it is necessary to follow the diet prescribed by the doctor, completely eliminate the consumption of fatty foods and alcohol, and also adhere to other methods of maintaining the body prescribed by the specialist.

Another type of complication is the formation of adhesions, which occur in 30-35% of cases after surgery to remove the gallbladder. Adhesions are formations of connective tissue, with the help of which the patient’s body provides itself with protection in the place where the surgical intervention was localized. These formations begin to appear even after minimally invasive surgical treatment.
After the gallbladder is removed, a void appears in its place, which the patient’s body begins to fill with connective tissues. Symptoms of adhesions:
- tingling in the abdominal area;
- as well as the appearance of painful sensations radiating to the abdomen or right side.
It is very important to promptly prevent the development of such formations. After a minimally invasive operation, the patient can take a sitting position, and then get up after a couple of hours and move; lying down for a long time is not recommended. Performing movements helps to activate the intensive performance of the body and the processes of its restoration, therefore, the formation of adhesions in this case will not occur.
You will not be able to remove adhesions on your own; here, even the medicinal recipes of traditional healers using various medicinal herbs, which can only lead to the development of individual intolerance to the medications taken, will be powerless. To prevent the development of disability, treatment of diseased adhesive formations should be carried out only under the clear guidance of the attending physician.
Rules of behavior during the postoperative period
Pain in the right hypochondrium when the gallbladder is removed is normal in the postoperative period. The first week after gallbladder removal surgery is considered the postoperative week. When the patient comes out of anesthesia, he should remain at rest for at least five hours. After which it is allowed to perform basic movements (stand up, roll over). During the first day after the gallbladder is removed, eating is prohibited. It is allowed to drink drinking water without gas, a decoction based on rose hips without adding sugar.
On the second day after surgery, drink a liter of kefir (necessarily low-fat). Divide this amount of product into several doses. After a day, if there are no complications, you can introduce low-fat cottage cheese, lean meats (boiled or steamed), vegetable broth, fresh non-acidic fruits, and fermented milk products into the diet. Be sure to adhere to the correct diet - drink large amounts of clean, still water between main meals.
Further, the diet gradually expands, it is forbidden to eat only spicy, fatty, smoked, spicy foods, alcoholic drinks, black bread, soda, spicy dishes, sausages, canned food, marinades, chocolate and coffee. For some time after removal of the gallbladder, pain will be felt in the right side in the place where the injections were made. Reviews from many patients and surgery confirm this. Sometimes even sleeping on the right side hurts. This is normal until the injured tissue recovers.
If there is pain on the right after removal of the gallbladder, it is recommended to consult a doctor; he should examine the intervention site and assess the condition of the tissues. After surgical treatment, a tube is inserted into the patient on the right side, which provides drainage. If the discharge stops, it is removed after a day. During this period, physical activity is prohibited. Wearing soft underwear is recommended. The postoperative period ends with the removal of sutures. Another week after discharge, the patient is usually on sick leave until all the wounds have completely healed.
In some cases, complications may occur - compaction, redness or discharge in the intervention areas. In such cases, conservative therapy is extended. If the patient does not follow a gentle regimen for his body, hernias may form at the puncture sites, they are painful, and if they are pinched, constipation occurs. You cannot shower for five days after the operation; the wounds are lubricated with iodine, fucorcin or cutasept. If your back hurts in your side when the gallbladder is removed, this is normal in the postoperative period. To relieve pain, doctors prescribe painkillers and antispasmodics.
Laparoscopy is not an abdominal operation. After 6 months, complete rehabilitation of the patient was completed. The main goal of the postoperative period is to reconstruct the functions of the organs of the digestive system so that they can perform their work in the absence of the gallbladder. Digestion will gradually improve, but only if the person strictly follows all medical prescriptions. Doctor's recommendations after cholecystectomy:
Follow a healthy diet after gallbladder removal
- Limiting the consumption of fats, spicy and fried foods.
- You cannot have sex for three weeks.
- Make sure there is no constipation in the first days after surgery.
- Limit physical activity for a month and a half.
- Adhere to proper nutrition - avoid heavy foods that cause disturbances in the functions of the digestive system.
- Take vitamin complexes prescribed by your doctor.
The specified diet is observed for at least two years if the gallstone is removed. In the absence of an organ, you should avoid eating heavy foods for life. Thanks to this, you can completely restore the process of food digestion and bile secretion. Do not consume cold or hot foods. If alarming signs appear, especially if the organ has already been removed a long time ago, it is imperative to visit a doctor, who, based on examination, symptoms and other diagnostic measures, can draw conclusions about the patient’s condition. Visit your doctor from time to time for consultation.
How does gallbladder removal affect the pancreas?
After surgery to remove the gallbladder, most people experience a noticeable improvement in their general condition. Pancreatitis ceases to manifest itself over a long period of time, moving into a stage of prolonged remission. The so-called “cholelithiasis pancreatitis” can only worsen when drinking alcohol-containing drinks or if the diet is violated.
Many people lead normal lives after undergoing surgery to eliminate the bladder, and the key to their success is a diet that completely excludes alcoholic beverages and foods with a high percentage of fat.
Physical stress after bladder removal
In terms of physical activity, the operated person must strictly adhere to the following simple instructions:
- During the first 5-8 days after surgery, you need to rest more. Any physical activity can significantly worsen your health. Therefore, there is no need to rush to start living as usual. Otherwise, do not complain that your stitches hurt after removal of the gallbladder and other unpleasant phenomena are observed.
