Thickening of the walls of the gallbladder is a pathology that can be detected using ultrasound diagnostics. Compaction can be caused by various reasons and have a different nature, so treatment in each case must be selected individually. What are the diagnostic features and are there effective methods to eliminate this problem? Let's look at these questions in more detail.
Why do seals occur?
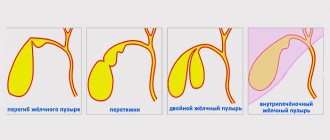
The reasons for the increase in the density and size of the bile wall are varied and lie not only in diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. The compaction has a different character and structure, which is also due to factors that cause deviations from the norm. Let us clarify the known compaction characters:
- formation of scar (connective) tissue;
- proliferation of the mucous membrane of the gallbladder;
- swelling;
- fat deposits on the wall of the bladder;
- tumor-like growths;
- bending and deformation of the organ.
Diseases as the root cause of pathological changes
Diseases in which compaction develops in the gallbladder:
- Inflammatory processes in the organ itself (chronic and calculous cholecystitis). As a rule, in these diseases, changes in the wall are sclerotic in nature.
- Polyposis - proliferation of the mucous membrane thickens the wall.
- Cardiovascular insufficiency is the cause of the development of edema throughout the body, including the gallbladder.
- Ascites (dropsy) is an accumulation of fluid in the abdominal cavity. It is a consequence of liver cirrhosis.
- Liver diseases, necrosis, cirrhosis, hepatitis. The parenchymal tissue of the organ is replaced by connective tissue, and adhesions are formed. This process also affects the gall bladder, and its walls thicken.
- Benign and malignant neoplasms can cause changes in the functioning of an organ; cancerous tumors pose a particular danger due to metastasis to neighboring tissues.
- Acquired or congenital deformation of the gall bladder, its bending may be accompanied by thickening of the walls.
- Cholesterosis - disturbances in the functioning of the organ are associated with the pathology of lipid metabolism, which leads to the deposition of fats on the inner wall of the bladder.
Complications and prevention
Without treatment, the pathology quickly develops into complications. Prolonged disruption of the organ’s condition contributes to the appearance of:
- Dyskinesia.
- Spread of infection to other organs.
- Metastases, if the compaction is caused by tumors.
If the thin channels of the bile change their shape, general intoxication of the body occurs. The entry of insufficient bile into the digestive organs disrupts the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract. And this starts a chain of serious diseases.
What will be seen on an ultrasound
For many people, a completed ultrasound examination form is a sealed secret. Sometimes it’s even scary to read into incomprehensible words, and the given dimensions and parameters drive you into a stupor. The easiest way to figure out how different the result obtained is from the norm is to contact the doctor conducting the study and ask him to explain the results. As a last resort, you can consult your doctor and find out his assessment of the ultrasound diagnostic results.
It is quite possible to independently understand the data obtained. Normally, in an adult, the gallbladder parameters are as follows:
| Length, mm | 60-100 |
| Width, mm | 30-50 |
| Wall thickness, mm | 3-4 |
| Form | Pear-shaped or cone-shaped, no bend or constriction |
| Wall structure | Equal echogenicity, homogeneous, clear edges, no thickening |
| Width of ducts, mm | General – 6-8, fractional 2-3 |
If the walls are compacted, then ultrasound will show an increase in echo density. In inflammatory processes and chronic cholecystitis, a uniform (diffuse) increase in echogenicity is observed.
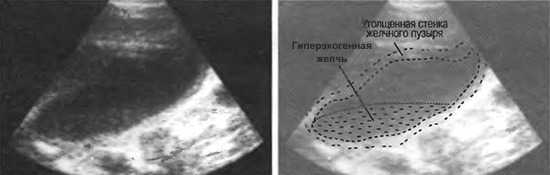
Polyps appear on the monitor as formations that have the same echo density as the walls of the bladder. The presence of stones is reflected as the presence of hyperechogenic areas that can move when the position of the body changes. Sand is defined as hyperechoic areas that also move with movement. The deformation of the organ is detected by ultrasound. Detection of such a pathology will help the doctor make the right decision when treating the disease.
Digestion and bile
The liver performs many functions, one of them is the disposal of blood cells that have become unusable.
Through complex chemical transformations, the liver creates bile from hemoglobin - a dark (brown with a yellowish or greenish tint) liquid with a specific odor.
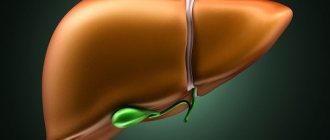
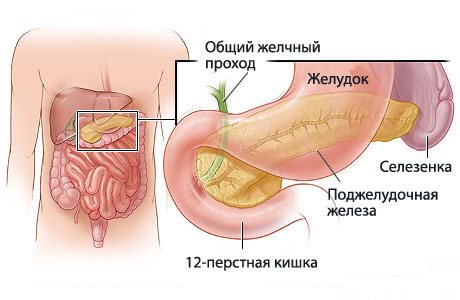
Bile reserves through the hepatic ducts enter the gallbladder - a bag for its storage and ripening (concentration).