- After 14-17 days, you can gradually expose the body to minor physical activity, which is monitored by a physical therapy specialist. You need to start with a half-hour walk (preferably in the fresh air).
The quality and quantity of food plays a dominant role in the recovery process of all functions of the body of the operated person. Therefore, it is so important to strictly follow all nutritional recommendations:
- Cold food and liquids are contraindicated, as this can cause stomach cramps, which is not good in this case.
- Your diet should not include spicy, smoked, fried or fatty foods. They are also contraindicated for you. However, as well as products such as sweets, wine, vinegar, lard, concentrated broths and all kinds of syrups. The use of any of them, even in small quantities, can provoke pain (after removal of the gallbladder, such a symptom must be treated with extreme caution).
- The most suitable diet in this case is table No. 5.
Important! During the day you need to take about five to six meals of the recommended food. Moreover, each of them should be small in volume, since a significant amount of food entering the stomach is poorly digested.
If you continue to eat incorrectly, then do not ask your doctor a question about why your side hurts after removal of your gallbladder.
The occurrence of pancreatitis after cholecystectomy
The development of pancreatic pathology in the pancreatic cavity after cholecystectomy can only be observed in the event of a violation of dietary nutrition, consumption of foods on the exclusion list, and drinking of alcoholic beverages.

The cause of an acute attack of pancreatic pathology may be the bile ducts taking over the functionality of the removed bladder. During this process, bile enters the intestinal cavity in small portions, and not as before - when bile entered in large quantities. Such changes provoke a decrease in the bactericidal properties of bile and changes in the microflora in the intestinal cavity, which leads to the formation of diarrhea, heartburn and constipation. Such changes begin to have a negative impact on the functionality of all internal organs included in the digestive tract system, including the pancreas.
A disrupted diet with chaotic consumption of prohibited foods and drinking alcohol-containing products will soon after cholecystectomy lead to the development of inflammation in the cavity of the parenchymal organ, called pancreatitis.
Treatment of pancreatitis with removed gallbladder
By ensuring proper diet, treatment methods for pancreatitis after gallbladder removal involve minimal use of medications. In hospital settings, for three days after surgery, antibacterial therapy is carried out using drugs with an antibiotic spectrum of action.
Taking analgesic and antispasmodic drugs will help eliminate painful symptoms; Drotaverine or Buscopan is prescribed. And also to prevent the formation of stones in the pancreatic cavity, the drug Ursolfac is prescribed for half a year to 2 years.
Therapy in the fight against illness
Treatment of pain after removal of the gallbladder is carried out comprehensively, and is mainly aimed at eliminating disturbances in the functioning of the stomach, liver and the entire gastrointestinal tract. The following groups of drugs are prescribed from medications:
- Enzyme-containing. They help improve the functioning of the digestive tract (for example, “Pancreatin” or “Festal”); facilitate the process of bile removal, intestinal function, and prevent the development of food fermentation (“Mezim” or “Espumizan”).
- Anesthetics. They are best administered intravenously. The tablet form is the worst option.
- Painkillers. In order to cope with pain after removal of the gallbladder, medications such as Mebeverine, Ketanov, Drotaverine or Ketorol are suitable.
- Probiotics. They contribute to the creation of new and healthy microflora (“Bifidumbacterin”, “Linex”).
- Hepatoprotectors. For those who complain that the right side hurts after removal of the gallbladder, remedies such as Ursosan or milk thistle extract, which are designed to protect, restore and maintain the liver in normal condition, are suitable.
- Antispasmodics. They are needed to cope with spasms in the bile ducts (for example, Buscopan or No-Shpa).
- Antipyretics (in case of high body temperature).
Important! You should not self-medicate for pain after gallbladder removal. You may make your health situation worse.
Sometimes it happens that drug therapy does not give the desired positive results. In this case, it is necessary to prescribe a second diagnosis and another operation.
In addition to taking medications, the specialist prescribes a course of physical therapy and diet.
Diet for pancreatitis after removal of the gallbladder
Over the next 2 months of the postoperative period, pureed soups, as well as pureed vegetables boiled in water or stewed, can be used as food.

As drinks, it is allowed to use weak rosehip-based decoctions, weakly brewed green tea drink, and freshly squeezed juices must be diluted with boiled water in a 1:1 ratio.
What products are prohibited?
During the rehabilitation period, as well as after it, all types of dishes with a high percentage of fat content, spiciness and salt, as well as those prepared by frying, are prohibited from consumption.
Exceptions should also be:
- all varieties of fish;
- strong tea and coffee;
- alcohol;
- all confectionery and bakery products;
- all types of chocolate.
Is it possible to remove the gallbladder for pancreatitis?
It is important to remember that the development of cholecystitis can often be triggered by the progressive stage of pancreatic pathology in the pancreatic cavity. And then many patients are alarmed by the question of whether it is possible to cut out the gallbladder for pancreatitis?
The fact is that in such cases the issue of eliminating the gallbladder is not even discussed and is put on the priority list. This is due to the fact that accumulated stones prevent the outflow of bile, which leads to its penetration into the pancreatic cavity and activation of pancreatic enzymes, which trigger the process of self-destruction in the gland with the development of pancreatic necrotic lesions, characterized by the death of gland tissue, the restoration of which will no longer be possible.
Consequences of surgery to remove the gallbladder
Patients are often mistaken in thinking that after removal of the gallbladder, the functions of this organ are assigned to the pancreas, and as a result of its excessive load, pancreatitis occurs. Unfortunately, these organs do not replace each other, and chronic pancreatitis occurs due to inflammatory processes in the gallbladder. Patients after cholecystectomy (removal of the gallbladder) experience improved health, and remission lasts longer. But doctors often witness a different picture: the bile ducts perform the function of a bladder, therefore, bile enters little by little, which is why its bactericidal property decreases, the microflora of the small intestine undergoes changes, and digestion is disrupted. This negative effect makes itself felt on all digestive organs, the pancreas is especially affected, and as a result, pancreatitis occurs.
When suffering from cholelithiasis, inflammation of the pancreas is detected, which provokes a disease such as biliary pancreatitis.
And depending on the location of the stones in the gall bladder, the severity of the disease is determined.
Some patients complain of loose stools, rapid weight loss, increased fatigue and weakness, which may indicate postcholecystectomy syndrome. It develops due to a disorder of certain organs after removal of the gallbladder, liver disease, reorganization of the digestive system, and the formation of abnormalities due to surgery. Postcholecystectomy syndrome often entails pancreatitis.
Causes of pain in the right side
Removing the gallbladder is stressful for the body. Primary pain may be due to the healing of the skin, healing of the intestinal walls and liver. The body is trying to function without an important storage organ. If the pain continues for more than a week, there are several reasons.
- Sphincter of Oddi dysfunction. The gallbladder created tonic substances for the sphincter, causing it to contract and unclench in time. After cholecystectomy, work on the production of tonic substances is stopped. Bile enters the intestines aportionally, constantly flowing into the digestive organ. The intestinal walls are provoked, being constantly in an acidic environment, the risk of infections, irritable bowels, and upset bowels increases. Pain is detected in the right hypochondrium, near the duodenum and at the beginning of the small intestine, in the lower abdomen. Appears after eating, after a long absence of meals, at night. With prolonged dysfunction of the sphincter of Oddi, inflammation of the small intestine, duodenum, biliary tract, and pancreas in the abdomen is possible.
- Cholangitis. Inflammation of the bile ducts due to infection from the intestines, pancreas, and blood. The cause is a gallstone, toxoplasmosis. Cholecystitis often occurs when stones are carried; after surgery to remove the bile ducts, the infection brought by the stones into the body could persist. Toxoplasmosis is a parasitic disease transmitted from animals. After the procedure, a person is most susceptible to this disease, because the body’s immunity system decreases and weakness is present.
- Surgical intervention, postcholecystectomy syndrome. Each person experiences surgery differently. Severe stress and mental illness provoke malunion and metabolic disorders in the digestive tract. Surgical adhesions on the biliary tract, scar formation on the delicate tissues of the bile ducts and intestinal mucosa. Stress causes constipation and bloating, which interfere with the healing process.
What will you have to give up to prevent pancreatitis?
To avoid the occurrence of pancreatitis, you should follow a few simple rules. You need to start by eliminating stress on the nervous system; Avoid eating fried, fatty and spicy foods; quit bad habits (if any). You can stabilize your diet by adding fresh fruits and vegetables, juices and natural foods. It is important to always ensure that your diet is rational and nutritious.
Our readers recommend
Our regular reader recommended an effective method! New discovery! Novosibirsk scientists have identified the best remedy for recovery after gallbladder removal. 5 years of research. Self-treatment at home! After carefully reviewing it, we decided to offer it to your attention.
If pancreatitis has already been identified, you need to adhere to a strict diet and follow all the recommendations of specialists so as not to aggravate the process. You need to realize that now many delicious and previously favorite foods are contraindicated and you will have to forget about them. However, you should not despair, since a healthy pancreas is much more important than any goodies.
What else may bother you besides pain in the side?
If the patient complains that the right side hurts after removal of the gallbladder, what other manifestations may bother you? Among them are the following:
- chills;
- gagging;
- nausea (especially in the morning);
- hyperthermia (that is, increased body temperature);
- unpleasant bitterness in the mouth;
- the development of a disease such as jaundice;
- frequent and prolonged delays in defecation;
- interruptions in the functioning of the digestive tract;
- flatulence;
- weakness;
- itching of the skin;
- changes (for the worse) in the quality of urine and blood, which can be detected during a clinical examination.
What should be present in the diet after gallbladder removal
A strict diet after surgery is not the pretentiousness of doctors, but a vital condition. Ignoring medical instructions can lead to serious complications. The main goal of such a diet is to prevent the accumulation of bile in the ducts. You should familiarize yourself with the following recommendations:
- It is necessary to eat only warm foods; it is better to exclude cold foods from the diet, since the latter can cause spasms in the bile ducts.
- You should eat small portions 5-6 times a day.
- Food should contain vegetable and milk fats, which accelerate the excretion of bile.
- Consume fermented milk products several times a day: cottage cheese, pudding, soufflé.
- Don't ignore beef and chicken. Lean sea fish optimizes the absorption of fats in the body.
- It is better to choose bread with yesterday's release date, slightly dried. Freshly baked bread is highly discouraged. Add bran to your diet as well.