The scene where bile manifests itself is the first section of the intestine, the duodenum. Here, fats that enter the body with food are converted into energy that body cells are able to absorb.
An excess of fatty, especially fried foods creates an increased load on the gallbladder, which results in various diseases, one of the most dangerous is cholecystitis.
However, the first signs are dysfunctional conditions in which the organ is not able to perform its tasks in full. One of them is dyskinesia of the gallbladder and biliary tract.
The walls of the organ and its ducts are equipped with muscles, the contraction of which ensures the supply of bile to the duodenum when they receive a signal about the arrival of fatty foods.
READ Method for crushing gallstones
However, it happens that the body needs to digest fat, but bile does not enter the intestines. This indicates a weakness in the muscular system of the gallbladder.
The opposite situation is also possible, when bile is thrown into the duodenum when there is no fat there. This is a sign of increased muscle work.
If, after removing the gallbladder, bile stopped flowing into the duodenum, then the organ would be considered vital, since digestion, and, consequently, life without bile is impossible.
However, bile continues to participate in this process, coming directly from the liver. Such bile is less concentrated, therefore, the body is able to digest less food, especially fat.
The gallbladder is not one of the vital organs, but considering it an unimportant part of the system is a huge mistake.
Even the slightest disturbances in its functioning lead to other disturbances and symptoms, which can lead to complete digestive disorders.
To be convinced of this, it is enough to read the reviews of those 30–40% of people for whom cholecystectomy surgery resulted in complications or successful treatment forced them to change their lifestyle and constantly monitor their diet and well-being.
Treatment
Since there are many reasons for compaction and thickening of the gallbladder wall, the root cause of this pathology should be treated. If the thickening is caused by polyps on the mucous membrane of the gallbladder, then it is necessary to remove them, because there is a high probability that they will turn into malignant neoplasms.
Depending on the severity of the disease, treatment can be radical or conservative. Surgery is required when the function of the organ is severely impaired, as well as in the presence of gallstones. Conservative treatment is aimed at increasing the proportion of plant foods in the diet, using choleretic agents and bile acid preparations. The use of antibacterial drugs is justified when an infectious process is associated.
In some cases, treatment is carried out using antispasmodics and immunomodulatory drugs. In the presence of hormonal disorders, corrective therapy is prescribed.
Heart failure and cirrhosis of the liver require long-term treatment under the supervision of a doctor, and sometimes in a hospital setting.
Manifestations of the disease
The child complains of nausea, lack of appetite, heaviness or acute abdominal pain that occurs immediately after eating or on an empty stomach. Painful sensations can either be localized at one point (usually in the area of the right hypochondrium), or be of a diffuse, indefinite nature, occupying the entire epigastric area. It’s good if parents try to find the reasons for the deterioration of the baby’s well-being, and do not prescribe treatment on their own.
A pediatrician may suspect a functional disorder during examination. The child is active and does not look sick. The skin and mucous membranes are clean and pink. The tongue often has a white or yellowish coating, and there may be a slight yellowness of the sclera. The abdomen is soft, sensitive at the point of projection of the pyloroduodenal zone. Palpation of the gallbladder, as a rule, is not informative, but there may be pain in its reflexogenic points. The liver and other abdominal organs are not enlarged visually or upon palpation.
Proper nutrition and healthy lifestyle
A general recommendation for pathology of the gallbladder walls is a change in diet and adherence to the prescribed diet. You should avoid eating fatty meats and fish, and sweet drinks. The best foods for such a patient are lactic acid foods, stale bread, tea without sugar, chicken and other lean meats.
The effectiveness of a healthy lifestyle and healthy habits has been proven by time. Systematic adherence to doctor’s recommendations and diet is not an easy test, the reward for which is health and a fulfilling life.
Previous article: What is dangerous about the bending of the gallbladder, causes of the disease and methods of treatment Next article: Causes of deformation of the gallbladder, symptoms and signs, modern approaches to treatment
Thickening of the gallbladder walls: causes and treatment
The appearance of heaviness on the right side and pain after eating food may be signs of problems with the gallbladder. For diagnosis, the specialist prescribes an ultrasound of the internal organs to the patient. Our article describes the causes of thickening of the gallbladder walls and the selection of therapy.
Gall
What is the gallbladder
The bladder is a kind of reservoir for the accumulation of bile, which then enters the duodenum through the bile ducts. Bile is important for digestion because it dissolves fats. In order for bile to have a good outflow, the gall bladder must contract correctly.