- A variety of cereals must be present, which can be sweetened with jam, honey, jam, marshmallows, dried fruits and berries.
- Avoid caffeinated drinks.
- Enrich your table with products containing plant fiber. It can be bran, brown rice, oatmeal.
- Steamed or boiled food, lightly stewed or baked without crust, should predominate.
If you had to deal with the removal of the gallbladder and pancreatitis, you need to understand that a lifelong type of diet is now prescribed, requiring repeated restrictions in certain foods or their complete exclusion.
At the same time, by adhering to all the rules and instructions, you can achieve excellent health and protect your body from risks and complications.
Diet and diagnosis after surgery
To save yourself from complications, you should follow a simple diet and doctors’ recommendations after surgery in advance. What risks will be reduced? Life will become better, metabolism will accelerate, metabolism will be restored.
- Drink water on a regular basis. Before eating, drink a glass of water; this will improve the digestion process, making it easier for the organs of the digestive system affected by surgery. Water will help your liver function. Slags and toxins are eliminated with reduced acidity.
- Eat 5-6 times a day. Frequency and proper diet will help bile to be released evenly. The intestines will not suffer from increased acidity, and the risks of complications will decrease. Eating 5-6 times a day does not imply a large amount of food. Food products are divided into breakfast, lunch and dinner. Every 2-3 hours between main meal intervals you can eat fruits, nuts, and vegetables. Don't overload your body. Light snacks needed.
- All food does not exceed normal temperatures. It is impossible and not recommended to eat food that is very hot or very cold. Ice cream, hot tea, pizza from the oven - you will have to give up in favor of healthy, warm, optimally chilled food.
- Do not sit at a banquet table immediately after surgery. Portions during the week should be small, the size that fits in the palms of your hands. The body needs a fasting day to adapt to new digestive techniques.
- After the first week, focus on protein foods. Chicken, meat, legumes are products that dilute bile. Remember, the body is not used to the constant secretion of bile into the abdominal cavity. Improper nutrition with foods of high acidity leads to the operating table.
- Forget the word “fried.” Steam, stew, eat raw - the principle after the procedure. Avoid fatty, fried, smoked foods.
- Drinking coffee and strong tea is prohibited. Hibiscus, mint tea, green teas, mineral water are substitutes for usual drinks.
- Fast food, soda, carbonated drinks, alcoholic beverages, drugs with high iron content, activated carbon. Do not touch the substances for more than six months.
- Hot spices, salt, pepper, oregano, cloves, paprika, hot sauces, ketchup, mayonnaise, garlic, onions are now prohibited.
- Sausage and sausage products.
- Fat and blue cheeses.
- Meals should be simple and balanced, with more vegetables. Fruits are eaten in small quantities - frequent consumption sometimes leads to bloating. There is no need to disturb the intestines.
What products are prohibited?
Various diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, including pancreatitis due to the removal of the gallbladder, imply a stop list for many products. Among these are the following:
- mushrooms;
- baked goods and confectionery (cakes, sweets);
- various sauces, mustard, mayonnaise;
- spices with a pronounced taste effect (curry, pepper, cinnamon, coriander);
- sparkling water;
- marinade, pickled vegetables, preserves;
- ice cream.
Symptoms indicating the development of pancreatitis
Is it possible to recognize pancreatitis on your own? Only a gastroenterologist can make a 100% diagnosis. In any case, it is possible to familiarize yourself with the symptoms of this disease. Acute pancreatitis is characterized by the following:
- Dull or cutting severe pain. The concentration of pain is observed in the right hypochondrium.
- Prolonged hiccups.
- Nausea. In rare cases, it is accompanied by vomiting containing bile.
- Flatulence, heartburn.
- Temperature increase.
- Profuse sweating, characterized by sticky sweat.
- Increase/decrease in blood pressure.
- Dryness appears in the mouth, and a yellow coating appears on the tongue.
- Cases of diarrhea or constipation.
- Hardening of the abdomen.
- Dyspnea.
- Significant weight loss.
With chronic pancreatitis, the symptoms are somewhat different. Pain that makes itself felt during attacks can torment a person for several years. This feeling intensifies after eating junk food (fried, fatty, smoked, alcohol). The localization of pain was noted in the same area as in the acute form of this disease.
The symptoms also affect the patient’s appearance. With pancreatitis, the skin on the face turns pale and in the lumbar region becomes bluish-gray. The groin area takes on a gray-green tint. Such skin changes occur due to abnormalities in blood flow due to an inflamed pancreas, when blood can get under the skin. With the sclerosing form of pancreatitis, the skin may acquire a yellow tint, and the same happens to the whites of the eyes. Often chronic pancreatitis after removal of the gallbladder occurs without visible symptoms or with minor properties. Therefore, the patient cannot always detect the disease in the initial stages. Chronic pancreatitis is characterized by structural changes in the pancreas and impaired insulin production. Because of the latter, the level of glucose in the blood increases, and this can be dangerous due to the onset of diabetes mellitus. It is worth seeking help from your doctor at the stage of acute pancreatitis. This will prevent it from becoming chronic.
Postoperative complications
Laparoscopy is used to remove the gallbladder.
More often, laparoscopic techniques are used to remove the gallbladder. Despite the minimally invasive nature, tissue injury is possible, so the body’s reaction in the form of slight inflammation is normal. That is why pain under the ribs and throughout the abdomen is not a deviation. A bad sign is increased pain under the ribs. This happens for many reasons, but mostly due to non-compliance with medical recommendations regarding the rules and diet, physical activity.
Often the removed organ continues to be bothered by pain of the same intensity as previously in different parts of the abdomen, under the ribs or shoulder blades. This happens due to the following factors:
- occurrence of complications;
- making mistakes during the intervention;
- exacerbation of existing diseases of the digestive system in a chronic form;
- development of postcholecystectomy syndrome.
Treatment of pancreatitis after cholecystectomy
Doctors identify the main cause of pancreatitis as improper nutrition after surgery. Failure to follow the basic rules of eating healthy food leads to the diagnosis of biliary pancreatitis in 75% of cases.
After the operation, a small amount of medication is required. Immediately after the operation itself, antibacterial therapy with antibiotics is carried out. It is 3 days. To get rid of pain you need to take antispasmodics and analgesics like Drotaverine and Buscopan. Substances that prevent the formation of stones in the bile ducts are contained in Ursolfak. Gastroenterologists also recommend Pancreatin, which helps improve digestion processes. In order to prevent pancreatitis and a number of other diseases that are possible after removal of the gallbladder, one cannot do without taking choleretic agents, enzymes and drugs, the use of which will normalize the intestinal microflora.
Causes of pain
There can be many causes of pain in the abdominal area:
- As a consequence of chronic diseases aggravated as a result of surgical intervention or new ones that have arisen.
- Part of the pain in the side after removal of the gallbladder may be due to the fact that during the operation a sterile gas is injected into the peritoneum, which evaporates after a short time, and this discomfort goes away without a trace.
- Inflammatory processes due to infection introduced either by poorly sterilized instruments or with air.
Important! In order to quickly stop an infectious disease, body temperature should be constantly monitored. If it increases to 38 degrees or more, the onset of the inflammatory process can be diagnosed.
- The presence of postoperative complications, for example, a significant reduction in the bile ducts or the formation of adhesions.
- Due to residual stones that came out into the ducts before the operation and made themselves felt after the surgical intervention was performed.
- Also, causes of pain after removal of the gallbladder may include physical activity not permitted by a doctor and a diet that differs from that recommended by a specialist.
On a note! If cholecystectomy was performed using a scalpel (that is, in an open manner), then the pain syndrome may be due to a relatively large-scale (compared to laparoscopy) dissection of the abdominal tissue.
Having trouble recovering from gallbladder removal?
- Many methods have been tried, but nothing helps.
- And now you are ready to take advantage of any opportunity that will give you the long-awaited well-being!
An effective remedy exists. Follow the link and find out what doctors recommend!
Biliary pancreatitis occurs in most people after gallbladder removal. There is a misconception that after resection of the gallbladder, the pancreas takes over its work, and under the influence of such a load, its parenchyma begins to collapse. These two organs of the digestive system complement each other's work, but are in no way interchangeable. The mechanism of development of pancreatitis can be started even before surgery, due to cholecystitis. Pancreatitis often appears after surgery, but due to the fault of the excretory ducts. They continue to supply the secretion of liver cells to the duodenum, but not in the usual quantity.
What happens to the pancreas when the gallbladder is removed?
Many patients mistakenly believe that after resection of the bladder, all its “responsibilities” begin to be performed by the pancreas. This is not true at all.
Read also: What herbs to drink after gallbladder removal?
If the occurrence of biliary pancreatitis was a consequence of cholelithiasis, cholecystectomy can not only trigger remission of pancreatitis, but also contribute to its complete cure.
If the operation is carried out as planned and in a timely manner, the likelihood of a complete recovery is very high. After cholecystectomy, in more than 50 percent of operated patients, pancreatic function returns to normal.
If surgery is performed at a late stage of the disease (when gallstones have already led to serious complications), or if the operation itself was performed with any errors, the so-called postcholecystectomy syndrome (PCES) may occur.
As a rule, its appearance is associated with:
- disturbances of normal liver function;
- dysfunctions of other nearby organs, aggravated after resection of the bladder;
- incorrect tactics of intervention or mistakes made during its course;
- adaptation of the digestive system to new working conditions;
- development of a new disease as a result of complications after cholecystectomy;
- reasons of a psychological nature.
The likelihood of chronic pancreatitis occurring after gallstone resection is directly dependent on how long the course of cholelithiasis lasted. The earlier the resection is performed, the better the prognosis.
Postoperative treatment in such cases implies mandatory adherence to a special regime and diet, which are regulated by a diet called “Treatment Table No. 5.”
The fact is that in the absence of a removed bladder, bile has nowhere to accumulate, and it gradually penetrates into the intestines, regardless of the presence of food in it. Since bile is a rather aggressive environment, its presence in an empty intestine provokes inflammation and reduces the level of resistance of other organs (including the pancreas), causing pancreatitis. In addition, the normal state of the intestinal microflora is disrupted, which can cause stool disorders (diarrhea or constipation).