The wall consists of:
- Mucous. It is covered with epithelium, which provides metabolism and blood supply.
- Muscles that cause contractions for the flow of bile.
- The serous membrane that protects the gall bladder.
Hardening of this wall can cause serious health problems.
How inflammation manifests itself
Due to poor nutrition and functional disorders of biliary motility, inflammation occurs, called cholecystitis. Because of this, gallstones gradually increase in size, which further affects the mucous membrane.
Inflammation causes swelling. In order to increase blood flow and ensure an influx of immune cells, capillaries dilate. Leukocytes will flow from the blood into the tissues to destroy the infection, which is necessarily observed during inflammation.
Due to swelling, the walls of the gallbladder become thicker and denser. Chronic inflammation causes the growth of connective tissue resembling a scar. This is what causes the gallbladder to thicken.
Important! A dense bladder stops contracting properly, and problems with it become more and more frequent.
What does an ultrasound of the bile duct show?
A gastroenterologist treats the disease. Ultrasound is one of the best methods for studying pathologies of the biliary system. With its help, doctors determine:
- gall size and wall thickness;
- presence of cholelithiasis;
- correct bile secretion;
- duct diameter;
- condition of the pancreas and liver.
Thickening of the walls of the gallbladder up to 4 mm in adults and up to 2.5 mm in children is considered normal. In a healthy state, they have a uniform structure and smooth contours. Inflammation dramatically changes this picture. When a patient develops cholecystitis, the walls of the bladder thicken unevenly. The maximum rate is observed in the area of the calculus.
The heterogeneous structure of the gallbladder is manifested on ultrasound by increased signal and hyperechogenicity. In the photo, the affected areas are bright. This is typical for chronic inflammation. In some situations, the thickening resembles layering.
Another typical manifestation of thickening is the formation of “flakes” of thick bile. This condition is caused by excessive consumption of fatty foods, which leads to an increase in the concentration of cholesterol and lecithin. If a person does not adjust his diet, stones will begin to form.
Reasons for the development of thickening
The occurrence of pathology is influenced by the state of the body and the functioning of its organs and systems.
Most often, thickening of the walls of the gallbladder is a consequence of:
- Housing and communal services Because of the stones, the tissues begin to become inflamed and swollen. This is common in diabetics, obese people and Crohn's syndrome.
- Acute cholecystitis. Inflammation causes swelling, causing tissue thickening. This is caused by infectious diseases, parasites or viruses.
- Chronic cholecystitis. Due to the duration of the inflammatory process, scars remain on the tissue after healing. A large number of them causes compaction.
- Cholesterosis. Impaired lipid metabolism causes the accumulation of LDL in the bladder. As a result, it stops contracting correctly, becomes inflamed and thickens.
- Improper functioning of the heart. Due to heart problems, not only limbs, but also organs can swell.
- Neoplasms. Polyps often seal the walls of the bladder. Oncology is rarely diagnosed, but there is always such a risk.
- Hereditary factors and deformations. The bladder may become denser due to congenital or acquired kinks.
- Dropsy. A large amount of serous matter causes many problems, for example:
- renal and heart failure;
- chronic pancreatitis;
- hepatic cirrhosis;
- oncological formations.
Thickening may occur due to gallstones
In adults
Thickening of the bladder in adult patients occurs due to excessive consumption of junk food and bad habits. Alcohol, fried and fatty foods, diets, snacking on flour products on the go - all this negatively affects health.
In children
Children are less susceptible to developing this pathology. At a young age, it occurs due to impaired functionality of the nervous system.
Sometimes thickening occurs due to cholecystitis. It is provoked by parasites that have entered the bile ducts from the intestines. Helminths clog the pathways and enter the vessels, which leads to inflammation and intoxication.
Important! Over the years, the sympathetic and parasympathetic systems change tone. This can disrupt the functioning of the digestive system and gall bladder.
Symptoms of wall thickening
Signs of the development of the disease most often appear at a late stage. This is manifested by the following symptoms:
- nagging pain from the right side of the abdomen, which is felt in the lower back and shoulder blade;
- attacks of nausea;
- gagging;
- chills and fever;
- yellowing of the eyeballs and skin.
Chills Yellowing of the eyeball
In some cases, the intensity of symptoms increases as the disease worsens.
The list of additional signs is presented:
- belching, often with bile;
- bitterness in the mouth;
- constant heartburn;
- darkening of urine and feces.
Constant heartburn
The progression of these conditions can cause various complications, for example:
- biliary dyskinesia - a violation of the contractile function of the bladder, which provokes an abnormal decrease in bile and digestive disorders;
- infectious infection - stagnation of bile creates ideal conditions for the proliferation of microbes that easily affect the intestines, pancreas and liver;
- liver failure.