Inna Lavrenko
auto RU
The basic rules of this diet are:
- split meals, in which you should eat little but often (five to six times a day), maintaining equal time intervals between meals;
- avoidance of fatty, spicy and fried foods;
- refusal of canned food, smoked meats and pickles (including homemade ones);
- food should be steamed, boiled or baked and consumed warm (neither hot nor cold);
- Alcoholic and carbonated drinks, fast food, legumes, mushrooms, sweets, chocolate, baked goods, baked goods, sour berries and fruits, as well as vegetables with a high content of essential oils (garlic, onions, radishes, spinach, etc.) are also prohibited. P.);
- You should also not eat sauces (mayonnaise, ketchup, etc.), spices, seasonings and products containing preservatives, flavor enhancers, dyes, substitutes and flavorings.
Read also: How does gallbladder cancer manifest and how to treat it?
The doctor selects a specific menu and list of permitted products individually, based on the condition of a particular patient.
When is gallbladder removal necessary and how is the operation performed?
The reason for surgery to remove the gallbladder is usually cholelithiasis, complicated by cholecystitis (inflammation of the walls of the bladder) or acute pancreatitis. When stones are in the gallbladder, they obstruct the flow of bile into the duodenum. Liver secretions begin to penetrate the excretory ducts of the pancreas and burn them. This factor leads to biliary pancreatitis and pancreatic necrosis.
The first sign that a patient needs urgent surgery is severe, constant pain in the right side that cannot be relieved with medications.
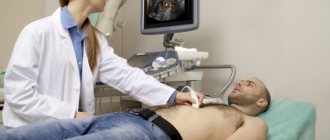
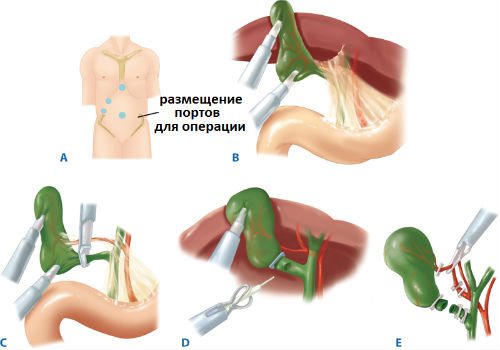
Preparation for bladder resection is carried out using ultrasound. The procedure helps to assess the characteristics of gallstone disease and study the condition of nearby organs. To perform surgical intervention, a low-traumatic method is used - laparoscopy.
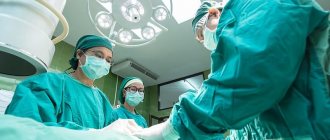
The operation is performed under general anesthesia. So that the surgeon can see the area being operated on, carbon dioxide is injected into certain parts of the abdominal cavity through a needle, followed by the necessary instruments and a video camera. Simultaneously with the bile reservoir, the cystic duct and the adjacent gallbladder artery are cut out. Therefore, fixing clips are first applied to them in a certain place.
If the cystic canal is left untouched or a smaller part of it is excised, then over time it will be filled with the secretion of liver cells, expand and become similar to a gall bladder. Since its walls have no possibility of contraction, the bile in it will begin to stagnate. Over time, stones form in it, which subsequently provoke an exacerbation of pancreatitis.
The excised organ is removed through the largest incision in the abdominal cavity. Sutures are placed in the operated area, and a thin drainage tube is placed to the bladder bed. If during the operation the surgeon discovers that the walls of the gallbladder are inflamed, and the organ itself is enlarged or neighboring organs have grown to it, then the surgical intervention is completed with open abdominal surgery. The laparoscopic method can cause damage and disease to other organs. The patient is warned about the possibility of this problem even when discussing the operation.
Basic principle of laparoscopic surgery
The essence of the method is that 4 small punctures are made in the abdominal cavity using a stylet (that is, a device resembling a thin dagger with a vertical hole), into which hollow tubes with valves (the so-called trocars) are inserted. It is through them that a special surgical instrument is inserted to perform the necessary manipulations. In addition to them, the surgeon uses a laparoscope (it has two optical channels) connected to a monitor. That is, a specialist has the opportunity to keep the entire process under control. Through one channel, cold light is supplied to the peritoneum, and through the second, a “picture” of what is happening inside is transmitted (first to a television camera and then to a monitor). This is what technical progress means!
Important! The examination that is carried out before the operation is carried out under local anesthesia, but the surgical intervention itself is performed using general anesthesia (that is, the person being operated on does not experience absolutely any pain) and a special-purpose device that provides artificial ventilation.
To create the space in the abdominal cavity necessary for visual examination (on a screen, of course) and surgical manipulations, a sterile gas (usually carbon monoxide) is injected into it. Next, the surgeon cuts off the adhesions located around the gallbladder; pumps out excess liquid from it (if necessary); compresses the bladder duct and artery using clips; separates the diseased organ from the liver; removes it through a cosmetic puncture located in the navel area? and sews up (or seals) punctures in the fabric.
On a note! One of the punctures is not stitched up. Leave the drainage tube in it for a day. This is done in order to completely remove the antiseptic liquid (it is with this that the peritoneum is washed at the last stage of the operation in order to avoid the development of the inflammatory process). If the pathology is uncomplicated (that is, without bile entering the peritoneum), drainage is not installed.
What happens after surgery
As a rule, surgery to remove the gallbladder is not considered difficult and does not pose a risk to human health. The bladder is located away from the main bile duct, so at the time of excision of the organ, the likelihood of damage to it is minimal.
Consequences for the whole body
Due to the successful anatomical location of the gallbladder, the movement of bile continues, even after its removal, along the common excretory duct. After the operation, the functions of the bladder, which served as a reservoir for temporary storage of bile, are taken over by the excretory hepatic ducts (right and left), as well as the common duct.
The absence of gall does not greatly affect the health of the body. Over time, a person adapts to life without this organ. The majority of operated patients experience improved health.
Symptoms of biliary pancreatitis, which is a pathology caused by a violation of the outflow of bile, weaken and disappear over time. An exacerbation of the disease can occur in people who do not follow the doctor’s recommendations regarding lifestyle and nutrition.
Complications on the pancreas
If pancreatitis worsens after removal of the gallbladder, then the cause comes down to a violation of therapeutic nutrition and alcohol consumption. Pancreatic dysfunction can also occur due to minimal flow of bile into the colon.
Exacerbation of chronic pancreatitis after removal of the gallbladder is also quite common. Clinical symptoms of chronic pancreatitis very rarely occur immediately after surgery, usually within six months. They do not differ from the symptoms that occur in patients with the independent development of the disease, which is characterized by periods of exacerbation and remission.
Poor nutrition
For diet therapy, table No. 5 is most suitable.
The digestive organs react especially acutely to the quality and quantity of food after surgery. Regular food is the main reason for the deterioration of the condition and slowdown of the rehabilitation process. Important nuances to consider during diet therapy:
- Do not eat or drink cold food with liquid. This can provoke a gastric spasm, which will reflexively affect the bile ducts and sphincters.
- You can't overeat. Excessive amounts of food consumed at one time make it difficult to digest and evacuate the food bolus from the stomach. As a result, bile does not enter the intestines.
- Fatty, spicy, fried and other unhealthy foods should be excluded from the diet. This applies to lard, margarine, concentrated broths, beer, wines, syrups, vinegar, and sweets. Such foods are especially difficult for the stomach in the postoperative period. After consuming even a small amount, a spasm of the bile ducts may occur, which will manifest itself as pain on the right under the ribs or in the pit of the stomach.
- The most suitable diet is table No. 5. The goal of diet therapy is to restore the function of the liver and pancreas and relieve inflammation in the biliary tract.
- It is important to maintain a fractional diet - up to 7 times in small portions.
Inna Lavrenko
Reading time: 5 minutes
A A
The liver is in close connection with the gallbladder. It is not for nothing that doctors call this pair of organs the biliary system. Therefore, after removal of the gallbladder (cholecystectomy), the load on the digestive system in general and on the liver in particular increases, which can cause some discomfort (especially at first after surgery to remove the gallbladder).
The operation to excise this organ is carried out in two ways - traditional abdominal and laparoscopic. After laparoscopy of the gallbladder, complications rarely arise and recovery is much faster, so the laparoscopic technique is used more often than the traditional one (if there are no contraindications and the technical equipment of the medical institution allows).
Before we figure out why, if the gallbladder is removed, the liver hurts, the treatment of this pain syndrome, let's first figure out why a person needs a gallbladder.
Hepatocytes (the so-called liver cells) constantly produce bile, which, through the bile duct system, enters the gallbladder and accumulates in this reservoir, which is located just below the liver. Its shape is similar to a pear, the capacity of which ranges from 40 to 70 milliliters. The muscles of the walls of this tank are very elastic and can stretch greatly.
The main functions of the gallbladder are:
- accumulation of bile produced by the liver;
- bringing this liver secretion to the required concentration;
- delivery of bile to the duodenum when food enters the gastrointestinal tract.
The gallbladder and intestine are connected to each other by a common bile duct, at the end of which there is the so-called sphincter of Oddi, which ensures a portioned flow of bile into the digestive system.
Bile, which accumulates in the gallbladder, is a complex mixture of various components, such as:
- special bile acids;
- fatty acid;
- set of enzymes;
- complex of minerals;
- cholesterol;
- products produced during hormonal metabolism, and so on.
The main component of this liver secretion is water, which ensures its fluidity. Bile is involved in the breakdown of food (especially heavy fats), as well as in the process of removing harmful substances from the body. The liver of a healthy person produces more than one liter of this secretion during the day.
The main functions of bile:
- emulsification of fats for their subsequent absorption;
- strengthening and activation of the action of enzymes produced by the pancreas (lipase, amylase and trypsin);
- neutralization of pepsin (the environment in the intestines is alkaline, and in the stomach it is acidic; it is with the help of bile that gastric digestion changes to intestinal);
- stimulation of intestinal peristalsis, which ensures better movement of food and its effective digestion;
- removal from the body of products of hormonal and drug metabolism, as well as various toxins and other harmful substances;
- participation in the breakdown of fats, proteins and carbohydrates;
- improved absorption of minerals and vitamins;
- maintaining the normal state of intestinal microflora by preventing the appearance and further spread of pathogenic bacteria.
Diet to prevent pancreatitis
Table 5 is always prescribed after removal of the gallbladder for pancreatitis. The need to strictly follow a diet in order to prevent exacerbation of pancreatitis remains for at least a year. This is exactly the amount of time required to restore the body after resection of an internal organ. The diet for a removed gallbladder and pancreatitis is formed from foods high in vitamins, micro- and macroelements. The goal of a healthy diet is to reduce the load on the bile duct and liver.
Dietary table No. 5 provides for compliance with the following rules:
- Every day the menu should contain food that is a source of carbohydrates and proteins.
- The restriction is imposed on products containing animal fats.
- The cooking process involves steaming, baking and boiling foods.