If the disease is caused by oncology, the tumor can affect other organs.
The likelihood of developing complications is influenced by genetic predisposition and adherence to a correct lifestyle.
Treatment of the disease
The disease requires complex therapy, consisting of:
- medicines;
- special food;
- exercise therapy;
- folk recipes.
Let's look at the features of each method.
Medicines
Treatment involves prescribing:
- Antibiotics. They are selected individually for each patient and help eliminate inflammation of the bladder.
- “Cholenzima”, “Allochola” and “Nikodima” to normalize the amount of bile in the gallbladder and liver.
- “Papaverine”, “Atropine” and “Amizil” to relieve spasm and pain.
- Antibacterial agents to treat and prevent infection.
- Magnesium preparations for a positive effect on muscles.
- Herbal medicine to combat inflammation.
"Allohol" "Papaverine"
Important! The dosage and duration of taking medications is determined only by a qualified specialist. Self-medication is strictly prohibited.
Therapeutic diet
When the increase in the thickness of the bladder walls exceeds the permissible millimeter, in addition to the use of medications, the patient urgently needs to adjust his diet. The patient's diet should be based on:
- weak herbal, berry and fruit tea;
- fermented milk drinks, cottage cheese;
- a small amount of butter and sour cream;
- 1 homemade egg per day;
- dietary varieties of meat and fish;
- stale bread;
- compotes and jelly;
- vegetable soups;
- cereals;
- light salads with vegetable oil;
- steam cutlets;
- pasta;
- cottage cheese casseroles;
- stewed vegetables.
The patient's diet should not contain:
- strong coffee and tea;
- alcoholic drinks;
- bakery products;
- fatty and fried meat;
- chocolate, ice cream;
- smoked meats, spices, pickles;
- mushroom dishes;
- rich broths;
- pancakes, pancakes and pies.
Compliance with dietary nutrition will have a positive effect on the patient’s well-being and will make it easier to endure the disease.
Exercise therapy and physiotherapy
When the disease goes into remission, the patient may be prescribed tubage. This procedure ensures better channel patency and bile drainage. The patient needs:
- drink choleretic liquid;
- lie on your right side;
- apply a heating pad.
The procedure lasts no more than an hour.
Exercise therapy is prescribed to strengthen the abdominal muscles and activate the outflow of bile. This effect is achieved by performing certain exercises daily.
Important! When performing exercise therapy, you cannot load the right side, as this will negatively affect bile outflow.
Wellness procedures and treatment in the sanatorium have a positive effect on the entire body as a whole.
If stones are found in the bladder, they are removed using:
- lithotripsy - crushing stones with ultrasound and laser;
- cholecystectomy - removal of the gallbladder.
As a rule, the first method is used more often. Otherwise, they resort to surgical intervention.
Alternative medicine
The use of folk recipes helps to enhance the effectiveness of the use of medications and exercise therapy:
- Dandelion salad. Soak 15 g of dried leaves in salted water for 15 minutes. Then chop and mix with chopped boiled egg. The dish can be used for medicinal and preventive purposes.
- A mixture of barberry, walnut and lemon balm. Soak 18 g of leaves in cold water for 30 minutes. Then boil the water, strain and cool. Take a tablespoon three times a day before meals.
- Celandine is good at eliminating polyps. Pour 25 g of dried plant with water and leave for 2 hours. Take 30 ml 20 minutes before meals.
- Sugar beets dissolve stones well. Peel it, cut it into cubes, add water and cook over medium heat until the liquid thickens. Pour the finished broth into a jar and place in a dark, cool place. Take 50 ml before each meal for eight weeks.
- Pour two teaspoons of dried sage into 0.5 liters of boiling water and leave for 30 minutes. Take 15 ml every three hours.
Despite the use of natural ingredients, traditional medicine can cause great harm to the body. To prevent this from happening, use its recipes only as prescribed by your doctor.
Possible complications
Ignoring the disease or choosing the wrong therapy can lead to the development of:
- perforation (opening of a hole) in the wall of the gallbladder;
- purulent inflammation (empyema);
- peritonitis;
- pancreatitis, if the stone ends up in the pancreatic duct;
- hepatitis A;
- liver cirrhosis.
Treatment of the above diseases is very long and often not successful.
Disease prevention
You can prevent the development of gallstone problems if:
- Healthy food;
- drink alcohol in minimal quantities;
- avoid hypothermia;
- if your health worsens, seek qualified help;
- practice adequate physical activity;
- do not abuse medications;
- after treatment of helminthiasis, go on a cleansing diet;
- control salt intake;
- Do not go on weight loss diets unless they are designed specifically for you.
Timely diagnosis and treatment ensure the patient’s full recovery.