- If the diet contains products containing fiber, then they are served only in crushed form.
- Products that promote gas formation are excluded from the menu.
- Salt is allowed to be used in a minimal amount, and hot spices and seasonings should be completely avoided.
- Meals after gallbladder removal are fractional. The patient should eat often (at least 6 times a day), but little by little and at the same time. Food should be warm.
The daily diet of a patient with biliary pancreatitis after removal of the gallbladder involves eating food containing the following amounts of fats, proteins and carbohydrates:
- Vegetable proteins - 40 g, animal proteins - 40 g.
- Fats - up to 90 g. Of these, the recommended amount of vegetable fats is 30%.
- Carbohydrates - up to 400 g.
- Water - 1.5 liters or more.
- Salt - up to 10 g.
For some patients, doctors recommend supplementing the diet with medications that improve liver function (Karsil, Essentiale).

A mandatory rule that all patients with pancreatitis must follow is drinking water on an empty stomach. It can be mineral or regular. Tea, compote or juice are perceived by the body as food, and the pancreas produces a bicarbonate alkali solution only thanks to water. The latter neutralizes the acid entering the intestines with food.
Allowed foods and dishes after gallbladder removal and for pancreatitis:
- Main dishes of the menu. Soups: vegetable - with potatoes and carrots; cereal - with buckwheat, rice, pearl barley; milk - with pasta; fruity - with dried apples, dried apricots, raisins. Vegetable cabbage soup, beetroot soup, borscht in low-fat meat broth.
- Second: pasta, porridge made from rice, millet, buckwheat, pilaf with dried fruits. For pancreatitis, it is good to add flax seeds to such food.
- Meat dishes from low-fat fish (hake, tuna, pollock) and dietary meat (rabbit, beef, chicken). Steamed, baked in foil or simply boiled.
- Bread. Bran bread, wheat crackers, and dried biscuits are allowed.
- Fermented milk products with a fat content of no more than 2%. Sour cream, yogurt, kefir, cottage cheese.
- Vegetables (consumed in grated form). Cauliflower and Chinese cabbage, broccoli, carrots, beets, zucchini, pumpkin, seaweed, celery. Tomatoes and bell peppers - limited quantities.
- Fruits and berries (limited quantities and as prescribed by a doctor). Soft apples of sweet varieties are baked. Bananas, pomegranates, watermelons. Dried melon, prunes, dried apricots are added to dishes.
- Drinks (lightly sweetened). Weak black tea, non-acidic juices diluted with water, rosehip decoction, compotes and dried fruit jelly.
The list of completely prohibited foods for pancreatitis includes coffee, chocolate, mushroom soups, okroshka, fatty meat, hot spices and dressings, baked goods made from puff pastry and butter dough, fresh bread, nuts, seeds, and soda.
Treatment of pancreatitis after cholecystectomy
After removal of the gallbladder, the patient is prescribed treatment with a minimum amount of medications:
- Antibiotics. Prescribed immediately after surgery to prevent inflammation of the bladder bed, the organs near which it was located, and its main excretory duct. Taking antibacterial drugs lasts 3-5 days.
- Painkiller. To relieve pain and spasms that may appear after removal of the gallbladder, analgesics (Baralgin, Pentalgin) and antispasmodics (Drotaverine, Buscopan) are prescribed.
- Suspension or tablets Ursofalk - prevent the formation of stones in the bile duct.
- Pancreatin tablets - to improve digestion.
On an individual basis, some patients are prescribed choleretic agents and enzymes to prevent pancreatitis, which normalize the intestinal microflora and improve the functioning of the entire digestive system.
When the gallbladder is removed, exacerbations of chronic pancreatitis become more frequent. To relieve pain, doctors prescribe such patients to take analgesics and anti-inflammatory drugs (Paracetamol, Ketanov, Diclofenac). In severe cases, the patient is hospitalized and intravenous painkillers are administered to relieve pain.
Complications after gallbladder removal are rare and most often due to poor diet. Therefore, it is very important for the first year after surgery to follow all the instructions of the attending physician.
Exacerbation of diseases
A person who has had their gallbladder removed is likely to develop diseases of the liver, intestines, and pancreas.
The most difficult period of life with a removed gallbladder is considered to be half of the first year after surgery. During this time, old gastrointestinal pathologies may worsen or new ones may develop. Without gall, the first to suffer are:
- liver;
- pancreas;
- duodenum of the intestine.
The following pathologies can cause severe pain under the ribs:
- inflammation of the pancreas (pancreatitis);
- ulcerative lesion of the duodenum;
- adhesions in the bile ducts;
- hepatitis;
- untreated cholelithiasis (remnants of stone in the main bile duct);
- duodenitis;
- biliary dyskinesia.
You can determine which specific disease has worsened by the accompanying symptoms and the nature of the pain, for example:
- if pain occurs in the right side, the stomach, back and collarbone hurt, inflammation of the bile ducts of the liver occurs;
- if pain occurs in the peri-umbilical region and in the left hypochondrium, then the pancreas is inflamed;
- if the pain radiates to the left side and back, then the inflammation affects the spleen or other organs.
Additional symptoms are:
- constant nausea;
- flatulence;
- instability of stool consistency, frequency and color.
If the discomfort does not disappear after 2 days while following a diet, and pain medication does not help, you should immediately consult a doctor.